bearing replace SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 414 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 432 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2A-1 Suspension General Diagnosis:
Suspension
Suspension General Diagnosis
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Suspension, Wheels and Tires Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B2104001
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Vehicle pulls (Leads) Mismatched or uneven tires Replace tires.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Radial tire lateral force Replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Brake dragging in one road wheel Repair brake.
Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts Tighten or replace related suspension parts.
Abnormal or excessive
tire wear Sagging or broken coil spring
Replace coil spring.
Tire out of balance Adjust balance or replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Hard driving Replace tires.
Overloaded vehicle Replace tires and check suspension parts.
Not rotated tires Replace or rotate tires.
Worn or loose wheel bearing Replace wheel bearing.
Wobbly wheel or tire Replace wheel or tire.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Wheel tramp Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Improper strut (shock absorber) action Replace strut (shock absorber).
Shimmy, shake or
vibration Tire or wheel out of balance
Balance wheel or replace tire and/or wheel.
Loosen wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Worn tie-rod ends Replace tie-rod ends.
Worn lower ball joints Replace front suspension control arm.
Excessive wheel runout Repair or replace wheel and/or tire.
Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Excessively loaded radial runout of tire /
wheel assembly Replace tire or wheel.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Loose or worn steering linkage Tighten or replace steering linkage.
Loose steering gear case bolts Tighten steering gear case bolts.
Abnormal noise, front end Worn, sticky or loose tie-rod ends, lower
ball joints, tie-rod in side ball joints or
drive shaft joints Replace tie-rod end, su
spension arm, tie-rod
or drive shaft joint.
Damaged struts or mountings Repair or replace struts or mountings.
Worn suspension arm bushings Replace suspension arm bushings.
Loose stabilizer bar Tighten bolts or nuts and/or replace bushes.
Loose wheel nuts Tighten wheel nuts.
Loose suspension bolts or nuts Tighten suspension bolts or nuts.
