450 SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 633 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-59
Installation
CAUTION!
Do not pull or twist wire harness more than
necessary when installing front wheel speed
sensor.
1) Check that no foreign material is attached to sensor(1) and mating encoder (2).
2) Install it by reversing removal procedure.
Tightening torque
Front wheel speed sensor bolt (a): 11 N·m (1.1
kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
Front wheel speed sensor harness clamp bolt
(b): 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
3) Check that there is no clearance between sensor and knuckle.
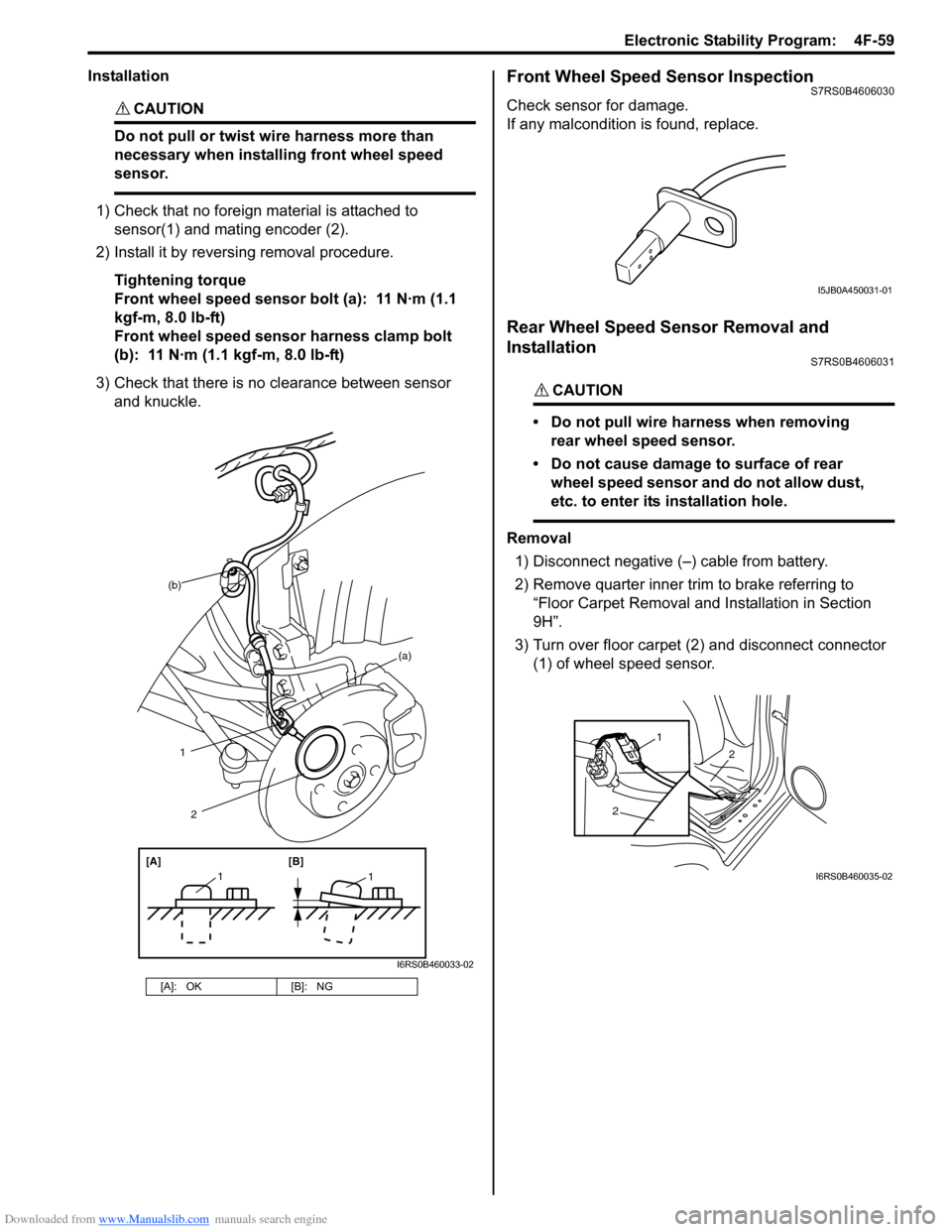
Front Wheel Speed Sensor InspectionS7RS0B4606030
Check sensor for damage.
If any malcondition is found, replace.
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B4606031
CAUTION!
• Do not pull wire harness when removing rear wheel speed sensor.
• Do not cause damage to surface of rear wheel speed sensor and do not allow dust,
etc. to enter its installation hole.
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable from battery.
