warning SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 497 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 4-iii
ABS Warning Lamp Check ............................... 4F-14
EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp) Check .............................................................. 4F-15
DTC Check ....................................................... 4F-15
DTC Table ......................................................... 4F-15
DTC Clearance ................................................. 4F-18
Fail-Safe Table ................ .................................. 4F-19
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 4F-20
Visual Inspection ............................................... 4F-21
ESP ® Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at
Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4F-21
ESP ® Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady......... 4F-22
ABS Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch ON .......................................... 4F-23
ABS Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady............ 4F-24
EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp) Comes ON Steady .......................................... 4F-24
Serial Data Link Circuit Check .......................... 4F-26
DTC C1016: Stop Lamp Swit ch Circuit Failure .. 4F-28
DTC C1017 / C1023: Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Failure ............................................ 4F-29
DTC C1018: Brake Fluid Le vel Switch Failure .. 4F-30
DTC 1020: Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor Power Supply Failure ...................................... 4F-31
DTC C1021, C1022 / C1025, C1026 / C1031, C1032 / C1035, C1036: Wheel Speed
Sensor Circuit or Encode r Failure ................... 4F-32
DTC C1024: Steering Angle Sensor Circuit
Failure ............................................................. 4F-34
DTC C1027: ESP ® OFF Switch Circuit
Failure ............................................................. 4F-34
DTC C1028: Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor Circuit Failure ....... .............................. 4F-35
DTC C1034: Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Power Supply Failure ...................................... 4F-36
DTC C1037: Steering Angle Sensor Power Supply Failure ................................................. 4F-37
DTC C1038: Steering Angle Sensor Detect Rolling Counter Fa ilure from ESP® Control
Module ............................................................ 4F-38
DTC C1039: Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Internal Failure .............. .................................. 4F-39
DTC C1040: Stability Control System Function Failure .............................................. 4F-39
DTC C1041 / C1042 / C1043 / C1044 / C1045 / C1046 / C1051 / C1052 / C1053 / C1054 /
C1055 / C1056: Solenoid Circuit Failure ......... 4F-40
DTC C1057: ESP ® Control Module Power
Supply Circuit Failure .... .................................. 4F-41
DTC C1061: Pump Motor and/or Motor Driver Circuit Failure .................................................. 4F-42
DTC C1063: Solenoid Valve Power Supply Driver Circuit Failure ....................................... 4F-43
DTC 1071: ESP ® Control Module Internal
Defect.............................................................. 4F-44 DTC C1073: Lost Communication With Yaw
Rate / G Sensor Assembly .............................. 4F-45
DTC C1075 / 1076 / 1078: Sensor Calibration Incomplete.......................... ............................. 4F-46
DTC C1090: Invalid Communication with
ECM ................................................................ 4F-47
DTC C1091 / C1094: ECM Data in CAN Line Failure / Invalid Torque Control
Communication with ECM .. ............................. 4F-48
DTC U1073: Control Module Communication Bus Off ............................................................ 4F-49
DTC U1100: Lost Communication with ECM (Reception Error)............................................. 4F-50
DTC U1126: Lost Communication with Steering Angle Sensor (Reception Error)........ 4F-51
DTC U1140: Lost Communication with BCM (Reception Error)............................................. 4F-52
Repair Instructions ........... ................................. 4F-54
ESP® Hydraulic Unit Operation Check ............. 4F-54
Sensor Calibration............................................. 4F-54
ESP® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection .................... 4F-55
ESP ® Hydraulic
Unit / Control Module
Assembly Removal and Inst allation ................ 4F-56
Front / Rear Wheel Speed Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4F-57
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-58
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection ............. 4F-59
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-59
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection .............. 4F-60
Front Wheel Encode r On-Vehicle Inspection .... 4F-61
Front Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-61
Rear Wheel Encoder On-Veh icle Inspection..... 4F-61
Rear Wheel Encoder Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-61
Master Cylinder Pressure Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection ........................................................ 4F-61
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection ........................................................ 4F-62
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Assembly Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-63
Yaw Rate / G Sensor Inspection ....................... 4F-64
Steering Angle Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection .. 4F-64
Steering Angle Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 4F-65
Steering Angle Sensor Inspection ..................... 4F-65
ESP® OFF Switch Removal an d Installation .... 4F-65
ESP® OFF Switch Inspection ........................... 4F-65
Specifications .................... ................................. 4F-66
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 4F-66
Special Tools and Equipmen t ........................... 4F-66
Special Tool ...................................................... 4F-66
Page 499 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-1
Brakes
Brake Control System and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on BrakeS7RS0B4100001
Air Bag Warning
Refer to “Air Bag System Service Warning in Section 00”.
Brakes Diagnosis Note
Refer to “Brakes Diagnosis Note”.
