Cam shaft SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 393 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-1
Engine
Ignition System
General Description
Ignition System ConstructionS7RS0B1801001
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below.
• ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the si gnals from the sensors, determines the most suitable
ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primar y coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power unit) in the
ignition coil assembly.
• Ignition coil assembly (including an ignitor)
The ignition coil assembly has a built -in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is induced
in the secondary coil.
• High-tension cords and spark plugs
• CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression stroke,
detects the crank angle and adjusts in itial ignition timing automatically.
• TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor, MAF sensor, IAT sensor, knock sensor and other sensors / switches
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and No.4
spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). W hen an ignition signal is sent from ECM to the ignitor in
the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary coil and that
passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simultaneously. Likewise,
when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the ot her ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3 spark plugs spark
simultaneously.
Page 396 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-4 Ignition System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
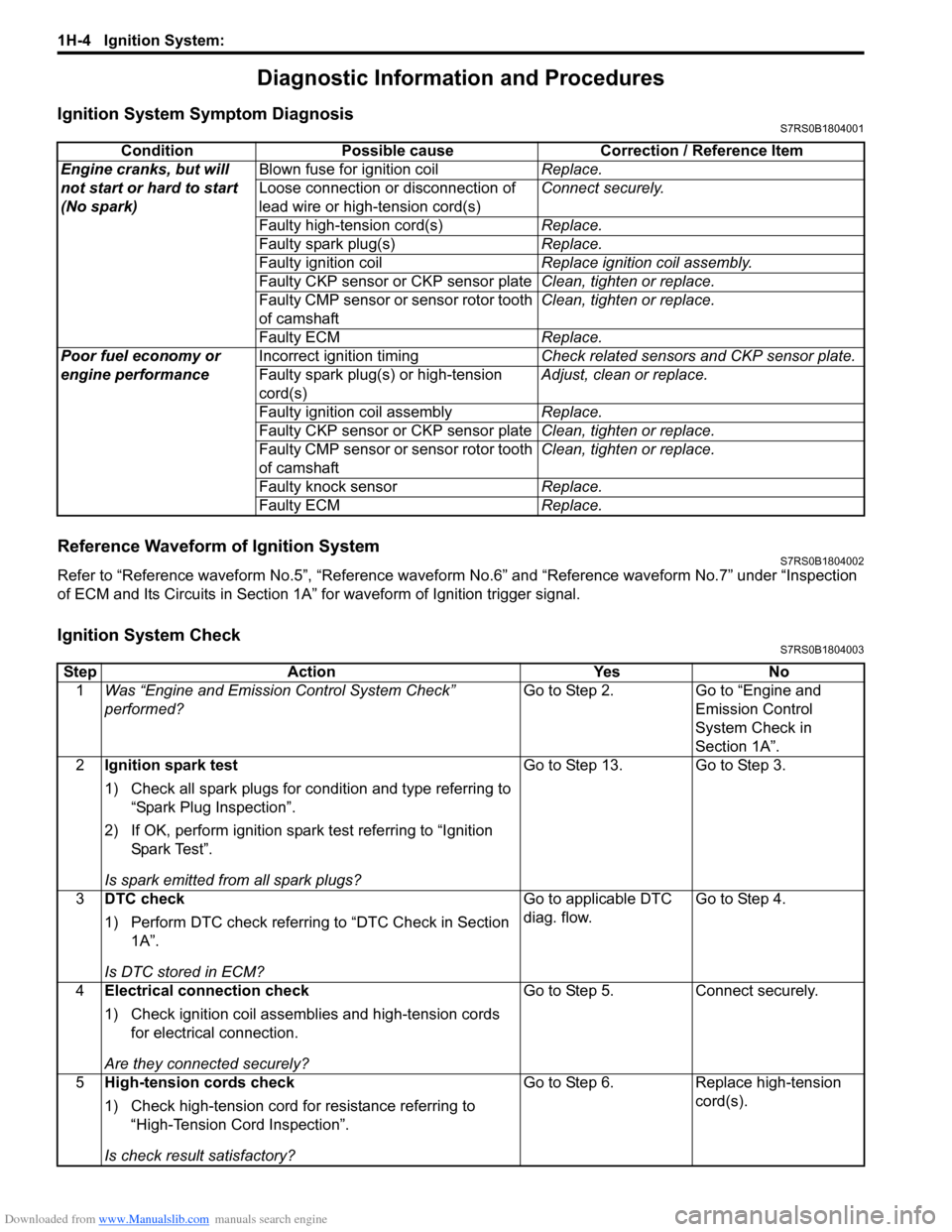
Ignition System Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1804001
Reference Waveform of Ignition SystemS7RS0B1804002
Refer to “Reference waveform No.5”, “Reference waveform No.6” and “Reference waveform No.7” under “Inspection
of ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A” for waveform of Ignition trigger signal.
