oil type SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: JIMNY, Model: SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.GPages: 687, PDF Size: 13.38 MB
Page 430 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-73
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Check vehicle and environmental condition for :
–Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Ambient temp. : –10 °C, 14 °F or higher
–Intake air temp. : 70 °C, 158 °F or lower
–Engine coolant temp. : – 10 – 110 °C, 14 – 230 °F
4) Start engine and keep it at idle for 2 min. or more.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
6) If DTC is not detected at idle, consult usual driving based on information obtained in “Customer complaint
analysis” and “Freeze frame data check”.
INSPECTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Engine under other than high revolution condition
Not on rough road
Engine speed changing rate (below specified value)
Manifold absolute pressure changing rate (below
specified value)
Throttle opening changing rate (below specified
value)
Misfire rate per 200 or 1000 engine revolutions (how
much and how often crankshaft revolution speed
changes) is higher than specified valueEngine overheating
Vacuum leaks (air inhaling) from air intake system
Ignition system malfunction (spark plug(s), high-
tension cord(s), ignition coil assembly)
Fuel pressure out of specification
Fuel injector malfunction (clogged or leakage)
Engine compression out of specification
Valve lash (clearance) out of specification
Manifold absolute pressure sensor malfunction
Engine coolant temp. sensor malfunction
PCV valve malfunction
EVAP control system malfunction
EGR system malfunction
NOTE:
Among different types of random misfire, if misfire occurs at cylinders 1 and 4 or cylinders 3 and 2
simultaneously, it may not possible to reconfirm DTC by using the following DTC confirmation proce-
dure. When diagnosing the trouble of DTC P0300 (Random misfire detected) of the engine which is
apparently misfiring, even if DTC P0300 cannot be reconfirmed by using the following DTC confirma-
tion procedure, proceed to the following Diag. Flow Table.
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diag. Flow Table” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine
Diag. Flow Table”.
2 Is there DTC other than Fuel system (DTC P0171/
P0172) and misfire (DTC P0300 – P0304)?Go to applicable DTC
Diag. Flow Table.Go to Step 3.
Page 484 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-3
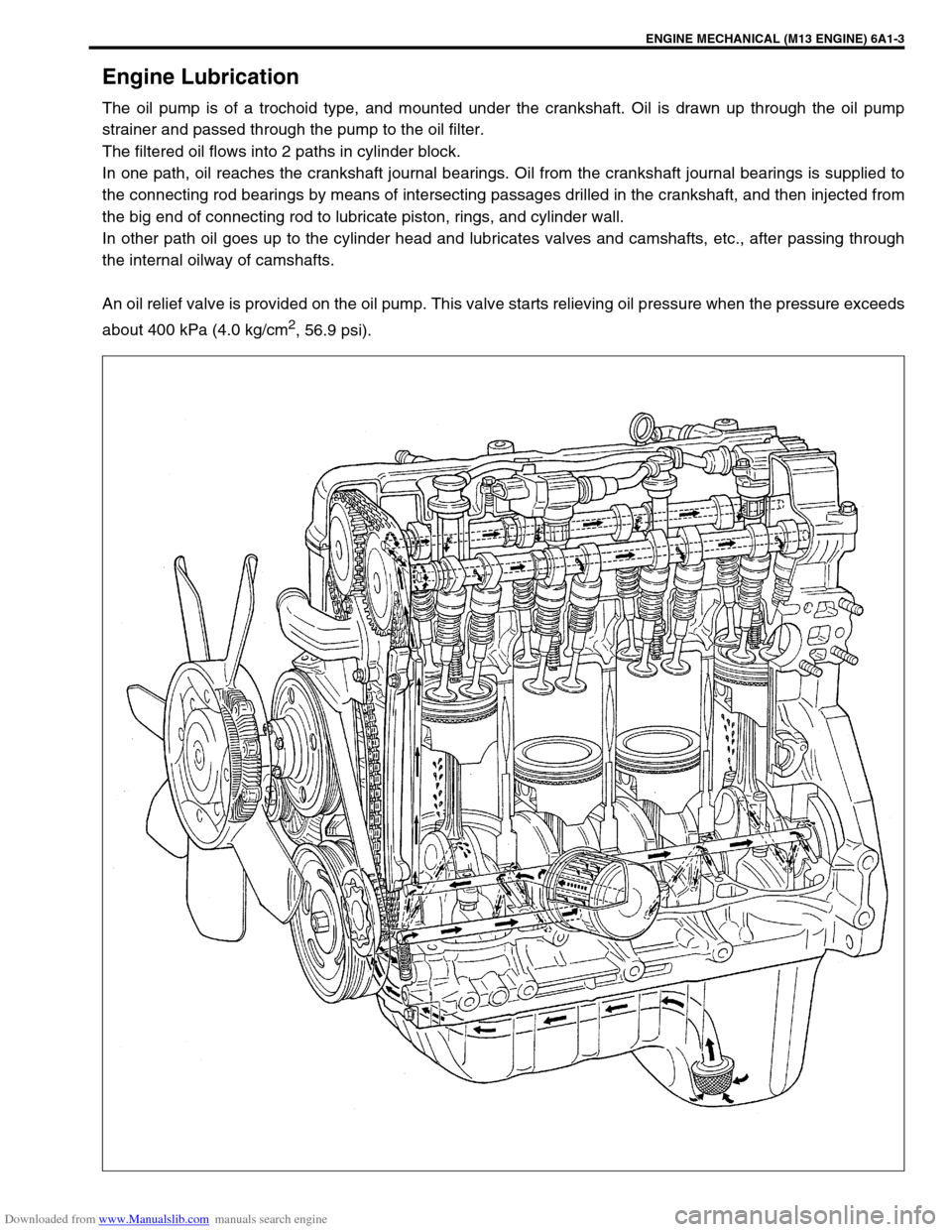
Engine Lubrication
The oil pump is of a trochoid type, and mounted under the crankshaft. Oil is drawn up through the oil pump
strainer and passed through the pump to the oil filter.
