Arm SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 269 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Aux. Emission Control Devices: 1B-2
EVAP Canister Purge Valve and Its Circuit
Inspection
S7RS0B1206002
WARNING!
Do not apply vacuum by mouth; otherwise
harmful fuel vapor can be breathed in.
CAUTION!
Do not apply vacuum more than –86 kPa (–
12.47 psi); otherwise EVAP canister purge
valve could be damaged.
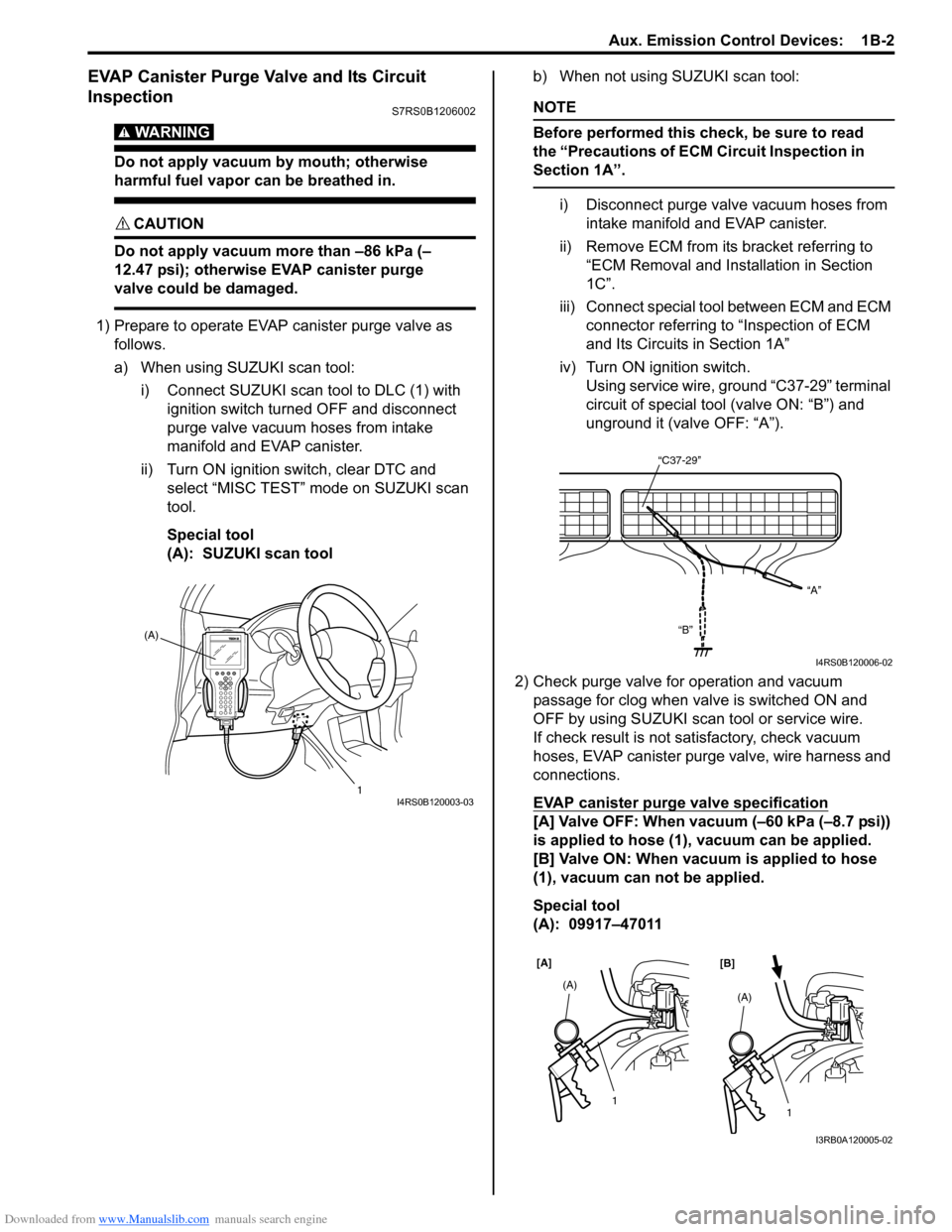
1) Prepare to operate EVAP canister purge valve as follows.
a) When using SUZUKI scan tool:
i) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC (1) with ignition switch turned OFF and disconnect
purge valve vacuum hoses from intake
manifold and EVAP canister.
ii) Turn ON ignition switch, clear DTC and select “MISC TEST” mode on SUZUKI scan
tool.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool b) When not using SUZUKI scan tool:
NOTE
Before performed this check, be sure to read
the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection in
Section 1A”.
i) Disconnect purge valve vacuum hoses from
intake manifold and EVAP canister.
ii) Remove ECM from it s bracket referring to
“ECM Removal and Inst allation in Section
1C”.
iii) Connect special tool between ECM and ECM connector referring to “Inspection of ECM
and Its Circuits in Section 1A”
iv) Turn ON ignition switch. Using service wire, ground “C37-29” terminal
circuit of special tool (valve ON: “B”) and
unground it (valve OFF: “A”).
2) Check purge valve for operation and vacuum passage for clog when valve is switched ON and
OFF by using SUZUKI scan tool or service wire.
If check result is not satisfactory, check vacuum
hoses, EVAP canister purge valve, wire harness and
connections.
EVAP canister purge valve specification
[A] Valve OFF: When vacuum (–60 kPa (–8.7 psi))
is applied to hose (1), vacuum can be applied.
[B] Valve ON: When vacuum is applied to hose
(1), vacuum can not be applied.