Broken or damaged wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Broken suspension springs Replace suspension springs.
Poorly lubricated or worn strut bearings Replace strut bearing.
Malfunction of Power Steering System Check and correct malfunction.
Low or uneven trim height
NOTE
See NOTE *1.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Over loaded Check loading.
Incorrect coil springs Replace coil spring.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Ride too soft Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Suspension bottoms Overloaded Check loading.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Incorrect, broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil spring.
Page 433 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Suspension General Diagnosis: 2A-2
NOTE
*1: Right-to-left trim height (“H”) difference should be within 15 mm (0.6 in.) with curb weight. (same
with rear side.)
Body leans or sways in
corners Loose stabilizer bar
Tighten stabilizer bar bolts or nuts, or replace
bushes.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) or
mounting Replace strut (shock absorber) or tighten
mounting.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Overloaded Check loading.
Cupped tires Front struts defective Replace struts.
Worn wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Excessive tire or wheel run-out Replace tire and/or wheel.
Worn ball joints Replace front suspension control arm.
Tire out of balance Adjust tire balance.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
“H”
I2RH01210001-01
Page 436 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-3 Front Suspension:
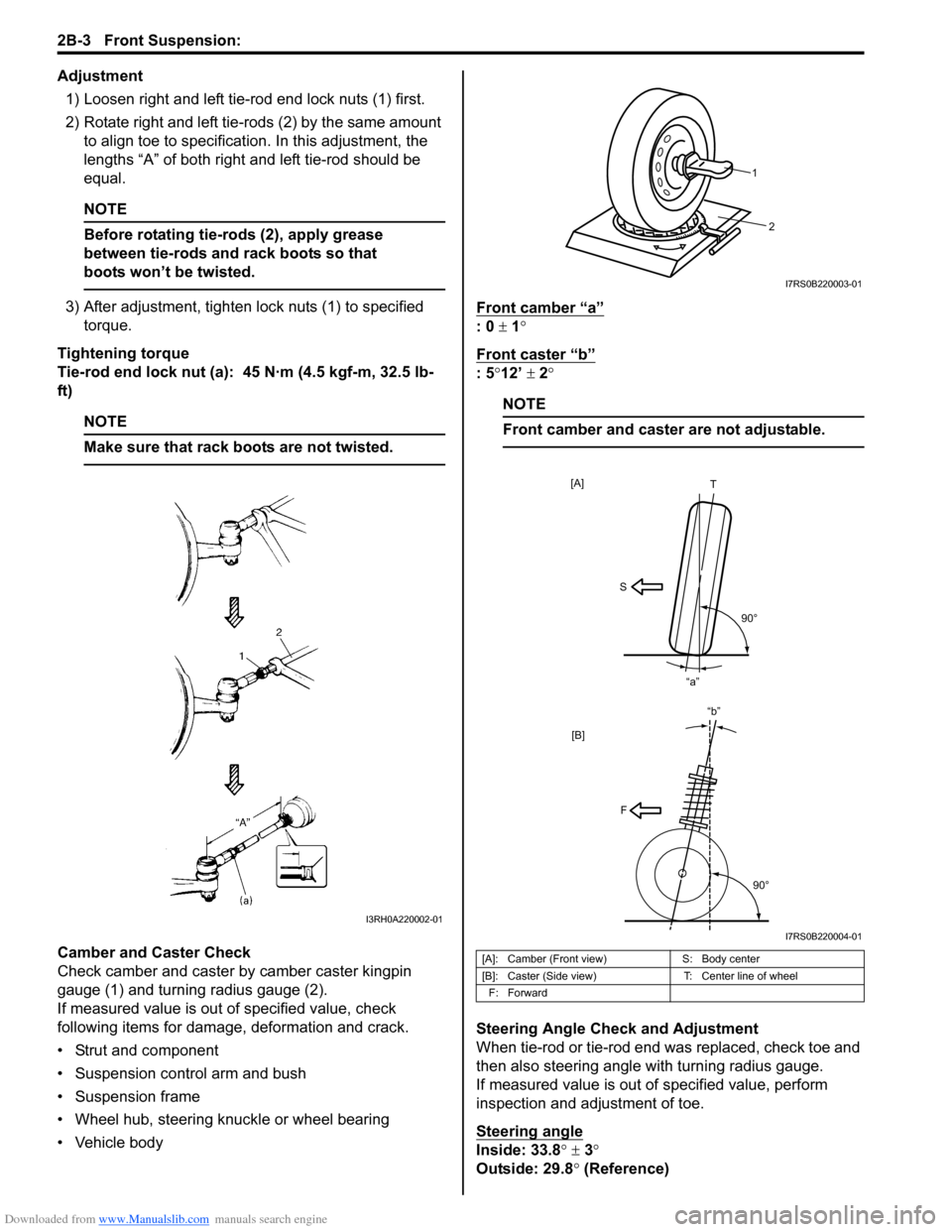
Adjustment1) Loosen right and left tie-rod end lock nuts (1) first.
2) Rotate right and left tie-rods (2) by the same amount to align toe to specification. In this adjustment, the
lengths “A” of both right and left tie-rod should be
equal.
NOTE
Before rotating tie-rods (2), apply grease
between tie-rods and rack boots so that
boots won’t be twisted.
3) After adjustment, tighten lock nuts (1) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Tie-rod end lock nut (a): 45 N·m (4.5 kgf-m, 32.5 lb-
ft)
NOTE
Make sure that rack boots are not twisted.
Camber and Caster Check
Check camber and caster by camber caster kingpin
gauge (1) and turning radius gauge (2).
If measured value is out of specified value, check
following items for damage, deformation and crack.
• Strut and component
• Suspension control arm and bush