Ignition System CheckS7RS0B1804003
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Engine cranks, but will
not start or hard to start
(No spark) Blown fuse for ignition coil
Replace.
Loose connection or disconnection of
lead wire or high-tension cord(s) Connect securely.
Faulty high-tension cord(s) Replace.
Faulty spark plug(s) Replace.
Faulty ignition coil Replace ignition coil assembly.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty CMP sensor or sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Poor fuel economy or
engine performance Incorrect ignition timing
Check related sensors and CKP sensor plate.
Faulty spark plug(s) or high-tension
cord(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil assembly Replace.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty CMP sensor or sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty knock sensor Replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
StepAction YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check in
Section 1A”.
2 Ignition spark test
1) Check all spark plugs for condition and type referring to
“Spark Plug Inspection”.
2) If OK, perform ignition spark test referring to “Ignition Spar k Tes t”.
Is spark emitted from all spark plugs? Go to Step 13. Go to Step 3.
3 DTC check
1) Perform DTC check referring to “DTC Check in Section
1A”.
Is DTC stored in ECM? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 4.
4 Electrical connection check
1) Check ignition coil assemblies and high-tension cords
for electrical connection.
Are they connected securely? Go to Step 5.
Connect securely.
5 High-tension cords check
1) Check high-tension cord for resistance referring to
“High-Tension Cord Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 6.
Replace high-tension
cord(s).
Page 397 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-5
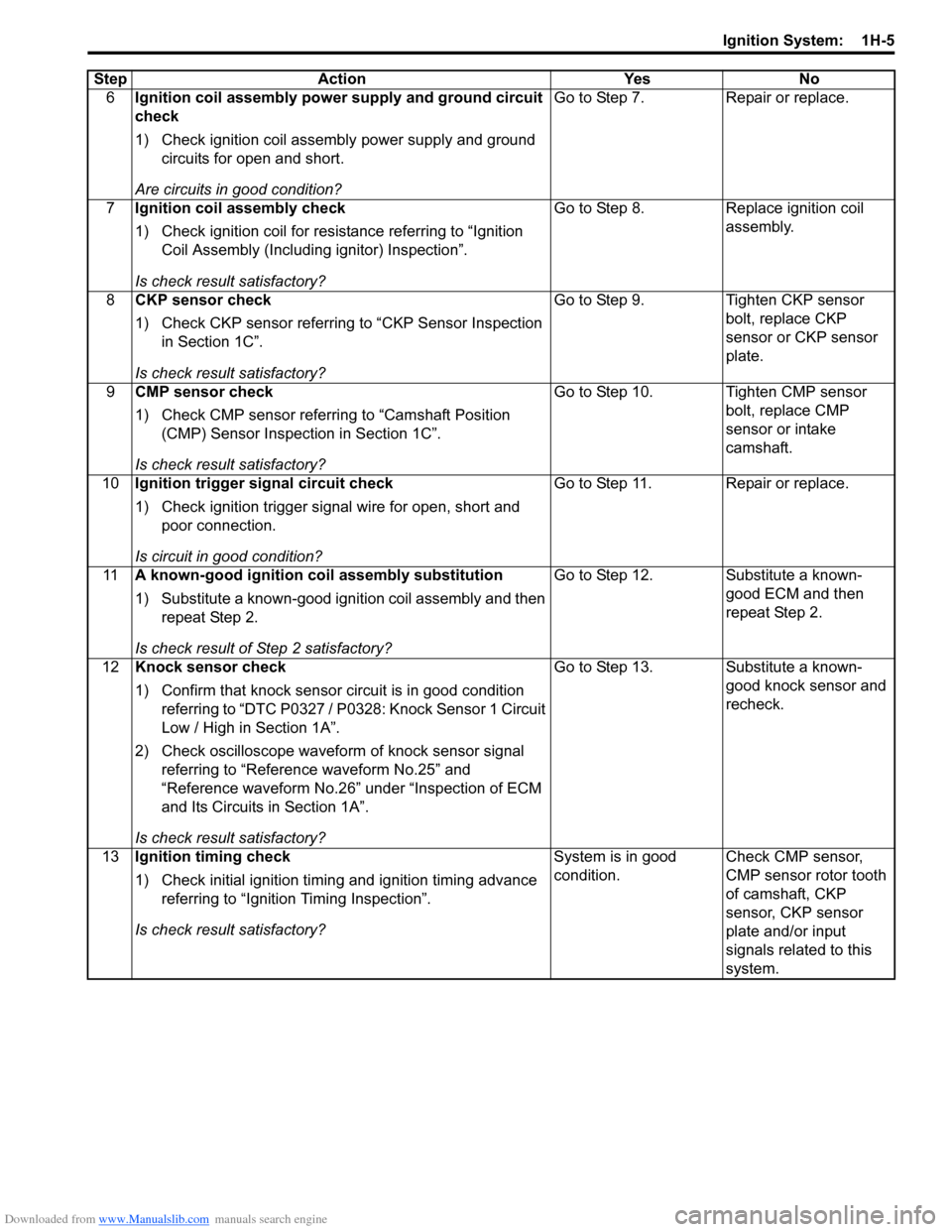
6Ignition coil assembly power supply and ground circuit