Special tool
(A): 09917–47011
(A)
1
I4RS0B120003-03
“C37-29”“A”
“B”
I4RS0B120006-02
[A] [B]
1
(A)1
(A)
I3RB0A120005-02
Page 270 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1B-3 Aux. Emission Control Devices:
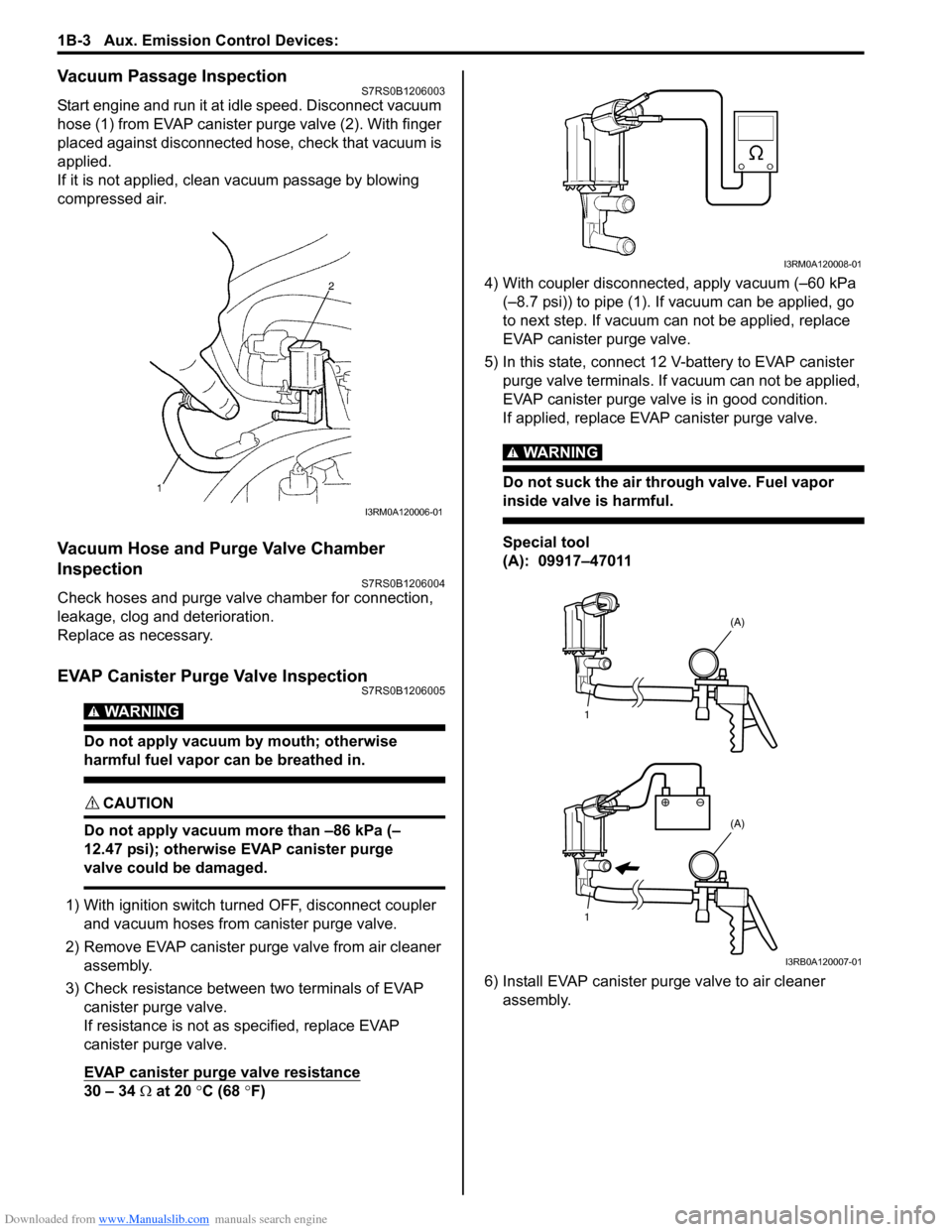
Vacuum Passage InspectionS7RS0B1206003
Start engine and run it at idle speed. Disconnect vacuum
hose (1) from EVAP canister purge valve (2). With finger
placed against disconnected hose, check that vacuum is
applied.
If it is not applied, clean vacuum passage by blowing
compressed air.
Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber
Inspection
S7RS0B1206004
Check hoses and purge valv e chamber for connection,
leakage, clog and deterioration.
Replace as necessary.
EVAP Canister Purge Valve InspectionS7RS0B1206005
WARNING!
Do not apply vacuum by mouth; otherwise
harmful fuel vapor can be breathed in.
CAUTION!
Do not apply vacuum more than –86 kPa (–
12.47 psi); otherwise EVAP canister purge
valve could be damaged.
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect coupler and vacuum hoses from canister purge valve.
2) Remove EVAP canister purge valve from air cleaner assembly.
3) Check resistance between two terminals of EVAP canister purge valve.
If resistance is not as specified, replace EVAP
canister purge valve.
EVAP canister purge valve resistance
30 – 34 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F) 4) With coupler disconnected, apply vacuum (–60 kPa
(–8.7 psi)) to pipe (1). If vacuum can be applied, go
to next step. If vacuum can not be applied, replace
EVAP canister purge valve.
5) In this state, connect 12 V-battery to EVAP canister purge valve terminals. If vacuum can not be applied,
EVAP canister purge valve is in good condition.
If applied, replace EVAP canister purge valve.
WARNING!
Do not suck the air through valve. Fuel vapor
inside valve is harmful.
Special tool
(A): 09917–47011
6) Install EVAP canister purge valve to air cleaner assembly.
