Combination meter engine speed SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 58 of 1496
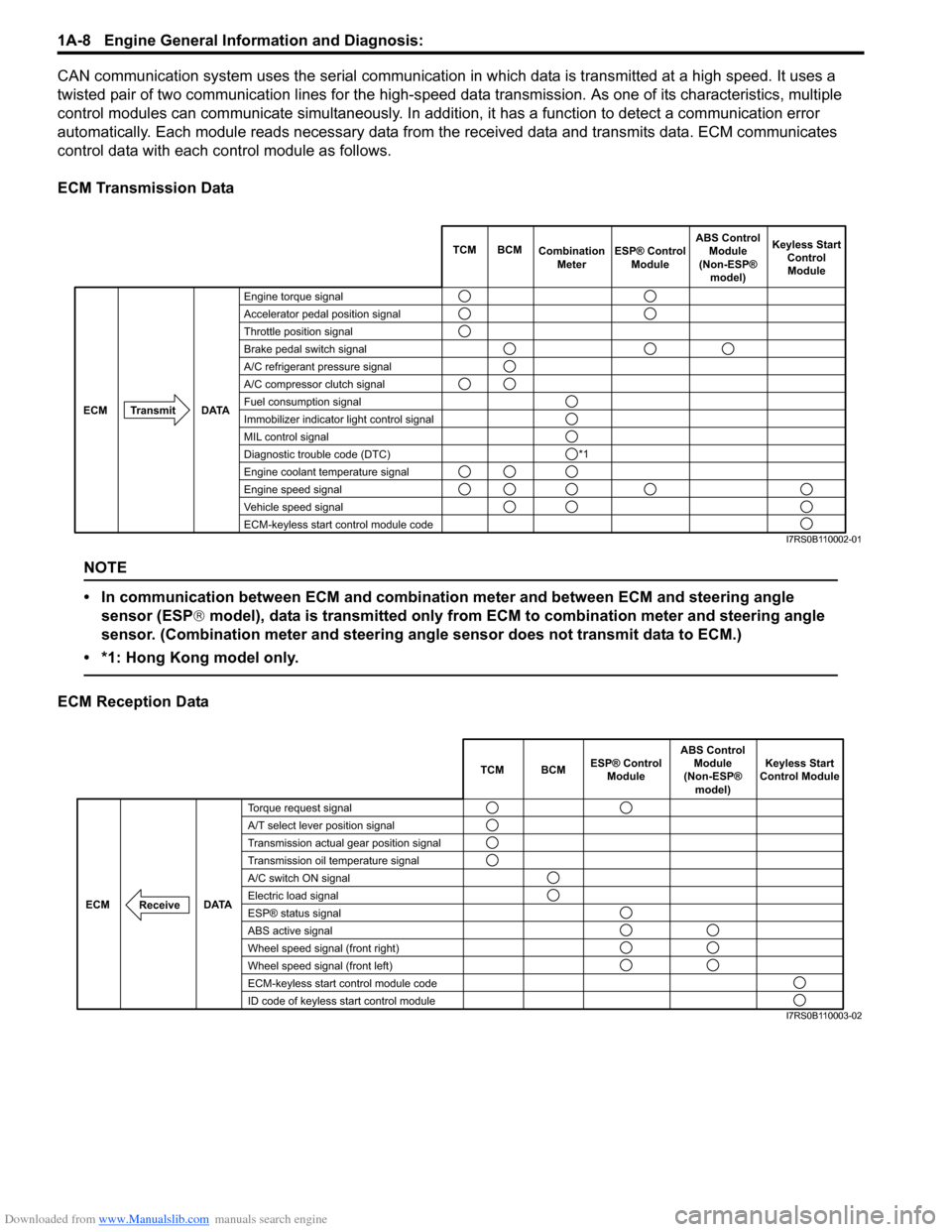
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
CAN communication system uses the serial communication in which data is transmitted at a high speed. It uses a
twisted pair of two communication lines for the high-speed da ta transmission. As one of its characteristics, multiple
control modules can communicate simultaneously. In addition, it has a function to detect a communication error
automatically. Each module reads necessary data from the received data and transmits data. ECM communicates
control data with each control module as follows.
ECM Transmission Data
NOTE
• In communication between ECM and combination meter and between ECM and steering angle sensor (ESP ® model), data is transmitted only from ECM to combination meter and steering angle
sensor. (Combination meter and steering angle sensor does not transmit data to ECM.)
• *1: Hong Kong model only.
