SUBARU LEGACY 2008 4.G Owners Manual
Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2008, Model line: LEGACY, Model: SUBARU LEGACY 2008 4.GPages: 444, PDF Size: 14.1 MB
Page 421 of 444
13-4Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
!Maximum load rating
The load rating at the maximum
permissible weight load for this tire.
For example, “MAX. LOAD 730 kg
(1609 LBS) @ 300 kpa (44 PSI)
MAX. PRESS. ”
WARNING
Maximum load rating applies
only to the tire, not to the
vehicle. Putting a load rated
tire on any vehicle does not
mean the vehicle can be
loaded up to the tire ’s rated
load.
! Construction type
Applicable construction of this tire.
For example, “TUBELESS STEEL
BELTED RADIAL ”
! Construction
The generic name of each cord
material used in the plies (both
sidewall and tread area) of this tire.
For example, “PLIES: TREAD 2 STEEL + 2 POLYESTER + 1
NYLON SIDEWALL 2 POLYE- STER
”
! Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG)
For details, refer to “Uniform tire
quality grading standards ”in this
chapter.
Page 422 of 444

&Recommended tire inflation pressure
! Recommended cold tire inflation pressure
Recommended cold tire inflation pressure for your vehicle ’s tires is as follows,
Tire size P205/
55R16 89H P225/
60R16 97H P205/
50R17 88V 215/45R17
91W P225/
55R17 95V 215/45R18
89Y P215/
45R18 89W
Wheel size 16 66.5JJ 17 67JJ 18 67JJ
Pres- sure Front
32 psi
(220 kPa, 2.2 kgf/
cm
2) 32 psi
(220 kPa, 2.2 kgf/
cm2) 33 psi
(230 kPa, 2.3 kgf/
cm2) 35 psi
(240 kPa, 2.4 kgf/
cm2) 32 psi
(220 kPa, 2.2 kgf/
cm2) 33 psi
(230 kPa,
2.3 kgf/cm2)
Rear 30 psi
(210 kPa,
2.1 kgf/ cm
2) 30 psi
(210 kPa,
2.1 kgf/ cm2) 32 psi
(220 kPa,
2.2 kgf/ cm2) 33 psi
(230 kPa,
2.3 kgf/ cm2) 30 psi
(210 kPa,
2.1 kgf/ cm2) 32 psi
(220 kPa,
2.2 kgf/cm2)
Rear attrailer towing –
32 psi
(220 kPa,
2.2 kgf/
cm
2) –
32 psi
(220 kPa,
2.2 kgf/ cm2) –
Tempor-ary spare tire Size
T135/
80R16 T155/
70D17 T135/
80R16 T135/
70D17 T155/
70D17 T155/70D17
Pres- sure 60 psi (420 kPa, 4.2 kgf/cm
2)
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
13-5
– CONTINUED –
Page 423 of 444
13-6Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
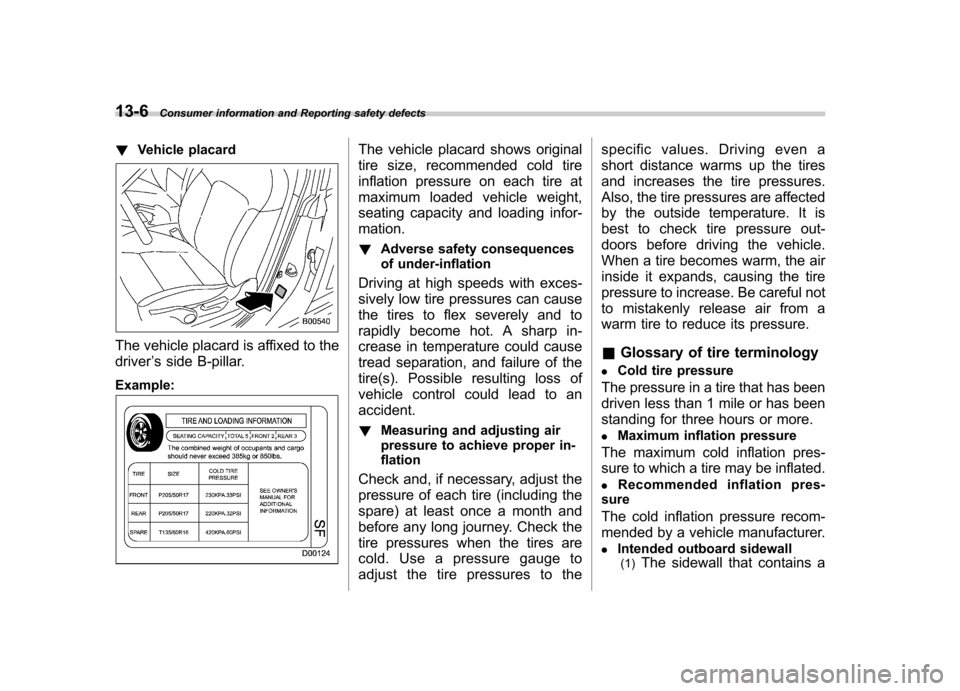
! Vehicle placard
The vehicle placard is affixed to the driver ’s side B-pillar.
Example:
The vehicle placard shows original
tire size, recommended cold tire
inflation pressure on each tire at
maximum loaded vehicle weight,
seating capacity and loading infor-mation. ! Adverse safety consequences
of under-inflation
Driving at high speeds with exces-
sively low tire pressures can cause
the tires to flex severely and to
rapidly become hot. A sharp in-
crease in temperature could cause
tread separation, and failure of the
tire(s). Possible resulting loss of
vehicle control could lead to anaccident. ! Measuring and adjusting air
pressure to achieve proper in-
flation
Check and, if necessary, adjust the
pressure of each tire (including the
spare) at least once a month and
before any long journey. Check the
tire pressures when the tires are
cold. Use a pressure gauge to
adjust the tire pressures to the specific values. Driving even a
short distance warms up the tires
and increases the tire pressures.
Also, the tire pressures are affected
by the outside temperature. It is
best to check tire pressure out-
doors before driving the vehicle.
When a tire becomes warm, the air
inside it expands, causing the tire
pressure to increase. Be careful not
to mistakenly release air from a
warm tire to reduce its pressure. &
Glossary of tire terminology
. Cold tire pressure
The pressure in a tire that has been
driven less than 1 mile or has been
standing for three hours or more.. Maximum inflation pressure
The maximum cold inflation pres-
sure to which a tire may be inflated. . Recommended inflation pres-
sure
The cold inflation pressure recom-
mended by a vehicle manufacturer.. Intended outboard sidewall
(1) The sidewall that contains a
Page 424 of 444

