Ger SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 471 of 1496
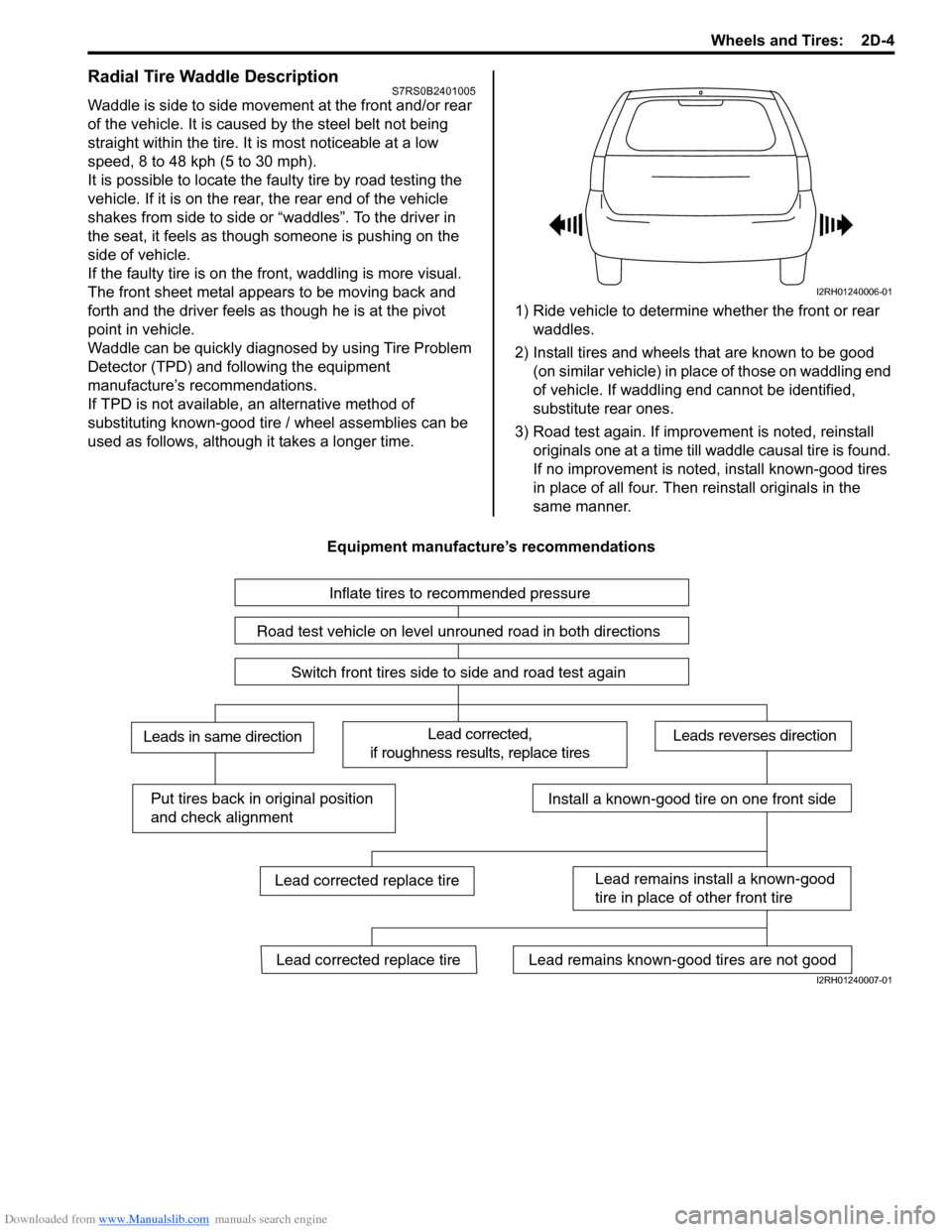
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-4
Radial Tire Waddle DescriptionS7RS0B2401005
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear
of the vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being
straight within the tire. It is most noticeable at a low
speed, 8 to 48 kph (5 to 30 mph).
It is possible to locate the f aulty tire by road testing the
vehicle. If it is on the rear , the rear end of the vehicle
shakes from side to side or “waddles”. To the driver in
the seat, it feels as though someone is pushing on the
side of vehicle.
If the faulty tire is on the front, waddling is more visual.
The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and
forth and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot
point in vehicle.
Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment
manufacture’s recommendations.
If TPD is not available, an alternative method of
substituting known-good tire / wheel assemblies can be
used as follows, although it takes a longer time. 1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear
waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on waddling end
of vehicle. If waddling end cannot be identified,
substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall originals one at a time till w addle causal tire is found.
If no improvement is noted, install known-good tires
in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the
same manner.
Equipment manufacture’s recommendations
I2RH01240006-01
Inflate tires to recommended pressure
Road test vehicle on level unrouned road in both directions
Switch front tires side to side and road test again
Lead corrected,
if roughness results, replace tiresLeads in same directionLeads reverses direction
Put tires back in original position
and check alignmentInstall a known-good tire on one front side
Lead remains install a known-good
tire in place of other front tire
Lead remains known-good tires are not goodLead corrected replace tire
Lead corrected replace tire
I2RH01240007-01
Page 472 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-5 Wheels and Tires:
Radial Tire Lead / Pull DescriptionS7RS0B2401006
“Lead / Pull” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight
path on a level road even with no pressure on the
steering wheel.
Lead is usually caused by the following conditions.
• Improper tire and wheel alignment.
• Uneven brake assemblies.
• Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead in a
vehicle. An example of this is placement of the belt. Off
center belts on radial tires can cause the tire to develop
a side force while rolling straight down the road. If one
side of the tire has a little larger diameter than the other,
the tire will tend to roll to one side. This will develop a
side force which can produce vehicle lead.
The procedure in the figure (Lead Diagnosis) should be
used to make sure that wheel alignment is not mistaken
for tire lead.
• Part of the lead diagnosis procedure is different from the proper tire rotation pattern currently in the owner
and service manuals. If a medium to high mileage tire
is moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to
check that ride roughness has not developed.
• Rear tires will not cause lead.
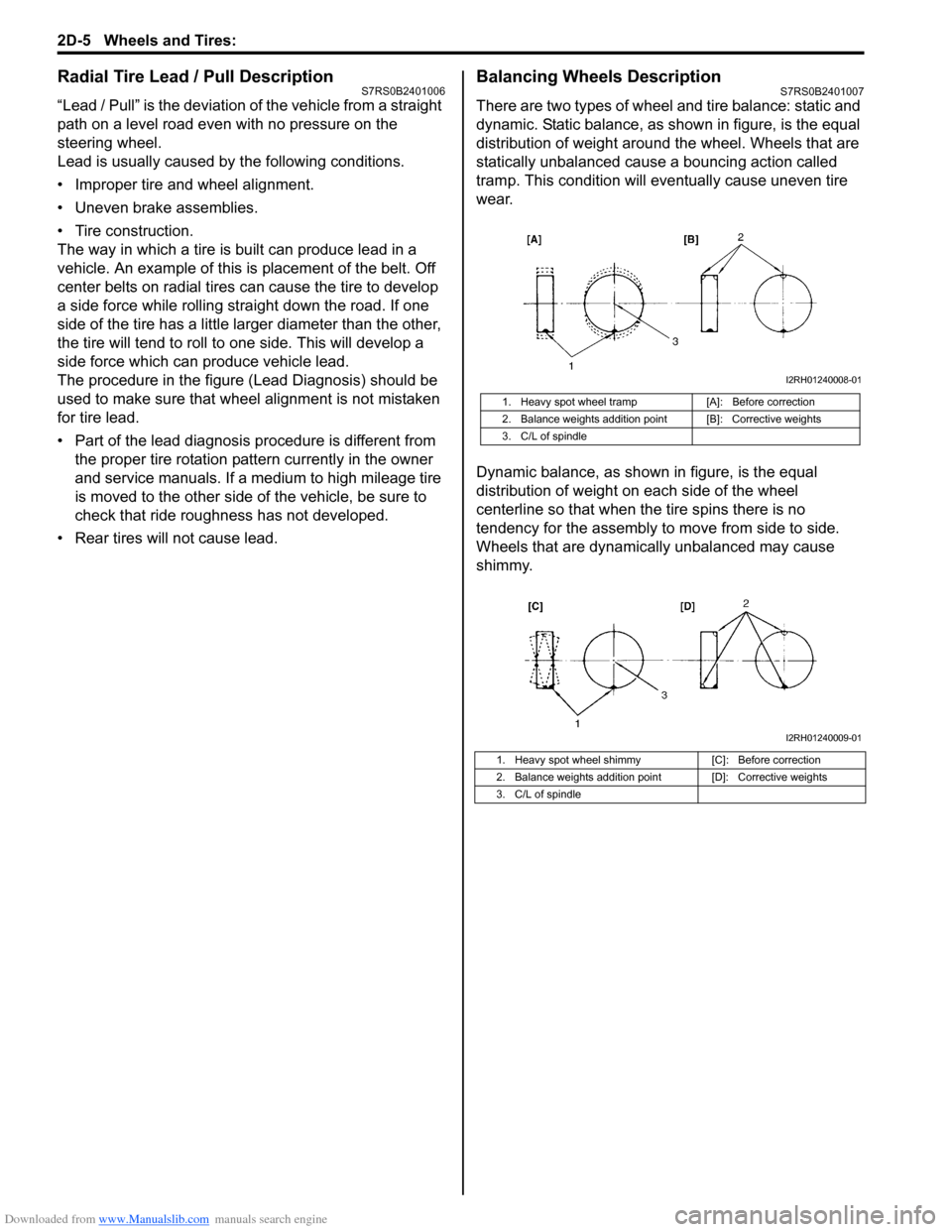
Balancing Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401007
There are two types of wheel an d tire balance: static and
dynamic. Static balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight around the wheel. Wheels that are
statically unbalanced cause a bouncing action called
tramp. This condition will eventually cause uneven tire
wear.
Dynamic balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight on each side of the wheel
centerline so that when the tire spins there is no
tendency for the assembly to move from side to side.
Wheels that are dynamically unbalanced may cause
shimmy.
1. Heavy spot wheel tramp [A]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [B]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
1. Heavy spot wheel shimmy [C]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [D]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
I2RH01240008-01
I2RH01240009-01
Page 512 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-14 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
6) Fill reservoir with specified fluid.
7) After completing the work, bleed air from brake and clutch system referring to “Air Bleeding of Brake
System” and “Air Bleeding of Clutch System in
Section 5C” (M/T model).
8) Install cowl top panel referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
9) Install windshield wiper referring to “Windshield
Wiper Removal and Insta llation in Section 9D”.
10) Perform brake test and check each installed part for fluid leakage.
