Dtc SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 8 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-3 Precautions:
WARNING!
SDM
• For handling and storage of a SDM, select a place where the ambient temperature
below 65 °C (150 °F), without high humidity
and away from electric noise.
• During service procedures, be very careful when handling a Sensing and Diagnostic
Module (SDM). Never strike or jar the SDM.
• Never power up the air bag system when the SDM is not rigidly attached to the
vehicle. All SDM and mounting bracket
fasteners must be carefully torqued and
the arrow must be pointing toward the
front of the vehicle to ensure proper
operation of the air bag system.
The SDM could be activated when powered
while not rigidly att ached to the vehicle
which could cause deployment and result
in personal injury.
WARNING!
Driver and Passenger Seat Belt
Pretensioners
• For handling and storage of a live seat belt pretensioner, select a place where the
ambient temperature below 65 °C (150 ° F),
without high humidity and away from
electric noise.
• Never carry seat belt pretensioner by wire or connector of pretensioner. When
placing a live seat belt pretensioner on the
workbench or some place like that, never
put something on seat belt pretensioner.
Otherwise, personal injury may result.
• Never dispose of live (inactivated) seat belt pretensioners (drive and passenger). If
disposal is necessary, be sure to activate
them according to activation procedures
described in “Air Bag (Inflator) Module and
Seat Belt Pretensioner Disposal in Section
8B” before disposal.
• The seat belt pretensioner immediately after activation is very hot. Wait for at least
half an hour to cool it off before
proceeding the work.
• With many service procedures, gloves and safety glasses should be worn to prevent
any possible irritation of the skin or eyes.
• Even when the accident was light enough not to cause air bags to activate, be sure to inspect system
parts and other related parts according to instructions
under “Repair and Inspection Required after Accident
in Section 8B”.
• When servicing parts other than air bag system, if shocks may be applied to air bag system component
parts, remove those parts beforehand.
• When handling the air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side and curtain), seat belt pretensioners
(driver and passenger), forward sensor, side sensors
or SDM, be careful not to drop it or apply an impact to
it. If an excessive impact was applied, never attempt
disassembly or repair but replace it with a new one.
• When grease, cleaning agent, oil, water, etc. has got onto air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side
and curtain) or seat belt pretensioners (drive and
passenger), wipe off immediately with a dry cloth.
• Air bag wire harness is included in floor and instrument panel wire harnesses. Air bag wire
harness branched off from floor and instrument panel
wire harnesses can be identifie d easily as it is covered
with a yellow protection tube and it has yellow
connectors. Be very ca reful when handling it.
• When an open in air bag wire harness, damaged wire harness, connector or terminal is found, replace wire
harness, connectors and terminals as an assembly.
• Do not apply power to the air bag system unless all components are connected or a diagnostic flow
requests it, as this will set a DTC.
• Never use air bag system component parts from another vehicle.
• When using electric welding, be sure to disconnect all air bag (inflator) module connectors and pretensioner
connectors from air bag wire harness respectively.
• Never expose air bag system component parts directly to hot air (drying or baking the vehicle after
painting) or flames.
• WARNING / CAUTION labels are attached on each
part of air bag system components. Be sure to follow
the instructions.
• After vehicle is completely repaired, perform “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check in Section 8B”.
Page 10 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-5 Precautions:
• When performing service to electrical parts that does not require use of battery power, disconnect the
negative cable of the battery.
• When disconnecting the negative cable from the battery, be careful to the following.
– Check and record DTCs in ECM and HVAC control module if necessary before disconnecting.
– Record displayed contents of the clock and/or audio system, etc. before disconnecting and reset it
as before after connecting.
– For vehicle equipped with electric throttle body system, perform electric throttle body system
calibration referring to “Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1C” after
reconnecting the negative cable to the battery.
– For vehicle equipped with ESP ®, calibrate steering
angle sensor referring to “Sensor Calibration in
Section 4F” after reconnecting the negative cable
to the battery.
• When removing the battery, be sure to disconnect the negative cable first and then the positive cable. When
reconnecting the battery, connect the positive cable
first and then the negative cable, and replace the
terminal cover. • When removing parts that are to be reused, be sure to
keep them arranged in an orderly manner so that they
may be reinstalled in the proper order and position.
