flat tire SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 246 of 698

WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-1
6F1
6F2
6G
3F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 3F
WHEELS AND TIRES
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................... 3F-2
TIRES ............................................................ 3F-2
WHEELS ....................................................... 3F-2
REPLACEMENT TIRES ................................ 3F-2
REPLACEMENT WHEELS ........................... 3F-2
HOW TO MEASURE WHEEL RUNOUT... 3F-3
METRIC LUG NUTS AND WHEEL
STUDS ...................................................... 3F-3
DIAGNOSIS ...................................................... 3F-3
DIAGNOSIS TABLE ...................................... 3F-3
BALANCING WHEELS ................................. 3F-3
GENERAL BALANCE PROCEDURES ......... 3F-4
OFF-VEHICLE BALANCING ..................... 3F-4
ON-VEHICLE BALANCING....................... 3F-4MAINTENANCE AND MINOR
ADJUSTMENTS ............................................... 3F-5
WHEEL MAINTENANCE .............................. 3F-5
WHEEL ATTACHING STUDS .................. 3F-5
MATCHED TIRES AND WHEELS ............ 3F-5
TIRE MAINTENANCE................................... 3F-5
TIRE PLACARD ........................................ 3F-5
INFLATION OF TIRES .............................. 3F-6
TIRE ROTATION ...................................... 3F-6
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE ................................... 3F-7
WHEEL ......................................................... 3F-7
TIRE .............................................................. 3F-8
MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING ........... 3F-8
REPAIR ..................................................... 3F-8
NOTE:
All wheel fasteners are important attaching parts in that they could affect the performance of vital
parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one of the
same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a replace-
ment part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reas-
sembly to assure proper retention of all parts.
There is to be no welding as it may result in extensive damage and weakening of the metal.
Page 247 of 698

3F-2 WHEELS AND TIRES
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
TIRES
This vehicle is equipped with the following tire.
Tire size
: 165/70R14
The tire is of tubeless type. The tire is designed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation pressures.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an important influence on tire life. Heavy cornering, excessively
rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp braking increase tire wear.
WHEELS
Standard equipment wheels are the following steel wheel.
Wheel size
: 14 x 4 1/2 J
REPLACEMENT TIRES
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment type tire should be used. Refer to the “Tire Placard”.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride, handling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to equalize braking traction.
The metric term for tire inflation pressure is the kilo pascal (kPa).
Tire pressures is usually printed in both kPa and psi on the “Tire
Placard”.
Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The chart, shown the table, converts commonly used inflation
pressures from kPa to psi.
REPLACEMENT WHEELS
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have excessive lateral or radial runout, air leak through
