oil type SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 10 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-5 Precautions:
• When performing service to electrical parts that does not require use of battery power, disconnect the
negative cable of the battery.
• When disconnecting the negative cable from the battery, be careful to the following.
– Check and record DTCs in ECM and HVAC control module if necessary before disconnecting.
– Record displayed contents of the clock and/or audio system, etc. before disconnecting and reset it
as before after connecting.
– For vehicle equipped with electric throttle body system, perform electric throttle body system
calibration referring to “Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1C” after
reconnecting the negative cable to the battery.
– For vehicle equipped with ESP ®, calibrate steering
angle sensor referring to “Sensor Calibration in
Section 4F” after reconnecting the negative cable
to the battery.
• When removing the battery, be sure to disconnect the negative cable first and then the positive cable. When
reconnecting the battery, connect the positive cable
first and then the negative cable, and replace the
terminal cover. • When removing parts that are to be reused, be sure to
keep them arranged in an orderly manner so that they
may be reinstalled in the proper order and position.
• Whenever you use oil seals, gaskets, packing, O- rings, locking washers, split pins, self-locking nuts,
and certain other parts as specified, be sure to use
new ones. Also, before installing new gaskets,
packing, etc., be sure to remove any residual material
from the mating surfaces.
• Make sure that all parts used in reassembly are perfectly clean.
When use of a certain type of lubricant, bond or
sealant is specified, be sure to use the specified type.
“A”: Water tight sealant 99000–31250 (SUZUKI
Bond No.1207F)
I2RH01010026-01
I2RH01010027-01
I2RH01010028-01
I2RH01010029-01
I2RH01010030-01
Page 51 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-1
Engine
Engine General Information and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on Engine ServiceS7RS0B1100001
CAUTION!
The following information on engine service
should be noted carefully, as it is important in
preventing damage, and in contributing to
reliable engine performance.
• When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do
not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against
oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer,
resulting in damaged oil pick-up unit.
• It should be kept in mind , while working on engine,
that 12-volt electrical syste m is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals
can be grounded, ground cable of the battery should
be disconnected at battery.
• Any time the air cleaner, throttle body or intake manifold is removed, the intake opening should be
covered. This will protect against accidental entrance
of foreign material which could follow intake passage
into cylinder and cause extensive damage when
engine is started.
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System
S7RS0B1100005
There are two types of On -Board Diagnostic (OBD)
system, Euro OBD system and non-Euro-OBD system,
depending on the vehicle specification.
As the diagnosis function is different between these two
types, be sure to fully understand the OBD system
referring to “On-Board Diagnostic System Description”.
OBD System Summary Table
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B1100002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• Don’t disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable
from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine
or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information
in ECM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checke d by using SUZUKI scan
tool or OBD generic scan tool. Before using scan tool,
read its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to
have good understanding as to what functions are
available and how to use it.
For Euro OBD model it is indistinguishable which
module turns on MIL because not only ECM but also
TCM (A/T model) turns on MIL (For details of on-
board diagnostic system for A/T model, refer to “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description in Section 5A”).
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM (A/T model) for
DTC when MIL lights on.
When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– OBD generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM (A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instructi on in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected)
Euro OBD
model Non-Euro-OBD
model
Quantity of DTC
related to engine
control Approx. 80 Approx. 60
Freeze frame
data Available Not available
SUZUKI scan
tool Available Available
OBD generic
scan tool Available Not available
Page 77 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-27
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B1104004
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Using Scan Tool1) Connect OBD generic scan to ol or SUZUKI scan tool
to data link connector in the same manner as when
making this connection for DTC check.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and then ON.
3) Erase DTC and pending DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool. Refer to scan
tool operator’s manual for further details.
4) After completing the clear ance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
NOTE
DTC and freeze frame data stored in ECM
memory are also cleared in the following
cases. Be careful not to clear them before
keeping their record.
• When power to ECM is cut off (by disconnecting battery cable, removing
fuse or disconnecting ECM connectors).
• When the same malfunction (DTC) is not detected again during 40 engine warm-up
cycles. (See “Warm-Up Cycle” of “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description”.)
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model)
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect battery negative cable for specified time below to erase diagnostic trouble code stored in
ECM memory and reconnect it.