I3RM0A120006-01
I3RM0A120008-01
1
1 (A)
(A)
I3RB0A120007-01
Page 271 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Aux. Emission Control Devices: 1B-4
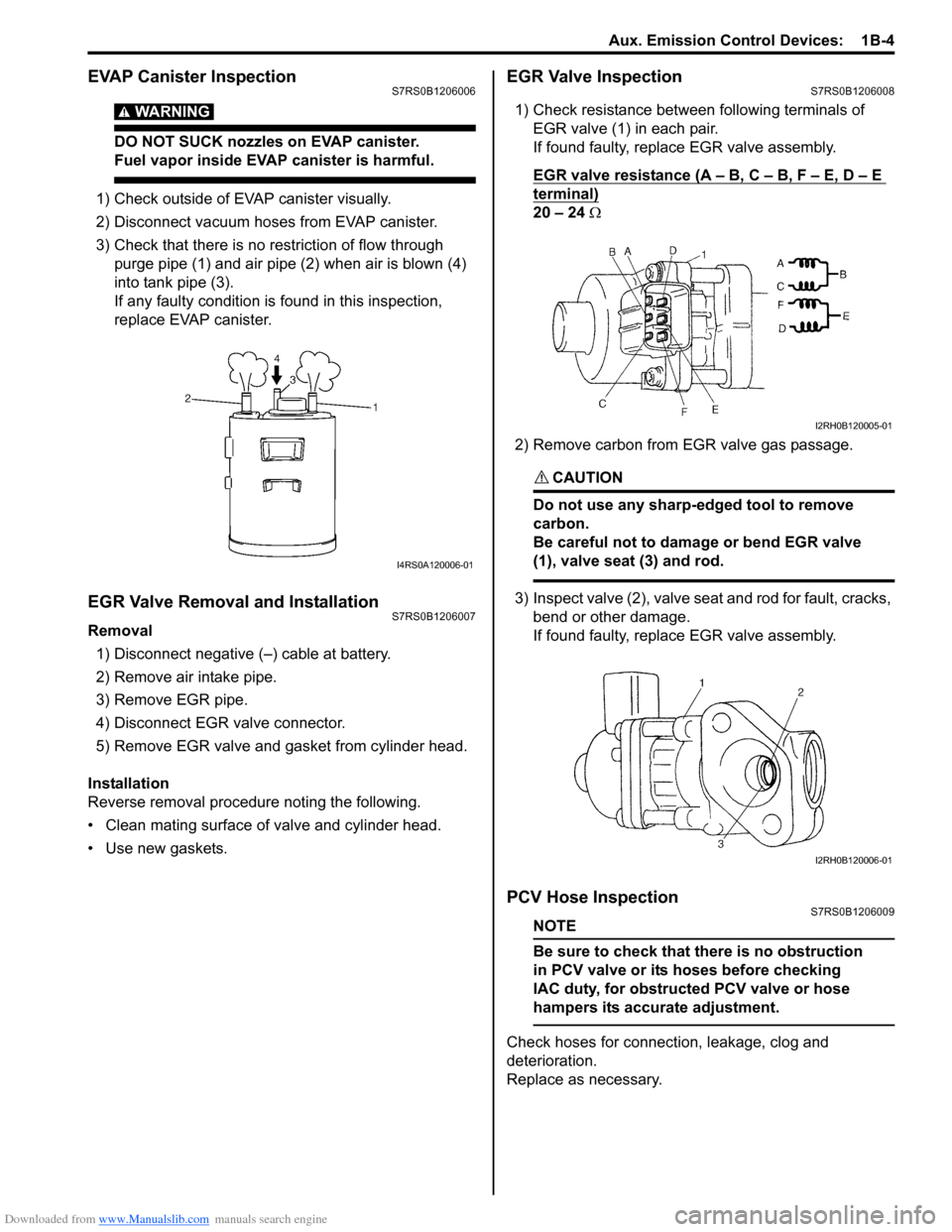
EVAP Canister InspectionS7RS0B1206006
WARNING!
DO NOT SUCK nozzles on EVAP canister.
Fuel vapor inside EVAP canister is harmful.
1) Check outside of EVAP canister visually.
2) Disconnect vacuum hoses from EVAP canister.
3) Check that there is no restriction of flow through purge pipe (1) and air pipe (2) when air is blown (4)
into tank pipe (3).
If any faulty condition is found in this inspection,
replace EVAP canister.
EGR Valve Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1206007
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove air intake pipe.
3) Remove EGR pipe.
4) Disconnect EGR valve connector.
5) Remove EGR valve and gasket from cylinder head.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Clean mating surface of valve and cylinder head.
• Use new gaskets.
EGR Valve InspectionS7RS0B1206008
1) Check resistance between following terminals of EGR valve (1) in each pair.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
EGR valve resistance (A – B, C – B, F – E, D – E
terminal)
20 – 24 Ω
2) Remove carbon from EGR valve gas passage.
CAUTION!
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to remove
carbon.
Be careful not to damage or bend EGR valve
(1), valve seat (3) and rod.
3) Inspect valve (2), valve seat and rod for fault, cracks, bend or other damage.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
PCV Hose InspectionS7RS0B1206009
NOTE
Be sure to check that there is no obstruction
in PCV valve or its hoses before checking
IAC duty, for obstructed PCV valve or hose
hampers its accurate adjustment.
Check hoses for connection, leakage, clog and
deterioration.
Replace as necessary.