ECM Reception Data
Engine torque signal
Accelerator pedal position signal
Throttle position signal
Brake pedal switch signal
A/C refrigerant pressure signal
A/C compressor clutch signal
Fuel consumption signal
Immobilizer indicator light control signal
MIL control signal
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Engine coolant temperature signal
Engine speed signal
Vehicle speed signal
ECM-keyless start control module code TCM BCM
Combination
Meter Keyless Start
ControlModule
Transmit DATA
ECM
ESP® Control
Module ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
*1
I7RS0B110002-01
TCM BCM Keyless Start
Control Module
DATA
ECM
Torque request signal
A/T select lever position signal
Transmission actual gear position signal
Transmission oil temperature signal
A/C switch ON signal
Electric load signal
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ECM-keyless start control module code
ID code of keyless start control module
Receive
ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
ESP® Control
Module
I7RS0B110003-02
Page 61 of 1496
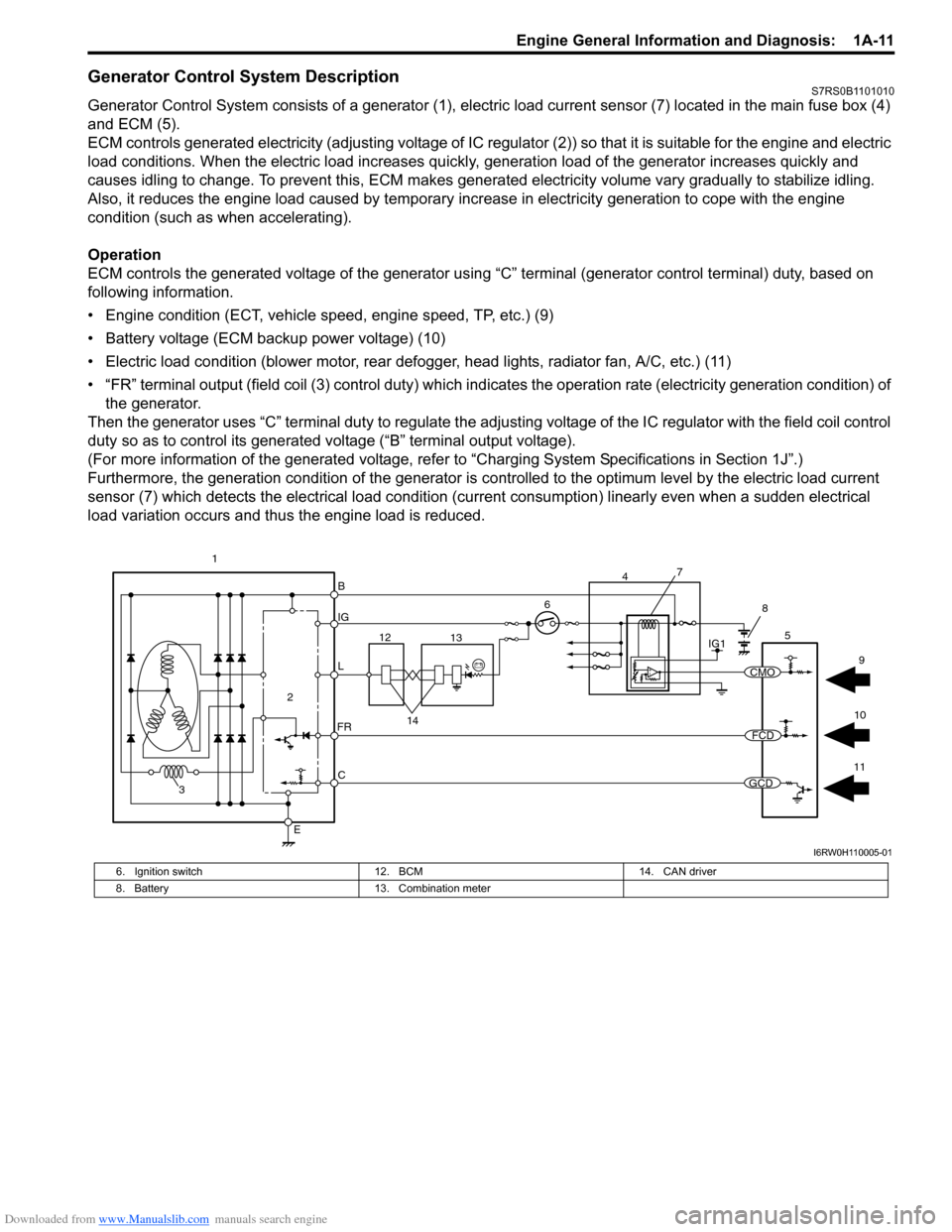
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-11
Generator Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101010
Generator Control System consists of a generator (1), electric load current sensor (7) located in the main fuse box (4)
and ECM (5).
ECM controls generated electricity (adjusting voltage of IC regulator (2)) so that it is suitable for the engine and electric
load conditions. When the electric load increases quickly, generation load of the generator increases quickly and
causes idling to change. To prevent this, ECM makes generated electricity volume vary gradually to stabilize idling.
Also, it reduces the engine load caused by temporary incr ease in electricity generation to cope with the engine
condition (such as when accelerating).
Operation
ECM controls the generated voltage of the generator using “C” terminal (generator control terminal) duty, based on
following information.
• Engine condition (ECT, vehicle speed, engine speed, TP, etc.) (9)
• Battery voltage (ECM backup power voltage) (10)
• Electric load condition (blower motor, rear defogger, head lights, radiator fan, A/C, etc.) (11)
• “FR” terminal output (field coil (3) cont rol duty) which indicates the operation rate (electricity generation condition) of
the generator.
Then the generator uses “C” terminal duty to regulate the adju sting voltage of the IC regulator with the field coil control
duty so as to control its generated voltage (“B” terminal output voltage).
(For more information of the generated voltage, refer to “Charging System Specifications in Section 1J”.)
Furthermore, the generation condition of the generator is co ntrolled to the optimum level by the electric load current
sensor (7) which detects the electrical load condition (cur rent consumption) linearly even when a sudden electrical
load variation occurs and thus the engine load is reduced.