Time required to erase DTC
DTC TableS7RS0B1104005
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
• For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• For non-Euro-OBD model, some of DTC No. with delta ( �U) mark in the following table can not be
detected by ECM depending on vehicl e specification and local regulation.
• DTC with square ( �†) mark in the following table can be detected only for Hong Kong model.
• DTC with circle ( �{) mark in the following table can be detected only for Euro OBD model and Hong
Kong model.
• For Euro OBD model, with the generic scan tool, onl y star (*) marked DTC No. in the following table
can be read.
• 1 driving cycle: MIL lights up when DTC is detected during 1 driving cycle.
• 2 driving cycles: MIL lights up when the same DTC is detected also in the next driving cycle after DTC is detected and stored temporarily in the first driving cycle.
• *2 driving cycles: MIL blinks or lights up. Refer to “DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304: Random / Multiple
Cylinder Misfire Detected / Cylinder 1 / Cylinder 2 / Cylinder 3 / Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected” for
details.
Ambient temperature Time to cut power to ECM
Over 0 °C (32 ° F) 30 sec. or longer
Under 0 °C (32 °F) Not specifiable.
Select a place with higher
than 0 °C (32 °F)
temperature.
DTC No. Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL
�) *P0010 “A” camshaft position actuator
circuit Oil control valve circuit open or short. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0011 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-advanced or system
performance Actual value of advanced va
lve timing does not reach
target value, or valve timi ng is advanced although ECM
command is most retarding. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0012 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-retarded 2 driving
cycles
Page 353 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Lubrication System: 1E-1
Engine
Engine Lubrication System
General Description
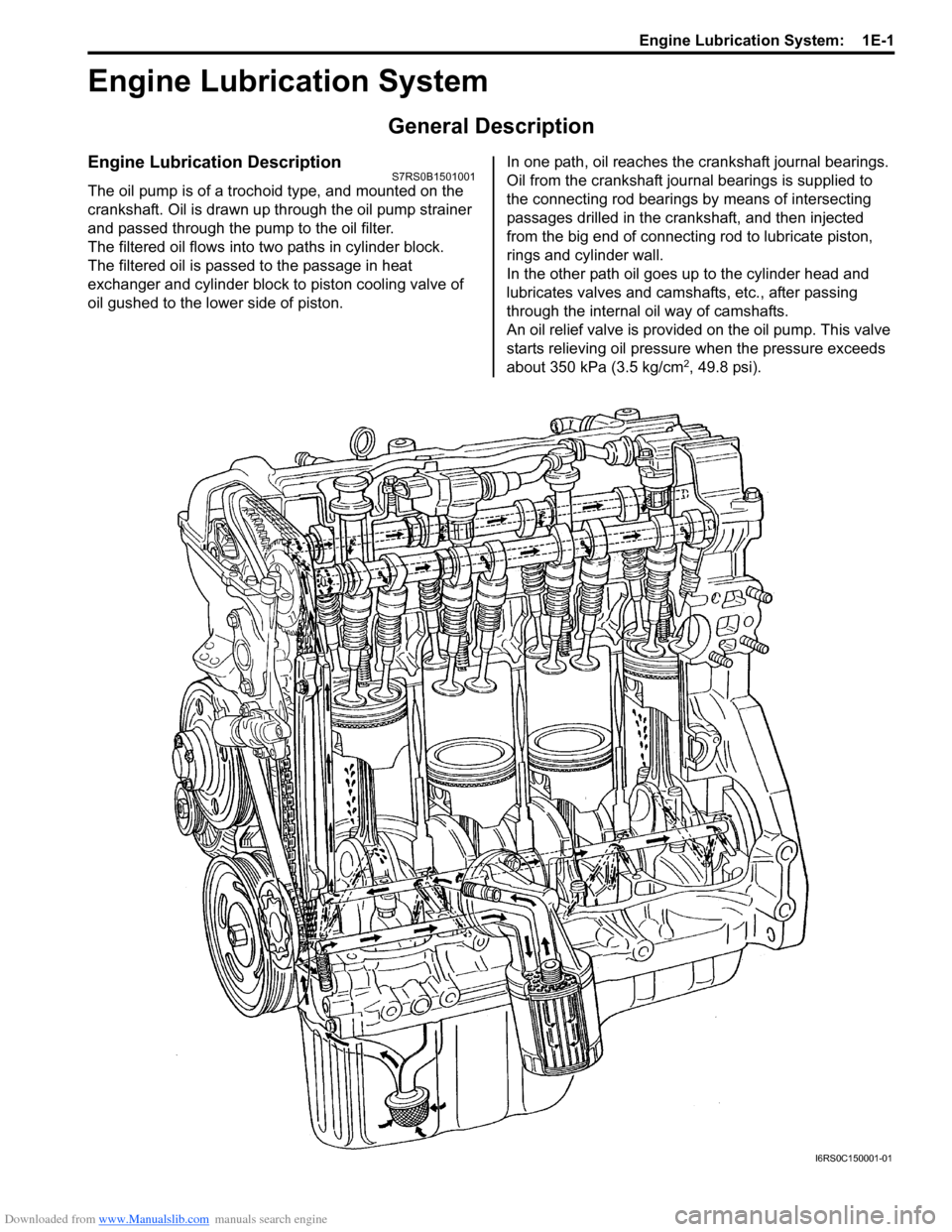
Engine Lubrication DescriptionS7RS0B1501001
The oil pump is of a trochoid type, and mounted on the
crankshaft. Oil is drawn up through the oil pump strainer
and passed through the pump to the oil filter.
The filtered oil flows into two paths in cylinder block.
The filtered oil is passed to the passage in heat
exchanger and cylinder block to piston cooling valve of
oil gushed to the lower side of piston. In one path, oil reaches the crankshaft journal bearings.
Oil from the crankshaft journal bearings is supplied to
the connecting rod bearings by means of intersecting
passages drilled in the cran
kshaft, and then injected
