Inspection SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 890 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-8 Power Assisted Steering System:
Step 2: DTC Check, Record and Clearance
First, check DTC, referring to “DTC Check”. If DTC is
indicated, print it or write them down and then clear them
by referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates
malfunction that occurred in the system but does not
indicate whether it exists now or it occurred in the past
and the normal condition has been restored now. To
check which case applies, check the symptom in
question according to Step 5 and recheck DTC
according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the P/S system
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “S tep 2: DTC Check, Record
and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble symptoms. Also,
reconfirm trouble symptom by performing test drive and
turning steering wheel fully to right and left at stopped
vehicle.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Steering Symptom Diagnosis and P/S
System Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic steering system check according to
“Steering Symptom Diagnosis in Section 6A” first. When
the end of the flow has been reached, check the parts of
the system suspected as a possible cause referring to
“P/S System Symptom Diagnosis” and based on
symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained
through steps of customer complaint analysis, trouble
symptom confirmation and/or basic P/S system check)
and repair or replace faulty parts, if any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, P/S control module or other part and
repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2. Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the P/
S system is free from any abnormal conditions. If what
has been repaired is related to the DTC, clear the DTC
once, perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm
that no DTC is indicated.
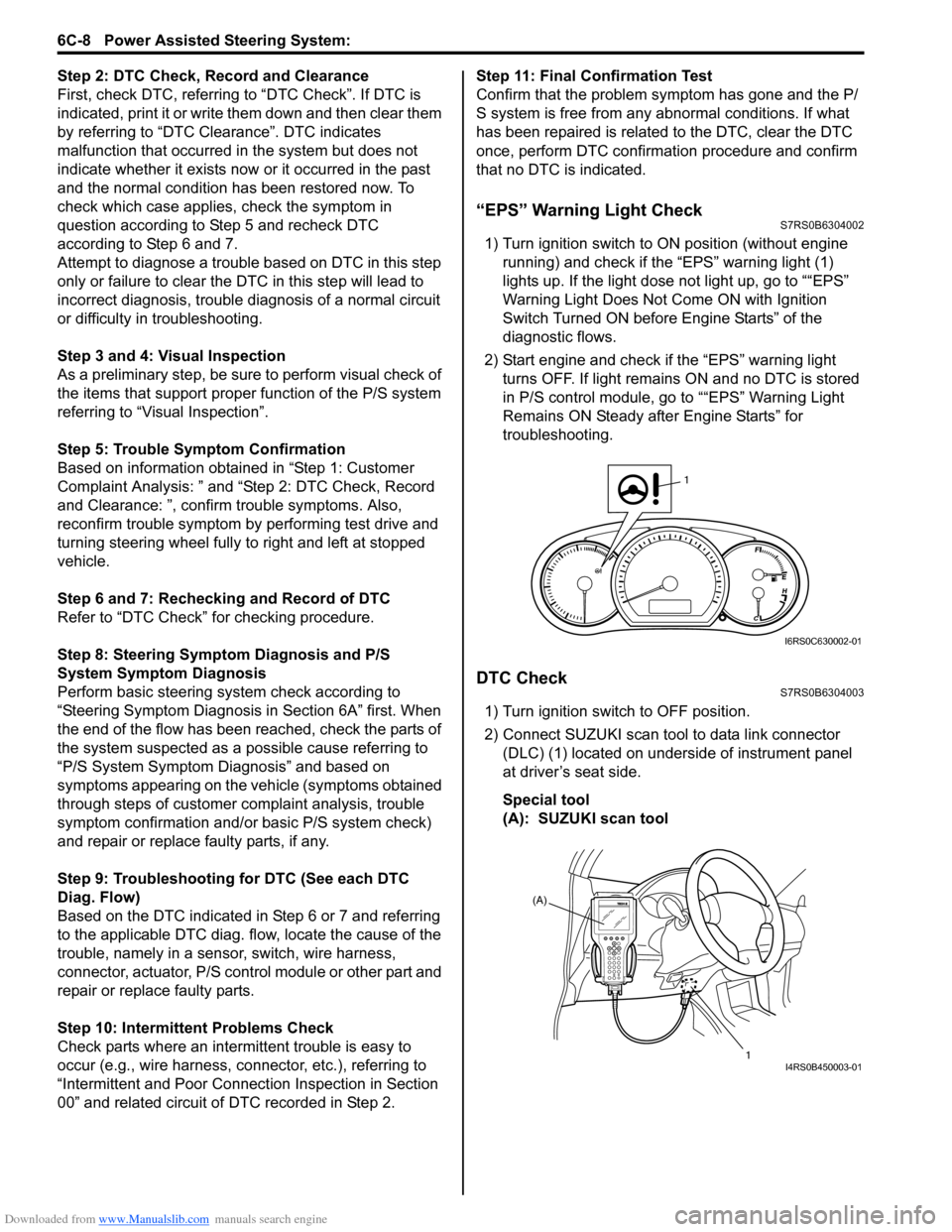
“EPS” Warning Light CheckS7RS0B6304002
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position (without engine
running) and chec k if the “EPS” warning light (1)
lights up. If the light dose not light up, go to ““EPS”
Warning Light Does Not Come ON with Ignition
Switch Turned ON before Engine Starts” of the
diagnostic flows.