whitewall, bears white lettering
or bears manufacturer, brand,
and/or model name molding that
is higher or deeper than the
same molding on the other side-
wall of the tire, or (2)The outward facing sidewall
of an asymmetrical tire that has
a particular side that must al-
ways face outward when mount-
ing on a vehicle.
. Accessory weight
The combined weight (in excess of
those standard items which may be
replaced) of floor mats, leather
seats and cross bars to the extent
that these items are available as
factory-installed equipment
(whether installed or not). . Curb weight
The weight of a motor vehicle with
standard equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil, and
coolant and air conditioning. . Maximum loaded vehicle weight
The sum of curb weight, accessory
weight, vehicle capacity weight and production options weight.
. Normal occupant weight
150 lbs (68 kg) times the number of
occupants (3 occupants). . Occupant distribution
Distribution of occupants in a vehi-
cle, 2 in front, 1 in rear seat.. Production options weight
The combined weight of those
installed regular production options
weighing over 5.1 lbs (2.3 kg) in
excess of those standards items
which they replace, not previously
considered in curb weight or acces-
sory weight. . Vehicle capacity weight
The total weight of cargo, luggage
and occupants that can be added to
the vehicle. . Vehicle maximum load on a tire
Load on an individual tire that is
determined by distributing to each
axle its share of the maximum
loaded vehicle weight and dividing
by two. . Vehicle normal load on a tire
Load on an individual tire that is determined by distributing to each
axle its share of the curb weight,
accessory weight, and normal oc-
cupant weight and dividing by two. &
Tire care –maintenance and
safety practices
. Check on a daily basis that the
tires are free from serious damage,
nails, and stones. At the same time,
check the tires for abnormal wear.. Inspect the tire tread regularly
and replace the tires before their
tread wear indicators become visi-
ble. When a tire ’s tread wear
indicator becomes visible, the tire
is worn beyond the acceptable limit
and must be replaced immediately.
With a tire in this condition, driving
at even low speeds in wet weather
can cause the vehicle to hydro-
plane. Possible resulting loss of
vehicle control can lead to anaccident. . To maximize the life of each tire
and ensure that the tires wear
uniformly, it is best to rotate the
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
13-7
– CONTINUED –
Page 425 of 444