General Description
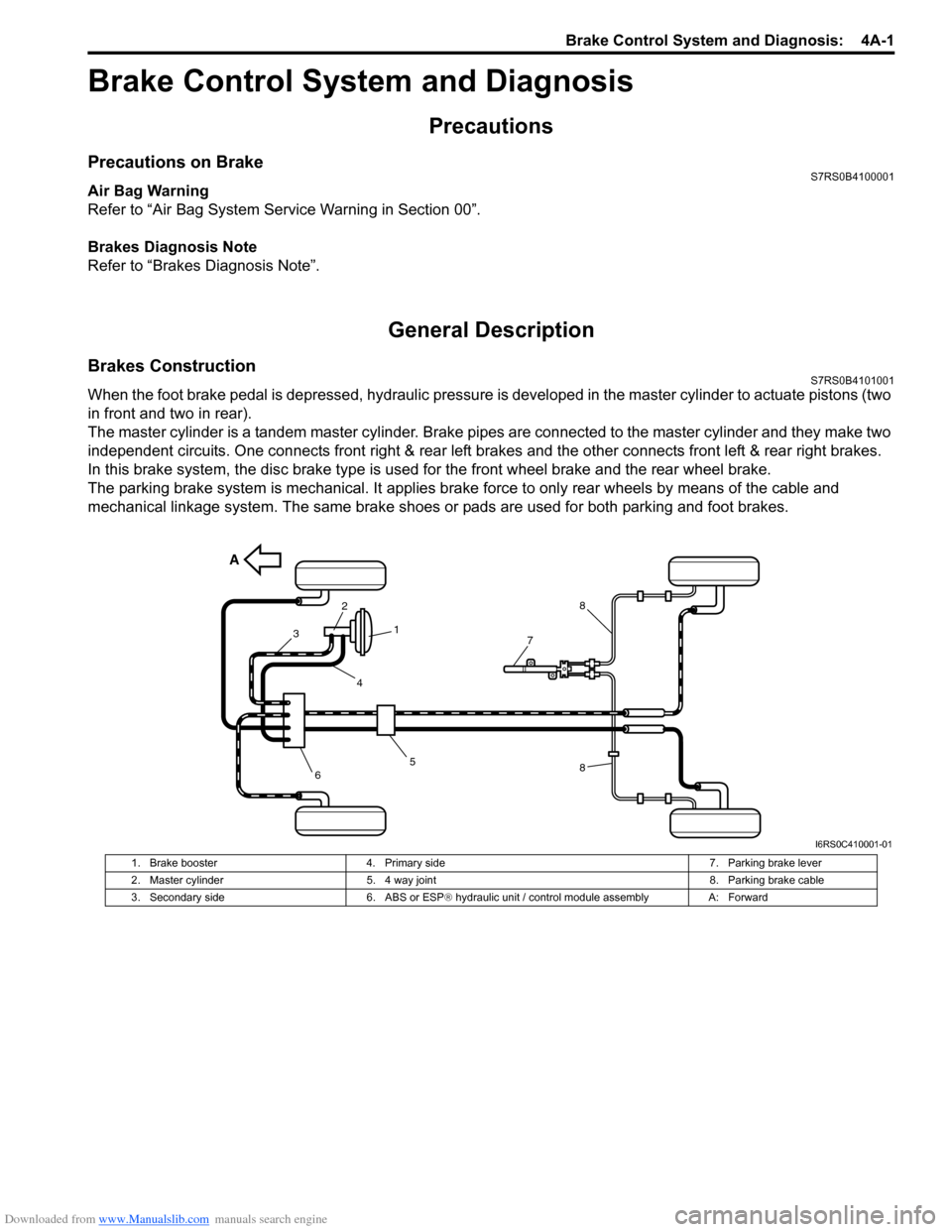
Brakes ConstructionS7RS0B4101001
When the foot brake pedal is depressed, hydraulic pressure is developed in the master cylinder to actuate pistons (two
in front and two in rear).
The master cylinder is a tandem master cylinder. Brake pipes are connected to the master cylinder and they make two
independent circuits. One connects front right & rear left brakes and the other connects front left & rear right brakes.
In this brake system, the disc brake type is used for the front wheel brake and the rear wheel brake.
The parking brake system is mechanical. It applies brake force to only rear wheels by means of the cable and
mechanical linkage system. The same brake shoes or pads are used for both parking and foot brakes.
A
5
3
2
1
4
8
8
6
7
I6RS0C410001-01
1. Brake booster 4. Primary side 7. Parking brake lever
2. Master cylinder 5. 4 way joint 8. Parking brake cable
3. Secondary side 6. ABS or ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly A: Forward
Page 504 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-6 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
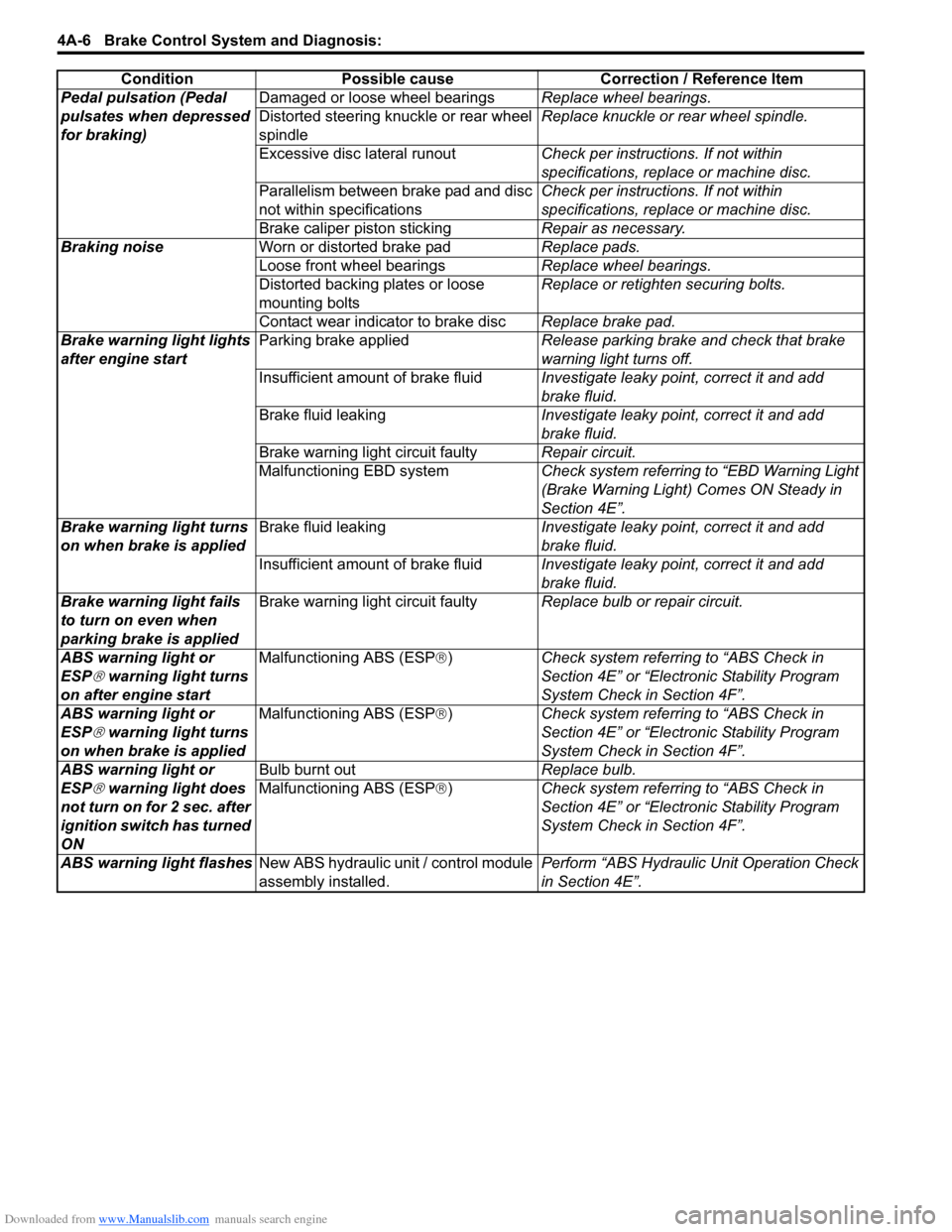
Pedal pulsation (Pedal
pulsates when depressed
for braking)Damaged or loose wheel bearings
Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted steering knuckle or rear wheel
spindle Replace knuckle or rear wheel spindle.
Excessive disc lateral runout Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Parallelism between brake pad and disc
not within specifications Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Braking noise Worn or distorted brake pad Replace pads.
Loose front wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted backing plates or loose
mounting bolts Replace or retighten securing bolts.
Contact wear indicator to brake disc Replace brake pad.
Brake warning light lights
after engine start Parking brake applied
Release parking brake and check that brake
warning light turns off.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake fluid leaking Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light circuit faulty Repair circuit.
Malfunctioning EBD system Check system referring to “EBD Warning Light
(Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady in
Section 4E”.
Brake warning light turns
on when brake is applied Brake fluid leaking
Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light fails
to turn on even when
parking brake is applied Brake warning light circuit faulty