from the big end of connecting rod to lubricate piston,
rings and cylinder wall.
In the other path oil goes up to the cylinder head and
lubricates valves and camshafts, etc., after passing
through the internal oil way of camshafts.
An oil relief valve is provided on the oil pump. This valve
starts relieving oil pressure when the pressure exceeds
about 350 kPa (3.5 kg/cm
2, 49.8 psi).
I6RS0C150001-01
Page 364 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1F-1 Engine Cooling System:
Engine
Engine Cooling System
General Description
Cooling System DescriptionS7RS0B1601001
The cooling system consists of the radiator cap, radiator, coolant reservoir, hoses, water pump, cooling fan and
thermostat. The radiator is of tube-and-fin type.
Coolant DescriptionS7RS0B1601002
WARNING!
• Do not remove radiator cap to check engine coolant level; check coolant visually at the see-through coolant reservoir. Coolant should be added only to reservoir as necessary.
• As long as there is pressure in the cooling system, the temperature can be considerably higher than the boiling temperature of the solution in the radiator without causing the solution to boil. Removal
of the radiator cap while engine is hot and pressure is high will cause the solution to boil
instantaneously and possibly with explosive force, spewing the solution over engine, fenders and
person removing cap. If the solution contains flammable anti-freeze such as alcohol (not
recommended for use at any time), there is also the possibility of causing a serious fire.
• Check to make sure that engine coolant temperature is cold before removing any part of cooling system.
• Also be sure to disconnect negative cable from battery terminal before removing any part.
The coolant recovery system is standard. The coolant in the radiator expands with heat, and the coolant is overflowed
to the reservoir.
When the system cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the radiator.
The cooling system has be en filled with a quality coolant that is a 50/50 mixture of water and ethylene glycol
antifreeze.
This 50/50 mixture coolant solution provides freezing protection to –36 °C (–33 °F).
• Maintain cooling system freeze protection at –36 °C (–33 °F) to ensure protection against corrosion and loss of
coolant from boiling. This should be done even if freezing temperatures are not expected.
• Add ethylene glycol base coolant when coolant has to be added because of coolant loss or to provide added protection against freezing at temperature lower than –36 °C (–33 °F).
NOTE
• Alcohol or methanol base coolant or plain water alone should not be used in cooling system at any
time as damage to cooling system could occur.
• Coolant must be mixed with deminerated water or distilled water.