I4RS0A120006-01
I2RH0B120005-01
I2RH0B120006-01
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 290 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
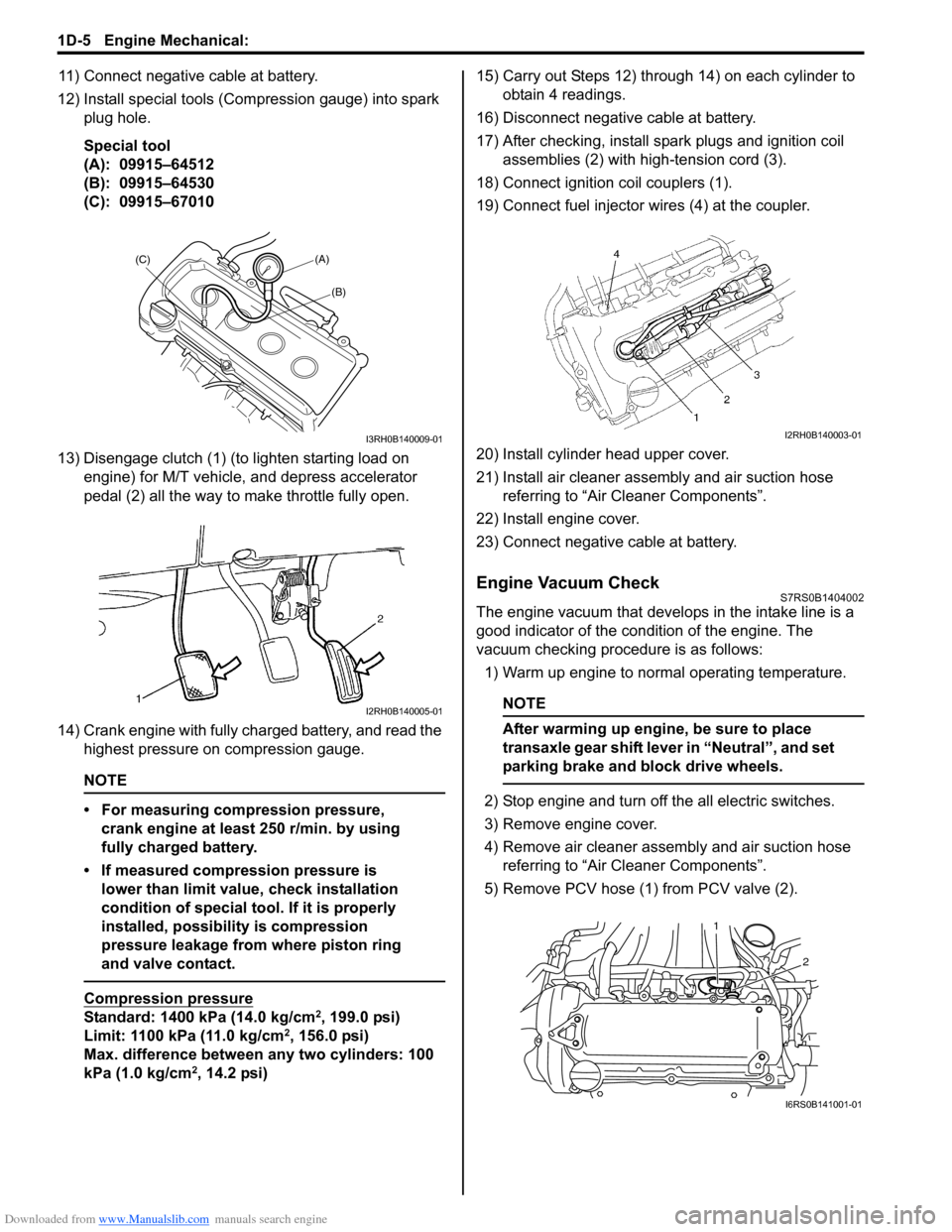
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 355 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Lubrication System: 1E-3
6) Start engine and warm engine up to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
Be sure to shift transaxle gear shift lever in
“Neutral” (shift select lever in “P” range for
A/T vehicle), set parking brake and block
drive wheels.
7) After warming up, raise engine speed to 4,000 r/min. and measure oil pressure.
Oil pressure specification
More than 270 kPa (2.7 kg/cm2, 39.8 psi) at 4,000
r/min. (rpm)
8) After checking oil pressure, stop engine and remove oil pressure gauge and attachment.
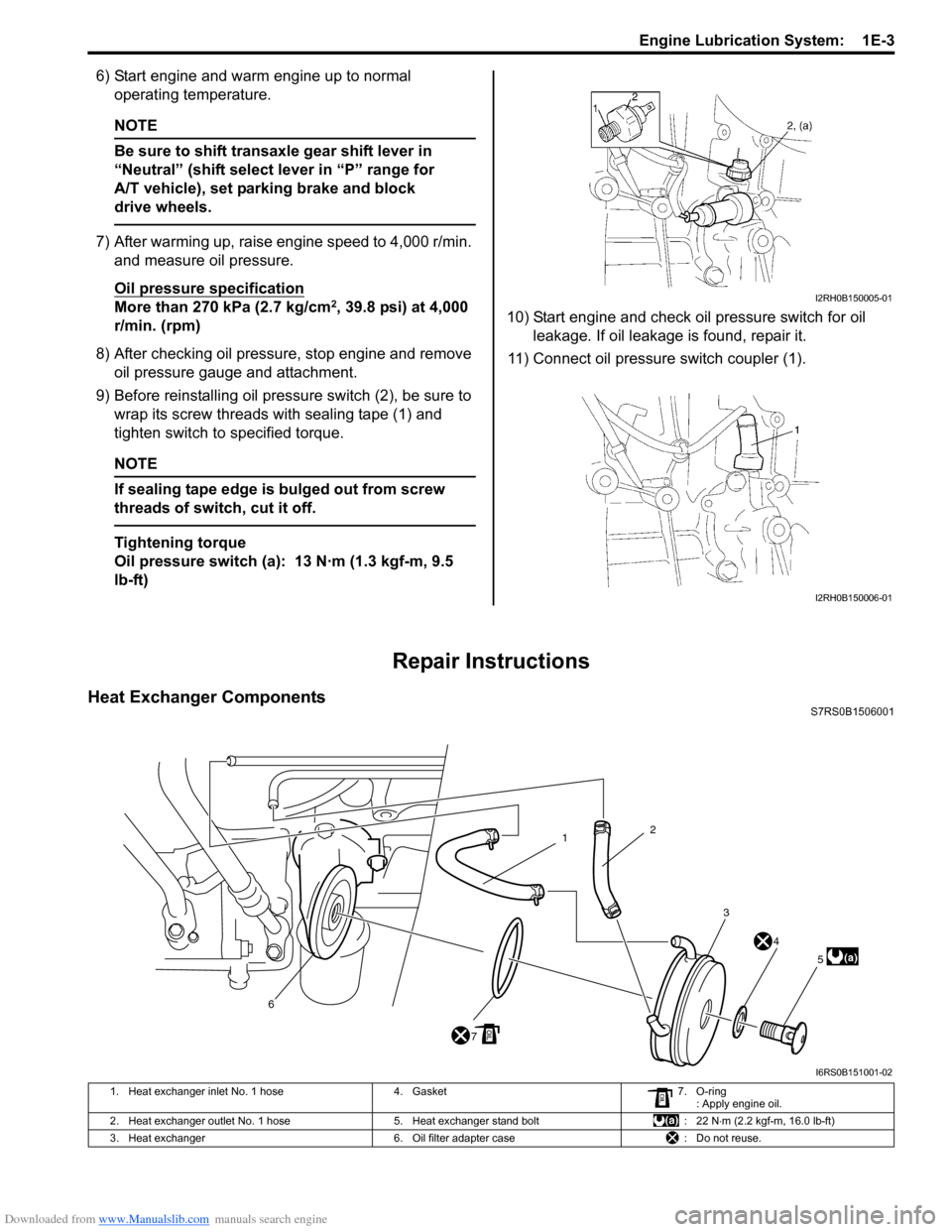
9) Before reinstalling oil pressure switch (2), be sure to
wrap its screw threads with sealing tape (1) and
tighten switch to specified torque.
