range SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 281 of 1496
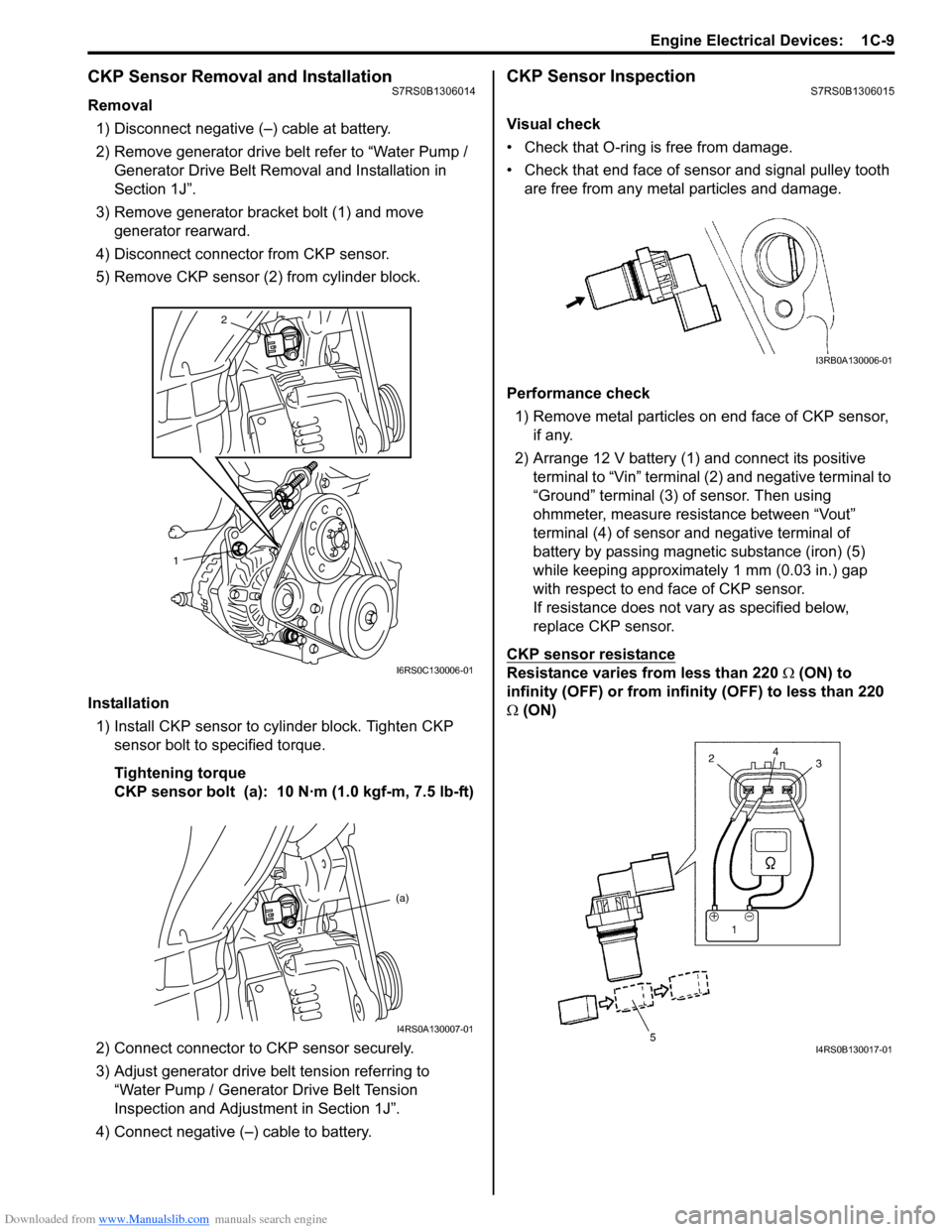
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-9
CKP Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306014
Removal1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove generator drive belt refer to “Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Remo val and Installation in
Section 1J”.
3) Remove generator bracket bolt (1) and move generator rearward.
4) Disconnect connector from CKP sensor.
5) Remove CKP sensor (2) from cylinder block.
Installation 1) Install CKP sensor to cylinder block. Tighten CKP sensor bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
CKP sensor bolt (a): 10 N·m (1.0 kgf-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to CKP sensor securely.
3) Adjust generator drive belt tension referring to “Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension
Inspection and Adjustment in Section 1J”.
4) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
CKP Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306015
Visual check
• Check that O-ring is free from damage.
• Check that end face of sensor and signal pulley tooth are free from any metal particles and damage.
Performance check 1) Remove metal particles on end face of CKP sensor, if any.
2) Arrange 12 V battery (1) and connect its positive terminal to “Vin” terminal (2) and negative terminal to
“Ground” terminal (3) of sensor. Then using
ohmmeter, measure resistance between “Vout”
terminal (4) of sensor and negative terminal of
battery by passing magnetic substance (iron) (5)
while keeping approximately 1 mm (0.03 in.) gap
with respect to end face of CKP sensor.
If resistance does not vary as specified below,
replace CKP sensor.