• Whenever you use oil seals, gaskets, packing, O- rings, locking washers, split pins, self-locking nuts,
and certain other parts as specified, be sure to use
new ones. Also, before installing new gaskets,
packing, etc., be sure to remove any residual material
from the mating surfaces.
• Make sure that all parts used in reassembly are perfectly clean.
When use of a certain type of lubricant, bond or
sealant is specified, be sure to use the specified type.
“A”: Water tight sealant 99000–31250 (SUZUKI
Bond No.1207F)
I2RH01010026-01
I2RH01010027-01
I2RH01010028-01
I2RH01010029-01
I2RH01010030-01
Page 15 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-10
Air Bag WarningS7RS0B0000009
WARNING!
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental
Restraint (Air Bag) System:
• Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed
only by an authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer
to “Air Bag System Components, Wiring
and Connectors Location in Section 8B” in
order to confirm whether you are
performing service on or near the air bag
system components or wiring. Please
observe all WARNINGS in Air Bag System
section and “Precautions on Service and
Diagnosis of Air Bag System in Section
8B” before performing service on or
around the air bag system components or
wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could
result in unintentional activation of the
system or could render the system
inoperative. Either of these two conditions
may result in severe injury.
• Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is
turned to the LOCK position and the
negative cable is disconnected from the
battery. Otherwise, the system may be
activated by reserve energy in the Sensing
and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
Air Bag System Service WarningS7RS0B0000010
WARNING!
• Service on or around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed
only by an authorized SUZUKI dealer.
Please observe all WARNINGS in Air Bag
System section and “Precautions on
Service and Diagnosis of Air Bag System
in Section 8B” before performing service
on or around the air bag system
components or wiring. Failure to follow
WARNINGS could result in unintended
activation of the system or could render
the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
• The procedures in the air bag system section must be followed in the order
listed to disable the air bag system
temporarily and prevent false DTCs from
setting. Failure to follow procedures could
result in possible activation of the air bag
system, personal injury or otherwise
unneeded air bag system repairs.
Fastener CautionS7RS0B0000011
CAUTION!
When fasteners are removed, always reinstall
them at the same location from which they
were removed. If a fastener needs to be
replaced, use the correct part number
fastener for that application. If the correct
part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or
stronger) may be used. Fasteners that are not
reused, and those requiring thread-locking
compound, will be called out. The correct
torque value must be used when installing
fasteners that require it. If the conditions are
not followed, parts or system damage could
result.
Suspension CautionS7RS0B0000012
CAUTION!
• All suspension fasteners are an important attaching part in that it could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems,
and/or could result in major repair
expense. They must be replaced with one
of the same part number or with an
equivalent part if replacement becomes
necessary. Do not use a replacement part
of lesser quality or substitute design.
Torque values must be used as specified
during reassembly to assure proper
retention of this part.
• Never attempt to heat, quench or straighten any suspension part. Replace it
with a new part or damage to the part may
result.
Wheels and Tires CautionS7RS0B0000013
CAUTION!
All wheel fasteners are important attaching
parts in that they could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems, and/
or could result in major repair expense. They
must be replaced with one of the same part
number or with an eq uivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use
a replacement part of lesser quality or
substitute design. Torque values must be
used as specified during reassembly to
assure proper retention of all parts.
There is to be no welding as it may result in
extensive damage and weakening of the
metal.
