APP SENSOR SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 93 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-43
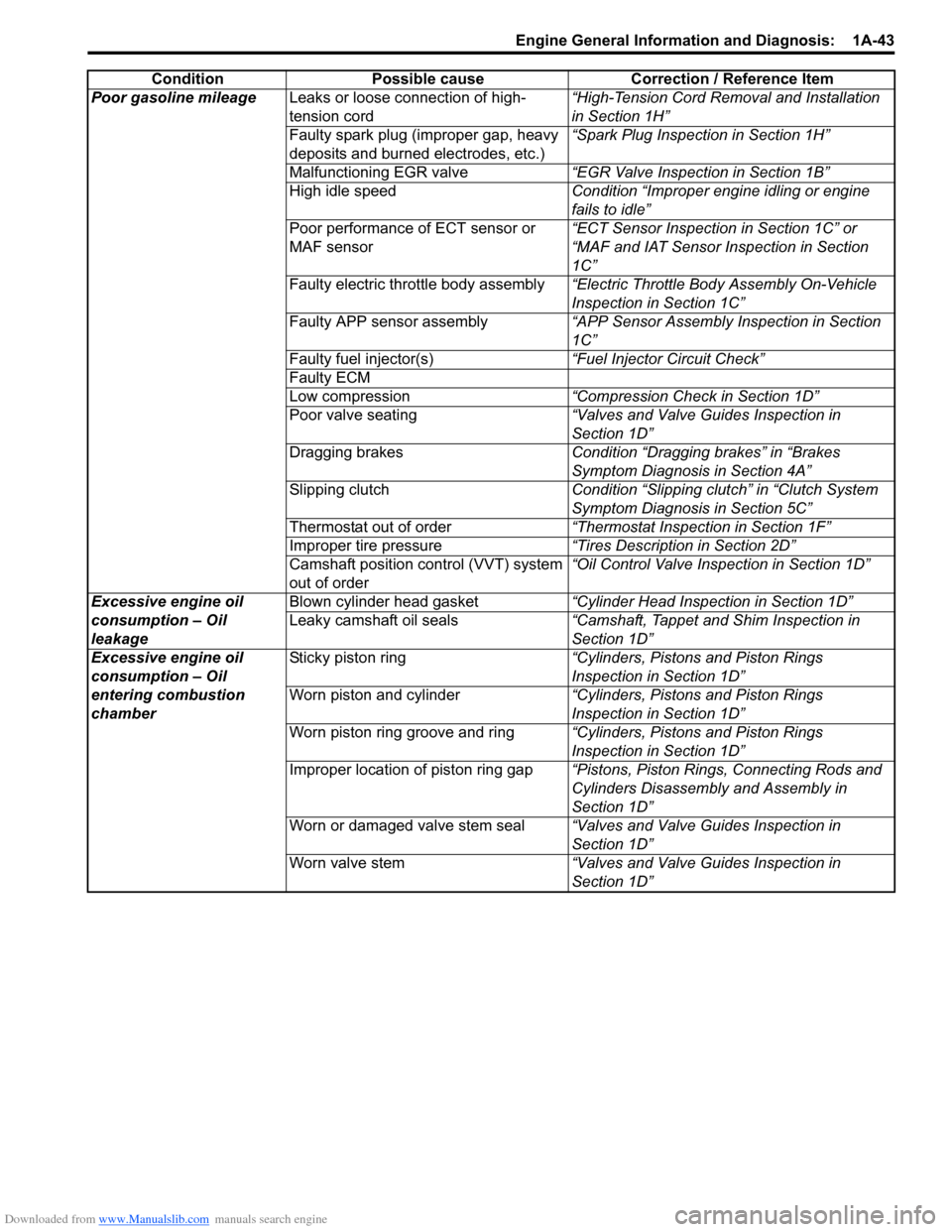
Poor gasoline mileageLeaks or loose connection of high-
tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy
deposits and burned electrodes, etc.) “Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
High idle speed Condition “Improper engine idling or engine
fails to idle”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor valve seating “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Thermostat out of order “Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Improper tire pressure “Tires Description in Section 2D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Excessive engine oil
consumption – Oil
leakage Blown cylinder head gasket