CKP sensor resistance
Resistance varies from less than 220 Ω (ON) to
infinity (OFF) or from infinity (OFF) to less than 220
Ω (ON)
2
1
I6RS0C130006-01
(a)
I4RS0A130007-01
I3RB0A130006-01
I4RS0B130017-01
Page 286 of 1496
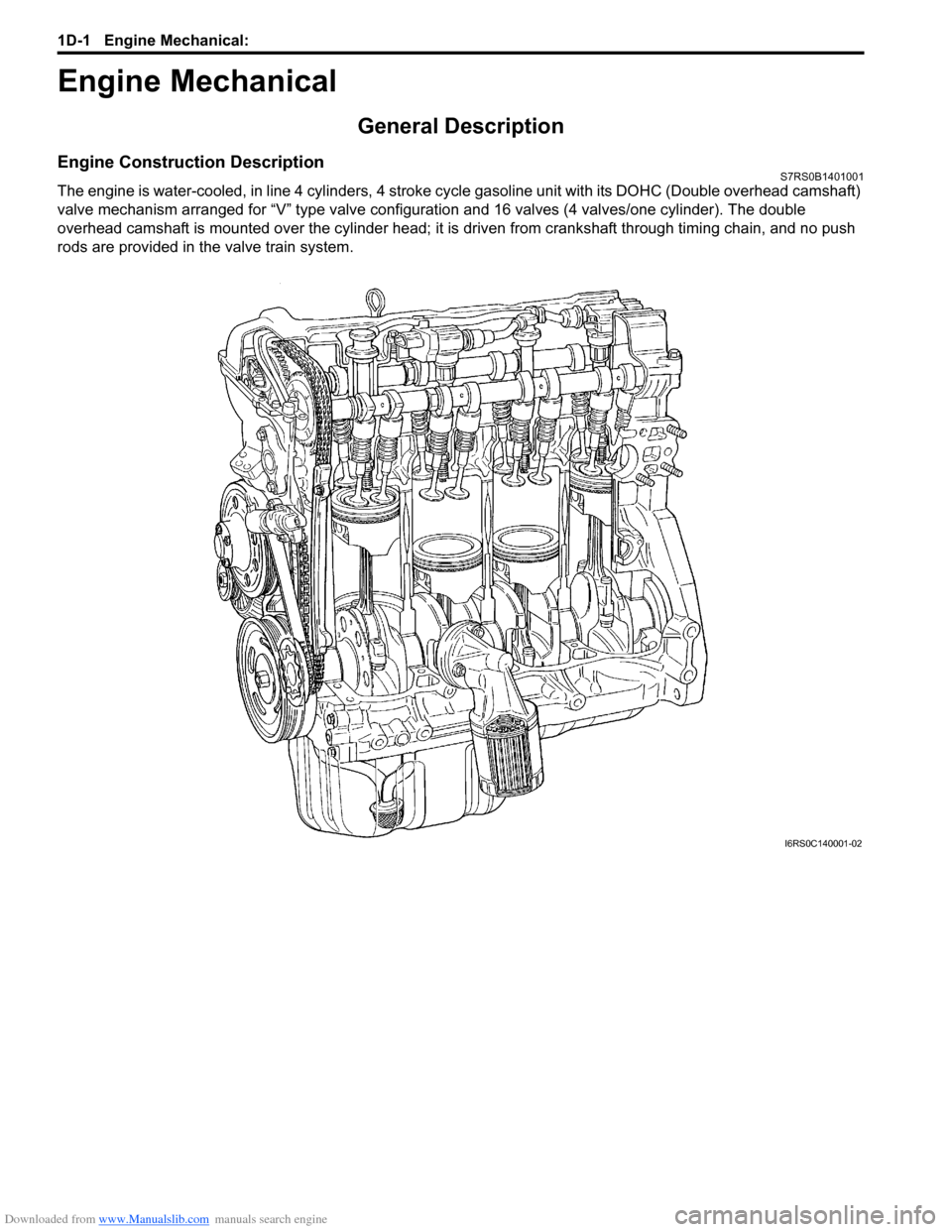
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-1 Engine Mechanical:
Engine
Engine Mechanical
General Description
Engine Construction DescriptionS7RS0B1401001
The engine is water-cooled, in line 4 cylinders, 4 stroke cycle gasoline unit with its DOHC (Double overhead camshaft)
valve mechanism arranged for “V” type valve configurat ion and 16 valves (4 valves/one cylinder). The double
overhead camshaft is mounted over the cy linder head; it is driven from crankshaft through timing chain, and no push
rods are provided in the valve train system.
