Ac system SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 61 of 1496
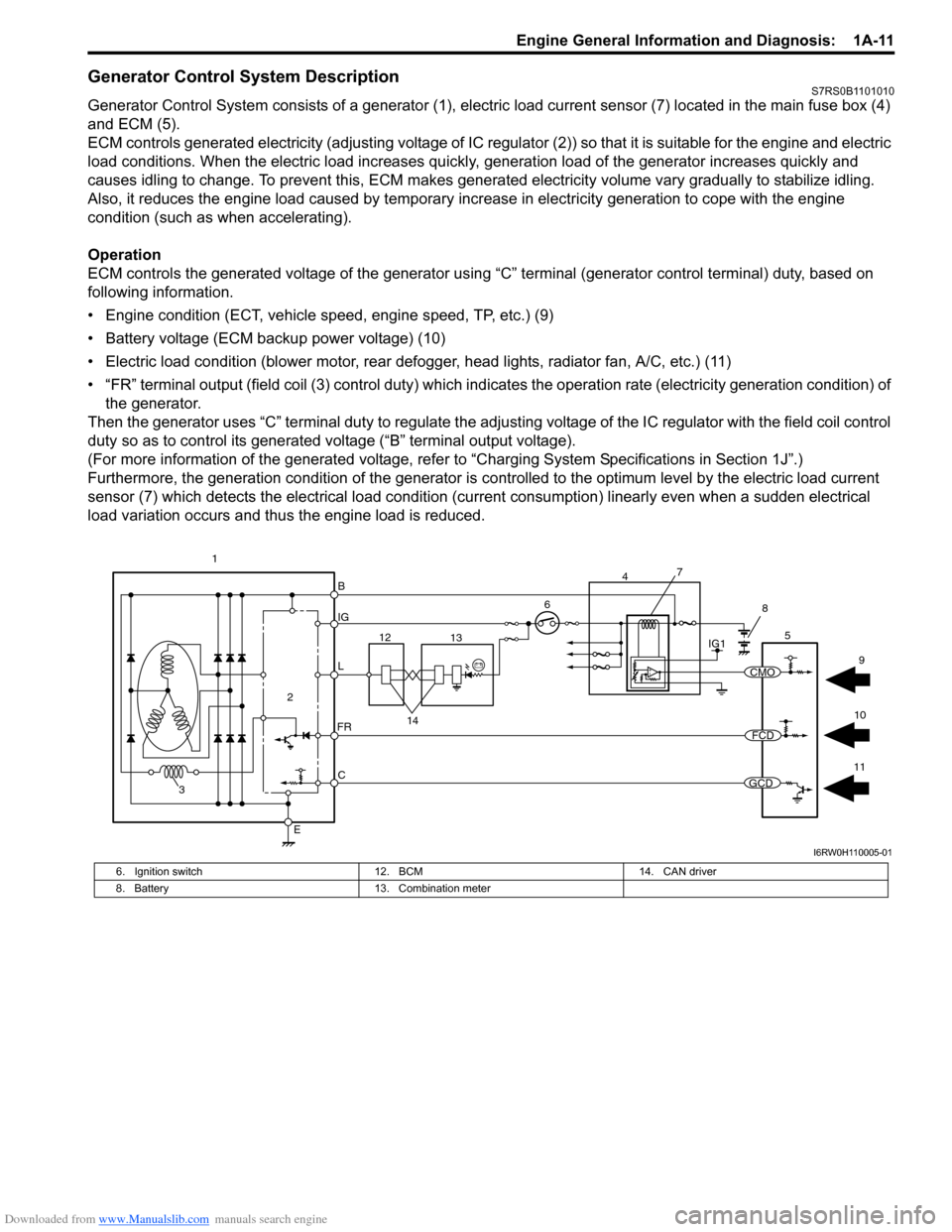
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-11
Generator Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101010
Generator Control System consists of a generator (1), electric load current sensor (7) located in the main fuse box (4)
and ECM (5).