2) Remove quarter inner trim to brake referring to
“Floor Carpet Removal and Installation in Section
9H”.
3) Turn over floor carpet (2) and disconnect connector (1) of wheel speed sensor.
[A]: OK [B]: NG
(b)
1
[A][B]
11
2
(a)
I6RS0B460033-02
I5JB0A450031-01
2
2
1
I6RS0B460035-02
Page 635 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-61
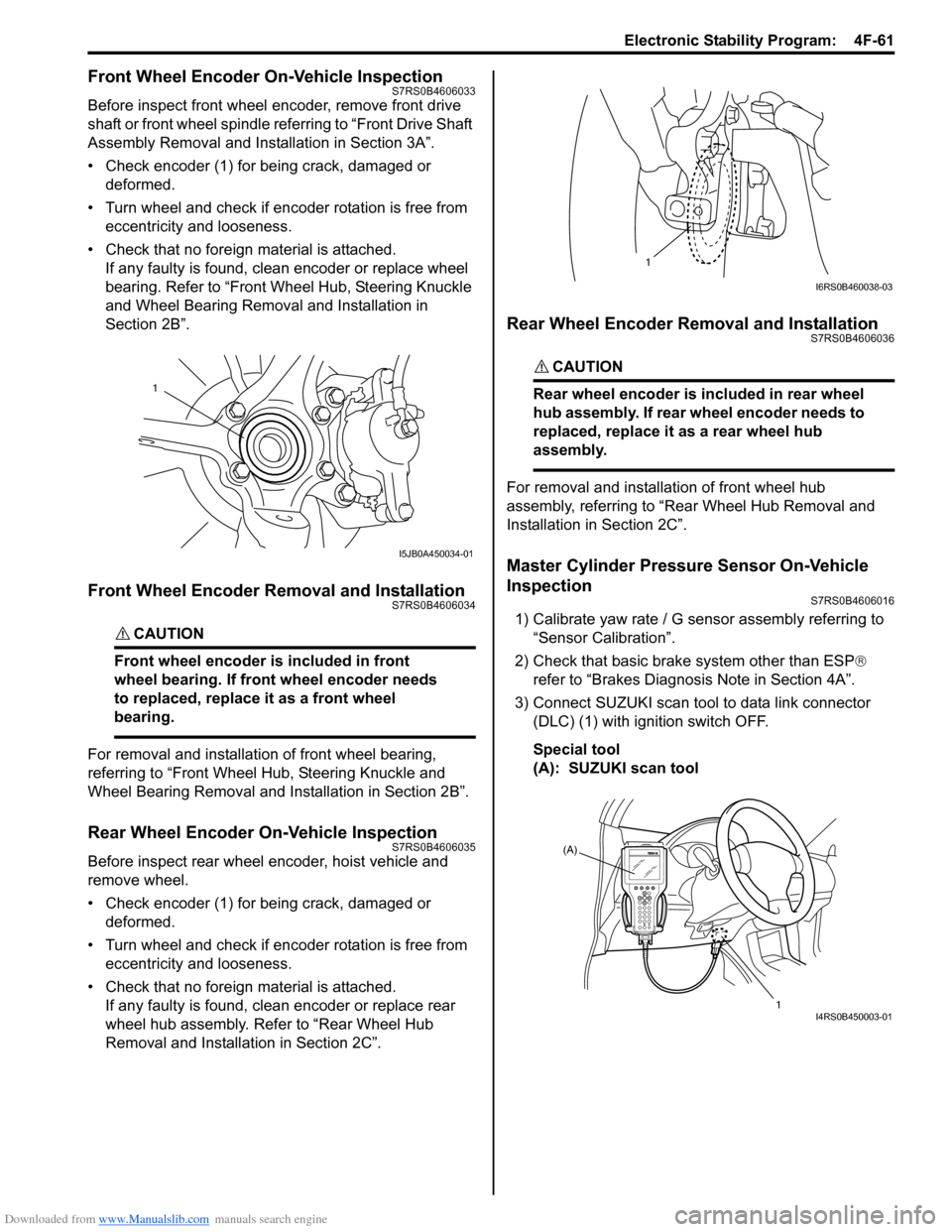
Front Wheel Encoder On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B4606033
Before inspect front wheel encoder, remove front drive
shaft or front wheel spindle referring to “Front Drive Shaft
Assembly Removal and Installation in Section 3A”.
• Check encoder (1) for being crack, damaged or deformed.
• Turn wheel and check if encoder rotation is free from eccentricity and looseness.
• Check that no foreign material is attached. If any faulty is found, cl ean encoder or replace wheel
bearing. Refer to “Front Wheel Hub, Steering Knuckle
and Wheel Bearing Removal and Installation in
Section 2B”.