I6RS0C140001-02
Page 287 of 1496
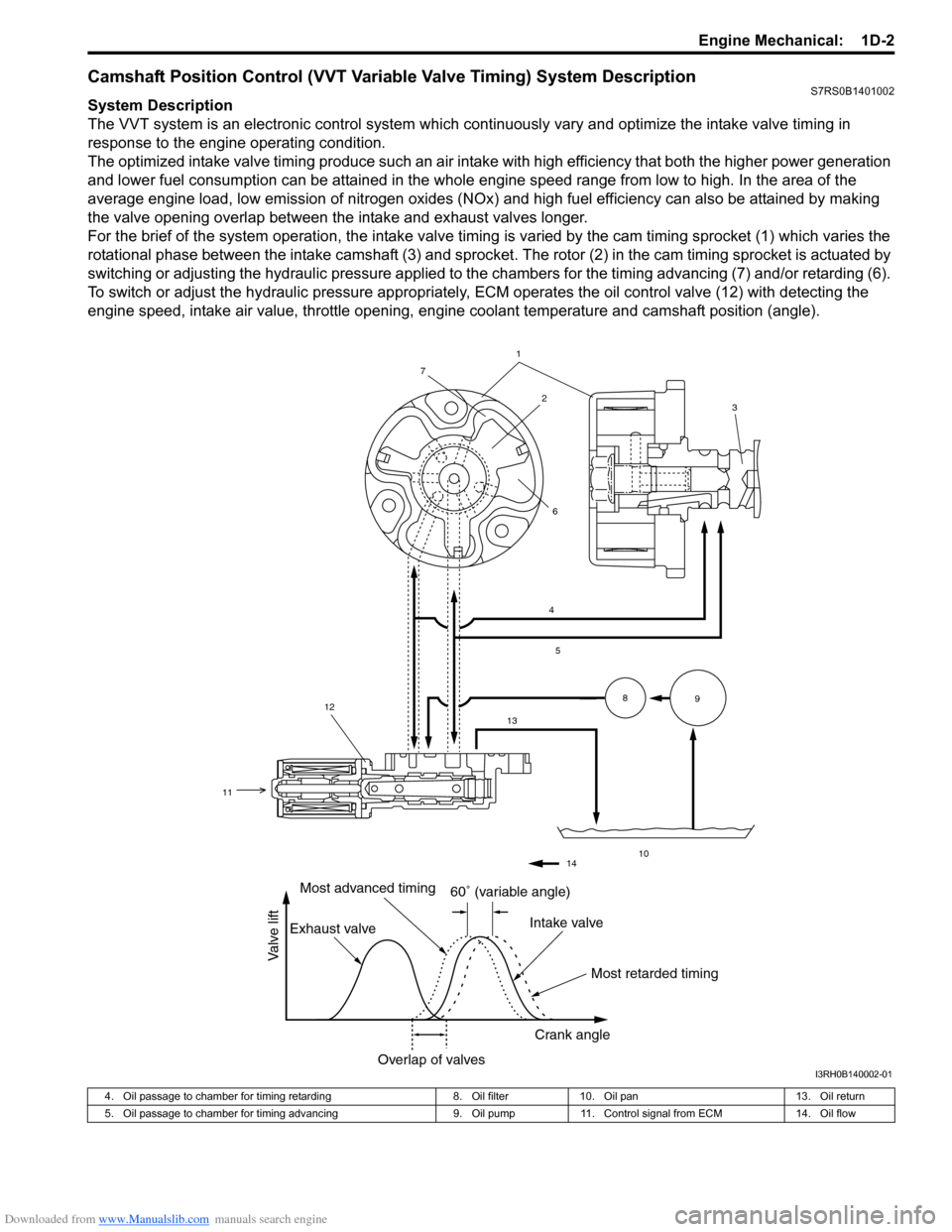
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
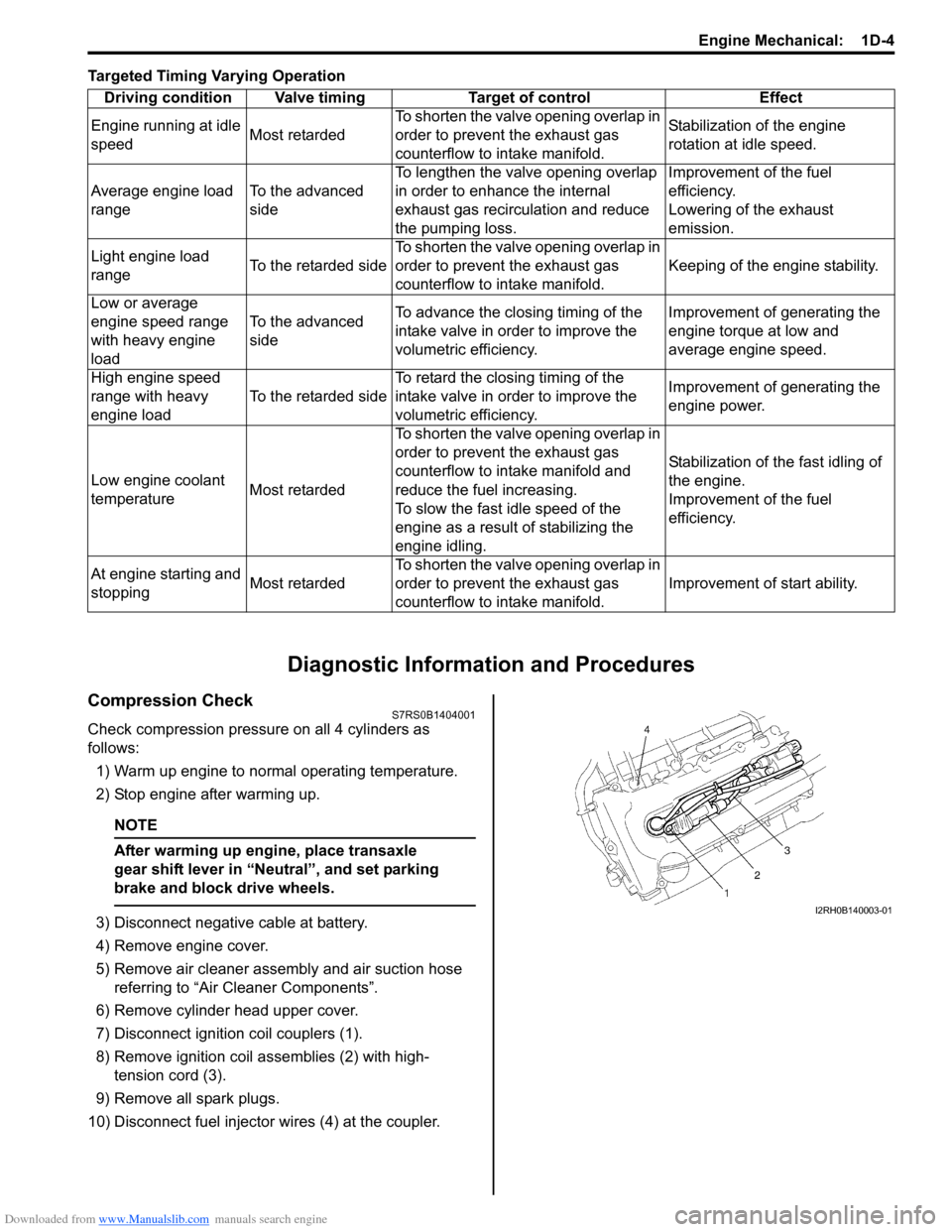
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 302 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-17 Engine Mechanical:
Engine Assembly Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1406011
NOTE
After replacing electric throttle body
assembly, perform calibration of throttle
valve referring to “Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1C”.
