checking oil SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 35 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-5
4) Screw new filter on oil filter stand by hand until the filter O-ring contacts mounting surface.
CAUTION!
To tighten oil filter prop erly, it is important to
accurately identify the position at which filter
O-ring first contacts mounting surface.
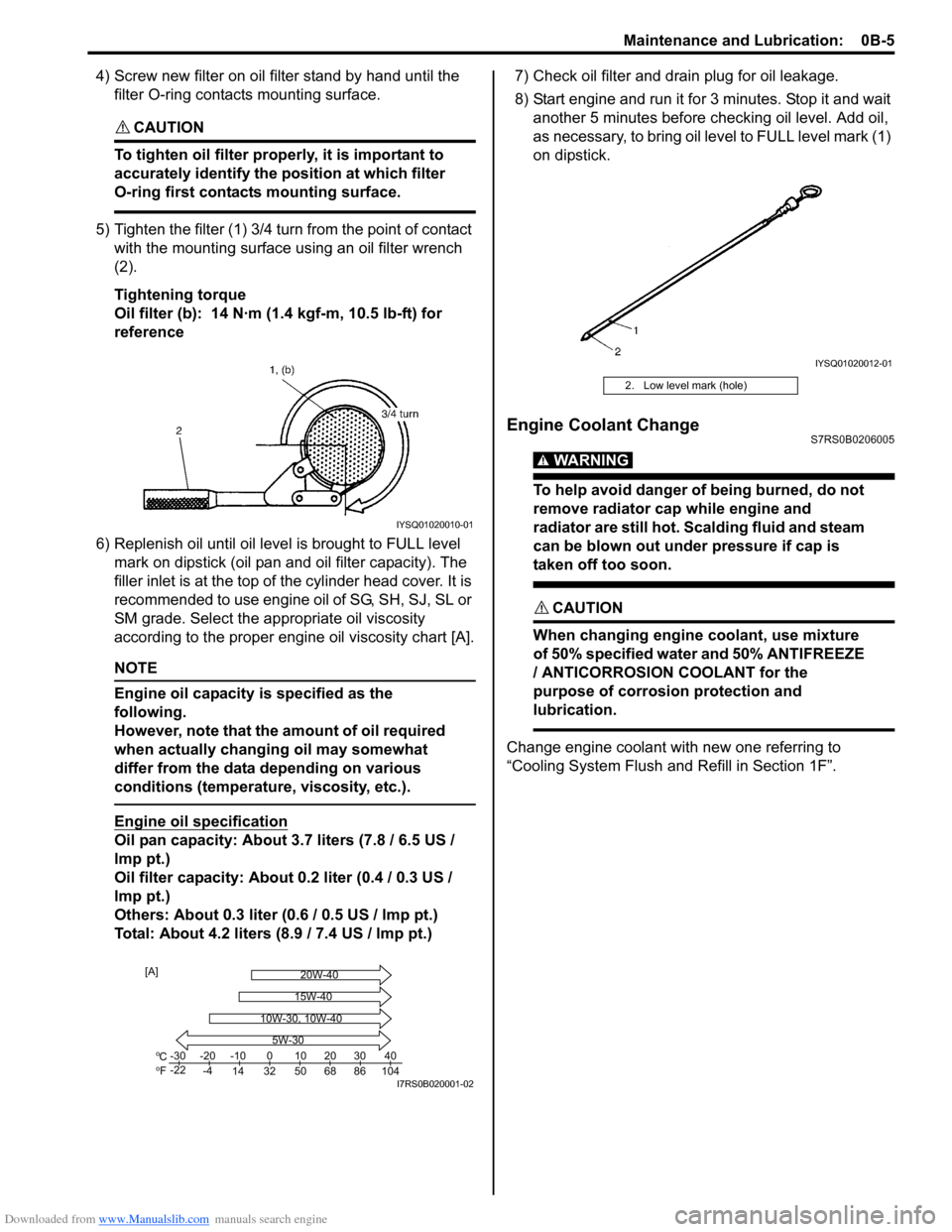
5) Tighten the filter (1) 3/4 tu rn from the point of contact
with the mounting surface using an oil filter wrench
(2).
Tightening torque
Oil filter (b): 14 N·m (1 .4 kgf-m, 10.5 lb-ft) for
reference
6) Replenish oil until oil leve l is brought to FULL level
mark on dipstick (oil pan and oil filter capacity). The
filler inlet is at the top of the cylinder head cover. It is
recommended to use engine oil of SG, SH, SJ, SL or
SM grade. Select the appropriate oil viscosity
according to the proper engine oil viscosity chart [A].
NOTE
Engine oil capacity is specified as the
following.
However, note that the amount of oil required
when actually changing oil may somewhat
differ from the data depending on various
conditions (temperature, viscosity, etc.).
Engine oil specification
Oil pan capacity: About 3.7 liters (7.8 / 6.5 US /
lmp pt.)
Oil filter capacity: About 0.2 liter (0.4 / 0.3 US /
lmp pt.)
Others: About 0.3 liter (0 .6 / 0.5 US / lmp pt.)
Total: About 4.2 liters (8.9 / 7.4 US / lmp pt.) 7) Check oil filter and drain plug for oil leakage.
8) Start engine and run it for 3 minutes. Stop it and wait
another 5 minutes before checking oil level. Add oil,
as necessary, to bring oil le vel to FULL level mark (1)
on dipstick.
Engine Coolant ChangeS7RS0B0206005
WARNING!
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam
can be blown out under pressure if cap is
taken off too soon.
