head SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 23 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine General Information: 0A-2
SAS: Steering Angle Sensor
SDM: Sensing and Diagnostic Module (Air Bag Controller, Air bag Control Module)
SDT: Smart Diagnostic Tester
SFI: Sequential Multipor t Fuel Injection
SOHC: Single Over Head Camshaft
T:
TBI: Throttle Body Fuel Injection (Single-Point Fuel
Injection, SPI)
TCC: Torque Converter Clutch
TCM: Transmission Control Module (A/T Controller, A/T
Control Module)
TDC: Top Dead Center
TP Sensor: Throttle Position Sensor TVV:
Thermal Vacuum Valve (Thermal Vacuum
Switching Valve, TVSV, Bi metal Vacuum Switching
Valve, BVSV)
TWC: Three Way Catalytic Converter (Three Way
Catalyst)
2WD: 2 Wheel Drive
U:
USB: Universal Serial Bus
V:
VIN: Vehicle Identification Number
VSS: Vehicle Speed Sensor
VVT: Variable Valve Timing (Camshaft Position Control)
W:
WU-OC: Warm Up Oxidation Catalytic Converter
WU-TWC: Warm Up Three Way Catalytic Converter
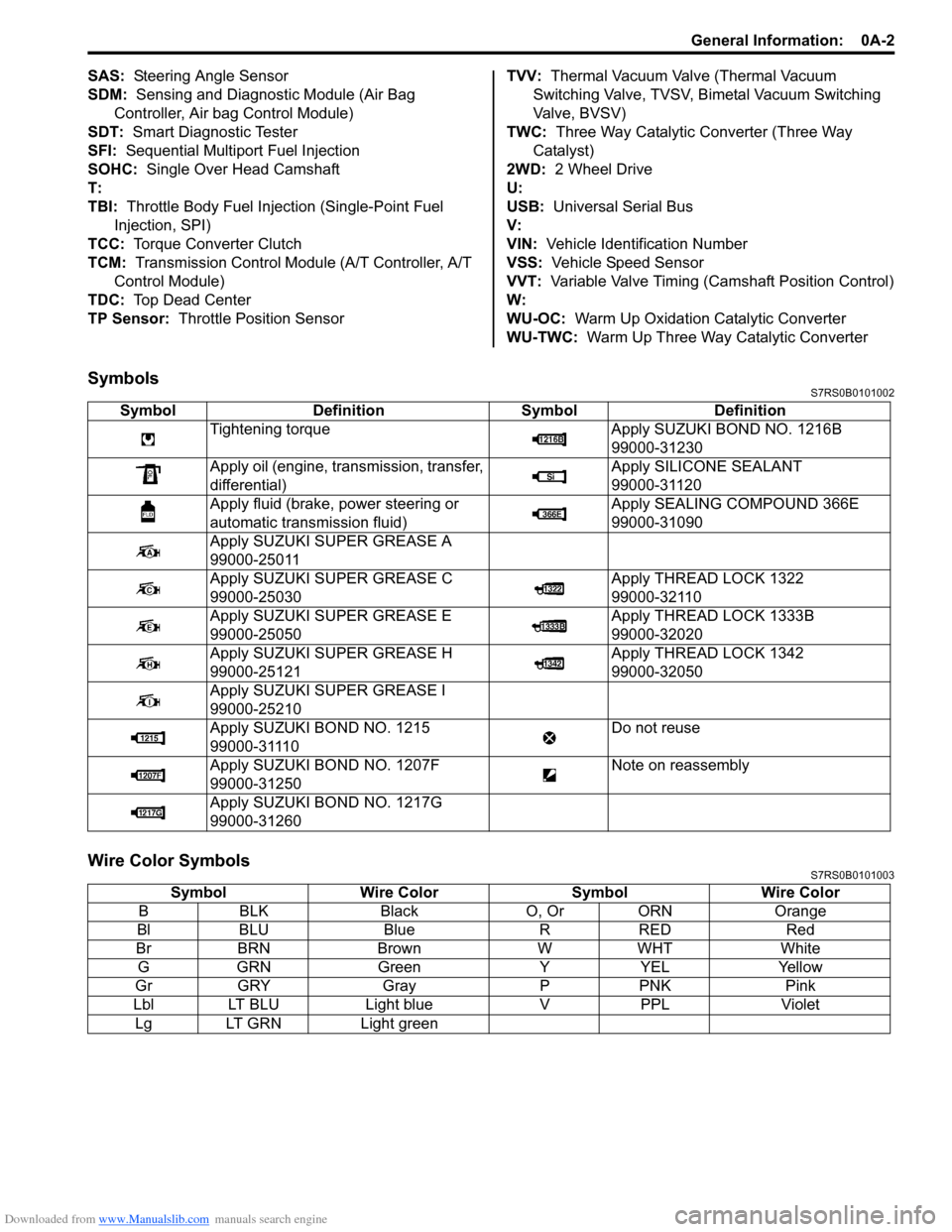
SymbolsS7RS0B0101002
Wire Color SymbolsS7RS0B0101003
Symbol Definition SymbolDefinition
Tightening torque Apply SUZUKI BOND NO. 1216B
99000-31230
Apply oil (engine, transmission, transfer,
differential) Apply SILICONE SEALANT
99000-31120
Apply fluid (brake, power steering or
automatic transmission fluid) Apply SEALING COMPOUND 366E
99000-31090
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE A
99000-25011
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE C
99000-25030 Apply THREAD LOCK 1322
99000-32110
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE E
99000-25050 Apply THREAD LOCK 1333B
99000-32020
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE H
99000-25121 Apply THREAD LOCK 1342
99000-32050
Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE I
99000-25210
Apply SUZUKI BOND NO. 1215
99000-31110 Do not reuse
Apply SUZUKI BO ND NO. 1207F
99000-31250 Note on reassembly
Apply SUZUKI BO ND NO. 1217G
99000-31260
Symbol Wire Color SymbolWire Color
B BLK Black O, Or ORN Orange
Bl BLU Blue RRED Red
Br BRN Brown WWHT White
G GRN Green YYEL Yellow
Gr GRY Gray PPNK Pink
Lbl LT BLU Light blueVPPL Violet
Lg LT GRN Light green
Page 24 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-3 General Information:
There are two kinds of colored wire used in this vehicle. One is single-colored wire and the other is dual-colored
(striped) wire.