Removal1) Relieve fuel pressure according to “Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure in Section 1G”.
2) Disconnect negative and pos itive cable at battery.
3) Remove battery and tray.
4) Remove engine hood after disconnecting windshield washer hose.
5) Remove right and left side engine under covers.
6) Remove A/C compressor belt by referring to “Compressor Drive Belt Remo val and Installation in
Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive Belt Removal and
Installation in Section 7B”.
7) Drain engine oil, transaxle oil and coolant.
8) Remove cowl top plate referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
9) Remove air cleaner assembly referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
10) With hose connected, detach A/C compressor from its bracket (A/C model) referring to “Compressor
Assembly Removal and Installation in Section 7B” or
“Compressor Assembly Removal and Installation in
Section 7B”.
CAUTION!
Suspend removed A/C compressor at a place
where no damage will be caused during
removal and installation of engine assembly.
11) Remove intake manifold rear stiffener (1) from intake manifold and cylinder block. 12) Disconnect the following electric wires:
• MAP sensor (1)
• ECT sensor (2)
•EGR valve (3)
• CMP sensor (4)
• Electric throttle body assembly (5)
• Ignition coil assembly (6)
• Injectors (7)
• Heated oxygen sensor No. 2 (8) and No. 1 (9)
• Oil control valve (10)
• Engine oil pressure switch (11)
• CKP sensor (12)
• Knock sensor (13)
• Back up light switch (14)
• Generator (15)
• Starting motor (16)
• Ground terminal (17) from intake manifold
• Battery ground terminal (18) from exhaust manifold
• Battery ground cable (19) from transaxle
• Magnet clutch switch of A/C compressor (A/C model)
• Each wire harness clamps
• Output shaft speed sensor (VSS) (34) (A/T model)
• Solenoid valve (33) (A/T model)
• Transmission range sensor (32) (A/T model)
• Input shaft speed sensor (31) (A/T model)
13) Remove fuse box from its bracket.
14) Disconnect the following cables: • Gear select control cable (23) (M/T model)
• Gear shift control cable (24) (M/T model)
• A/T select cable (A/T model)
15) Disconnect the following hoses: • Brake booster hose (26) from intake manifold
• Radiator inlet and outlet hoses (20) from each pipe
• Heater inlet and outlet hoses (21) from each pipe
• Fuel feed hoses (22) from fuel feed pipe
• EVAP canister purge valve hose (30) from purge pipe
• A/T fluid cooler hoses (A/T model)
16) With hose connected, detach clutch operating cylinder (25). (M/T model)
CAUTION!
Suspend removed clutch operating cylinder
at a place where no damage will be caused
during removal and installation of engine
assembly.