Master Cylinder Assembly Disassembly and
Assembly
S7RS0B4106013
Disassembly
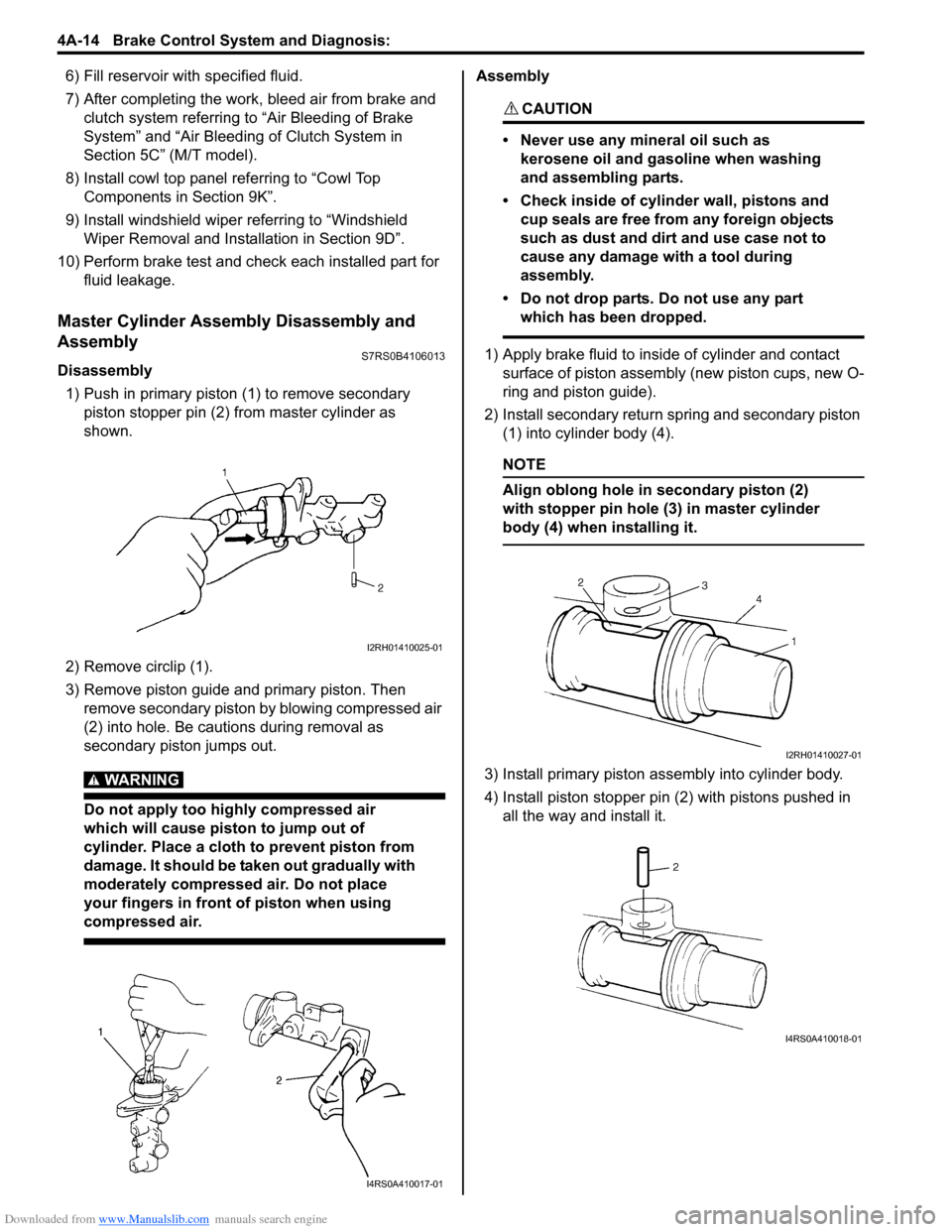
1) Push in primary piston (1) to remove secondary
piston stopper pin (2) from master cylinder as
shown.
2) Remove circlip (1).
3) Remove piston guide and primary piston. Then remove secondary piston by blowing compressed air
(2) into hole. Be cautions during removal as
secondary piston jumps out.
WARNING!
Do not apply too highly compressed air
which will cause piston to jump out of
cylinder. Place a cloth to prevent piston from
damage. It should be taken out gradually with
moderately compressed air. Do not place
your fingers in front of piston when using
compressed air.
Assembly
CAUTION!
• Never use any mineral oil such as kerosene oil and gasoline when washing
and assembling parts.
• Check inside of cylinder wall, pistons and cup seals are free from any foreign objects
such as dust and dirt and use case not to
cause any damage with a tool during
assembly.
• Do not drop parts. Do not use any part which has been dropped.
1) Apply brake fluid to inside of cylinder and contact surface of piston assembly (new piston cups, new O-
ring and piston guide).
2) Install secondary return spring and secondary piston (1) into cylinder body (4).
NOTE
Align oblong hole in secondary piston (2)
with stopper pin hole (3) in master cylinder
body (4) when installing it.
3) Install primary piston assembly into cylinder body.
4) Install piston stopper pin (2) with pistons pushed in all the way and install it.
I2RH01410025-01
I4RS0A410017-01
I2RH01410027-01
I4RS0A410018-01
Page 515 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-17
2) Hold brake pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If pedal height does not change, condition is good. But it isn’t
if pedal rises.
Brake Booster Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4106017
Removal
1) Recover refrigerant from A/C system by using recovery and recycling equipment referring to
“Operation Procedure for Refrigerant Charge in
Section 7B” or “Operation Procedure for Refrigerant
Charge in Section 7B”.
2) Remove master cylinder assembly from booster referring to “Master Cylin der Assembly Removal and
Installation”.