Replace bulb or repair circuit.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on after engine start Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on when brake is applied Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light does
not turn on for 2 sec. after
ignition switch has turned
ON Bulb burnt out
Replace bulb.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light flashes New ABS hydraulic unit / control module
assembly installed. Perform “ABS Hydraulic
Unit Operation Check
in Section 4E”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 506 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-8 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Excessive Pedal Travel InspectionS7RS0B4106003
1) Start engine.
2) Depress brake pedal a few times.
3) With brake pedal depressed with approximately 300 N (30 kg, 66 lbs) load, measure brake pedal to wall
(dash panel silencer) clearance “a”. If clearance “a”
is less than specification, the most possible cause is
air in lines. Should clearance “a” remain less than
specification even after bleeding of system, other
possible infrequent cause is booster push rod length
out of adjustment.
• Bleed brake system. Refer to “Air Bleeding of Brake System”.
Brake arm pedal to wall clearance “a”
When pedal depressed at 300 N (30 kg, 66 lbs):
over 75 mm (2.95 in.)
Brake Fluid Level InspectionS7RS0B4106004
1) Check master cylinder, reservoir and reservoir hose (if equipped) for crack, damage and brake fluid
leakage. If any faulty condition exists, correct or
replace.
2) Check that brake fluid level is between MAX and MIN marks on reservoir.
NOTE
Be sure to use particular brake fluid either as
indicated on reservoir cap of that vehicle or
recommended in owner’s manual which
comes along with that vehicle. Use of any
other fluid is strictly prohibited.
Fluid level should be between MIN and MAX
lines marked on reservoir.
When brake warning lamp lights sometimes
during driving, replenis h fluid to MAX level.
When fluid decreases quickly, inspect brake
system for leakage. Correct leaky points and
then refill to specified level.
CAUTION!
Do not use shock absorber fluid or any other
fluid which contains mineral oil. Do not use a
container which has been used for mineral oil
or a container which is wet from water.
Mineral oil will cause swelling and distortion
of rubber parts in hydraulic brake system and
water mixed into brake fluid will lower fluid
boiling point. Keep all fluid containers
capped to prevent contamination.
