air condition SUZUKI SWIFT 2004 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2004, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2004 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 627 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-53
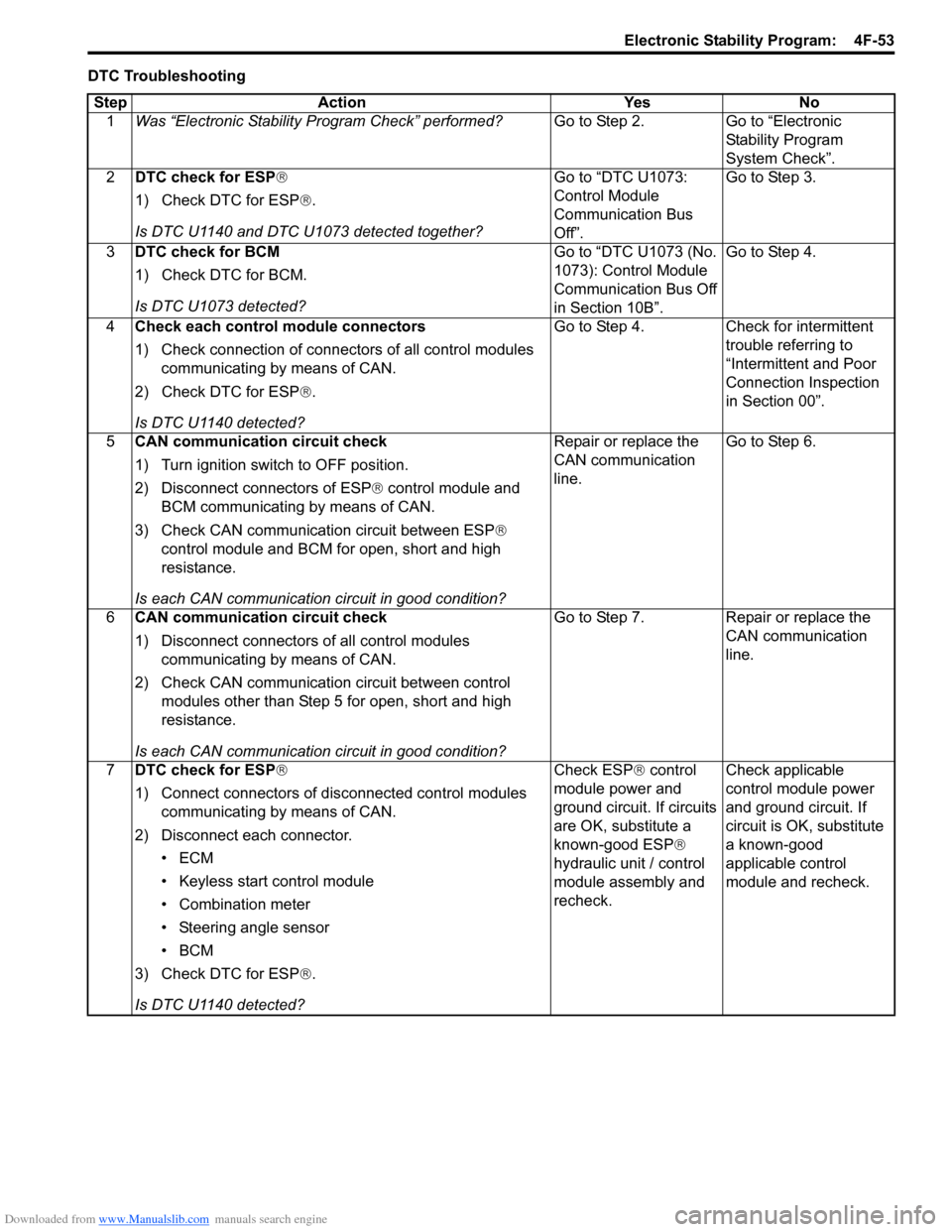
DTC TroubleshootingStep Action Yes No 1 Was “Electronic Stability Pr ogram Check” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Electronic
Stability Program
System Check”.
2 DTC check for ESP®
1) Check DTC for ESP ®.
Is DTC U1140 and DTC U1073 detected together? Go to “DTC U1073:
Control Module
Communication Bus
Off”.Go to Step 3.
3 DTC check for BCM
1) Check DTC for BCM.
Is DTC U1073 detected? Go to “DTC U1073 (No.
1073): Control Module
Communication Bus Off
in Section 10B”.Go to Step 4.
4 Check each control module connectors
1) Check connection of connectors of all control modules
communicating by means of CAN.
2) Check DTC for ESP ®.
Is DTC U1140 detected? Go to Step 4. Check for intermittent
trouble referring to
“Intermittent and Poor
Connection Inspection
in Section 00”.
5 CAN communication circuit check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect connectors of ESP ® control module and
BCM communicating by means of CAN.
3) Check CAN communication circuit between ESP®
control module and BCM for open, short and high
resistance.
Is each CAN communication circuit in good condition? Repair or replace the
CAN communication
line.
Go to Step 6.
6 CAN communication circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors of all control modules
communicating by means of CAN.
2) Check CAN communication circuit between control modules other than Step 5 for open, short and high
resistance.
Is each CAN communication circuit in good condition? Go to Step 7. Repair or replace the
CAN communication
line.
