on-board diagnostic system description SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 45 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1- i
1
Section 1
CONTENTS
Engine
Precautions ................................................. 1-1
Precautions............................................................. 1-1
Precautions for Engine .......................................... 1-1
Engine General Information and
Diagnosis ............. .................................... 1A-1
Precautions........................................................... 1A-1
Precautions on Engine Service ........................... 1A-1
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System .............................................................. 1A-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble ..................... 1A-1
Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection................ 1A-2
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration ......................................................... 1A-2
General Description ............................................. 1A-2 Statement on Cleanliness and Care ................... 1A-2
Engine Diagnosis General Description ............... 1A-3
On-Board Diagnostic System Description ........... 1A-3
Data Link Connector (DLC) ................................. 1A-6
Engine and Emission Control System Description ........................................................ 1A-6
CAN Communication System Description........... 1A-7
Air Intake System Description ............................. 1A-9
Description of Electric Throttle Body System ...... 1A-9
Description of Electric Throttle Body System Calibration ....................................................... 1A-10
Fuel Cut Control Description ............................. 1A-10
Generator Control System Description ............. 1A-11
Electronic Control System Description .............. 1A-12
Engine and Emission Control Input / Output Table ............................................................... 1A-18
Schematic and Routing Diagram ...................... 1A-19 Engine and Emission Control System Diagram .......................................................... 1A-19
Component Locatio n ......................................... 1A-21
Electronic Control System Components Location .......................................................... 1A-21
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 1A-22 Engine and Emission Control System Check.... 1A-22
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check .......... 1A-25
DTC Check ....................................................... 1A-26
DTC Clearance ................................................. 1A-27
DTC Table ......................................................... 1A-27
Fail-Safe Table ................ .................................. 1A-31 Scan Tool Data ................................................. 1A-33
Visual Inspection ............................................... 1A-37
Engine Basic Inspection .................................... 1A-38
Engine Symptom Diagnosis .............................. 1A-41
MIL Does Not Come ON with Ignition Switch
ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can Be
Started) ........................................................... 1A-47
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after Engine Starts................................................... 1A-48
DTC P0010: “A” Camshaft Position Actuator Circuit .............................................................. 1A-49
DTC P0011 / P0012: “A” Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System
Performance / -Retarded................................. 1A-52
DTC P0031 / P0032: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High (Sensor-1) .......................... 1A-54
DTC P0037 / P0038: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High (Sensor-2) .......................... 1A-56
DTC P0101: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range / Performance ...................................... 1A-58
DTC P0102: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input......................................................... 1A-61
DTC P0103: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit High Input ........................................................ 1A-63
DTC P0106: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circuit Range /
Performance.................................................... 1A-64
DTC P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circ uit Low Input............ 1A-66
DTC P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circ uit High Input ........... 1A-67
DTC P0111: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Range / Performance ........................... 1A-69
DTC P0112: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Low ...................................................... 1A-72
DTC P0113: Intake Air Temperature 1 Sensor Circuit High...................................................... 1A-74
DTC P0116: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range / Performance ........................... 1A-76
DTC P0117: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low ...................................................... 1A-79
DTC P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High...................................................... 1A-81
DTC P0122: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “A” (Main) Circuit Low ........................ 1A-83
Page 51 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-1
Engine
Engine General Information and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on Engine ServiceS7RS0B1100001
CAUTION!
The following information on engine service
should be noted carefully, as it is important in
preventing damage, and in contributing to
reliable engine performance.
• When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do
not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against
oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer,
resulting in damaged oil pick-up unit.
• It should be kept in mind , while working on engine,
that 12-volt electrical syste m is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals
can be grounded, ground cable of the battery should
be disconnected at battery.
• Any time the air cleaner, throttle body or intake manifold is removed, the intake opening should be
covered. This will protect against accidental entrance
of foreign material which could follow intake passage
into cylinder and cause extensive damage when
engine is started.
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System
S7RS0B1100005
There are two types of On -Board Diagnostic (OBD)
system, Euro OBD system and non-Euro-OBD system,
depending on the vehicle specification.
As the diagnosis function is different between these two
types, be sure to fully understand the OBD system
referring to “On-Board Diagnostic System Description”.
OBD System Summary Table
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B1100002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• Don’t disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable
from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine
or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information
in ECM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be cleared as well as checke d by using SUZUKI scan
tool or OBD generic scan tool. Before using scan tool,
read its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to
have good understanding as to what functions are
available and how to use it.