CAUTION!
When changing engine coolant, use mixture
of 50% specified water and 50% ANTIFREEZE
/ ANTICORROSION COOLANT for the
purpose of corrosion protection and
lubrication.
Change engine coolant with new one referring to
“Cooling System Flush and Refill in Section 1F”.
IYSQ01020010-01
Co
Fo-30
-22 -20
-4 -10
14 32 50 68 86 104 010203040
5W-30
20W-40
15W-40
10W-30, 10W-40
[A]
I7RS0B020001-02
2. Low level mark (hole)
IYSQ01020012-01
Page 51 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-1
Engine
Engine General Information and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on Engine ServiceS7RS0B1100001
CAUTION!
The following information on engine service
should be noted carefully, as it is important in
preventing damage, and in contributing to
reliable engine performance.
• When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do
not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against
oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer,
resulting in damaged oil pick-up unit.
• It should be kept in mind , while working on engine,
that 12-volt electrical syste m is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals
can be grounded, ground cable of the battery should
be disconnected at battery.
• Any time the air cleaner, throttle body or intake manifold is removed, the intake opening should be
covered. This will protect against accidental entrance
of foreign material which could follow intake passage
into cylinder and cause extensive damage when
engine is started.
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System
S7RS0B1100005
There are two types of On -Board Diagnostic (OBD)
system, Euro OBD system and non-Euro-OBD system,
depending on the vehicle specification.
As the diagnosis function is different between these two
types, be sure to fully understand the OBD system
referring to “On-Board Diagnostic System Description”.
OBD System Summary Table
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B1100002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• Don’t disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable
from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine
or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information
in ECM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checke d by using SUZUKI scan
tool or OBD generic scan tool. Before using scan tool,