The filtered oil flows into 2 paths in cylinder block.
In one path, oil reaches the crankshaft journal bearings. Oil from the crankshaft journal bearings is supplied to
the connecting rod bearings by means of intersecting passages drilled in the crankshaft, and then injected from
the big end of connecting rod to lubricate piston, rings, and cylinder wall.
In other path oil goes up to the cylinder head and lubricates valves and camshafts, etc., after passing through
the internal oilway of camshafts.
An oil relief valve is provided on the oil pump. This valve starts relieving oil pressure when the pressure exceeds
about 400 kPa (4.0 kg/cm
2, 56.9 psi).
Page 618 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E-13
ECM TERMINAL ARRANGEMENT TABLE
For TYPE A (See NOTE)
CONNEC-
TORTERMINAL WIRE COLOR CIRCUITCONNEC-
TORTERMINAL WIRE COLOR CIRCUIT
E191 B Ground for ECM
E187 W Backup power source
2 B/R Ground for drive circuit
8R/GImmobilizer indicator lamp
(if equipped)
3 B/R Ground for drive circuitDuty output terminal (vehicle without
immobilizer indicator lamp)
4 Bl/G Canister purge valve 9––
5 Bl/OrPower steering pressure switch
(if equipped)10 Bl Main relay
6 G/Y IAC valve 11 Br Tachometer
7 P/B Heater of HO2S-1 (if equipped) 12 Y/B Data link connector (5 V)
8 W/B No.4 fuel injector 13 WHeated oxygen sensor-2
(if equipped)
9 R/W No.1 fuel injector 14 W/BIDiagnosis switch terminal
(vehicle without immobilizer indicator
lamp)
10 B/Bl Ground for sensor circuit 15 PTest switch terminal
(vehicle without immobilizer indicator
lamp)
11 W CMP sensor 16 G/W A/C SW signal (if equipped)
12––17 R/Y Lighting switch
13R
R/BlHeated oxygen sensor-1
(if equipped)
CO adjusting resistor (w/o HO2S)18 P/B A/C condenser fan relay (if equipped)
14 G/B ECT sensor 19 W/G Fuel pump relay
15 Lg/B IAT sensor 20 B/Bl Ground for sensor
16 Lg TP sensor 21 B/RThrottle opening signal output for A/T
(A/T)
17 Gr/BIEGR valve (stepper motor coil 3, if
equipped)22 Y/RFuel level gauge (vehicle with immo-
bilizer indicator lamp)
18 GrEGR valve (stepper motor coil 1, if
equipped)23––
19 Br/BIG coil assembly for No.2 and 3 spark
plugs24 Bl/Y Heater blower switch
20 Br/WIG coil assembly for No.1 and 4 spark
plugs
21 R/G No.2 fuel injector
E171––
22 Lg/R Power supply for sensor 2 R R-range signal (A/T)
23 G/R CKP sensor 3––
24––4––
25 W Knock sensor 5 B/Or Overdrive cut signal (A/T)
26 G MAP sensor 6 G/Y D-range idle-up signal (A/T)
27 W/R A/C evaporator temp. sensor 7 G/W Stop lamp switch
28 Gr/BEGR valve (stepper motor coil 4, if
equipped)8––
29 Gr/REGR valve (stepper motor coil 2, if
equipped)9 B/W Ignition switch
30––10––
31 W/G No.3 fuel injector 11 Y Vehicle speed sensor
12 G ABS signal (if equipped)