For Euro OBD model it is indistinguishable which
module turns on MIL because not only ECM but also
TCM (A/T model) turns on MIL (For details of on-
board diagnostic system for A/T model, refer to “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description in Section 5A”).
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM (A/T model) for
DTC when MIL lights on.
When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– OBD generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM (A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instructi on in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected)
Euro OBD
model Non-Euro-OBD
model
Quantity of DTC
related to engine
control Approx. 80 Approx. 60
Freeze frame
data Available Not available
SUZUKI scan
tool Available Available
OBD generic
scan tool Available Not available
Page 53 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-3
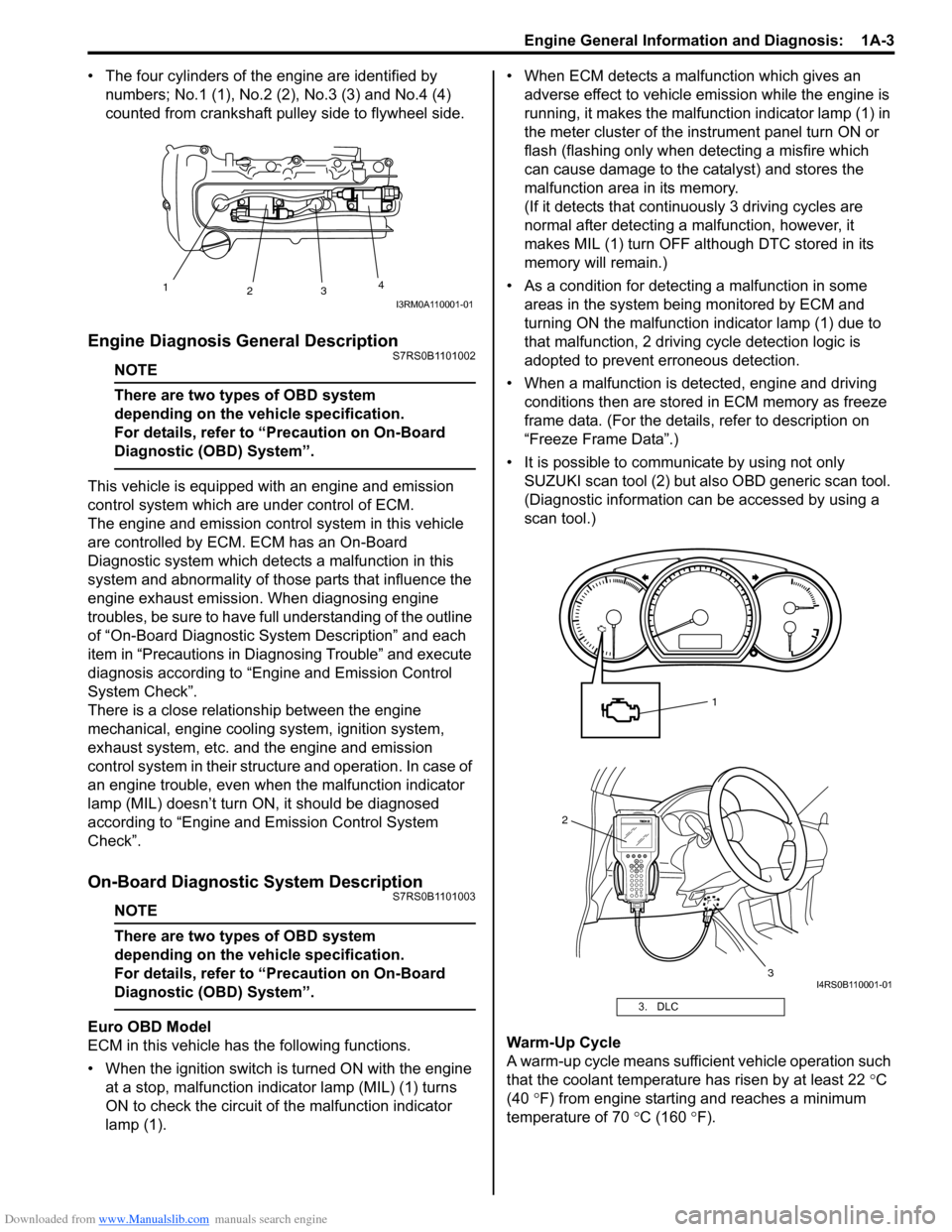
• The four cylinders of the engine are identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2 ), No.3 (3) and No.4 (4)
counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
Engine Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B1101002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission
control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle
are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board
Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this
system and abnormality of those parts that influence the
engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine
troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “Engine and Emission Control
System Check”.