read its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to
have good understanding as to what functions are
available and how to use it.
For Euro OBD model it is indistinguishable which
module turns on MIL because not only ECM but also
TCM (A/T model) turns on MIL (For details of on-
board diagnostic system for A/T model, refer to “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description in Section 5A”).
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM (A/T model) for
DTC when MIL lights on.
When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– OBD generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM (A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instructi on in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected)
Euro OBD
model Non-Euro-OBD
model
Quantity of DTC
related to engine
control Approx. 80 Approx. 60
Freeze frame
data Available Not available
SUZUKI scan
tool Available Available
OBD generic
scan tool Available Not available
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 91 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-41
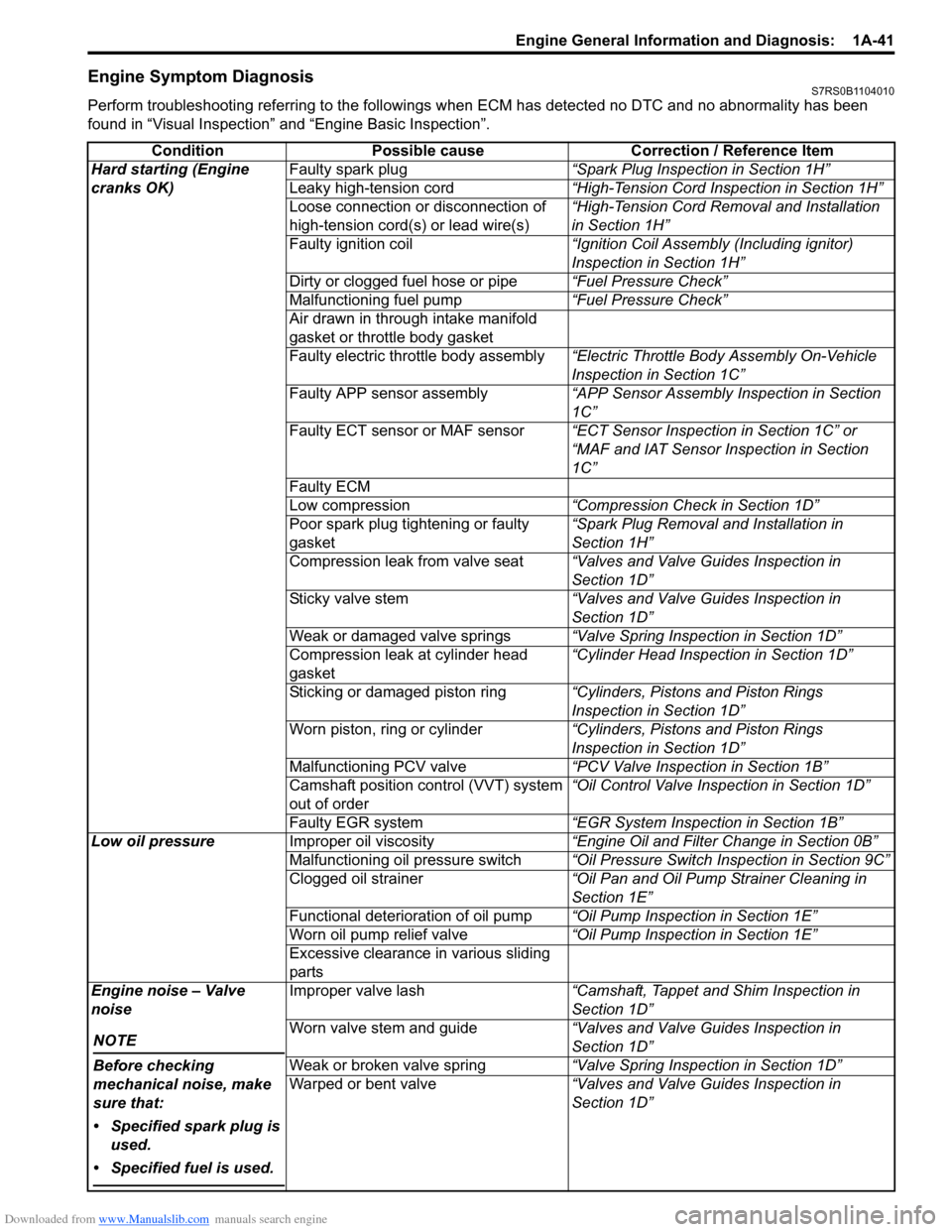
Engine Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1104010
Perform troubleshooting referring to the followings when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in “Visual Inspection” and “Engine Basic Inspection”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Hard starting (Engine
cranks OK) Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cord(s) or lead wire(s) “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump “Fuel Pressure Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor spark plug tightening or faulty
gasket “Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”
Compression leak from valve seat “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Sticky valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or damaged valve springs “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Compression leak at cylinder head
gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Sticking or damaged piston ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston, ring or cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Malfunctioning PCV valve “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Low oil pressure Improper oil viscosity “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch “Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
