plugs SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 31 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-1
General Information
Maintenance and Lubrication
Precautions
Precautions for Maintenance and LubricationS7RS0B0200001
Air Bag Warning
Refer to “Air Bag Warning in Section 00”.
Scheduled Maintenance
Maintenance Schedule under Normal Driving ConditionsS7RS0B0205001
NOTE
• This interval should be judged by odometer reading or months, whichever comes first.
• This table includes service as scheduled up to 90,000 km (54,000 miles) mileage. Beyond 90,000 km
(54,000 miles), carry out the same services at the same intervals respectively.
Interval Km (x 1,000) 15 30 45 60 75 90
Miles (x 1,000) 9 18 27 36 45 54
Months 12 24 36 48 60 72
Engine
Accessory drive belt (I: �), R: �))——I——R
Valve lash (clearance) (I: �)) —I—I—I
Engine oil and oil filter (R: �)) RRRRRR
Engine coolant (R: �))— —R— — R
Exhaust system (I: �)) —I—I—I
Ignition system
Spark plugs (R: �) )When unleaded fuel is used Iridium Plug
Replace every 60,000 km (36,000
miles) or 48 months
When leaded fuel is used, refer to “Maintenance Recommended under Severe Driving
Conditions”.
Fuel system
Air cleaner filter (R: �), I: �)) Paved-road
I I R I I R
Dusty conditions Refer to “Maintenance Recommended
under Severe Driv
ing Conditions”.
Fuel lines and connections (I: �)) —I—I—I
Fuel filter (R: �)) (See NOTE below) Replace every 105,000 km (63,000
miles)
Fuel tank (I: �))— —I— — I
Emission control system
PCV valve (I: �)) ————— I
Fuel evaporative emission control system (I: �)) ————— I
Brake
Brake discs and pads (thickness, wear, damage) (I: �)) IIIIII
Brake hoses and pipes (leakage, damage, clamp) (I: �)) —I—I—I
Brake fluid (R: �)) —R—R—R
Brake lever and cable (damage, stroke, operation) (I: �)) Inspect at first 15,000 km (9,000 miles
only)
Chassis and body
Clutch (fluid leakage, level) (I: �)) —I—I—I
Tires (wear, damage, rotation) / wheels (damage) (I: �) / �) ) IIIIII
Suspension system (tightness, damage, rattle, breakage) (I: �)) —I—I—I
Steering system (tightness, damage, breakage, rattle) (I: �)) —I—I—I
Drive shaft (axle) boots (I: �))— —I— — I
Manual transaxle oil (leakage, level) (I: �) 1st 15,000 km only) (R: �))I—R——R
Page 32 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-2 Maintenance and Lubrication:
NOTE
• “R”: Replace or change
• “I”: Inspect and correct, replace or lubricate if necessary
• For spark plugs, replace every 50,000 km if the local law requires.
• Periodic replacement of fuel filter is not necessary if it is not instructed in “Periodic Maintenance Schedule” section of the Owner’s manual. The scheduled maintenance varies depending on the
vehicle specification.
Maintenance Recommended under Severe Driving ConditionsS7RS0B0205002
If the vehicle is usually used under the conditions corres ponding to any severe condition code given below, IT IS
RECOMMENDED that applicable maintenance operation be per formed at the particular interval as shown in the
following table.