“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Leaky camshaft oil seals “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Excessive engine oil
consumption – Oil
entering combustion
chamber Sticky piston ring
“Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston and cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston ring groove and ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Improper location of piston ring gap “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly in
Section 1D”
Worn or damaged valve stem seal “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 94 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-44 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
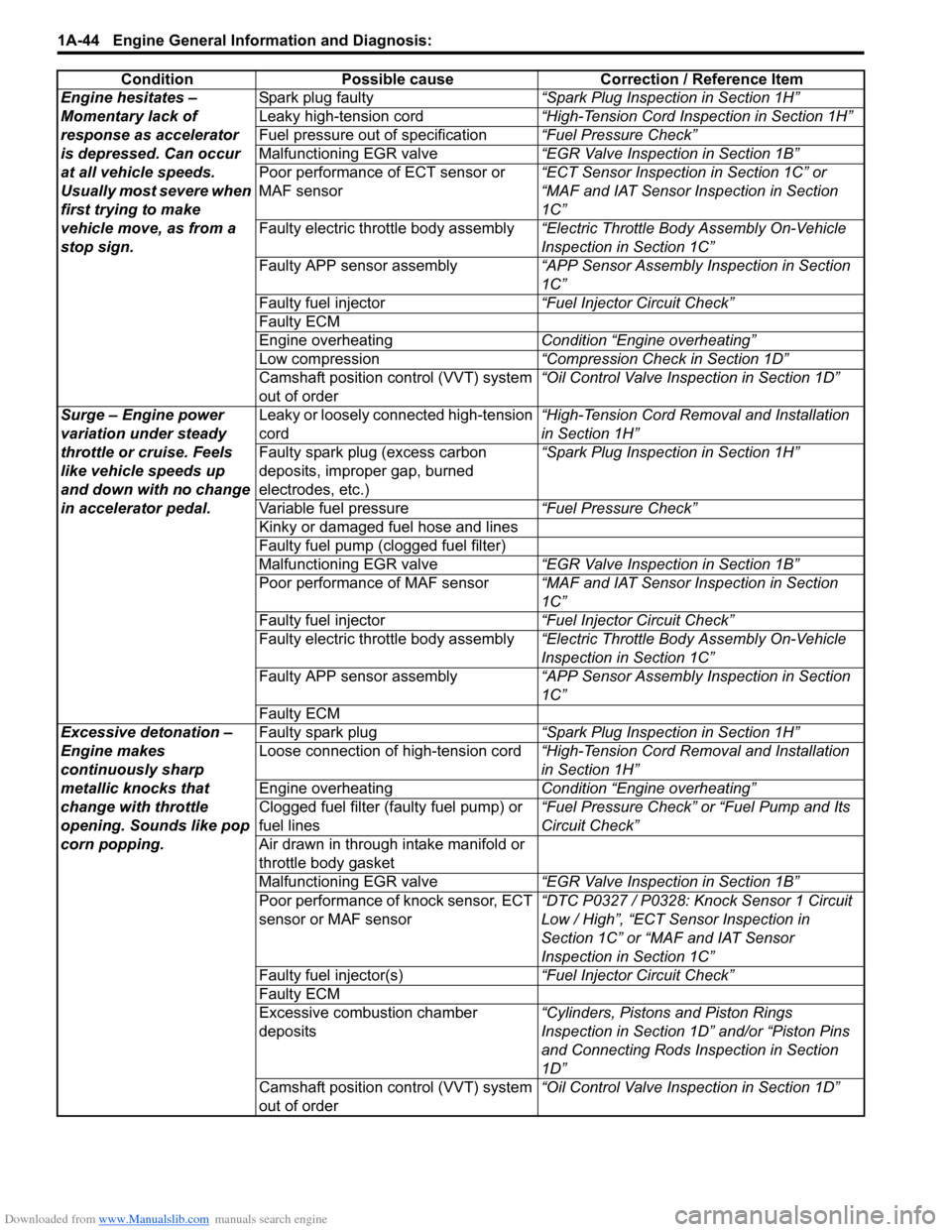
Engine hesitates –
Momentary lack of
response as accelerator
is depressed. Can occur
at all vehicle speeds.