welds, have elongated bolt holes, if lug nuts won’t stay tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater
runout than shown in figure below may cause objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim with
offset and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground clearance and tire clearance to body and chassis.WARNING:
Do not mix different types of tires on the same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-belted tires except
in emergencies, because handling may be seriously affected and may result in loss of control.
kPa kgf/cm²pis
160 1.6 23
180 1.8 26
200 2.0 29
220 2.2 32
240 2.4 35
260 2.6 38
280 2.8 41
300 3.0 44
Page 251 of 698
3F-6 WHEELS AND TIRES
INFLATION OF TIRES
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully calculated to give a satisfactory ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for 3 hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should be
checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the specifications on the “Tire Placard” located on the left
door (right door for right-hand side steering vehicle) lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure to increase when the tires become hot during driving.
Do not bleed or reduce tire pressure after driving. Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure”.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause :
Hard ride
Tire bruising or carcass damage
Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause :
Uneven braking
Steering lead
Reduced handling
Swerve on acceleration
Lower than recommended pressure can cause :
Tire squeal on turns
Hard Steering
Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
Tire rim bruises and rupture
Tire cord breakage
High tire temperature
Reduced handling
High fuel consumption
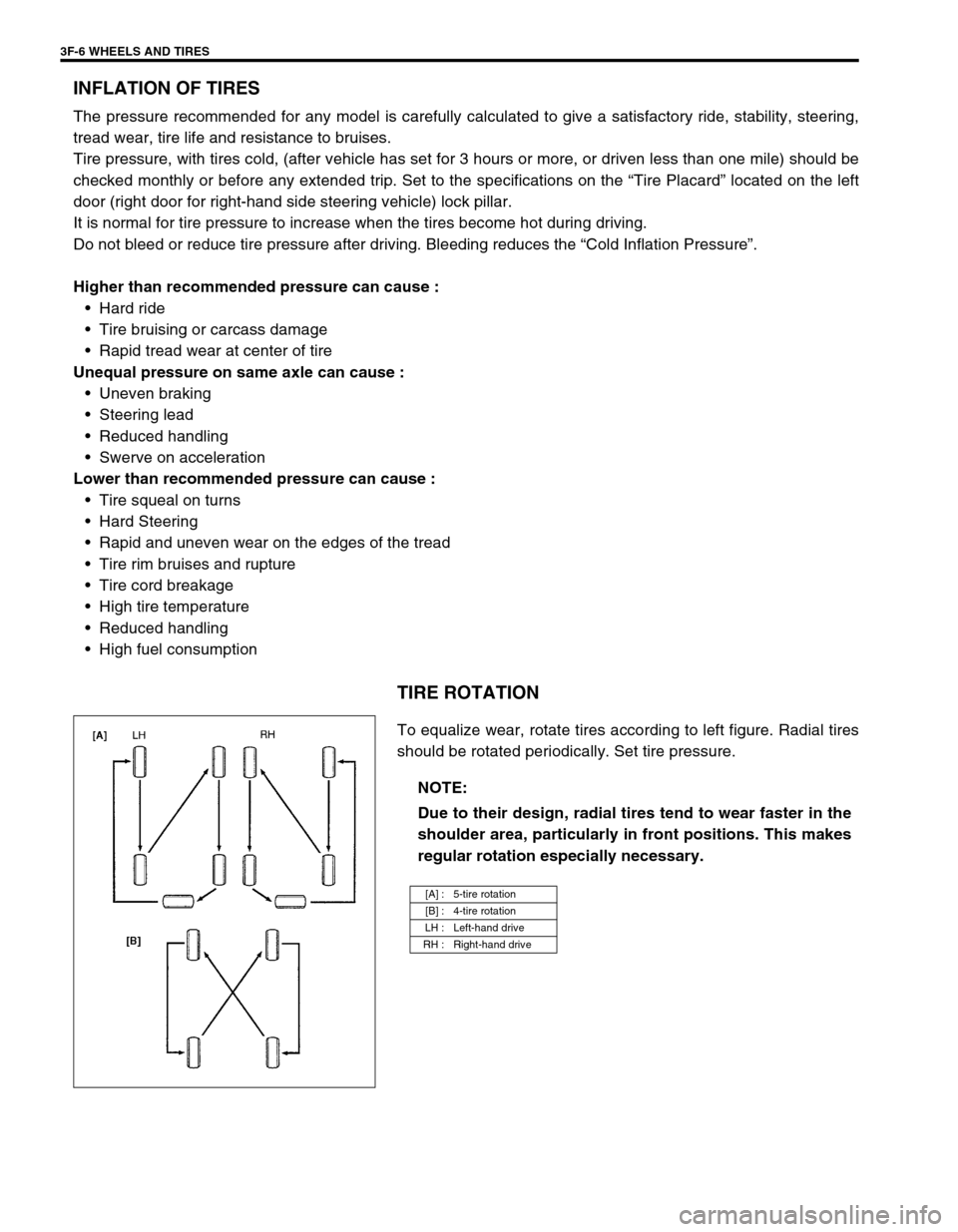
TIRE ROTATION
To equalize wear, rotate tires according to left figure. Radial tires
should be rotated periodically. Set tire pressure.
NOTE:
Due to their design, radial tires tend to wear faster in the
shoulder area, particularly in front positions. This makes
regular rotation especially necessary.
[A] : 5-tire rotation
[B] : 4-tire rotation
LH : Left-hand drive
RH : Right-hand drive
Page 253 of 698

3F-8 WHEELS AND TIRES
TIRE
MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING
Use a tire changing machine to mount or dismount tires. Follow equipment manufacturer’s instructions. Do not
use hand tools or tire irons alone to change tires as they may damage tire beads or wheel rim.
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, old rubber and
light rust. Before mounting or dismounting a tire, bead area should be well lubricated with approved tire lubri-
cant.
After mounting, inflate to specified pressure shown on tire placard so that beads are completely seated.
Install valve core and inflate to proper pressure.
REPAIR
There are many different materials and techniques on the market to repair tires. As not all of these work on all
types of tires, tire manufacturers have published detailed instructions on how and when to repair tires. These
instructions can be obtained from each tire manufacturer.WARNING:
Do not stand over tire when inflating. Bead may break when bead snaps over rim’s safety hump and
cause serious personal injury.
Do not exceed specified pressure when inflating. If specified pressure will not seat beads, deflate, re-
lubricate and reinflate.
Over inflation may cause bead to break and cause serious personal injury.