Severe condition code:
A: Repeated short trips
B: Driving on rough and/or muddy roads
C: Driving on dusty roads
D: Driving in extremely cold weather and/or salted roads
E: Repeated short trips in extremely cold weather
F: Leaded fuel use
G: – – – – –
H: Towing a trailer (if admitted) Automatic transaxle fluid
Fluid level (I:
�)) —I—I—I
Fluid change (R: �)) Replace every 165,000 km (99,000
miles)
Fluid hose (I: �))———I——
All latches, hinges and locks (I: �)) —I—I—I
HVAC air filter (if equipped) (I: �) ) (R: �))— IR — IR
Interval
Km (x 1,000)
15 30 45 60 75 90
Miles (x 1,000) 9 18 27 36 45 54
Months 12 24 36 48 60 72
Severe
condition code MaintenanceMaintenance
operation Maintenance interval
– B C D – – – – Accessory drive belt �)
I Every 15,000 km
(9,000 miles) or 12 months
�) R Every 45,000 km
(27,000 miles) or 36 months
A – C D E F – H Engine oil and oil filter �) R Every 7,500 km
(4,500 miles) or 6 months
– – C – – – – – Air cleaner filter *1 �)
I Every 2,500 km
(1,500 miles)
�) R Every 30,000 km
(18,000 miles) or 24 months
A B C – E F – H Spark plugs Iridium plug �) R Every 30,000 km (18,000 miles) or
24 months
– B C D – – – H Wheel bearings �) I Every 15,000 km
(9,000 miles) or 12 months
– B – D E – – H Drive shaft (axle) boots �) I Every 15,000 km
(9,000 miles) or 12 months
– B – – E – – H Manual transaxle oil �) R First time only:
15,000 km (9,000 miles) or 12
months
Second time and after:
Every 30,000 km (18,000 miles) or
24 months reckoning from 0 km (0
mile) or 0 month
Page 36 of 1496
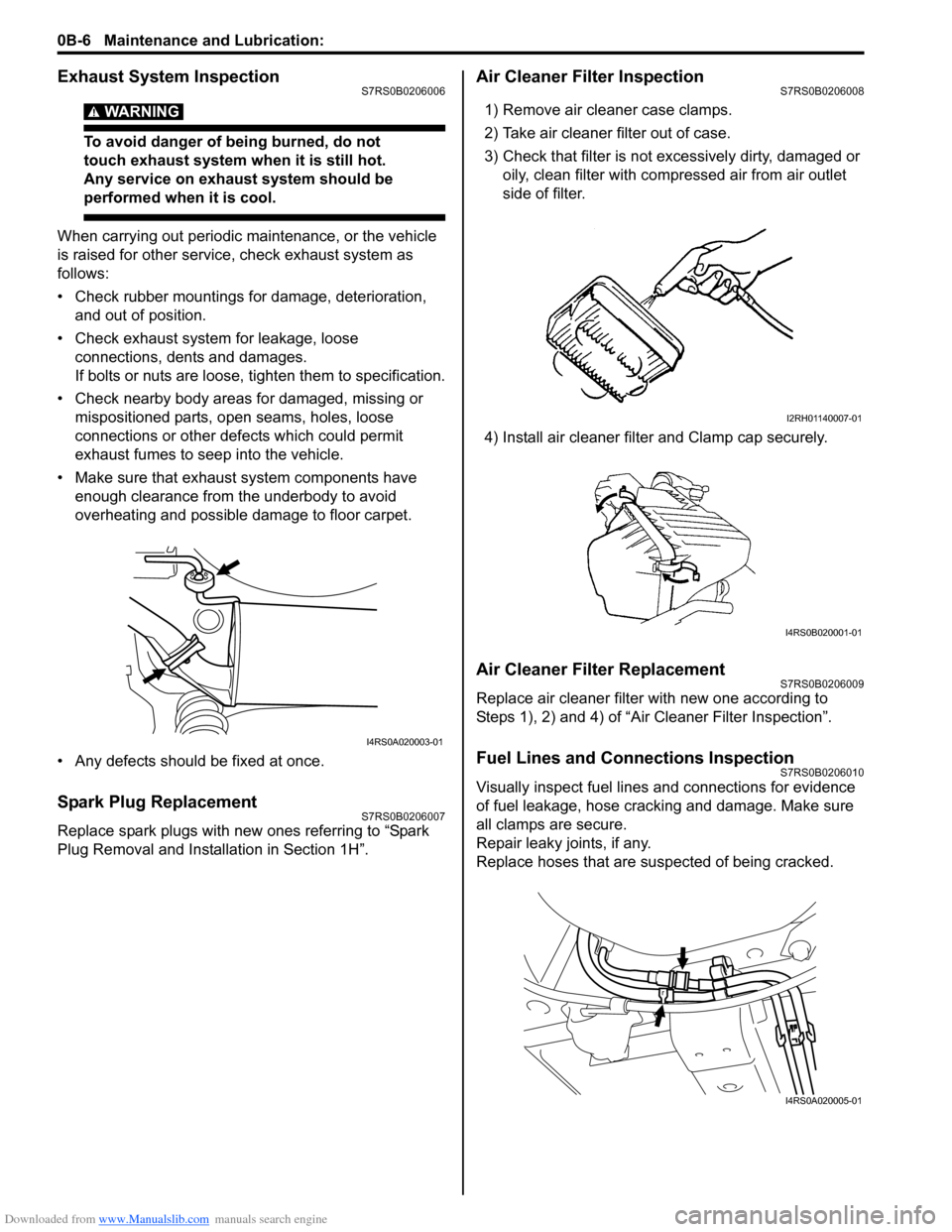
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-6 Maintenance and Lubrication:
Exhaust System InspectionS7RS0B0206006
WARNING!