Usually most severe when
first trying to make
vehicle move, as from a
stop sign.Spark plug faulty
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Fuel pressure out of specification “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Surge – Engine power
variation under steady
throttle or cruise. Feels
like vehicle speeds up
and down with no change
in accelerator pedal. Leaky or loosely connected high-tension
cord
“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (excess carbon
deposits, improper gap, burned
electrodes, etc.) “Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Variable fuel pressure “Fuel Pressure Check”
Kinky or damaged fuel hose and lines
Faulty fuel pump (clogged fuel filter)
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of MAF sensor “MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Excessive detonation –
Engine makes
continuously sharp
metallic knocks that
change with throttle
opening. Sounds like pop
corn popping. Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection of high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Clogged fuel filter (faulty fuel pump) or
fuel lines “Fuel Pressure Check” or “Fuel Pump and Its
Circuit Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold or
throttle body gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of knock sensor, ECT
sensor or MAF sensor “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High”, “ECT Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C” or “MAF and IAT Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Excessive combustion chamber
deposits “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D” and/or “Piston Pins
and Connecting Rods In
spection in Section
1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 95 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-45
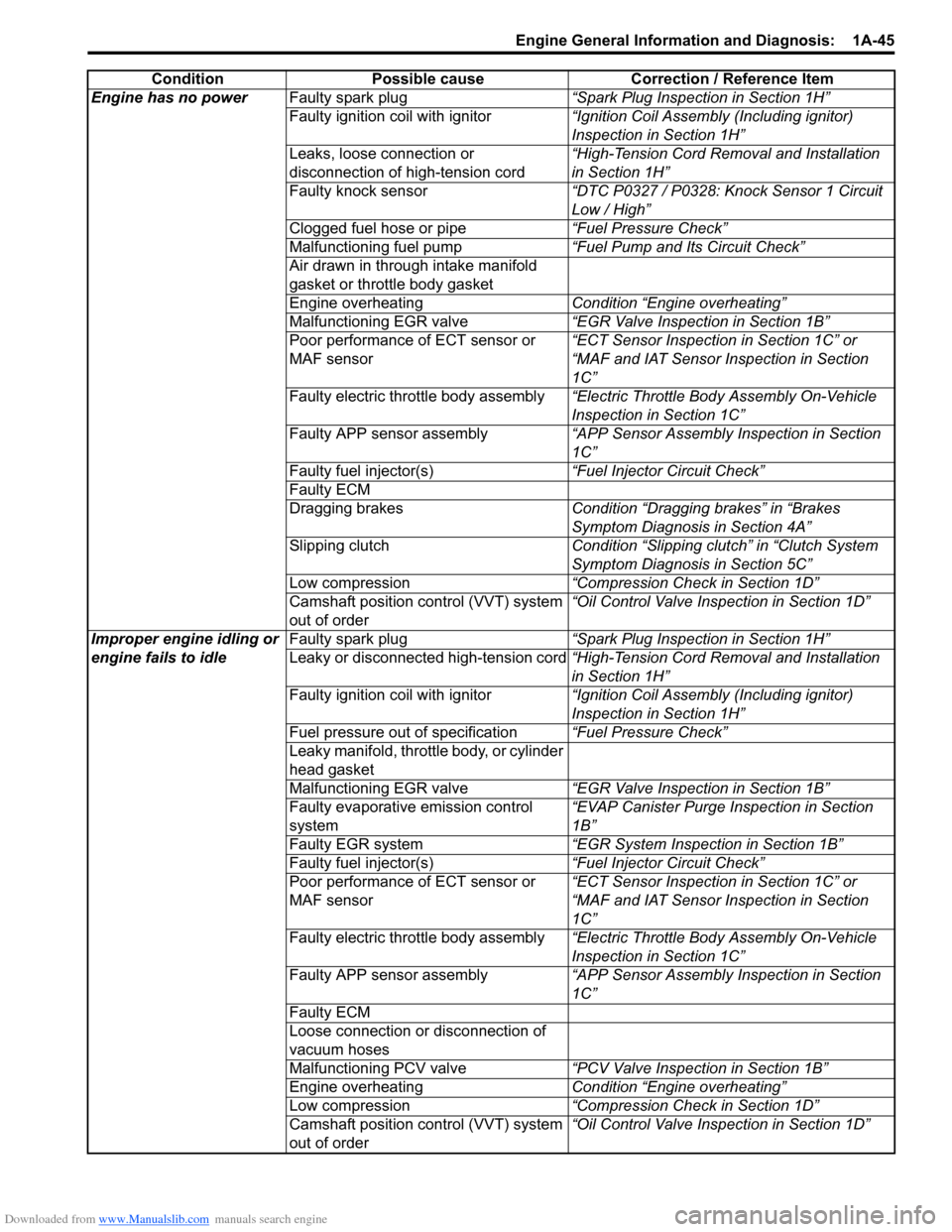
Engine has no powerFaulty spark plug “Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaks, loose connection or
disconnection of high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty knock sensor “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High”
Clogged fuel hose or pipe “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump “Fuel Pump and Its Circuit Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Improper engine idling or
engine fails to idle Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky or disconnected high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Fuel pressure out of specification “Fuel Pressure Check”
Leaky manifold, throttle body, or cylinder
head gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve “EGR Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Faulty evaporative emission control
system “EVAP Canister Purge Inspection in Section
1B”
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Faulty fuel injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Loose connection or disconnection of
vacuum hoses
Malfunctioning PCV valve “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Engine overheating Condition “Engine overheating”
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 96 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-46 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
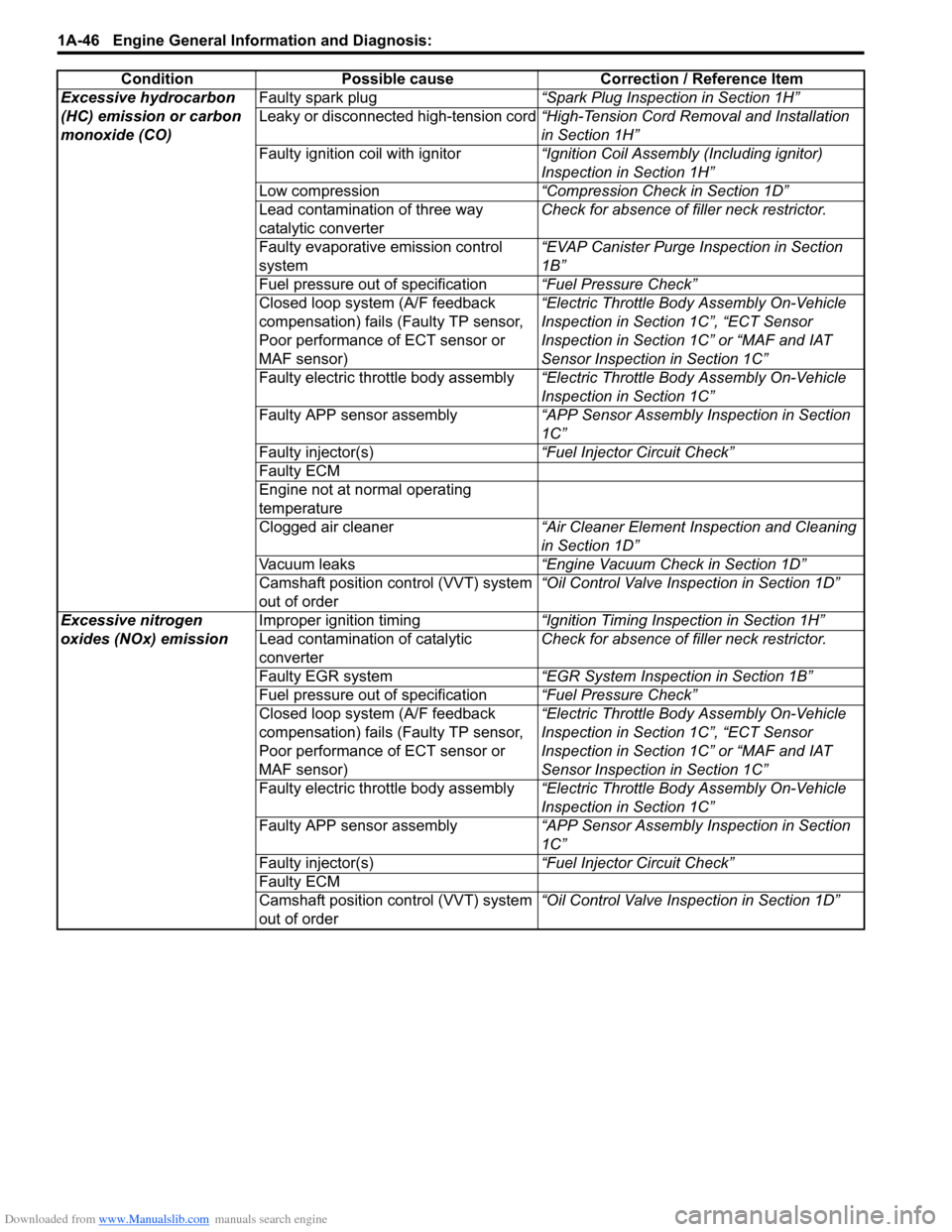
Excessive hydrocarbon
(HC) emission or carbon
monoxide (CO)Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky or disconnected high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Lead contamination of three way
catalytic converter Check for absence of f
iller neck restrictor.