ECM controls generated electricity (adjusting voltage of IC regulator (2)) so that it is suitable for the engine and electric
load conditions. When the electric load increases quickly, generation load of the generator increases quickly and
causes idling to change. To prevent this, ECM makes generated electricity volume vary gradually to stabilize idling.
Also, it reduces the engine load caused by temporary incr ease in electricity generation to cope with the engine
condition (such as when accelerating).
Operation
ECM controls the generated voltage of the generator using “C” terminal (generator control terminal) duty, based on
following information.
• Engine condition (ECT, vehicle speed, engine speed, TP, etc.) (9)
• Battery voltage (ECM backup power voltage) (10)
• Electric load condition (blower motor, rear defogger, head lights, radiator fan, A/C, etc.) (11)
• “FR” terminal output (field coil (3) cont rol duty) which indicates the operation rate (electricity generation condition) of
the generator.
Then the generator uses “C” terminal duty to regulate the adju sting voltage of the IC regulator with the field coil control
duty so as to control its generated voltage (“B” terminal output voltage).
(For more information of the generated voltage, refer to “Charging System Specifications in Section 1J”.)
Furthermore, the generation condition of the generator is co ntrolled to the optimum level by the electric load current
sensor (7) which detects the electrical load condition (cur rent consumption) linearly even when a sudden electrical
load variation occurs and thus the engine load is reduced.
B
IG
L
C
E
6
2
3
FR
5
12 13
14
1IG1
7
4
8
11
10 9
CMO
FCD
GCD
I6RW0H110005-01
6. Ignition switch
12. BCM 14. CAN driver
8. Battery 13. Combination meter
Page 62 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Electronic Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101011