NOTE
If sealing tape edge is bulged out from screw
threads of switch, cut it off.
Tightening torque
Oil pressure switch (a): 13 N·m (1.3 kgf-m, 9.5
lb-ft) 10) Start engine and check oil pressure switch for oil
leakage. If oil leakage is found, repair it.
11) Connect oil pressure switch coupler (1).
Repair Instructions
Heat Exchanger ComponentsS7RS0B1506001
I2RH0B150005-01
I2RH0B150006-01
3
4
5
7
6
(a)
2
1
I6RS0B151001-02
1. Heat exchanger inlet No. 1 hose 4. Gasket7. O-ring
: Apply engine oil.
2. Heat exchanger outlet No. 1 hose 5. Heat exchanger stand bolt : 22 N⋅m (2.2 kgf-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
3. Heat exchanger 6. Oil filter adapter case : Do not reuse.
Page 365 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Cooling System: 1F-2
Coolant capacity
For M/T model:• Engine, radiator and heater: 5.5 liters (11.62/9.68 US/lmp pt.)
• Reservoir: 0.7 liters (1.48/1.23 US/lmp pt.)
• Total: 6.2 liters (13.10/10.91 US/lmp pt.)
For A/T model: • Engine, radiator and heater: 5.4 liters (11.41/9.50 US/lmp pt.)
• Reservoir: 0.7 liters (1.48/1.23 US/lmp pt.)
• Total: 6.1 liters (12.89/10.74 US/lmp pt.)
Schematic and Routing Diagram
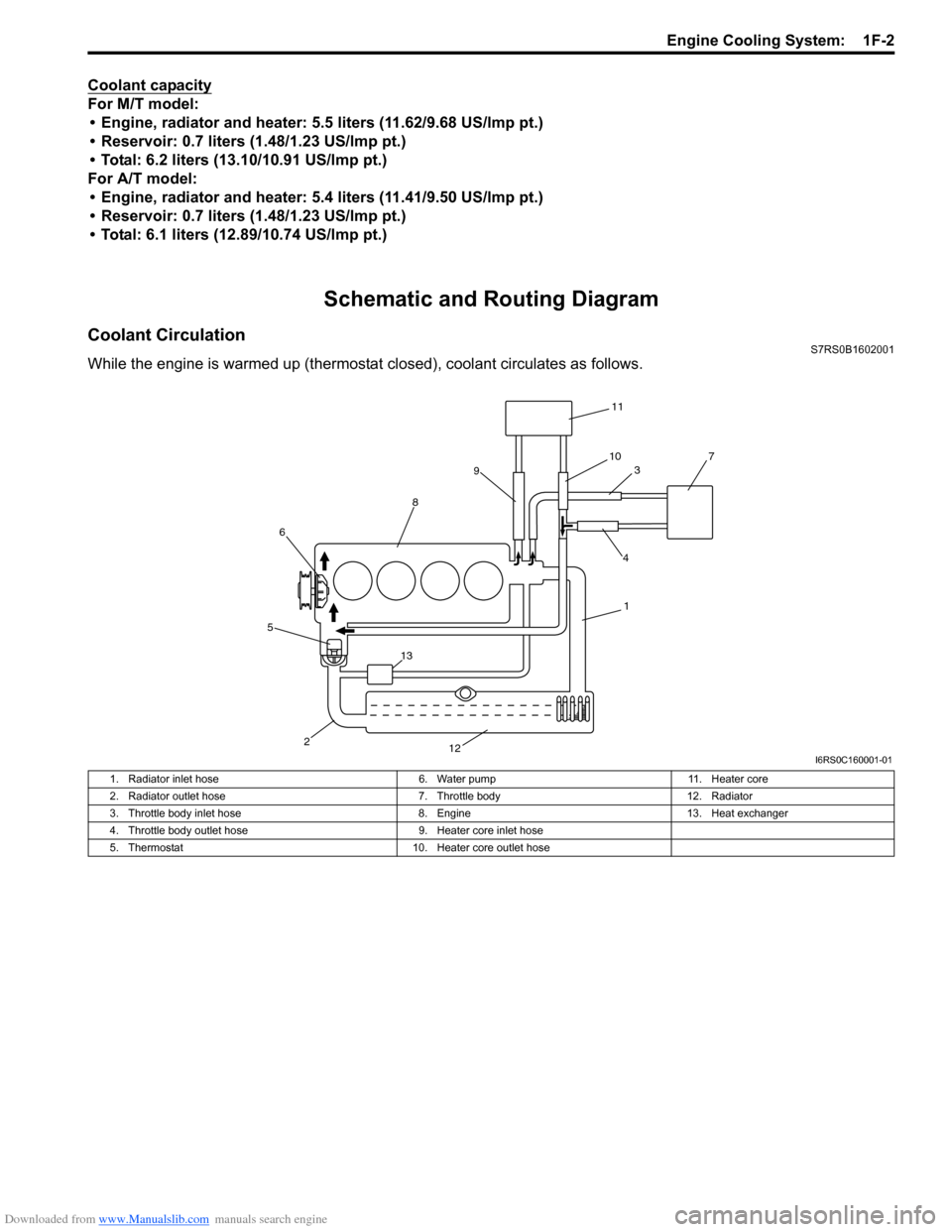
Coolant CirculationS7RS0B1602001
While the engine is warmed up (thermosta t closed), coolant circulates as follows.