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 45 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1- i
1
Section 1
CONTENTS
Engine
Precautions ................................................. 1-1
Precautions............................................................. 1-1
Precautions for Engine .......................................... 1-1
Engine General Information and
Diagnosis ............. .................................... 1A-1
Precautions........................................................... 1A-1
Precautions on Engine Service ........................... 1A-1
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System .............................................................. 1A-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble ..................... 1A-1
Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection................ 1A-2
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration ......................................................... 1A-2
General Description ............................................. 1A-2 Statement on Cleanliness and Care ................... 1A-2
Engine Diagnosis General Description ............... 1A-3
On-Board Diagnostic System Description ........... 1A-3
Data Link Connector (DLC) ................................. 1A-6
Engine and Emission Control System Description ........................................................ 1A-6
CAN Communication System Description........... 1A-7
Air Intake System Description ............................. 1A-9
Description of Electric Throttle Body System ...... 1A-9
Description of Electric Throttle Body System Calibration ....................................................... 1A-10
Fuel Cut Control Description ............................. 1A-10
Generator Control System Description ............. 1A-11
Electronic Control System Description .............. 1A-12
Engine and Emission Control Input / Output Table ............................................................... 1A-18
Schematic and Routing Diagram ...................... 1A-19 Engine and Emission Control System Diagram .......................................................... 1A-19
Component Locatio n ......................................... 1A-21
Electronic Control System Components Location .......................................................... 1A-21
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 1A-22 Engine and Emission Control System Check.... 1A-22
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check .......... 1A-25
DTC Check ....................................................... 1A-26
DTC Clearance ................................................. 1A-27
DTC Table ......................................................... 1A-27
Fail-Safe Table ................ .................................. 1A-31 Scan Tool Data ................................................. 1A-33
Visual Inspection ............................................... 1A-37
Engine Basic Inspection .................................... 1A-38
Engine Symptom Diagnosis .............................. 1A-41
MIL Does Not Come ON with Ignition Switch
ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can Be
Started) ........................................................... 1A-47
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after Engine Starts................................................... 1A-48
DTC P0010: “A” Camshaft Position Actuator Circuit .............................................................. 1A-49
DTC P0011 / P0012: “A” Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System
Performance / -Retarded................................. 1A-52
DTC P0031 / P0032: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High (Sensor-1) .......................... 1A-54
DTC P0037 / P0038: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High (Sensor-2) .......................... 1A-56
DTC P0101: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range / Performance ...................................... 1A-58
DTC P0102: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input......................................................... 1A-61
DTC P0103: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit High Input ........................................................ 1A-63
DTC P0106: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circuit Range /
Performance.................................................... 1A-64
DTC P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circ uit Low Input............ 1A-66
DTC P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circ uit High Input ........... 1A-67
DTC P0111: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Range / Performance ........................... 1A-69
DTC P0112: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Low ...................................................... 1A-72
DTC P0113: Intake Air Temperature 1 Sensor Circuit High...................................................... 1A-74
DTC P0116: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range / Performance ........................... 1A-76
DTC P0117: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low ...................................................... 1A-79
DTC P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High...................................................... 1A-81
DTC P0122: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “A” (Main) Circuit Low ........................ 1A-83
Page 46 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1-ii Table of Contents
DTC P0123: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “A” (Main) Circuit High ....................... 1A-85
DTC P0131 / P0132: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Low Voltage / High Voltage (Sensor-
1) ..................................................................... 1A-88
DTC P0133: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Slow
Response (Sensor- 1) ...................................... 1A-91
DTC P0134: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit No Activity Detected (Sensor -1) ........................... 1A-92
DTC P0137 / P0138: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Low Voltage / High Voltage (Sensor-
2) ..................................................................... 1A-94
DTC P0140: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit No Activity Detected (Sensor -2) ........................... 1A-97
DTC P0171 / P0172: Fuel System Too Lean / Rich ................................................................. 1A-98
DTC P0222: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “B” (Sub) Circuit Low ....................... 1A-100
DTC P0223: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “B” (Sub) Circuit High ...................... 1A-102
DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304: Random / Multiple Cylin der Misfire Detected
/ Cylinder 1 / Cylinder 2 / Cylinder 3 /
Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected ........................... 1A-105
DTC P0327 / P0328: Knoc k Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High ..................................................... 1A-107
DTC P0335: Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor “A” Circuit .......................................... 1A-109