Front Wheel Encoder Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4606034
CAUTION!
Front wheel encoder is included in front
wheel bearing. If front wheel encoder needs
to replaced, replace it as a front wheel
bearing.
For removal and installation of front wheel bearing,
referring to “Front Wheel Hub, Steering Knuckle and
Wheel Bearing Removal and Installation in Section 2B”.
Rear Wheel Encoder On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B4606035
Before inspect rear wheel encoder, hoist vehicle and
remove wheel.
• Check encoder (1) for being crack, damaged or deformed.
• Turn wheel and check if encoder rotation is free from eccentricity and looseness.
• Check that no foreign material is attached. If any faulty is found, cl ean encoder or replace rear
wheel hub assembly. Refer to “Rear Wheel Hub
Removal and Installati on in Section 2C”.
Rear Wheel Encoder Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4606036
CAUTION!
Rear wheel encoder is included in rear wheel
hub assembly. If rear wheel encoder needs to
replaced, replace it as a rear wheel hub
assembly.
For removal and installation of front wheel hub
assembly, referring to “Rear Wheel Hub Removal and
Installation in Section 2C”.
Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B4606016
1) Calibrate yaw rate / G sens or assembly referring to
“Sensor Calibration”.
2) Check that basic brake system other than ESP ®
refer to “Brakes Diagnosi s Note in Section 4A”.
3) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
1
I5JB0A450034-01
1
I6RS0B460038-03
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
Page 636 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-62 Electronic Stability Program:
4) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu “DATA LIST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool. Refer to
scan tool operator's manual for further derails.
5) When brake pedal is released, check “Master Cyl Press” under “DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool.
If pressure is out of specification, replace ESP ®
hydraulic unit / cont rol module assembly.
Master cylinder pressure specification
Brake pedal released: 0 ± 0.8 MPa (0 ± 8 kg/cm2, 0
± 113 psi)
6) Hoist vehicle and remove right-side front wheel.
7) Connect special tool with rubber hose (1) to Front brake caliper bleeder plug (2).
Special tool
(A): 09956–02311
8) When bleeder plug loosen and depress brake pedal to make special tool gauge reading 10 MPa (100 kg/
cm
2, 1422 psi), check “Master Cyl Press” under
“DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool.
If pressure displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is out of
specification, replace ESP ® hydraulic unit / control
module assembly.
Master cylinder pressure specification
Brake pedal depressed 10 MPa (100 kg/cm2, 1422
psi): 10 ± 1.2 MPa (100 ± 12 kg/cm2, 1422 ± 170
psi)
9) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
10) Tighten bleeder plug and bleed air from brake system, referring to “Air Bleeding of Brake System in
Section 4A”.
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B4606017
Lateral G Inspection
1) Calibrate yaw rate / G sens or assembly referring to
“Sensor Calibration”.
2) Park and level the vehicle with parking brake and fix wheels with chokes.
3) Check yaw rate / G sensor assembly installation
condition. 4) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector
(DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
5) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu “DATA LIST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool. Refer to
scan tool operator's manual for further derails.
6) Check “G Sensor (lateral)” under “DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool in the following vehicle conditions.
• Level condition
• Right-up condition
• Left-up condition
If Lateral G condition is ou t of specification, replace
yaw rate / G sensor assembly.
Lateral G sp ecification
2
(A)
1
I6JB01460025-01
Vehicle condition G Sensor (lateral)
Level condition 0 ± 0.1 G
Right-up condition 0.1 ± 0.1 G
Left-up condition –0.1 ± 0.1 G
[A]: Right-up condition “a”: Approx 350 mm (13.78 in.)
[B]: Left-up condition 1. Safety stand
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
[A]
[B]“a”
1
“a”1
I6RS0B460039-02
Page 637 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-63
Yaw Rate Inspection1) Calibrate yaw rate / G sens or assembly referring to
“Sensor Calibration”.
2) Check yaw rate / G sensor assembly installation
condition.
3) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
4) Turn ignition switch to ON position and select menu
“DATA LIST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool. Refer to
scan tool operator's manual for further derails.
5) Check “Yaw rate sensor” under “DATA LIST” of SUZUKI scan tool in the following vehicle conditions.
• Parking condition
• Drive vehicle in right turning condition with steering wheel fully turned
• Drive vehicle in left tu rning condition with steering
wheel fully turned
If yaw rate condition is ou t of specification, replace
yaw rate / G sensor assembly.
Yaw rate specification
NOTE
• Drive the vehicle on level ground and at 10 km/h (6.2 mph).