B
IG
L
C
E
6
2
3
FR
5
12 13
14
1IG1
7
4
8
11
10 9
CMO
FCD
GCD
I6RW0H110005-01
6. Ignition switch
12. BCM 14. CAN driver
8. Battery 13. Combination meter
Page 63 of 1496
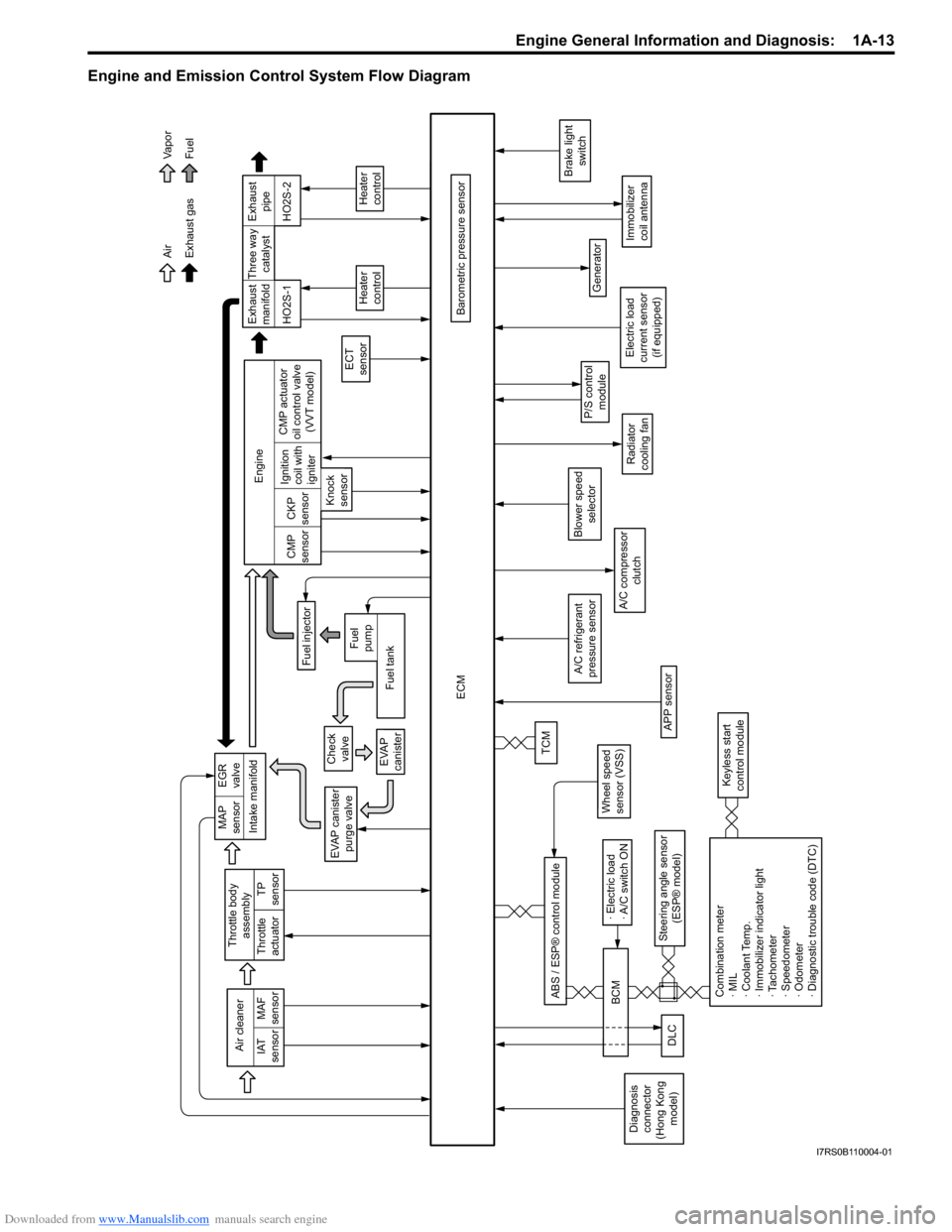
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-13
Engine and Emission Control System Flow Diagram
Intake manifold
Exhaust gas AirFuel
Va p o r
EVAP canister purge valve
ECM
Barometric pressure sensor
A/C compressor clutch
Generator
Immobilizer
coil antenna
P/S controlmodule
Brake light switch
Air cleaner
IAT
sensor MAF
sensor
A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor
TP
sensor
Throttle body
assembly
Throttle
actuator
Wheel speed
sensor (VSS)
Steering angle sensor (ESP® model)
ABS / ESP® control module
Blower speed
selector
MAP
sensor EGR
valve
Check valve
EVAP
canisterTCM
Exhaust
manifold Exhaust
pipe
Fuel injector
ECT
sensor
Heater
control
HO2S-1 HO2S-2
Engine
CMP
sensor CKP
sensor
Knock
sensor Ignition
coil with
igniter
Fuel tank
Fuel
pump CMP actuator
oil control valve (VVT model) Three way
catalyst
Heater
control
Radiator
cooling fan
Combination meter
· MIL
· Coolant Temp.