There is a close relationship between the engine
mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system,
exhaust system, etc. and the engine and emission
control system in their structure and operation. In case of
an engine trouble, even when the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed
according to “Engine and Emission Control System
Check”.
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B1101003
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Euro OBD Model
ECM in this vehicle has the following functions.
• When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns
ON to check the circuit of the malfunction indicator
lamp (1). • When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an
adverse effect to vehicle emission while the engine is
running, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in
the meter cluster of the inst rument panel turn ON or
flash (flashing only when detecting a misfire which
can cause damage to the catalyst) and stores the
malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that contin uously 3 driving cycles are
normal after detecting a malfunction, however, it
makes MIL (1) turn OFF although DTC stored in its
memory will remain.)
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data”.)
• It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also OBD generic scan tool.
(Diagnostic information can be accessed by using a
scan tool.)
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficie nt vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 ° F).
1
23 4
I3RM0A110001-01
3. DLC
2
3
1
I4RS0B110001-01
Page 77 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-27
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B1104004
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Using Scan Tool1) Connect OBD generic scan to ol or SUZUKI scan tool
to data link connector in the same manner as when
making this connection for DTC check.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and then ON.
3) Erase DTC and pending DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool. Refer to scan
tool operator’s manual for further details.
4) After completing the clear ance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
NOTE
DTC and freeze frame data stored in ECM
memory are also cleared in the following
cases. Be careful not to clear them before
keeping their record.
• When power to ECM is cut off (by disconnecting battery cable, removing
fuse or disconnecting ECM connectors).
• When the same malfunction (DTC) is not detected again during 40 engine warm-up
cycles. (See “Warm-Up Cycle” of “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description”.)
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model)
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect battery negative cable for specified time below to erase diagnostic trouble code stored in
ECM memory and reconnect it.
Time required to erase DTC
DTC TableS7RS0B1104005
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
• For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• For non-Euro-OBD model, some of DTC No. with delta ( �U) mark in the following table can not be
detected by ECM depending on vehicl e specification and local regulation.
• DTC with square ( �†) mark in the following table can be detected only for Hong Kong model.
• DTC with circle ( �{) mark in the following table can be detected only for Euro OBD model and Hong
Kong model.
• For Euro OBD model, with the generic scan tool, onl y star (*) marked DTC No. in the following table
can be read.
• 1 driving cycle: MIL lights up when DTC is detected during 1 driving cycle.
• 2 driving cycles: MIL lights up when the same DTC is detected also in the next driving cycle after DTC is detected and stored temporarily in the first driving cycle.
• *2 driving cycles: MIL blinks or lights up. Refer to “DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304: Random / Multiple
Cylinder Misfire Detected / Cylinder 1 / Cylinder 2 / Cylinder 3 / Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected” for
details.
Ambient temperature Time to cut power to ECM
Over 0 °C (32 ° F) 30 sec. or longer
Under 0 °C (32 °F) Not specifiable.
Select a place with higher
than 0 °C (32 °F)
temperature.
DTC No. Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL
�) *P0010 “A” camshaft position actuator
circuit Oil control valve circuit open or short. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0011 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-advanced or system
performance Actual value of advanced va
lve timing does not reach
target value, or valve timi ng is advanced although ECM
command is most retarding. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0012 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-retarded 2 driving
cycles
Page 83 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-33
Scan Tool DataS7RS0B1104007
As the data values are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the normally operating vehicles
by using a scan tool, use them as re ference values. Even when the vehicle is in good condition, there may be cases
where the checked value does not fall within each specified data range. Therefore, judgment as abnormal should not
be made by checking with these data alone.
Also, conditions that can be checked by the scan tool are those detected by ECM and output from ECM as commands
and there may be cases where the engine or actuator is not operating (in the condition) as indicated by the scan tool.
Be sure to use the timing light to check the ignition timing.
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• With the generic scan tool, only star (*) marked data in the following table can be read.
• When checking the data with the engine running at idle or racing, be sure to shift M/T gear to the neutral position and A/T gear to the “Park” position and pull the parking brake fully. Also, if nothing
or “no load” is indicated, turn O FF A/C (if equipped with A/C), all electric loads, P/S and all the other
necessary switches.