3) Remove cowl top cover and cowl top panel referring to “Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
4) Remove suction hose referring to “Major Components of A/C System in Section 7B” or “Major
Components of A/C System in Section 7B”.
5) Disconnect vacuum hose from booster referring to “Brake Booster Components”.
6) Remove push rod clevis pin and booster mounting nuts and then remove booster. Installation
1) Loosen brake pedal bracket mounting bolt.
2) Install booster (2) to dash panel. Then connect push rod clevis (3) to pedal arm with clevis pin (1) and clip
(4).
3) Tighten booster mounting nuts (a) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Booster mounting nut (a): 13 N·m (1.3 kgf-m, 9.5
lb-ft)
4) Tighten brake pedal bracket mounting bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Brake pedal bracket mounting bolt (b): 13 N·m (
1.3 kgf-m, 9.5 lb-ft)
5) Install suction hose referring to “Major Components of A/C System in Section 7B” or “Major Components
of A/C System in Section 7B”.
6) Install cowl top panel and cowl top cover referring to
“Cowl Top Components in Section 9K”.
7) Install master cylinder assembly to booster referring to “Master Cylinder Assembly Removal and
Installation”.
8) Fill reservoir with specified fluid.
9) Bleed air from brake system.
H: Hold
T: 30 seconds
I2RH01410010-01
1
2 4
3
I6RS0C410006-02
(b)
(a)
I4RS0B410021-02
Page 516 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-18 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
10) Check pedal height and play referring to “Brake Pedal Free Height Inspection” and “Brake Pedal
Play Inspection”.
11) Check each installed part for fluid leakage and perform brake test.
12) Evacuate and charge refrigerant by referring to “Evacuating of A/C Syst em” and “Procedure of
Charging” under “Operation Procedure for
Refrigerant Charge in Section 7B” or “Operation
Procedure for Refrigerant Charge in Section 7B”.
Brake Booster Inspection and AdjustmentS7RS0B4106018
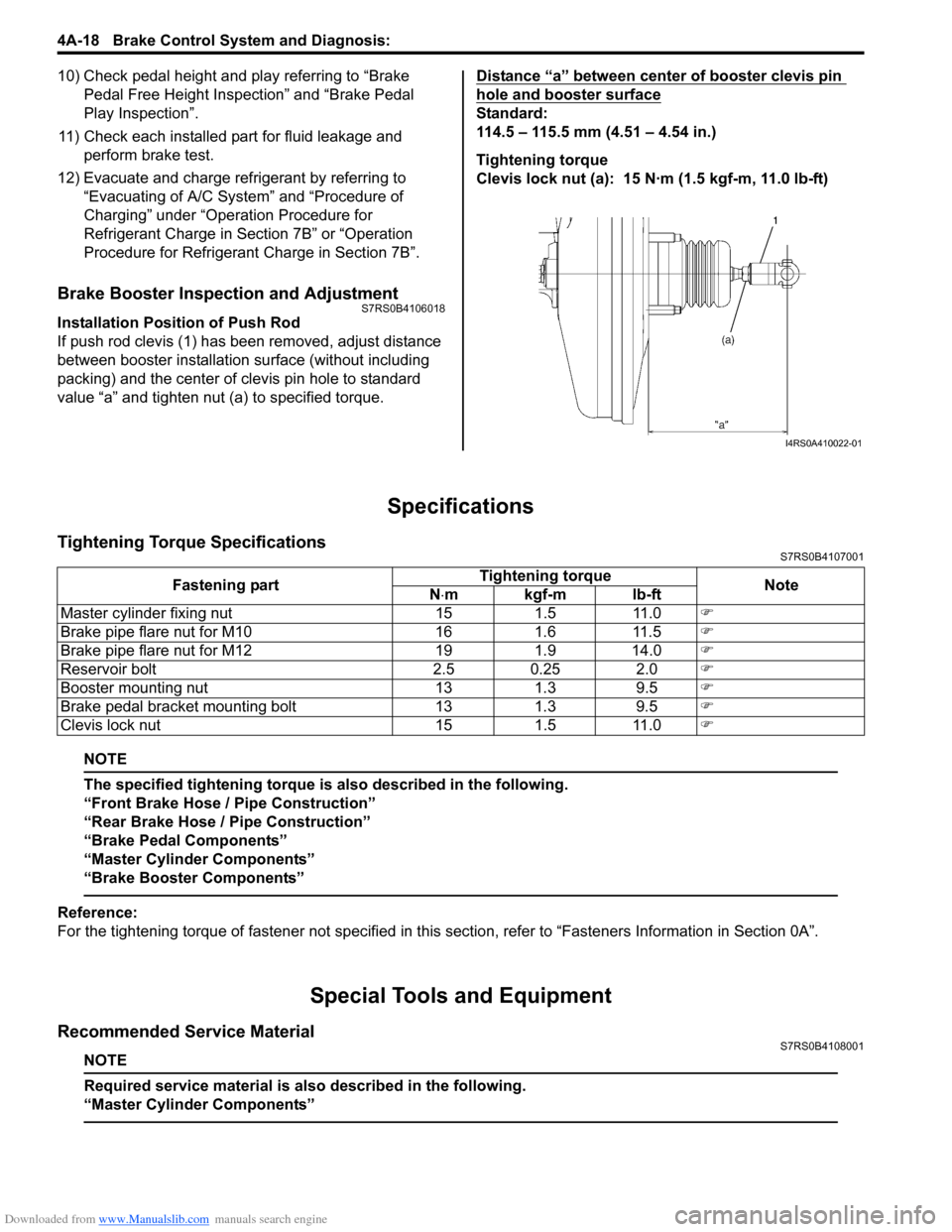
Installation Position of Push Rod
If push rod clevis (1) has b een removed, adjust distance
between booster installation surface (without including
packing) and the center of clevis pin hole to standard
value “a” and tighten nut (a) to specified torque. Distance “a” between center of booster clevis pin
hole and booster surface
Standard:
114.5 – 115.5 mm (4.51 – 4.54 in.)