Clogged oil strainer “Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning in
Section 1E”
Functional deterioration of oil pump “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Worn oil pump relief valve “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Excessive clearance in various sliding
parts
Engine noise – Valve
noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Improper valve lash “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem and guide “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or broken valve spring “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Warped or bent valve “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Page 92 of 1496
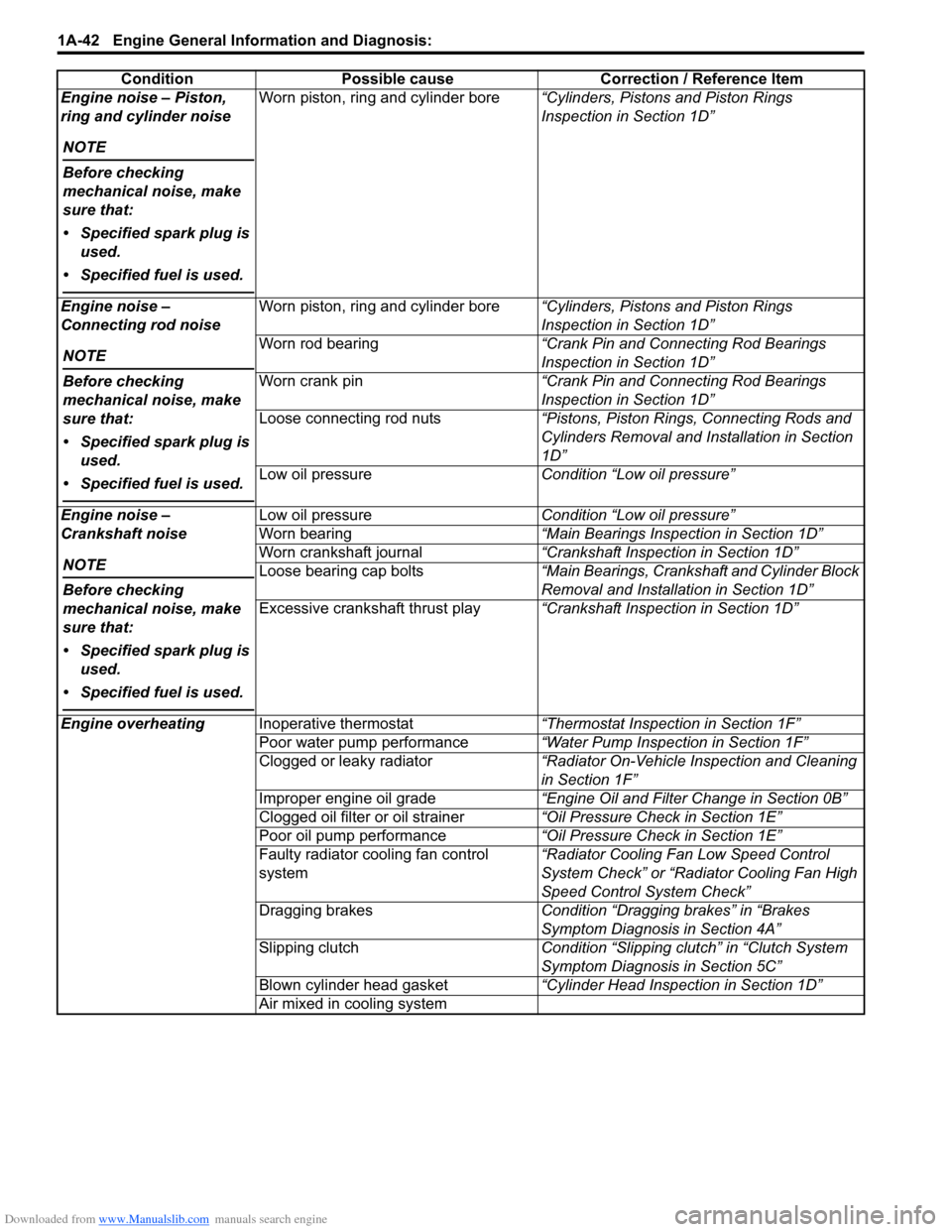
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-42 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine noise – Piston,
ring and cylinder noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine noise –
Connecting rod noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn rod bearing “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crank pin “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose connecting rod nuts “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation in Section
1D”
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Engine noise –
Crankshaft noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Worn bearing “Main Bearings Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crankshaft journal “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose bearing cap bolts “Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”
Excessive crankshaft thrust play “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine overheating Inoperative thermostat “Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Poor water pump performance “Water Pump Inspection in Section 1F”
Clogged or leaky radiator “Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1F”
Improper engine oil grade “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Poor oil pump performance “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Faulty radiator cooling fan control
system “Radiator Cooling Fan Low Speed Control
System Check” or “Rad
iator Cooling Fan High