The single-colored wire uses only one color symbol (i.e. “GRN”).
The dual-colored wire uses two color sy mbols (i.e. “GRN/YEL”). The first symbo l represents the base color of the wire
(“GRN” in the figure) and the second symbol represents the color of the stripe (“YEL” in the figure).
Fasteners InformationS7RS0B0101004
Metric Fasteners
Most of the fasteners used for this vehicle are JIS-
defined and ISO-defined metric fasteners. When
replacing any fasteners, it is most important that
replacement fasteners be the correct diameter, thread
pitch and strength.
CAUTION!
Even when the nominal diameter (1) of thread
is the same, the thread pitch (2) or the width
across flats (3) may vary between ISO and
JIS. Refer to JIS-TO-ISO Main Fasteners
Comparison Table below for the difference.
Installing a mismatched bolt or nut will cause
damage to the thread.
Before installing, check the thread pitch for
correct matching and then tighten it by hand
temporarily. If it is tight, recheck the thread
pitch.
JIS-TO-ISO Main Fasteners Comparison Table Fastener Strength Identification
Most commonly used metric fastener strength property
classes are 4T, 6.8, 7T, 8.8 and radial line with the class
identification embossed on the head of each bolt. Some
metric nuts will be marked with punch, 6 or 8 mark
strength identification on the nut face. Figure shows the
different strength markings.
When replacing metric fasteners, be careful to use bolts
and nuts of the same strength or greater than the original
fasteners (the same number marking or higher). It is
likewise important to select replacement fasteners of the
correct diameter and thread
pitch. Correct replacement
bolts and nuts are available through the parts division.
Metric bolts: Identification class numbers or marks
correspond to bolt strength (increasing numbers
represent increasing strength).
I2RH01010010-01
Nominal diameter
M6 M8 M10 M12 M14
JIS Thread pitch 1.0 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.5
Width across flats 10 12 14 17 19
ISO Thread pitch 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.5 1.5
Width across flats 10 13 16 18 21
I4RH0A010005-01
1. Nut strength identification
I5RH01010001-01
Page 35 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-5
4) Screw new filter on oil filter stand by hand until the filter O-ring contacts mounting surface.
CAUTION!
To tighten oil filter prop erly, it is important to
accurately identify the position at which filter
O-ring first contacts mounting surface.
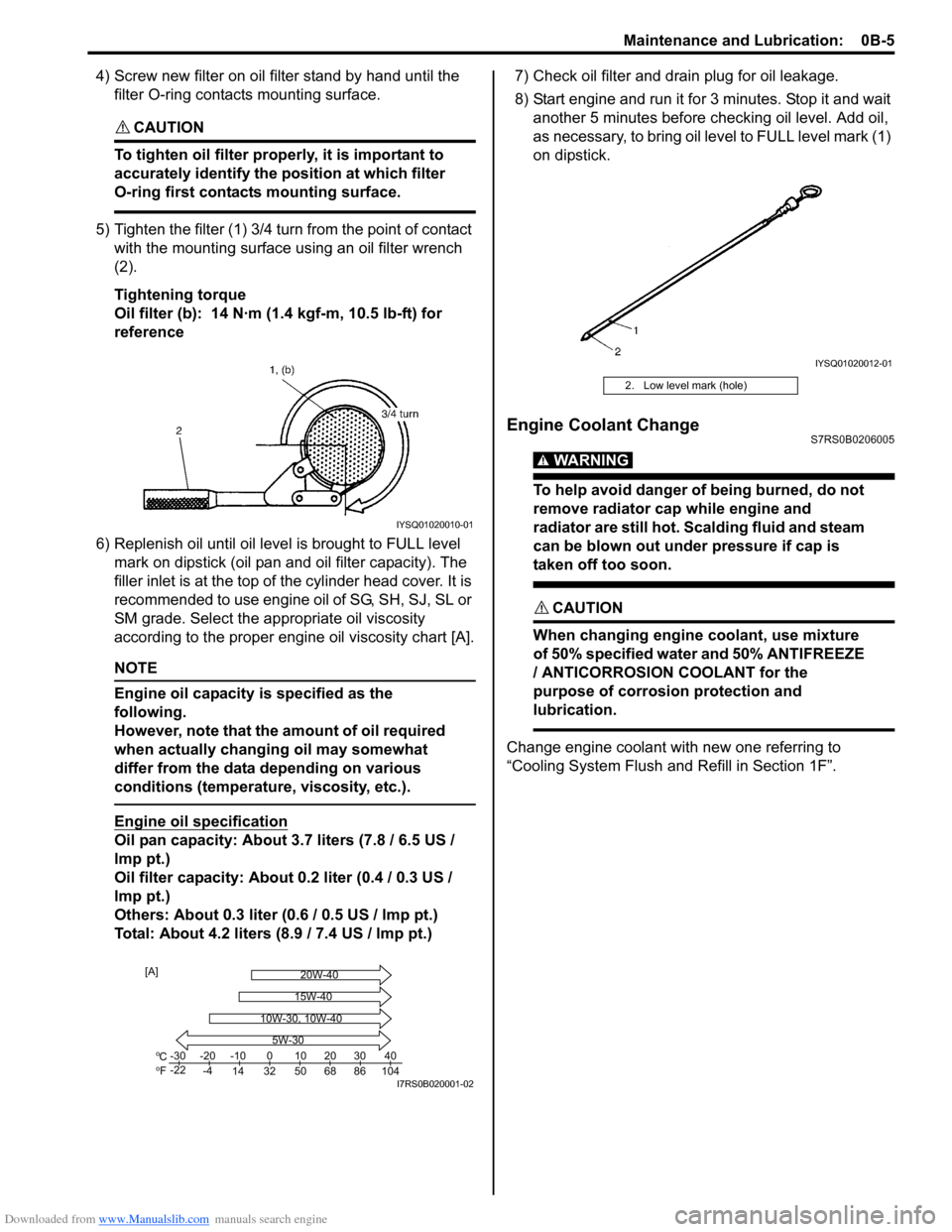
5) Tighten the filter (1) 3/4 tu rn from the point of contact
with the mounting surface using an oil filter wrench
(2).
