Shim SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 317 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-32
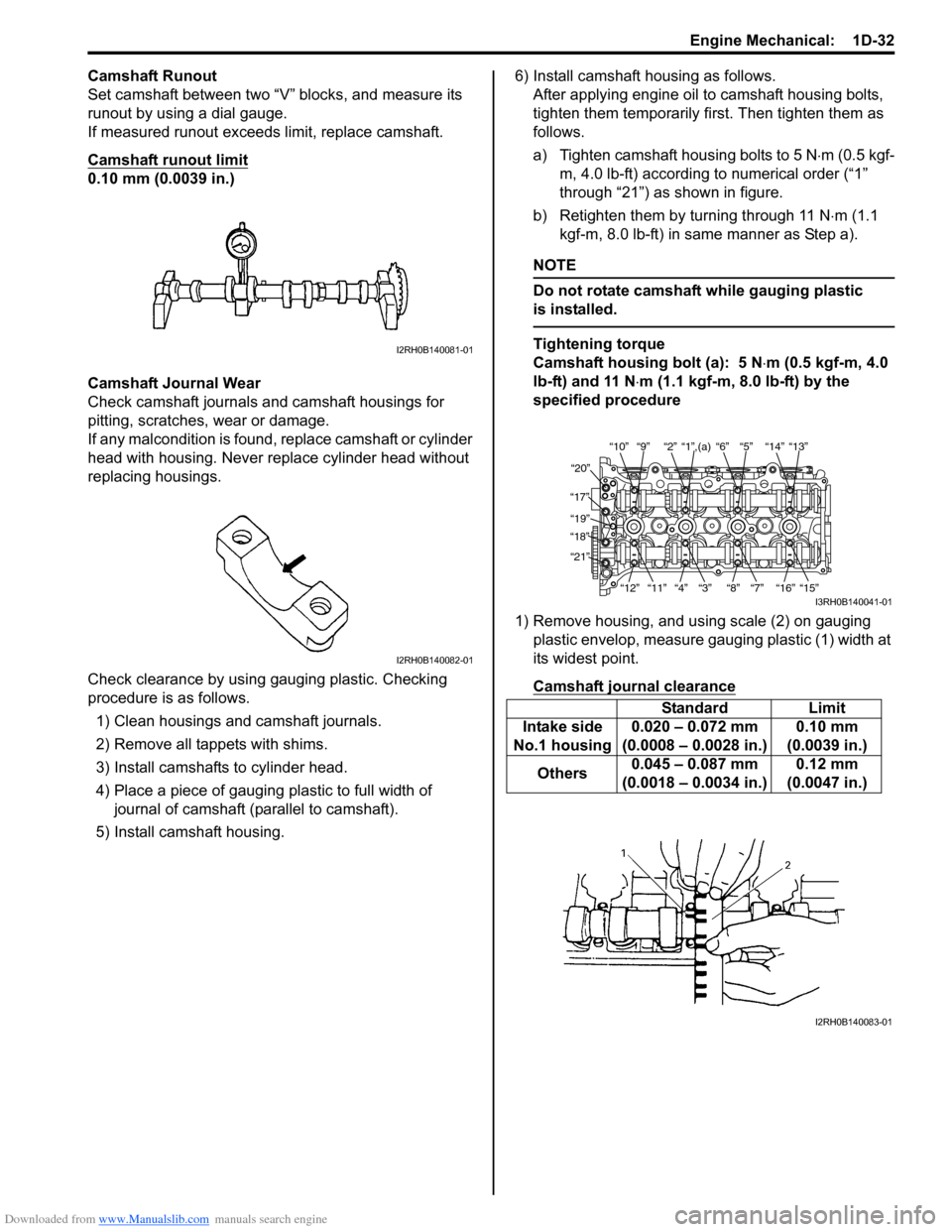
Camshaft Runout
Set camshaft between two “V” blocks, and measure its
runout by using a dial gauge.
If measured runout exceeds limit, replace camshaft.
Camshaft runout limit
0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Camshaft Journal Wear
Check camshaft journals and camshaft housings for
pitting, scratches, wear or damage.
If any malcondition is found, replace camshaft or cylinder
head with housing. Never re place cylinder head without
replacing housings.
Check clearance by using ga uging plastic. Checking
procedure is as follows.
1) Clean housings and camshaft journals.
2) Remove all tappets with shims.
3) Install camshafts to cylinder head.
4) Place a piece of gauging plastic to full width of
journal of camshaft (parallel to camshaft).
5) Install camshaft housing. 6) Install camshaft housing as follows.
After applying engine oil to camshaft housing bolts,
tighten them temporarily first. Then tighten them as
follows.
a) Tighten camshaft housing bolts to 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-
m, 4.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order (“1”
through “21”) as shown in figure.
b) Retighten them by turning through 11 N ⋅m (1.1
kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) in same manner as Step a).
NOTE
Do not rotate camshaft while gauging plastic
is installed.
Tightening torque
Camshaft housing bolt (a): 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-m, 4.0
lb-ft) and 11 N ⋅m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) by the
specified procedure
1) Remove housing, and using scale (2) on gauging plastic envelop, measure gauging plastic (1) width at
its widest point.
Camshaft journal clearanceI2RH0B140081-01
I2RH0B140082-01
Standard Limit
Intake side
No.1 housing 0.020 – 0.072 mm
(0.0008 – 0.0028 in.) 0.10 mm
(0.0039 in.)
Others 0.045 – 0.087 mm
(0.0018 – 0.0034 in.) 0.12 mm
(0.0047 in.)