2) Start engine and check if the “EPS” warning light turns OFF. If light remains ON and no DTC is stored
in P/S control module, go to ““EPS” Warning Light
Remains ON Steady after Engine Starts” for
troubleshooting.
DTC CheckS7RS0B6304003
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) located on underside of instrument panel
at driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
1
I6RS0C630002-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
Page 894 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-12 Power Assisted Steering System:
Scan Tool Data Definitions
Battery Voltage
This parameter indicates battery positive voltage.
TQS Power Supply (Torque Sensor Power Supply, V)
This parameter indicates the power supply voltage which
the P/S control module supplies to the torque sensor.
TQS Main Torque (Torque Sensor Main Torque, N ⋅m)
The torque sensor is installed to detect the steering force
and the steering directio n. It consists of two
potentiometers and the main torque sensor is one of
these.
TQS Sub Torque (Torque Sensor Sub Torque, N ⋅m)
The torque sensor is installed to detect the steering force
and the steering directio n. It consists of two
potentiometers and the sub-torque sensor is one of
these. Its output characteristics are compared with those
of the main torque sensor.
Assist Torque (N ⋅m)
This parameter is an internal parameter of the P/S
control module. It is obtained by computing the torque
sensor input signal. Motor Control (Motor Control Current, A)
Based on the input signal, the P/S control module
determines the assist amount
and controls the current to
the motor suitable for that a ssist amount. This parameter
indicates that control value.
Motor Monitor (Motor Monitor Current, A)
This parameter indicates the actually measured value of
the current flowing to the motor. The motor circuit
condition is diagnosed by co mparing this parameter with
“Motor Control” parameter described previously.
Vehicle Speed (km/h, MPH)
Vehicle speed signal is fed from BCM. P/S control
module determines the amount of power assist based on
this vehicle speed signal and the torque sensor signal.
Engine Speed (rpm)
Engine speed signal is fed from the ECM so that it can
be used for trouble diagnos is of the electric power
steering system.
Motor Volt (V)
This parameter indicates the voltage between motor
terminals.
Ignition switch (ON, OFF)
This parameter indicates the condition of the power
supply through the ignition switch.
Visual InspectionS7RS0B6304007
Visually check the following pats and system.
P/S System Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B6304008
This section describes trouble diagnosis of the P/S system parts whose trouble is not indicated by the on-board
diagnostic system (self-diagnostic functi on). When no malfunction is indicated by the on-board diagnostic system
(self-diagnosis function) and those stee ring basic parts as described in “Steering Symptom Diagnosis in Section 6A”
are all in good condition, check the following power steer ing system parts which may be a possible cause for each
symptom of the steering. Inspection Item Referring section
Battery Level, leakage, color “Batte ry Description in Section 1J”
Connectors of electric wire
harness Disconnection friction “Intermittent and Poor
Connection Inspection in Section 00”
Fuses Burning “Cautions in Body Electric al System Servicing in Section 9A”
Parts Installation, damage
Other parts that can be checked visually
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Steering wheel feels
heavy (Perform “Steering
Force Check” before
diagnosis.) Steering wheel installed improperly
(twisted)
Install steering wheel correctly.
Poor performance of torque sensor Check torque sensor referring to “Torque
Sensor and Its Circuit Inspection”.
Poor performance of P/S motor Check motor referring to “P/S Motor and Its
Circuit Inspection”.
Steering gear case assembly faulty Replace.
Poor performance of vehicle speed
signal from ECM Check vehicle speed signal circuit referring to
“DTC C1121 / C1123 / C1124: VSS Circuit
Failure”.