The electronic control system consists of 1) various sensors which detect the state of engine and driving conditions, 2)
ECM which controls various devices ac cording to the signals from the sensors and 3) various controlled devices.
Functionally, it is divided into the following sub systems:
• Fuel injection control system
• Ignition control system
• Electric throttle body control system
• Fuel pump control system
• Radiator cooling fan control system
• Evaporative emission control system
• EGR system
• Oxygen sensor heater control system
• A/C control system (A/C model)
• Camshaft position control system
• Immobilizer control system
• Generator control system
• Controller (computer) communication system
Especially, ECM, BCM, combination meter, TCM (A/T model), ABS/ESP ® control module, steering angle sensor
(ESP® model) and keyless start control module (if equipped) intercommunicate by means of CAN communication.
Page 63 of 1496
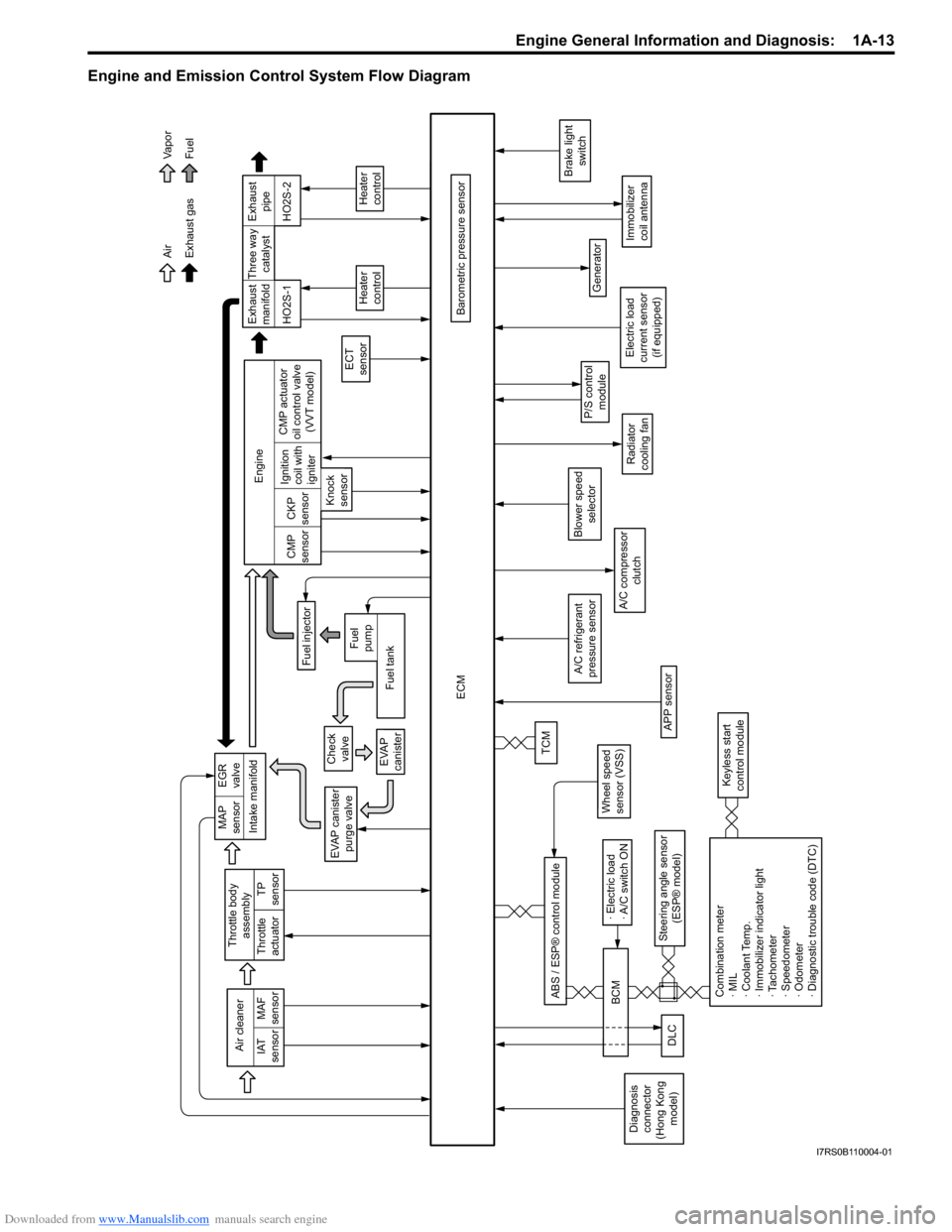
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-13
Engine and Emission Control System Flow Diagram
Intake manifold
Exhaust gas AirFuel
Va p o r
EVAP canister purge valve
ECM
Barometric pressure sensor
A/C compressor clutch
Generator
Immobilizer
coil antenna
P/S controlmodule
Brake light switch
Air cleaner
IAT
sensor MAF
sensor
A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor
TP
sensor
Throttle body
assembly
Throttle
actuator
Wheel speed
sensor (VSS)
Steering angle sensor (ESP® model)
ABS / ESP® control module
Blower speed
selector
MAP
sensor EGR
valve
Check valve
EVAP
canisterTCM
Exhaust
manifold Exhaust
pipe
Fuel injector
ECT
sensor
Heater
control
HO2S-1 HO2S-2
Engine
CMP
sensor CKP
sensor
Knock
sensor Ignition
coil with
igniter
Fuel tank
Fuel
pump CMP actuator
oil control valve (VVT model) Three way
catalyst
Heater
control
Radiator
cooling fan
Combination meter
· MIL
· Coolant Temp.