Page 278 of 698
BRAKES 5-5
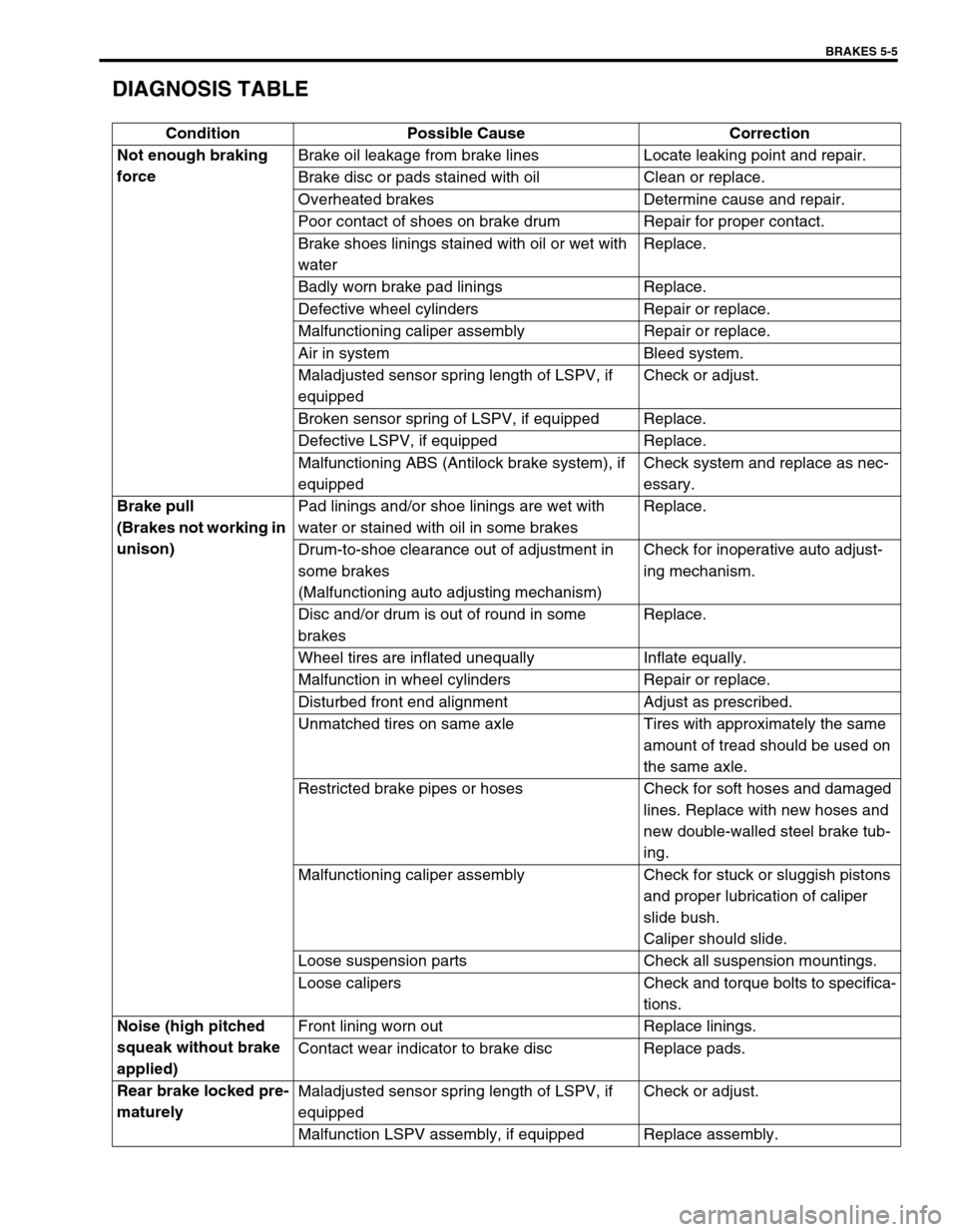
DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Not enough braking
forceBrake oil leakage from brake lines Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or pads stained with oil Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes Determine cause and repair.
Poor contact of shoes on brake drum Repair for proper contact.
Brake shoes linings stained with oil or wet with
waterReplace.
Badly worn brake pad linings Replace.
Defective wheel cylinders Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Repair or replace.
Air in system Bleed system.
Maladjusted sensor spring length of LSPV, if
equippedCheck or adjust.
Broken sensor spring of LSPV, if equipped Replace.
Defective LSPV, if equipped Replace.
Malfunctioning ABS (Antilock brake system), if
equippedCheck system and replace as nec-
essary.
Brake pull
(Brakes not working in
unison)Pad linings and/or shoe linings are wet with
water or stained with oil in some brakesReplace.
Drum-to-shoe clearance out of adjustment in
some brakes
(Malfunctioning auto adjusting mechanism)Check for inoperative auto adjust-
ing mechanism.
Disc and/or drum is out of round in some
brakesReplace.
Wheel tires are inflated unequally Inflate equally.
Malfunction in wheel cylinders Repair or replace.
Disturbed front end alignment Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle Tires with approximately the same
amount of tread should be used on
the same axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses and damaged
lines. Replace with new hoses and
new double-walled steel brake tub-
ing.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Check for stuck or sluggish pistons
and proper lubrication of caliper
slide bush.
Caliper should slide.
Loose suspension parts Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers Check and torque bolts to specifica-
tions.
Noise (high pitched
squeak without brake
applied)Front lining worn out Replace linings.
Contact wear indicator to brake disc Replace pads.
Rear brake locked pre-
maturelyMaladjusted sensor spring length of LSPV, if
equippedCheck or adjust.
Malfunction LSPV assembly, if equipped Replace assembly.