Page 895 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-13
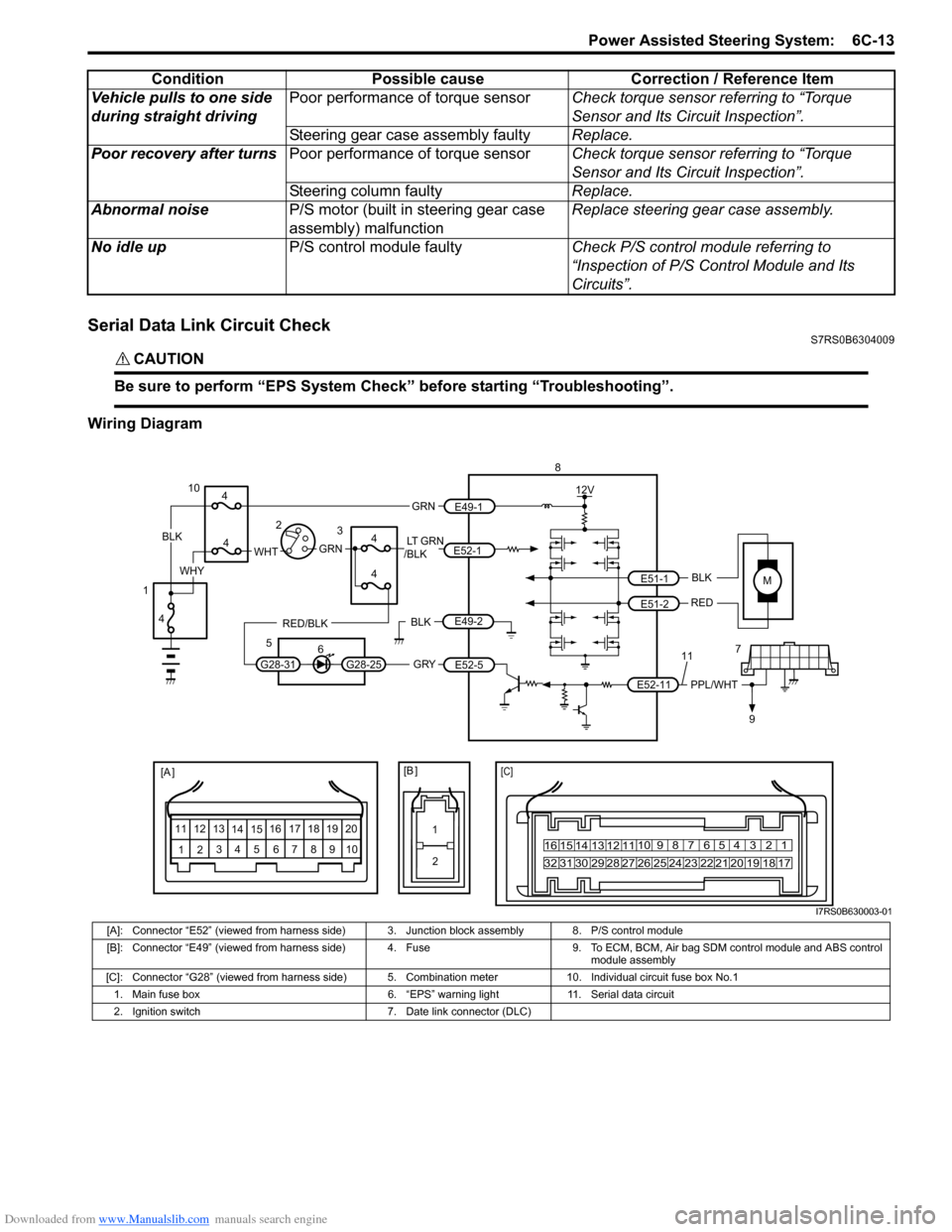
Serial Data Link Circuit CheckS7RS0B6304009
CAUTION!
Be sure to perform “EPS System Check” before starting “Troubleshooting”.
Wiring DiagramVehicle pulls to one side
during straight driving
Poor performance of torque sensor
Check torque sensor referring to “Torque
Sensor and Its Circuit Inspection”.
Steering gear case assembly faulty Replace.
Poor recovery after turns Poor performance of torque sensor Check torque sensor referring to “Torque
Sensor and Its Circuit Inspection”.
Steering column faulty Replace.
Abnormal noise P/S motor (built in steering gear case
assembly) malfunction Replace steering gear case assembly.
No idle up P/S control module faulty Check P/S control module referring to
“Inspection of P/S Control Module and Its
Circuits”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
MBLK
RED
E52-11 E51-1
E51-2PPL/WHT
[A ]
12
3
4 5 67
89
11
10
12 13
141516
17 18 19 2010 9 8 7654 3 21
16 15 14 13 12 11
26 25 24 2322 21 20 19 18 17
32 31 30 29 28 27
[C]
8
79
12V
[B ]
11
12
GRY
LT GRN
/BLK
E52-1
E52-5
E49-1
GRNGRNWHTBLK
WHY
G28-25G28-31
RED/BLK
10
3
4
4
5 6
4
4
1 2
4
E49-2BLK
I7RS0B630003-01
[A]: Connector “E52” (viewed from harness side) 3. Junction block assembly 8. P/S control module
[B]: Connector “E49” (viewed from harness side) 4. Fuse 9. T o ECM, BCM, Air bag SDM control module and ABS control
module assembly
[C]: Connector “G28” (viewed from harness side) 5. Comb ination meter 10. Individual circuit fuse box No.1
1. Main fuse box 6. “EPS” warning light 11. Serial data circuit
2. Ignition switch 7. Date link connector (DLC)
Page 900 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-18 Power Assisted Steering System:
4Torque sensor signal (main) voltage check
1) Check for voltage between “E53-5” (“WHT” wire)
terminal and body ground with ignition switch ON.