11
10 3 7
4
9
8
6
5
2 12 1
13
I6RS0C160001-01
1. Radiator inlet hose
6. Water pump11. Heater core
2. Radiator outlet hose 7. Throttle body12. Radiator
3. Throttle body inlet hose 8. Engine13. Heat exchanger
4. Throttle body outlet hose 9. Heater core inlet hose
5. Thermostat 10. Heater core outlet hose
Page 366 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1F-3 Engine Cooling System:
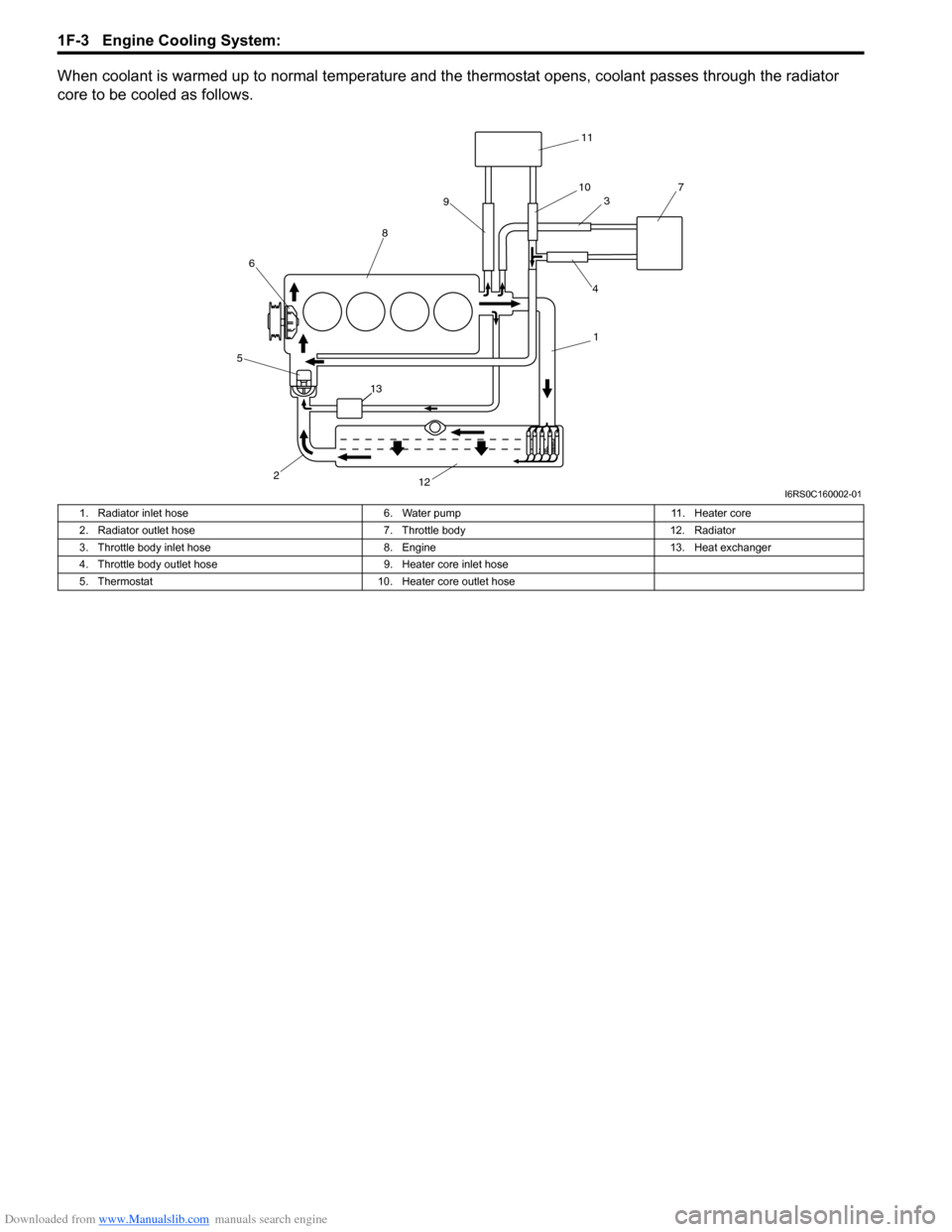
When coolant is warmed up to normal temperature and the thermostat opens, coolant passes through the radiator
core to be cooled as follows.
11
10 3 7
4
9
8
6
5
2 12 1
13
I6RS0C160002-01
1. Radiator inlet hose
6. Water pump11. Heater core
2. Radiator outlet hose 7. Throttle body12. Radiator
3. Throttle body inlet hose 8. Engine13. Heat exchanger
4. Throttle body outlet hose 9. Heater core inlet hose
5. Thermostat 10. Heater core outlet hose
Page 369 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Cooling System: 1F-6
Coolant Level CheckS7RS0B1606002
WARNING!