To avoid danger of being burned, do not
touch exhaust system when it is still hot.
Any service on exhaust system should be
performed when it is cool.
When carrying out periodic maintenance, or the vehicle
is raised for other service, check exhaust system as
follows:
• Check rubber mountings for damage, deterioration, and out of position.
• Check exhaust system for leakage, loose connections, dents and damages.
If bolts or nuts are loose, tighten them to specification.
• Check nearby body areas for damaged, missing or mispositioned parts, ope n seams, holes, loose
connections or other defects which could permit
exhaust fumes to seep into the vehicle.
• Make sure that exhaust system components have enough clearance from the underbody to avoid
overheating and possible damage to floor carpet.
• Any defects should be fixed at once.
Spark Plug ReplacementS7RS0B0206007
Replace spark plugs with new ones referring to “Spark
Plug Removal and Installation in Section 1H”.
Air Cleaner Filter InspectionS7RS0B0206008
1) Remove air cleaner case clamps.
2) Take air cleaner filter out of case.
3) Check that filter is not excessively dirty, damaged or oily, clean filter with compressed air from air outlet
side of filter.
4) Install air cleaner filter and Clamp cap securely.
Air Cleaner Filter ReplacementS7RS0B0206009
Replace air cleaner filter with new one according to
Steps 1), 2) and 4) of “Air Cleaner Filter Inspection”.
Fuel Lines and Connections InspectionS7RS0B0206010
Visually inspect fuel lines and connections for evidence
of fuel leakage, hose cracking and damage. Make sure
all clamps are secure.
Repair leaky joints, if any.
Replace hoses that are suspected of being cracked.
I4RS0A020003-01
I2RH01140007-01
I4RS0B020001-01
I4RS0A020005-01
Page 65 of 1496
![SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-15
Terminal Arrangement of ECM Coupler (Viewed from Harness Side)
[A]: Manual A/C model24. ABS / SUZUKI SWIFT 2007 2.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-15
Terminal Arrangement of ECM Coupler (Viewed from Harness Side)