check
1) Check ignition coil assembly power supply and ground
circuits for open and short.
Are circuits in good condition? Go to Step 7.
Repair or replace.
7 Ignition coil assembly check
1) Check ignition coil for resistance referring to “Ignition
Coil Assembly (Including ignitor) Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 8.
Replace ignition coil
assembly.
8 CKP sensor check
1) Check CKP sensor referring to “CKP Sensor Inspection
in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 9.
Tighten CKP sensor
bolt, replace CKP
sensor or CKP sensor
plate.
9 CMP sensor check
1) Check CMP sensor referring to “Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 10. Tighten CMP sensor
bolt, replace CMP
sensor or intake
camshaft.
10 Ignition trigger signal circuit check
1) Check ignition trigger signal wire for open, short and
poor connection.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 11. Repair or replace.
11 A known-good ignition coil assembly substitution
1) Substitute a known-good ignition coil assembly and then
repeat Step 2.
Is check result of Step 2 satisfactory? Go to Step 12. Substitute a known-
good ECM and then
repeat Step 2.
12 Knock sensor check
1) Confirm that knock sensor circuit is in good condition
referring to “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High in Section 1A”.
2) Check oscilloscope waveform of knock sensor signal
referring to “Reference waveform No.25” and
“Reference waveform No.26” under “Inspection of ECM
and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 13. Substitute a known-
good knock sensor and
recheck.
13 Ignition timing check
1) Check initial ignition timing and ignition timing advance
referring to “Ignition Timing Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? System is in good
condition.
Check CMP sensor,
CMP sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft, CKP
sensor, CKP sensor
plate and/or input
signals related to this
system.