Tightening torque
Clevis lock nut (a): 15 N·m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft)
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B4107001
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Front Brake Hose / Pipe Construction”
“Rear Brake Hose / Pipe Construction”
“Brake Pedal Components”
“Master Cylinder Components”
“Brake Booster Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this
section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B4108001
NOTE
Required service material is also described in the following.
“Master Cylinder Components”
I4RS0A410022-01
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Master cylinder fixing nut 15 1.5 11.0 �)
Brake pipe flare nut for M10 16 1.6 11.5 �)
Brake pipe flare nut for M12 19 1.9 14.0 �)
Reservoir bolt 2.5 0.25 2.0 �)
Booster mounting nut 13 1.3 9.5 �)
Brake pedal bracket mounting bolt 13 1.3 9.5 �)
Clevis lock nut 15 1.5 11.0 �)
Page 520 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-4 Front Brakes:
Installation1) Torque caliper pin bolts (a) to specification.
NOTE
• Make sure that boots are fit into groove securely.
• If brake pads are replaced, use new caliper pin bolts included in repair kit. (if included)
Tightening torque
Caliper pin bolt (a): 26 N·m (2.6 kgf-m, 19.0 lb-ft)
2) Connect caliper to flexible hose.
3) Torque flexible hose jo int bolt to specification.
Tightening torque
Flexible hose joint bolt (b): 23 N·m (2.3 kgf-m,
17.0 lb-ft)
WARNING!
Make sure that flexible hose is not twisted
when tightening joint bolt. If it is twisted,
reconnect it using care not to twist it.
4) Tighten bleeder plug to specified torque. Tightening torque
Bleeder plug (c): 8.0 N·m (0.8 kgf-m, 6.0 lb-ft)
5) Lower hoist and torque wheel nuts to specifications. Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
6) After completing installation, fill reservoir with brake
fluid and bleed air from brake system referring to “Air
Bleeding of Brake System in Section 4A”.
7) Check each installed part for fluid leakage.