Tightening torque
Oil filter (b): 14 N·m (1 .4 kgf-m, 10.5 lb-ft) for
reference
6) Replenish oil until oil leve l is brought to FULL level
mark on dipstick (oil pan and oil filter capacity). The
filler inlet is at the top of the cylinder head cover. It is
recommended to use engine oil of SG, SH, SJ, SL or
SM grade. Select the appropriate oil viscosity
according to the proper engine oil viscosity chart [A].
NOTE
Engine oil capacity is specified as the
following.
However, note that the amount of oil required
when actually changing oil may somewhat
differ from the data depending on various
conditions (temperature, viscosity, etc.).
Engine oil specification
Oil pan capacity: About 3.7 liters (7.8 / 6.5 US /
lmp pt.)
Oil filter capacity: About 0.2 liter (0.4 / 0.3 US /
lmp pt.)
Others: About 0.3 liter (0 .6 / 0.5 US / lmp pt.)
Total: About 4.2 liters (8.9 / 7.4 US / lmp pt.) 7) Check oil filter and drain plug for oil leakage.
8) Start engine and run it for 3 minutes. Stop it and wait
another 5 minutes before checking oil level. Add oil,
as necessary, to bring oil le vel to FULL level mark (1)
on dipstick.
Engine Coolant ChangeS7RS0B0206005
WARNING!
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not
remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam
can be blown out under pressure if cap is
taken off too soon.
CAUTION!
When changing engine coolant, use mixture
of 50% specified water and 50% ANTIFREEZE
/ ANTICORROSION COOLANT for the
purpose of corrosion protection and
lubrication.
Change engine coolant with new one referring to
“Cooling System Flush and Refill in Section 1F”.
IYSQ01020010-01
Co
Fo-30
-22 -20
-4 -10
14 32 50 68 86 104 010203040
5W-30
20W-40
15W-40
10W-30, 10W-40
[A]
I7RS0B020001-02
2. Low level mark (hole)
IYSQ01020012-01
Page 47 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1-iii
EVAP Canister Purge Valve and Its Circuit
Inspection.......................................................... 1B-2
Vacuum Passage Inspection .............................. 1B-3
Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber Inspection.......................................................... 1B-3
EVAP Canister Purge Valve Inspection .............. 1B-3
EVAP Canister Inspection ... ................................ 1B-4
EGR Valve Removal and Installation .................. 1B-4
EGR Valve Inspection ......................................... 1B-4
PCV Hose Inspection .......................................... 1B-4
PCV Valve Inspection ......................................... 1B-5
Special Tools and Equipmen t ............................. 1B-5
Special Tool ........................................................ 1B-5
Engine Electrical Devices .. ..................... 1C-1
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1C-1
ECM Removal and Installation ............................ 1C-1
MAP Sensor Inspection ...................................... 1C-2
Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-2
Electric Throttle Body System Calibration ........... 1C-5
APP Sensor Assembly On-V ehicle Inspection .... 1C-5
APP Sensor Assembly Removal and Installation ......................................................... 1C-5
APP Sensor Assembly Inspection ...................... 1C-6
ECT Sensor Removal and In stallation ................ 1C-6
ECT Sensor Inspection ....................................... 1C-7
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Heater On-Vehicle Inspection.......................................................... 1C-7
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Removal and Installation ......................................................... 1C-7
CMP Sensor Removal and In stallation ............... 1C-8
Camshaft Position (CMP) Se nsor Inspection ...... 1C-8
CKP Sensor Removal and Installation ................ 1C-9
CKP Sensor Inspection ....................................... 1C-9
Knock Sensor Removal and Installation ........... 1C-10
Main Relay, Fuel Pump Relay and Starting
Motor Control Relay Inspection....................... 1C-10
MAF and IAT Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection .... 1C-11
MAF and IAT Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 1C-11
MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection ....................... 1C-12
Electric Load Current Sensor On-Vehicle Inspection........................................................ 1C-12
Specifications ..................................................... 1C-13
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 1C-13
Engine Mechanical ......... ......................... 1D-1