�) P2122 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“D” (main)
circuit low input
• ECM turns off throttle actuator control relay and throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
• ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P2123 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“D” (main)
circuit high input
�) P2127 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“E” (sub)
circuit low input
�) P2128 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“E” (sub)
circuit high input
�) P2135 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“A”/“B”
(main) / (sub) voltage correction
�) P2138 Throttle pedal position sensor/switch “D”/“E”
(main) / (sub) voltage correlation
�) P2227 Barometric pressure sensor performance problem ECM controls actuators assuming that barometric
pressure is 101.33 kPa (762 mmHg).
DTC No. Detected item Fail-safe operation
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
* �) COOLANT TEMP At specified idle speed after warming up 80 – 100 °C, 176 – 212 °F
* �) INTAKE AIR TEMP. At specifie d idle speed after warming up –5
°C (23 °F) + environmental
temp. to 40 °C (104 °F) +
environmental temp.
* �) ENGINE SPEED It idling with no load after warming upDesired idle speed ± 50 rpm
�) INJ PULSE WIDTH At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
2.0 – 4.0 msec.
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 2.0 – 3.6 msec.
�) DESIRED IDLE It idling with radiator cooling fan stopped and all electrical
parts turned OFF after warming up, M/T at neutral 700 rpm
* �) SHORT FT B1 At specified idle speed after warming up –20 – +20%
* �) LONG FT B1 At specified idle speed after warming up –20 – +20%
�) TOTAL FUEL TRIM
B1 At specified idle speed after warming up
–35 – +35%
* �) MAF At specified idle speed wit
h no load after warming up 1.0 – 4.0 g/s 0.14 – 0.52 lb/
min.
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 4.0 – 12.0 g/s 0.53 – 1.58 lb/
min.
* �) CALC LOAD At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
18 – 28%
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 13 – 23%
* �)
THROTTLE
POSITION Ignition switch ON /
warmed up engine
stoppedAccelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
Page 641 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 5- i
5
Section 5
CONTENTS
Transmission / Transaxle
Precautions ................................................. 5-1
Precautions............................................................. 5-1
Precautions on Transmission / Transaxle ............. 5-1
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle ....... 5A-1
Precautions........................................................... 5A-1Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble ..................... 5A-1
Precautions for Disassembly and Reassembly ...................................................... 5A-1
General Description ............................................. 5A-3 A/T Description ................................................... 5A-3
Clutch / Brake / Planetary Gear Function of Automatic Transaxle ......................................... 5A-6
Table of Component Operation ........................... 5A-7
Brake Interlock System Construction .................. 5A-8
A/T Diagnosis General Description ..................... 5A-8
On-Board Diagnostic System Description ........... 5A-8
CAN Communication System Description........... 5A-9
Schematic and Routing Diagram ...................... 5A-10 Transmission Control Module (TCM) Wiring
Diagram .......................................................... 5A-10
Automatic Gear Shift Table ............................... 5A-12
Component Locatio n ......................................... 5A-13
Electronic Shift Cont rol System Components
Location .......................................................... 5A-13
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 5A-15 A/T System Check ............................................ 5A-15