8) Perform brake test and check fluid leakage.
Front Disc Brake Caliper Disassembly and
Assembly
S7RS0B4206006
Disassembly
CAUTION!
• Clean around caliper with brake fluid before disassembly.
• Be careful not to damage inside (bore side) of cylinder.
1) Remove piston with air blown into flexible hose bolt installation hole.
WARNING!
Do not apply too highly compressed air
which will cause piston to jump out of
cylinder. Place a cloth (1) to prevent piston
from damage. It should be taken out
gradually with moderately compressed air.
Do not place your fingers in front of piston
when using compressed air.
2) Remove cylinder boot.
3) Remove piston seal using a thin blade like a thickness gauge, etc.
4) Remove bleeder plug and cap from caliper.
(a)
I4RS0A420003-01
I6RS0C420004-01
I2RH01420011-01
I2RH01420013-01
Page 521 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Brakes: 4B-5
Assembly
Assemble parts in reverse order of disassembly,
observing the following instructions.
CAUTION!
• Wash each part cleanly before installation in the same fluid as the one used in master
cylinder reservoir.
• Never use other fluid or thinner.
• Before installing piston seal or cylinder boot to cylinder, apply brake fluid to them.
• Install a new piston seal into groove in cylinder securely making sure that it is not
twisted.
• Before installing caliper to carrier, check for slid pin smooth movement in thrust
direction.
• After reassembling brake lines, bleed air from them.
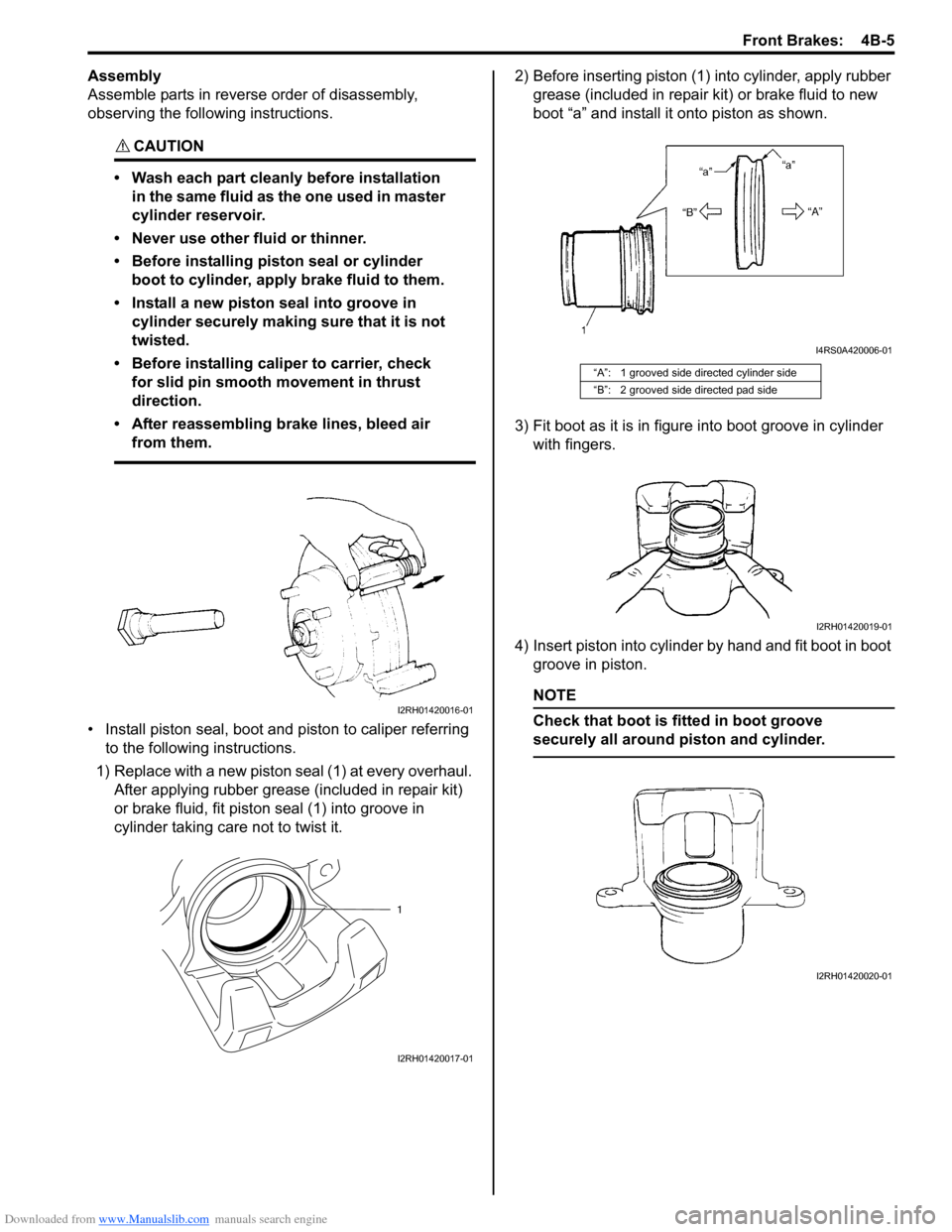
• Install piston seal, boot and piston to caliper referring to the following instructions.
1) Replace with a new piston seal (1) at every overhaul. After applying rubber grease (included in repair kit)
or brake fluid, fit piston seal (1) into groove in
cylinder taking care not to twist it. 2) Before inserting piston (1) into cylinder, apply rubber
grease (included in repair kit) or brake fluid to new
boot “a” and install it onto piston as shown.
3) Fit boot as it is in figure into boot groove in cylinder with fingers.