Is it about 0 V? Go to Step 5. Torque sensor signal
circuit is shorted to
other circuit.
5 Torque sensor signal (main) resistance check
1) Check for resistance “E53-5” (“WHT” wire) terminal and
body ground terminal with ignition switch OFF.
Is it about 1 M
Ω? Go to Step 6. Go to Step 8.
6 Torque sensor output voltage check
1) Connect connector to torque sensor with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Check torque sensor out put voltage referring to “Torque Sensor and Its Circuit Inspection”.
Is torque sensor in good condition? Substitute a known-
good P/S control
module and recheck.
Replace steering gear
case.
7 Torque sensor (sub) circuit wire check
1) Disconnect P/S control module.
2) Check that torque sensor signal (sub) circuit is as
follows.
• Insulation resistance of wire harness is infinity between “Torque sensor signal (sub) circuit” terminal
and other terminal at torque sensor connector.
• Wiring harness resistance of “Torque sensor signal (sub) circuit” is less than 1 Ω.
• Insulation resistance between “Torque sensor (sub) signal circuit” and vehicle body ground is infinity.
• Circuit voltage between “Torque sensor signal (sub) circuit” circuit and ground circuit is 0 – 1 V with ignition
switch turned ON.
Is circuit in good condition? Replace P/S control
module.
Repair or replace
defective circuit.
8 Torque sensor (main) circuit wire check
1) Disconnect P/S control module.
2) Check that torque sensor (main) signal circuit is as
follows.
• Insulation resistance of wire harness is infinity between “Torque sensor (main) signal circuit” terminal
and other terminal at torque sensor connector.
• Wiring harness resistance of “Torque sensor (main) signal circuit” is less than 1 Ω.
• Insulation resistance between “Torque sensor (main) signal circuit” and vehicle body ground is infinity.
Is circuit in good condition? Replace P/S control
module.
Repair or replace
defective circuit.
Step Action Yes No
Page 909 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-27
DTC TroubleshootingStep Action Yes No 1 Was “EPS System Check” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “EPS System
Check”.
2 DTC check
DTC Check for ECM referring to “DTC Check in Section 1A”.
Is there any DTC detected? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 3.
3 DTC check
1) Check ABS control module for DTC referring to “DTC
Check in Section 4E”.
Is there any DTC detected? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 4.
4 Vehicle speed signal circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect connectors
from ECM.
2) Check ECM connector for proper connection.
3) If OK, turn ON ignition switch, measure voltage between “E23-25” wire terminal of ECM connector and body
ground.
Is voltage 4 – 5 V? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 5.
5 Vehicle speed signal circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect P/S control
module connector “E52”.
2) Check for proper terminal connection to P/S control module connector and ECM connector.
3) If connections are OK, chec k that “Vehicle speed signal
circuit” is as following.
• Insulation resistance of “Vehicle speed signal circuit” wire harness is infinity between its terminal and other
terminals at ECM and P/S control module connector.
• Wiring resistance of “Vehicle speed signal circuit” is less than 1 Ω.
• Insulation resistance of “Vehicle speed signal circuit” between its circuit and vehicle body ground is infinity.
• Circuit voltage between “Vehicle speed signal” circuit and ground circuit is 0 – 1 V with ignition switch turned
ON.
Is circuit in good condition? Replace P/S control
module.
Repair or replace
defective circuit.
6 ECM voltage check
1) Connect P/S control mo dule and ECM connectors.
2) Check ECM for vehicle speed signal output referring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.
Is check result in good condition? Replace P/S control
module.
Replace ECM.
Page 911 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-29
DTC TroubleshootingStep Action Yes No 1 Was “EPS System Check” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “EPS System
Check”.
2 DTC check
1) Clear DTC(s) referring to “DTC Clearance”.
2) Run engine at idle speed.
3) Check if any DTC is detecte d referring to “DTC Check”.
Is DTC C1122 still detected? Go to Step 3. Check intermittent
trouble referring to
“Intermittent and Poor
Connection Inspection
in Section 00”.
3 DTC check
1) Check ECM for DTC referring to “DTC Check in Section
1A”.
Is there any DTC related to engine speed? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 4.
4 Engine speed signal circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect P/S control
module connector.
2) Check P/S control module connector for proper connection.