“10”“9” “2” “1”,(a) “6” “5” “14” “13”
“20”
“17” “19”
“18”
“21”
“12”“11”
“4” “3” “8” “7” “16” “15”
I3RH0B140041-01
I2RH0B140083-01
Page 318 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-33 Engine Mechanical:
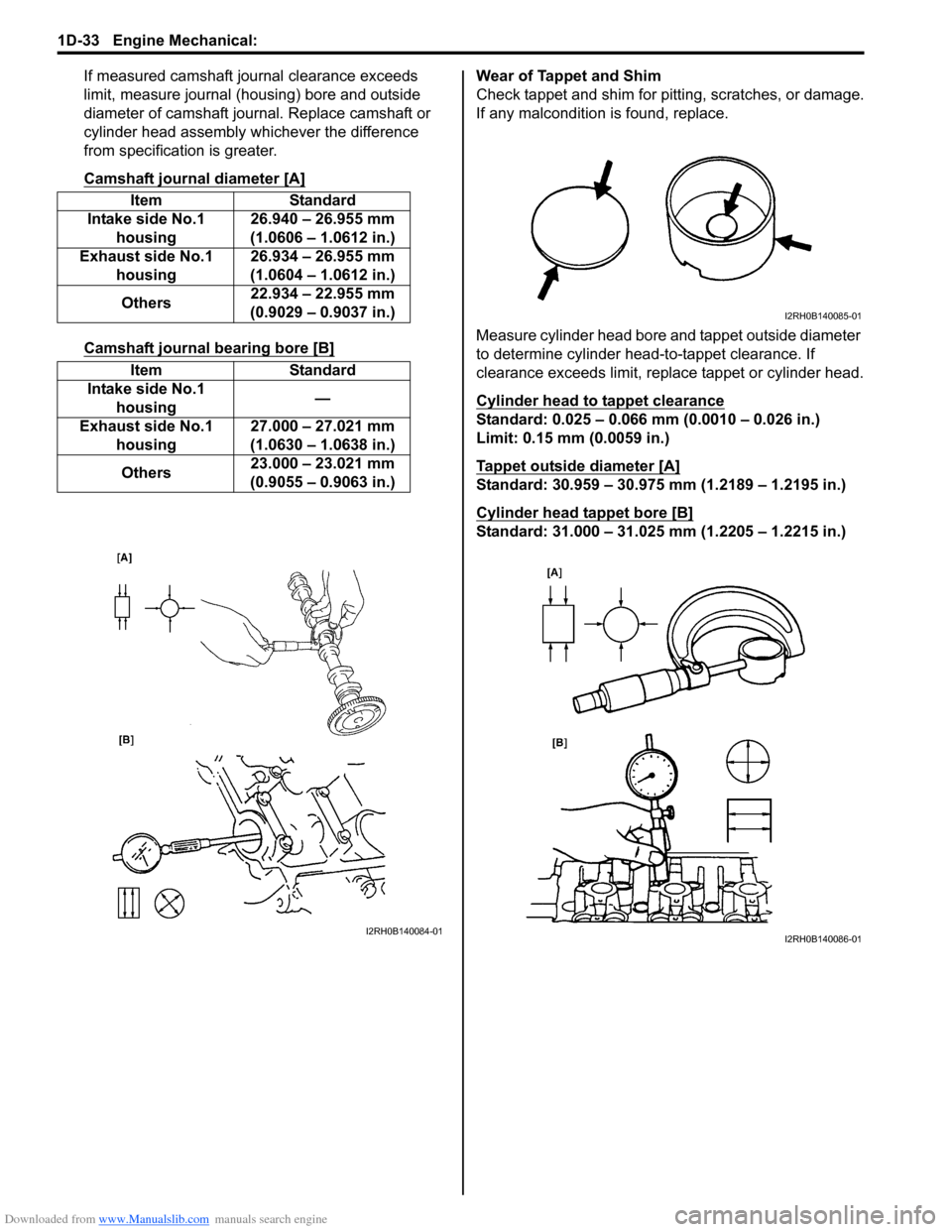
If measured camshaft journal clearance exceeds
limit, measure journal (housing) bore and outside
diameter of camshaft journal. Replace camshaft or
cylinder head assembly whichever the difference
from specification is greater.
Camshaft journal diameter [A]
Camshaft journal bearing bore [B]
Wear of Tappet and Shim
Check tappet and shim for pitting, scratches, or damage.
If any malcondition is found, replace.
Measure cylinder head bore and tappet outside diameter
to determine cylinder head-to-tappet clearance. If
clearance exceeds limit, replace tappet or cylinder head.
Cylinder head to tappet clearance
Standard: 0.025 – 0.066 mm (0.0010 – 0.026 in.)
Limit: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in.)
Tappet outside diameter [A]
Standard: 30.959 – 30.975 mm (1.2189 – 1.2195 in.)
Cylinder head tappet bore [B]
Standard: 31.000 – 31.025 mm (1.2205 – 1.2215 in.)
Item Standard
Intake side No.1 housing 26.940 – 26.955 mm
(1.0606 – 1.0612 in.)
Exhaust side No.1 housing 26.934 – 26.955 mm
(1.0604 – 1.0612 in.)
Others 22.934 – 22.955 mm
(0.9029 – 0.9037 in.)
Item Standard
Intake side No.1 housing —
Exhaust side No.1 housing 27.000 – 27.021 mm
(1.0630 – 1.0638 in.)
Others 23.000 – 23.021 mm
(0.9055 – 0.9063 in.)
I2RH0B140084-01
I2RH0B140085-01
I2RH0B140086-01
Page 320 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-35 Engine Mechanical:
Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B1406024
Removal1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Strainer Removal and Installation in Section 1E”.
3) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
4) Remove timing chain cover referring to Steps 2) to 11) of “Removal” in “Tim ing Chain Cover Removal
and Installation”.
5) Remove timing chain referring to Steps 2) to 6) of “Removal” in “Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Removal and Installation”.
6) Remove intake and exhaust camshafts referring to Steps 3) to 8) of “Removal” in “Camshaft, Tappet and
Shim Removal and Installation”.