E181 P A/C compressor clutch (if equipped) 13B/Y (M/T)
B/R (A/T)Engine start signal
2 V/Y Malfunction indicator lamp 14––
3 P/G Data link connector (12 V) 15––
4 R/BI Heater of HO2S-2 (if equipped) 16 R/W Rear defogger switch (if equipped)
5 Bl/B Power source 17 G/RA/T failure signal (A/T) (vehicle with
immobilizer indicator lamp)
6 Bl/B Power source
NOTE:
See NOTE in “ECM INPUT / OUTPUT CIRCUIT DIAGRAM” for applicable model.
Page 619 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6E-14 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
For TYPE B (See NOTE)
CONNEC-
TORTERMINAL WIRE COLOR CIRCUITCONNEC-
TORTERMINAL WIRE COLOR CIRCUIT
E191 B Ground for ECM
E187 W Backup power source
2 B/R Ground for drive circuit
8R/GImmobilizer indicator lamp
(if equipped)
3 B/R Ground for drive circuitDuty output terminal (vehicle without
immobilizer indicator lamp)
4 Bl/G Canister purge valve 9––
5 Bl/OrPower steering pressure switch
(if equipped)10 Bl Main relay
6 G/Y IAC valve 11 B/W Ignition switch
7 P/B Heater of HO2S-1 (if equipped) 12 R/W Rear defogger switch
8 W/B No.4 fuel injector 13––
9 R/W No.1 fuel injector 14 W/BIDiagnosis switch terminal
(vehicle without immobilizer indicator
lamp)
10 B/Bl Ground for sensor circuit 15 PTest switch terminal
(vehicle without immobilizer indicator
lamp)
11 W CMP sensor 16 G/W A/C SW signal (if equipped)
12––17 R/Y Lighting switch
13R
R/BlHeated oxygen sensor-1
(if equipped)
CO adjusting resistor (w/o HO2S)18 P/B A/C condenser fan relay (if equipped)
14 G/B ECT sensor 19 W/G Fuel pump relay
15 Lg/B IAT sensor 20B/Y (M/T)
B/R (A/T)Engine start signal
16 Lg TP sensor 21 G/W Stop lamp switch
17 Gr/BIEGR valve (stepper motor coil 3, if
equipped)22 Y Vehicle speed sensor
18 GrEGR valve (stepper motor coil 1, if
equipped)23––
19 Br/BIG coil assembly for No.2 and 3 spark
plugs24––
20 Br/WIG coil assembly for No.1 and 4 spark
plugs
21 R/G No.2 fuel injector
E171 W/R A/C evaporator temp. sensor
22 Lg/R Power supply for sensor 2 R R-range signal (A/T)
23 G/R CKP sensor 3––
24––4––
25 W Knock sensor 5 B/Or Overdrive cut signal (A/T)
26 G MAP sensor 6 G/Y D-range idle-up signal (A/T)
27––7 Y/B Data link connector
28 Gr/BEGR valve (stepper motor coil 4, if
equipped)8––
29 Gr/REGR valve (stepper motor coil 2, if
equipped)9 V/Y Malfunction indicator lamp
30––10––
31 W/G No.3 fuel injector 11 P/G Data link connector (12 V)
12 G ABS signal (if equipped)
E181 P A/C compressor clutch (if equipped) 13 Bl/Y Heater blower switch
2––14 B/Bl Ground for sensor
3––15 B/R Throttle opening sensor
4 R/BI Heater of HO2S-2 (if equipped) 16 Br Tachometer
5 Bl/B Power source 17––
6 Bl/B Power source
NOTE:
See NOTE in “ECM INPUT / OUTPUT CIRCUIT DIAGRAM” for applicable model.