13-8Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
tires every 7,500 miles (12,000 km).
Rotating the tires involves switch-
ing the front and rear tires on the
right-hand side of the vehicle and
similarly switching the front and
rear tires on the left-hand side of
the vehicle. (Each tire must be kept
on its original side of the vehicle.)
Replace any damaged or unevenly
worn tire at the time of rotation.
After tire rotation, adjust the tire
pressures and make sure the wheel
nuts are correctly tightened. A
tightening torque specification and
a tightening sequence specification
for the wheel nuts can be found“ Flat tires
”section in chapter 9.
& Vehicle load limit –how to
determine
The load capacity of your vehicle is
determined by weight, not by avail-
able cargo space. The load limit of
your vehicle is shown on the
vehicle placard attached to the
driver ’s side B-pillar. Locate the
statement “The combined weight of occupants and cargo should
never exceed XXX kg or XXX lbs
”
on your vehicle ’s placard.
Thevehicleplacardalsoshows
seating capacity of your vehicle.
The total load capacity includes the
total weight of driver and all pas-
sengers and their belongings, any
cargo, any optional equipment such
as a trailer hitch, roof rack or bike
carrier, etc., and the tongue load of
a trailer. Therefore cargo capacity
can be calculated by the followingmethod.
Cargo capacity = Load limit �(total
weight of occupants + total weight
of optional equipment + tongue
load of a trailer (if applicable))
For towing capacity information and
weight limits, refer to “Trailer towing
”
section in chapter 8. ! Calculating total and load ca-
pacities varying seating con-
figurations
Calculate the available load capa-
city as shown in the following examples:
Example 1A
Vehicle capacity weight of the
vehicle is 800 lbs (363 kg), which
is indicated on the vehicle placard
with the statement "The combined
weight of occupants and cargo
should never exceed 363 kg or
800 lbs".
For example, if the vehicle has one
occupant weighing 154 lbs (70 kg)
plus cargo weighing 551 lbs (250kg). 1.
Calculate the total weight.
Page 426 of 444

2.Calculate the available load ca-
pacity by subtracting the total
weight from the vehicle capacity
weight of 800 lbs (363 kg).
3. The result of step 2 shows that a
further 95 lbs (43 kg) of cargo can
be carried. Example 1B
For example, if a person weighing
176 lbs (80 kg) now enters the
same vehicle (bringing the number
of occupants to two), the calcula-
tions are as follows: 1.
Calculate the total weight.
2.Calculate the available load ca-
pacity.
3. The total weight now exceeds
the capacity weight by 81 lbs (37
kg), so the cargo weight must be
reduced by 81 lbs (37 kg) or more.
Example 2A
Vehicle capacity weight of the
vehicle is 800 lbs (363 kg), which
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
13-9
– CONTINUED –
Page 427 of 444

13-10Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
is indicated on the vehicle placard
with the statement “The combined
weight of occupants and cargo
should never exceed 363 kg or
800 lbs ”.
For example, the vehicle has one
occupant weighing 165 lbs (75 kg)
plus cargo weighing 265 lbs (120
kg). In addition, the vehicle is fitted
with a trailer hitch weighing 22 lbs
(10 kg), to which is attached a
trailer weighing 1,764 lbs (800 kg).
10% of the trailer weight is applied
to the trailer tongue (i.e. Tongue
load = 176 lbs (80 kg)). 1. Calculate the total weight.
2.Calculate the available load ca-
pacity.
3. The result of step 2 shows that a
further 172 lbs (78 kg) of cargo can
be carried.
Example 2B
For example, if a person weighing
143 lbs (65 kg) and a child weighing
40 lbs (18 kg) now enter the same vehicle (bringing the number of
occupants to three), and a child
restraint system weighing 11 lbs (5
kg) is installed in the vehicle for the
child to use, the calculations are asfollows: 1.
Calculate the total weight.
2.Calculate the available load ca-
pacity.
Page 428 of 444

3.The total weight now exceeds
the capacity weight by 22 lbs (10
kg), so the cargo weight must be
reduced by 22 lbs (10 kg) or more. & Determining compatibility of
tire and vehicle load capaci-ties
The sum of four tires ’maximum
load ratings must exceed the max-
imum loaded vehicle weight( “GVWR ”). In addition, sum of the
maximum load ratings of two front
tires and of two rear tires must
exceed each axle ’s maximum
loaded capacity ( “GAWR ”). Original
equipment tires are designed to
fulfill those conditions.
The maximum loaded vehicle
weight is referred to Gross Vehicle
Weight Rating (GVWR). And each axle
’s maximum loaded capacity is
referred to Gross Axle Weight Rat-
ing (GAWR). The GVWR and each axle ’s GAWR are shown on the
vehicle certification label affixed to
the driver ’s door.
The GVWR and front and rear
GAWRs are determined by not only
the maximum load rating of tires but
also loaded capacities of the vehi-cle ’s suspension, axles and other
parts of the body.
Therefore, this means that the
vehicle cannot necessarily be
loaded up to the tire ’s maximum
load rating on the tire sidewall.
& Adverse safety conse-
quences of overloading on
handling and stopping and
on tires
Overloading could affect vehicle
handling, stopping distance, vehicle
and tire as shown in the following.
This could lead to an accident and
possibly result in severe personal
injury. .
Vehicle stability will deteriorate.
. Heavy and/or high-mounted
loads could increase the risk of
rollover.. Stopping distance will increase.
. Brakes could overheat and fail.
. Suspension, bearings, axles and
other parts of the body could break
or experience accelerated wear
that will shorten vehicle life. . Tires could fail.
. Tread separation could occur.
. Tire could separate from its rim.
& Steps for Determining Cor-
rect Load Limit
1. Locate the statement “The com-
bined weight of occupants and
cargo should never exceed XXXpounds ”on your vehicle ’s placard.
2. Determine the combined weight
of the driver and passengers that
will be riding in your vehicle. 3. Subtract the combined weight of
the driver and passengers from
XXX kilograms or XXX pounds. 4. The resulting figure equals the
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
13-11
– CONTINUED –
Page 429 of 444