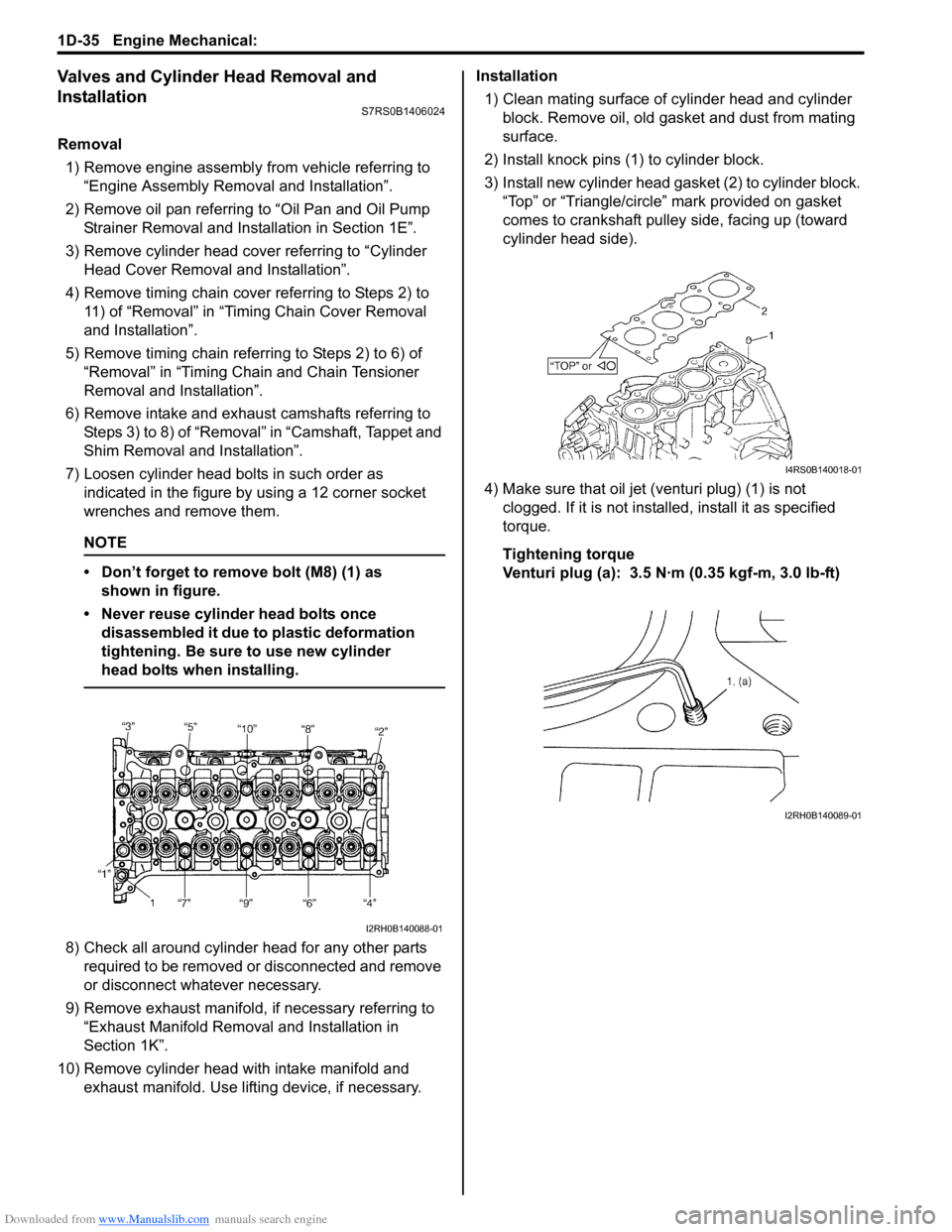
7) Loosen cylinder head bolts in such order as indicated in the figure by using a 12 corner socket
wrenches and remove them.
NOTE
• Don’t forget to remove bolt (M8) (1) as shown in figure.
• Never reuse cylinder head bolts once disassembled it due to plastic deformation
tightening. Be sure to use new cylinder
head bolts when installing.
8) Check all around cylinder head for any other parts required to be removed or disconnected and remove
or disconnect whatever necessary.
9) Remove exhaust manifold, if necessary referring to
“Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation in
Section 1K”.
10) Remove cylinder head wi th intake manifold and
exhaust manifold. Use lifting device, if necessary. Installation
1) Clean mating surface of cylinder head and cylinder block. Remove oil, old gasket and dust from mating
surface.
2) Install knock pins (1) to cylinder block.
3) Install new cylinder head gasket (2) to cylinder block. “Top” or “Triangle/circle” mark provided on gasket
comes to crankshaft pulley side, facing up (toward
cylinder head side).
4) Make sure that oil jet (venturi plug) (1) is not clogged. If it is not install ed, install it as specified
torque.
Tightening torque
Venturi plug (a): 3.5 N·m (0.35 kgf-m, 3.0 lb-ft)
I2RH0B140088-01
I4RS0B140018-01
I2RH0B140089-01
Page 321 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-36
5) Install cylinder head to cylinder block.Apply engine oil to new cylinder head bolts and
tighten them gradually as follows.