Stop Light Switch AdjustmentS7RS0B4106005
Adjustment should be made as follows. Pull up brake
pedal toward you and while holding it there, adjust
switch position so that clea rance between end of thread
and brake pedal is as specified. Then lock it by turning
clockwise.
Clearance between brake pedal and stop light switch
“a”: 1.2 – 2.2 mm (0.05 – 0.08 in.)
I6RS0C410005-02
I4RS0B410006-01
I4RS0A410007-01
Page 512 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-14 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
6) Fill reservoir with specified fluid.
7) After completing the work, bleed air from brake and clutch system referring to “Air Bleeding of Brake
System” and “Air Bleeding of Clutch System in
Section 5C” (M/T model).
8) Install cowl top panel referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
9) Install windshield wiper referring to “Windshield
Wiper Removal and Insta llation in Section 9D”.
10) Perform brake test and check each installed part for fluid leakage.
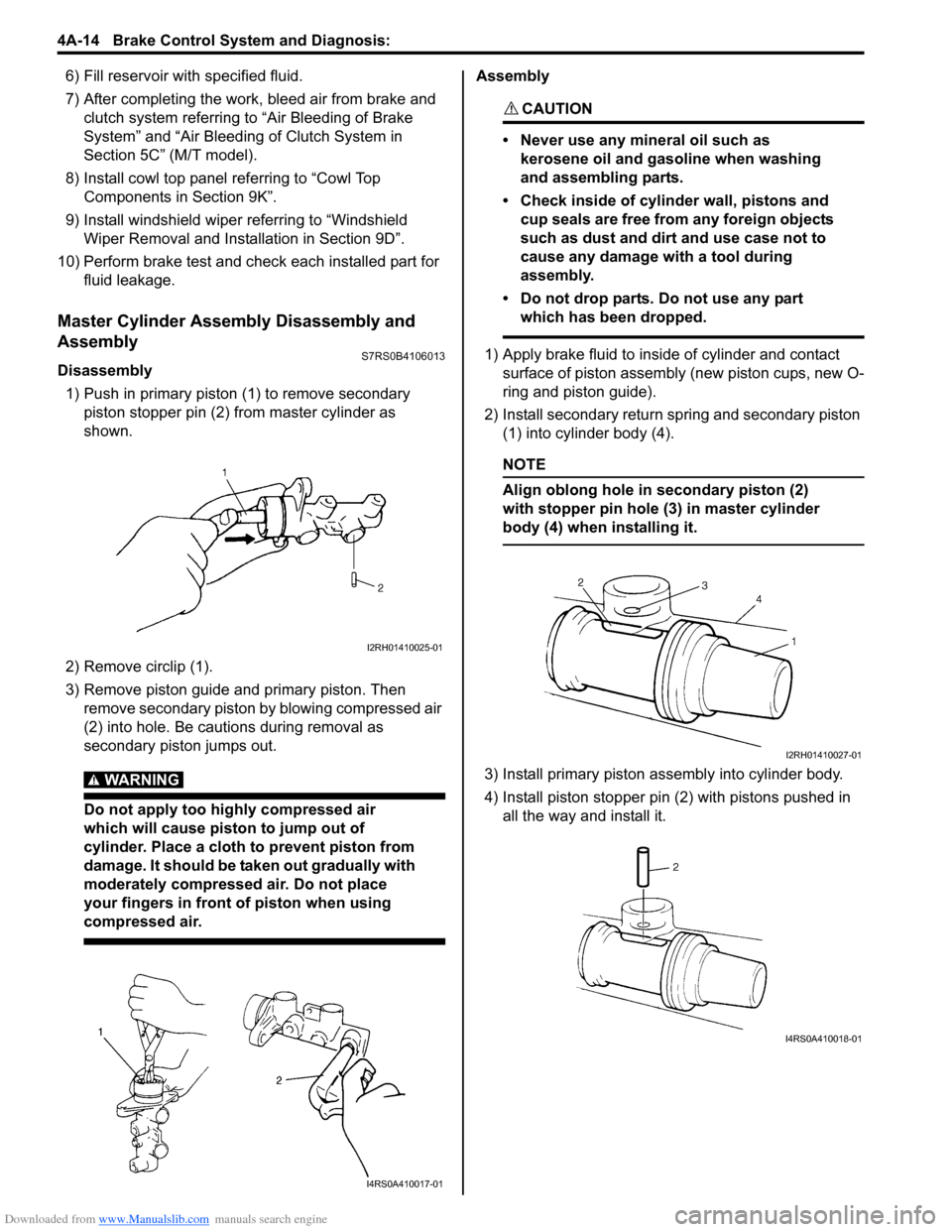
Master Cylinder Assembly Disassembly and
Assembly
S7RS0B4106013
Disassembly
1) Push in primary piston (1) to remove secondary
piston stopper pin (2) from master cylinder as
shown.
2) Remove circlip (1).
3) Remove piston guide and primary piston. Then remove secondary piston by blowing compressed air
(2) into hole. Be cautions during removal as
secondary piston jumps out.
WARNING!
Do not apply too highly compressed air
which will cause piston to jump out of
cylinder. Place a cloth to prevent piston from
damage. It should be taken out gradually with
moderately compressed air. Do not place
your fingers in front of piston when using
compressed air.
Assembly
CAUTION!
• Never use any mineral oil such as kerosene oil and gasoline when washing
and assembling parts.
• Check inside of cylinder wall, pistons and cup seals are free from any foreign objects
such as dust and dirt and use case not to
cause any damage with a tool during
assembly.