Visual Inspection ............................................... 5A-18
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check .......... 5A-18
Transmission Warning Ligh t Check .................. 5A-18
DTC Table ......................................................... 5A-19
DTC Check ....................................................... 5A-20
DTC Clearance ................................................. 5A-20
Fail-Safe Table ................ .................................. 5A-21
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 5A-23
A/T Basic Check ............................................... 5A-26
Road Test ......................................................... 5A-27
Manual Road Test ........... .................................. 5A-29
Engine Brake Test ............................................ 5A-30
Stall Test ........................................................... 5A-30
Time Lag Test ................................................... 5A-31
Line Pressure Test .......... .................................. 5A-32
“P” Range Test.................................................. 5A-33
A/T Symptom Diagnosis ..... .............................. 5A-34 No Gear Shift to 4th gear .................................. 5A-41
No Lock-Up Occurs ........................................... 5A-42
Transmission Warning Light Circuit Check –
Light Does Not Come “ON” at Ignition Switch
ON ................................................................... 5A-43
Transmission Warning Light Circuit Check – Light Remains “ON” at Ignition Switch ON ...... 5A-43
DTC P0602: Control Module Programming Error ................................................................ 5A-44
DTC P0705: Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Malfunction (PRNDL input) .................. 5A-44
DTC P0707: Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Low ...................................................... 5A-46
DTC P0712: Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit Low ... ................................. 5A-48
DTC P0713: Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor “A” Circuit High .. ................................. 5A-49
DTC P0717: Input / Turbine Speed Sensor “A” Circuit Malfunction........................................... 5A-51
DTC P0722: Output Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal .............................................................. 5A-52
DTC P0787: Shift / Timing Solenoid Low .......... 5A-54
DTC P0788: Shift / Timing Solenoid High ......... 5A-56
DTC P0961: Pressure Control Solenoid “A”
Control Circuit Range / Performance .............. 5A-58
DTC P0962: Pressure Control Solenoid “A”
Control Circuit Low .......................................... 5A-60
DTC P0963: Pressure Control Solenoid “A”
Control Circuit High ......................................... 5A-62
DTC P0973 / P0976: Shift Solenoid “A” Control Circuit Low / Shift Solenoid “B”
Control Circuit Low .......................................... 5A-64
DTC P0974 / P0977: Shift Solenoid “A” / Shift Solenoid “B” Control Circuit High .................... 5A-66
DTC P1702: Internal Co ntrol Module Memory
Check Sum Error............................................. 5A-68
DTC P1703: Can Invalid Data - TCM ................ 5A-68
DTC P1723: Range Select Switch Malfunction ...................................................... 5A-69
DTC P1774: CAN Communication Bus Off ....... 5A-71
DTC P1777: TCM Lost Communication with ECM (Reception Error).................................... 5A-73
DTC P1778: TCM Lost Communication with BCM (Reception Error).................................... 5A-74
Page 652 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-8 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
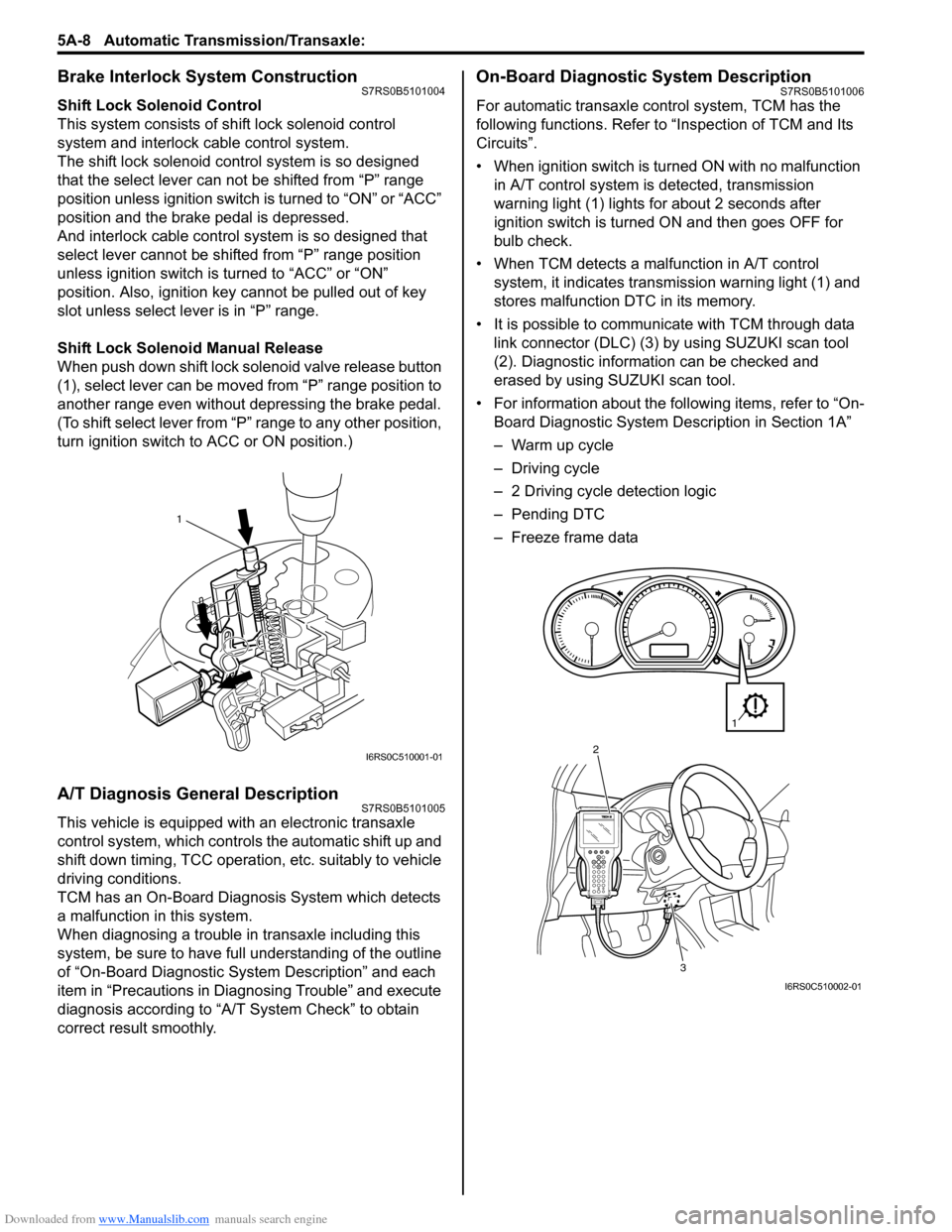
Brake Interlock System ConstructionS7RS0B5101004
Shift Lock Solenoid Control
This system consists of shift lock solenoid control
system and interlock cable control system.