7 DTC check for ESP®
1) Connect connectors of disconnected control modules
communicating by means of CAN.
2) Disconnect each connector. •ECM
• Keyless start control module
• Combination meter
• Steering angle sensor
•BCM
3) Check DTC for ESP ®.
Is DTC U1140 detected? Check ESP
® control
module power and
ground circuit. If circuits
are OK, substitute a
known-good ESP ®
hydraulic unit / control
module assembly and
recheck. Check applicable
control module power
and ground circuit. If
circuit is OK, substitute
a known-good
applicable control
module and recheck.
Page 628 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-54 Electronic Stability Program:
Repair Instructions
ESP® Hydraulic Unit Operation CheckS7RS0B4606025
1) Check that basic brake system other than ESP ® is
in good condition.
2) Check that battery voltage is 11 V or higher.
3) Lift up vehicle.
4) Set transmission to neutral and release parking brake.
5) Turn each wheel gradually by hand to check if braked ragging occurs. If it does, correct.
6) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
7) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu press / depress in “HYDRAULIC CONTROL TEST”
under “miscellaneous test” (“MISC. TEST”) mode of
SUZUKI scan tool.
Refer to SUZUKI scan tool operator’s manual for
further details.
8) Perform the following checks with help of another person.
• Depressurization checkStep on brake pedal (1) and then select testing
wheel by SUZUKI scan tool and the wheel (2)
should be turned by another person’s hand. At this
time, check whether the wheel rotates freely due
to brake depressurization. • Pressurization check
Step off brake pedal (1) and then select testing
wheel by SUZUKI scan tool and the wheel (2)
should be turned by another person’s hand. At this
time, check whether the wheel locks due to brake
pressurization.
NOTE
Pressurization / Depressurization by SUZUKI
scan tool is available for 0.5 second.
9) Check for all 4-wheels condition respectively. If a faulty condition is found, replace hydraulic unit /
control module assembly.
10) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
Sensor CalibrationS7RS0B4606015
CAUTION!
If any DTC(s) other than C1075, C1076 or
C1078 are detected, sensor calibration can
not be completed. Repair the detected DTC
first.
NOTE
Steering angle sensor calibration is needed
when battery, “DOME” fuse or the steering
angle sensor is removed.
This sensor calibration can be done with/
without SUZUKI Scan Tool.
When ESP ® control module and/or yaw rate /
G sensor assembly is removed, sensor
calibration is needed with SUZUKI Scan Tool.
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
I4RH01450021-01
Page 629 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-55
Sensor Calibration (Using SUZUKI Scan Tool)1) Set steering wheel in straight-ahead position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position and confirm that
only any of DTC(s) C1075, C1076 and/or C1077 is
detected. If any other DTC are detected, repair the
detected DTC.
4) Park and level the vehicle with parking brake, stop engine with ignition switch ON, set steering in
straight and without step ping on the brake pedal.
NOTE
Hold the above condition in Step 4) to
calibrate sensor correctly until sensor
calibration is completed.
5) Select menu “SENSOR CALIBRATION” under
“MISC. TEST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool and
calibrate sensor. Refer to scan tool operator's
manual for further derails.
6) After completing the calibra tion, turn ignition switch
to OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool
from DLC. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration (Not Using
SUZUKI Scan Tool)
1) Set steering wheel in straight-ahead position.
2) Connect battery terminals and/or fuse and start engine.
NOTE
When power is not supplied to the steering
angle sensor by removing battery or fuse,
DTC C1075 is detected and SLIP indicator
lamp (1) flashes.
If DTC other than C1075 is detected, SLIP
indicator lamp flushes and other indicator
illuminate. In that case, repair the detected
DTC first.
3) Drive vehicle straight on level ground at 15 km/h (9.5 mph) or above for few seconds without spinning
wheels. And confirm that SLIP indicator lamp is OFF.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection
S7RS0B4606027
CAUTION!
Never disassemble ESP ® hydraulic unit /
control module assembly, loosen blind plug
or remove motor. Pe rforming any of these
prohibited services will affect original
performance of ESP ® hydraulic unit / control
module assembly.
Check hydraulic unit for fluid leakage.
If any, repair or replace.
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
1
I6RS0B460028-02
Page 636 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-62 Electronic Stability Program:
4) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu “DATA LIST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool. Refer to
scan tool operator's manual for further derails.
5) When brake pedal is released, check “Master Cyl Press” under “DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool.
If pressure is out of specification, replace ESP ®
hydraulic unit / cont rol module assembly.