• Do not drop parts. Do not use any part which has been dropped.
1) Apply brake fluid to inside of cylinder and contact surface of piston assembly (new piston cups, new O-
ring and piston guide).
2) Install secondary return spring and secondary piston (1) into cylinder body (4).
NOTE
Align oblong hole in secondary piston (2)
with stopper pin hole (3) in master cylinder
body (4) when installing it.
3) Install primary piston assembly into cylinder body.
4) Install piston stopper pin (2) with pistons pushed in all the way and install it.
I2RH01410025-01
I4RS0A410017-01
I2RH01410027-01
I4RS0A410018-01
Page 518 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-2 Front Brakes:
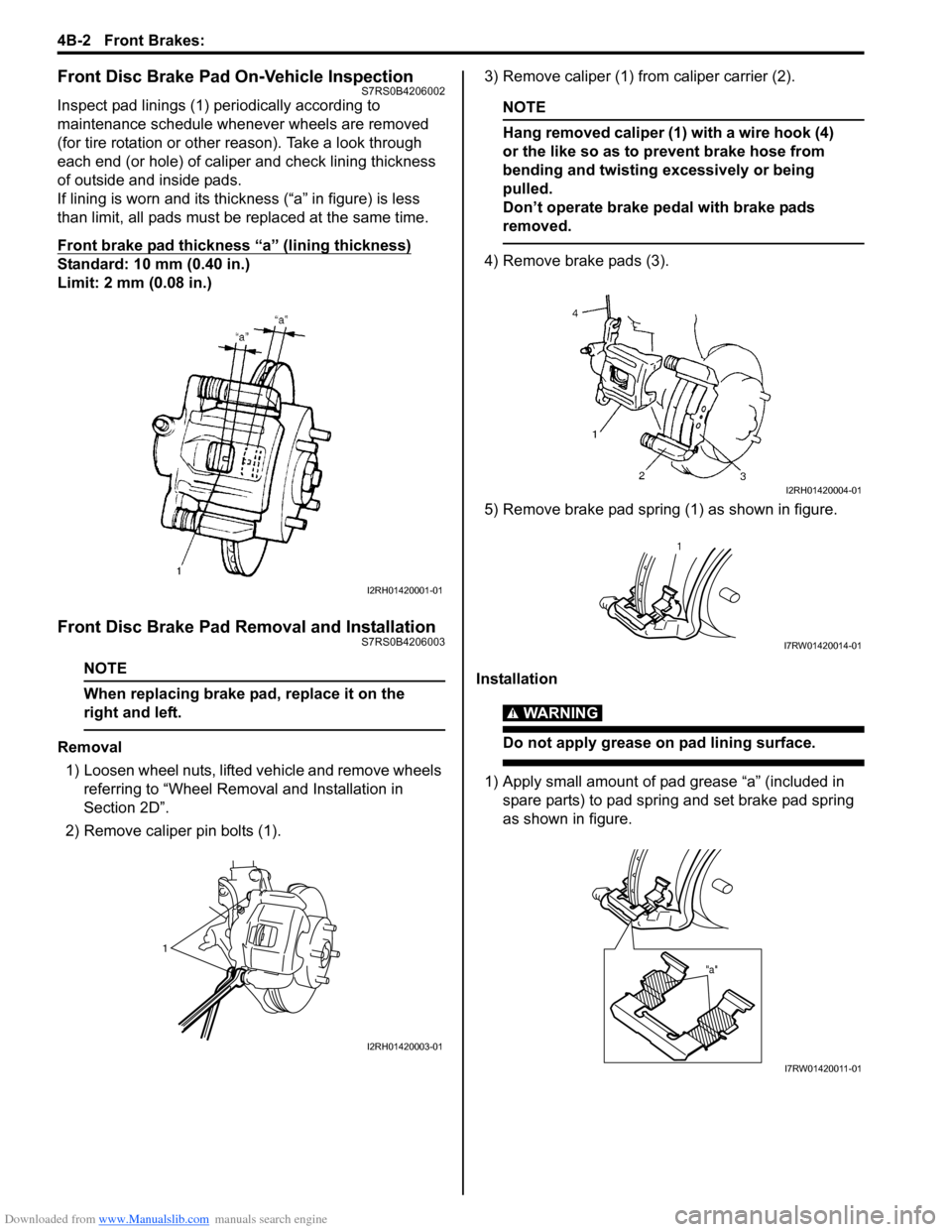
Front Disc Brake Pad On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B4206002
Inspect pad linings (1) periodically according to
maintenance schedule whenever wheels are removed
(for tire rotation or other reason). Take a look through
each end (or hole) of caliper and check lining thickness
of outside and inside pads.
If lining is worn and its thic kness (“a” in figure) is less
than limit, all pads must be replaced at the same time.
Front brake pad thickness “a” (lining thickness)
Standard: 10 mm (0.40 in.)
Limit: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
Front Disc Brake Pad Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4206003
NOTE
When replacing brake pad, replace it on the
right and left.
Removal
1) Loosen wheel nuts, lifted vehicle and remove wheels referring to “Wheel Remova l and Installation in
Section 2D”.
2) Remove caliper pin bolts (1). 3) Remove caliper (1) from caliper carrier (2).
NOTE
Hang removed caliper (1) with a wire hook (4)
or the like so as to prevent brake hose from
bending and twisting excessively or being
pulled.
Don’t operate brake pedal with brake pads
removed.