• Minimum turning radius is 5.2 m (17.1 ft).
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B4606018
CAUTION!
• When yaw rate / G sensor assembly is replaced, ESP ® control module needs zero
calibration. Perform zero calibration by
SUZUKI scan tool referring to “Sensor
Calibration”.
• Regarding yaw rate / G sensor assembly removal/installation, confirm specified
torque and never use impact wrench to
avoid damage.
• When handling the yaw rate / G sensor assembly, be careful not to drop it or apply
an impact to it.
If an excessive impact was applied, never
attempt disassembly or repair but replace
it with a new one.
Vehicle condition Yaw rate
Parking 0 ± 4 deg/s
Right turning 30 ± 4 deg/s
Left turning –30 ± 4 deg/s
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
[A]: Right turning“a”: Approx 5.2 m (17.1 ft.)
[B]: Left turning
[A]
[B] “a”
“a”
I6RS0B460040-02
Page 638 of 1496
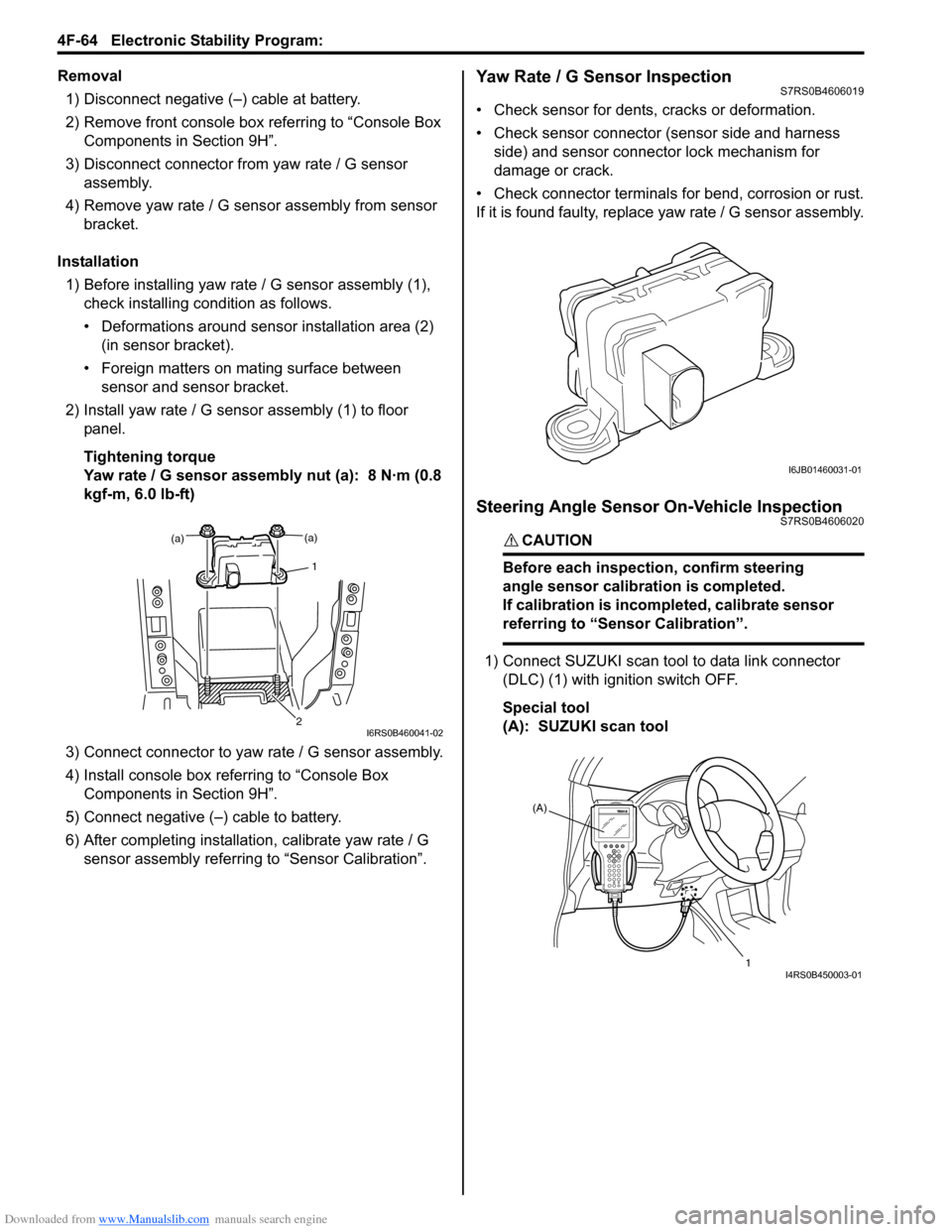
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-64 Electronic Stability Program:
Removal1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove front console box referring to “Console Box Components in Section 9H”.