1
I6RS0B141014-01
Page 310 of 1496
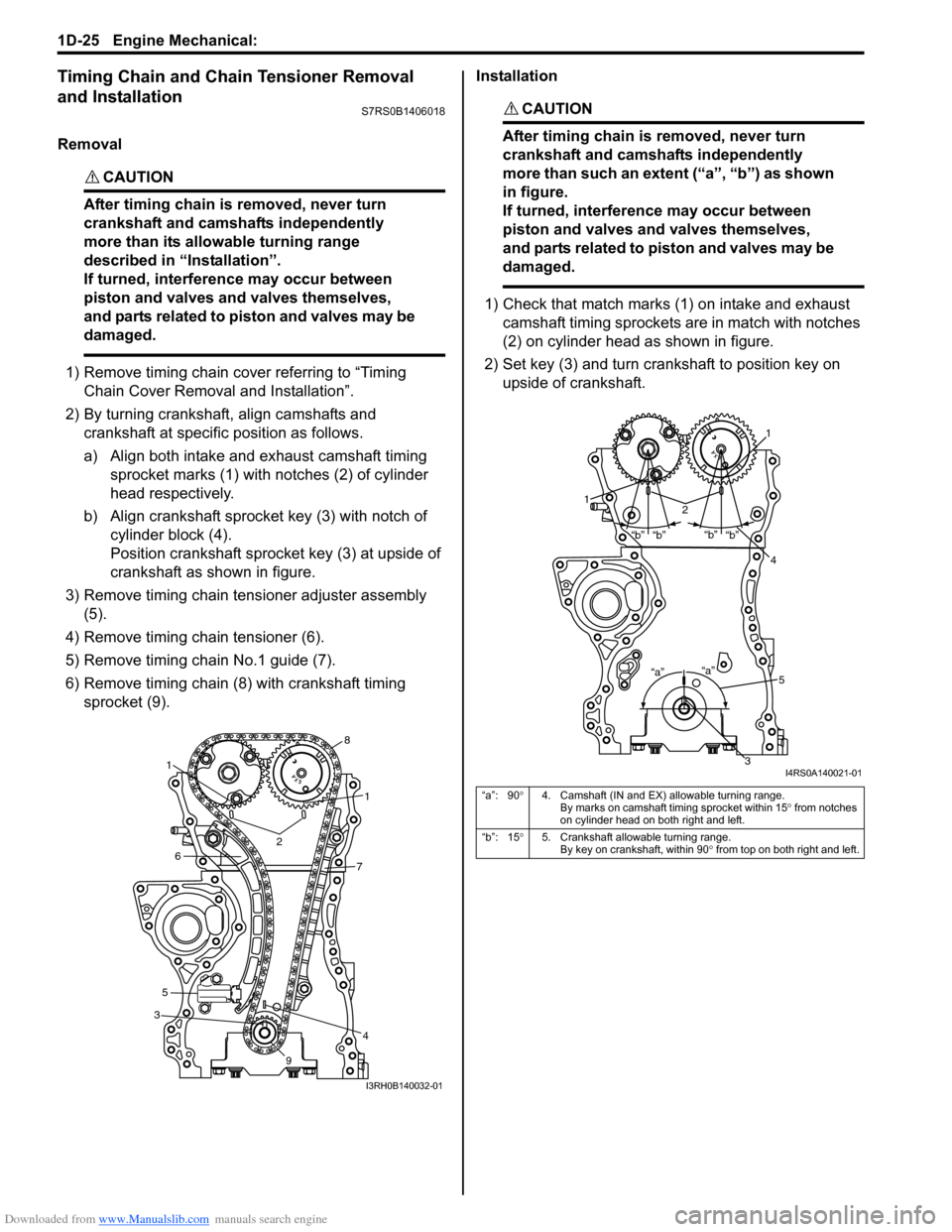
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-25 Engine Mechanical:
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Removal
and Installation
S7RS0B1406018
Removal
CAUTION!
After timing chain is removed, never turn
crankshaft and camshafts independently
more than its allowable turning range
described in “Installation”.
If turned, interferen ce may occur between
piston and valves and valves themselves,
and parts related to piston and valves may be
damaged.
1) Remove timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation”.
2) By turning crankshaft, align camshafts and crankshaft at specific position as follows.
a) Align both intake and exhaust camshaft timing sprocket marks (1) with notches (2) of cylinder
head respectively.
b) Align crankshaft sprocket key (3) with notch of cylinder block (4).
Position crankshaft sprocke t key (3) at upside of
crankshaft as shown in figure.
3) Remove timing chain tensioner adjuster assembly (5).
4) Remove timing chain tensioner (6).
5) Remove timing chain No.1 guide (7).
6) Remove timing chain (8) with crankshaft timing sprocket (9). Installation
CAUTION!
After timing chain is removed, never turn
crankshaft and camshafts independently
more than such an extent (“a”, “b”) as shown
in figure.
If turned, interferen
ce may occur between
piston and valves and valves themselves,
and parts related to piston and valves may be
damaged.
1) Check that match marks (1) on intake and exhaust camshaft timing sprockets are in match with notches
(2) on cylinder head as shown in figure.
2) Set key (3) and turn crankshaft to position key on upside of crankshaft.
3
4
1
1
2
5
67
8
9
I3RH0B140032-01
“a”: 90 °4. Camshaft (IN and EX) allowable turning range.
By marks on camshaft timing sprocket within 15 ° from notches
on cylinder head on both right and left.
“b”: 15 °5. Crankshaft allowable turning range.
By key on crankshaft, within 90 ° from top on both right and left.