4) Insert piston into cylinder by hand and fit boot in boot groove in piston.
NOTE
Check that boot is fitted in boot groove
securely all around piston and cylinder.
I2RH01420016-01
1
I2RH01420017-01
“A”: 1 grooved side directed cylinder side
“B”: 2 grooved side directed pad side
I4RS0A420006-01
I2RH01420019-01
I2RH01420020-01
Page 531 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Brakes: 4C-7
Assembly
CAUTION!
• Wash each part cleanly before installation in the same fluid as the one used in master
cylinder reservoir.
• Never use other fluid or thinner.
• Before installing caliper to brake caliper carrier, install slide pins with grease
applied into carrier hole and check for its
smooth movement in thrust direction.
• Before installing piston seal to cylinder, apply fluid to them.
• Install a piston seal into groove in cylinder securely making sure that it is not twisted.
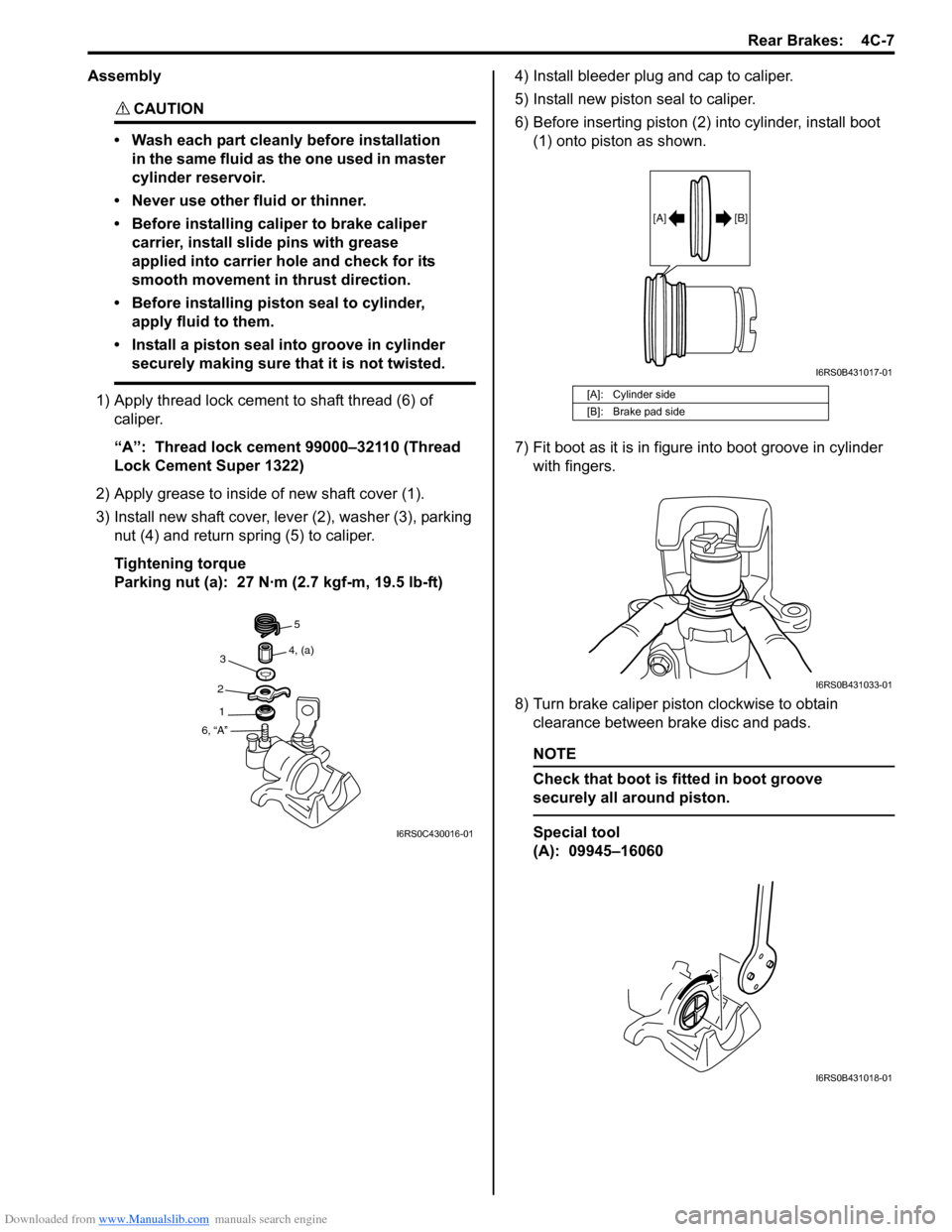
1) Apply thread lock cement to shaft thread (6) of caliper.
“A”: Thread lock cement 99000–32110 (Thread
Lock Cement Super 1322)
2) Apply grease to inside of new shaft cover (1).
3) Install new shaft cover, leve r (2), washer (3), parking
nut (4) and return spring (5) to caliper.
Tightening torque
Parking nut (a): 27 N·m (2.7 kgf-m, 19.5 lb-ft) 4) Install bleeder plug and cap to caliper.
5) Install new piston seal to caliper.
6) Before inserting piston (2) into cylinder, install boot
(1) onto piston as shown.
7) Fit boot as it is in figure into boot groove in cylinder with fingers.
8) Turn brake caliper piston clockwise to obtain clearance between brake disc and pads.
NOTE
Check that boot is fitted in boot groove
securely all around piston.
Special tool
(A): 09945–16060
5
4, (a)
2
3
1
6, “A”
I6RS0C430016-01
[A]: Cylinder side
[B]: Brake pad side
[A] [B]
I6RS0B431017-01
I6RS0B431033-01
I6RS0B431018-01
Page 576 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-2 Electronic Stability Program:
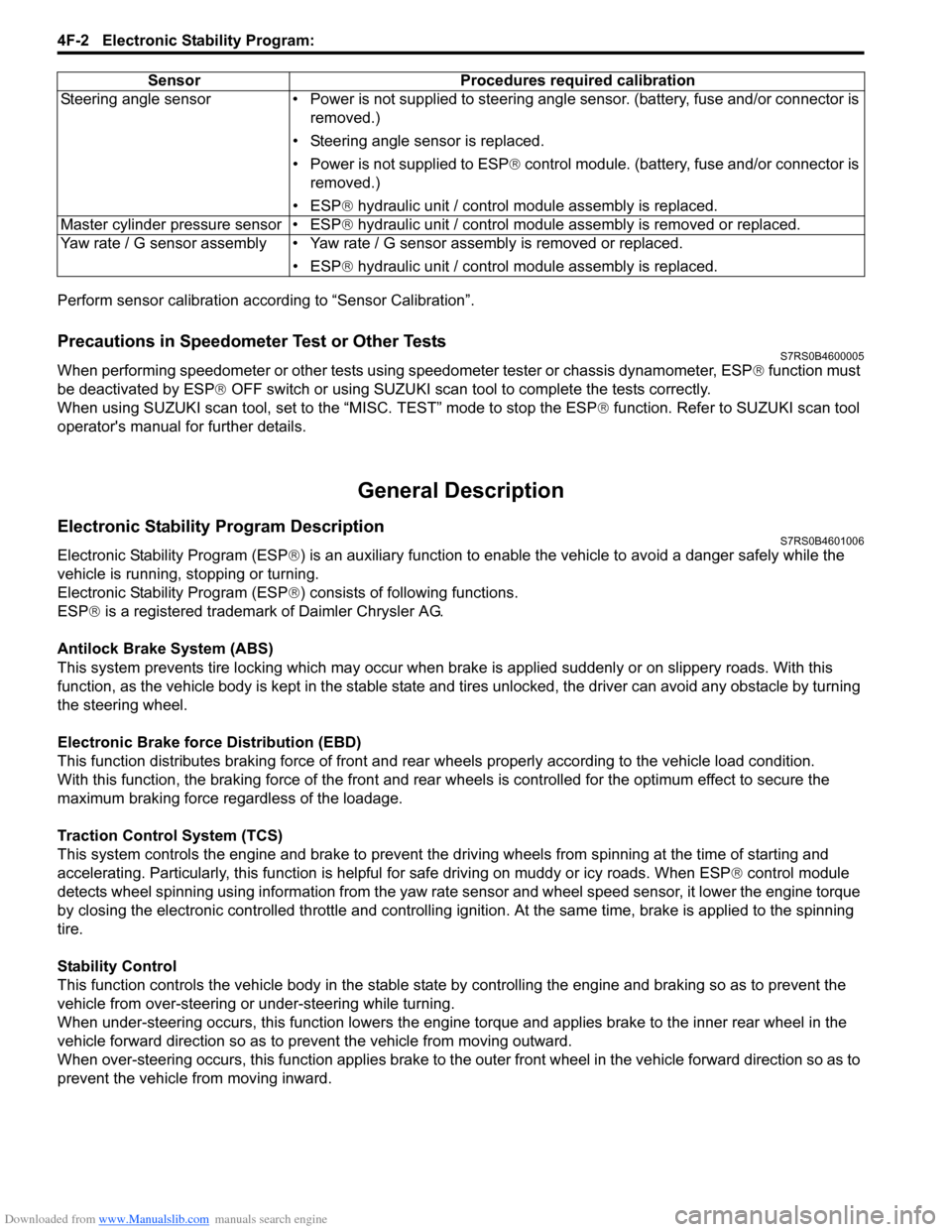
Perform sensor calibration according to “Sensor Calibration”.