· Immobilizer indicator light
· Tachometer
· Speedometer
· Odometer
· Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Keyless start
control module
DLC
· Electric load
· A/C switch ON
BCM
Diagnosis
connector
(Hong Kong model) Electric load
current sensor (if equipped)
APP sensor
I7RS0B110004-01
Page 67 of 1496
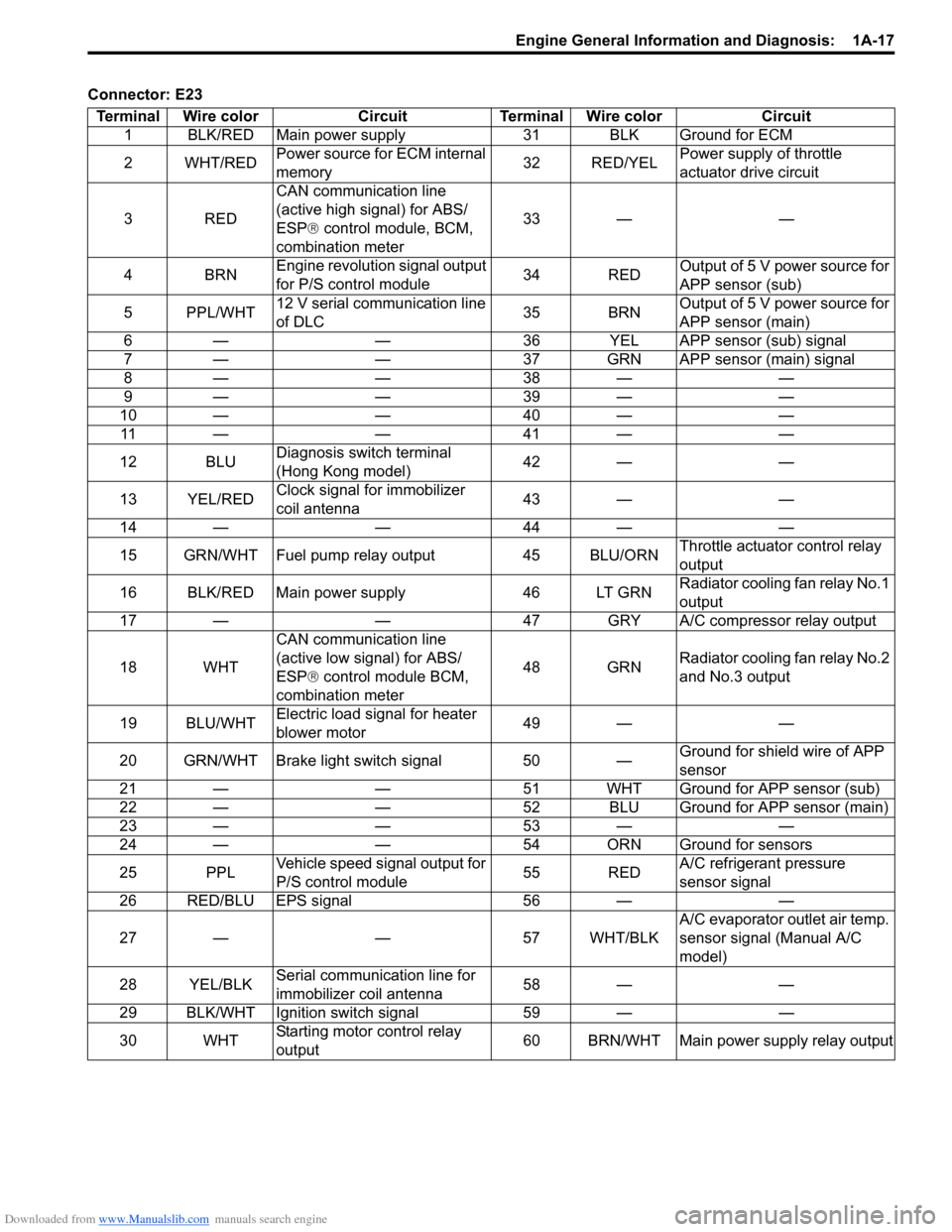
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-17
Connector: E23Terminal Wire color Circuit Terminal Wire color Circuit 1 BLK/RED Main power supply 31 BLK Ground for ECM
2WHT/RED Power source for ECM internal
memory 32 RED/YELPower supply of throttle
actuator drive circuit
3RED CAN communication line
(active high signal) for ABS/
ESP®
control module, BCM,
combination meter 33 — —
4BRN Engine revolution signal output
for P/S control module 34 REDOutput of 5 V power source for
APP sensor (sub)
5 PPL/WHT 12 V serial communication line
of DLC 35 BRNOutput of 5 V power source for
APP sensor (main)
6 — — 36 YEL APP sensor (sub) signal
7 — — 37 GRN APP sensor (main) signal
8— — 38— —
9— — 39— —
10——40—— 11——41——
12 BLU Diagnosis switch terminal
(Hong Kong model) 42 — —
13 YEL/RED Clock signal for immobilizer
coil antenna 43 — —
14——44——
15 GRN/WHT Fuel pump relay output 45 BLU/ORN Throttle actuator control relay
output
16 BLK/RED Main power supply 46 LT GRN Radiator cooling fan relay No.1
output
17 — — 47 GRY A/C compressor relay output
18 WHT CAN communication line
(active low signal) for ABS/
ESP®
control module BCM,
combination meter 48 GRN
Radiator cooling fan relay No.2
and No.3 output
19 BLU/WHT Electric load signal for heater
blower motor 49 — —
20 GRN/WHT Brake light switch signal 50 — Ground for shield wire of APP
sensor
21 — — 51 WHT Ground for APP sensor (sub)
22 — — 52 BLU Ground for APP sensor (main)
23——53——
24 — — 54 ORN Ground for sensors
25 PPL Vehicle speed signal output for
P/S control module 55 REDA/C refrigerant pressure
sensor signal
26 RED/BLU EPS signal 56 — —
27 — — 57 WHT/BLK A/C evaporator outlet air temp.