Master cylinder pressure specification
Brake pedal released: 0 ± 0.8 MPa (0 ± 8 kg/cm2, 0
± 113 psi)
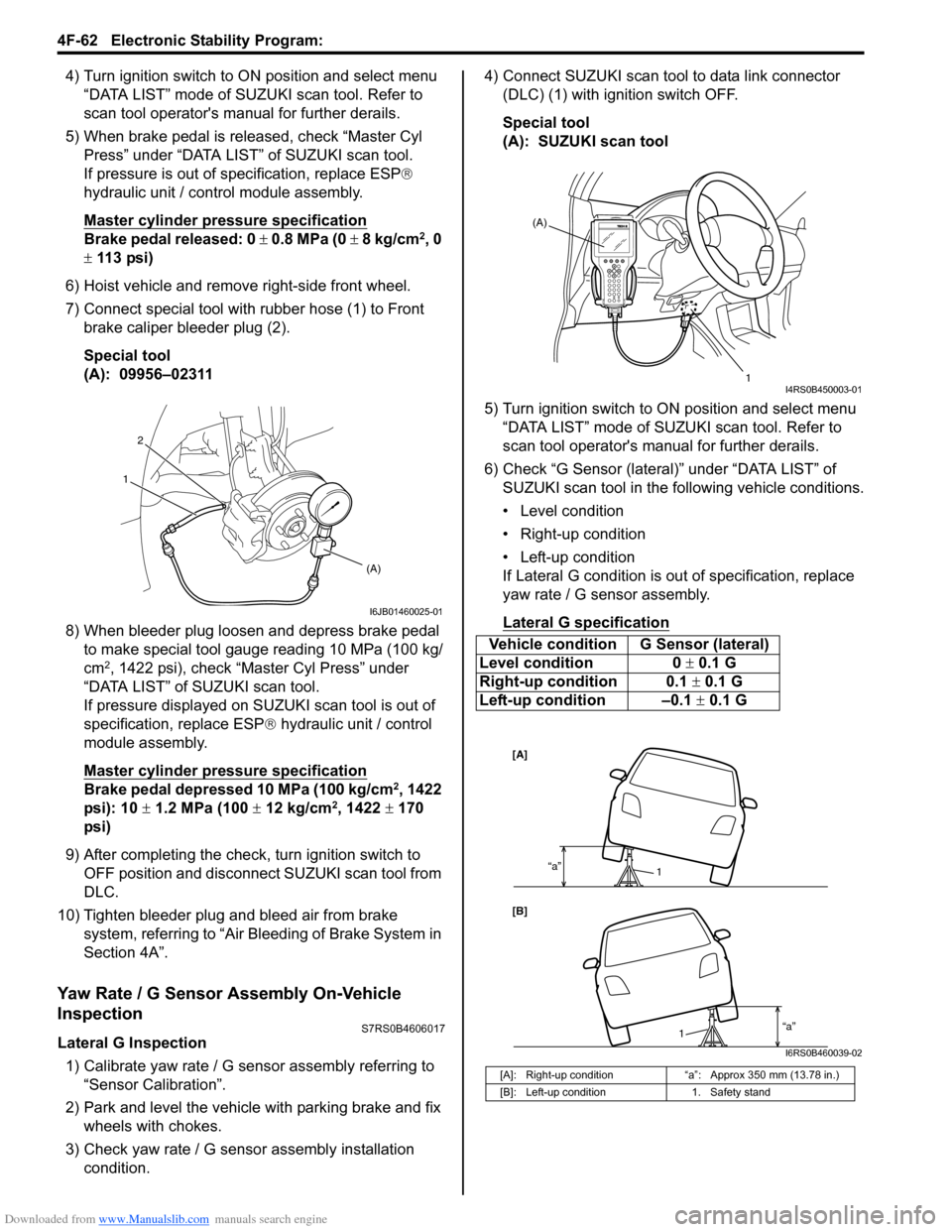
6) Hoist vehicle and remove right-side front wheel.
7) Connect special tool with rubber hose (1) to Front brake caliper bleeder plug (2).
Special tool
(A): 09956–02311
8) When bleeder plug loosen and depress brake pedal to make special tool gauge reading 10 MPa (100 kg/
cm
2, 1422 psi), check “Master Cyl Press” under
“DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool.
If pressure displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is out of
specification, replace ESP ® hydraulic unit / control
module assembly.
Master cylinder pressure specification
Brake pedal depressed 10 MPa (100 kg/cm2, 1422
psi): 10 ± 1.2 MPa (100 ± 12 kg/cm2, 1422 ± 170
psi)
9) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
10) Tighten bleeder plug and bleed air from brake system, referring to “Air Bleeding of Brake System in
Section 4A”.
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B4606017
Lateral G Inspection
1) Calibrate yaw rate / G sens or assembly referring to
“Sensor Calibration”.
2) Park and level the vehicle with parking brake and fix wheels with chokes.
3) Check yaw rate / G sensor assembly installation
condition. 4) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector
(DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
5) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu “DATA LIST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool. Refer to
scan tool operator's manual for further derails.
6) Check “G Sensor (lateral)” under “DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool in the following vehicle conditions.
• Level condition
• Right-up condition
• Left-up condition
If Lateral G condition is ou t of specification, replace
yaw rate / G sensor assembly.
Lateral G sp ecification
2
(A)
1
I6JB01460025-01
Vehicle condition G Sensor (lateral)
Level condition 0 ± 0.1 G
Right-up condition 0.1 ± 0.1 G
Left-up condition –0.1 ± 0.1 G
[A]: Right-up condition “a”: Approx 350 mm (13.78 in.)
[B]: Left-up condition 1. Safety stand
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
[A]
[B]“a”
1
“a”1
I6RS0B460039-02
Page 637 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-63
Yaw Rate Inspection1) Calibrate yaw rate / G sens or assembly referring to
“Sensor Calibration”.
2) Check yaw rate / G sensor assembly installation
condition.