3) If OK, turn ON ignition switch, measure voltage between “E52-12” wire terminal of P/S control module connector
and vehicle body ground.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 5.
5 1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect ECM connector.
2) Check for proper connection to the P/S control module and ECM at each “Engine speed signal circuit” terminal.
3) If connections are OK, chec k that “Engine speed signal
circuit” is as following.
• Insulation resistance of “Engine speed signal circuit” wire is infinity between its terminal and other terminals
at ECM and P/S control module connector.
• Wiring resistance of “Engine speed signal circuit” terminal are less than 1 Ω.
• Insulation resistance of “Engine speed signal circuit” between its terminal and vehicle body ground is
infinity.
• Circuit voltage between “Engine speed signal circuit” and ground circuit is 0 – 1 V with ignition switch turned
ON.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 6.
Repair engine speed
signal circuit.
6 ECM voltage check
1) Connect P/S control mo dule and ECM connectors.
2) Check ECM for engine speed signal and vehicle speed signal output voltage to P/S control module referring to
“Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.
Is check result in good condition? Substitute a known-
good P/S control
module and recheck.
Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Page 913 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-31
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC TroubleshootingDTC detecting condition Trouble area
DTC C1141:
Voltage between both motor drive circuits is more than 8.5
V or less than 0.2 V for 0.5 seconds continuously while
motor is not drived
(1 driving cycle detection logic)
DTC C1142:
Measured motor drive current is more than 10 A as
compared with target motor drive current.
(1 driving cycle detection logic)
DTC C1143:
Measured motor drive current is more than 50 A.
(1 driving cycle detection logic)
DTC C1145:
Measured motor drive current is less than 2 A
continuously for more than 3 seconds even though target