DTC P0340: Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor “A” Circuit .......................................... 1A-111
DTC P0350: Ignition Coil Primary / Secondary Circuit ............................................................ 1A-114
DTC P0401 / P0402: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected /
Excessive Detected ...................................... 1A-116
DTC P0403: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control Circuit ................... ............................ 1A-118
DTC P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency
below Threshold ................ ............................ 1A-120
DTC P0443: Evaporativ e Emission System
Purge Control Valve Circuit ........................... 1A-122
DTC P0480: Fan 1 (Radiator Cooling Fan) Control Circuit ................... ............................ 1A-124
DTC P0500: Vehicle Speed Sensor “A” Malfunction .................................................... 1A-128
DTC P0532: A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor “A” Circuit Low ... ............................... 1A-130
DTC P0533: A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor “A” Circuit High ................................. 1A-132
DTC P0601 / P0602 / P0607: Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error / Control
Module Programming Error / Control Module
Performance ................................................. 1A-134
DTC P0616: Starter Relay Circuit Low............ 1A-135
DTC P0617: Starter Relay Circuit High ........... 1A-136
DTC P0620: Generator Control Circuit ........... 1A-137
DTC P0625 / P0626: Generator Field Terminal Circuit Low / High . .......................... 1A-139
DTC P1501 / P1502: Electric Load Current Sensor Circuit Low / High . ............................ 1A-141 DTC P1510: ECM Back-Up Power Supply
Malfunction .................................................... 1A-143
DTC P1603: TCM Trouble Code Detected ..... 1A-144
DTC P1674: CAN Communication (Bus Off Error) ............................................................. 1A-145
DTC P1676: CAN Communication (Reception Error for TCM) ............................................... 1A-148
DTC P1678: CAN Communication (Reception Error for BCM) ............................................... 1A-149
DTC P1685: CAN Communication (Reception Error for ABS/ESP ® Control Module) ........... 1A-150
DTC P2101: Throttle Actuator Control Motor Circuit Range / Performance ......................... 1A-152
DTC P2102: Throttle Actuator Control Motor Circuit Low .................................................... 1A-154
DTC P2103: Throttle Actuator Control Motor Circuit High.................................................... 1A-155
DTC P2111 / P2112: Throttle Actuator Control System - Stuck Open / Closed ...................... 1A-156
DTC P2119: Throttle Actu ator Control Throttle
Body Range / Performance ........................... 1A-157
DTC P2122: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “D” (Main) Circuit Low Input............. 1A-159
DTC P2123: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “D” (Main) Circuit High Input ............ 1A-161
DTC P2127: Throttle Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “E” (Sub) Circuit Low Input ................ 1A-164
DTC P2128: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor
/ Switc
h “E” (Sub) Circuit High Input ............. 1A-166
DTC P2135: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “A”/“B” (Main / Sub) Voltage
Correlation..................................................... 1A-168
DTC P2138: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “D”/“E” (Main / Sub) Voltage
Correlation..................................................... 1A-171
DTC P2227 / P2228 / P2229: Barometric Pressure Circuit Malfunction ......................... 1A-173
Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits .................. 1A-175
ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check........... 1A-194
Fuel Injector Circuit Check .............................. 1A-198
Fuel Pump and Its Circuit Check..................... 1A-200
Fuel Pressure Check....................................... 1A-203
A/C System Circuits Check ............................. 1A-205
Electric Load Signal Circuit Check .................. 1A-209
Radiator Cooling Fan Low Speed Control System Check ............................................... 1A-211
Radiator Cooling Fan High Speed Control System Check ............................................... 1A-213
Repair Instructions ......... .................................1A-216
Idle Speed and IAC Throttle Valve Opening Inspection ...................................................... 1A-216
Special Tools and Equipmen t .........................1A-217
Special Tool .................................................... 1A-217
Aux. Emission Control Devices ............. 1B-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............1B-1
EGR System Inspection ...................................... 1B-1
Repair Instructions ............ ..................................1B-1
EVAP Canister Purge Inspec tion ........................ 1B-1
Page 51 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-1
Engine
Engine General Information and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on Engine ServiceS7RS0B1100001
CAUTION!
The following information on engine service
should be noted carefully, as it is important in
preventing damage, and in contributing to
reliable engine performance.
• When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do
not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against
oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer,
resulting in damaged oil pick-up unit.
• It should be kept in mind , while working on engine,
that 12-volt electrical syste m is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals
can be grounded, ground cable of the battery should
be disconnected at battery.
• Any time the air cleaner, throttle body or intake manifold is removed, the intake opening should be
covered. This will protect against accidental entrance
of foreign material which could follow intake passage
into cylinder and cause extensive damage when
engine is started.
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System
S7RS0B1100005
There are two types of On -Board Diagnostic (OBD)
system, Euro OBD system and non-Euro-OBD system,
depending on the vehicle specification.
As the diagnosis function is different between these two
types, be sure to fully understand the OBD system
referring to “On-Board Diagnostic System Description”.
OBD System Summary Table
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B1100002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• Don’t disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable
from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine
or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information
in ECM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checke d by using SUZUKI scan
tool or OBD generic scan tool. Before using scan tool,
read its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to
have good understanding as to what functions are
available and how to use it.