Page 653 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6F-4 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
IGNITION SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diagnostic Flow Table” in Section 6 per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine Diag.
Flow Table” in Section
6.
2Ignition Spark Test
1) Check all spark plugs for condition and type refer-
ring to “Spark Plugs” section.
2) If OK, perform ignition spark test, referring to “Igni-
tion Spark Test” section.
Is spark emitted from all spark plugs?Go to Step 11. Go to Step 3.
3Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check
Is DTC stored in ECM?Go to applicable DTC
Diag. Flow Table in
Section 6.Go to Step 4.
4Electrical Connection Check
1) Check ignition coil assemblies and high-tension
cords for electrical connection.
Are they connected securely?Go to Step 5. Connect securely.
5High-tension Cords Check
1) Check high-tension cord for resistance referring to
“High-Tension Cords” section.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 6. Replace high-tension
cord(s).
6Ignition Coil Assembly Power Supply and Ground Cir-
cuit Check
1) Check ignition coil assembly power supply and
ground circuits for open and short.
Are circuits in good condition?Go to Step 7. Repair or replace.
7Ignition Coil Assembly Check
1) Check ignition coil for resistance referring to “Igni-
tion Coil Assembly” section.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 8. Replace ignition coil
assembly.
8Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Check
1) Check crankshaft position sensor referring to Step
2 and 6 of “DTC P0335 (No.23) CKP Sensor Cir-
cuit Malfunction” in Section 6.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 9. Tighten CKP sensor
bolt, replace CKP sen-
sor or CKP sensor
plate.
9Ignition Trigger Signal Circuit Check
1) Check ignition trigger signal wire for open, short
and poor connection.
Is circuit in good condition?Go to Step 10. Repair or replace.
10A Known-good Ignition Coil Assembly Substitution
1) Substitute a known-good ignition coil assembly
and then repeat Step 2.
Is check result of Step 2 satisfactory?Go to Step 11. Substitute a known-
good ECM and then
repeat Step 2.
11Ignition Timing Check
1) Check initial ignition timing and ignition timing
advance referring to “Ignition Timing” section.
Is check result satisfactory?System is in good con-
dition.Check CKP sensor,
CKP sensor plate and
input signals related to
this system.