3) Disconnect connector from yaw rate / G sensor
assembly.
4) Remove yaw rate / G sens or assembly from sensor
bracket.
Installation 1) Before installing yaw rate / G sensor assembly (1),
check installing condition as follows.
• Deformations around sensor installation area (2) (in sensor bracket).
• Foreign matters on mating surface between sensor and sensor bracket.
2) Install yaw rate / G sensor assembly (1) to floor panel.
Tightening torque
Yaw rate / G sensor assembly nut (a): 8 N·m (0.8
kgf-m, 6.0 lb-ft)
3) Connect connector to yaw rate / G sensor assembly.
4) Install console box referring to “Console Box Components in Section 9H”.
5) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
6) After completing installation, calibrate yaw rate / G
sensor assembly referring to “Sensor Calibration”.Yaw Rate / G Sensor InspectionS7RS0B4606019
• Check sensor for dents, cracks or deformation.
• Check sensor connector (sensor side and harness
side) and sensor connector lock mechanism for
damage or crack.
• Check connector terminals for bend, corrosion or rust.
If it is found faulty, replace yaw rate / G sensor assembly.
Steering Angle Sensor On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B4606020
CAUTION!
Before each inspection, confirm steering
angle sensor calibration is completed.
If calibration is incompleted, calibrate sensor
referring to “Sensor Calibration”.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector
(DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
(a)
1
(a)
2I6RS0B460041-02
I6JB01460031-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
Page 767 of 1496
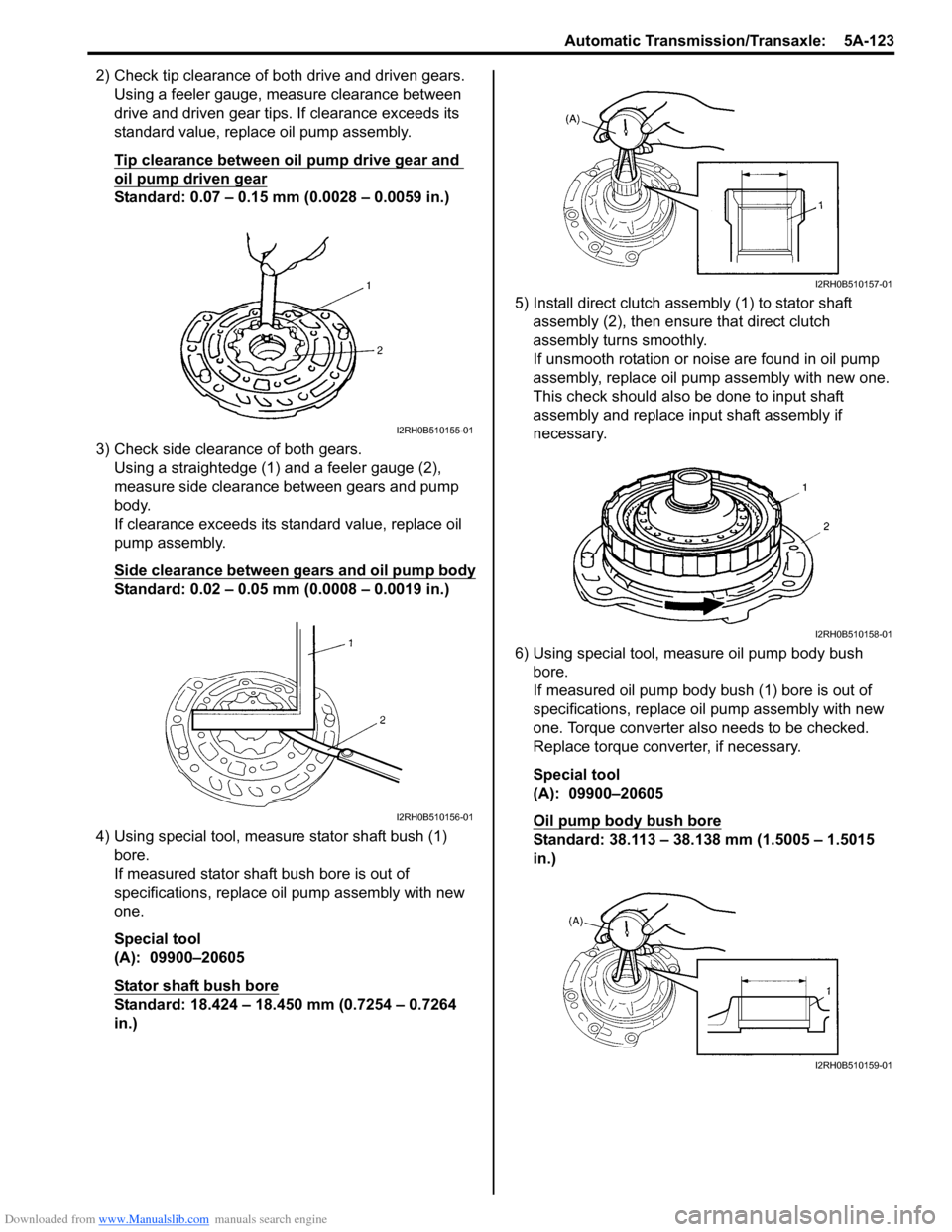
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-123
2) Check tip clearance of both drive and driven gears.Using a feeler gauge, m easure clearance between
drive and driven gear tips. If clearance exceeds its
standard value, replace oil pump assembly.