Speed Control System Check”
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Blown cylinder head gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Air mixed in cooling system
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 290 of 1496
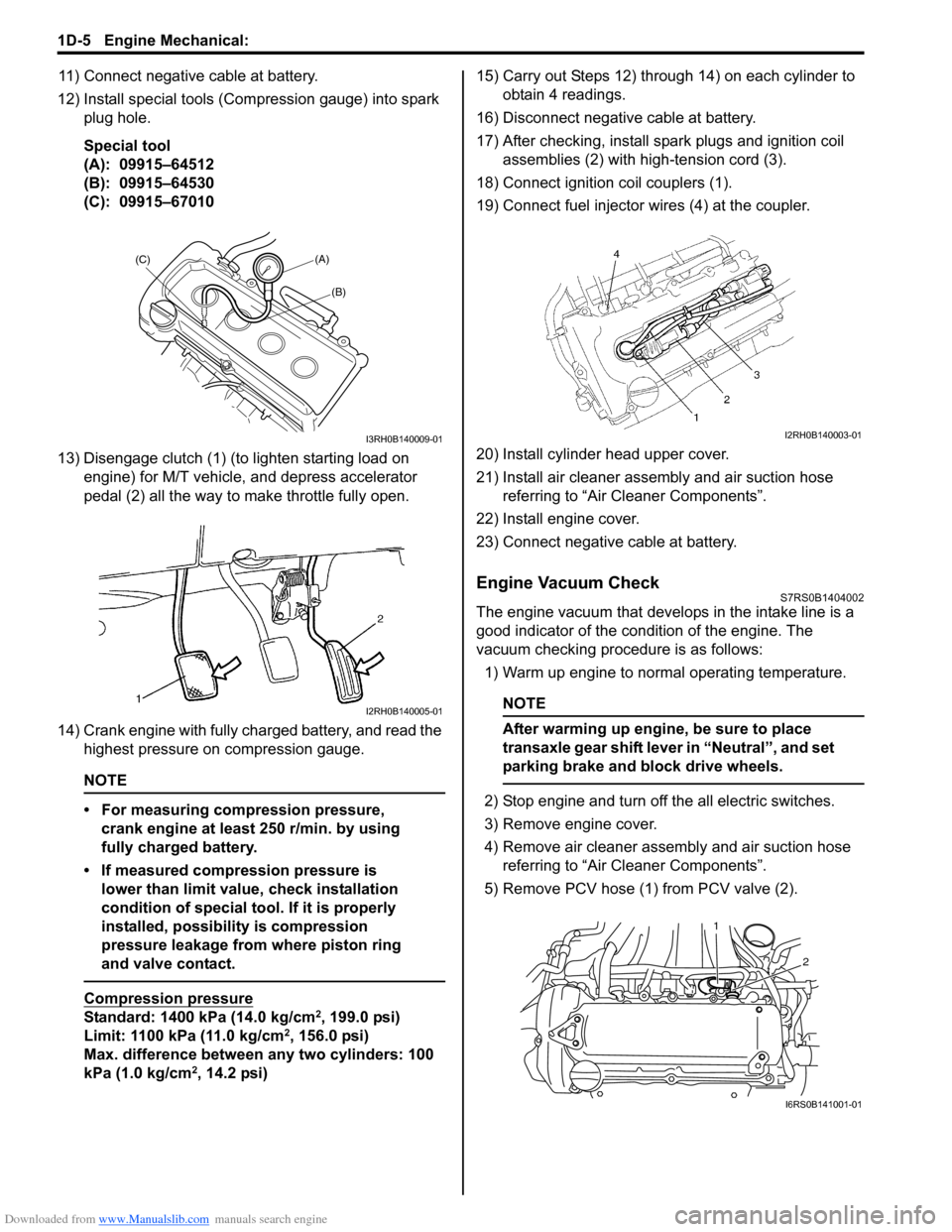
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 317 of 1496
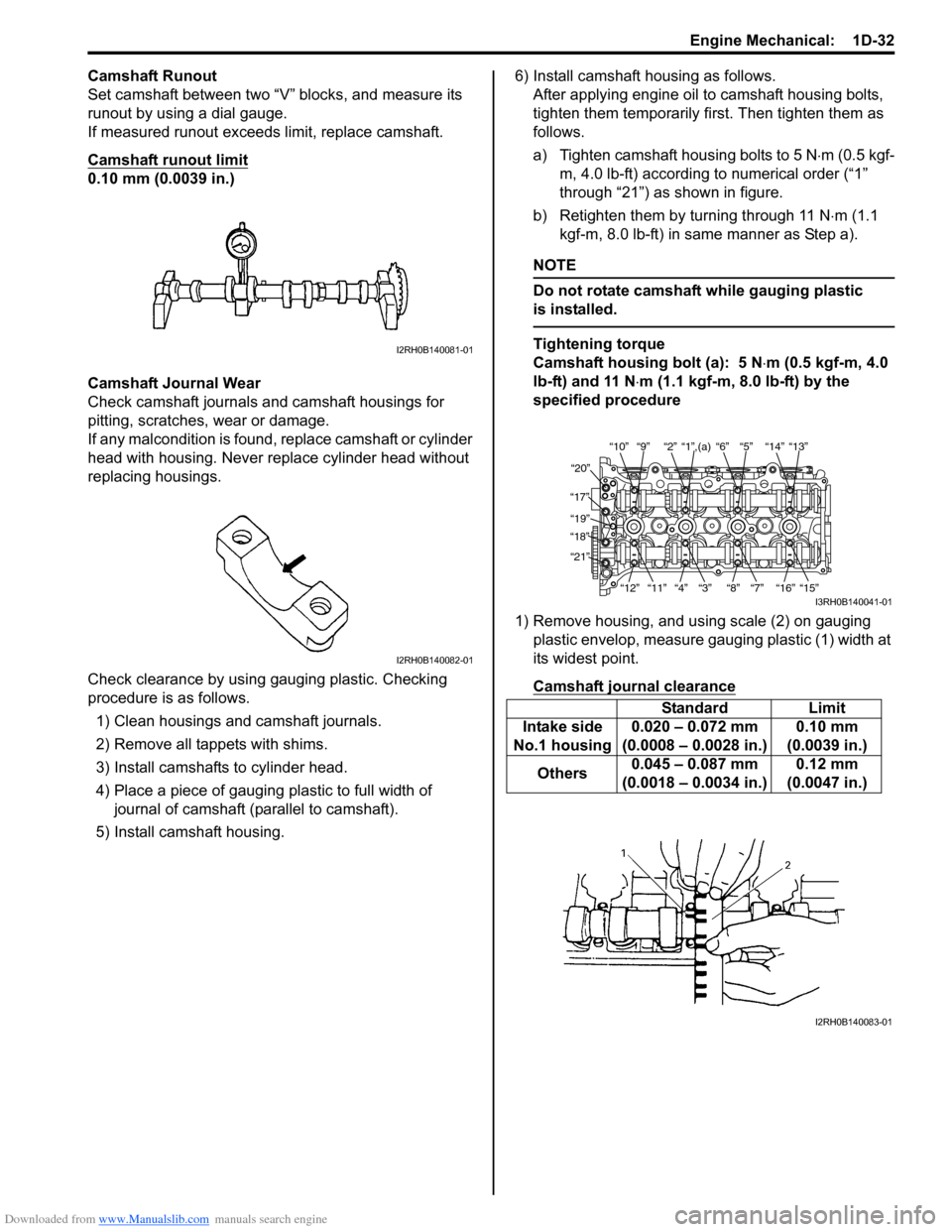
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-32
Camshaft Runout
Set camshaft between two “V” blocks, and measure its
runout by using a dial gauge.
If measured runout exceeds limit, replace camshaft.
Camshaft runout limit
0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Camshaft Journal Wear
Check camshaft journals and camshaft housings for
pitting, scratches, wear or damage.
If any malcondition is found, replace camshaft or cylinder
head with housing. Never re place cylinder head without
replacing housings.
Check clearance by using ga uging plastic. Checking
procedure is as follows.
1) Clean housings and camshaft journals.
2) Remove all tappets with shims.
3) Install camshafts to cylinder head.
4) Place a piece of gauging plastic to full width of
journal of camshaft (parallel to camshaft).
5) Install camshaft housing. 6) Install camshaft housing as follows.
After applying engine oil to camshaft housing bolts,
tighten them temporarily first. Then tighten them as
follows.
a) Tighten camshaft housing bolts to 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-
m, 4.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order (“1”
through “21”) as shown in figure.
b) Retighten them by turning through 11 N ⋅m (1.1
kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) in same manner as Step a).
NOTE
Do not rotate camshaft while gauging plastic
is installed.
Tightening torque
Camshaft housing bolt (a): 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-m, 4.0
lb-ft) and 11 N ⋅m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) by the
specified procedure
1) Remove housing, and using scale (2) on gauging plastic envelop, measure gauging plastic (1) width at
its widest point.
Camshaft journal clearanceI2RH0B140081-01
I2RH0B140082-01
Standard Limit
Intake side
No.1 housing 0.020 – 0.072 mm
(0.0008 – 0.0028 in.) 0.10 mm
(0.0039 in.)
Others 0.045 – 0.087 mm
(0.0018 – 0.0034 in.) 0.12 mm
(0.0047 in.)