• Suspension frame
• Wheel hub, steering knuckle or wheel bearing
• Vehicle body Front camber “a”
: 0
± 1°
Front caster “b”
: 5 °12’ ± 2°
NOTE
Front camber and caster are not adjustable.
Steering Angle Check and Adjustment
When tie-rod or tie-rod end was replaced, check toe and
then also steering angle with turning radius gauge.
If measured value is out of specified value, perform
inspection and adjustment of toe.
Steering angle
Inside: 33.8 ° ± 3 °
Outside: 29.8 ° (Reference)
I3RH0A220002-01
[A]: Camber (Front view) S: Body center
[B]: Caster (Side view) T: Center line of wheel
F: Forward
2
1
I7RS0B220003-01
[B]
S T
90°
“a”
[A]
F
90°
“b”
I7RS0B220004-01
Page 440 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-7 Front Suspension:
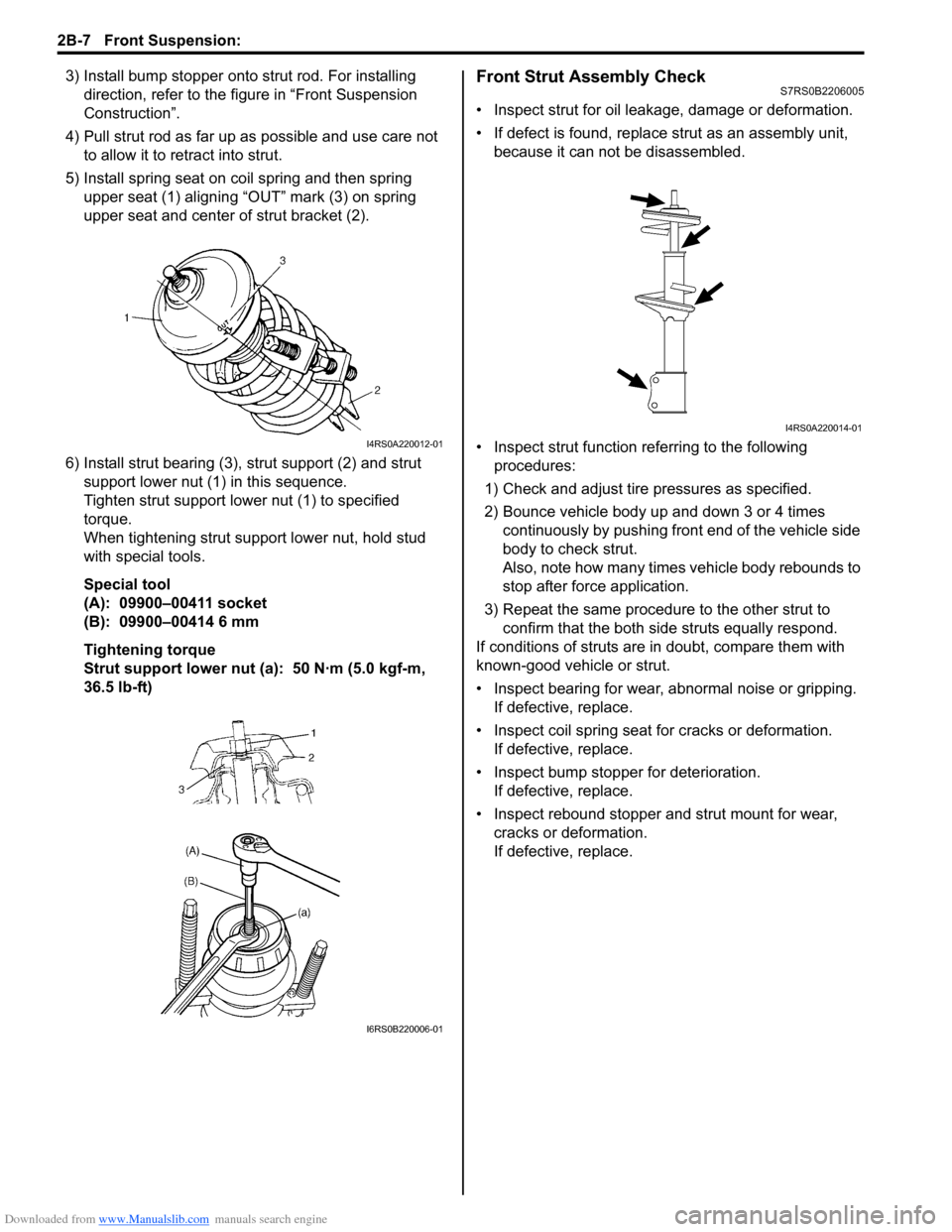
3) Install bump stopper onto strut rod. For installing
direction, refer to the figure in “Front Suspension
Construction”.
4) Pull strut rod as far up as possible and use care not to allow it to re tract into strut.
5) Install spring seat on coil spring and then spring upper seat (1) aligning “OUT” mark (3) on spring
upper seat and center of strut bracket (2).
6) Install strut bearing (3), strut support (2) and strut
support lower nut (1) in this sequence.
Tighten strut support lower nut (1) to specified
torque.
When tightening strut support lower nut, hold stud
with special tools.
Special tool
(A): 09900–00411 socket
(B): 09900–00414 6 mm
Tightening torque
Strut support lower nut (a): 50 N·m (5.0 kgf-m,
36.5 lb-ft)Front Strut Assembly CheckS7RS0B2206005
• Inspect strut for oil leakage, damage or deformation.
• If defect is found, replace strut as an assembly unit, because it can not be disassembled.
• Inspect strut function re ferring to the following
procedures:
1) Check and adjust tire pressures as specified.
2) Bounce vehicle body up and down 3 or 4 times continuously by pushing front end of the vehicle side
body to check strut.
Also, note how many times vehicle body rebounds to
stop after force application.
3) Repeat the same procedure to the other strut to confirm that the both side struts equally respond.
If conditions of struts are in doubt, compare them with
known-good vehicle or strut.
• Inspect bearing for wear, abnormal noise or gripping. If defective, replace.
• Inspect coil spring seat for cracks or deformation.
If defective, replace.
• Inspect bump stopper for deterioration. If defective, replace.
• Inspect rebound stopper and strut mount for wear, cracks or deformation.
If defective, replace.