“a”
“b”
“b”“b”
“b”
“a”
1
12
4
3
5
I4RS0A140021-01
Page 326 of 1496
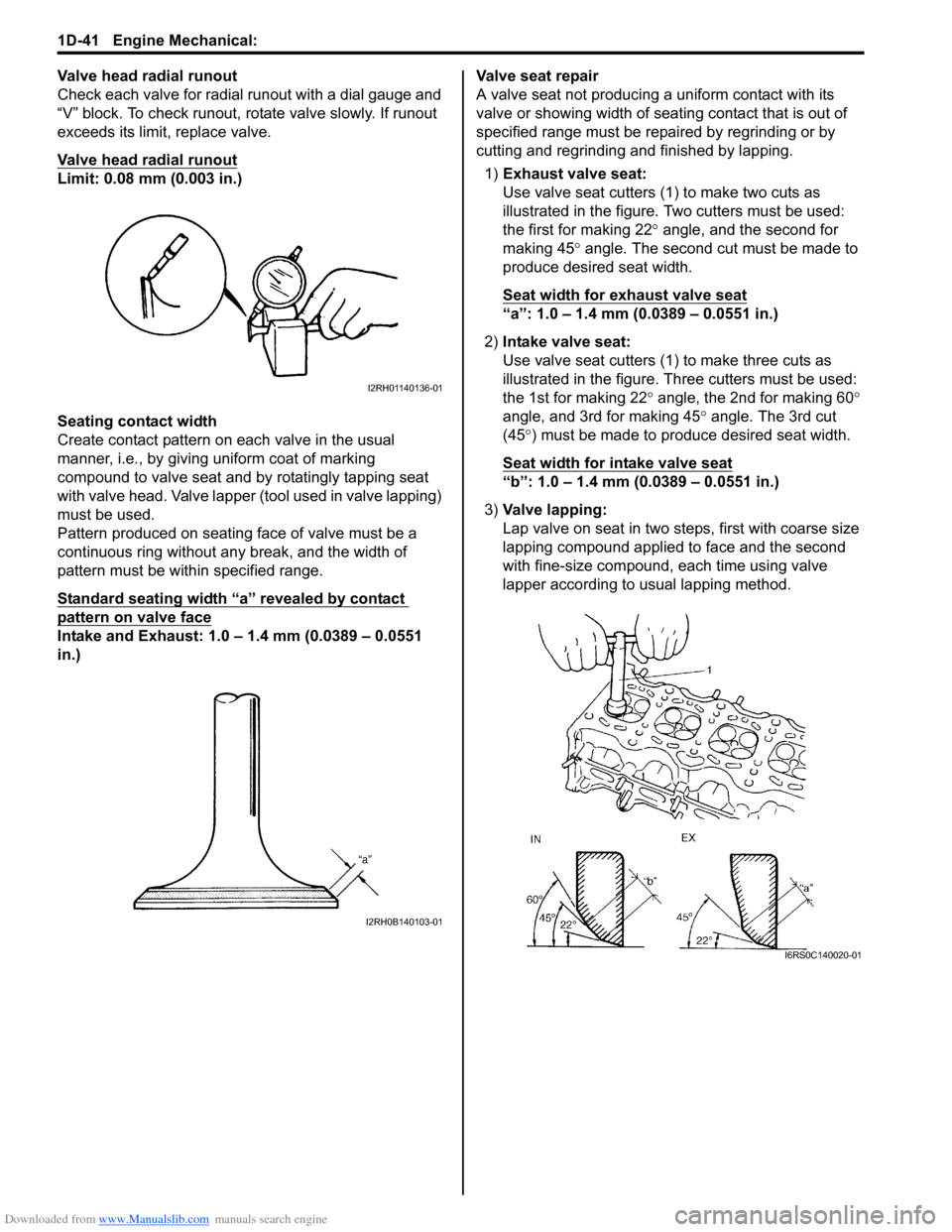
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-41 Engine Mechanical:
Valve head radial runout
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and
“V” block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping)
must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551
in.)Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing
a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
1) Exhaust valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1 ) to make two cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Two cutters must be used:
the first for making 22 ° angle, and the second for
making 45 ° angle. The second cut must be made to
produce desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
2) Intake valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Th ree cutters must be used:
the 1st for making 22 ° angle, the 2nd for making 60 °
angle, and 3rd for making 45 ° angle. The 3rd cut
(45 °) must be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
3) Valve lapping:
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse size
lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve
lapper according to usual lapping method.
I2RH01140136-01
I2RH0B140103-01
I6RS0C140020-01
Page 331 of 1496
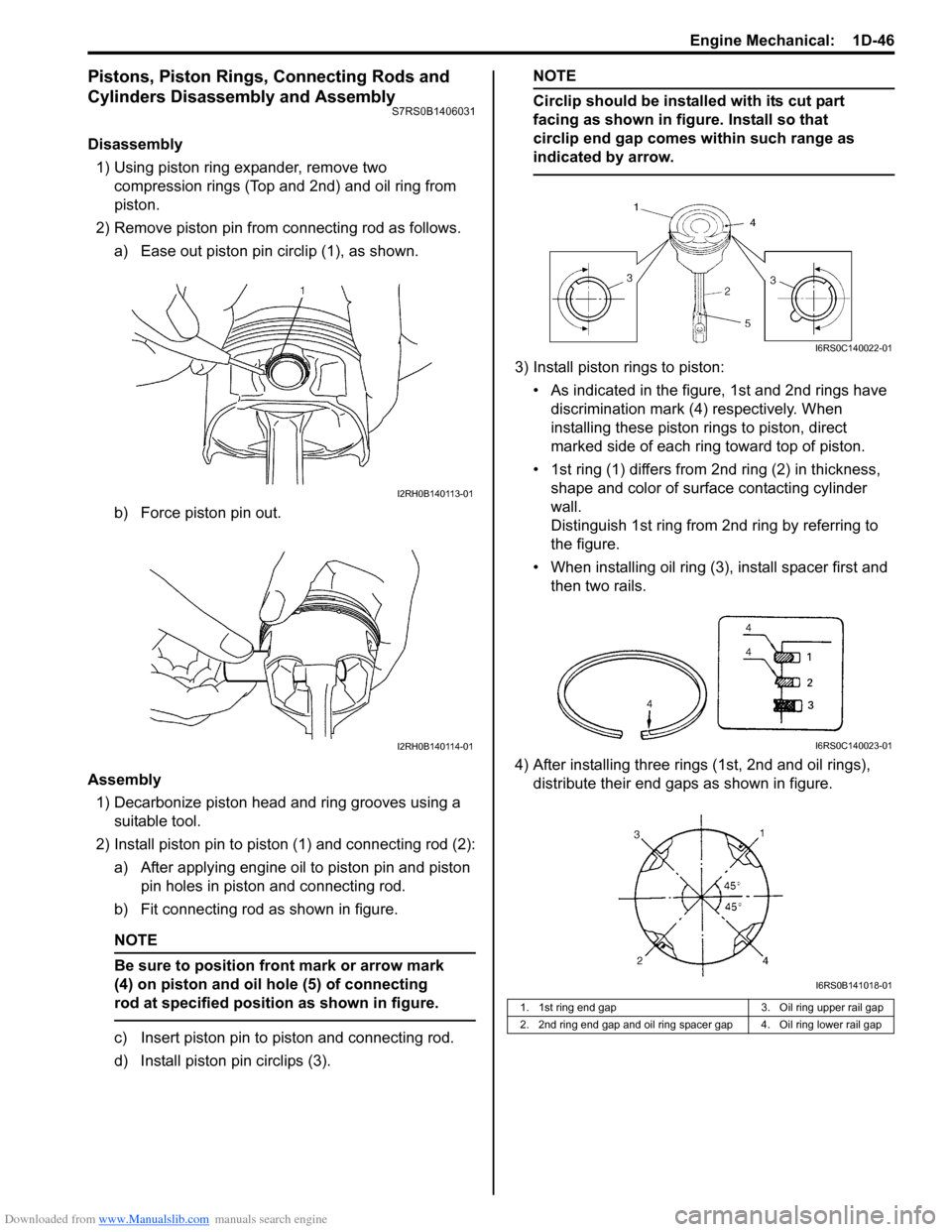
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-46
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly
S7RS0B1406031
Disassembly1) Using piston ring expander, remove two compression rings (Top and 2nd) and oil ring from
piston.
2) Remove piston pin from connecting rod as follows. a) Ease out piston pin circlip (1), as shown.
b) Force piston pin out.
Assembly 1) Decarbonize piston head and ring grooves using a suitable tool.
2) Install piston pin to piston (1) and connecting rod (2): a) After applying engine oil to piston pin and piston pin holes in piston and connecting rod.
b) Fit connecting rod as shown in figure.
NOTE
Be sure to position front mark or arrow mark
(4) on piston and oil hole (5) of connecting
rod at specified position as shown in figure.
c) Insert piston pin to piston and connecting rod.
d) Install piston pin circlips (3).
NOTE
Circlip should be installed with its cut part