4) Remove brake pads (3).
5) Remove brake pad spring (1) as shown in figure.
Installation
WARNING!
Do not apply grease on pad lining surface.
1) Apply small amount of pad grease “a” (included in spare parts) to pad spring and set brake pad spring
as shown in figure.
I2RH01420001-01
1
I2RH01420003-01
I2RH01420004-01
1
I7RW01420014-01
"a"
I7RW01420011-01
Page 520 of 1496
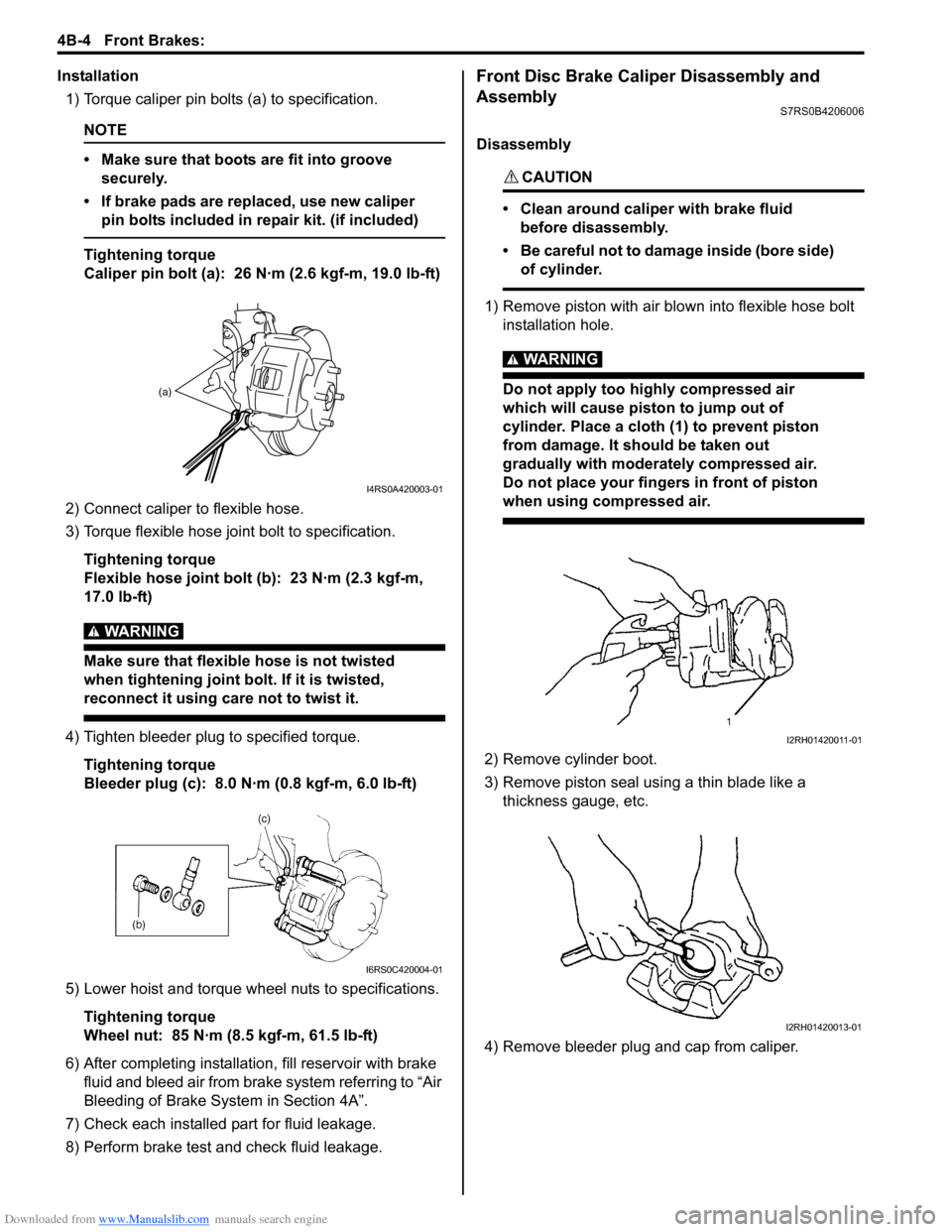
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-4 Front Brakes:
Installation1) Torque caliper pin bolts (a) to specification.
NOTE
• Make sure that boots are fit into groove securely.
• If brake pads are replaced, use new caliper pin bolts included in repair kit. (if included)
Tightening torque
Caliper pin bolt (a): 26 N·m (2.6 kgf-m, 19.0 lb-ft)
2) Connect caliper to flexible hose.
3) Torque flexible hose jo int bolt to specification.
Tightening torque
Flexible hose joint bolt (b): 23 N·m (2.3 kgf-m,
17.0 lb-ft)
WARNING!
Make sure that flexible hose is not twisted
when tightening joint bolt. If it is twisted,
reconnect it using care not to twist it.
4) Tighten bleeder plug to specified torque. Tightening torque
Bleeder plug (c): 8.0 N·m (0.8 kgf-m, 6.0 lb-ft)
5) Lower hoist and torque wheel nuts to specifications. Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
6) After completing installation, fill reservoir with brake
fluid and bleed air from brake system referring to “Air
Bleeding of Brake System in Section 4A”.
7) Check each installed part for fluid leakage.
8) Perform brake test and check fluid leakage.
Front Disc Brake Caliper Disassembly and
Assembly
S7RS0B4206006
Disassembly
CAUTION!