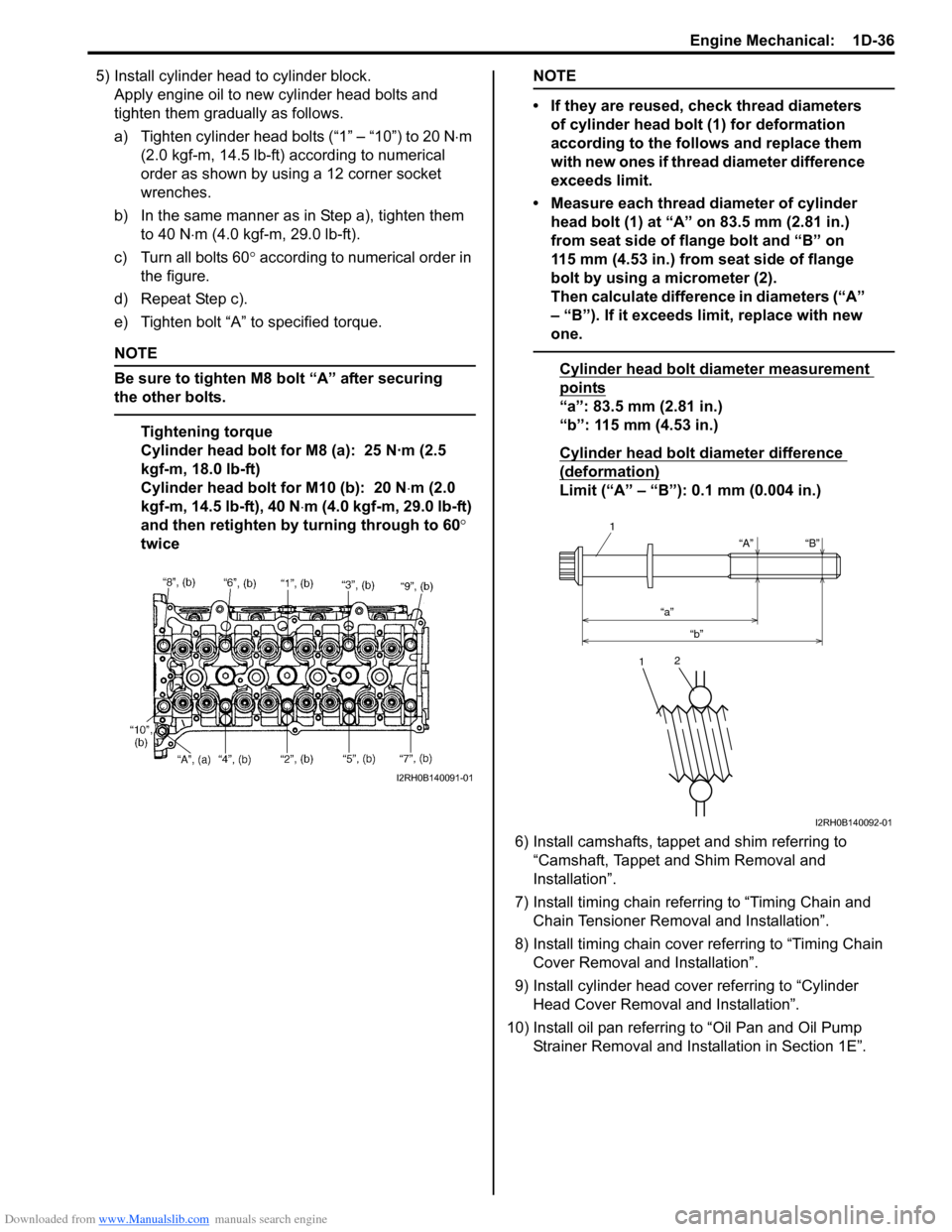
a) Tighten cylinder head bolts (“1” – “10”) to 20 N ⋅m
(2.0 kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft) according to numerical
order as shown by using a 12 corner socket
wrenches.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them to 40 N ⋅m (4.0 kgf-m, 29.0 lb-ft).
c) Turn all bolts 60 ° according to numerical order in
the figure.
d) Repeat Step c).
e) Tighten bolt “A” to specified torque.
NOTE
Be sure to tighten M8 bolt “A” after securing
the other bolts.
Tightening torque
Cylinder head bolt for M8 (a): 25 N·m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
Cylinder head bolt for M10 (b): 20 N ⋅m (2.0
kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft), 40 N ⋅m (4.0 kgf-m, 29.0 lb-ft)
and then retighten by turning through to 60 °
twice
NOTE
• If they are reused, check thread diameters of cylinder head bolt (1) for deformation
according to the follows and replace them
with new ones if thread diameter difference
exceeds limit.
• Measure each thread diameter of cylinder head bolt (1) at “A” on 83.5 mm (2.81 in.)
from seat side of flange bolt and “B” on
115 mm (4.53 in.) from seat side of flange
bolt by using a micrometer (2).
Then calculate difference in diameters (“A”
– “B”). If it exceeds limit, replace with new
one.
Cylinder head bolt diameter measurement
points
“a”: 83.5 mm (2.81 in.)
“b”: 115 mm (4.53 in.)
Cylinder head bolt diameter difference
(deformation)
Limit (“A” – “B”): 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
6) Install camshafts, tappet and shim referring to “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and
Installation”.
7) Install timing chain referring to “Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Remova l and Installation”.
8) Install timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation”.
9) Install cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
10) Install oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Strainer Removal and Inst allation in Section 1E”.
I2RH0B140091-01
“A”
“a” “b” “B”
1
1
2
I2RH0B140092-01
Page 342 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-57 Engine Mechanical:
11) Install flywheel (drive plate for A/T).Using special tool, lock flyw heel or drive plate, and
tighten flywheel or drive plate bolts to specified
torque.
NOTE
Use new flywheel or drive plate bolts.
Special tool
(A): 09924–17811
Tightening torque
Flywheel or drive plate bolt (a): 70 N·m (7.0 kgf-
m, 51.0 lb-ft)
12) Install piston and connecting rod referring to “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation”.
13) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
14) Install camshafts, tappet and shim referring to “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and
Installation”.
15) Install timing chain referring to “Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Removal and Installation”.
16) Install timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation”.
17) Install cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
18) Install oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Strainer Removal and Installation in Section 1E”
19) Install engine assembly to vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
Crankshaft InspectionS7RS0B1406037
Crankshaft Runout
Using a dial gauge, measure runout at center journal.
Rotate crankshaft slowly. If runout exceeds its limit,
replace crankshaft.
Crankshaft runout
Limit: 0.02 mm (0.0008 in.)
Crankshaft Thrust Play
1) Measure this play with crankshaft set in cylinder block in the normal manner, that is with thrust
bearing (1) and journal bearing caps installed.
Thickness of crankshaft thrust bearing
Standard: 2.500 mm (0.0984 in.)
Oversize (0.125 mm (0.0049 in.)): 2.563 mm
(0.1009 in.)