motor drive current is more than 4 A.
or
Measured motor drive current is less than 0.8 A for total 1
second even though motor cont rol duty is more than 90%
while target motor drive current is less than 8 A.
(1 driving cycle detection logic) • P/S motor circuit
• P/S motor
• P/S control module
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “EPS System Check” performed? Go to Step 2.Go to “EPS System
Check”.
2 DTC check
Is DTC C1153 and/or DTC C1155 indicated together? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 3.
3 Power supply and ground circuit check
1) Check P/S control module power supply and ground
circuit referring to “P/S Control Module Power Supply
and Ground Circuit Check”.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Repair or replace
defective circuit.
4 Motor circuit check
1) With ignition switch tuned OFF, disconnect P/S motor
connector (“E51”).
2) Check that P/S motor circuit is as follows. • Insulation resistance of wire harness is infinity between each “P/S motor circuit” terminal and other
terminal at P/S motor connector.
• Wiring harness resistance of each “P/S motor circuit”
is less than 1 Ω.
• Insulation resistance between each “P/S motor circuit” and vehicle body ground is infinity.
• Circuit voltage between each “P/S motor circuit” and ground circuit is 0 – 1 V with ignition switch turned
ON.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 5.
Repair or replace
defective circuit.
5 P/S motor check
1) Check motor and its circuit referring to “P/S Motor and Its
Circuit Inspection”.
Is motor in good condition? Substitute a known-
good P/S control
module, and recheck.
Replace the steering
gear case assembly.
Page 917 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-35
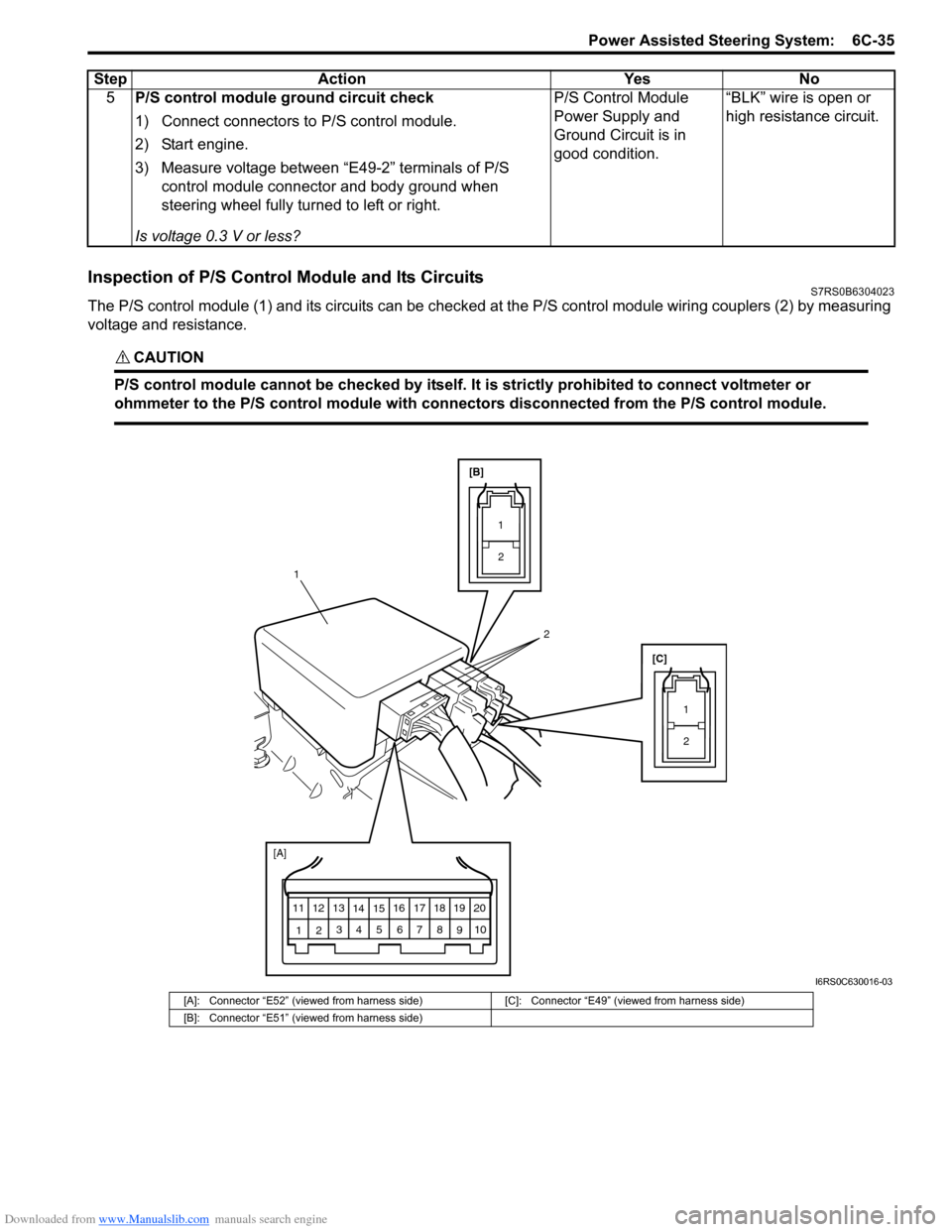
Inspection of P/S Control Module and Its CircuitsS7RS0B6304023
The P/S control module (1) and its circuits can be checked at the P/S control module wiring couplers (2) by measuring
voltage and resistance.
CAUTION!
P/S control module cannot be checked by itself. It is strictly prohibited to connect voltmeter or