13-12Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
available amount of cargo and
luggage load capacity. For exam-
ple, if the “XXX ”amount equals
1,400 lbs (635kg). and there will be
five- 150 lbs (68 kg) passengers in
your vehicle, the amount of avail-
able cargo and luggage load capa-
city is 650 lbs. (1,400 �750 (5 6
150) = 650 lbs.)
5. Determine the combined weight
of luggage and cargo being loaded
on the vehicle. That weight may not
safely exceed the available cargo
and luggage load capacity calcu-
lated in Step 4. 6. If your vehicle will be towing a
trailer, load from your trailer will be
transferred to your vehicle. Consult
this manual to determine how this
reduces the available cargo and
luggage load capacity of your ve-hicle. Uniform tire quality grading standards
This information indicates the rela-
tive performance of passenger car
tires in the area of treadwear,
traction, and temperature resis-
tance. This is to aid the consumer
in making an informed choice in the
purchase of tires.
Quality grades can be found where
applicable on the tire sidewall be-
tween tread shoulder and maxi-
mum section width. For example:
Treadwear 200 Traction AA Tem-
perature A
The quality grades apply to new
pneumatic tires for use on passen-
ger cars. However, they do not
apply to deep tread, winter type
snow tires, space-saver or tempor-
ary use spare tires, tires with
nominal rim diameters of 12 inches
or less, or to some limited produc-
tion tires.
All passenger car tires must con-form to Federal Safety Require-
ments in addition to these grades. &
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a compara-
tive rating based on the wear rate of
the tire when tested under con-
trolled conditions on a specified
government test course.
For example, a tire graded 150
would wear one and one-half (1-1/
2) times as well on the government
course as a tire graded 100. The
relative performance of tires de-
pends upon the actual conditions
of their use, however, and may
depart significantly from the norm
due to variations in driving habits,
service practices and differences in
road characteristics and climate. & Traction AA, A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to
lowest, are AA, A, B and C. Those
grades represent the tire ’s ability to
stop on wet pavement as measured
under controlled conditions on spe-
Page 430 of 444

cified government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete. A tire marked
C may have poor traction perfor- mance.
WARNING
The traction grade assigned to
this tire is based on straight-
ahead braking traction tests,
and does not include accel-
eration, cornering, hydroplan-
ing, or peak traction charac-teristics.
& Temperature A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the
highest), B, and C, representing thetire ’s resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate heat
when tested under controlled con-
ditions on a specified indoor labora-
tory test wheel. Sustained high
temperature can cause the material
of the tire to degenerate and reduce
tire life, and excessive temperature
can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of
performance which all passenger
car tires must meet under the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Stan-
dards No. 109. Grades B and A
represent higher levels of perfor-
mance on the laboratory test wheel
than the minimum required by law.
WARNING
The temperature grade for this
tire is established for a tire
that is properly inflated and
not overloaded. Excessive
speed, underinflation, or ex-
cessive loading, either sepa-
rately or in combination, can
cause heat buildup and possi-
ble tire failure. Reporting safety defects (USA)
If you believe that your vehicle has
a defect which could cause a
crash or could cause injury or
death, you should immediately in-
form the National Highway Traffic
Safety Administration (NHTSA) in
addition to notifying Subaru of
America, Inc.
If NHTSA receives similar com-
plaints, it may open an investiga-
tion, and if it finds that a safety
defect exists in a group of vehi-
cles, it may order a recall and
remedy campaign. However,
NHTSA cannot become involved
in individual problems between
you, your dealer, or Subaru of
America, Inc. To contact NHTSA,
you may call the Vehicle Safety
Hotline toll-free at 1-888-327-4236
(TTY: 1-800-424-9153); go to
http://www.safercar.gov; or write
to: Administrator, NHTSA, 400
Seventh Street, SW., Washington,
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
13-13
– CONTINUED –