sensor signal (Manual A/C
model)
28 YEL/BLK Serial communication line for
immobilizer coil antenna 58 — —
29 BLK/WHT Ignition switch signal 59 — —
30 WHT Starting motor control relay
output 60 BRN/WHT Main power supply relay output
Page 70 of 1496
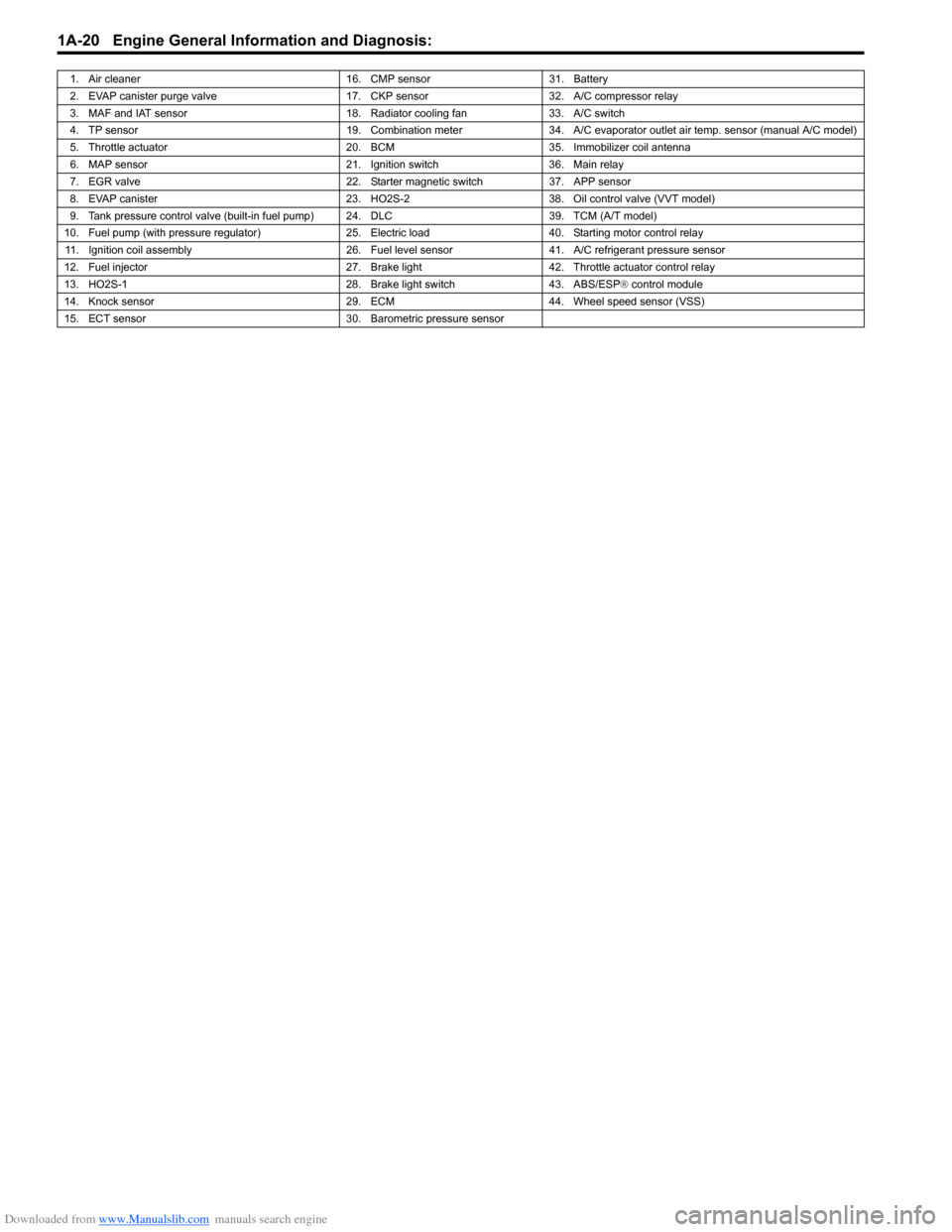
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-20 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
1. Air cleaner16. CMP sensor31. Battery
2. EVAP canister purge valve 17. CKP sensor32. A/C compressor relay
3. MAF and IAT sensor 18. Radiator cooling fan33. A/C switch
4. TP sensor 19. Combination meter34. A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. Throttle actuator 20. BCM35.Immobilizer coil antenna
6. MAP sensor 21. Ignition switch36. Main relay
7. EGR valve 22. Starter magnetic switch37. APP sensor
8. EVAP canister 23. HO2S-238. Oil control valve (VVT model)
9. Tank pressure control valve (built-in fuel pump) 24. DLC 39. TCM (A/T model)
10. Fuel pump (with pressure regulator) 25. Electric load40. Starting motor control relay
11. Ignition coil assembly 26. Fuel level sensor41. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
12. Fuel injector 27. Brake light42. Throttle actuator control relay
13. HO2S-1 28. Brake light switch43. ABS/ESP® control module
14. Knock sensor 29. ECM44. Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
15. ECT sensor 30. Barometric pressure sensor
Page 71 of 1496
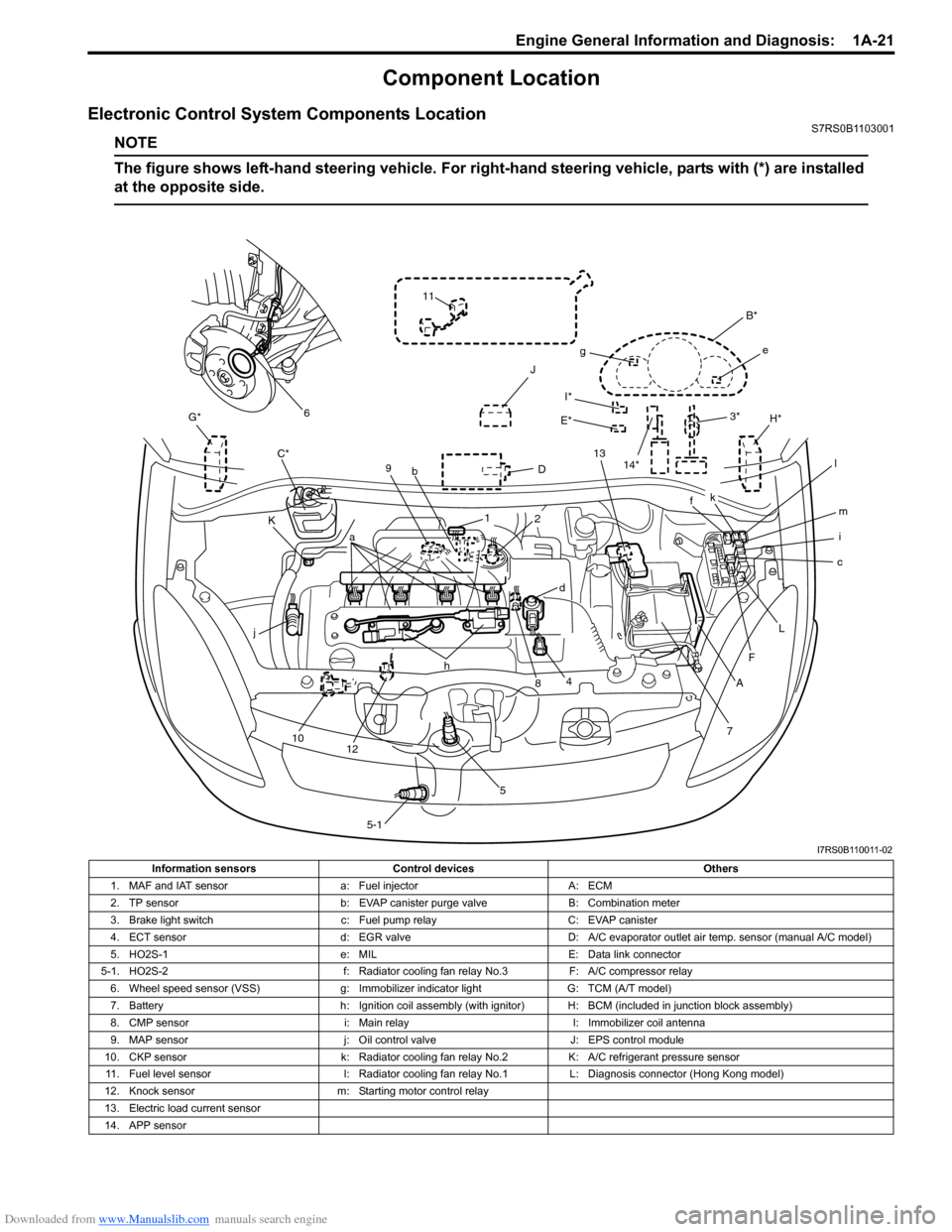
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-21
Component Location
Electronic Control System Components LocationS7RS0B1103001
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
I*
E*
G*
D
K H*
J
C*
7
A
F
c
L
i m
f
B*
e
g
k
l
13
3*
4
j
10 12 h
58
a
9
b
1
5-1
d
2
11
6
14*