[A]: Manual A/C model24. ABS /](/img/20/7607/w960_7607-64.png)
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-15
Terminal Arrangement of ECM Coupler (Viewed from Harness Side)
[A]: Manual A/C model24. ABS / ESP® control module 49. Radiator cooling fan motor
[B]: Auto A/C model 25. TCM 50. “RDTR FAN” fuse
1. ECM 26. To other control module connected CAN 51. A/C compressor relay
2. APP sensor assembly 27. Generator 52. Magnet clutch of compressor (A/C model)
3. Shield wire 28. Electric load current sensor (if equipped) 53. “A/C CPRSR” fuse
4. CMP sensor 29. Brake light 54. Ignition coil assembly (for No.1 and No.4 spark
plugs)
5. CKP sensor 30. Brake light switch 55. Ignition coil assembly (for No.2 and No.3 spark
plugs)
6. MAF and IAT sensor 31. Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model) 56. P/S control module
7. MAP sensor 32. Throttle actuator control relay 57. “RADIO” fuse
8. ECT sensor 33. “THR MOT” fuse 58. Main relay
9. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor 34. Throttle throttle body assembly 59. “IG COIL” fuse
10. A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (Manual A/C model) 35. Throttle actuator
60. Ignition switch
11. HO2S-1 36. TP sensor 61. “IG ACC” fuse
12. HO2S-2 37. Injector No.1 62. “FI” fuse
13. Knock sensor 38. Injector No.2 63. Starting motor control relay
14. Blower motor relay 39. Injector No.3 64. “ST SIG” fuse
15. Blower motor 40. Injector No.4 65. “ST MOT” fuse
16. Blower motor resistor 41. EVAP canister purge valve66. Transmission range switch (A/T model) or CPP
switch (Hong Kong model with M/T)
17. Blower speed selector 42. EGR valve 67. Starting motor
18. A/C switch 43. Oil control valve (Camshaft position
control) (VVT model) 68. Immobilizer coil antenna
19. Blower motor controller 44. Fuel pump relay 69. Main fuse box
20. HVAC control module 45. Fuel pump 70. Battery
21. Data link connector (DLC) 46. Radiator cooling fan motor relay No.1 71. Barometric pressure sensor
22. To other control module connected with DLC 47. Radiator cooling fan motor relay No.2
72. Engine ground
23. BCM 48. Radiator cooling fan motor relay No.3 73. Body ground