Anti-freeze proportioning table
For M/T model For A/T model
Freezing temperature °
C –36 –36
° F –33 –33
Anti-freeze / Anti-corrosion coolant concentration % 50 50
Ratio of compound to cooling water ltr. 3.10/3.10 3.05/3.05
US pt. 6.55/6.55 6.44/6.44
Imp pt. 5.46/5.46 5.37/5.37
Page 396 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-4 Ignition System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Ignition System Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1804001
Reference Waveform of Ignition SystemS7RS0B1804002
Refer to “Reference waveform No.5”, “Reference waveform No.6” and “Reference waveform No.7” under “Inspection
of ECM and Its Circuits in Section 1A” for waveform of Ignition trigger signal.
Ignition System CheckS7RS0B1804003
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Engine cranks, but will
not start or hard to start
(No spark) Blown fuse for ignition coil
Replace.
Loose connection or disconnection of
lead wire or high-tension cord(s) Connect securely.
Faulty high-tension cord(s) Replace.
Faulty spark plug(s) Replace.
Faulty ignition coil Replace ignition coil assembly.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty CMP sensor or sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Poor fuel economy or
engine performance Incorrect ignition timing
Check related sensors and CKP sensor plate.
Faulty spark plug(s) or high-tension
cord(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil assembly Replace.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty CMP sensor or sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty knock sensor Replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
StepAction YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check in
Section 1A”.
2 Ignition spark test
1) Check all spark plugs for condition and type referring to
“Spark Plug Inspection”.
2) If OK, perform ignition spark test referring to “Ignition Spar k Tes t”.
Is spark emitted from all spark plugs? Go to Step 13. Go to Step 3.
3 DTC check
1) Perform DTC check referring to “DTC Check in Section
1A”.
Is DTC stored in ECM? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 4.
4 Electrical connection check
1) Check ignition coil assemblies and high-tension cords
for electrical connection.
Are they connected securely? Go to Step 5.
Connect securely.
5 High-tension cords check
1) Check high-tension cord for resistance referring to
“High-Tension Cord Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 6.
Replace high-tension
cord(s).
Page 398 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-6 Ignition System:
Ignition Spark TestS7RS0B1804004
1) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe.
2) Disconnect all injector couplers from injectors.
WARNING!
Without disconnection of injector couplers,
combustible gas may come out from spark
plug holes during this test and may get
ignited in engine room.
3) Remove spark plug and check it for condition and
type referring to “Spark Plug Inspection”.
4) If OK, connect ignition coil coupler to ignition coil assembly and connect spark plug to ignition coil
assembly or high-tension cord. Ground spark plug. 5) Crank engine and check if each spark plug sparks.
6) If no spark is emitted, inspect the related parts as
described in “Ignition System Symptom Diagnosis”.
Repair Instructions
High-Tension Cord Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1806001
Removal
1) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe and cylinder head upper cover.
2) Disconnect No.1 cylinder (2) and No.3 cylinder (3)
high-tension cords from ignition coil assemblies (1)
while gripping each cap.
3) Pull out high-tension cords from spark plugs while gripping each cap.
CAUTION!
• Removal of high-tension cords together with clamps will be recommended so as
not to damage their inside wire (resistive
conductor).
• For the same reason, pull out each connection by gripping cap portion.
Installation
1) Install No.1 cylinder (2) and No.3 cylinder (3) high-
tension cords to spark plugs and ignition coil
assemblies (1) while gripping each cap.
CAUTION!
• Never attempt to use metal conductor high-tension cords as replacing parts.
• Insert each cap portion fully when installing high-tension cords.
I4RS0A180006-01
I4RS0A180003-01
I4RS0A180004-01
Page 399 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-7
High-Tension Cord InspectionS7RS0B1806002
Measure resistance of high-tension cord (1) by using
ohmmeter.
If resistance exceeds specification, replace high-tension
cord(s).
High-tension cord resistance
No.1 cylinder high-tension cord resistance: 1.4 – 4.0
k Ω
No.3 cylinder high-tension cord resistance: 0.6 – 2.0
k Ω
Spark Plug Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1806003
Removal
1) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe and cylinder head upper cover.
2) Pull out high-tension cords by gripping their caps and then remove ignition coil assemblies referring to
“Ignition Coil Assembly (Inc luding ignitor) Removal
and Installation”.
3) Remove spark plugs.