Faulty evaporative emission control
system “EVAP Canister Purge Inspection in Section
1B”
Fuel pressure out of specification “Fuel Pressure Check”
Closed loop system (A/F feedback
compensation) fails (Faulty TP sensor,
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor) “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”, “ECT Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C” or “MAF and IAT
Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Engine not at normal operating
temperature
Clogged air cleaner “Air Cleaner Element Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1D”
Vacuum leaks “Engine Vacuum Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Excessive nitrogen
oxides (NOx) emission Improper ignition timing
“Ignition Timing Inspection in Section 1H”
Lead contamination of catalytic
converter Check for absence of f
iller neck restrictor.
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Fuel pressure out of specification “Fuel Pressure Check”
Closed loop system (A/F feedback
compensation) fails (Faulty TP sensor,
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor) “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”, “ECT Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C” or “MAF and IAT
Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty injector(s) “Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 109 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-59
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that the following conditions are satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 °F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) to 150 °C (302 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature. (ECT approx. 90 – 95 °C, 194 – 203 °F)
4) Drive vehicle with engine speed: more than 2500 rpm for 1 min.
5) Increase vehicle speed to 80 km/h (45 mile/h) at 5th gear or D range.
6) Release accelerator pedal to decrease vehicle speed to 40 km/h (25 mile/h).
7) Stop vehicle and run it idle for 1 min.
8) Check DTC and pending DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Visual inspection
Check MAF sensor and air intake system for:
• Objects which block measuring duct and resistor of MAF
sensor.
• Other air flow which does not pass the MAF sensor.
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 3.
Repair or replace.
3 MAF sensor and its circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Start engine and warm up to normal operation
temperature.
3) Check MAF value using scan tool. (Refer to “Scan Tool Data” for normal value.)
Is each value within specified range? Go to Step 11. Go to Step 4.
Page 115 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-65
DTC Confirmation Procedure
NOTE
Check to make sure that the following conditions are satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) to 150 °C (302 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool and warm up engine completely.
3) Increase engine speed up to 2000 rpm or more for 10 seconds.
4) Run engine at idle speed for 1 min.
5) Check DTC and pending DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 MAP sensor and its circuit check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch.
3) Check DTC.
Is there DTC P0107 or DTC P0108? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 3.
3 MAP sensor output signal check
1) Check MAP sensor acco rding to “MAP Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Faulty MAP sensor.
4 MAP sensor circuit check
1) Check MAP sensor circuit referring to Step 3 to 6 of
“DTC P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure / Barometric
Pressure Circuit Low Input” or Step 3 to 8 of “DTC
P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure / Barometric
Pressure Circuit High Input”.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 5.
Repair or replace.
5 Air intake system check
1) Check air intake system for clog or leak.
Is it in good condition? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Repair or replace.
Page 120 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-70 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
NOTE
Check to make sure that following conditions are satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature at engine start: less than 30 °C (86 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) to 150 °C (302 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch, clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature. (ECT approx. 90 – 95 °C, 194 – 203 °F)
4) Run engine at idle speed for 10 min. or more.
5) Check DTC and pending DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
Difference of maximum IAT minus minimum IAT is less than 0.3 °C
(32.5 °F) while ECT is over 70 °C (158 °F) after 10 min from cold
engine start (ECT is lower than 30 °C (86 °F) at engine start).
(2 driving cycle detection logic) • High resistance circuit
• MAF and IAT sensor
•ECM
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 IAT sensor and its circuit check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
3) Check intake air temp. displayed on scan tool.