• Clean around caliper with brake fluid before disassembly.
• Be careful not to damage inside (bore side) of cylinder.
1) Remove piston with air blown into flexible hose bolt installation hole.
WARNING!
Do not apply too highly compressed air
which will cause piston to jump out of
cylinder. Place a cloth (1) to prevent piston
from damage. It should be taken out
gradually with moderately compressed air.
Do not place your fingers in front of piston
when using compressed air.
2) Remove cylinder boot.
3) Remove piston seal using a thin blade like a thickness gauge, etc.
4) Remove bleeder plug and cap from caliper.
(a)
I4RS0A420003-01
I6RS0C420004-01
I2RH01420011-01
I2RH01420013-01
Page 529 of 1496
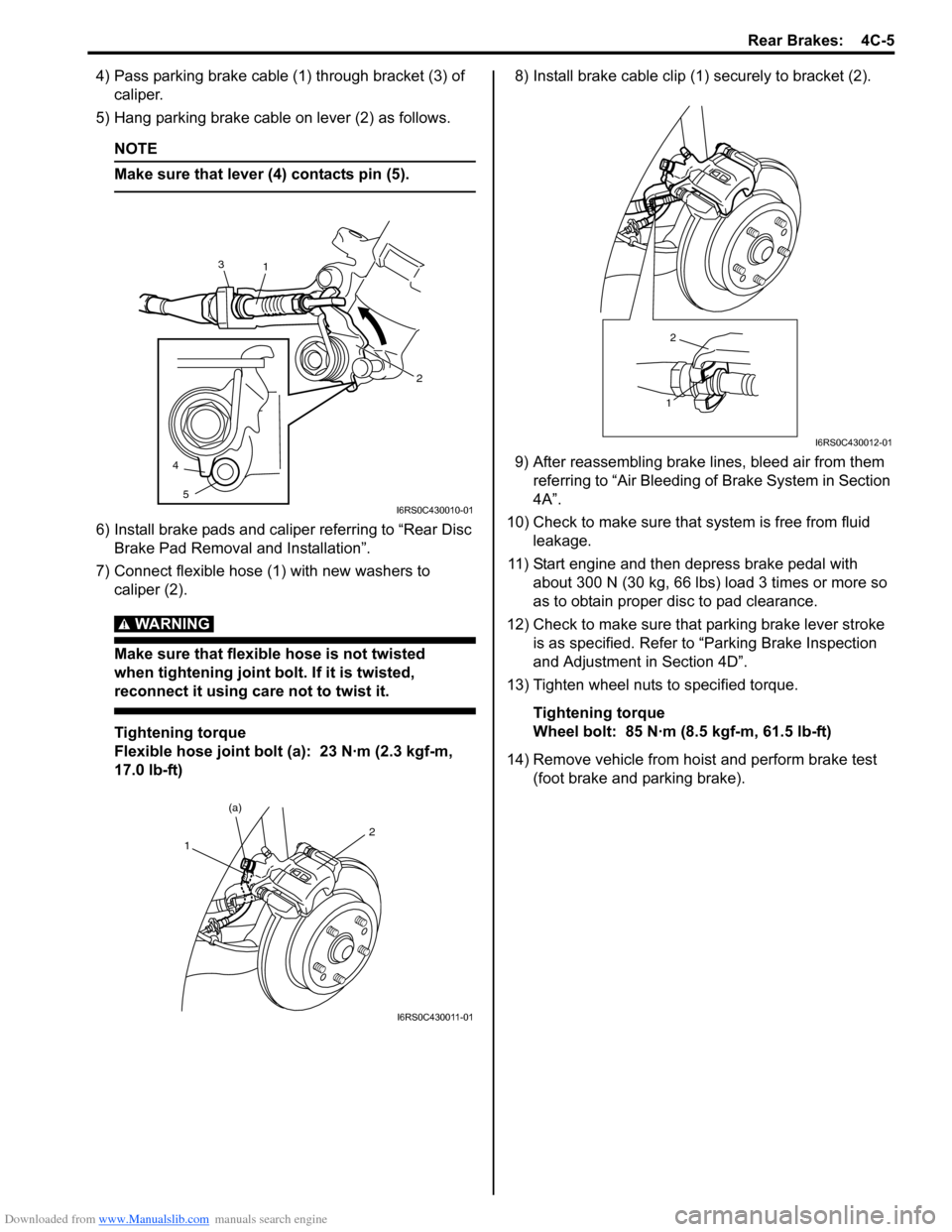
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Brakes: 4C-5
4) Pass parking brake cable (1) through bracket (3) of caliper.
5) Hang parking brake cable on lever (2) as follows.
NOTE
Make sure that lever (4) contacts pin (5).
6) Install brake pads and caliper referring to “Rear Disc Brake Pad Removal and Installation”.
7) Connect flexible hose (1) with new washers to caliper (2).
WARNING!
Make sure that flexible hose is not twisted
when tightening joint bolt. If it is twisted,
reconnect it using care not to twist it.
Tightening torque
Flexible hose joint bolt (a): 23 N·m (2.3 kgf-m,
17.0 lb-ft) 8) Install brake cable clip (1) securely to bracket (2).
9) After reassembling brake lines, bleed air from them
referring to “Air Bleeding of Brake System in Section
4A”.
10) Check to make sure that system is free from fluid
leakage.