The shift lock solenoid cont rol system is so designed
that the select lever can not be shifted from “P” range
position unless ignition switch is turned to “ON” or “ACC”
position and the brake pedal is depressed.
And interlock cable control system is so designed that
select lever cannot be shifted from “P” range position
unless ignition switch is turned to “ACC” or “ON”
position. Also, ignition key cannot be pulled out of key
slot unless select le ver is in “P” range.
Shift Lock Solenoid Manual Release
When push down shift lock solenoid valve release button
(1), select lever can be moved from “P” range position to
another range even without depressing the brake pedal.
(To shift select lever from “P” range to any other position,
turn ignition switch to ACC or ON position.)
A/T Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B5101005
This vehicle is equipped with an electronic transaxle
control system, which controls the automatic shift up and
shift down timing, TCC operation, etc. suitably to vehicle
driving conditions.
TCM has an On-Board Diagnosis System which detects
a malfunction in this system.
When diagnosing a trouble in transaxle including this
system, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “A/T System Check” to obtain
correct result smoothly.
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B5101006
For automatic transaxle co ntrol system, TCM has the
following functions. Refer to “Inspection of TCM and Its
Circuits”.
• When ignition switch is turned ON with no malfunction in A/T control system is detected, transmission
warning light (1) lights for about 2 seconds after
ignition switch is turned ON and then goes OFF for
bulb check.
• When TCM detects a malfunction in A/T control system, it indicates transmission warning light (1) and
stores malfunction DTC in its memory.
• It is possible to communicate with TCM through data link connector (DLC) (3) by using SUZUKI scan tool
(2). Diagnostic information can be checked and
erased by using SUZUKI scan tool.
• For information about the following items, refer to “On- Board Diagnostic System De scription in Section 1A”
– Warm up cycle
– Driving cycle
– 2 Driving cycle detection logic
– Pending DTC
– Freeze frame data
1
I6RS0C510001-01
3
2
1
I6RS0C510002-01
Page 663 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-19
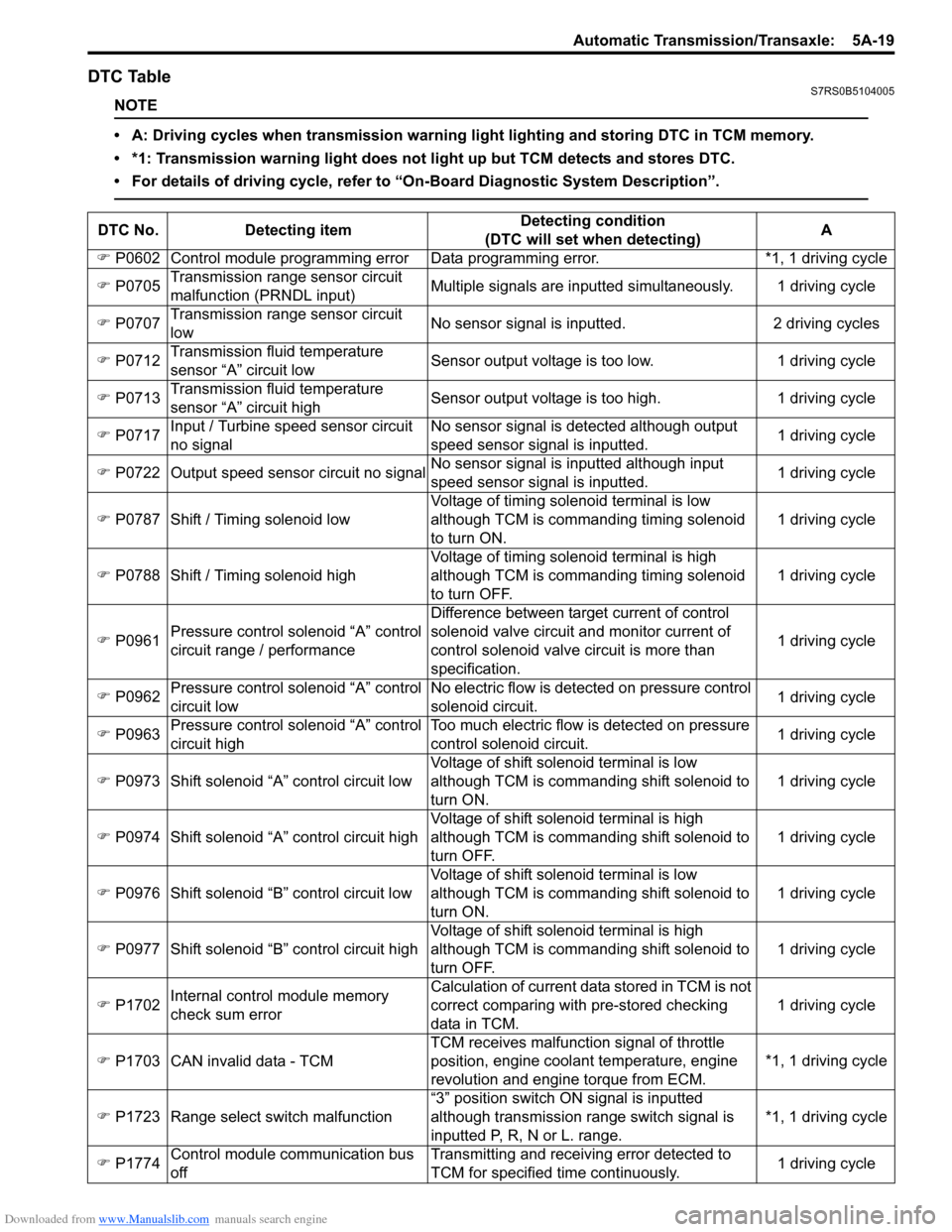
DTC TableS7RS0B5104005
NOTE
• A: Driving cycles when transmission warning light lighting and storing DTC in TCM memory.
• *1: Transmission warning light does not light up but TCM detects and stores DTC.
• For details of driving cycle, refer to “On-Board Diagnostic System Description”.