For Euro OBD model it is indistinguishable which
module turns on MIL because not only ECM but also
TCM (A/T model) turns on MIL (For details of on-
board diagnostic system for A/T model, refer to “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description in Section 5A”).
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM (A/T model) for
DTC when MIL lights on.
When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– OBD generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM (A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instructi on in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected)
Euro OBD
model Non-Euro-OBD
model
Quantity of DTC
related to engine
control Approx. 80 Approx. 60
Freeze frame
data Available Not available
SUZUKI scan
tool Available Available
OBD generic
scan tool Available Not available
Page 52 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement: When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglec ting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power
circuits of these sensors is shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, ABS/ESP ® control
module, combination meter, keyless start control
module, steering angle sensor (ESP ® model) and
TCM (A/T model), is esta blished by CAN (Controller
Area Network). (For more detail of CAN
communication for ECM, refer to “CAN
Communication System Description”). Therefore,
handle CAN communication line with care referring to
“Precaution for CAN Communication System in
Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS7RS0B1100003
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring ci rcuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into th e sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S7RS0B1100004
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P01 23, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2113, P2119, P2123,
P2127, P2128, P2135 and/or P2138
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor assembly
General Description
Statement on Cleanliness and CareS7RS0B1101001
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the thousands of an
millimeter (ten thous ands of an inch).
Accordingly, when any internal engine parts are
serviced, care and cleanliness are important.
It should be understood that proper cleaning and
protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part
of the repair procedure. This is considered standard
shop practice even if not specifically stated.
• A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate
the surfaces on initial operation. • Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston
rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft
journal bearings are removed for service, they should
be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in
the same locations and with the same mating
surfaces as when removed.
• Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to
wire harness or other electrical parts.
Page 53 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-3
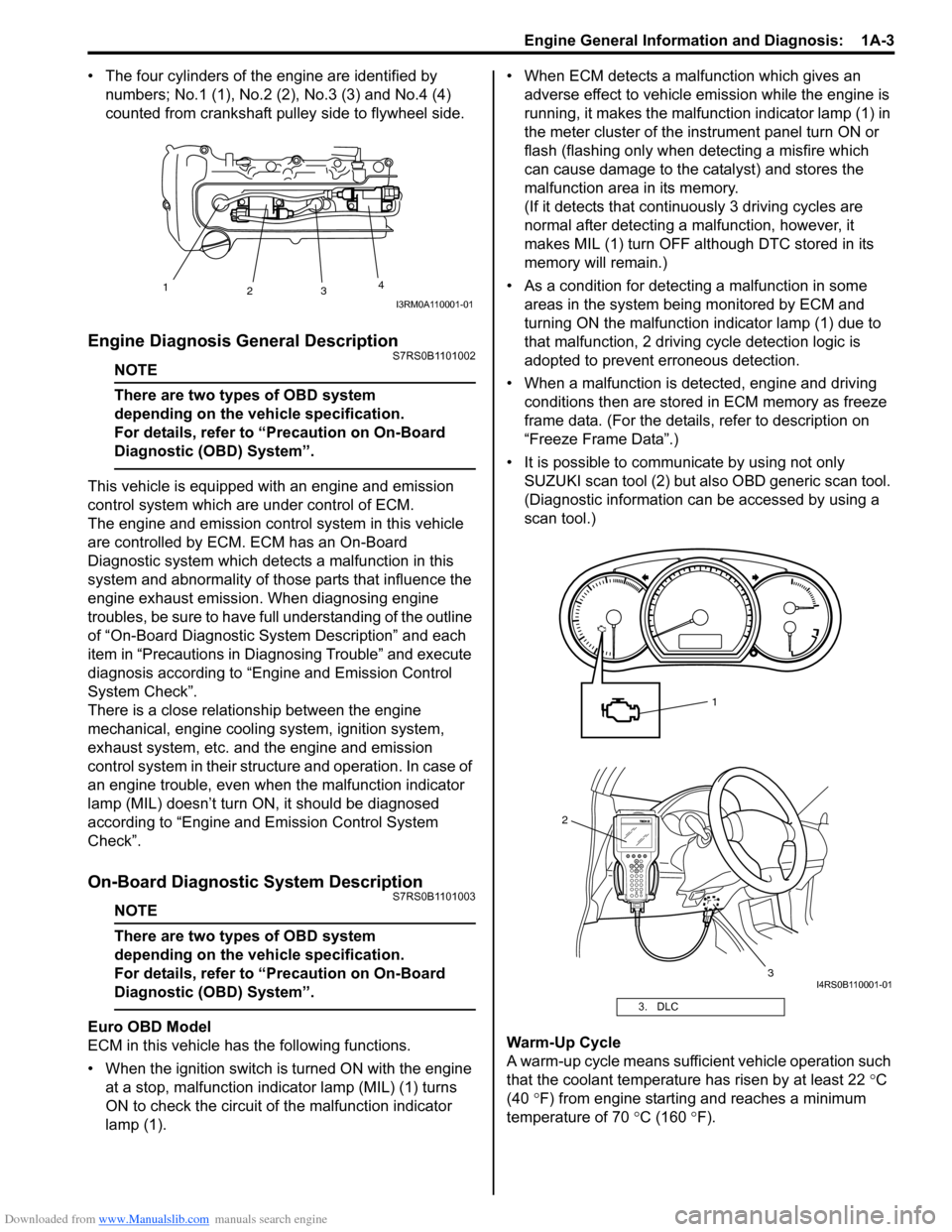
• The four cylinders of the engine are identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2 ), No.3 (3) and No.4 (4)
counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
Engine Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B1101002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission
control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle
are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board
Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this
system and abnormality of those parts that influence the
engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine
troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “Engine and Emission Control
System Check”.
There is a close relationship between the engine
mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system,
exhaust system, etc. and the engine and emission
control system in their structure and operation. In case of
an engine trouble, even when the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed
according to “Engine and Emission Control System
Check”.
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B1101003
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Euro OBD Model
ECM in this vehicle has the following functions.
• When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns
ON to check the circuit of the malfunction indicator
lamp (1). • When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an
adverse effect to vehicle emission while the engine is
running, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in
the meter cluster of the inst rument panel turn ON or
flash (flashing only when detecting a misfire which
can cause damage to the catalyst) and stores the
malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that contin uously 3 driving cycles are
normal after detecting a malfunction, however, it
makes MIL (1) turn OFF although DTC stored in its
memory will remain.)
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data”.)
• It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also OBD generic scan tool.
(Diagnostic information can be accessed by using a
scan tool.)
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficie nt vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 ° F).
1
23 4
I3RM0A110001-01
3. DLC
2
3
1
I4RS0B110001-01
Page 54 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-4 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Driving Cycle
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup and engine
shutoff.
2 Driving Cycle Detection Logic
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is
stored in ECM memory (in t he form of pending DTC) but