Tip clearance between oil pump drive gear and
oil pump driven gear
Standard: 0.07 – 0.15 mm (0.0028 – 0.0059 in.)
3) Check side clearance of both gears. Using a straightedge (1) and a feeler gauge (2),
measure side clearance between gears and pump
body.
If clearance exceeds its standard value, replace oil
pump assembly.
Side clearance between gears and oil pump body
Standard: 0.02 – 0.05 mm (0.0008 – 0.0019 in.)
4) Using special tool, measure stator shaft bush (1) bore.
If measured stator shaft bush bore is out of
specifications, replace oil pump assembly with new
one.
Special tool
(A): 09900–20605
Stator shaft bush bore
Standard: 18.424 – 18.450 mm (0.7254 – 0.7264
in.) 5) Install direct clutch asse
mbly (1) to stator shaft
assembly (2), then ensure that direct clutch
assembly turns smoothly.
If unsmooth rotation or noise are found in oil pump
assembly, replace oil pump assembly with new one.
This check should also be done to input shaft
assembly and replace input shaft assembly if
necessary.
6) Using special tool, measure oil pump body bush bore.
If measured oil pump body bush (1) bore is out of
specifications, replace o il pump assembly with new
one. Torque converter also needs to be checked.
Replace torque converter, if necessary.
Special tool
(A): 09900–20605
Oil pump body bush bore
Standard: 38.113 – 38.138 mm (1.5005 – 1.5015
in.)
I2RH0B510155-01
I2RH0B510156-01
I2RH0B510157-01
I2RH0B510158-01
I2RH0B510159-01
Page 834 of 1496
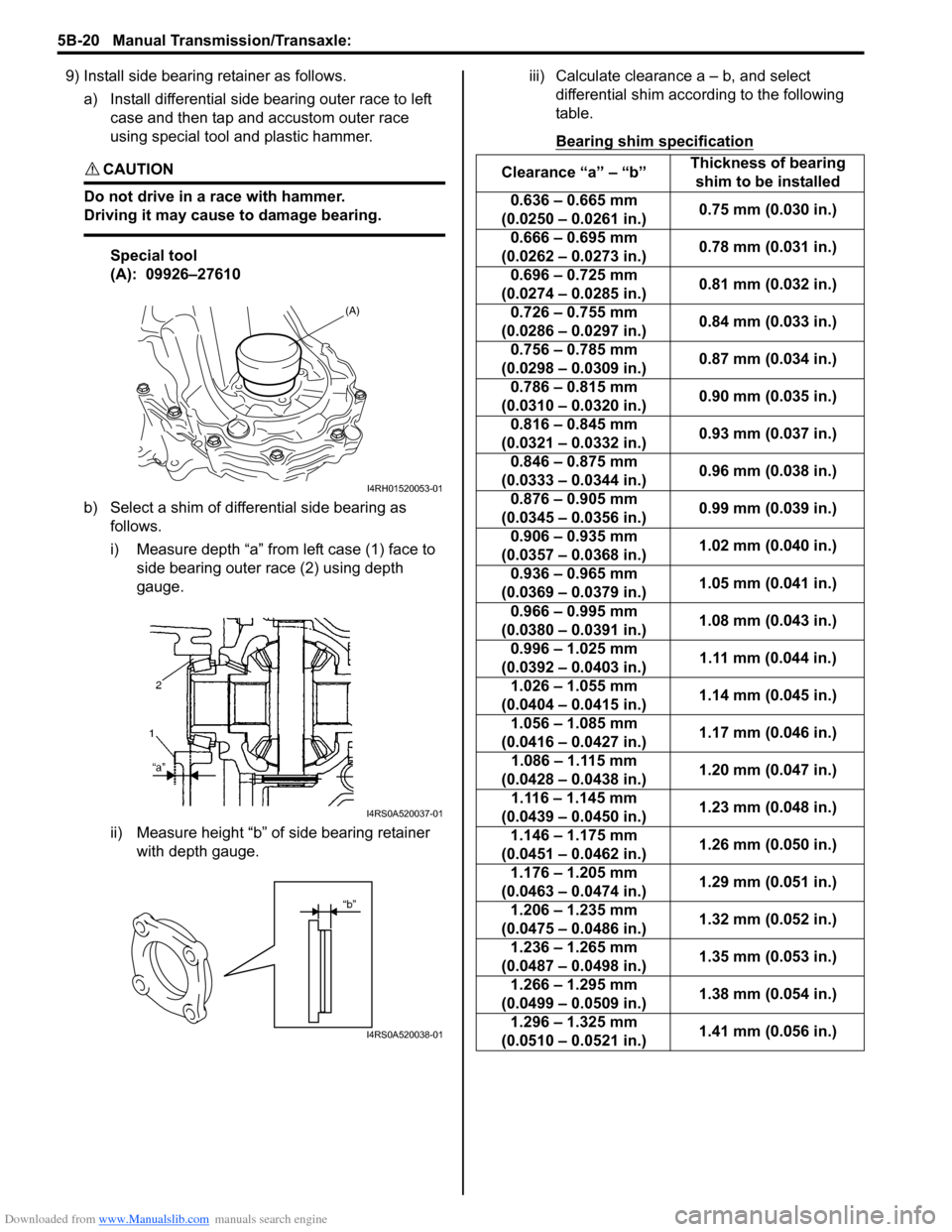
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5B-20 Manual Transmission/Transaxle:
9) Install side bearing retainer as follows.a) Install differential side bearing outer race to left case and then tap and accustom outer race