Step
Action YesNo
Page 401 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-9
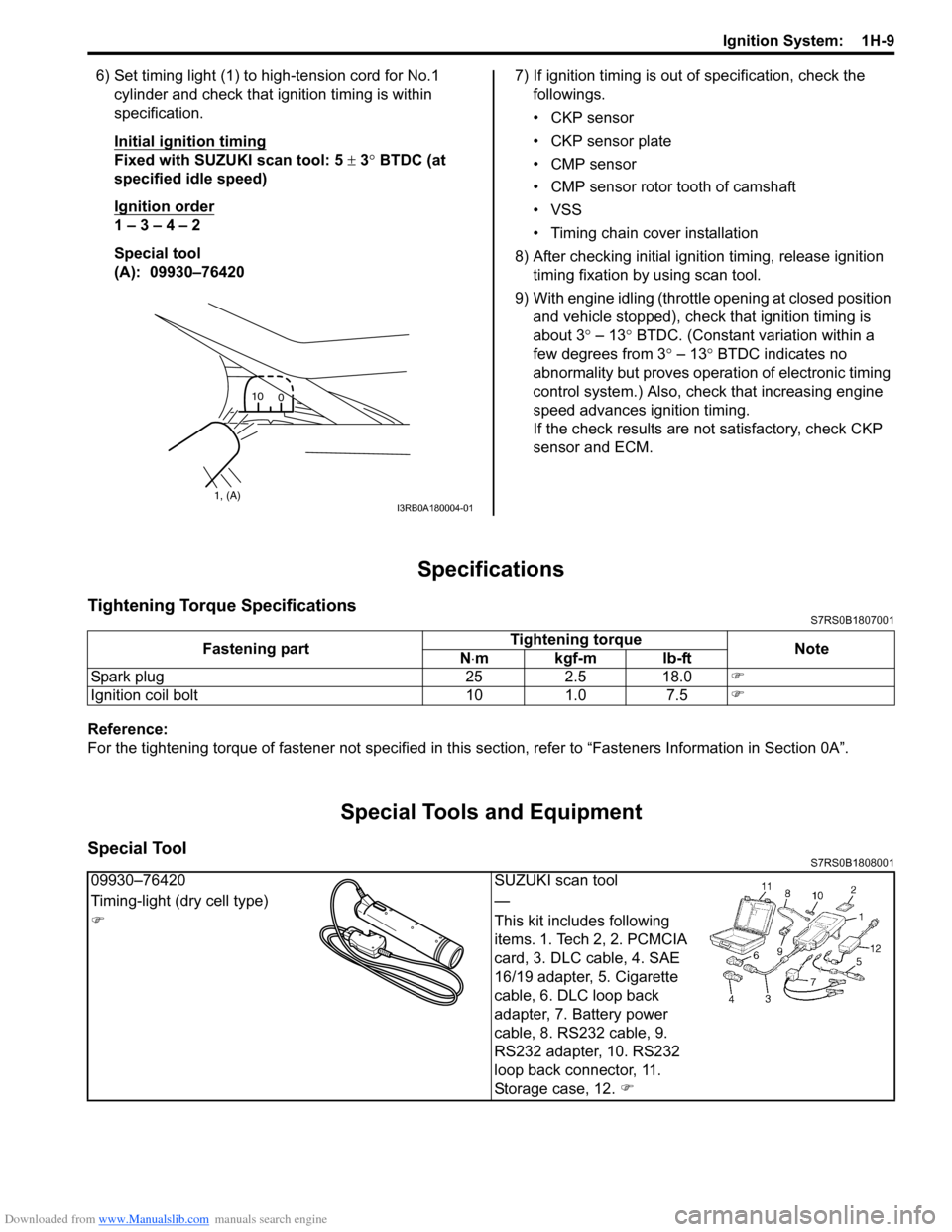
6) Set timing light (1) to high-tension cord for No.1 cylinder and check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing
Fixed with SUZUKI scan tool: 5 ± 3° BTDC (at
specified idle speed)
Ignition order
1 – 3 – 4 – 2
Special tool
(A): 09930–76420 7) If ignition timing is out
of specification, check the
followings.
• CKP sensor
• CKP sensor plate
• CMP sensor
• CMP sensor rotor tooth of camshaft
• VSS
• Timing chain cover installation
8) After checking initial igniti on timing, release ignition
timing fixation by using scan tool.
9) With engine idling (throttl e opening at closed position
and vehicle stopped), check that ignition timing is
about 3 ° – 13° BTDC. (Constant variation within a
few degrees from 3 ° – 13° BTDC indicates no
abnormality but proves operation of electronic timing
control system.) Also, check that increasing engine
speed advances ignition timing.