I4RS0A220012-01
I6RS0B220006-01
I4RS0A220014-01
Page 441 of 1496
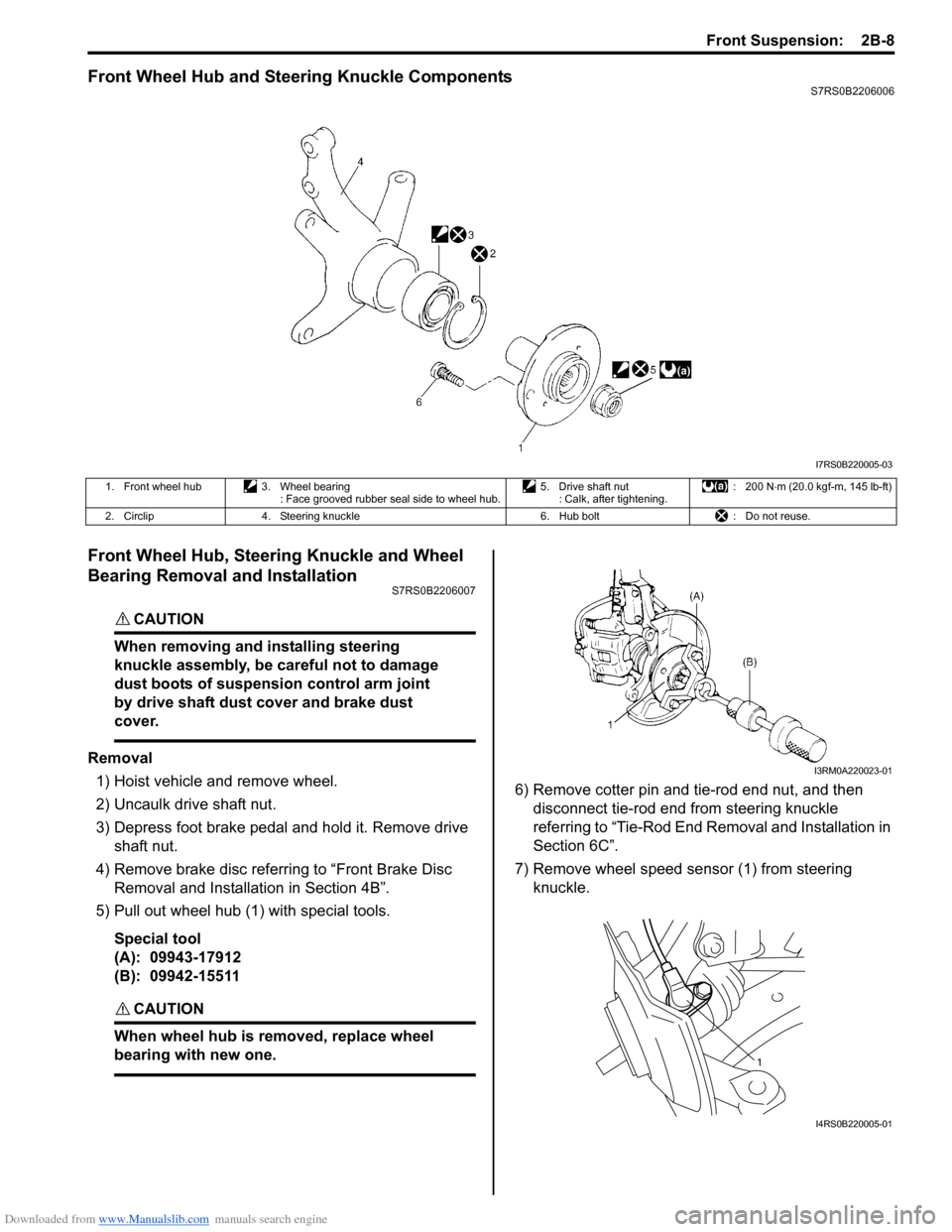
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-8
Front Wheel Hub and Steering Knuckle ComponentsS7RS0B2206006
Front Wheel Hub, Steering Knuckle and Wheel
Bearing Removal and Installation
S7RS0B2206007
CAUTION!
When removing and installing steering
knuckle assembly, be careful not to damage
dust boots of suspension control arm joint
by drive shaft dust cover and brake dust
cover.
Removal1) Hoist vehicle and remove wheel.
2) Uncaulk drive shaft nut.
3) Depress foot brake pedal and hold it. Remove drive shaft nut.
4) Remove brake disc referring to “Front Brake Disc Removal and Installa tion in Section 4B”.
5) Pull out wheel hub (1) with special tools.
Special tool
(A): 09943-17912
(B): 09942-15511
CAUTION!
When wheel hub is removed, replace wheel
bearing with new one.
6) Remove cotter pin and tie-rod end nut, and then disconnect tie-rod end from steering knuckle
referring to “Tie-Rod End Removal and Installation in
Section 6C”.
7) Remove wheel speed sensor (1) from steering knuckle.
I7RS0B220005-03
1. Front wheel hub 3. Wheel bearing
: Face grooved rubber seal side to wheel hub. 5. Drive shaft nut
: Calk, after tightening. : 200 N
⋅m (20.0 kgf-m, 145 lb-ft)