Is –40
°C (–40 °F) or 119 °C (246 °F) indicated? Go to Step 3. Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.
Page 121 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-71
3Wire harness check
1) Disconnect MAF and IAT sensor connector (1) with
ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to MAF and IAT sensor connector (1) at “BLK/YEL” wire terminal.
3) If OK, then with ignition switch turned ON, measure voltage between “BLK/YEL” wire terminal of MAF and
IAT sensor connector and vehicle body ground.
Is measured voltage applied to “BLK/YEL” wire terminal
about 4 – 6 V? Go to Step 8. Go to Step 4.
4 ECM voltage check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Remove ECM from its br acket with ECM connectors
connected.
3) Check for proper connection of ECM connector at “C37- 25” terminal.
4) If OK, then turn ON igniti on switch, measure voltage
between “C37-25” terminal of ECM connector and
vehicle body ground.
Is voltage about 4 – 6 V at terminal? “BLK/YEL” wire is open
circuit.
If wire and connection
are OK, go to Step 5.
Go to Step 5.
5 Wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “BLK/YEL” wire terminal of MAF and IAT sensor connector and vehicle body
ground.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 6. “BLK/YEL” wire is
shorted to ground or
other circuit.
If wire is OK, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
6 Wire circuit check
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
2) Measure voltage between “BLK/YEL” wire terminal of
MAF and IAT sensor connector and vehicle body
ground.
Is voltage about 0 V? Go to Step 7. “BLK/YEL” wire shorted
to other circuit.
If wire is OK, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
7 Wire circuit check
1) Measure resistance between “C37-25” terminal of ECM
connector and “BLK/YEL” wire terminal of MAF and IAT
sensor connector with ignition switch turned OFF.
Is resistance below 3
Ω? Go to Step 8.
“BLK/YEL” wire is high
resistance circuit.
Step
Action YesNo
I4RS0B110020-01
Page 128 of 1496
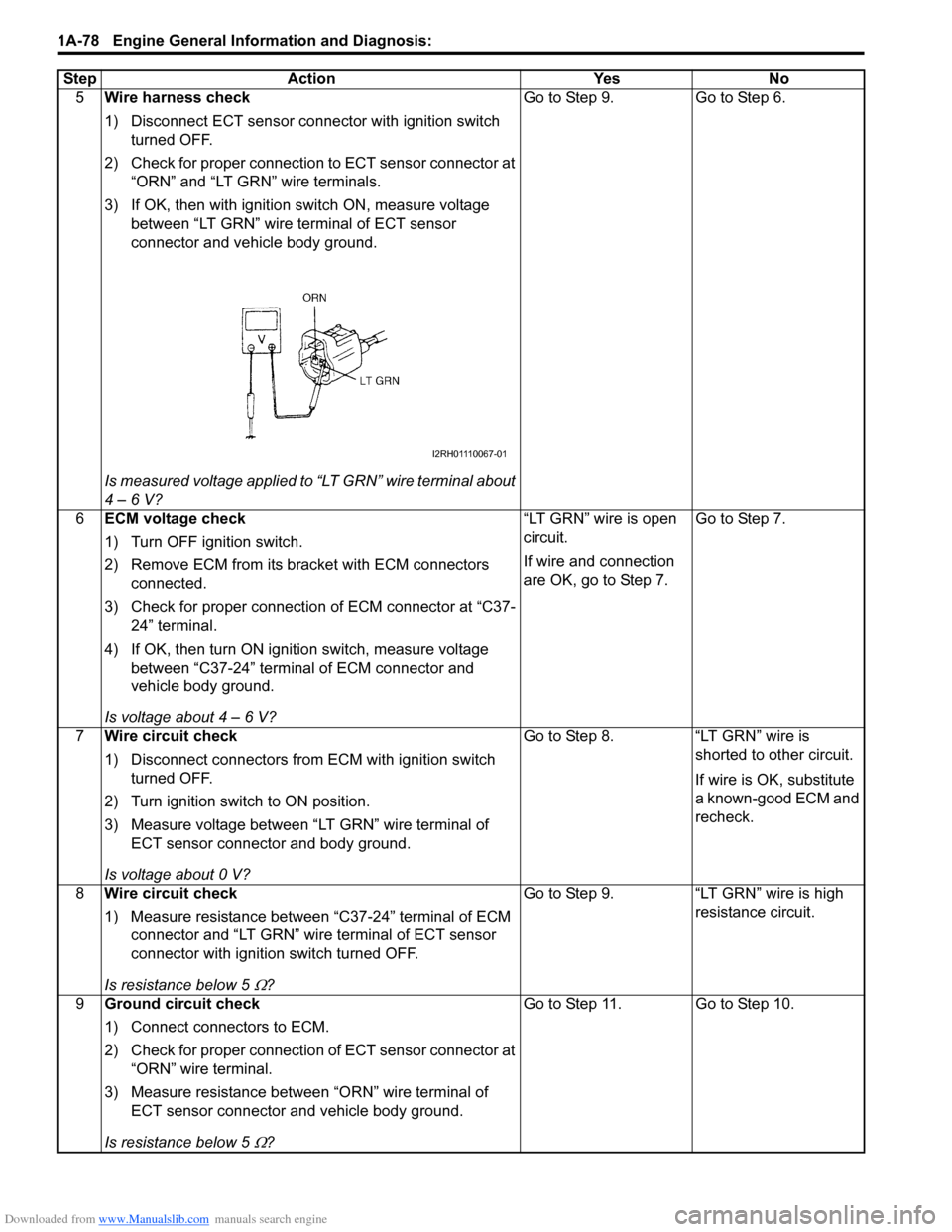
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-78 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
5Wire harness check
1) Disconnect ECT sensor connector with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to ECT sensor connector at “ORN” and “LT GRN” wire terminals.
3) If OK, then with ignition switch ON, measure voltage
between “LT GRN” wire terminal of ECT sensor
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is measured voltage applied to “LT GRN” wire terminal about
4 – 6 V? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 6.
6 ECM voltage check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Remove ECM from its br acket with ECM connectors