General Description ............................................. 1D-1
Engine Construction Description ......................... 1D-1
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System Description .................... 1D-2
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 1D-4 Compression Check ............................................ 1D-4
Engine Vacuum Check ....................................... 1D-5
Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection ..................... 1D-6
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1D-9 Air Cleaner Components ..................................... 1D-9
Air Cleaner Element Removal and Installation .... 1D-9 Air Cleaner Element Ins
pection and Cleaning ..1D-10
Cylinder Head Co ver Removal and
Installation .......................................................1D-10
Throttle Body and Intake Manifold
Components ....................................................1D-12
Throttle Body On-Vehicle Inspection.................1D-13
Electric Throttle Body Assembly Removal and Installation .......................................................1D-13
Throttle Body Cleaning......................................1D-14
Intake Manifold Removal and Installation .........1D-14
Engine Mountings Components ........................1D-16
Engine Assembly Removal and Installation ......1D-17
Timing Chain Cover Components .....................1D-20
Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation ..1D-21
Timing Chain Cover Inspection .........................1D-23
Oil Control Valve Removal and Installation .......1D-23
Oil Control Valve Inspection ..............................1D-24
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components ....................................................1D-24
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Removal and Installation ................................................1D-25
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Inspection ..1D-27
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components ........1D-28
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and Installation .......................................................1D-29
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection ............1D-31
Valves and Cylinder Head Components ...........1D-34
Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and
Installation .......................................................1D-35
Valves and Cylinder Head Disassembly and Assembly.........................................................1D-37
Valves and Valve Guides Inspection.................1D-40
Cylinder Head Inspection . .................................1D-42
Valve Spring Inspection ....................................1D-43
Pistons, Piston Rings , Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Components ....................................1D-44
Pistons, Piston Rings , Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation .................1D-45
Pistons, Piston Rings , Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly ............1D-46
Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings Inspection ........................................................1D-47
Piston Pins and Connecting Rods Inspection ...1D-49
Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings Inspection ........................................................1D-50
Main Bearings, Cran kshaft and Cylinder
Block Components ..........................................1D-53
Main Bearings, Cran kshaft and Cylinder
Block Removal and Installa tion .......................1D-54
Crankshaft Inspection .......................................1D-57
Main Bearings Inspection . .................................1D-59
Sensor Plate Inspection ....................................1D-63
Rear Oil Seal Inspection ...................................1D-63
Flywheel Inspection...........................................1D-63
Cylinder Block Inspection ..................................1D-63
Specifications .................... .................................1D-64
Tightening Torque Specifications ......................1D-64
Special Tools and Equipmen t ...........................1D-66
Recommended Service Material .......................1D-66
Special Tool ......................................................1D-66
Page 61 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-11
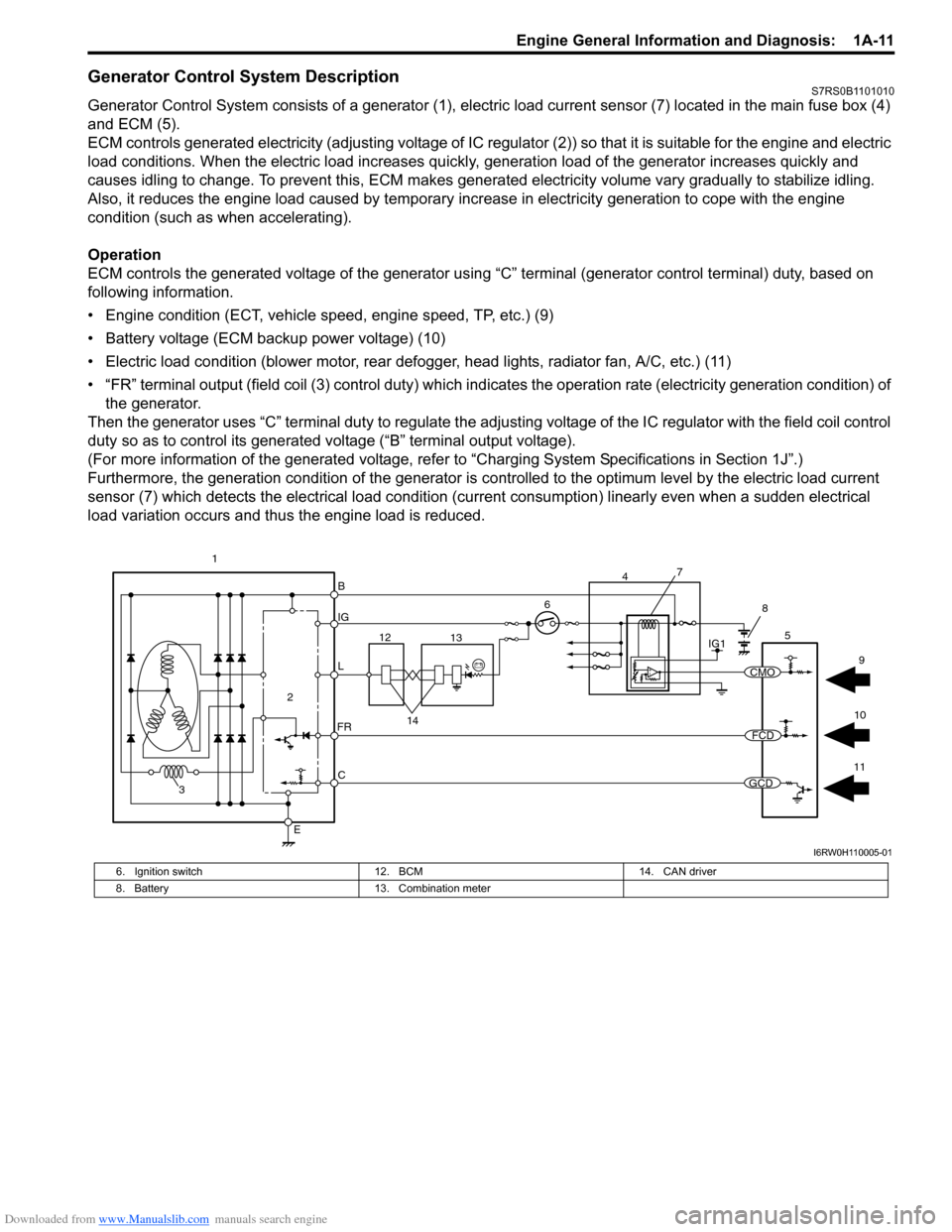
Generator Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101010
Generator Control System consists of a generator (1), electric load current sensor (7) located in the main fuse box (4)
and ECM (5).