2. Circlip 4. Steering knuckle 6. Hub bolt: Do not reuse.
I3RM0A220023-01
1
I4RS0B220005-01
Page 442 of 1496
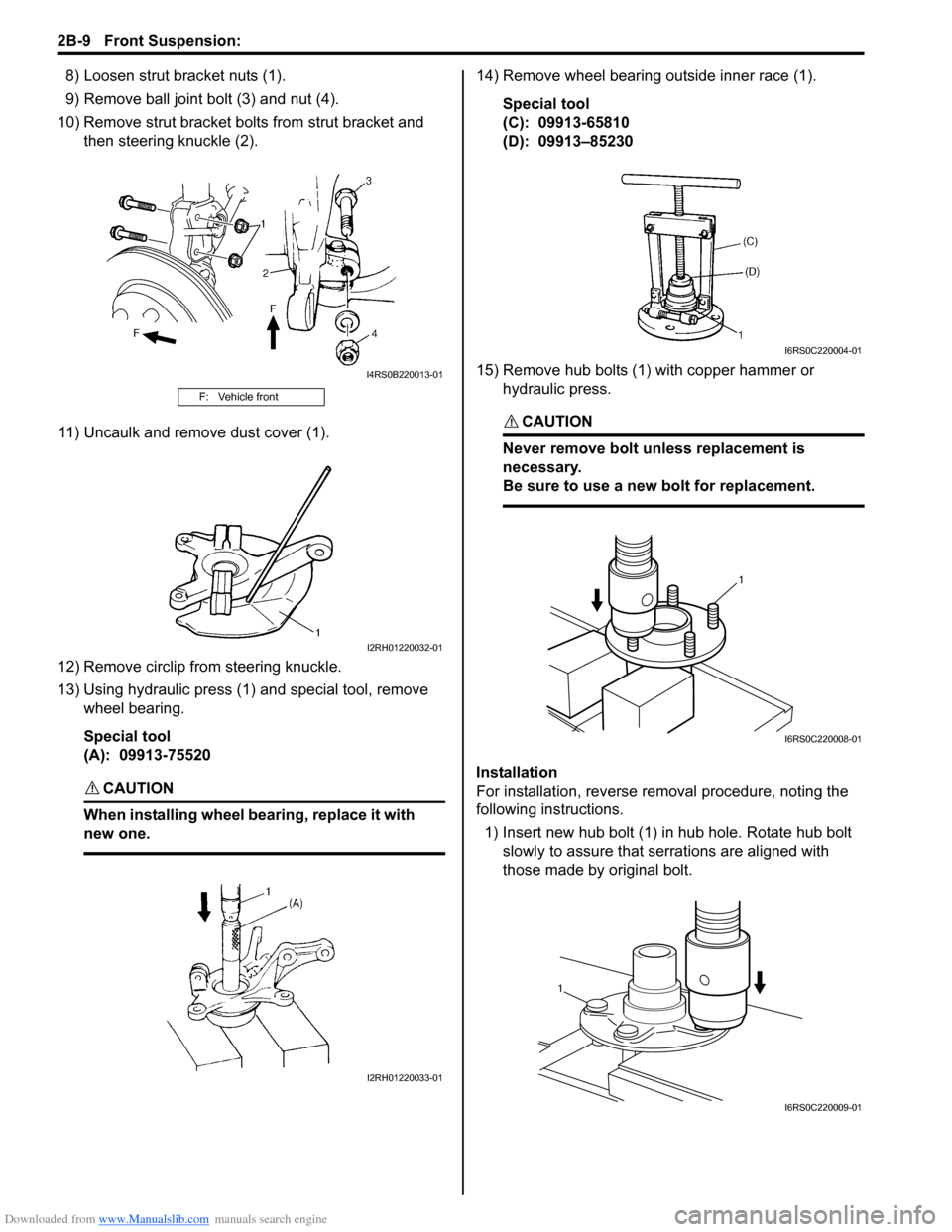
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-9 Front Suspension:
8) Loosen strut bracket nuts (1).
9) Remove ball joint bolt (3) and nut (4).
10) Remove strut bracket bolt s from strut bracket and
then steering knuckle (2).
11) Uncaulk and remove dust cover (1).
12) Remove circlip from steering knuckle.
13) Using hydraulic press (1) and special tool, remove wheel bearing.
Special tool
(A): 09913-75520
CAUTION!
When installing wheel bearing, replace it with
new one.
14) Remove wheel bearing outside inner race (1).
Special tool
(C): 09913-65810
(D): 09913–85230
15) Remove hub bolts (1) with copper hammer or hydraulic press.
CAUTION!
Never remove bolt unle ss replacement is
necessary.
Be sure to use a new bolt for replacement.
Installation
For installation, reverse removal procedure, noting the
following instructions.
1) Insert new hub bolt (1) in hub hole. Rotate hub bolt slowly to assure that serrations are aligned with
those made by original bolt.