E23 C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
I4RS0A110008-01
Page 90 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-40 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
11Check fuel pump for operation
Was fuel pump operating sou nd heard from fuel filler for
about 2 seconds after ignition switch ON and stop? Go to “Fuel Pressure
Check”.
Go to “Fuel Pump and
Its Circuit Check”.
12 Check ignition spark
1) Disconnect injector couplers.
2) Remove spark plugs and connect them to high-tension
cords or ignition coil assemblies.
3) Ground spark plugs.
4) Crank engine and check if each spark plug sparks.
Is it in good condition? Go to Step 13. Go to “Ignition Spark
Test in Section 1H”.
13 Check fuel injector for operation
1) Install spark plugs and connect injector connectors.
2) Using sound scope (1), check operating sound of each
injector (2) when cranking engine.
Was injector operating sound heard from all injectors? Go to “Engine Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Go to “Fuel Injector
Circuit Check”.
Step Action Yes No
I3RM0A110015-01
Page 164 of 1496
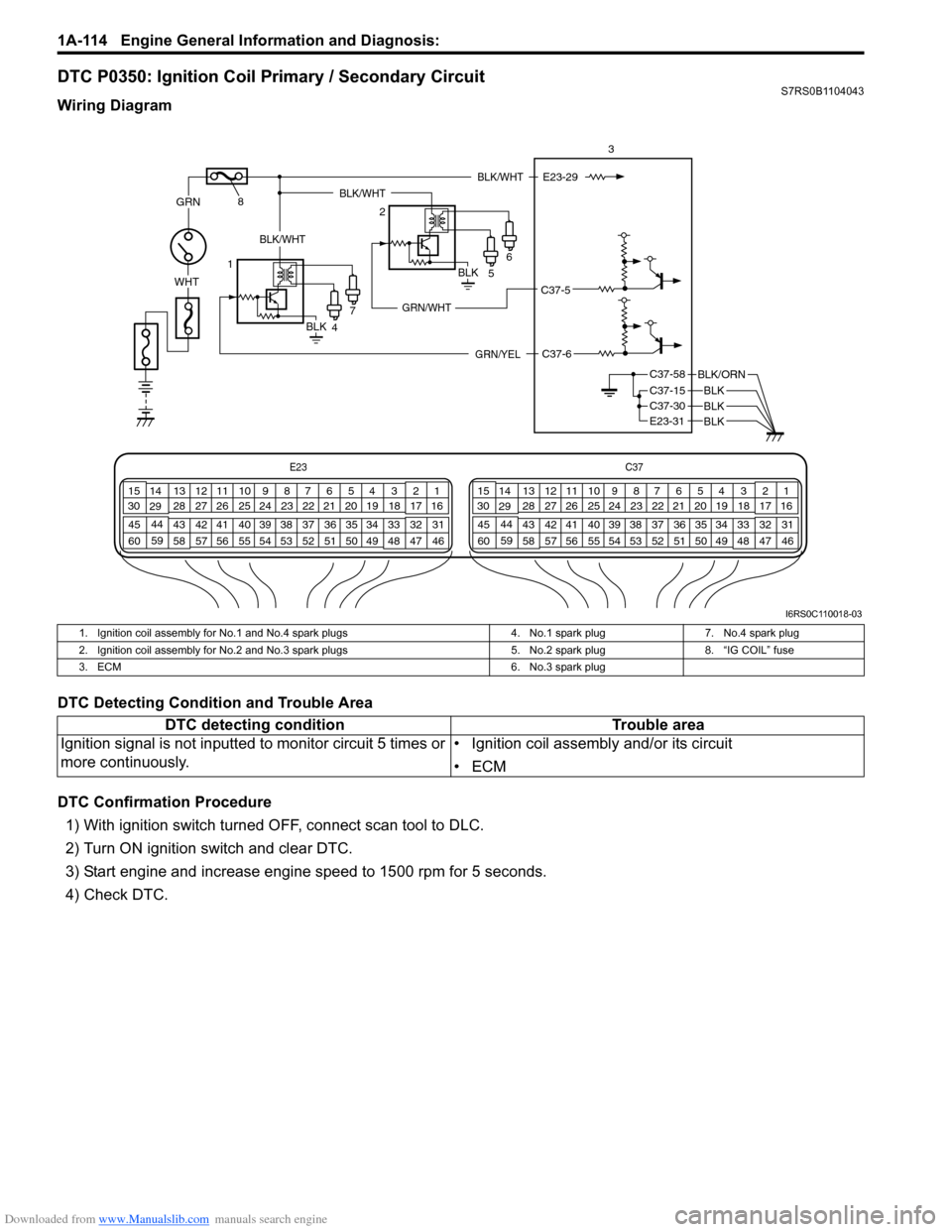
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-114 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC P0350: Ignition Coil Primary / Secondary CircuitS7RS0B1104043
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool to DLC.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC.
3) Start engine and increase engine speed to 1500 rpm for 5 seconds.
4) Check DTC.
BLK/WHT
GRN
WHT
BLK/ORN
BLKBLK
BLK/WHT
4 3
1 7
GRN/YEL
GRN/WHT
C37-6
C37-5
C37-58
C37-15C37-30
BLKE23-31
E23 C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 48 32 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
55
57 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
40
42 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
8BLK/WHT
E23-29
BLK
5 6BLK
2
I6RS0C110018-03
1. Ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs
4. No.1 spark plug7. No.4 spark plug
2. Ignition coil assembly for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs 5. No.2 spark plug8. “IG COIL” fuse