ECM controls generated electricity (adjusting voltage of IC regulator (2)) so that it is suitable for the engine and electric
load conditions. When the electric load increases quickly, generation load of the generator increases quickly and
causes idling to change. To prevent this, ECM makes generated electricity volume vary gradually to stabilize idling.
Also, it reduces the engine load caused by temporary incr ease in electricity generation to cope with the engine
condition (such as when accelerating).
Operation
ECM controls the generated voltage of the generator using “C” terminal (generator control terminal) duty, based on
following information.
• Engine condition (ECT, vehicle speed, engine speed, TP, etc.) (9)
• Battery voltage (ECM backup power voltage) (10)
• Electric load condition (blower motor, rear defogger, head lights, radiator fan, A/C, etc.) (11)
• “FR” terminal output (field coil (3) cont rol duty) which indicates the operation rate (electricity generation condition) of
the generator.
Then the generator uses “C” terminal duty to regulate the adju sting voltage of the IC regulator with the field coil control
duty so as to control its generated voltage (“B” terminal output voltage).
(For more information of the generated voltage, refer to “Charging System Specifications in Section 1J”.)
Furthermore, the generation condition of the generator is co ntrolled to the optimum level by the electric load current
sensor (7) which detects the electrical load condition (cur rent consumption) linearly even when a sudden electrical
load variation occurs and thus the engine load is reduced.
B
IG
L
C
E
6
2
3
FR
5
12 13
14
1IG1
7
4
8
11
10 9
CMO
FCD
GCD
I6RW0H110005-01
6. Ignition switch
12. BCM 14. CAN driver
8. Battery 13. Combination meter
Page 84 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-34 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
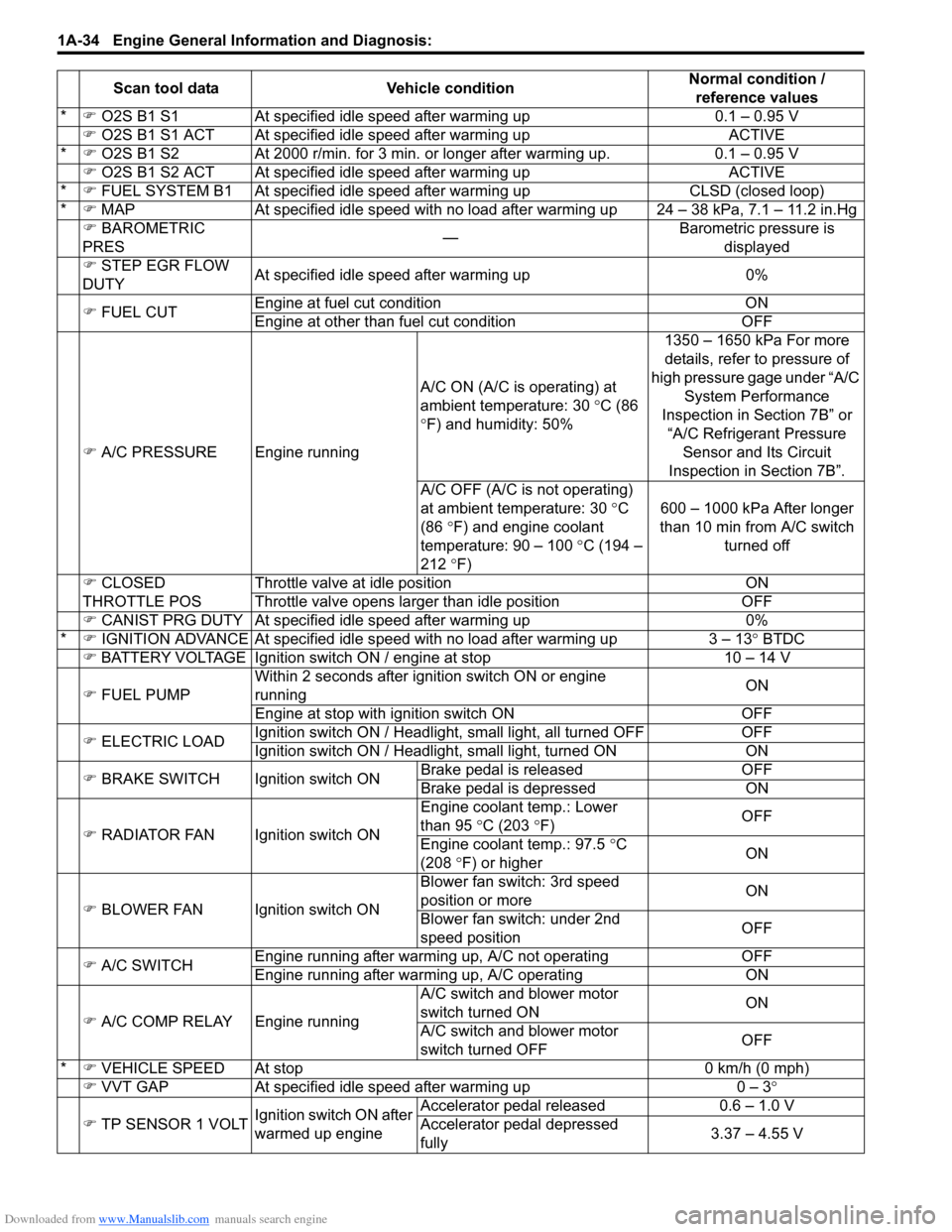
*�) O2S B1 S1 At specified idle speed after warming up 0.1 – 0.95 V
�) O2S B1 S1 ACT At specified id le speed after warming up ACTIVE
* �) O2S B1 S2 At 2000 r/min. for 3 min. or longer after warming up. 0.1 – 0.95 V
�) O2S B1 S2 ACT At specified id le speed after warming up ACTIVE
* �) FUEL SYSTEM B1 At specif ied idle speed after warming up CLSD (closed loop)
* �) MAP At specified idle speed with no load after warming up 24 – 38 kPa, 7.1 – 11.2 in.Hg
�) BAROMETRIC
PRES —Barometric pressure is
displayed
�) STEP EGR FLOW
DUTY At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
�) FUEL CUT Engine at fuel cut condition ON
Engine at other than fuel cut condition OFF
�) A/C PRESSURE Engine running A/C ON (A/C is operating) at
ambient temperature: 30
°C (86
° F) and humidity: 50% 1350 – 1650 kPa For more
details, refer to pressure of
high pressure gage under “A/C System Performance
Inspection in Section 7B” or “A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor and Its Circuit
Inspection in Section 7B”.
A/C OFF (A/C is not operating)
at ambient temperature: 30 ° C
(86 °F) and engine coolant
temperature: 90 – 100 °C (194 –
212 °F) 600 – 1000 kPa After longer
than 10 min from A/C switch turned off
�) CLOSED
THROTTLE POS Throttle valve at idle position ON
Throttle valve opens larger than idle position OFF