Installation 1) Install spark plugs and tighten them to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Spark plug: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
2) Install ignition coil assemblies referring to “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor) Removal and
Installation”.
3) Install high-tension cords securely by gripping their caps.
4) Install cylinder head upper cover and air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe.
Spark Plug InspectionS7RS0B1806004
CAUTION!
• When servicing the iridium / platinum
spark plugs (slender center electrode type
plugs), do not touch the center electrode
to avoid damage to it. The electrode is not
strong enough against mechanical force
as it is slender and its material is not
mechanically tough.
• Do not clean or adjust gap for the iridium / platinum spark plugs.
Inspect spark plug for:
• Electrode wear
• Carbon deposits
• Insulator damage
If any abnormality is found for nickel spark plugs, adjust
air gap, clean with spark plug cleaner or replace them
with specified new plugs.
For iridium / platinum spark plugs, replace them with
new plugs.
Spark plug air gap
“a”
: 1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.040 – 0.043 in.)
Spark plug type
NGK: IFR6J11 (Iridium)
NOTE
NGK IFR6J11 is highly recommended for
better engine starting performance under –25
°C (–13 °F).
I2RH0B180005-01
IYSQ01181012-01
Page 401 of 1496
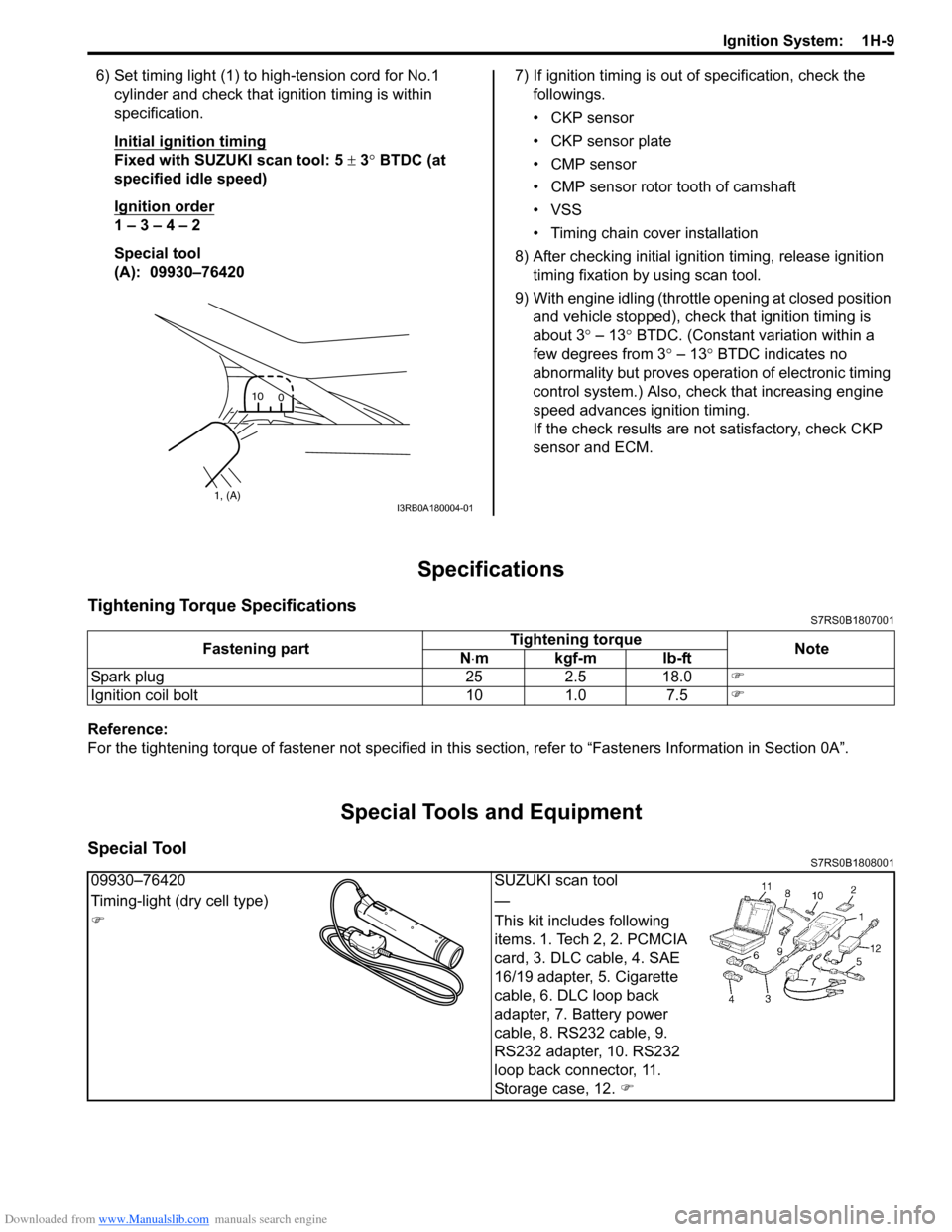
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-9
6) Set timing light (1) to high-tension cord for No.1 cylinder and check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing
Fixed with SUZUKI scan tool: 5 ± 3° BTDC (at
specified idle speed)
Ignition order
1 – 3 – 4 – 2
Special tool
(A): 09930–76420 7) If ignition timing is out
of specification, check the
followings.