facing as shown in figure. Install so that
circlip end gap comes within such range as
indicated by arrow.
3) Install piston rings to piston:
• As indicated in the figure, 1st and 2nd rings have discrimination mark (4) respectively. When
installing these piston rings to piston, direct
marked side of each ring toward top of piston.
• 1st ring (1) differs from 2nd ring (2) in thickness, shape and color of surface contacting cylinder
wall.
Distinguish 1st ring from 2nd ring by referring to
the figure.
• When installing oil ring (3), install spacer first and then two rails.
4) After installing three rings (1st, 2nd and oil rings), distribute their end gaps as shown in figure.
I2RH0B140113-01
I2RH0B140114-01
1. 1st ring end gap 3. Oil ring upper rail gap
2. 2nd ring end gap and oil ring spacer gap 4. Oil ring lower rail gap
I6RS0C140022-01
I6RS0C140023-01
I6RS0B141018-01
Page 355 of 1496
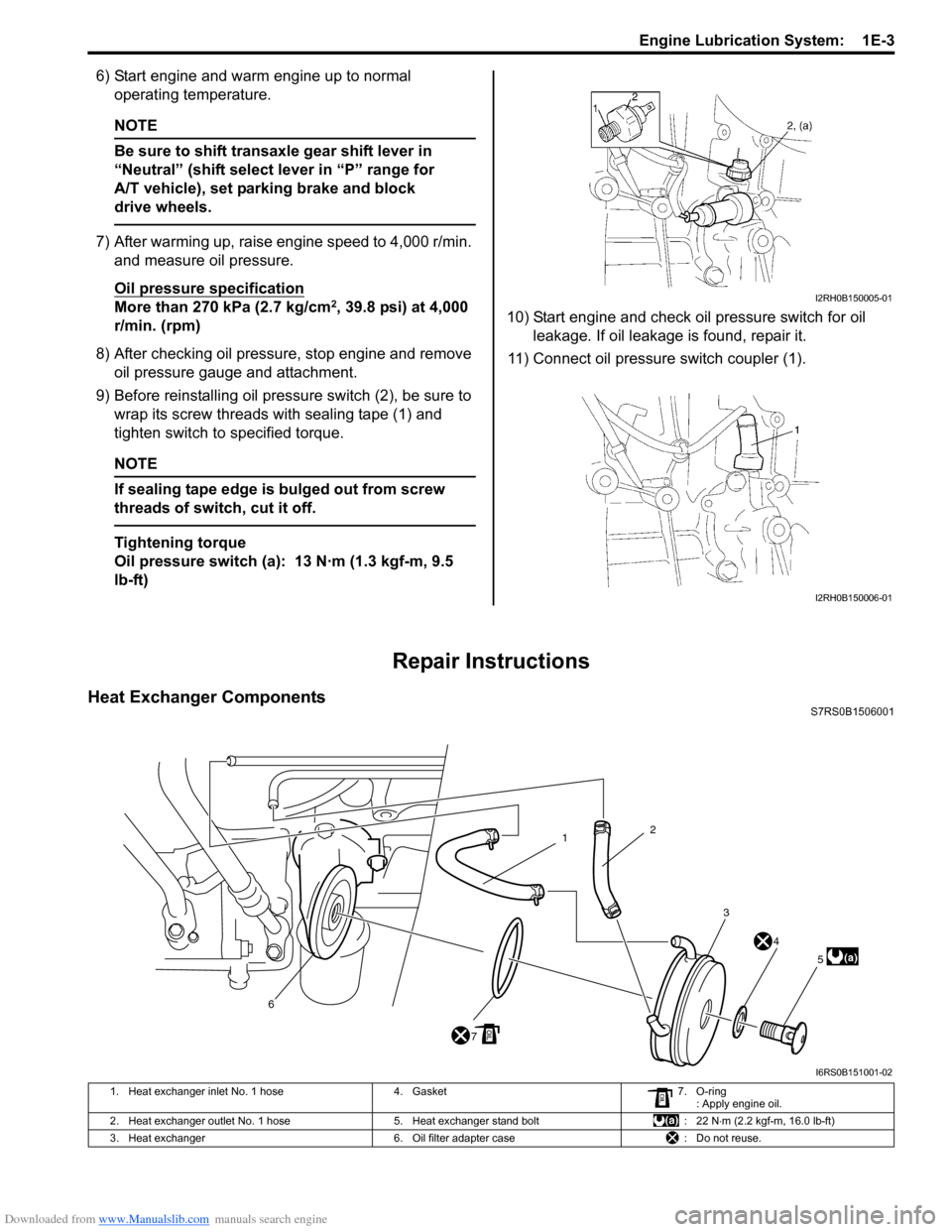
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Lubrication System: 1E-3
6) Start engine and warm engine up to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
Be sure to shift transaxle gear shift lever in
“Neutral” (shift select lever in “P” range for
A/T vehicle), set parking brake and block
drive wheels.
7) After warming up, raise engine speed to 4,000 r/min. and measure oil pressure.
Oil pressure specification
More than 270 kPa (2.7 kg/cm2, 39.8 psi) at 4,000
r/min. (rpm)
8) After checking oil pressure, stop engine and remove oil pressure gauge and attachment.
9) Before reinstalling oil pressure switch (2), be sure to
wrap its screw threads with sealing tape (1) and
tighten switch to specified torque.
NOTE
If sealing tape edge is bulged out from screw
threads of switch, cut it off.
Tightening torque
Oil pressure switch (a): 13 N·m (1.3 kgf-m, 9.5
lb-ft) 10) Start engine and check oil pressure switch for oil
leakage. If oil leakage is found, repair it.
11) Connect oil pressure switch coupler (1).
Repair Instructions
Heat Exchanger ComponentsS7RS0B1506001
I2RH0B150005-01
I2RH0B150006-01
3
4
5
7
6
(a)
2
1
I6RS0B151001-02
1. Heat exchanger inlet No. 1 hose 4. Gasket7. O-ring
: Apply engine oil.
2. Heat exchanger outlet No. 1 hose 5. Heat exchanger stand bolt : 22 N⋅m (2.2 kgf-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