the malfunction indicator lamp does not light at this time.
It lights up at the second detection of same malfunction
also in the next driving cycle.
Pending DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored
temporarily at 1 driving cycle of the DTC which is
detected in the 2 driving cycle detection logic.
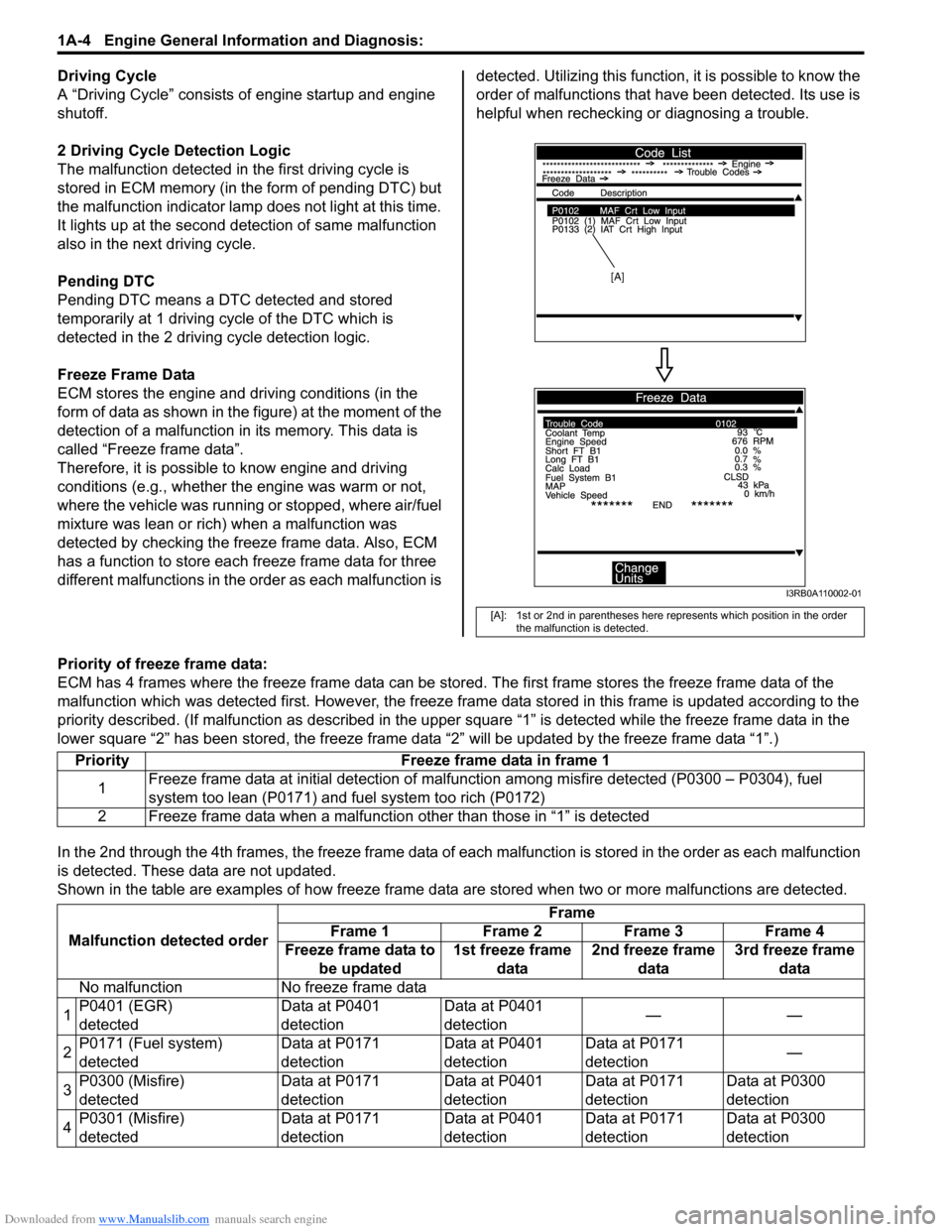
Freeze Frame Data
ECM stores the engine and driving conditions (in the
form of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the
detection of a malfunction in its memory. This data is
called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving
conditions (e.g., whether the engine was warm or not,
where the vehicle was running or stopped, where air/fuel
mixture was lean or rich) when a malfunction was
detected by checking the freeze frame data. Also, ECM
has a function to store each freeze frame data for three
different malfunctions in the order as each malfunction is detected. Utilizing this function,
it is possible to know the
order of malfunctions that ha ve been detected. Its use is
helpful when rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
Priority of freeze frame data:
ECM has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stor ed. The first frame stores the freeze frame data of the
malfunction which was detected first. Howe ver, the freeze frame data stored in this frame is updated according to the
priority described. (If malfunction as described in the upper square “1” is detected while the freeze frame data in the
lower square “2” has been stored, the freeze frame data “2” will be updated by the freeze frame data “1”.)
In the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each malfunction is stored in the order as each malfunction
is detected. These data are not updated.
Shown in the table are examples of how freeze frame data are stored when two or more malfunctions are detected.
[A]: 1st or 2nd in parentheses here represents which position in the order
the malfunction is detected.
[A]
I3RB0A110002-01
Priority Freeze frame data in frame 1
1 Freeze frame data at initial detection of malfuncti
on among misfire detected (P0300 – P0304), fuel
system too lean (P0171) and fuel system too rich (P0172)
2 Freeze frame data when a malfunctio n other than those in “1” is detected
Malfunction detected order Frame
Frame 1 Frame 2 Frame 3 Frame 4
Freeze frame data to be updated 1st freeze frame
data 2nd freeze frame
data 3rd freeze frame
data
No malfunction No freeze frame data
1 P0401 (EGR)
detected Data at P0401
detectionData at P0401
detection
——
2 P0171 (Fuel system)
detected Data at P0171
detectionData at P0401
detectionData at P0171
detection
—
3 P0300 (Misfire)
detected Data at P0171
detectionData at P0401
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection
4 P0301 (Misfire)
detected Data at P0171
detectionData at P0401
detectionData at P0171
detectionData at P0300
detection