I6RS0B141029-01
I2RH0B140135-01
I2RH0B140136-01
Page 350 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-65 Engine Mechanical:
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Air Cleaner Components”
“Throttle Body and Intake Manifold Components”
“Engine Mountings Components”
“Timing Chain Cover Components”
“Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components”
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components”
“Valves and Cylinder Head Components”
“Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders Components”
“Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
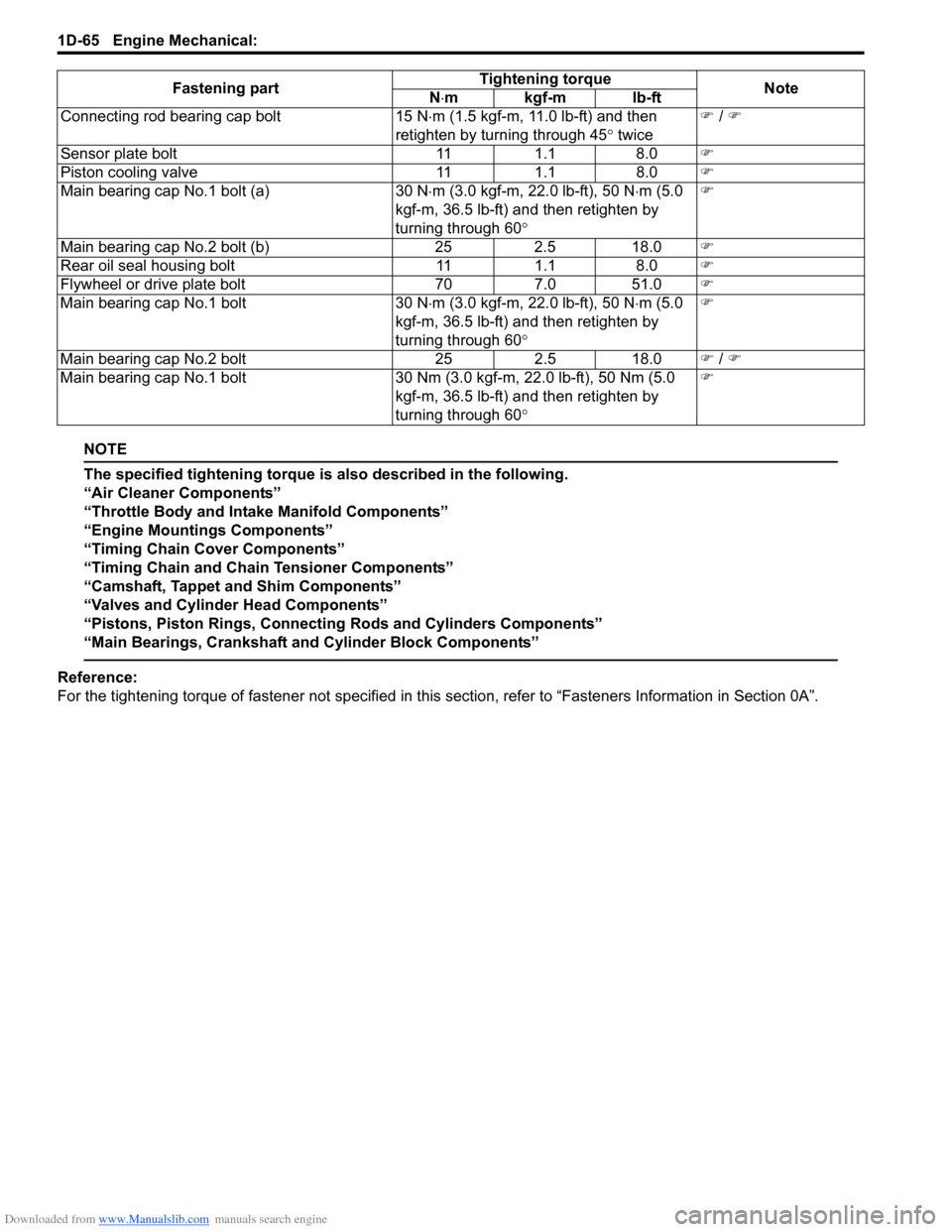
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt
15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then
retighten by turning through 45 ° twice �)
/ �)
Sensor plate bolt 111.1 8.0 �)
Piston cooling valve 111.1 8.0 �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt (a) 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt (b) 252.5 18.0 �)
Rear oil seal housing bolt 111.1 8.0 �)
Flywheel or drive plate bolt 707.0 51.0 �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt 252.5 18.0 �) / �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt 30 Nm (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 Nm (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Fastening part
Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Page 351 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-66
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B1408001
NOTE
Required service material is also described in the following.
“Timing Chain Cover Components”
“Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components”
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components”
“Valves and Cylinder Head Components”
“Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders Components”
“Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block Components”
Special ToolS7RS0B1408002
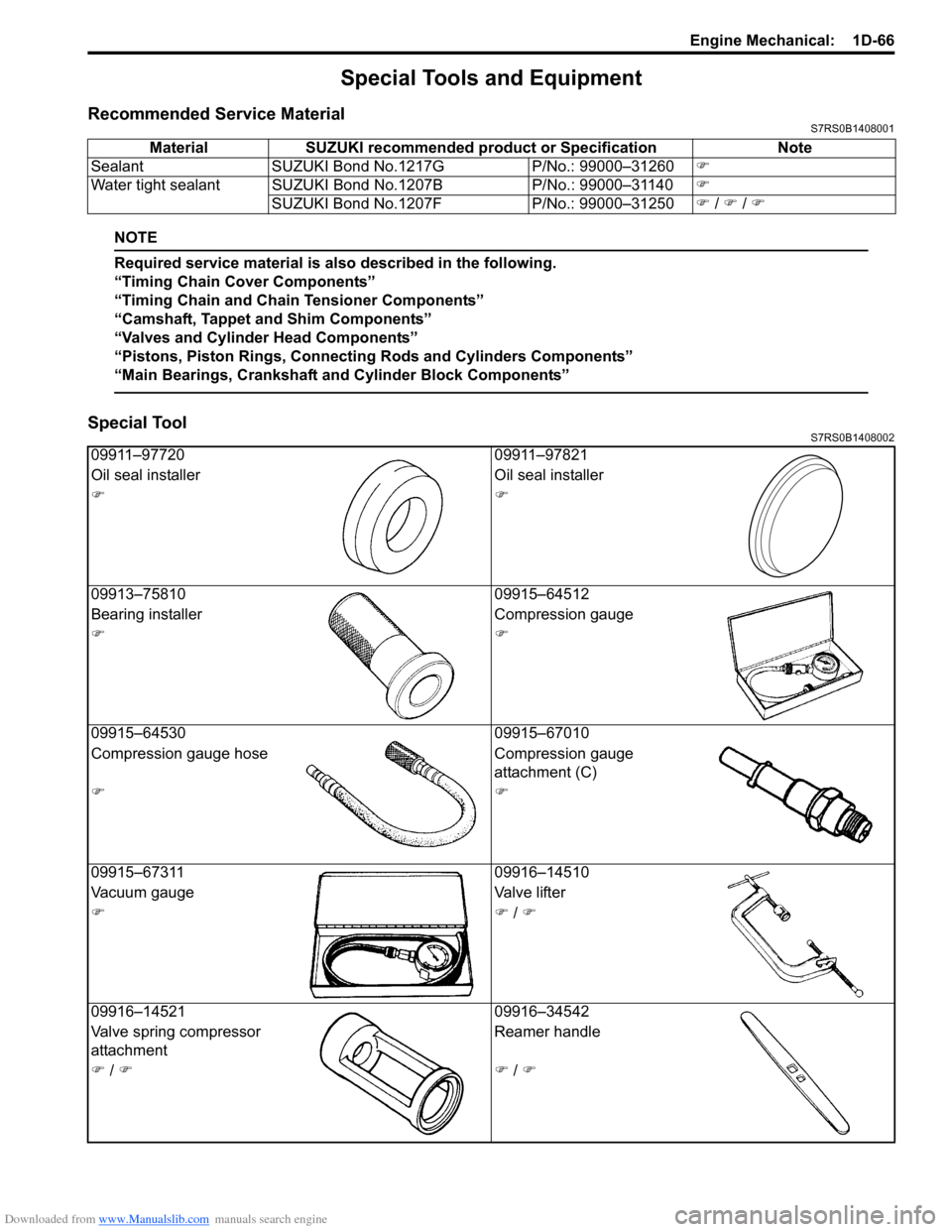
Material SUZUKI recommended product or Specification Note
Sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1217G P/No.: 99000–31260�)
Water tight sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1207B P/No.: 99000–31140�)
SUZUKI Bond No.1207F P/No.: 99000–31250�) / �) / �)
09911–97720 09911–97821
Oil seal installer Oil seal installer
�)�)
09913–75810 09915–64512
Bearing installer Compression gauge
�)�)
09915–64530 09915–67010
Compression gauge hose Compression gauge
attachment (C)
�)�)
09915–67311 09916–14510
Vacuum gauge Valve lifter
�)�) / �)
09916–14521 09916–34542
Valve spring compressor
attachment Reamer handle
�) / �)�) / �)
Page 432 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2A-1 Suspension General Diagnosis:
Suspension
Suspension General Diagnosis
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Suspension, Wheels and Tires Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B2104001
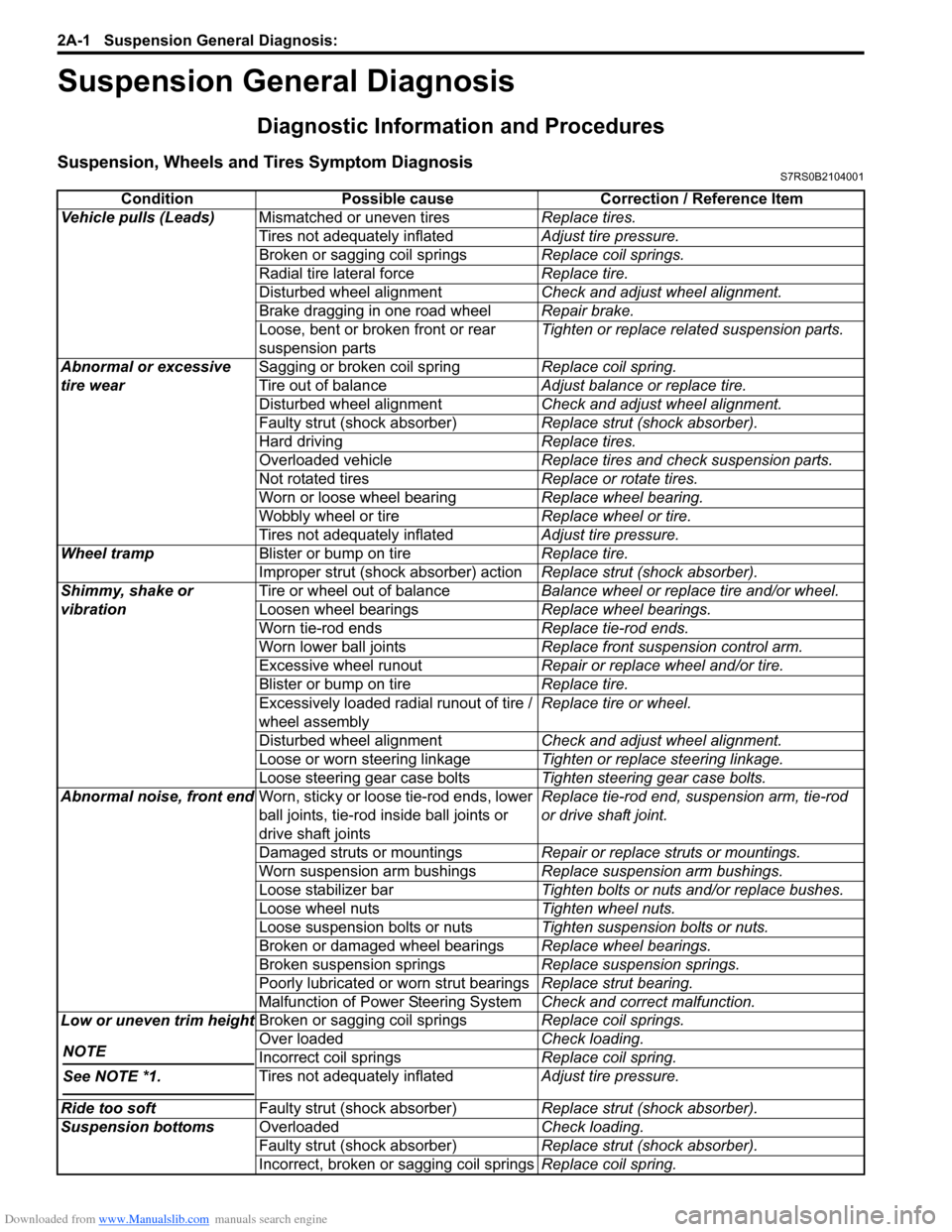
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Vehicle pulls (Leads) Mismatched or uneven tires Replace tires.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Radial tire lateral force Replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Brake dragging in one road wheel Repair brake.
Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts Tighten or replace related suspension parts.
Abnormal or excessive
tire wear Sagging or broken coil spring
Replace coil spring.
Tire out of balance Adjust balance or replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Hard driving Replace tires.
Overloaded vehicle Replace tires and check suspension parts.
Not rotated tires Replace or rotate tires.
Worn or loose wheel bearing Replace wheel bearing.
Wobbly wheel or tire Replace wheel or tire.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Wheel tramp Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Improper strut (shock absorber) action Replace strut (shock absorber).
Shimmy, shake or
vibration Tire or wheel out of balance
Balance wheel or replace tire and/or wheel.
Loosen wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Worn tie-rod ends Replace tie-rod ends.
Worn lower ball joints Replace front suspension control arm.
Excessive wheel runout Repair or replace wheel and/or tire.
Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Excessively loaded radial runout of tire /
wheel assembly Replace tire or wheel.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Loose or worn steering linkage Tighten or replace steering linkage.
Loose steering gear case bolts Tighten steering gear case bolts.
Abnormal noise, front end Worn, sticky or loose tie-rod ends, lower
ball joints, tie-rod in side ball joints or
drive shaft joints Replace tie-rod end, su
spension arm, tie-rod
or drive shaft joint.
Damaged struts or mountings Repair or replace struts or mountings.
Worn suspension arm bushings Replace suspension arm bushings.
Loose stabilizer bar Tighten bolts or nuts and/or replace bushes.
Loose wheel nuts Tighten wheel nuts.
Loose suspension bolts or nuts Tighten suspension bolts or nuts.
Broken or damaged wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Broken suspension springs Replace suspension springs.
Poorly lubricated or worn strut bearings Replace strut bearing.
Malfunction of Power Steering System Check and correct malfunction.
Low or uneven trim height
NOTE
See NOTE *1.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Over loaded Check loading.
Incorrect coil springs Replace coil spring.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Ride too soft Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Suspension bottoms Overloaded Check loading.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Incorrect, broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil spring.
Page 472 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-5 Wheels and Tires:
Radial Tire Lead / Pull DescriptionS7RS0B2401006
“Lead / Pull” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight
path on a level road even with no pressure on the
steering wheel.
Lead is usually caused by the following conditions.
• Improper tire and wheel alignment.
• Uneven brake assemblies.
• Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead in a
vehicle. An example of this is placement of the belt. Off
center belts on radial tires can cause the tire to develop
a side force while rolling straight down the road. If one
side of the tire has a little larger diameter than the other,
the tire will tend to roll to one side. This will develop a
side force which can produce vehicle lead.
The procedure in the figure (Lead Diagnosis) should be
used to make sure that wheel alignment is not mistaken
for tire lead.
• Part of the lead diagnosis procedure is different from the proper tire rotation pattern currently in the owner
and service manuals. If a medium to high mileage tire
is moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to
check that ride roughness has not developed.
• Rear tires will not cause lead.
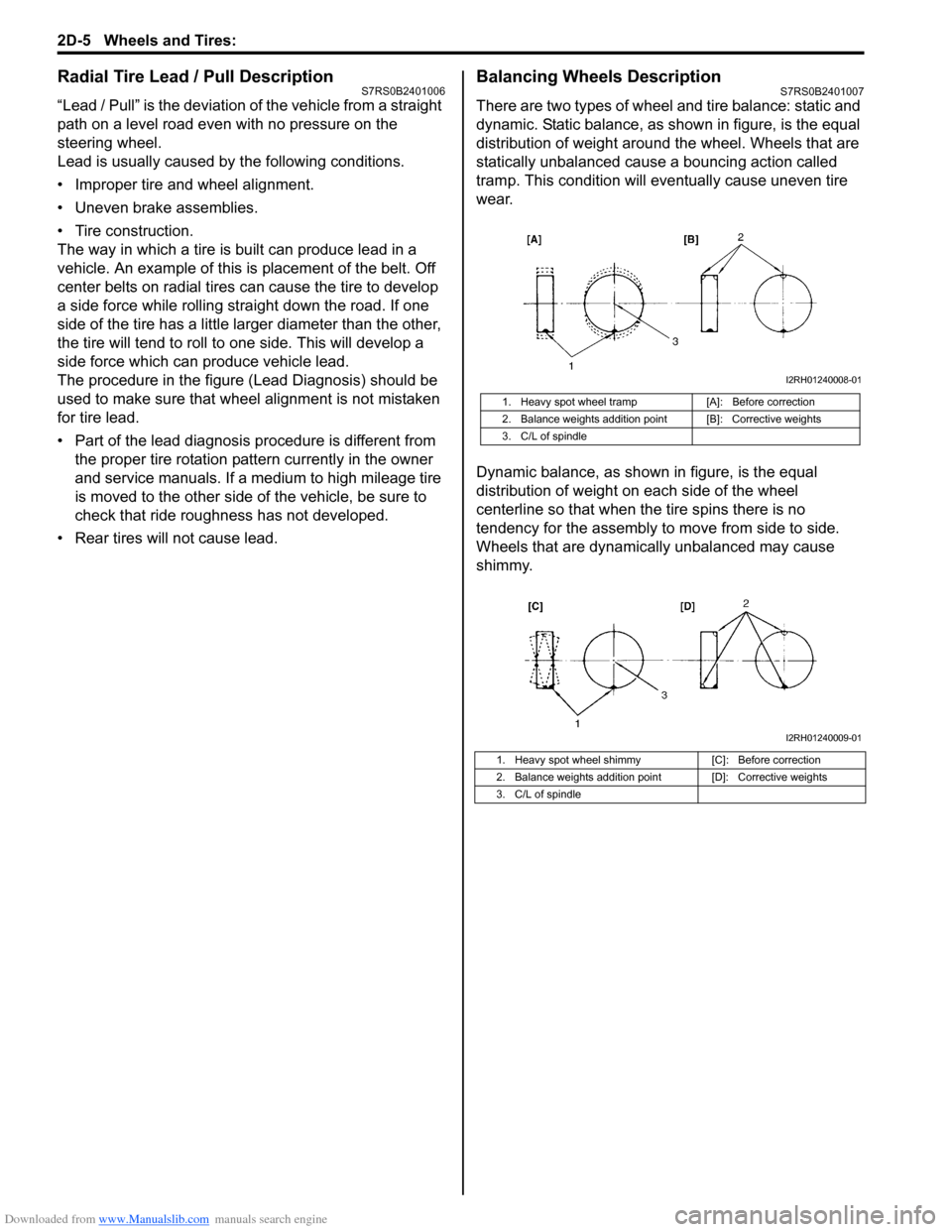
Balancing Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401007
There are two types of wheel an d tire balance: static and
dynamic. Static balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight around the wheel. Wheels that are
statically unbalanced cause a bouncing action called
tramp. This condition will eventually cause uneven tire
wear.