• CKP sensor
• CKP sensor plate
• CMP sensor
• CMP sensor rotor tooth of camshaft
• VSS
• Timing chain cover installation
8) After checking initial igniti on timing, release ignition
timing fixation by using scan tool.
9) With engine idling (throttl e opening at closed position
and vehicle stopped), check that ignition timing is
about 3 ° – 13° BTDC. (Constant variation within a
few degrees from 3 ° – 13° BTDC indicates no
abnormality but proves operation of electronic timing
control system.) Also, check that increasing engine
speed advances ignition timing.
If the check results are not satisfactory, check CKP
sensor and ECM.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1807001
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Special ToolS7RS0B1808001
1, (A)10
0I3RB0A180004-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Spark plug 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Ignition coil bolt 10 1.0 7.5 �)
09930–76420SUZUKI scan tool
Timing-light (dry cell type) —
�) This kit includes following
items. 1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA
card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE
16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette
cable, 6. DLC loop back
adapter, 7. Battery power
cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9.
RS232 adapter, 10. RS232
loop back connector, 11.
Storage case, 12. �)
Page 468 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-1 Wheels and Tires:
Suspension
Wheels and Tires
Precautions
Precaution for Emergency Flat Tire Repair KitS7RS0B2400001
WARNING!
Flat tire repair sealant including in kit is
harmful. Be sure to observe the following.
Otherwise, your health may be ruined.
• If swallowed, get medical attention immediately.
• Keep out of reach of children.
• Select place where there is good ventilation for this work.
• If it enters eye or contacts skin, wash thoroughly with water. If anything
abnormal still rema ins, get medical
attention immediately.
• Do not discard tire containing sealant as it is. Make sure to remove sealant from tire,
referring to “Tire Repair for Emergency
Repaired-Tire with Sealant”.
• Dispose of sealant as waste oil.
CAUTION!
• When tire repaired with Emergency Flat Tire Repair Kit is brought in, remove flat
tire repair sealant from tire and repair flat
tire referring to “Tire Repair for Emergency
Repaired-Tire with Sealant”.
• Sealant expiration date is printed on bottle label. if it expires, sealant should be
replaced with a new one to ensure
emergency flat tire repair.
General Description
Tires DescriptionS7RS0B2401001
The tire is of tubeless type. The tire is designed to
operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation
pressures.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an
important influence on tire life. Heavy cornering,
excessively rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp
braking increase tire wear.
Tire Placard
The “Tire Placard” is located on the left or right door lock
pillar and should be referred to tire information.
The placard lists the maximum load, tire size and cold
tire pressure where applicable.
NOTE
Whether rim size and/or maximum load are
listed or not depends on regulations of each
country.
Inflation of Tires
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully
calculated to give a satisfacto ry ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for 3
hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should be
checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the
specifications on the “Tire Placard” located on the left
door lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure to increase when the tires
become hot during driving.
Do not bleed or reduce tire pressure after driving.
Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure”.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause:
• Hard ride
• Tire bruising or carcass damage
• Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause:
• Uneven braking
• Steering lead
• Reduced handling
• Swerve on acceleration