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam
can be blown out under pressure if radiator
cap is taken off too soon.
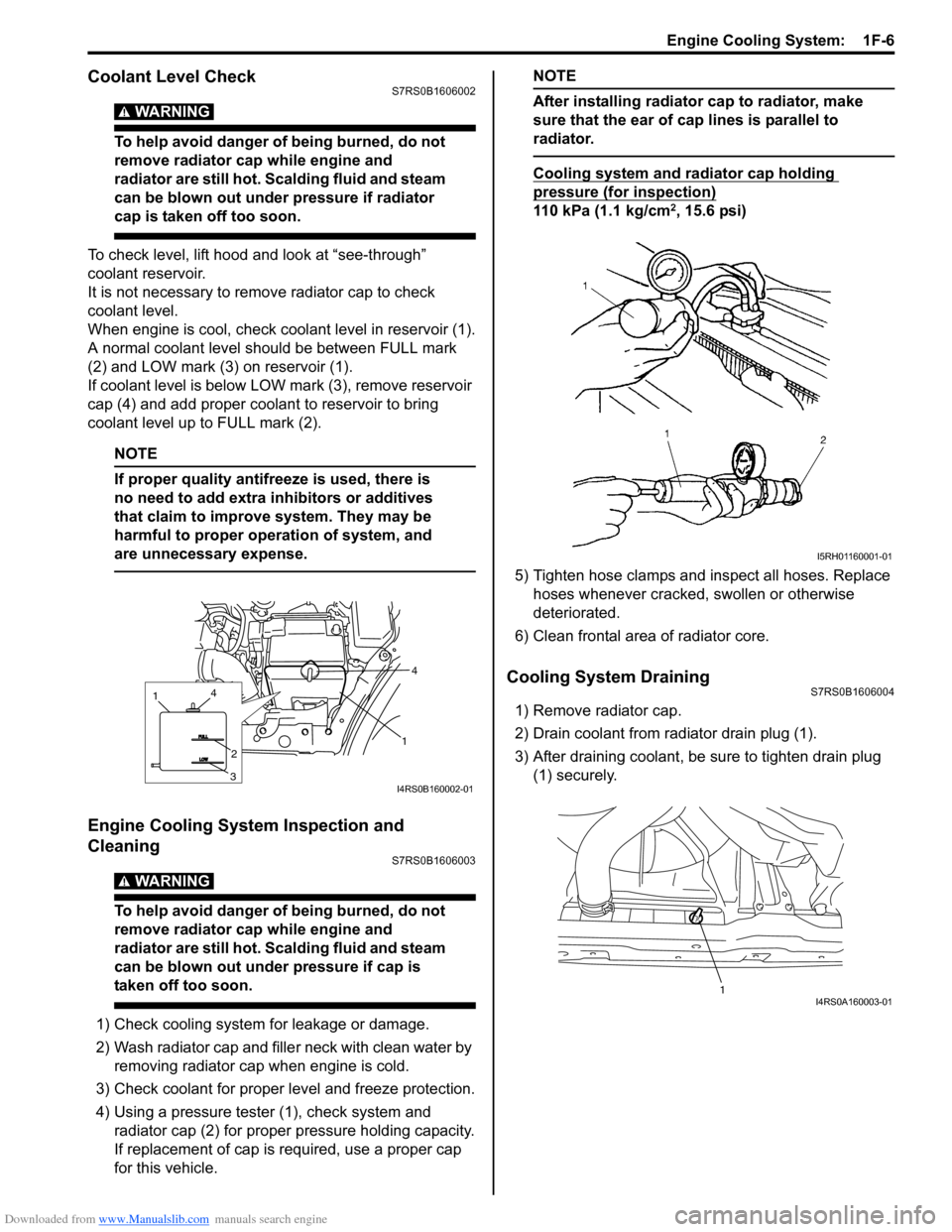
To check level, lift hood and look at “see-through”
coolant reservoir.
It is not necessary to remove radiator cap to check
coolant level.
When engine is cool, check coolant level in reservoir (1).
A normal coolant level should be between FULL mark
(2) and LOW mark (3) on reservoir (1).
If coolant level is below LOW mark (3), remove reservoir
cap (4) and add proper coolant to reservoir to bring
coolant level up to FULL mark (2).
NOTE
If proper quality antifreeze is used, there is
no need to add extra inhibitors or additives
that claim to improve system. They may be
harmful to proper operation of system, and
are unnecessary expense.
Engine Cooling System Inspection and
Cleaning
S7RS0B1606003
WARNING!
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam
can be blown out under pressure if cap is
taken off too soon.
1) Check cooling system for leakage or damage.
2) Wash radiator cap and fille r neck with clean water by
removing radiator cap when engine is cold.
3) Check coolant for proper level and freeze protection.
4) Using a pressure tester (1), check system and radiator cap (2) for proper pressure holding capacity.
If replacement of cap is required, use a proper cap
for this vehicle.
NOTE
After installing radiator cap to radiator, make
sure that the ear of cap lines is parallel to
radiator.
Cooling system and radiator cap holding
pressure (for inspection)
110 kPa (1.1 kg/cm2, 15.6 psi)
5) Tighten hose clamps and inspect all hoses. Replace hoses whenever cracked, swollen or otherwise
deteriorated.
6) Clean frontal area of radiator core.
Cooling System DrainingS7RS0B1606004
1) Remove radiator cap.
2) Drain coolant from radiator drain plug (1).
3) After draining coolant, be sure to tighten drain plug (1) securely.
1
4
1
3
2
4
I4RS0B160002-01
I5RH01160001-01
1I4RS0A160003-01
Page 378 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-3 Fuel System:
4) Check that battery voltage is 11 V or more.