Dynamic balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight on each side of the wheel
centerline so that when the tire spins there is no
tendency for the assembly to move from side to side.
Wheels that are dynamically unbalanced may cause
shimmy.
1. Heavy spot wheel tramp [A]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [B]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
1. Heavy spot wheel shimmy [C]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [D]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
I2RH01240008-01
I2RH01240009-01
Page 517 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Brakes: 4B-1
Brakes
Front Brakes
Repair Instructions
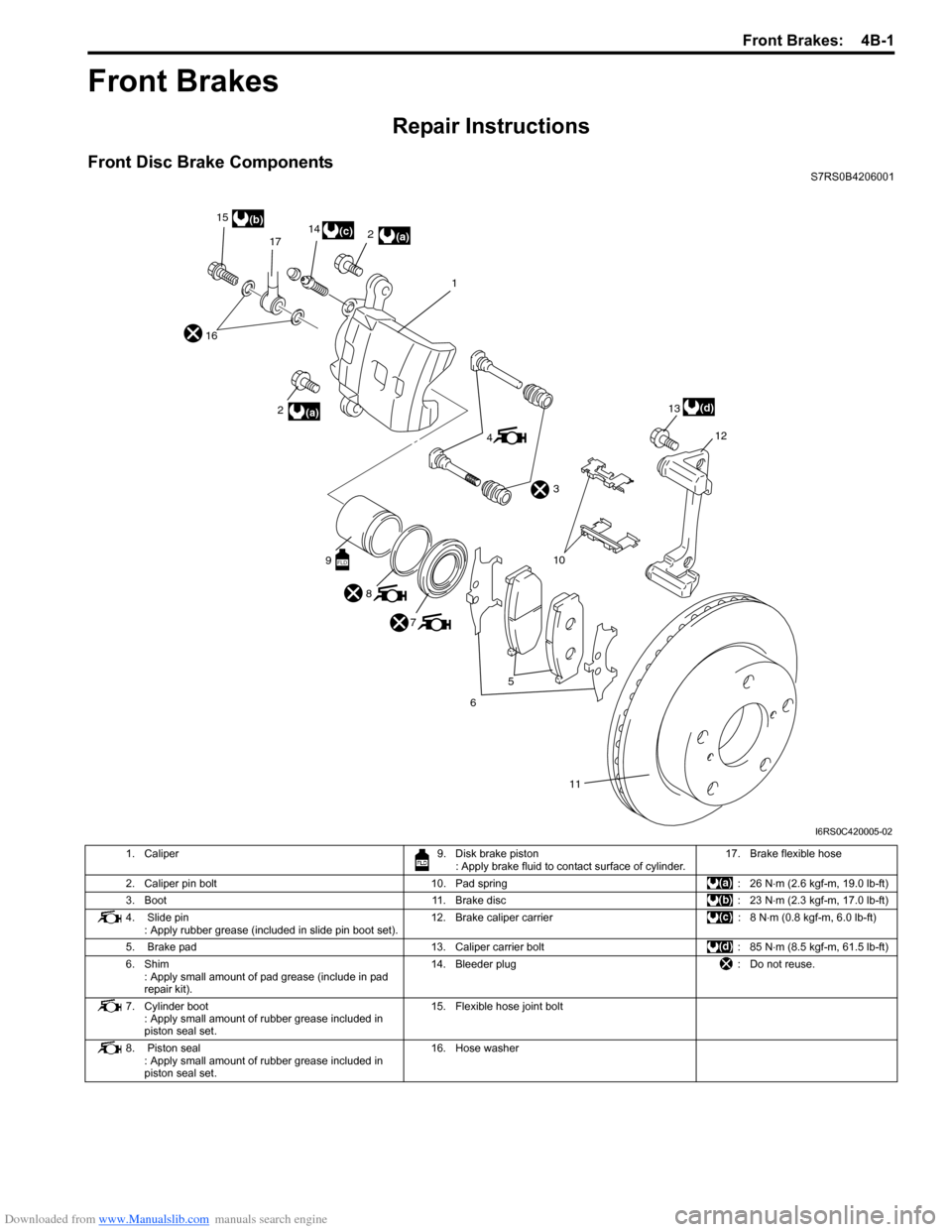
Front Disc Brake ComponentsS7RS0B4206001
11
5
6
10
4
1
16
17
12
8
7
3
2(a)
15
(b)
14(c)2(a)
13
(d)
9
FLD
I6RS0C420005-02
1. Caliper 9. Disk brake piston
: Apply brake fluid to contact surface of cylinder. 17. Brake flexible hose
2. Caliper pin bolt 10. Pad spring : 26 N⋅m (2.6 kgf-m, 19.0 lb-ft)
3. Boot 11. Brake disc: 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
4. Slide pin : Apply rubber grease (included in slide pin boot set). 12. Brake caliper carrier
: 8 N⋅m (0.8 kgf-m, 6.0 lb-ft)
5. Brake pad 13. Caliper carrier bolt : 85 N⋅m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
6. Shim : Apply small amount of pad grease (include in pad
repair kit). 14. Bleeder plug
: Do not reuse.
7. Cylinder boot : Apply small amount of rubber grease included in
piston seal set. 15. Flexible hose joint bolt
8. Piston seal : Apply small amount of rubber grease included in
piston seal set. 16. Hose washer