“10”“9” “2” “1”,(a) “6” “5” “14” “13”
“20”
“17” “19”
“18”
“21”
“12”“11”
“4” “3” “8” “7” “16” “15”
I3RH0B140041-01
I2RH0B140083-01
Page 330 of 1496
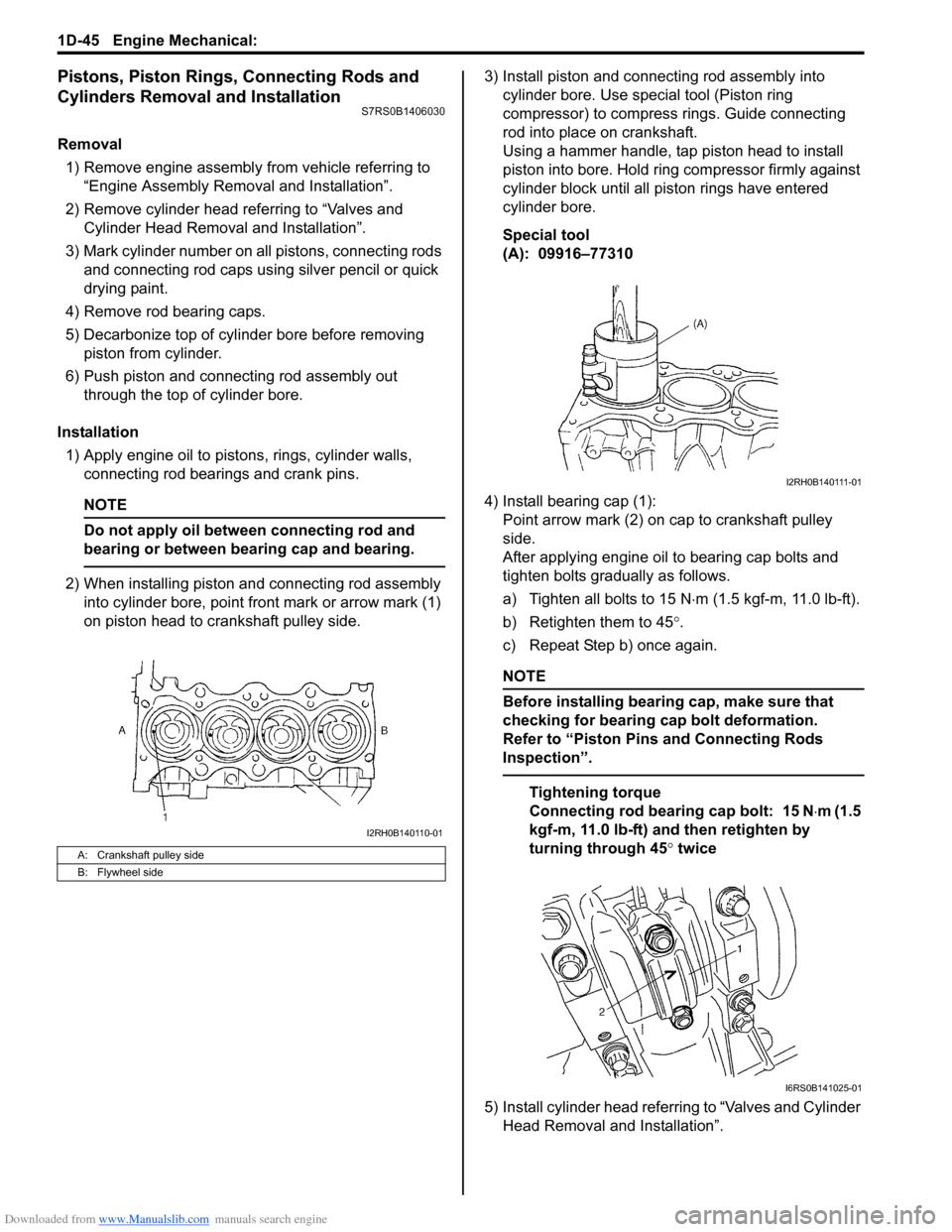
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-45 Engine Mechanical:
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1406030
Removal1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
3) Mark cylinder number on all pistons, connecting rods
and connecting rod caps using silver pencil or quick
drying paint.
4) Remove rod bearing caps.
5) Decarbonize top of cylinder bore before removing piston from cylinder.
6) Push piston and connecting rod assembly out through the top of cylinder bore.
Installation 1) Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls, connecting rod bearings and crank pins.
NOTE
Do not apply oil between connecting rod and
bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
2) When installing piston and connecting rod assembly into cylinder bore, point front mark or arrow mark (1)
on piston head to crankshaft pulley side. 3) Install piston and connecting rod assembly into
cylinder bore. Use special tool (Piston ring
compressor) to compress rings. Guide connecting
rod into place on crankshaft.
Using a hammer handle, tap piston head to install
piston into bore. Hold ring compressor firmly against
cylinder block until all piston rings have entered
cylinder bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–77310
4) Install bearing cap (1): Point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley
side.
After applying engine oil to bearing cap bolts and
tighten bolts gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all bolts to 15 N ⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft).
b) Retighten them to 45 °.
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
NOTE
Before installing bearing cap, make sure that
checking for bearing cap bolt deformation.
Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecting Rods
Inspection”.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt: 15 N ⋅m (1.5
kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 45 ° twice
5) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
A: Crankshaft pulley side
B: Flywheel side
I2RH0B140110-01
I2RH0B140111-01
I6RS0B141025-01
Page 333 of 1496
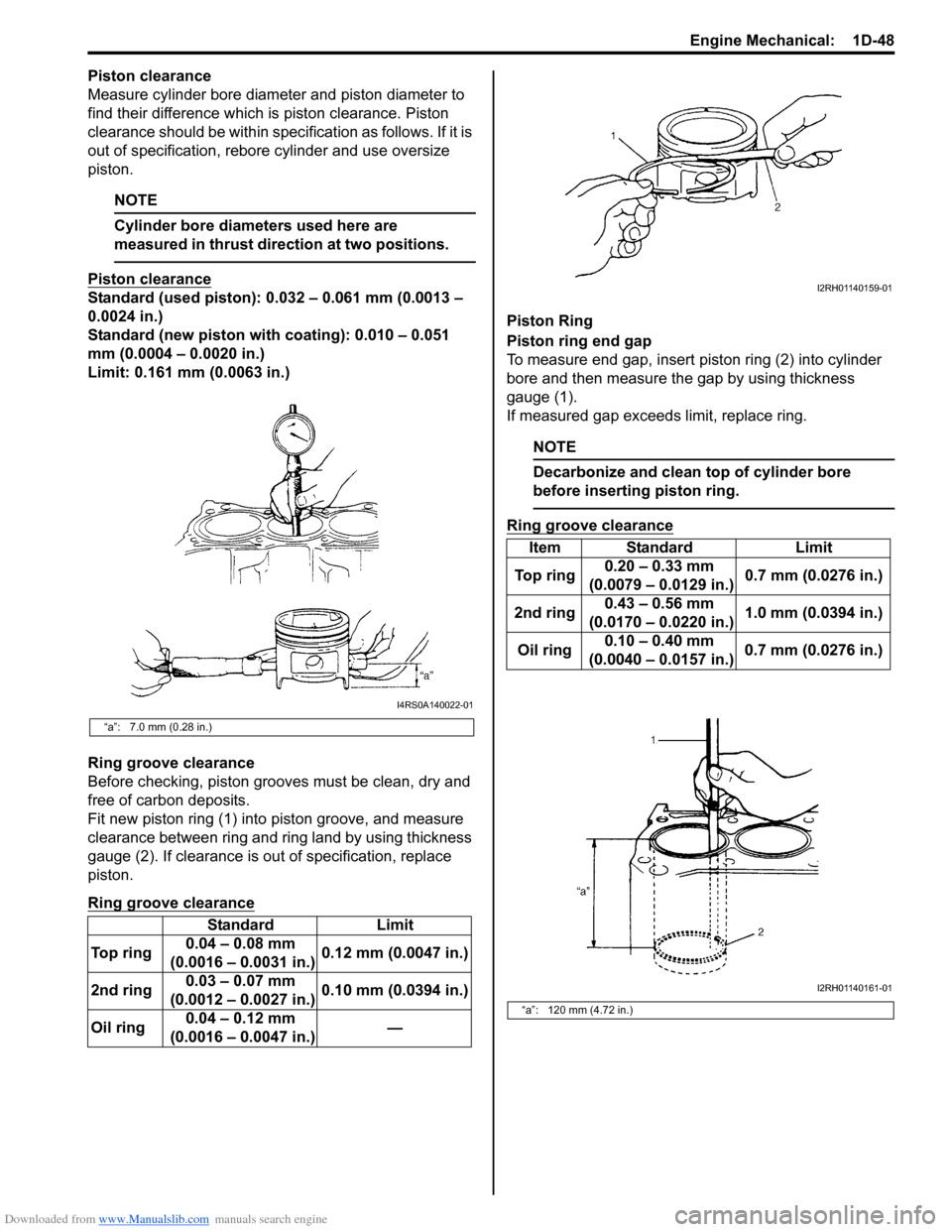
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-48
Piston clearance
Measure cylinder bore diameter and piston diameter to
find their difference which is piston clearance. Piston
clearance should be within spec ification as follows. If it is
out of specification, rebore cylinder and use oversize
piston.
NOTE
Cylinder bore diameters used here are
measured in thrust direction at two positions.
Piston clearance
Standard (used piston): 0.032 – 0.061 mm (0.0013 –
0.0024 in.)
Standard (new piston with coating): 0.010 – 0.051
mm (0.0004 – 0.0020 in.)
Limit: 0.161 mm (0.0063 in.)
Ring groove clearance
Before checking, piston grooves must be clean, dry and
free of carbon deposits.
Fit new piston ring (1) into piston groove, and measure
clearance between ring and ring land by using thickness
gauge (2). If clearance is ou t of specification, replace
piston.
Ring groove clearance
Piston Ring
Piston ring end gap
To measure end gap, insert piston ring (2) into cylinder
bore and then measure the gap by using thickness
gauge (1).
If measured gap exceeds limit, replace ring.
NOTE
Decarbonize and clean top of cylinder bore
before inserting piston ring.
Ring groove clearance
“a”: 7.0 mm (0.28 in.)
Standard Limit
Top ring 0.04 – 0.08 mm
(0.0016 – 0.0031 in.) 0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
2nd ring 0.03 – 0.07 mm
(0.0012 – 0.0027 in.) 0.10 mm (0.0394 in.)
Oil ring 0.04 – 0.12 mm
(0.0016 – 0.0047 in.) —
I4RS0A140022-01
Item Standard
Limit
To p r i n g 0.20 – 0.33 mm
(0.0079 – 0.0129 in.) 0.7 mm (0.0276 in.)
2nd ring 0.43 – 0.56 mm
(0.0170 – 0.0220 in.) 1.0 mm (0.0394 in.)
Oil ring 0.10 – 0.40 mm
(0.0040 – 0.0157 in.) 0.7 mm (0.0276 in.)
“a”: 120 mm (4.72 in.)