Page 654 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM 6F-5
On-Vehicle Service
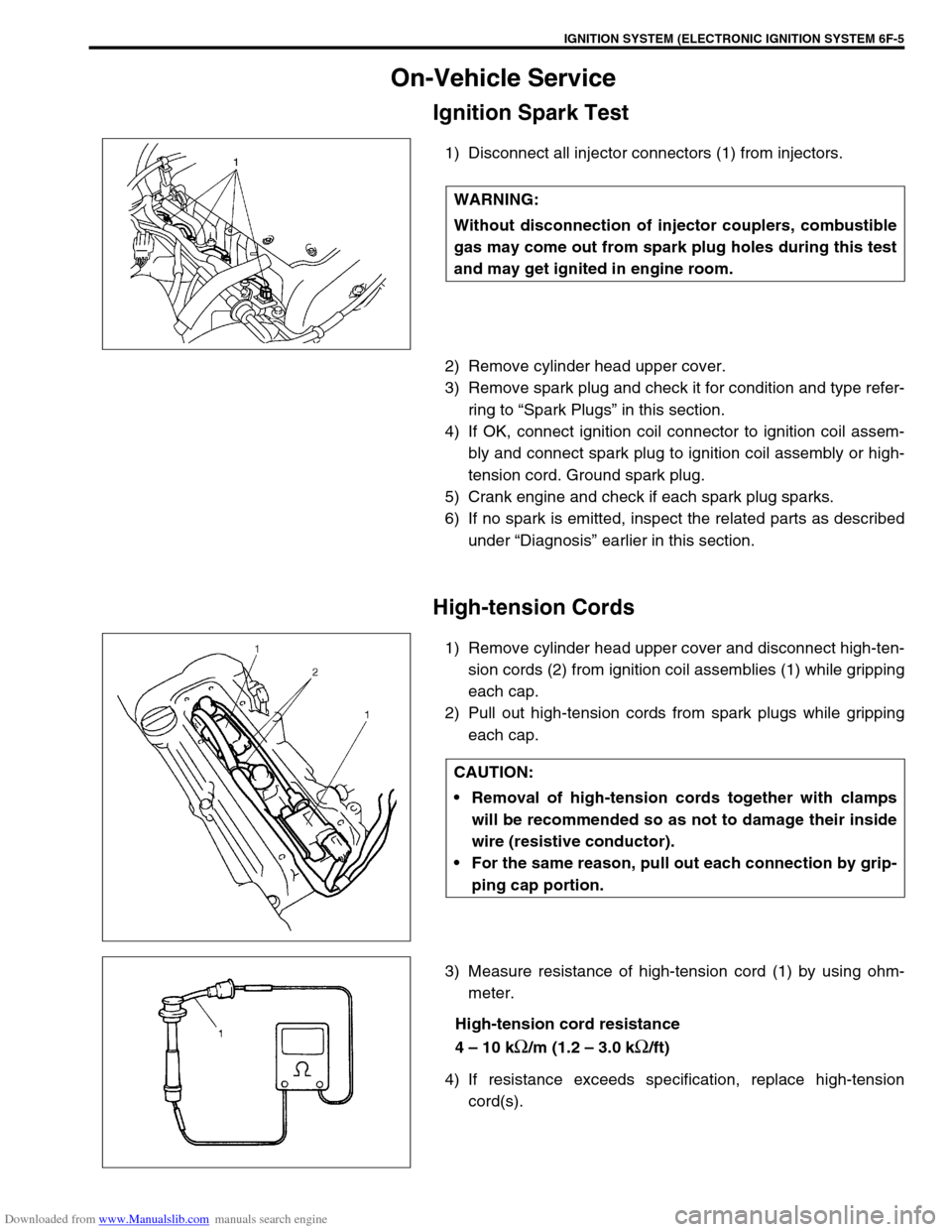
Ignition Spark Test
1) Disconnect all injector connectors (1) from injectors.
2) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
3) Remove spark plug and check it for condition and type refer-
ring to “Spark Plugs” in this section.
4) If OK, connect ignition coil connector to ignition coil assem-
bly and connect spark plug to ignition coil assembly or high-
tension cord. Ground spark plug.
5) Crank engine and check if each spark plug sparks.
6) If no spark is emitted, inspect the related parts as described
under “Diagnosis” earlier in this section.
High-tension Cords
1) Remove cylinder head upper cover and disconnect high-ten-
sion cords (2) from ignition coil assemblies (1) while gripping
each cap.
2) Pull out high-tension cords from spark plugs while gripping
each cap.
3) Measure resistance of high-tension cord (1) by using ohm-
meter.
High-tension cord resistance
4 – 10 k
Ω/m (1.2 – 3.0 kΩ/ft)
4) If resistance exceeds specification, replace high-tension
cord(s). WARNING:
Without disconnection of injector couplers, combustible
gas may come out from spark plug holes during this test
and may get ignited in engine room.