�) CANIST PRG DUTY At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
* �) IGNITION ADVANCE At specified idle s peed with no load after warming up 3 – 13 ° BTDC
�) BATTERY VOLTAGE Ignition switch ON / engine at stop 10 – 14 V
�) FUEL PUMP Within 2 seconds after ignition switch ON or engine
running
ON
Engine at stop with ignition switch ON OFF
�) ELECTRIC LOAD Ignition switch ON / Headligh
t, small light, all turned OFF OFF
Ignition switch ON / Headli ght, small light, turned ON ON
�) BRAKE SWITCH Igni tion switch ONBrake pedal is released OFF
Brake pedal is depressed ON
�) RADIATOR FAN Ignition switch ON Engin
e coolant temp.: Lower
than 95 °C (203 °F) OFF
Engine coolant temp.: 97.5 °C
(208 °F) or higher ON
�) BLOWER FAN Ignition switch ON Blower fan switch: 3rd speed
position or more
ON
Blower fan switch: under 2nd
speed position OFF
�) A/C SWITCH Engine running after warming up, A/C not operating
OFF
Engine running after warming up, A/C operating ON
�) A/C COMP RELAY Engine running A/C switch and blower motor
switch turned ON
ON
A/C switch and blower motor
switch turned OFF OFF
* �) VEHICLE SPEED At stop 0 km/h (0 mph)
�) VVT GAP At specified idle speed after warming up 0 – 3°
�) TP SENSOR 1 VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
0.6 – 1.0 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.37 – 4.55 V
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
Page 86 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-36 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
O2S B1 S1 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-1,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates activation condition of HO2S-1.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
O2S SENSOR B1 S2 (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
V)
It indicates output voltage of HO2S-2 installed on
exhaust pipe (post-catalyst). It is used to detect catalyst
deterioration.
O2S B1 S2 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates acti vation condition of HO2S-2.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
FUEL SYSTEM (FUEL SYSTEM STATUS)
Air/fuel ratio feedback loop status displayed as one of
the followings.
OPEN: Open-loop has not yet satisfied conditions to go
closed loop.
CLOSED: Closed-loop using oxygen sensor(s) as
feedback for fuel control.
OPEN-DRIVE COND: Open-loop due to driving
conditions (Power enrichment, etc.).
OPEN SYS FAULT: Open-loop due to detected system
fault.
MAP (MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE, in.Hg,
kPa)
This value indicates how much correction is necessary
to keep the air/fuel mixture stoichiometrical.
It is detected by manifold absolute pressure sensor.
BAROMETRIC PRESS (kPa, in.Hg)
This parameter represents a measurement of barometric
air pressure and is used for al titude correction of the fuel
injection quantity and IAC valve control.
STEP EGR FLOW DUTY (%)
This parameter indicates opening rate of EGR valve
which controls the amount of EGR flow.
FUEL CUT (ON/OFF)
ON: Fuel being cut (output signal to injector is stopped)
OFF: Fuel not being cut
A/C PRESSURE (A/C REFRIGERANT ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE, kPa)
This parameter indicates A/C refrigerant absolute
pressure calculated by ECM.