If the check results are not satisfactory, check CKP
sensor and ECM.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1807001
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B1808001
1, (A)10
0I3RB0A180004-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Spark plug 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Ignition coil bolt 10 1.0 7.5 �)
09930–76420SUZUKI scan tool
Timing-light (dry cell type) —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12. �)
Page 825 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Manual Transmission/Transaxle: 5B-11
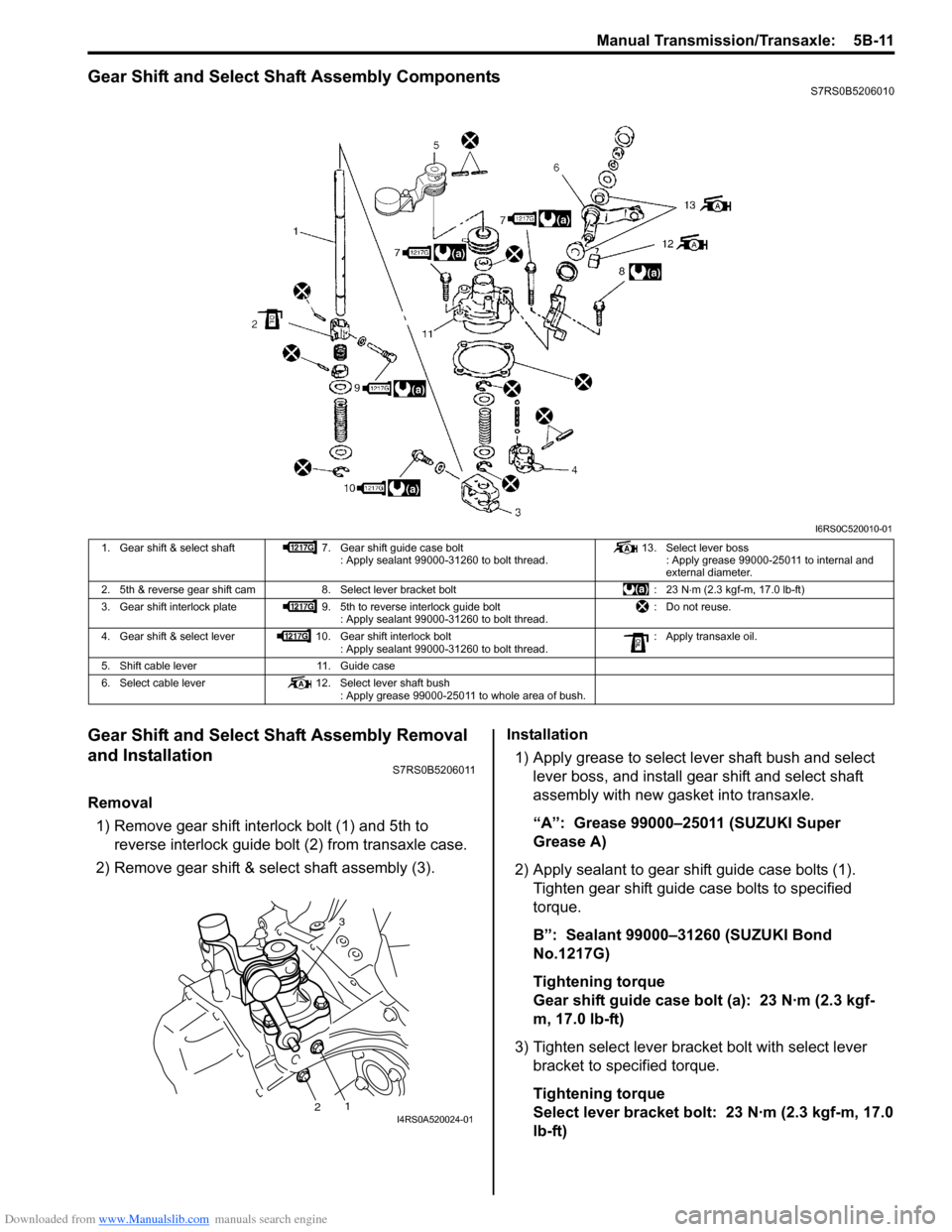
Gear Shift and Select Shaft Assembly ComponentsS7RS0B5206010
Gear Shift and Select Shaft Assembly Removal
and Installation
S7RS0B5206011
Removal1) Remove gear shift interlock bolt (1) and 5th to reverse interlock guide bolt (2) from transaxle case.