F: Vehicle front
I4RS0B220013-01
I2RH01220032-01
I2RH01220033-01
I6RS0C220004-01
1
I6RS0C220008-01
1
I6RS0C220009-01
Page 443 of 1496
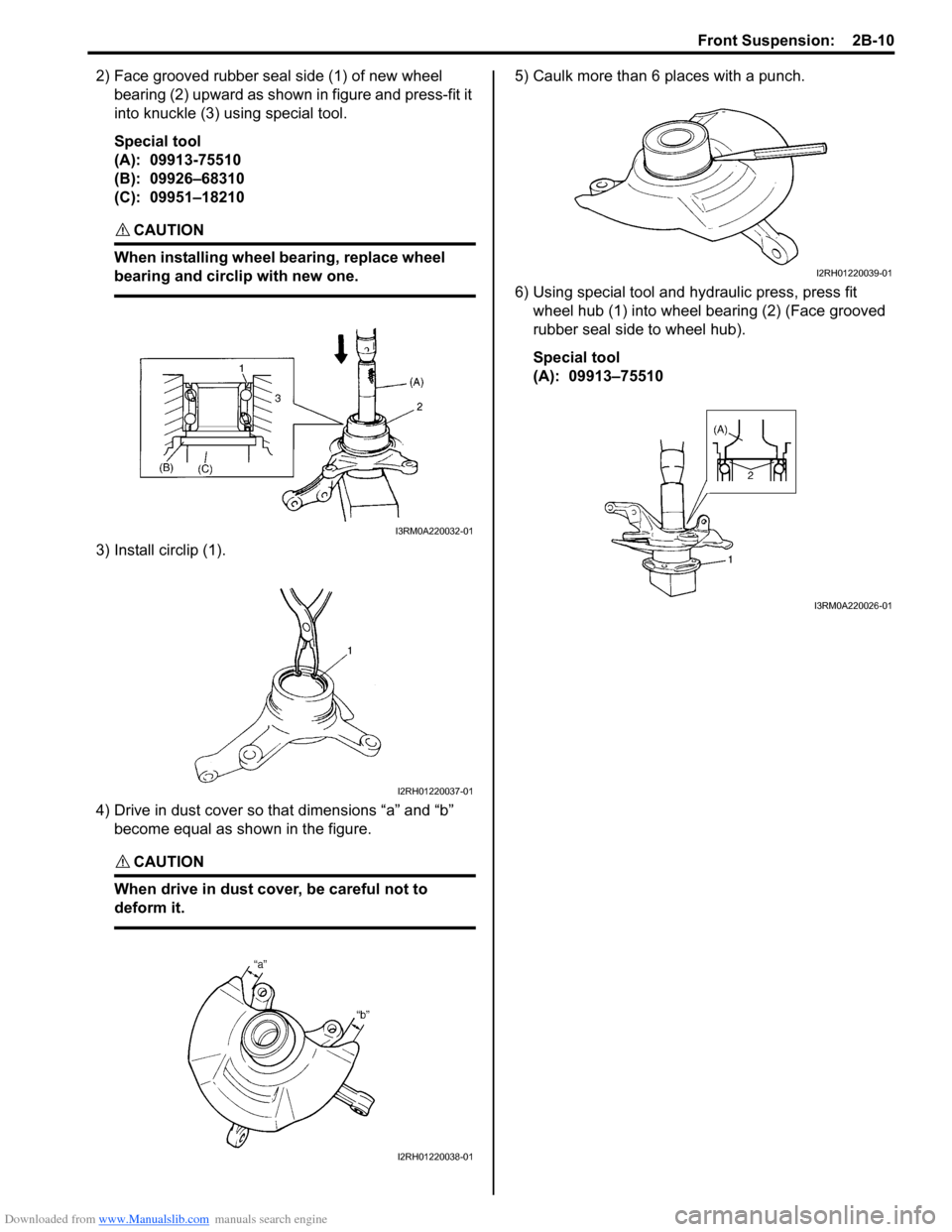
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-10
2) Face grooved rubber seal side (1) of new wheel bearing (2) upward as shown in figure and press-fit it
into knuckle (3) using special tool.
Special tool
(A): 09913-75510
(B): 09926–68310
(C): 09951–18210
CAUTION!
When installing wheel bearing, replace wheel
bearing and circlip with new one.
3) Install circlip (1).
4) Drive in dust cover so that dimensions “a” and “b” become equal as shown in the figure.
CAUTION!
When drive in dust cover, be careful not to
deform it.
5) Caulk more than 6 places with a punch.
6) Using special tool and hydraulic press, press fit
wheel hub (1) into wheel bearing (2) (Face grooved
rubber seal side to wheel hub).