using special tool and plastic hammer.
CAUTION!
Do not drive in a race with hammer.
Driving it may cause to damage bearing.
Special tool
(A): 09926–27610
b) Select a shim of differential side bearing as follows.
i) Measure depth “a” from left case (1) face to side bearing outer race (2) using depth
gauge.
ii) Measure height “b” of side bearing retainer with depth gauge. iii) Calculate clearance a – b, and select
differential shim acco rding to the following
table.
Bearing shim specification
(A)
I4RH01520053-01
I4RS0A520037-01
“b”
I4RS0A520038-01
Clearance “a” – “b” Thickness of bearing
shim to be installed
0.636 – 0.665 mm
(0.0250 – 0.0261 in.) 0.75 mm (0.030 in.)
0.666 – 0.695 mm
(0.0262 – 0.0273 in.) 0.78 mm (0.031 in.)
0.696 – 0.725 mm
(0.0274 – 0.0285 in.) 0.81 mm (0.032 in.)
0.726 – 0.755 mm
(0.0286 – 0.0297 in.) 0.84 mm (0.033 in.)
0.756 – 0.785 mm
(0.0298 – 0.0309 in.) 0.87 mm (0.034 in.)
0.786 – 0.815 mm
(0.0310 – 0.0320 in.) 0.90 mm (0.035 in.)
0.816 – 0.845 mm
(0.0321 – 0.0332 in.) 0.93 mm (0.037 in.)
0.846 – 0.875 mm
(0.0333 – 0.0344 in.) 0.96 mm (0.038 in.)
0.876 – 0.905 mm
(0.0345 – 0.0356 in.) 0.99 mm (0.039 in.)
0.906 – 0.935 mm
(0.0357 – 0.0368 in.) 1.02 mm (0.040 in.)
0.936 – 0.965 mm
(0.0369 – 0.0379 in.) 1.05 mm (0.041 in.)
0.966 – 0.995 mm
(0.0380 – 0.0391 in.) 1.08 mm (0.043 in.)
0.996 – 1.025 mm
(0.0392 – 0.0403 in.) 1.11 mm (0.044 in.)
1.026 – 1.055 mm
(0.0404 – 0.0415 in.) 1.14 mm (0.045 in.)
1.056 – 1.085 mm
(0.0416 – 0.0427 in.) 1.17 mm (0.046 in.)
1.086 – 1.115 mm
(0.0428 – 0.0438 in.) 1.20 mm (0.047 in.)
1.116 – 1.145 mm
(0.0439 – 0.0450 in.) 1.23 mm (0.048 in.)