connected.
3) Check for proper connection of ECM connector at “C37- 24” terminal.
4) If OK, then turn ON igniti on switch, measure voltage
between “C37-24” terminal of ECM connector and
vehicle body ground.
Is voltage about 4 – 6 V? “LT GRN” wire is open
circuit.
If wire and connection
are OK, go to Step 7.
Go to Step 7.
7 Wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
3) Measure voltage between “LT GRN” wire terminal of ECT sensor connector and body ground.
Is voltage about 0 V? Go to Step 8.
“LT GRN” wire is
shorted to other circuit.
If wire is OK, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.
8 Wire circuit check
1) Measure resistance between “C37-24” terminal of ECM
connector and “LT GRN” wire terminal of ECT sensor
connector with ignition switch turned OFF.
Is resistance below 5
Ω? Go to Step 9. “LT GRN” wire is high
resistance circuit.
9 Ground circuit check
1) Connect connectors to ECM.
2) Check for proper connection of ECT sensor connector at
“ORN” wire terminal.
3) Measure resistance between “ORN” wire terminal of ECT sensor connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance below 5
Ω? Go to Step 11. Go to Step 10.
Step Action Yes No
I2RH01110067-01
Page 141 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-91
DTC P0133: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Slow Response (Sensor-1)S7RS0B1104032
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that following conditions ar e satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14 ° F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) to 150 °C (302 °F)
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature.
4) Drive vehicle at 40 mph (60 km/h) or higher. (engine speed: 2500 – 3000 r/min.)
5) Keep above vehicle speed for 6 min. or more. (Throt tle valve opening is kept constant in this step.)
6) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (with fuel cut for 3 sec. or more)
and then stop vehicle.
7) Check if DTC and pending DTC exist by using scan tool. If not, check if oxygen sensor monitoring test has been
completed by using scan tool. If not in both of above c hecks (i.e., no DTC and pending DTC and oxygen sensor
monitoring test not completed), check vehicle cond ition (environmental) and repeat Step 3) through 6).
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
Response time (time to change from lean to rich or from rich to lean) of HO2S-1 output
voltage is about 1 sec. at minimum or aver age time of 1 cycle is 5 sec. at minimum.
(*2 driving cycle detection logic, monitoring once per driving cycle) Heated oxygen sensor-1
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Is there DTC(s) other than HO2S-1 (DTC P0133)? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.Replace HO2S-1.