Special tool
(A): 09913–75510
I3RM0A220032-01
I2RH01220037-01
I2RH01220038-01
I2RH01220039-01
I3RM0A220026-01
Page 445 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-12
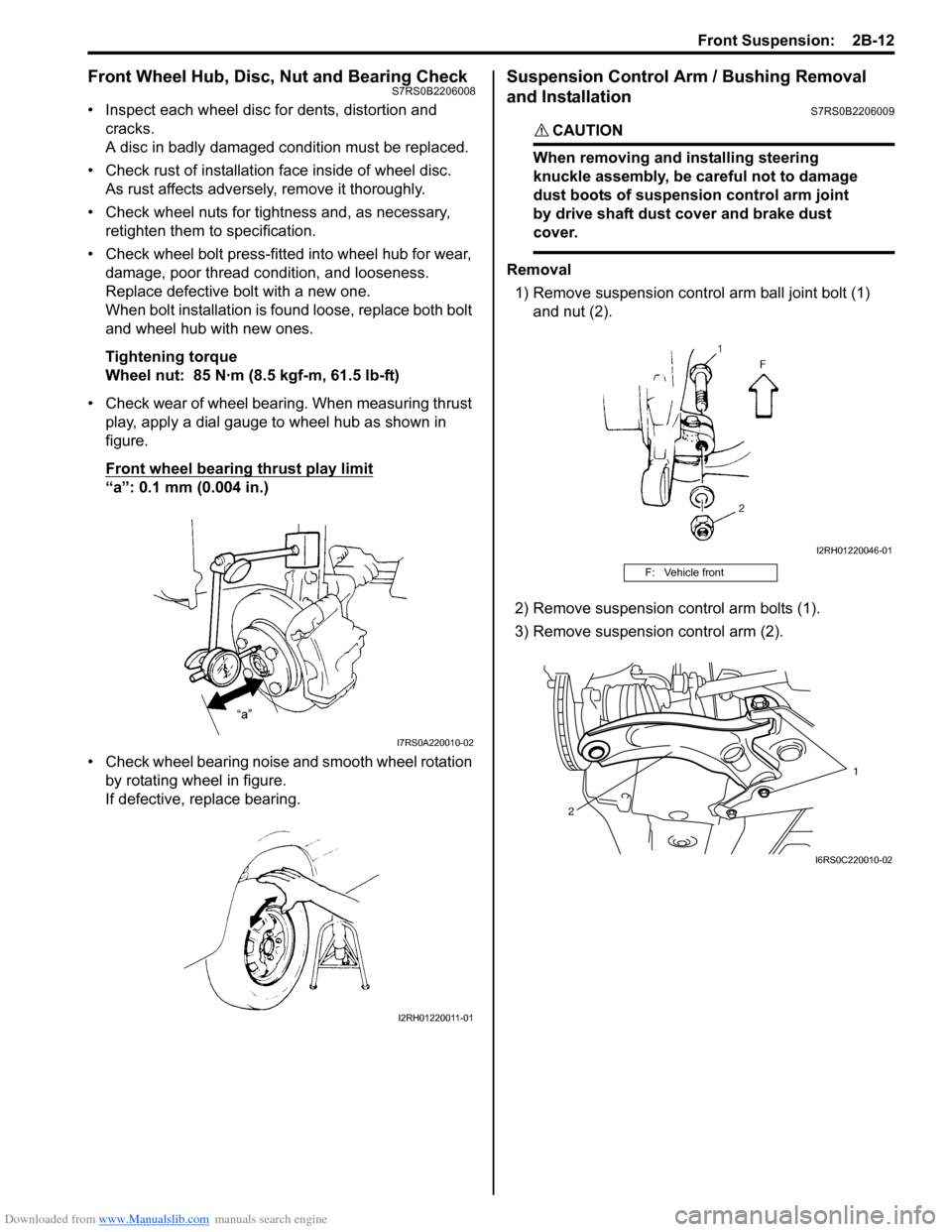
Front Wheel Hub, Disc, Nut and Bearing CheckS7RS0B2206008
• Inspect each wheel disc for dents, distortion and cracks.
A disc in badly damaged condition must be replaced.
• Check rust of installation face inside of wheel disc.
As rust affects adversely, remove it thoroughly.
• Check wheel nuts for tightness and, as necessary, retighten them to specification.
• Check wheel bolt press-fitted into wheel hub for wear, damage, poor thread condition, and looseness.
Replace defective bolt with a new one.
When bolt installation is found loose, replace both bolt
and wheel hub with new ones.
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
• Check wear of wheel bearing. When measuring thrust play, apply a dial gauge to wheel hub as shown in
figure.
Front wheel bearing thrust play limit
“a”: 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
• Check wheel bearing noise and smooth wheel rotation by rotating wheel in figure.
If defective, replace bearing.
Suspension Control Arm / Bushing Removal
and Installation
S7RS0B2206009
CAUTION!
When removing and installing steering
knuckle assembly, be ca reful not to damage
dust boots of suspension control arm joint
by drive shaft dust cover and brake dust
cover.
Removal
1) Remove suspension contro l arm ball joint bolt (1)
and nut (2).
2) Remove suspension control arm bolts (1).
3) Remove suspension control arm (2).
I7RS0A220010-02
I2RH01220011-01
F: Vehicle front
I2RH01220046-01
1
2
I6RS0C220010-02
Page 465 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Suspension: 2C-11
Installation
Install wheel hub by reversing removal procedure noting
the following instructions.
• Insert new wheel stud bolt in wheel hub hole and rotate it slowly to assure serrations are aligned with
those made by replaced bolt.
• Never apply grease to encoder (1).
• Install new rear axle nut (1) and tighten to specified torque.
CAUTION!