I7RS0B110011-02
Information sensors Control devices Others
1. MAF and IAT sensor a: Fuel injectorA: ECM
2. TP sensor b: EVAP canister purge valve B: Combination meter
3. Brake light switch c: Fuel pump relayC: EVAP canister
4. ECT sensor d: EGR valveD: A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. HO2S-1 e: MILE: Data link connector
5-1. HO2S-2 f: Radiator cooling fan relay No.3F: A/C compressor relay
6. Wheel speed sensor (VSS) g: Immobilizer indicator lightG: TCM (A/T model)
7. Battery h: Ignition coil assembly (with ignitor) H: BCM (included in junction block assembly)
8. CMP sensor i: Main relayI: Immobilizer coil antenna
9. MAP sensor j: Oil control valveJ: EPS control module
10. CKP sensor k: Radiator cooling fan relay No.2K: A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
11. Fuel level sensor l: Radiator cooling fan relay No.1L: Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model)
12. Knock sensor m: Starting motor control relay
13. Electric load current sensor
14. APP sensor
Page 230 of 1496
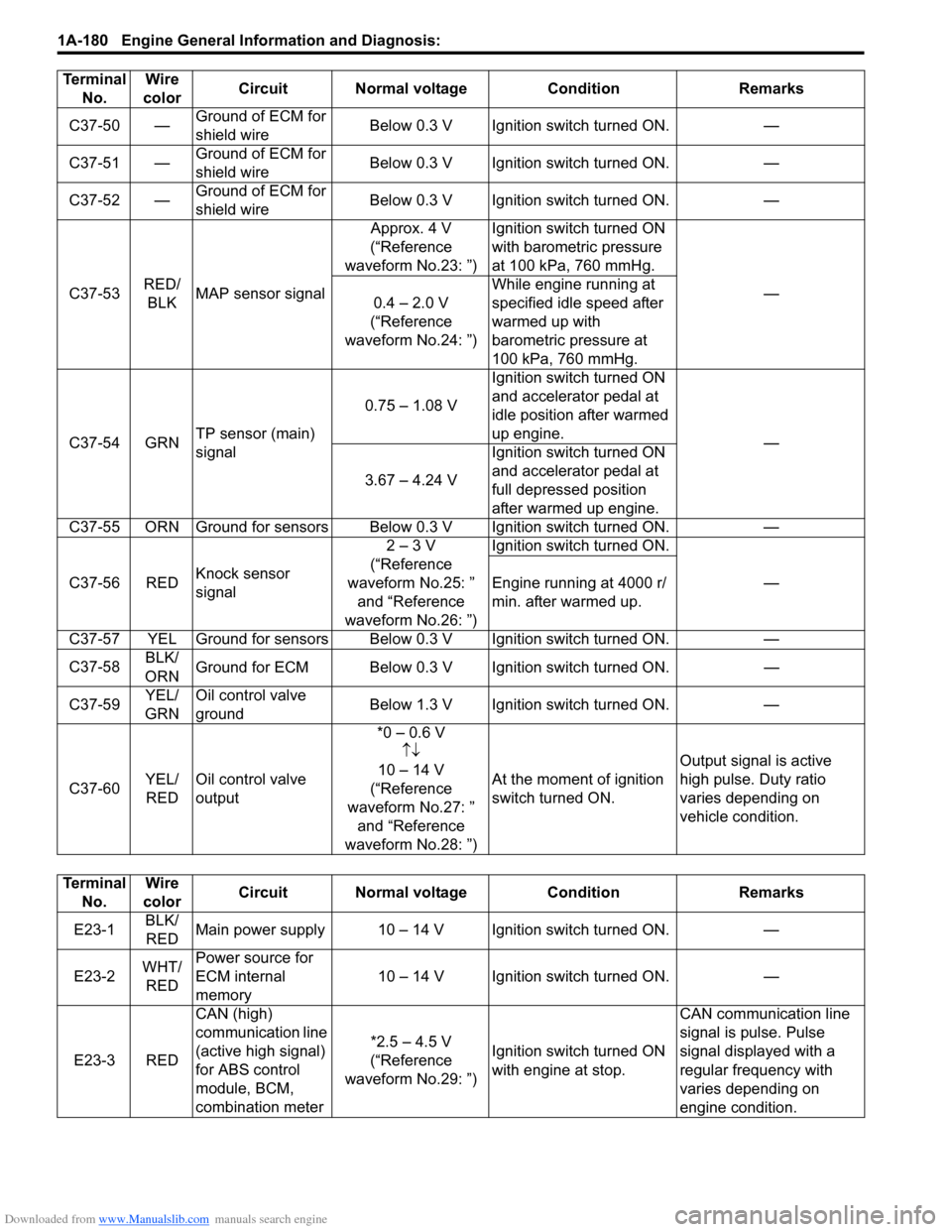
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-180 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
C37-50 —Ground of ECM for
shield wire Below 0.3 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
C37-51 — Ground of ECM for
shield wire Below 0.3 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
C37-52 — Ground of ECM for
shield wire Below 0.3 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
C37-53 RED/
BLK MAP sensor signal Approx. 4 V
(“Reference
waveform No.23: ”) Ignition switch turned ON
with barometric pressure
at 100 kPa, 760 mmHg.
—
0.4 – 2.0 V
(“Reference
waveform No.24: ”) While engine running at
specified idle speed after
warmed up with