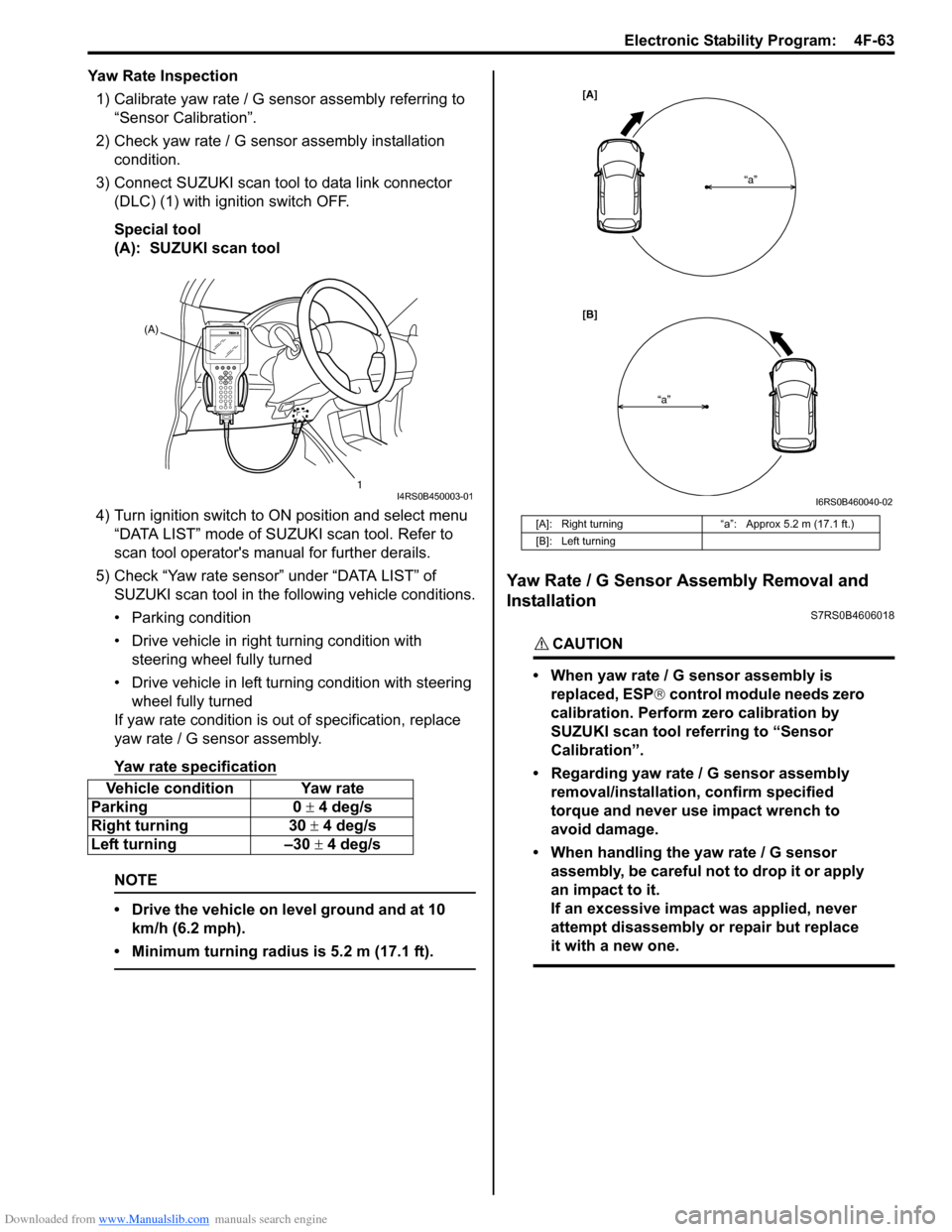
3) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
4) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu
“DATA LIST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool. Refer to
scan tool operator's manual for further derails.
5) Check “Yaw rate sensor” under “DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool in the following vehicle conditions.
• Parking condition
• Drive vehicle in right turning condition with steering wheel fully turned
• Drive vehicle in left tu rning condition with steering
wheel fully turned
If yaw rate condition is ou t of specification, replace
yaw rate / G sensor assembly.
Yaw rate specification
NOTE
• Drive the vehicle on level ground and at 10 km/h (6.2 mph).
• Minimum turning radius is 5.2 m (17.1 ft).
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B4606018
CAUTION!
• When yaw rate / G sensor assembly is replaced, ESP ® control module needs zero
calibration. Perform zero calibration by
SUZUKI scan tool referring to “Sensor
Calibration”.
• Regarding yaw rate / G sensor assembly removal/installation, confirm specified
torque and never use impact wrench to
avoid damage.
• When handling the yaw rate / G sensor assembly, be careful not to drop it or apply
an impact to it.
If an excessive impact was applied, never
attempt disassembly or repair but replace
it with a new one.
Vehicle condition Yaw rate
Parking 0 ± 4 deg/s
Right turning 30 ± 4 deg/s
Left turning –30 ± 4 deg/s
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
[A]: Right turning“a”: Approx 5.2 m (17.1 ft.)