1.146 – 1.175 mm
(0.0451 – 0.0462 in.) 1.26 mm (0.050 in.)
1.176 – 1.205 mm
(0.0463 – 0.0474 in.) 1.29 mm (0.051 in.)
1.206 – 1.235 mm
(0.0475 – 0.0486 in.) 1.32 mm (0.052 in.)
1.236 – 1.265 mm
(0.0487 – 0.0498 in.) 1.35 mm (0.053 in.)
1.266 – 1.295 mm
(0.0499 – 0.0509 in.) 1.38 mm (0.054 in.)
1.296 – 1.325 mm
(0.0510 – 0.0521 in.) 1.41 mm (0.056 in.)
Page 890 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-8 Power Assisted Steering System:
Step 2: DTC Check, Record and Clearance
First, check DTC, referring to “DTC Check”. If DTC is
indicated, print it or write them down and then clear them
by referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates
malfunction that occurred in the system but does not
indicate whether it exists now or it occurred in the past
and the normal condition has been restored now. To
check which case applies, check the symptom in
question according to Step 5 and recheck DTC
according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the P/S system
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “S tep 2: DTC Check, Record
and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble symptoms. Also,
reconfirm trouble symptom by performing test drive and
turning steering wheel fully to right and left at stopped
vehicle.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Steering Symptom Diagnosis and P/S
System Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic steering system check according to
“Steering Symptom Diagnosis in Section 6A” first. When
the end of the flow has been reached, check the parts of
the system suspected as a possible cause referring to
“P/S System Symptom Diagnosis” and based on
symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained
through steps of customer complaint analysis, trouble
symptom confirmation and/or basic P/S system check)
and repair or replace faulty parts, if any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, P/S control module or other part and
repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2. Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the P/
S system is free from any abnormal conditions. If what
has been repaired is related to the DTC, clear the DTC
once, perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm
that no DTC is indicated.
“EPS” Warning Light CheckS7RS0B6304002
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position (without engine
running) and chec k if the “EPS” warning light (1)
lights up. If the light dose not light up, go to ““EPS”
Warning Light Does Not Come ON with Ignition
Switch Turned ON before Engine Starts” of the
diagnostic flows.
2) Start engine and check if the “EPS” warning light turns OFF. If light remains ON and no DTC is stored
in P/S control module, go to ““EPS” Warning Light
Remains ON Steady after Engine Starts” for
troubleshooting.
DTC CheckS7RS0B6304003
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) located on underside of instrument panel
at driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
1
I6RS0C630002-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
Page 891 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-9
3) Start engine.
4) Read DTC according to the instructions displayed on
SUZUKI scan tool. For further details, refer to
operator’s manual for SUZUKI scan tool.
NOTE
• If communication between SUZUKI scan tool and the vehicle can not be
established, perform “Serial Data Link
Circuit Check”.
• DTC C1122 (engine speed signal failure) is indicated when ignition switch is at ON
position and engine is not running, but it
means there is nothing abnormal if
indication changes to a normal one when
engine is started.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B6304004
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) located on underside of instrument panel
at driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
4) Erase DTC according to the instructions displayed on SUZUKI scan tool. For further details, refer to
operator’s manual for SUZUKI scan tool.
5) After completing the clearance, turn ignition switch to OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool from
DLC.
DTC TableS7RS0B6304005
CAUTION!
Be sure to perform the “EPS Syst em Check” before starting troubleshooting corresponding to each
DTC.
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
DTC No. Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting) Trouble area MIL
No
CODES Normal — — —
�) C1113 Steering torque sensor (Main
and Sub) circuit correlation Voltage difference between torque
sensor main signal and sub signal
is more than 0.6 V for 1 second
continuously. • Torque sensor signal circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module
1 driving
cycle
�) C1114 Steering torque sensor
reference power supply
circuit Circuit voltage of torque sensor 5
V reference power supply voltage
is more than 5.7 V or less than 4.3
V for 1 second continuously. • Torque sensor circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module
1 driving
cycle
�) C1117 Steering torque sensor
failure signal circuit low Torque sensor internal failure
signal circuit voltage is less than
1.7 V when ignition switch turned
ON.
• Torque sensor signal circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module1 driving
cycle
�) C1118 Steering torque sensor
failure signal circuit high Torque sensor internal failure
signal circuit voltage is more than
3.7 V for 1 second continuously. 1 driving
cycle
�) C1119 Steering torque sensor
power supply circuit Circuit voltage of torque sensor
main power supply
is less than
7.5 V for 1 second continuously. • Torque sensor circuit
• Torque sensor
• P/S control module
1 driving
cycle