CAUTION:
Removal of high-tension cords together with clamps
will be recommended so as not to damage their inside
wire (resistive conductor).
For the same reason, pull out each connection by grip-
ping cap portion.
Page 656 of 687
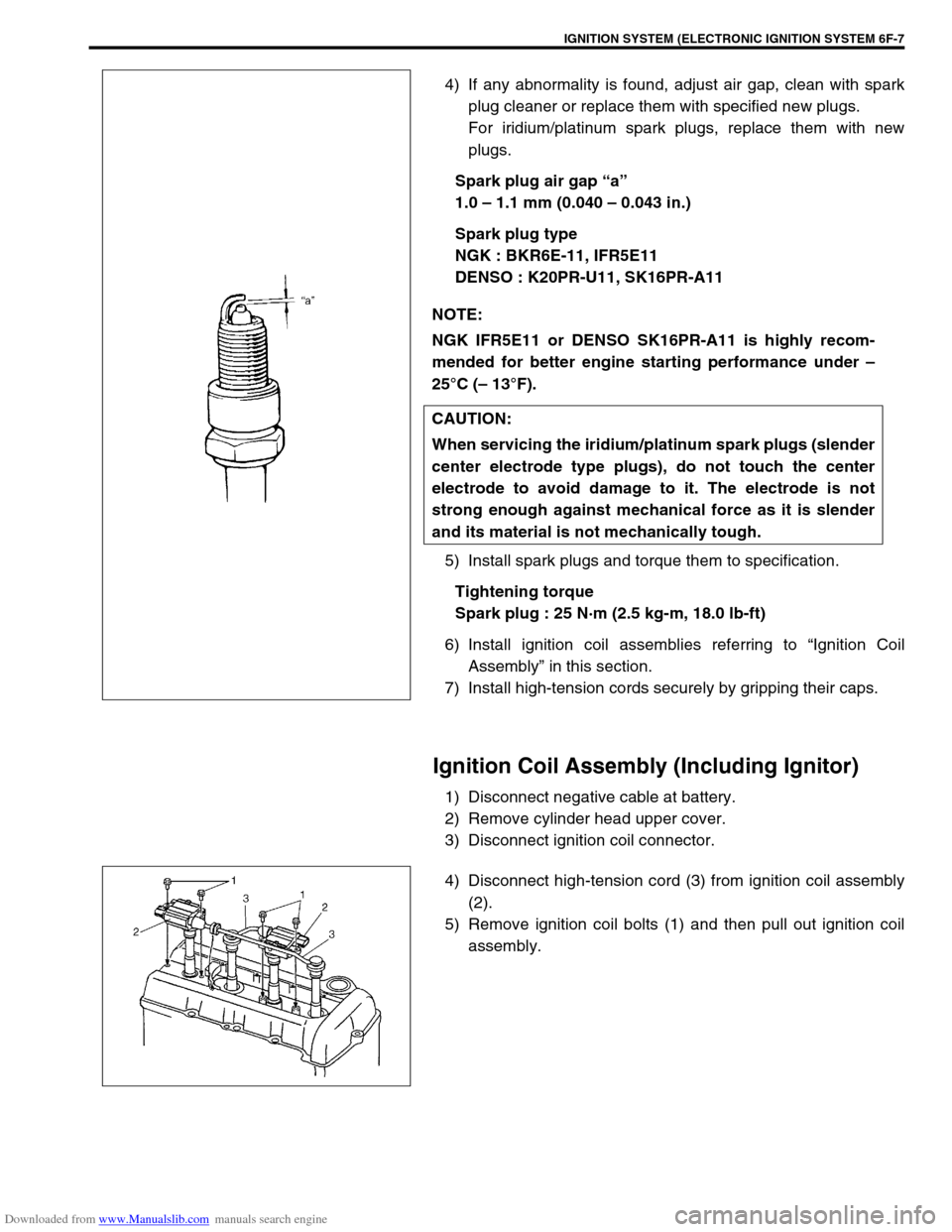
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM 6F-7
4) If any abnormality is found, adjust air gap, clean with spark
plug cleaner or replace them with specified new plugs.