[B]: Left turning
[A]
[B] “a”
“a”
I6RS0B460040-02
Page 659 of 1496
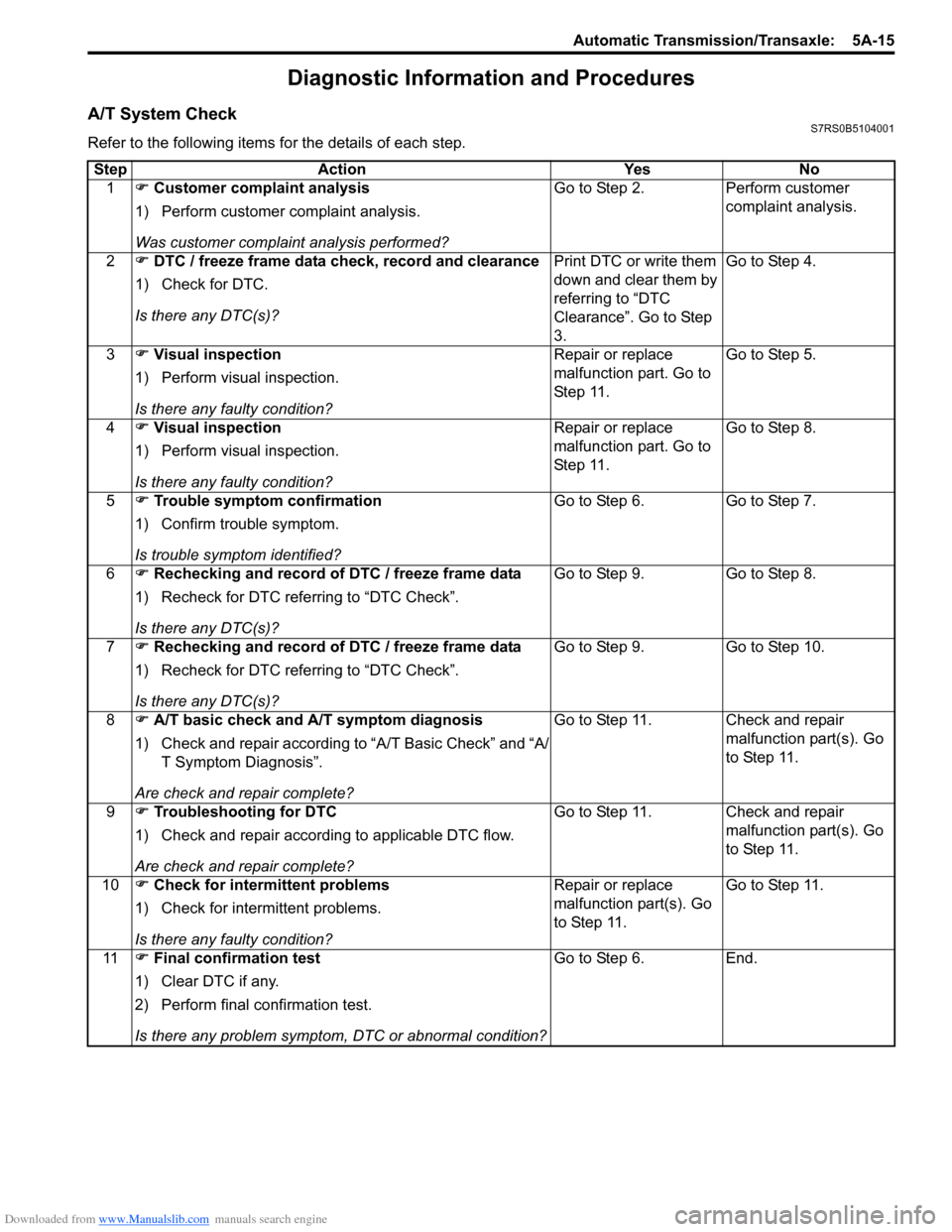
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-15
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
A/T System CheckS7RS0B5104001
Refer to the following items for the details of each step.Step Action Yes No 1 �) Customer complaint analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis.
Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to Step 2. Perform customer
complaint analysis.
2 �) DTC / freeze frame data check, record and clearance
1) Check for DTC.
Is there any DTC(s)? Print DTC or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC
Clearance”. Go to Step
3.Go to Step 4.
3 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part. Go to
St ep 11 .
Go to Step 5.
4 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part. Go to
St ep 11 .
Go to Step 8.
5 �) Trouble symptom confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom.
Is trouble symptom identified? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 7.
6 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 8.
7 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 10.
8 �) A/T basic check and A/T symptom diagnosis
1) Check and repair according to “A/T Basic Check” and “A/
T Symptom Diagnosis”.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s). Go
to Step 11.
9 �) Troubleshooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable DTC flow.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s). Go
to Step 11.
10 �) Check for intermittent problems
1) Check for interm ittent problems.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part(s). Go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 11.
11 �) Final confirmation test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test.
Is there any problem symptom, DTC or abnormal condition? Go to Step 6.
End.
Page 661 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-17
Step 2. DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and Clearance
First, referring to “DTC Check”, check DTC and pending DTC. If DTC exists, print or write down DTC and freeze frame
data and then clear malfunction DTC(s) by referring to “DTC Clearance”. Malfunction DTC indicates malfunction in the
system but it is not possible to know from it whether the malfunction is occurring now or it occurred in the past and
normal condition has been restored. In order to know that, check symptom in question according to Step 5 and then
recheck DTC according to Step 6.
Diagnosing a trouble based on the DTC in this step only or fa ilure to clear the DTC in this step may result in an faulty
diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit or difficulty in troubleshooting which is otherwise unnecessary.