barometric pressure at
100 kPa, 760 mmHg.
C37-54 GRN TP sensor (main)
signal 0.75 – 1.08 V
Ignition switch turned ON
and accelerator pedal at
idle position after warmed
up engine.
—
3.67 – 4.24 V Ignition switch turned ON
and accelerator pedal at
full depressed position
after warmed up engine.
C37-55 ORN Ground for sensors Below 0.3 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
C37-56 RED Knock sensor
signal 2 – 3 V
(“Reference
waveform No.25: ” and “Reference
waveform No.26: ”) Ignition switch turned ON.
—
Engine running at 4000 r/
min. after warmed up.
C37-57 YEL Ground for sensors Below 0.3 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
C37-58 BLK/
ORN Ground for ECM Below 0.3 V Ignition switch turned ON.
—
C37-59 YEL/
GRN Oil control valve
ground
Below 1.3 V Ignition switch turned ON.
—
C37-60 YEL/
RED Oil control valve
output *0 – 0.6 V
↑↓
10 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.27: ” and “Reference
waveform No.28: ”) At the moment of ignition
switch turned ON.
Output signal is active
high pulse. Duty ratio
varies depending on
vehicle condition.
Terminal
No. Wire
color Circuit Normal voltage
ConditionRemarks
Terminal
No. Wire
color Circuit Normal voltage Condition Remarks
E23-1 BLK/
RED Main power supply 10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-2 WHT/
RED Power source for
ECM internal
memory
10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-3 RED CAN (high)
communication line
(active high signal)
for ABS control
module, BCM,
combination meter *2.5 – 4.5 V
(“Reference
waveform No.29: ”) Ignition switch turned ON
with engine at stop. CAN communication line
signal is pulse. Pulse
signal displayed with a
regular frequency with
varies depending on
engine condition.