For iridium/platinum spark plugs, replace them with new
plugs.
Spark plug air gap “a”
1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.040 – 0.043 in.)
Spark plug type
NGK : BKR6E-11, IFR5E11
DENSO : K20PR-U11, SK16PR-A11
5) Install spark plugs and torque them to specification.
Tightening torque
Spark plug : 25 N·m (2.5 kg-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
6) Install ignition coil assemblies referring to “Ignition Coil
Assembly” in this section.
7) Install high-tension cords securely by gripping their caps.
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor)
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
3) Disconnect ignition coil connector.
4) Disconnect high-tension cord (3) from ignition coil assembly
(2).
5) Remove ignition coil bolts (1) and then pull out ignition coil
assembly. NOTE:
NGK IFR5E11 or DENSO SK16PR-A11 is highly recom-
mended for better engine starting performance under –
25°C (– 13°F).
CAUTION:
When servicing the iridium/platinum spark plugs (slender
center electrode type plugs), do not touch the center
electrode to avoid damage to it. The electrode is not
strong enough against mechanical force as it is slender
and its material is not mechanically tough.
Page 657 of 687
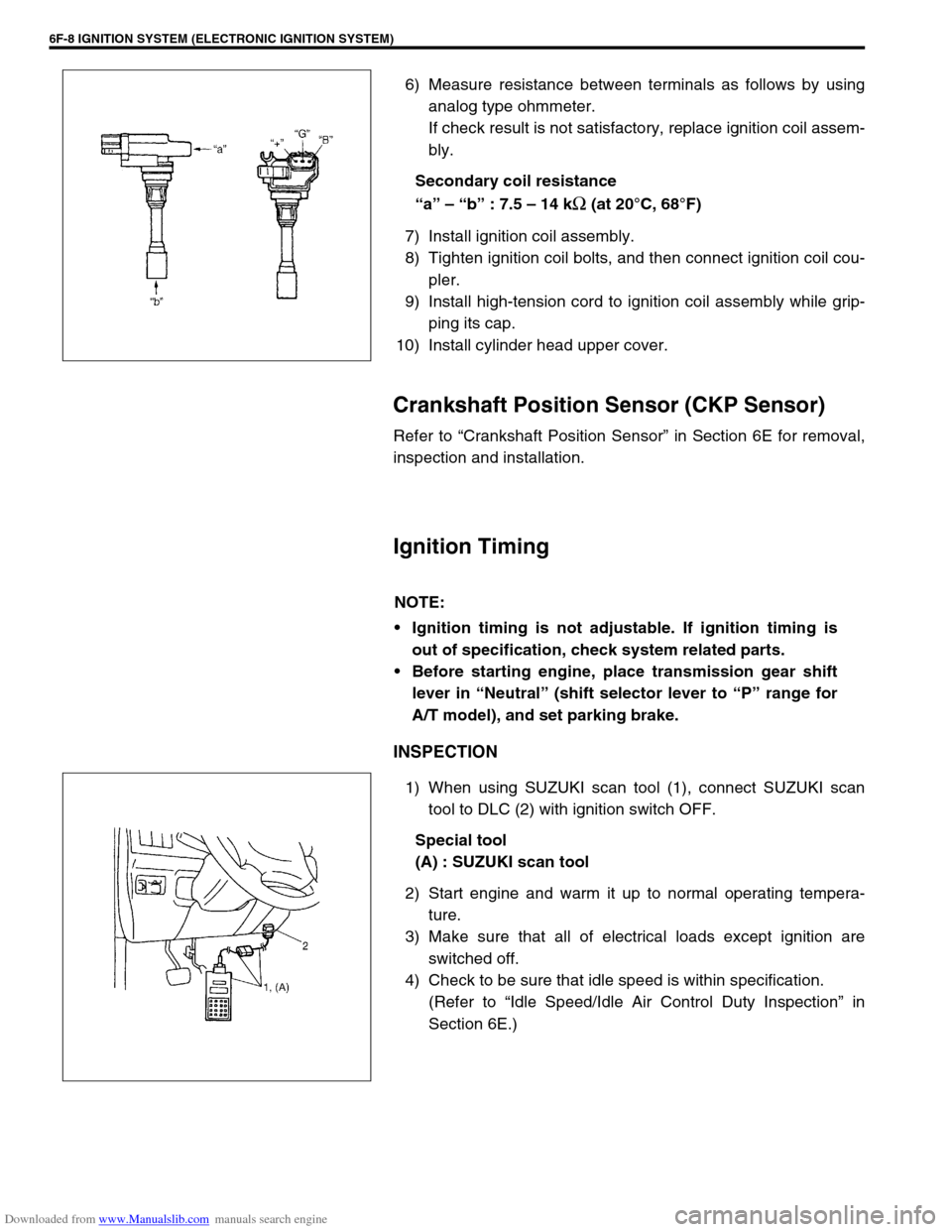
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6F-8 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
6) Measure resistance between terminals as follows by using
analog type ohmmeter.