DTC No.Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting) A
�) P0602 Control module programming error D ata programming error. *1, 1 driving cycle
�) P0705 Transmission range sensor circuit
malfunction (PRNDL input) Multiple signals are inputted
simultaneously. 1 driving cycle
�) P0707 Transmission range sensor circuit
low No sensor signal is inputted.
2 driving cycles
�) P0712 Transmission fluid temperature
sensor “A” circuit low Sensor output voltage is too low.
1 driving cycle
�) P0713 Transmission fluid temperature
sensor “A” circuit high Sensor output voltage is too high.
1 driving cycle
�) P0717 Input / Turbine speed sensor circuit
no signal No sensor signal is detected although output
speed sensor signal is inputted.
1 driving cycle
�) P0722 Output speed sensor circuit no signal No sensor signal is inputted although input
speed sensor signal is inputted. 1 driving cycle
�) P0787 Shift / Timing solenoid low Voltage of timing solenoid terminal is low
although TCM is commanding timing solenoid
to turn ON. 1 driving cycle
�) P0788 Shift / Timing solenoid high Voltage of timing solenoid terminal is high
although TCM is commanding timing solenoid
to turn OFF. 1 driving cycle
�) P0961 Pressure control solenoid “A” control
circuit range / performance Difference between target current of control
solenoid valve circuit and monitor current of
control solenoid valve circuit is more than
specification.
1 driving cycle
�) P0962 Pressure control solenoid “A” control
circuit low No electric flow is detected on pressure control
solenoid circuit.
1 driving cycle
�) P0963 Pressure control solenoid “A” control
circuit high Too much electric flow is detected on pressure
control solenoid circuit.
1 driving cycle
�) P0973 Shift solenoid “A” control circuit low Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is low
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn ON. 1 driving cycle
�) P0974 Shift solenoid “A” control circuit high Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is high
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn OFF. 1 driving cycle
�) P0976 Shift solenoid “B” control circuit low Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is low
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn ON. 1 driving cycle
�) P0977 Shift solenoid “B” control circuit high Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is high
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn OFF. 1 driving cycle
�) P1702 Internal control module memory
check sum error Calculation of current data stored in TCM is not
correct comparing with pre-stored checking
data in TCM.