Page 231 of 1496
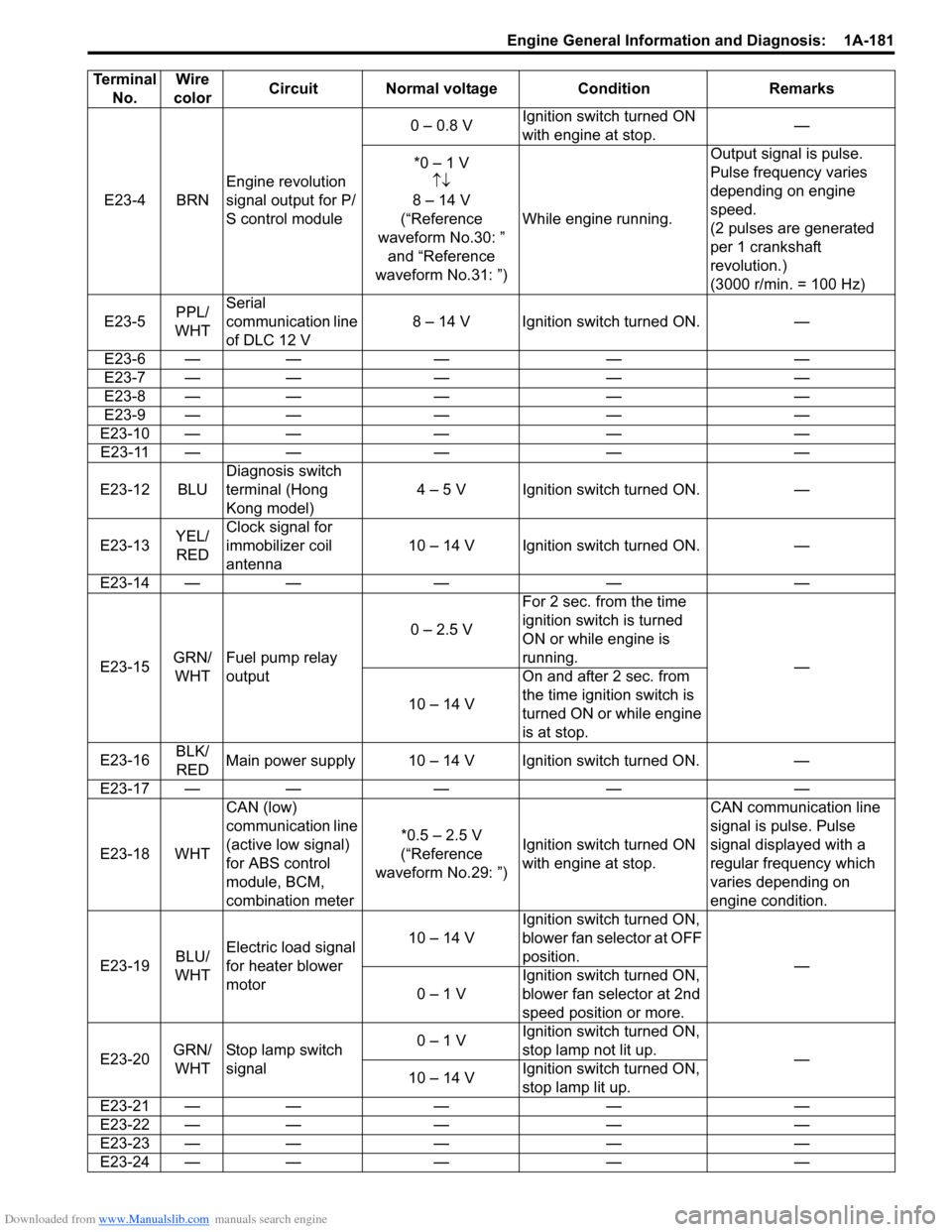
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-181
E23-4 BRNEngine revolution
signal output for P/
S control module 0 – 0.8 V
Ignition switch turned ON
with engine at stop. —
*0 – 1 V ↑↓
8 – 14 V
(“Reference
waveform No.30: ” and “Reference
waveform No.31: ”) While engine running. Output signal is pulse.
Pulse frequency varies
depending on engine
speed.
(2 pulses are generated
per 1 crankshaft
revolution.)
(3000 r/min. = 100 Hz)
E23-5 PPL/
WHT Serial
communication line
of DLC 12 V
8 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-6 — — — — —
E23-7 — — — — —
E23-8 — — — — —
E23-9 — — — — —
E23-10 — — — — — E23-11 — — — — —
E23-12 BLU Diagnosis switch
terminal (Hong
Kong model) 4 – 5 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-13 YEL/
RED Clock signal for
immobilizer coil
antenna
10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-14 — — — — —
E23-15 GRN/
WHT Fuel pump relay
output 0 – 2.5 V
For 2 sec. from the time
ignition switch is turned
ON or while engine is
running.
—
10 – 14 V On and after 2 sec. from
the time ignition switch is
turned ON or while engine
is at stop.
E23-16 BLK/
RED Main power supply 10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON. —
E23-17 — — — — —
E23-18 WHT CAN (low)
communication line
(active low signal)
for ABS control
module, BCM,
combination meter *0.5 – 2.5 V
(“Reference
waveform No.29: ”) Ignition switch turned ON
with engine at stop. CAN communication line
signal is pulse. Pulse
signal displayed with a
regular frequency which
varies depending on
engine condition.
E23-19 BLU/
WHT Electric load signal
for heater blower
motor 10 – 14 V
Ignition switch turned ON,
blower fan selector at OFF
position.
—
0 – 1 V Ignition switch turned ON,
blower fan selector at 2nd
speed position or more.
E23-20 GRN/
WHT Stop lamp switch
signal 0 – 1 V
Ignition switch turned ON,
stop lamp not lit up.
—
10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON,
stop lamp lit up.
E23-21 — — — — —
E23-22 — — — — —
E23-23 — — — — —
E23-24 — — — — —
Terminal
No. Wire
color Circuit Normal voltage Condition Remarks
Page 414 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.