Step 3 and 4. Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of the items that support proper function of the engine and
automatic transaxle referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5. Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Check trouble symptoms based on information obtained in “Step 1. Customer Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2. DTC
/ Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”.
Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC flow.
Step 6 and 7. Rechecking and Record of DTC and Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8. A/T Basic Check and A/T Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic check of A/T according to “A/T Basic Check” first. When the end of the flow has been reached, check
the parts of the system suspected as a possible cause referring to “A/T Symptom Diagnosis” and based on symptoms
appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained through step s of customer complaint analysis, trouble symptom
confirmation and/or A/T basic check) and re pair or replace faulty parts, if any.
Step 9. Troubleshooting for DTC
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 / 7 and referring to “a pplicable DTC flow”, locate the cause of the trouble,
namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator, TCM or other part and repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 10. Check for Intermittent Problem
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.g . wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection Inspection in Section 00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11. Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the vehicl e is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has been
repaired is related to the malfunction DTC, clear the DTC once and check to ensure that no malfunction DTC is
indicated.
Page 669 of 1496
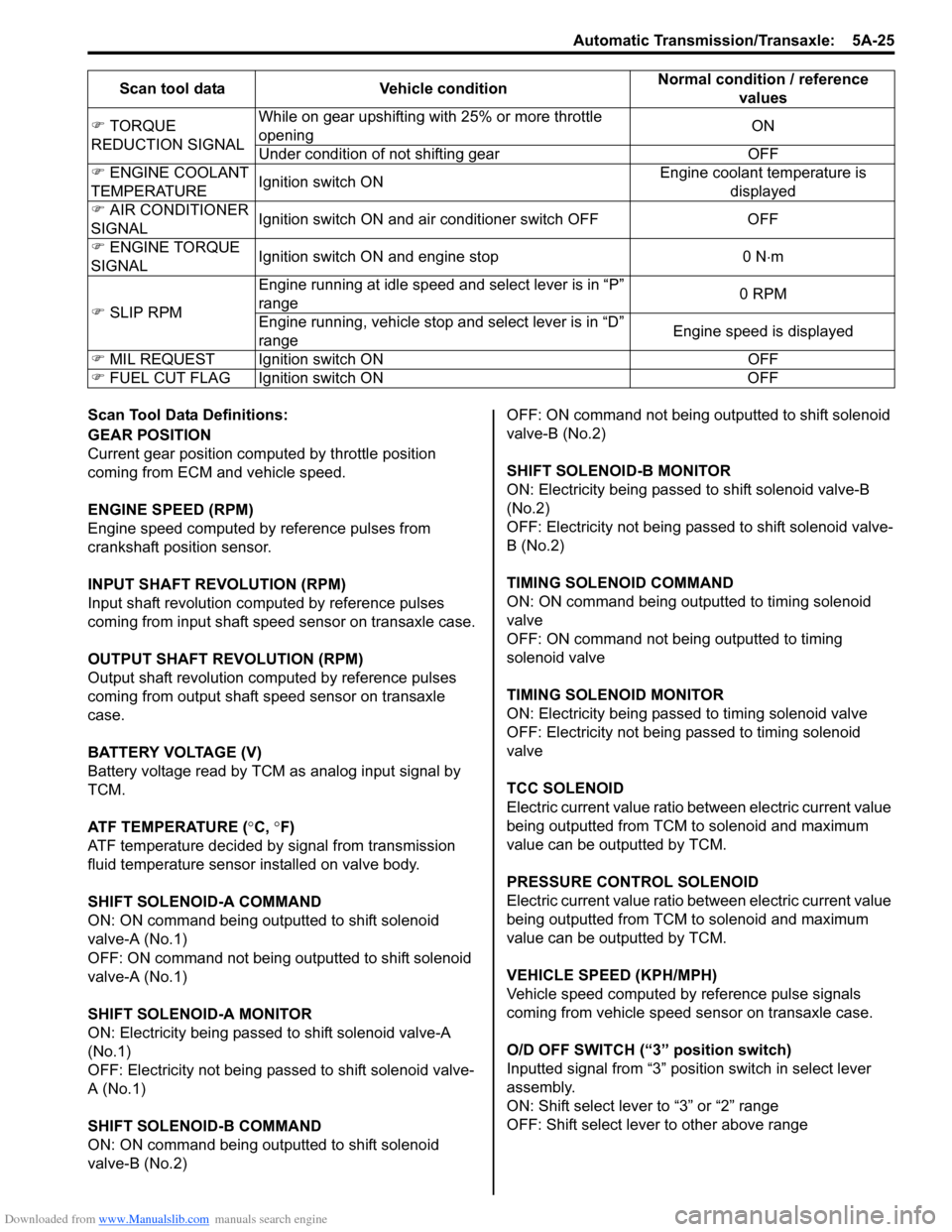
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-25
Scan Tool Data Definitions:
GEAR POSITION
Current gear position computed by throttle position
coming from ECM and vehicle speed.
ENGINE SPEED (RPM)
Engine speed computed by reference pulses from
crankshaft position sensor.
INPUT SHAFT REVOLUTION (RPM)
Input shaft revolution computed by reference pulses
coming from input shaft speed sensor on transaxle case.
OUTPUT SHAFT REVOLUTION (RPM)
Output shaft revolution computed by reference pulses
coming from output shaft speed sensor on transaxle
case.