If check result is not satisfactory, replace ignition coil assem-
bly.
Secondary coil resistance
“a” – “b” : 7.5 – 14 k
Ω (at 20°C, 68°F)
7) Install ignition coil assembly.
8) Tighten ignition coil bolts, and then connect ignition coil cou-
pler.
9) Install high-tension cord to ignition coil assembly while grip-
ping its cap.
10) Install cylinder head upper cover.
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP Sensor)
Refer to “Crankshaft Position Sensor” in Section 6E for removal,
inspection and installation.
Ignition Timing
INSPECTION
1) When using SUZUKI scan tool (1), connect SUZUKI scan
tool to DLC (2) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating tempera-
ture.
3) Make sure that all of electrical loads except ignition are
switched off.
4) Check to be sure that idle speed is within specification.
(Refer to “Idle Speed/Idle Air Control Duty Inspection” in
Section 6E.)
NOTE:
Ignition timing is not adjustable. If ignition timing is
out of specification, check system related parts.
Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift
lever in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for
A/T model), and set parking brake.
Page 671 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6H-4 CHARGING SYSTEM
When keeping battery on vehicle over a long period of time, follow
instructions given below.
Weekly, start the engine and run it until it reaches normal
operating temperature with engine speed of 2,000 to 3,000
rpm. Make sure all electric switches are off before storing the
vehicle.
Recharge the battery twice a month to prevent it from dis-
charging excessively. This is especially important when
ambient temperature is low.
The battery discharges even when it is not used, while vehi-
cles are being stored. Battery electrolyte can freeze and bat-
tery case can crack at cold ambient condition if battery is not
properly charged.
2) Keep the battery cable connections clean.
The cable connections, particularly at the positive (+) termi-
nal post, tend to become corroded. The product of corrosion,
or rust, on the mating faces of conductors resists the flow of
current.
Clean the terminals and fittings periodically to ensure good
metal-to-metal contact, and grease the connections after
each cleaning to protect them against rusting.
3) Be always in the know as to the state of charge of the bat-
tery. The simplest way to tell the state of charge is to carry
out a hydrometer test. The hydrometer is an instrument for
measuring the specific gravity (S.G.) of the battery electro-
lyte. The S.G. of the electrolyte is indicative of the state of
charge. Refer to “HYDROMETER TEST” in this section.
Generator
The generator is a small and high performance type with an IC regulator incorporated.
The internal components are connected electrically as shown below figure.
The generator features are as follows:
Solid state regulator is mounted inside the generator.
All regulator components are enclosed into a solid mold.
This unit along with the brush holder assembly is attached to the rear housing.
The IC regulator uses integrated circuits and controls the voltage produced by the generator, and the volt-
age setting cannot be adjusted.
The generator rotor bearings contain enough grease to eliminate the need for periodic lubrication. Two
brushes carry current through the two slip rings to the field coil mounted on the rotor, and under normal con-
ditions will provide long period of attention-free service.
The stator windings are assembled on the inside of a laminated core that forms part of the generator frame.
A condenser mounted in the rear housing suppresses radio noise.