ohmmeter to the P/S control module with connectors disconnected from the P/S control module.
5 P/S control module ground circuit check
1) Connect connectors to P/S control module.
2) Start engine.
3) Measure voltage between “E49-2” terminals of P/S
control module connector and body ground when
steering wheel fully turned to left or right.
Is voltage 0.3 V or less? P/S Control Module
Power Supply and
Ground Circuit is in
good condition.
“BLK” wire is open or
high resistance circuit.
Step Action Yes No
[A]
12
3
4 5 67
89
11
10
12 13
141516
17 18 19 20
[B]
[C]
12
1
1 2
2
I6RS0C630016-03
[A]: Connector “E52” (viewed from harness side) [C]: Connector “E49” (viewed from harness side)
[B]: Connector “E51” (viewed from harness side)
Page 918 of 1496
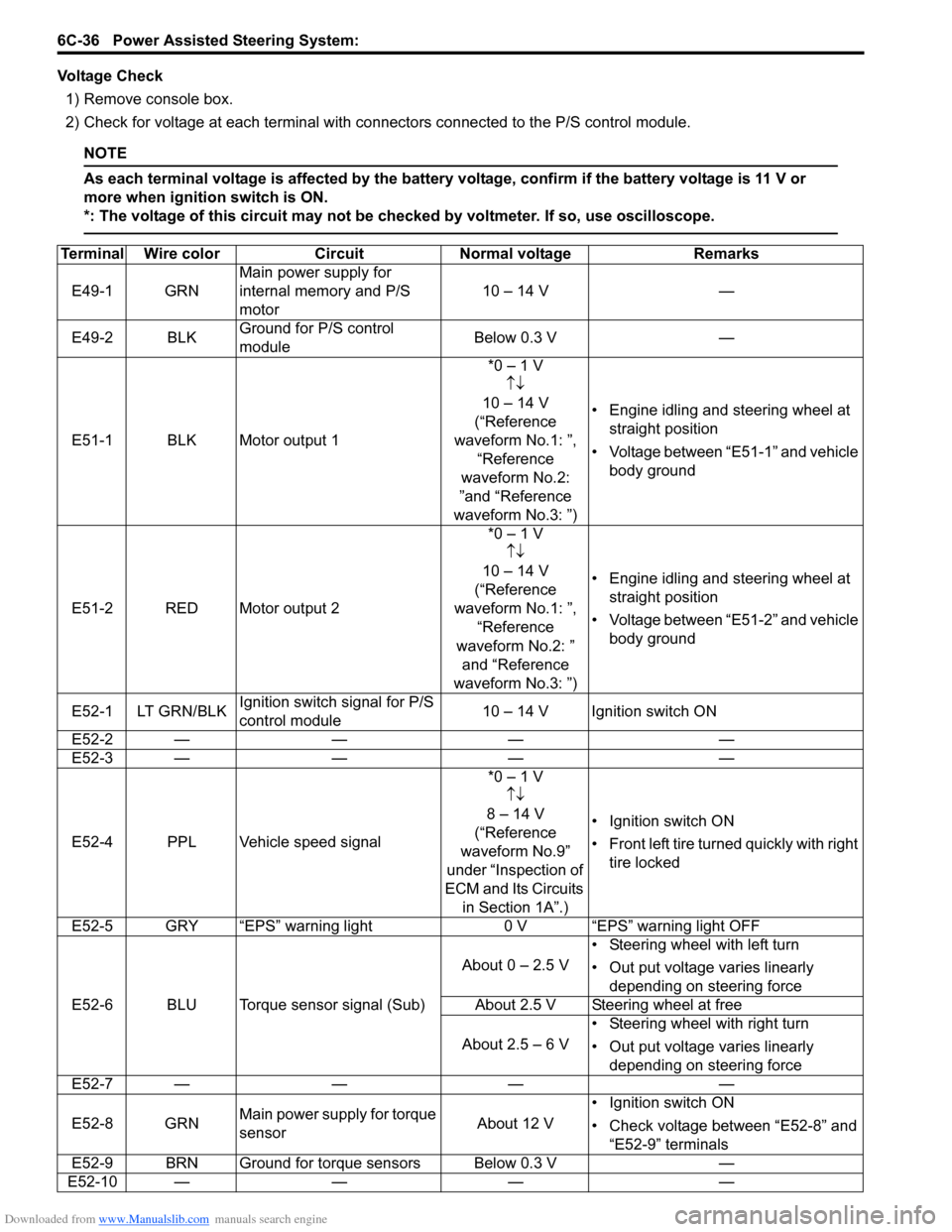
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-36 Power Assisted Steering System:
Voltage Check1) Remove console box.
2) Check for voltage at each terminal with co nnectors connected to the P/S control module.
NOTE
As each terminal voltage is affected by the battery voltage, confirm if the battery voltage is 11 V or
more when ignition switch is ON.
*: The voltage of this circuit may not be checked by voltmeter. If so, use oscilloscope.
Terminal Wire colorCircuit Normal voltage Remarks
E49-1 GRN Main power supply for
internal memory and P/S
motor 10 – 14 V
—
E49-2 BLK Ground for P/S control
module Below 0.3 V
—
E51-1 BLK Motor output 1 *0 – 1 V
↑↓
10 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.1: ”, “Reference
waveform No.2:
”and “Reference
waveform No.3: ”) • Engine idling and steering wheel at
straight position
• Voltage between “E51-1” and vehicle body ground
E51-2 RED Motor output 2 *0 – 1 V
↑↓
10 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.1: ”, “Reference
waveform No.2: ” and “Reference
waveform No.3: ”) • Engine idling and steering wheel at
straight position
• Voltage between “E51-2” and vehicle body ground
E52-1 LT GRN/BLK Ignition switch signal for P/S
control module 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