BATTERY VOLTAGE (V)
Battery voltage read by TCM as analog input signal by
TCM.
ATF TEMPERATURE (°C, °F)
ATF temperature decided by signal from transmission
fluid temperature sensor installed on valve body.
SHIFT SOLENOID-A COMMAND
ON: ON command being outputted to shift solenoid
valve-A (No.1)
OFF: ON command not being outputted to shift solenoid
valve-A (No.1)
SHIFT SOLENOID-A MONITOR
ON: Electricity being passed to shift solenoid valve-A
(No.1)
OFF: Electricity not being passed to shift solenoid valve-
A (No.1)
SHIFT SOLENOID-B COMMAND
ON: ON command being outputted to shift solenoid
valve-B (No.2) OFF: ON command not being outputted to shift solenoid
valve-B (No.2)
SHIFT SOLENOID-B MONITOR
ON: Electricity being passed to shift solenoid valve-B
(No.2)
OFF: Electricity not being passed to shift solenoid valve-
B (No.2)
TIMING SOLENOID COMMAND
ON: ON command being outputted to timing solenoid
valve
OFF: ON command not being outputted to timing
solenoid valve
TIMING SOLENOID MONITOR
ON: Electricity being passed to timing solenoid valve
OFF: Electricity not being passed to timing solenoid
valve
TCC SOLENOID
Electric current value ratio between electric current value
being outputted from TCM to solenoid and maximum
value can be outputted by TCM.
PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID
Electric current value ratio between electric current value
being outputted from TCM to solenoid and maximum
value can be outputted by TCM.
VEHICLE SPEED (KPH/MPH)
Vehicle speed computed by reference pulse signals
coming from vehicle speed sensor on transaxle case.
O/D OFF SWITCH (“3” position switch)
Inputted signal from “3” position switch in select lever
assembly.
ON: Shift select lever to “3” or “2” range
OFF: Shift select lever to other above range
�)
TORQUE
REDUCTION SIGNAL While on gear upshifting with 25% or more throttle
opening
ON
Under condition of not shifting gear OFF
�) ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE Ignition switch ON Engine coolant temperature is
displayed
�) AIR CONDITIONER
SIGNAL Ignition switch ON and air conditioner switch OFF OFF
�) ENGINE TORQUE
SIGNAL Ignition switch ON and engine stop 0 N
⋅m
�) SLIP RPM Engine running at idle speed
and select lever is in “P”
range 0 RPM
Engine running, vehicle stop and select lever is in “D”
range Engine speed is displayed
�) MIL REQUEST Ignition switch ON OFF
�) FUEL CUT FLAG Ignition switch ON OFFScan tool data Vehicle condition
Normal condition / reference
values
Page 670 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-26 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
TRANSAXLE RANGE
Transaxle range detected by signal fed from
transmission range sensor.
D RANGE SIGNAL
ON: Signal which TCM require ECM to increase idle
speed
OFF: Signal which TCM does not require ECM to
increase idle speed
THROTTLE POSITION (%)
Throttle opening ratio computed by CAN signal from
ECM.
BRAKE SWITCH
Inputted signal from brake light switch on pedal bracket.
ON: Brake pedal depressed
OFF: Brake pedal released
TORQUE REDUCTION SIGNAL
ON: Signal which TCM require ECM to reduce output
torque at shifting gear
OFF: Signal which TCM does not require ECM to reduce
output torque
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE ( °C, °F)
Engine coolant temperature computed by CAN signal
from ECM. AIR CONDITIONER SIGNAL
ON: Signal which inform that air conditioner compressor
is turned ON.
OFF: Signal which inform that air conditioner
compressor is not turned ON.
ENGINE TORQUE SIGNAL (N
⋅m)
Engine torque computed by duty pulse signal outputted
from ECM.
SLIP RPM (RPM)
This parameter indicates slip ping rotation in the torque
converter (difference between input shaft rotation and
engine rotation)
MIL REQUEST
ON: Signal which TCM requires combination meter to
turn on malfunction indicator lamp.
OFF: Signal which TCM does not require combination
meter to turn on malf unction indicator lamp.
FUEL CUT FLAG
ON: Signal which inform that fuel cut is operating.
OFF: Signal which inform that fuel cut is not operating.
A/T Basic CheckS7RS0B5104010
This check is important for troubleshooting when TCM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been noted in
“Visual Inspection”. Fo llow the flow carefully.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “A/T System Check” preformed? Go to Step 2.Go to “A/T System
Check”.
2 Perform “Road Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 3.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Road Test”.
3 Perform “Manual Road Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 4.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Manual Road Test”.
4 Perform “Engine Brake Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 5.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Engine Brake Test”.
5 Perform “Stall Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 6.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Stall Test”.
6 Perform “Time Lag Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 7.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Time Lag Test”.
7 Perform “Line Pressure Test”.
Is it OK? Go to Step 8.
Proceed to
“Troubleshooting” in
“Line Pressure Test”.
8 Proceed to “Trouble Diag nosis 1” in “A/T Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Is trouble identified? Repair or replace faulty
parts.
Go to Step 9.