Never reuse rear axle nut. Otherwise, nut may
loosen.
Tightening torque
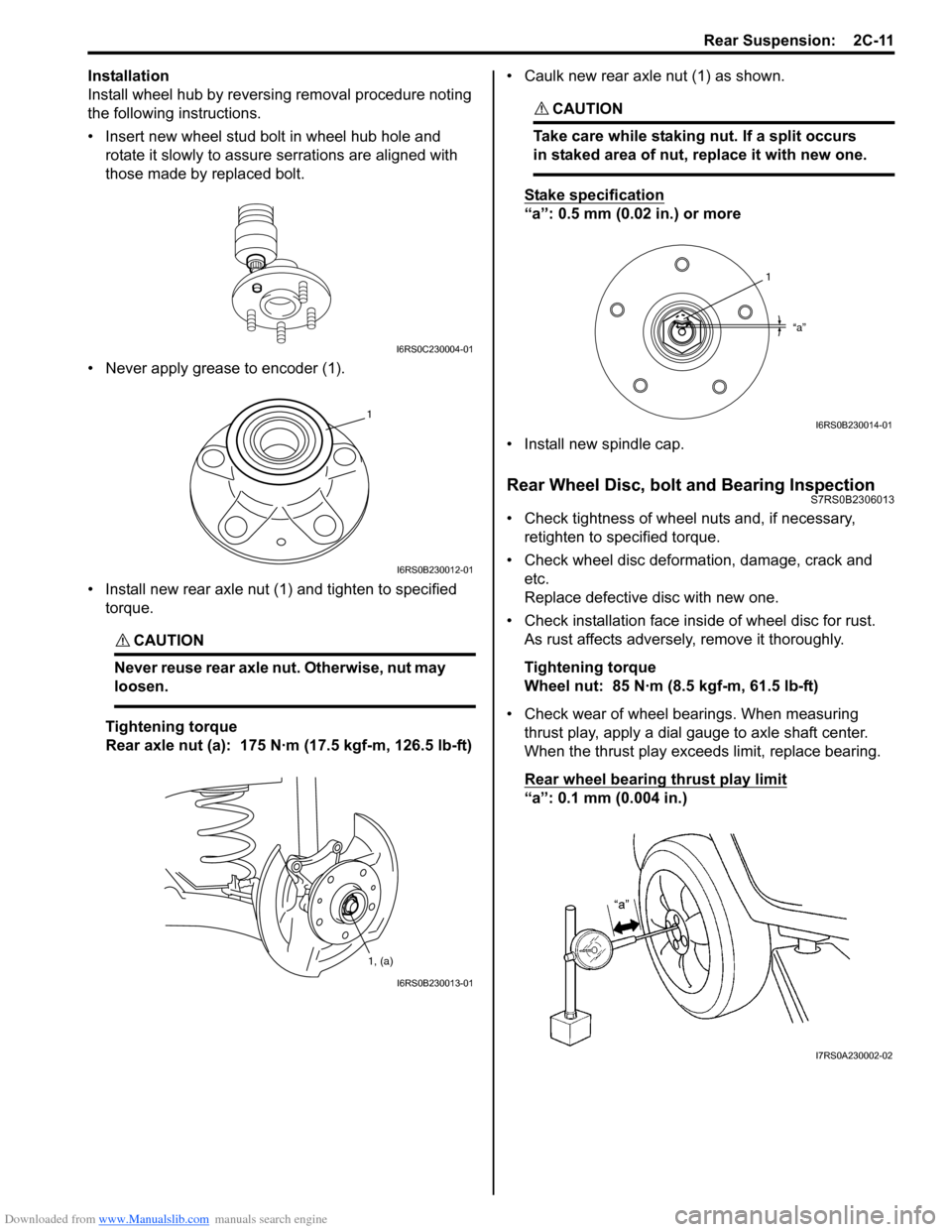
Rear axle nut (a): 175 N·m (17.5 kgf-m, 126.5 lb-ft) • Caulk new rear axle nut (1) as shown.
CAUTION!
Take care while staking nut. If a split occurs
in staked area of nut,
replace it with new one.
Stake specification
“a”: 0.5 mm (0.02 in.) or more
• Install new spindle cap.
Rear Wheel Disc, bolt and Bearing InspectionS7RS0B2306013
• Check tightness of wheel nuts and, if necessary, retighten to specified torque.
• Check wheel disc deformation, damage, crack and etc.
Replace defective disc with new one.
• Check installation face insi de of wheel disc for rust.
As rust affects adversely, remove it thoroughly.
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
• Check wear of wheel bearings. When measuring thrust play, apply a dial gauge to axle shaft center.
When the thrust play exce eds limit, replace bearing.
Rear wheel bearing thrust play
limit
“a”: 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
I6RS0C230004-01
1
I6RS0B230012-01
1, (a)
I6RS0B230013-01
1
“a”
I6RS0B230014-01
I7RS0A230002-02