Precautions in Speedometer Test or Other TestsS7RS0B4600005
When performing speedometer or other tests using speedometer tester or chassis dynamometer, ESP® function must
be deactivated by ESP ® OFF switch or using SUZUKI scan to ol to complete the tests correctly.
When using SUZUKI scan tool, set to the “MISC. TEST” mode to stop the ESP ® function. Refer to SUZUKI scan tool
operator's manual for further details.
General Description
Electronic Stability Program DescriptionS7RS0B4601006
Electronic Stability Program (ESP ®) is an auxiliary function to enable the vehicle to av oid a danger safely while the
vehicle is running, stopping or turning.
Electronic Stability Program (ESP ®) consists of following functions.
ESP ® is a registered trademark of Daimler Chrysler AG.
Antilock Brake System (ABS)
This system prevents tire locking which may occur when br ake is applied suddenly or on slippery roads. With this
function, as the vehicle body is kept in the stable state an d tires unlocked, the driver can avoid any obstacle by turning
the steering wheel.
Electronic Brake force Distribution (EBD)
This function distributes braking force of front and rear wheels properly according to the vehicle load condition.
With this function, the braking force of the front and rear wheels is controlled for the optimum effect to secure the
maximum braking force regardless of the loadage.
Traction Control System (TCS)
This system controls the engine and brake to prevent the dr iving wheels from spinning at the time of starting and
accelerating. Particularly, this fu nction is helpful for safe driving on muddy or icy roads. When ESP ® control module
detects wheel spinning using information from the yaw rate sensor and wheel speed sensor, it lower the engine torque
by closing the electronic controlled thro ttle and controlling ignition. At the same time, brake is applied to the spinning
tire.
Stability Control
This function controls the vehicle body in the stable state by controlling the engine and braking so as to prevent the
vehicle from over-steering or under-steering while turning.
When under-steering occurs, this function lowers the engine torque and applies brake to the inner rear wheel in the
vehicle forward direction so as to pr event the vehicle from moving outward.
When over-steering occurs, this function applies brake to the outer front wheel in the vehicle forward direction so as to
prevent the vehicle from moving inward. Sensor Procedures required calibration
Steering angle sensor • Power is not su pplied to steering angle sensor. (battery, fuse and/or connector is
removed.)
• Steering angle sensor is replaced.
• Power is not supplied to ESP ® control module. (battery, fuse and/or connector is
removed.)
• ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly is replaced.
Master cylinder pressure sensor • ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly is removed or replaced.
Yaw rate / G sensor assembly • Yaw rate / G sensor assembly is removed or replaced.
• ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly is replaced.
Page 674 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-30 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
Troubleshooting
Engine Brake TestS7RS0B5104013
WARNING!
Before test, make sure that there is no vehicle behind so as to prevent rear-end collision.
1) While driving vehicle in 3rd gear of “D” range, shift select lever down to “2” range and check if engine brake
operates.
2) In the same way as in Step 1), check engine brake for operation when select lever is shifted down to “L” range.
3) Engine brake should operate in the test.
Troubleshooting
Stall TestS7RS0B5104014
This test is to check overall performance of automatic tr ansaxle and engine by measuring stall speed at “D” and “R”
ranges. Be sure to perform this test only when transaxle fluid is at normal operating temperature and its level is
between FULL and LOW marks.
CAUTION!
• Do not run engine at stall more than 5 seconds continuously, or fluid temperature may rise excessively high.
• After performing stall test, be su re to leave engine running at idle for longer than 1 minute before
another stall test.
1) Apply parking brake and block wheels.
2) Install tachometer.
3) Start engine with select lever shifted to “P” range.
4) Depress brake pedal fully.
5) Shift select lever to “D” range and depress accelerator pedal fully while watching tachometer. Read engine rpm quickly when it has become constant (stall speed).
6) Release accelerator pedal immediately after stall speed is checked.
7) In the same way, check stall speed in “R” range.
8) Stall speed should be withi n the following specification.
Engine stall speed
Standard: 2100 – 2400 rpm Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Operated gear is not
correct Faulty valve body component
Replace valve body assembly.
Faulty clutch or brake Inspect clutch and brake. If any parts are faulty,
replace them.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Failure to operate when
shifted down to “2” range Faulty valve body component
Replace valve body assembly.
Faulty O/D and 2nd coast brake Inspect. If NG, replace.
Failure to operate when
shifted down to “L” range Faulty valve body component
Replace valve body assembly.
Faulty 1st and reverse brake Inspect. If NG, replace.