3. Heat exchanger 6. Oil filter adapter case : Do not reuse.
Page 378 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-3 Fuel System:
4) Check that battery voltage is 11 V or more.
5) Measure fuel pressure at each condition.If measured pressure is out of specification, refer to
“Fuel Pressure Check in Section 1A” and check each
possibly defective part. Replace if found defective.
a) Turn ignition switch ON to operate fuel pump and after 2 seconds turn it OFF. Repeat this 3 or 4
times and then check fuel pressure.
Fuel pressure specification
With fuel pump operating and engine
stopped: 270 – 310 kPa (2.7 – 3.1 kg/cm2, 38.4
– 44.0 psi)
b) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature, and measure fuel pressure at
idling.
Fuel pressure specification
At specified idle speed: 270 – 310 kPa (2.7 –
3.1 kg/cm2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi)
c) Stop engine, and measure fuel pressure at one minute after stopping.
Fuel pressure specification
With 1 min. after engine (fuel pump) stop
(Pressure reduces as time passes): Over 300
kPa (3.0 kg/cm
2, 42.7 psi)
6) After checking fuel pressure, remove fuel pressure gauge.
WARNING!
As fuel feed line is still under high fuel
pressure, make sure to release fuel pressure
according to the following procedures.
• Place fuel container under joint.
• Cover joint with rag and loosen joint nut slowly in order to release fuel pressure
gradually.
7) Remove special tools from fuel delivery pipe and fuel feed hose.
8) Connect fuel feed hose to fuel delivery pipe and clamp it securely.
9) With engine OFF and ignition switch ON, check for fuel leaks.
Fuel Cut Operation InspectionS7RS0B1704002
NOTE
Before inspection, make sure that gear shift
lever is in neutral positi on (shift select lever
is “P” range for A/T vehicle), A/C is OFF and
parking brake lever is pulled all the way up.
1) Warm engine up to normal operating temperature.
2) While listening to sound of injector (2) by using sound scope (1) or such, increase engine speed to
higher than 3,000 r/min.
3) Check to make sure that injector operation sound is stop when throttle valve is closed instantly and it is
heard again when engine speed is reduced to
approx. 2,000 r/min or less.
I2RH01170032-01
I2RH0B170004-01