CLOSED THROTTLE PO S (CLOSED THROTTLE
POSITION, ON/OFF)
This parameter reads ON wh en throttle valve is fully
closed, or OFF when it is not fully closed. CANIST PRG DUTY (EVAP CANISTER PURGE FLOW
DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates valve ON (valve open) time
rate within a certain set cycle of EVAP canister purge
valve which controls the amount of EVAP purge.
IGNITION ADVANCE (IGNITION TIMING ADVANCE
FOR NO.1 CYLINDER,
°)
Ignition timing of No.1 cylinder is commanded by ECM.
The actual ignition timing should be checked by using
the timing light.
BATTERY VOLTAGE (V)
This parameter indicates battery positive voltage
inputted from main relay to ECM.
FUEL PUMP (ON/OFF)
ON is displayed when ECM activates the fuel pump via
the fuel pump relay switch.
ELECTRIC LOAD (ON/OFF)
ON: Headlight or small light ON signal inputted.
OFF: Above electric loads all turned OFF.
BRAKE SW (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the brake switch.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN (RADIATOR COOLING
FAN CONTROL RELAY, ON/OFF)
ON: Command for radiator cooling fan control relay
operation being output.
OFF: Command for relay operation not being output.
BLOWER FAN (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the blower fan
motor switch.
A/C SWITCH (ON/OFF)
ON: Command for A/C operatio n being output from ECM
to HVAC.
OFF: Command for A/C oper ation not being output.
A/C COMP RELAY (A/C COMPRESSOR RELAY, ON/
OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the A/C switch.
VEHICLE SPEED (km/h, mph)
It is computed based on pulse signals from vehicle
speed sensor.
VVT GAP (TARGET-ACTUAL POSITION, °)
It is calculated using the formula: target valve timing
advance – actual valve timing advance.
TP SENSOR 1 VOLT (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(MAIN) OUTPUT VOLTAGE, V)
The TP sensor (main) reading provides throttle valve
opening information in the form of voltage.
Page 91 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-41
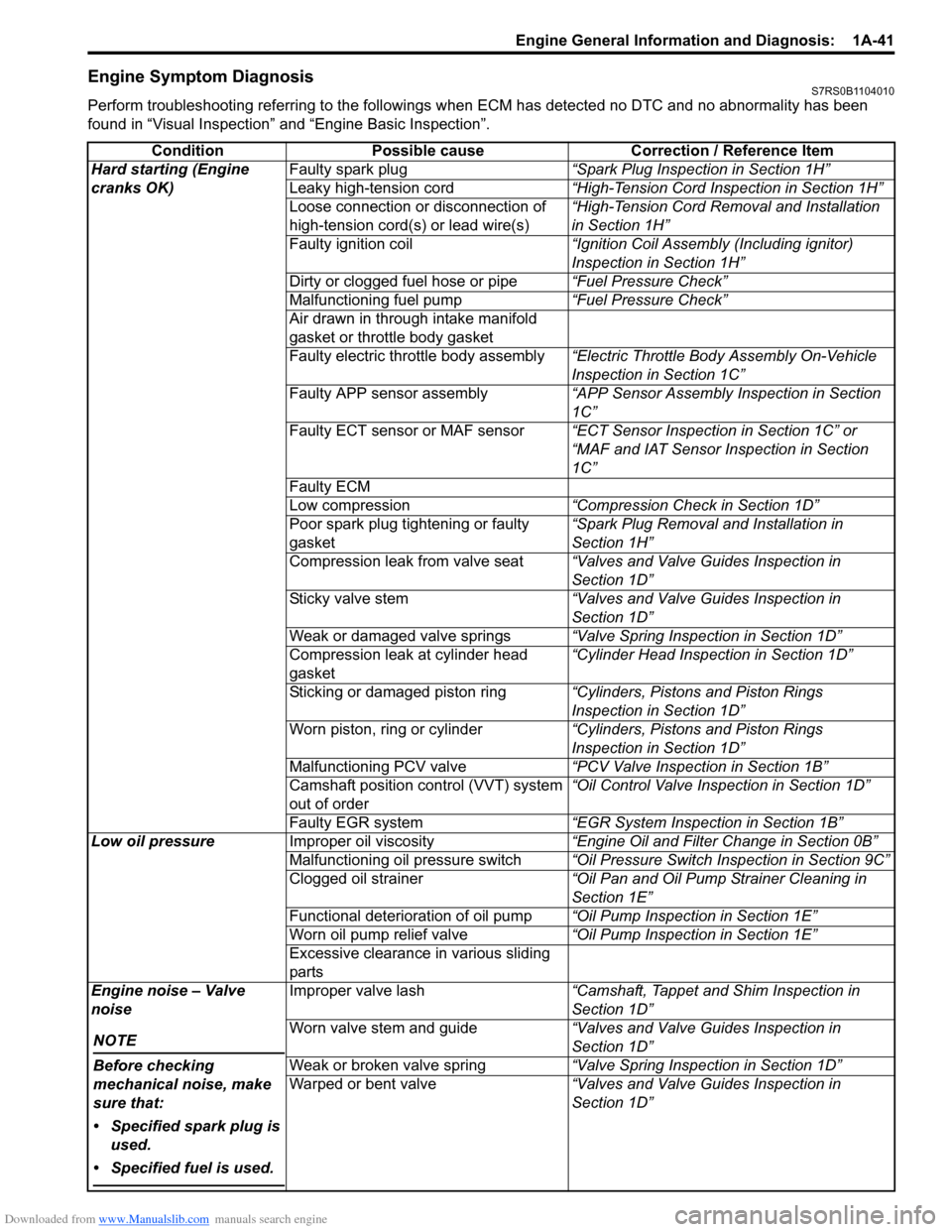
Engine Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1104010
Perform troubleshooting referring to the followings when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in “Visual Inspection” and “Engine Basic Inspection”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Hard starting (Engine
cranks OK) Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cord(s) or lead wire(s) “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump “Fuel Pressure Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor spark plug tightening or faulty
gasket “Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”
Compression leak from valve seat “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Sticky valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or damaged valve springs “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Compression leak at cylinder head
gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Sticking or damaged piston ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston, ring or cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Malfunctioning PCV valve “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Low oil pressure Improper oil viscosity “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch “Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
Clogged oil strainer “Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning in
Section 1E”
Functional deterioration of oil pump “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Worn oil pump relief valve “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Excessive clearance in various sliding
parts
Engine noise – Valve
noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Improper valve lash “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem and guide “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or broken valve spring “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Warped or bent valve “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Page 92 of 1496
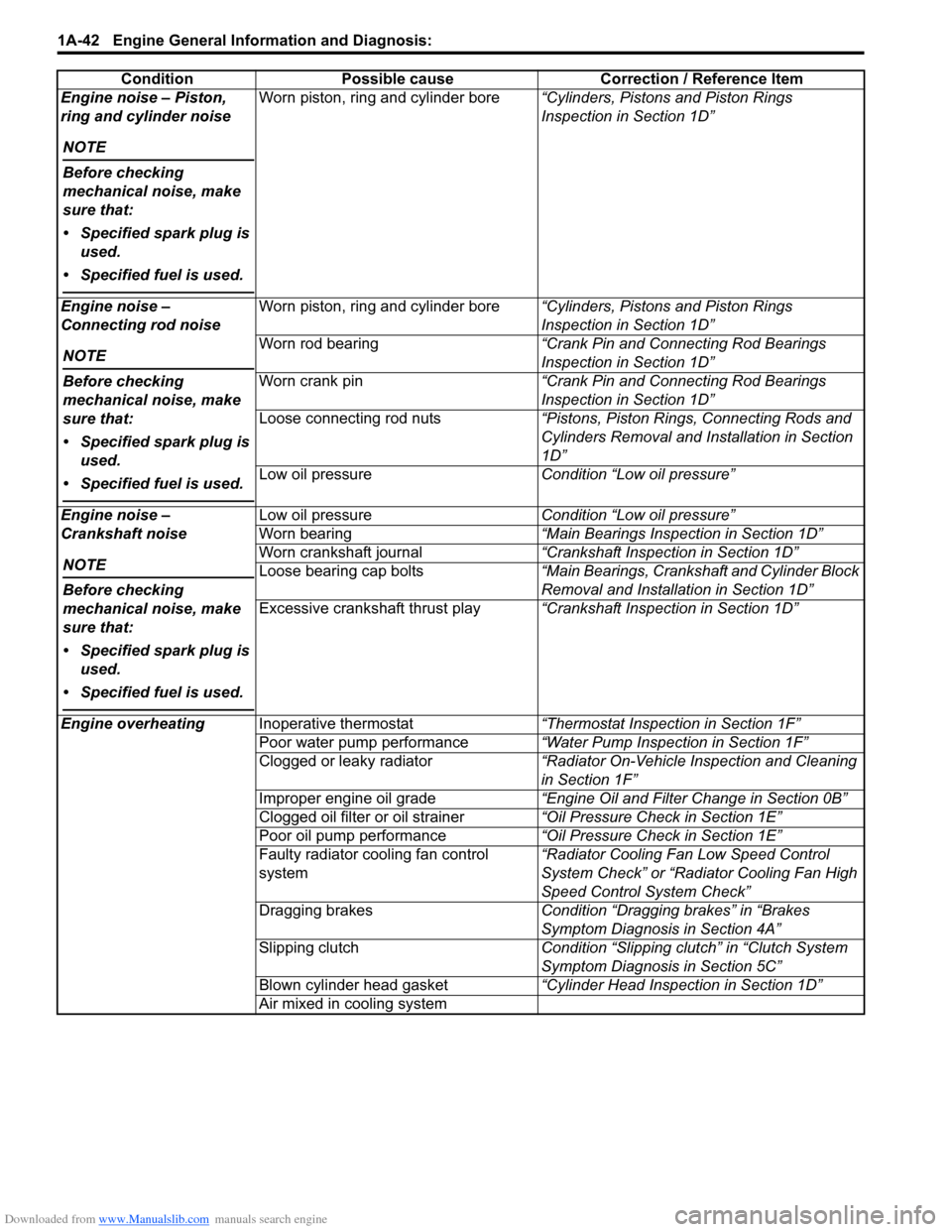
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-42 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine noise – Piston,
ring and cylinder noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine noise –
Connecting rod noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn rod bearing “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crank pin “Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose connecting rod nuts “Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation in Section
1D”
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Engine noise –
Crankshaft noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Low oil pressure Condition “Low oil pressure”
Worn bearing “Main Bearings Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn crankshaft journal “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Loose bearing cap bolts “Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”
Excessive crankshaft thrust play “Crankshaft Inspection in Section 1D”
Engine overheating Inoperative thermostat “Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Poor water pump performance “Water Pump Inspection in Section 1F”
Clogged or leaky radiator “Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1F”
Improper engine oil grade “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Poor oil pump performance “Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Faulty radiator cooling fan control
system “Radiator Cooling Fan Low Speed Control
System Check” or “Rad
iator Cooling Fan High
Speed Control System Check”
Dragging brakes Condition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C”
Blown cylinder head gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Air mixed in cooling system
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item