E52-2 — —— —
E52-3 — —— —
E52-4 PPL Vehicle speed signal *0 – 1 V
↑↓
8 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.9”
under “Inspection of
ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.) • Ignition switch ON
•Front left tire tu
rned quickly with right
tire locked
E52-5 GRY “EPS” warning light 0 V “EPS” warning light OFF
E52-6 BLU Torque sensor signal (Sub) About 0 – 2.5 V
• Steering wheel with left turn
• Out put voltage varies linearly
depending on steering force
About 2.5 V Steering wheel at free
About 2.5 – 6 V • Steering wheel with right turn
• Out put voltage varies linearly
depending on steering force
E52-7 — —— —
E52-8 GRN Main power supply for torque
sensor About 12 V• Ignition switch ON
• Check voltage between “E52-8” and
“E52-9” terminals
E52-9 BRN Ground for torque sensors Below 0.3 V —
E52-10 — —— —
Page 919 of 1496
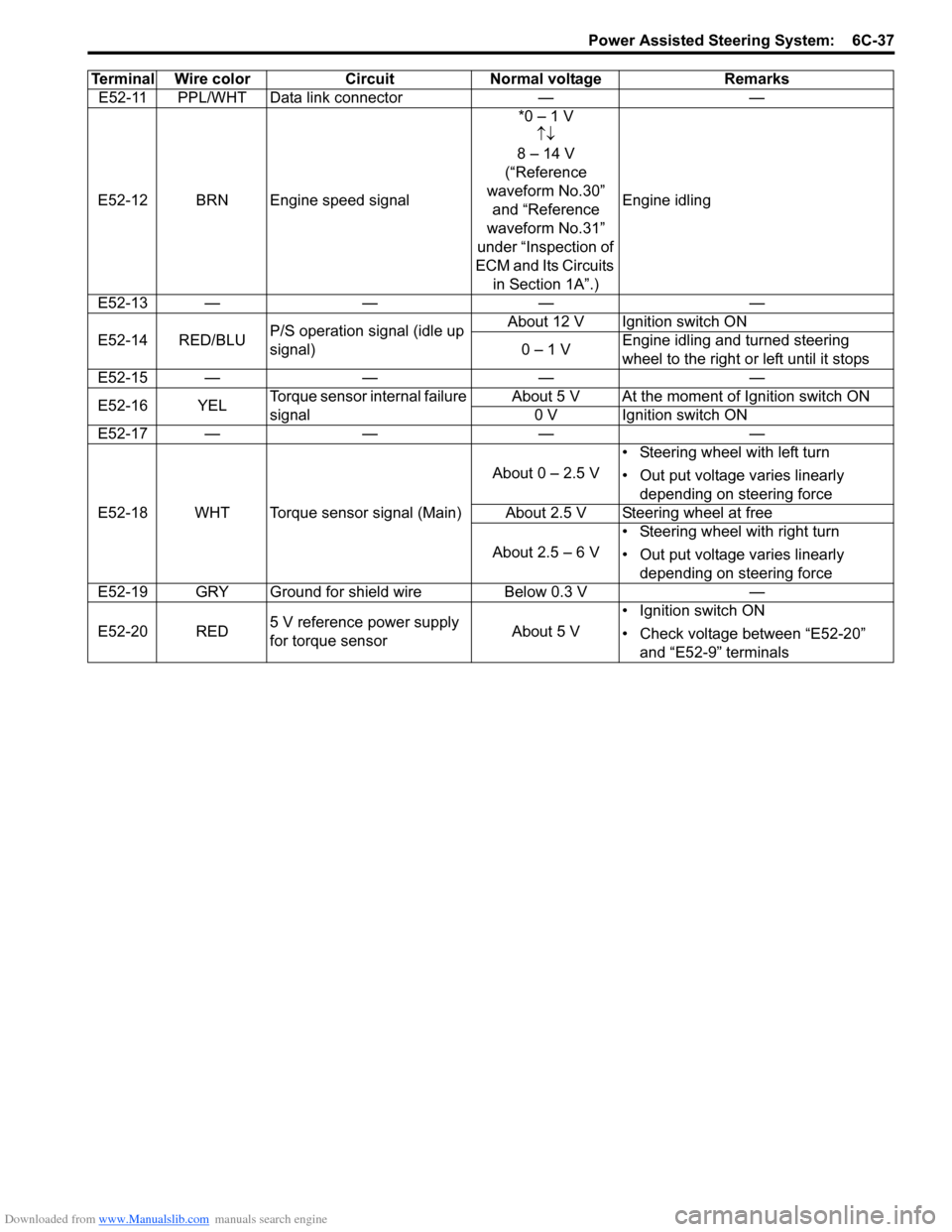
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-37
E52-11 PPL/WHT Data link connector——
E52-12 BRN Engine speed signal *0 – 1 V
↑↓
8 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.30” and “Reference
waveform No.31”
under “Inspection of
ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.) Engine idling
E52-13 — —— —
E52-14 RED/BLU P/S operation signal (idle up
signal) About 12 V Ignition switch ON
0 – 1 V Engine idling and turned steering
wheel to the right or left until it stops
E52-15 — —— —
E52-16 YEL Torque sensor internal failure
signal About 5 V At the moment of Ignition switch ON
0 V Ignition switch ON
E52-17 — —— —
E52-18 WHT Torque sensor signal (Main) About 0 – 2.5 V
• Steering wheel with left turn
• Out put voltage varies linearly
depending on steering force
About 2.5 V Steering wheel at free
About 2.5 – 6 V • Steering wheel with right turn
• Out put voltage varies linearly
depending on steering force
E52-19 GRY Ground for shield wire Below 0.3 V—
E52-20 RED 5 V reference power supply
for torque sensor About 5 V• Ignition switch ON
• Check voltage between “E52-20”
and “E52-9” terminals
Terminal Wire color
Circuit Normal voltage Remarks