2) Remove gear shift & select shaft assembly (3). Installation
1) Apply grease to select lever shaft bush and select lever boss, and install gear shift and select shaft
assembly with new gasket into transaxle.
“A”: Grease 99000–25011 (SUZUKI Super
Grease A)
2) Apply sealant to gear shift guide case bolts (1). Tighten gear shift guide case bolts to specified
torque.
B”: Sealant 99000–31260 (SUZUKI Bond
No.1217G)
Tightening torque
Gear shift guide case bolt (a): 23 N·m (2.3 kgf-
m, 17.0 lb-ft)
3) Tighten select lever brac ket bolt with select lever
bracket to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Select lever bracket bolt: 23 N·m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0
lb-ft)
I6RS0C520010-01
1. Gear shift & select shaft 7. Gear shift guide case bolt
: Apply sealant 99000-31260 to bolt thread. 13. Select lever boss
: Apply grease 99000-25011 to internal and
external diameter.
2. 5th & reverse gear shift cam 8. Select lever bracket bolt : 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
3. Gear shift interlock plate 9. 5th to reverse interlock guide bolt
: Apply sealant 99000-31260 to bolt thread. : Do not reuse.
4. Gear shift & select lever 10. Gear shift interlock bolt
: Apply sealant 99000-31260 to bolt thread. : Apply transaxle oil.
5. Shift cable lever 11. Guide case
6. Select cable lever 12. Select lever shaft bush
: Apply grease 99000-25011 to whole area of bush.
3
12I4RS0A520024-01
Page 826 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5B-12 Manual Transmission/Transaxle:
4) Install washer and gear shift interlock bolt (2) to which sealant have been app lied and then tighten it
to specified torque.
“B”: Sealant 99000–31260 (SUZUKI Bond
No.1217G)
Tightening torque
Gear shift interlock bolt (b): 23 N·m (2.3 kgf-m,
17.0 lb-ft)
5) Install washer and 5th to reverse interlock guide bolt (3) to which sealant have been applied and then
tighten it to specified torque.
“B”: Sealant 99000–31260 (SUZUKI Bond
No.1217G)
Tightening torque
5th to reverse interlock guide bolt (c): 23 N·m (
2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
Gear Shift and Select Shaft Disassembly and
Assembly
S7RS0B5206012
1) Push pins out using 2.8 – 3.0 mm (0.11 – 0.12 in.) commercially available spring pin remover and
specified spring pin removers as shown below.
Special tool
(A): 09922–85811 4.5 mm
(B): 09925–78210 6.0 mm
2) Inspect component parts for wear, distortion or
damage. If any detect is found, replace detective
part with new one.
NOTE
• Set new gear shift & select lever inner pin (8) and outer pin (9) facing each gap (“a”,
“b”) in the opposite direction as shown in
figure.
• When driving in pins, prevent shaft from being bent by supporting it with wood
block.
• Assemble 5th & reverse gear shift cam with its pit and pin aligned.
• Make sure to select an appropriate spring by identifying the painted colors to keep
gear shifting performance as designed.
– Low speed select spring – Light blue
– Reverse select spring – Yellow
“A” 1, (a), “B”
1, (a), “B” 2, (b), “B”
3, (c), “B”
I4RS0A520025-01
1. E-ring 10. Ball
2. Washer 11. Gear shift & select shaft
3. Reverse select spring 12. 5th & reverse gear shift cam
4. Gear shift interlock plate 13. 5th & reverse gear shift cam guide pin
5. Ball 14. Cam guide return spring
6. Gear shift interlock spring 15. 5th & reverse gear shift cam guide
7. Gear shift & select lever 16. Gear shift cam guide pin
8. Inner pin 17. Low speed select spring
9. Outer pin 18. Spring pin remover
I6RS0C520011-01