3. ECM 6. No.3 spark plug
DTC detecting conditionTrouble area
Ignition signal is not inputted to monitor circuit 5 times or
more continuously. • Ignition coil assembly and/or its circuit
•ECM
Page 165 of 1496
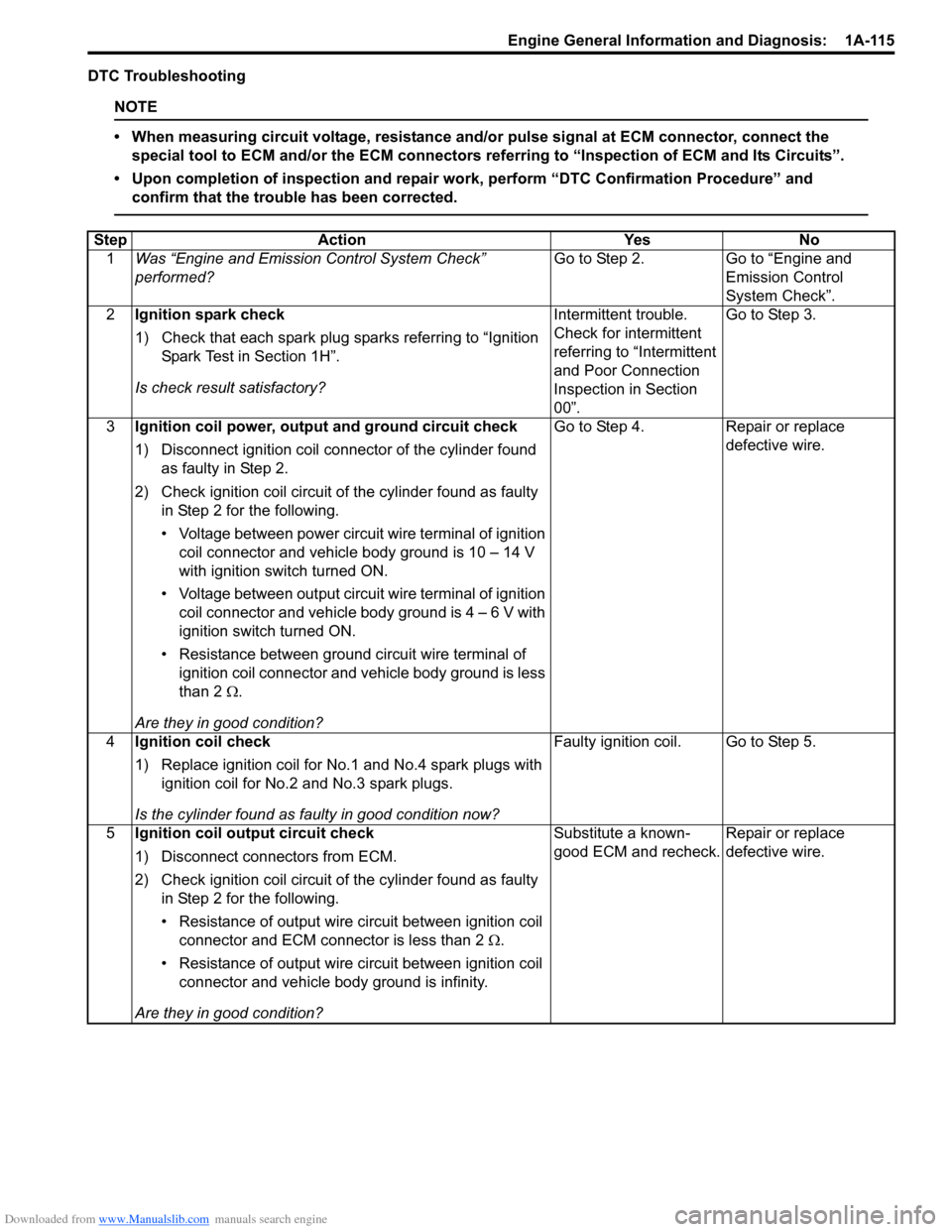
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-115
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 Ignition spark check
1) Check that each spark plug sparks referring to “Ignition
Spark Test in Section 1H”.
Is check result satisfactory? Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.Go to Step 3.
3 Ignition coil power, output and ground circuit check
1) Disconnect ignition coil connector of the cylinder found
as faulty in Step 2.
2) Check ignition coil circuit of the cylinder found as faulty in Step 2 for the following.
• Voltage between power circuit wire terminal of ignition coil connector and vehicle body ground is 10 – 14 V
with ignition switch turned ON.
• Voltage between output circuit wire terminal of ignition coil connector and vehicle body ground is 4 – 6 V with
ignition switch turned ON.
• Resistance between ground circuit wire terminal of ignition coil connector and vehicle body ground is less
than 2 Ω.
Are they in good condition? Go to Step 4.
Repair or replace
defective wire.
4 Ignition coil check
1) Replace ignition coil for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs with
ignition coil for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs.
Is the cylinder found as faulty in good condition now? Faulty ignition coil. Go to Step 5.
5 Ignition coil output circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM.
2) Check ignition coil circuit of the cylinder found as faulty
in Step 2 for the following.
• Resistance of output wire circuit between ignition coil
connector and ECM connector is less than 2 Ω.
• Resistance of output wire circuit between ignition coil connector and vehicle b ody ground is infinity.
Are they in good condition? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Repair or replace
defective wire.