Page 671 of 1496
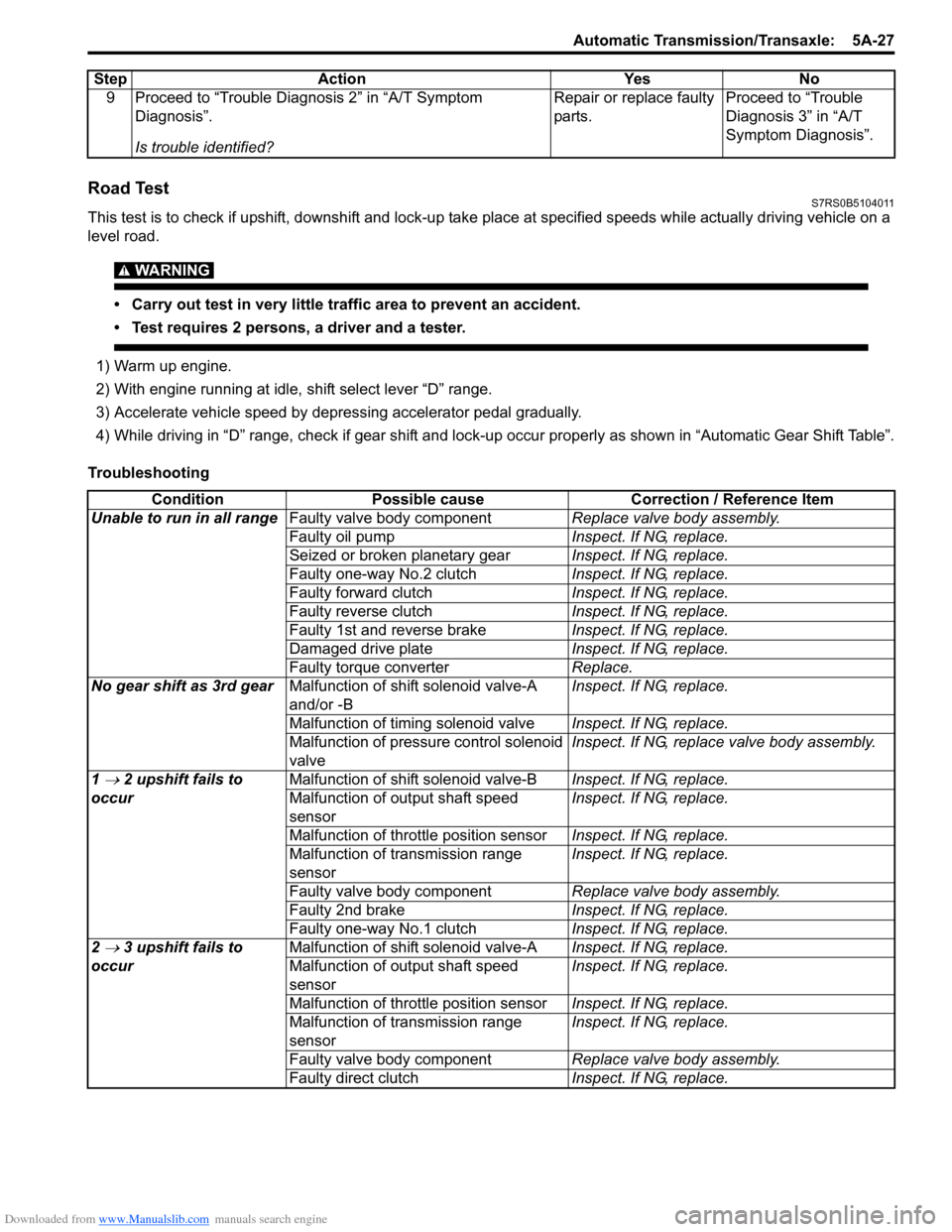
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-27
Road TestS7RS0B5104011
This test is to check if upshift, downshift and lock-up take place at specified speeds while actually driving vehicle on a
level road.
WARNING!
• Carry out test in very little traffic area to prevent an accident.
• Test requires 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
1) Warm up engine.
2) With engine running at idle, shift select lever “D” range.
3) Accelerate vehicle speed by depressing accelerator pedal gradually.
4) While driving in “D” range, check if gear shift and lock-up occur properly as shown in “Automatic Gear Shift Table”.
Troubleshooting 9 Proceed to “Trouble Diag
nosis 2” in “A/T Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Is trouble identified? Repair or replace faulty
parts.
Proceed to “Trouble
Diagnosis 3” in “A/T
Symptom Diagnosis”.
Step Action Yes No
Condition
Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Unable to run in all range Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Faulty oil pump Inspect. If NG, replace.
Seized or broken planetary gear Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.2 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty forward clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty reverse clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty 1st and reverse brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Damaged drive plate Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty torque converter Replace.
No gear shift as 3rd gear Malfunction of shift solenoid valve-A
and/or -B Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of timing solenoid valve Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of pressure control solenoid
valve Inspect. If NG, replace valve body assembly.
1
→ 2 upshift fails to
occur Malfunction of shif
t solenoid valve-B Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of output shaft speed
sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of throttle position sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of transmission range
sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Faulty 2nd brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty one-way No.1 clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.
2
→ 3 upshift fails to
occur Malfunction of shif
t solenoid valve-A Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of output shaft speed
sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of throttle position sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Malfunction of transmission range
sensor Inspect. If NG, replace.
Faulty valve body component Replace valve body assembly.
Faulty direct clutch Inspect. If NG, replace.