11) Start engine and then depress brake pedal with about 300 N (30 kg, 66 lbs) load 3 times or more so
as to obtain proper disc to pad clearance.
12) Check to make sure that parking brake lever stroke is as specified. Refer to “Parking Brake Inspection
and Adjustment in Section 4D”.
13) Tighten wheel nuts to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Wheel bolt: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
14) Remove vehicle from hoist and perform brake test (foot brake and parking brake).
1
23
45
I6RS0C430010-01
1 (a)2
I6RS0C430011-01
1
2
I6RS0C430012-01
Page 540 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4E-1 ABS:
Brakes
ABS
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing TroublesS7RS0B4500001
To ensure that the trouble diagnosis is done accurately
and smoothly, observe the following and follow “ABS
Check”.
• Diagnostic information stored in ABS cont rol module
memory can be cleared as well as checked by using
SUZUKI scan tool. Before us ing scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good
understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
• If the vehicles was operated in any of the following ways, ABS warning light may light momentarily but
this does not indicate anything abnormal in ABS.
– The vehicle was driven with parking brake pulled.
– The vehicle was driven with brake dragging.
– The vehicle was stuck in mud, sand, etc.
– Wheel spin occurred while driving.
– Wheel(s) was rotated while the vehicle was jacked up.
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• Be sure to use the trouble diagnosis procedure as described in “ABS Check”. Failure to follow it may
result in incorrect diagnosis. (Some other diagnosis
trouble code may be stored by mistake in the memory
of ABS control module during inspection.)
• When disconnecting ABS co ntrol module connector
(1), pull down lock lever (2) of connector.
When connecting, set the connector on ABS control
module assembly and pull up the lock lever (2) until it
locks. • Communication of ECM,
BCM, ABS control module,
keyless start control module (if equipped), and
combination meter is established by CAN (Controller
Area Network).
Therefore, be sure to read “Precautions for Installing
Mobile Communication Equipment in Section 00”
before inspection and handle CAN communication
line.
Precautions in On-Vehicle ServiceS7RS0B4500002
When connector is connected to ABS control module
assembly, do not disconnect connectors of sensors with
ignition switch ON. Otherwise, DTC will be set in ABS
control module.
Precautions in Hydraulic Unit Operation CheckS7RS0B4500003
ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly function is
checked by correct wheel lock / release condition when
brake pressure is pressurized / depressurized using
SUZUKI scan tool. The hydraulic unit operation check
referring to “ABS Hydraulic Unit Operation Check”
should be performed to confirm the correct brake pipe
connection in the following cases.
• ABS hydraulic unit / cont rol module assembly was
replaced.
• Brake pipe and/or hose ware replaced.
[A]: Disconnect C: Pull down to disconnect
[B]: Connect D: Pull up to connect
21
C D
[A]
[B]
I4RH01450001-01
Page 541 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ABS: 4E-2
General Description
ABS DescriptionS7RS0B4501001
The ABS (Antilock Brake System) controls the fluid
pressure applied to the wheel cylinder of each brake
from the master cylinder so that each wheel is not locked
even when hard braking is applied.
This ABS has also the following function.
While braking is applied, but before ABS control
becomes effective, braking force is distributed between
the front and rear so as to prevent the rear wheels from
being locked too early for better stability of the vehicle.
The main component parts of this ABS include the
following parts in addition to those of the conventional
brake system.
• Wheel speed sensor which senses revolution speed of each wheel and outputs its signal.
• ABS warning light which light s to inform abnormality
when system fails to operate properly.
• ABS hydraulic unit / cont rol module assembly is
incorporated ABS co ntrol module, ABS hydraulic unit
(actuator assembly), solenoid valve power supply
driver (transistor), solenoid valve driver (transistor),
pump motor driver (transistor).
– ABS control module which sends operation signal to ABS hydraulic unit to control fluid pressure
applied to each wheel cylinder based on signal
from each wheel speed sensor so as to prevent
wheel from locking.
– ABS hydraulic unit which operates according to signal from ABS control module to control fluid
pressure applied to wheel cylinder of each 4
wheels.
– Solenoid valve power supp ly driver (transistor)
which supplies power to solenoid valve in ABS
hydraulic unit.
– Solenoid valve driver (transistor) which controls each solenoid valves in ABS hydraulic unit.
– Pump motor driver (transistor) which supplies power to pump motor in ABS hydraulic unit.
This ABS is equipped with Electronic Brake force
Distribution (EBD) system that controls a fluid pressure
of rear wheels to best condition, which is the same
function as that of proportion ing valve, by the signal from
wheel sensor independently of change of load due to
load capacity and so on. An d if the EBD system fails to
operate properly, the brake warning light lights to inform
abnormality.
ABS Hydraulic Unit / Control Module Assembly
Description
S7RS0B4501002
ABS control module is a component of ABS hydraulic
unit / control module asse mbly and has the following
functions.
Self-Diagnosis Function
ABS control module diagnose s conditions of the system
component parts (whether or not there is any
abnormality) all the time and indicates the results
(warning of abnormality occurrence and DTC) through
the ABS warning light as described.
• When ignition switch is turned ON, ABS warning light lights for 2 seconds to check its circuit.
• When no abnormality has been detected (the system is in good condition), ABS warning light turns OFF
after 2 seconds.
• When an abnormality in th e system is detected, ABS
warning light lights and the area where that
abnormality lies is stored in the memory of EEPROM
in ABS control module.
1
I4RS0A450001-01