I2RH01140159-01
I2RH01140161-01
Page 336 of 1496
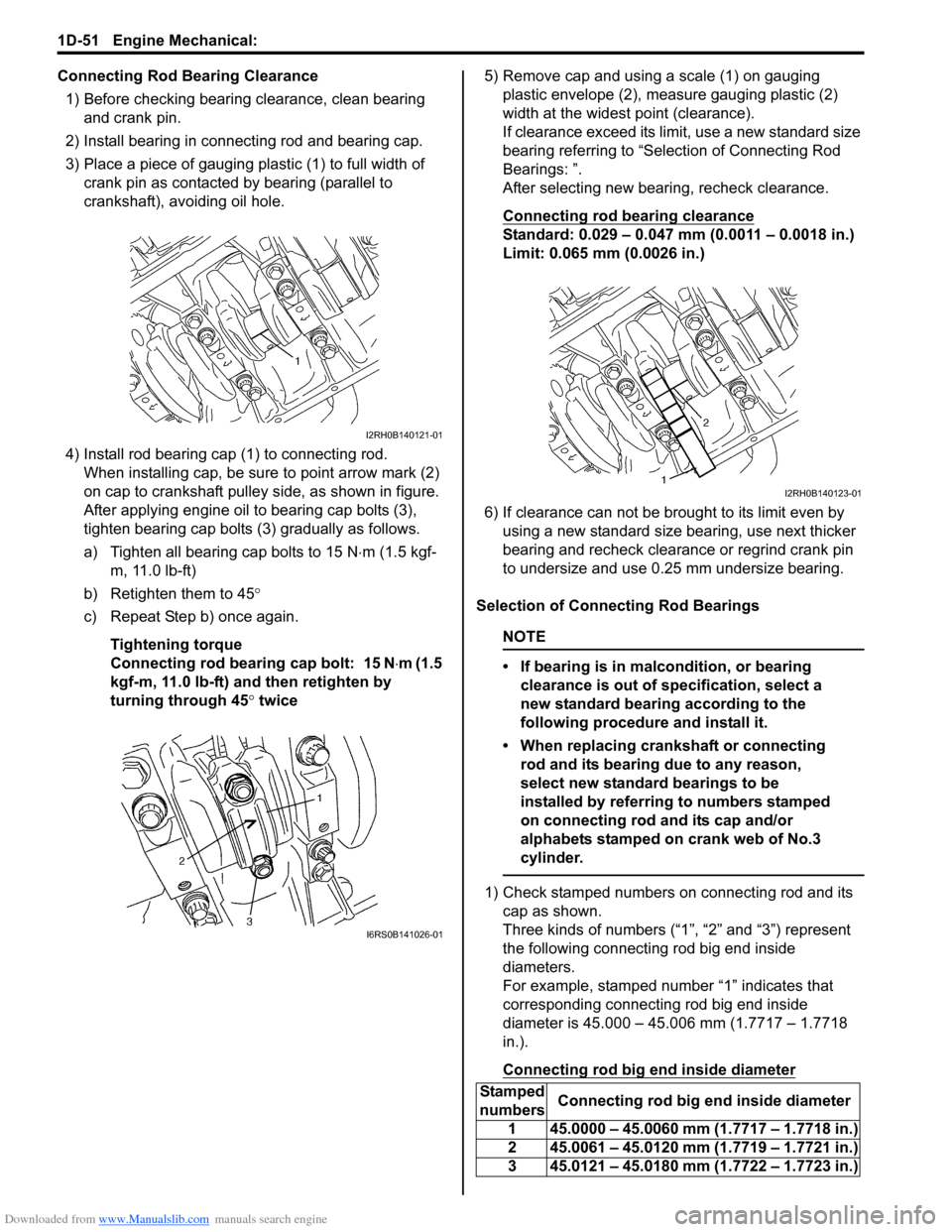
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-51 Engine Mechanical:
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance1) Before checking bearing clearance, clean bearing and crank pin.
2) Install bearing in connecting rod and bearing cap.
3) Place a piece of gauging plastic (1) to full width of crank pin as contacted by bearing (parallel to
crankshaft), avoiding oil hole.
4) Install rod bearing cap (1) to connecting rod. When installing cap, be sure to point arrow mark (2)
on cap to crankshaft pulley side, as shown in figure.
After applying engine oil to bearing cap bolts (3),
tighten bearing cap bolts (3) gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all bearing cap bolts to 15 N ⋅m (1.5 kgf-
m, 11.0 lb-ft)
b) Retighten them to 45°
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt: 15 N ⋅m (1.5
kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 45 ° twice 5) Remove cap and using a scale (1) on gauging
plastic envelope (2), measure gauging plastic (2)
width at the widest point (clearance).
If clearance exceed its limit, use a new standard size
bearing referring to “Selection of Connecting Rod
Bearings: ”.
After selecting new bearing, recheck clearance.
Connecting rod bearing clearance
Standard: 0.029 – 0.047 mm (0.0011 – 0.0018 in.)
Limit: 0.065 mm (0.0026 in.)
6) If clearance can not be brought to its limit even by using a new standard size bearing, use next thicker
bearing and recheck clearance or regrind crank pin
to undersize and use 0.25 mm undersize bearing.
Selection of Connecting Rod Bearings
NOTE
• If bearing is in malcondition, or bearing clearance is out of specification, select a
new standard bearing according to the
following procedure and install it.
• When replacing crankshaft or connecting rod and its bearing due to any reason,
select new standard bearings to be
installed by referring to numbers stamped
on connecting rod and its cap and/or
alphabets stamped on crank web of No.3
cylinder.
1) Check stamped numbers on connecting rod and its cap as shown.
Three kinds of numbers (“1”, “2” and “3”) represent
the following connecting rod big end inside
diameters.
For example, stamped number “1” indicates that
corresponding connecting rod big end inside
diameter is 45.000 – 45.006 mm (1.7717 – 1.7718
in.).
Connecting rod big end inside diameter
I2RH0B140121-01
I6RS0B141026-01
Stamped
numbers Connecting rod big end inside diameter
1 45.0000 – 45.0060 mm (1.7717 – 1.7718 in.)
2 45.0061 – 45.0120 mm (1.7719 – 1.7721 in.)
3 45.0121 – 45.0180 mm (1.7722 – 1.7723 in.)
I2RH0B140123-01