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
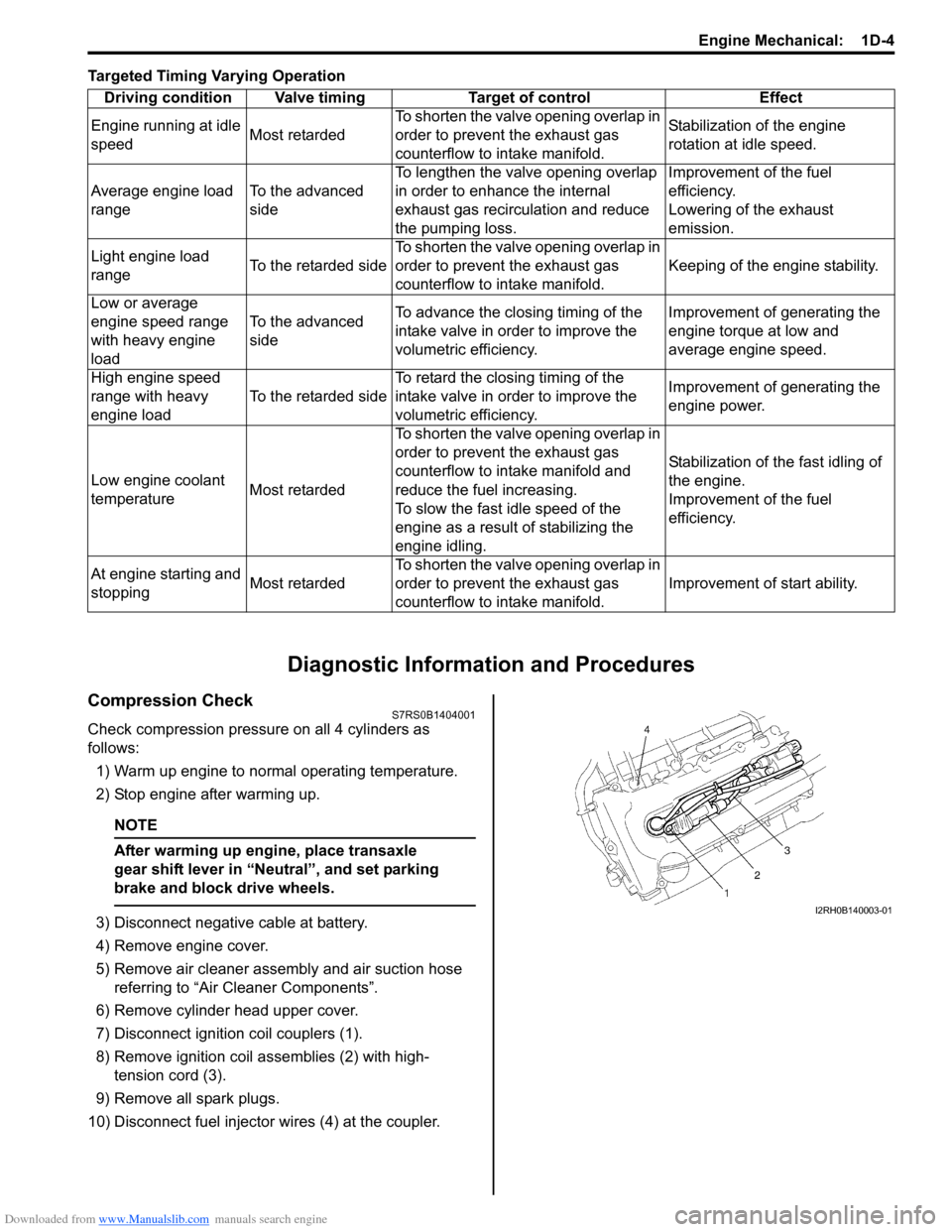
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 290 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
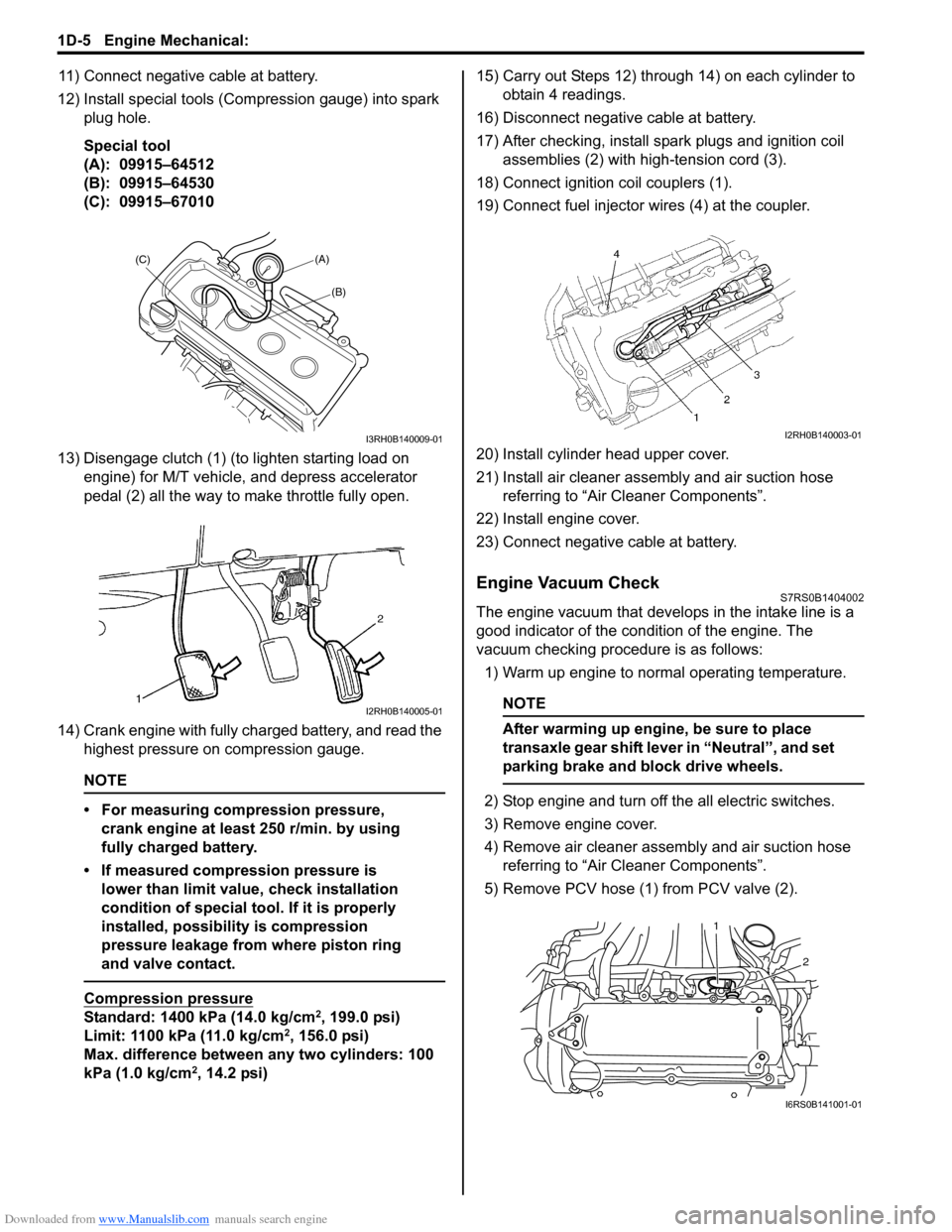
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 393 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-1
Engine
Ignition System
General Description
Ignition System ConstructionS7RS0B1801001
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below.
• ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the si gnals from the sensors, determines the most suitable
ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primar y coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power unit) in the
ignition coil assembly.
• Ignition coil assembly (including an ignitor)
The ignition coil assembly has a built -in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is induced
in the secondary coil.
• High-tension cords and spark plugs
• CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression stroke,
detects the crank angle and adjusts in itial ignition timing automatically.
• TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor, MAF sensor, IAT sensor, knock sensor and other sensors / switches
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and No.4
spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). W hen an ignition signal is sent from ECM to the ignitor in
the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary coil and that
passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simultaneously. Likewise,
when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the ot her ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3 spark plugs spark
simultaneously.