5) Measure fuel pressure at each condition.If measured pressure is out of specification, refer to
“Fuel Pressure Check in Section 1A” and check each
possibly defective part. Replace if found defective.
a) Turn ignition switch ON to operate fuel pump and after 2 seconds turn it OFF. Repeat this 3 or 4
times and then check fuel pressure.
Fuel pressure specification
With fuel pump operating and engine
stopped: 270 – 310 kPa (2.7 – 3.1 kg/cm2, 38.4
– 44.0 psi)
b) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature, and measure fuel pressure at
idling.
Fuel pressure specification
At specified idle speed: 270 – 310 kPa (2.7 –
3.1 kg/cm2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi)
c) Stop engine, and measure fuel pressure at one minute after stopping.
Fuel pressure specification
With 1 min. after engine (fuel pump) stop
(Pressure reduces as time passes): Over 300
kPa (3.0 kg/cm
2, 42.7 psi)
6) After checking fuel pressure, remove fuel pressure gauge.
WARNING!
As fuel feed line is still under high fuel
pressure, make sure to release fuel pressure
according to the following procedures.
• Place fuel container under joint.
• Cover joint with rag and loosen joint nut slowly in order to release fuel pressure
gradually.
7) Remove special tools from fuel delivery pipe and fuel feed hose.
8) Connect fuel feed hose to fuel delivery pipe and clamp it securely.
9) With engine OFF and ignition switch ON, check for fuel leaks.
Fuel Cut Operation InspectionS7RS0B1704002
NOTE
Before inspection, make sure that gear shift
lever is in neutral positi on (shift select lever
is “P” range for A/T vehicle), A/C is OFF and
parking brake lever is pulled all the way up.
1) Warm engine up to normal operating temperature.
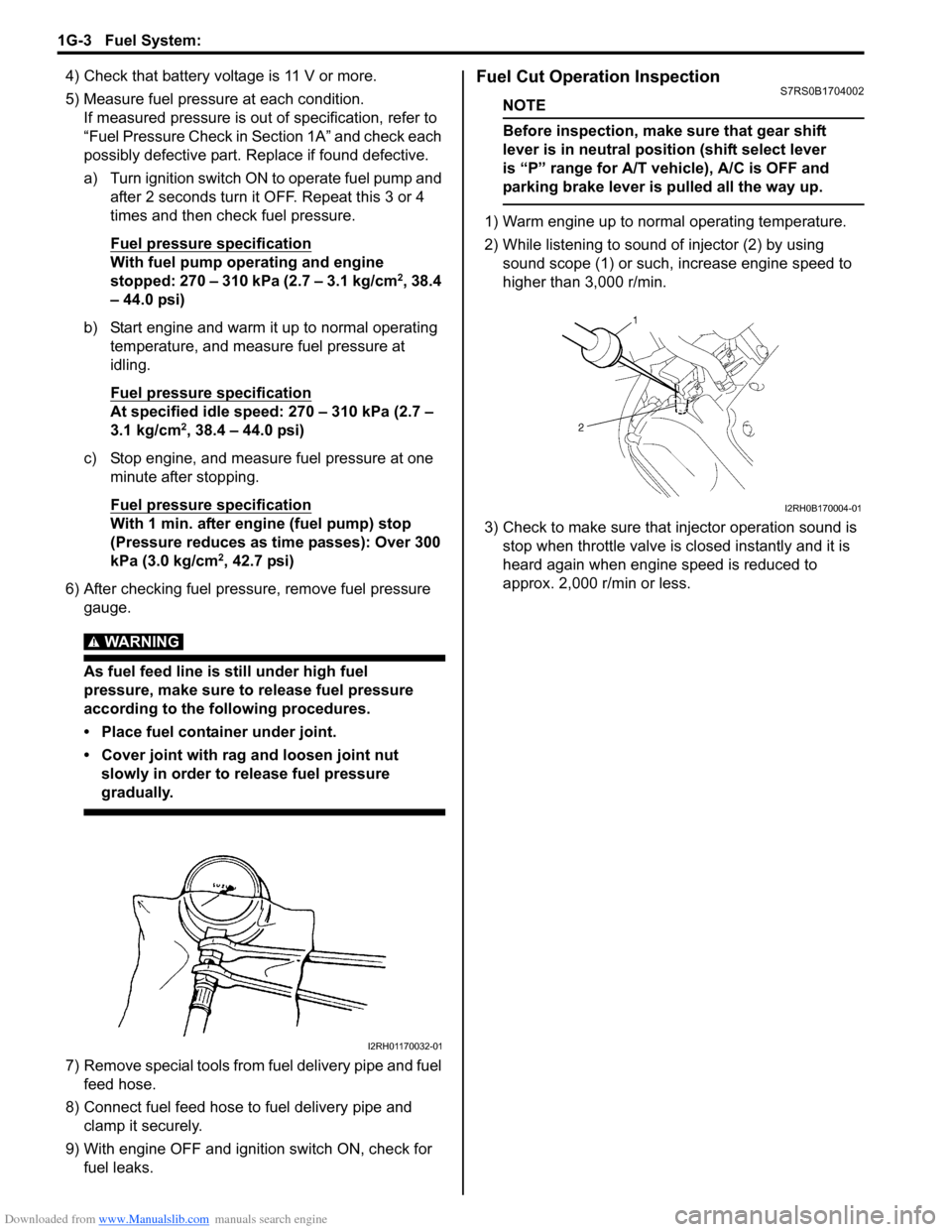
2) While listening to sound of injector (2) by using sound scope (1) or such, increase engine speed to
higher than 3,000 r/min.
3) Check to make sure that injector operation sound is stop when throttle valve is closed instantly and it is
heard again when engine speed is reduced to
approx. 2,000 r/min or less.
I2RH01170032-01
I2RH0B170004-01