1 driving cycle
�) P1703 CAN invalid data - TCM TCM receives malfunction signal of throttle
position
, engine coolan t temperature, engine
revolution and engine torque from ECM. *1, 1 driving cycle
�) P1723 Range select switch malfunction “3” position switch ON signal is inputted
although transmission range switch signal is
inputted P, R, N or L. range. *1, 1 driving cycle
�) P1774 Control module communication bus
off Transmitting and receiving error detected to
TCM for specified time continuously.
1 driving cycle
Page 867 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 6- i
6
Section 6
CONTENTS
Steering
Precautions ................................................. 6-1
Precautions............................................................. 6-1
Precautions on Steering........................................ 6-1
Steering General Diagnosi s.................... 6A-1
Precautions........................................................... 6A-1
Precautions for Steering Diagnosis ..................... 6A-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 6A-2 Steering Symptom Diagnosis .............................. 6A-2
Steering Wheel and Column ................... 6B-1
Precautions........................................................... 6B-1
Service Precautions of Steering Wheel and Column.............................................................. 6B-1
General Description ............................................. 6B-1 Steering Wheel and Column Construction .......... 6B-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 6B-2 Checking Steering Column for Accident Damage ............................................................ 6B-2
Repair Instructions .............................................. 6B-3 Steering Wheel and Column Construction .......... 6B-3
Steering Wheel Removal and Installation ........... 6B-4
Contact Coil Cable Assembly Removal and Installation ......................................................... 6B-5
Centering Contact Coil Cable Assembly ............. 6B-6
Contact Coil Cable Assembly Inspection ............ 6B-6
Steering Angle Sensor Removal and Installation ......................................................... 6B-6
Steering Angle Sensor Inspection ....................... 6B-6
Steering Column Removal and Installation ......... 6B-7
Steering Column Inspecti on ................................ 6B-8
Ignition Switch Cylinder Assembly Removal and Installation (Non- Keyless Start Model)...... 6B-9
Steering Lock Assembly (Ignition Switch) Removal and Installation................................... 6B-9
Steering Lower Shaft Removal and Installation ....................................................... 6B-10
Specifications ..................................................... 6B-11
Tightening Torque Specifications ...................... 6B-11
Special Tools and Equipmen t ........................... 6B-11
Special Tool ...................................................... 6B-11
Power Assisted Steering System........... 6C-1
Precautions........................................................... 6C-1 Steering System Note .........................................6C-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Troubles ...................6C-1
General Description .............................................6C-2 P/S System Description ......................................6C-2
EPS Diagnosis General Descr iption ...................6C-3
On-Board Diagnostic System Description ...........6C-3
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................6C-4 EPS System Wiring Circuit Diagram ...................6C-4
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............6C-5 EPS System Check .............. ...............................6C-5
“EPS” Warning Light Check . ...............................6C-8
DTC Check..........................................................6C-8
DTC Clearance ...................................................6C-9
DTC Table ...........................................................6C-9
Scan Tool Data .................................................6C-11
Visual Inspection ...............................................6C-12
P/S System Symptom Diagnosis ......................6C-12
Serial Data Link Circuit Check ..........................6C-13
“EPS” Warning Light Do es Not Come ON with
Ignition Switch Turn ed ON before Engine
Starts ...............................................................6C-15
“EPS” Warning Light Remains ON Steady after Engine Starts ..........................................6C-16
DTC C1113: Steering Torque Sensor (Main and Sub) Circuit Correlation ............................6C-17
DTC C1114: Steering Torque Sensor Reference Power Supply Circuit .....................6C-19
DTC C1117: Steering Torque Sensor Failure Signal Circuit Low ...........................................6C-21
DTC C1118: Steering Torque Sensor Failure Signal Circuit High...........................................6C-22
DTC C1119: Steering Torque Sensor Power Supply Circuit ..................................................6C-24
DTC C1121 / C1123 / C1124: VSS Circuit
Failure .............................................................6C-26
DTC C1122: Engine Speed Signal....................6C-28
DTC C1141 / C1142 / C1143 / C1145: P/S Motor Circuit Failure ........................................6C-30
DTC C1153: P/S Control Module Power Supply Circuit Voltage Low .............................6C-32
DTC C1155: P/S Control Module Failure ..........6C-33
P/S Control Module Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check ......................................6C-34
Inspection of P/S Control Module and Its Circuits ............................................................6C-35