· Immobilizer indicator light
· Tachometer
· Speedometer
· Odometer
· Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Keyless start
control module
DLC
· Electric load
· A/C switch ON
BCM
Diagnosis
connector
(Hong Kong model) Electric load
current sensor (if equipped)
APP sensor
I7RS0B110004-01
Page 69 of 1496
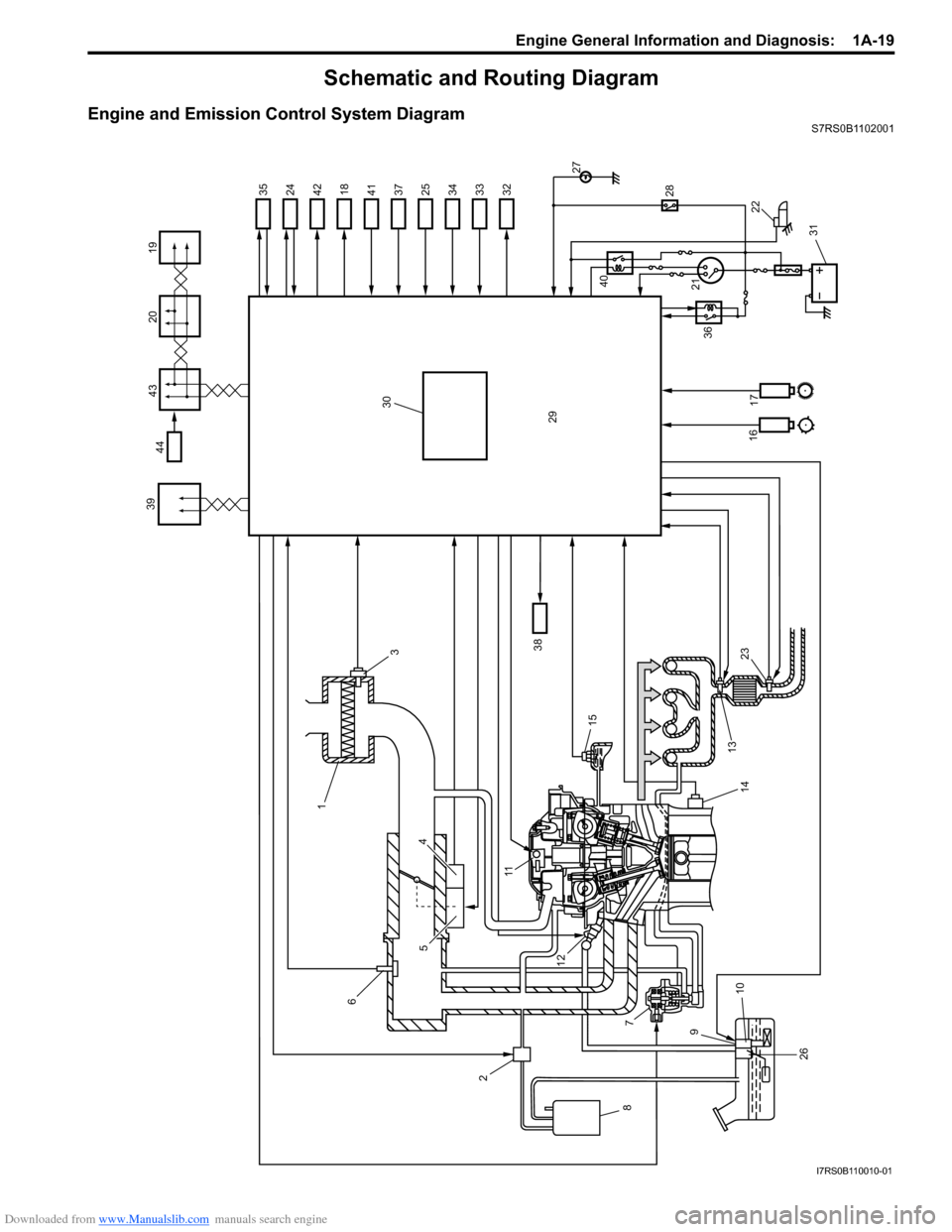
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-19
Schematic and Routing Diagram
Engine and Emission Control System DiagramS7RS0B1102001
26 10
9 7
8
14 13
23
11
15
12
2 6
5 1
3
30
29
38
1617 36
31
22
21 40
27
4
28
19
43
39
20
32184233342537413524
44
I7RS0B110010-01
Page 71 of 1496
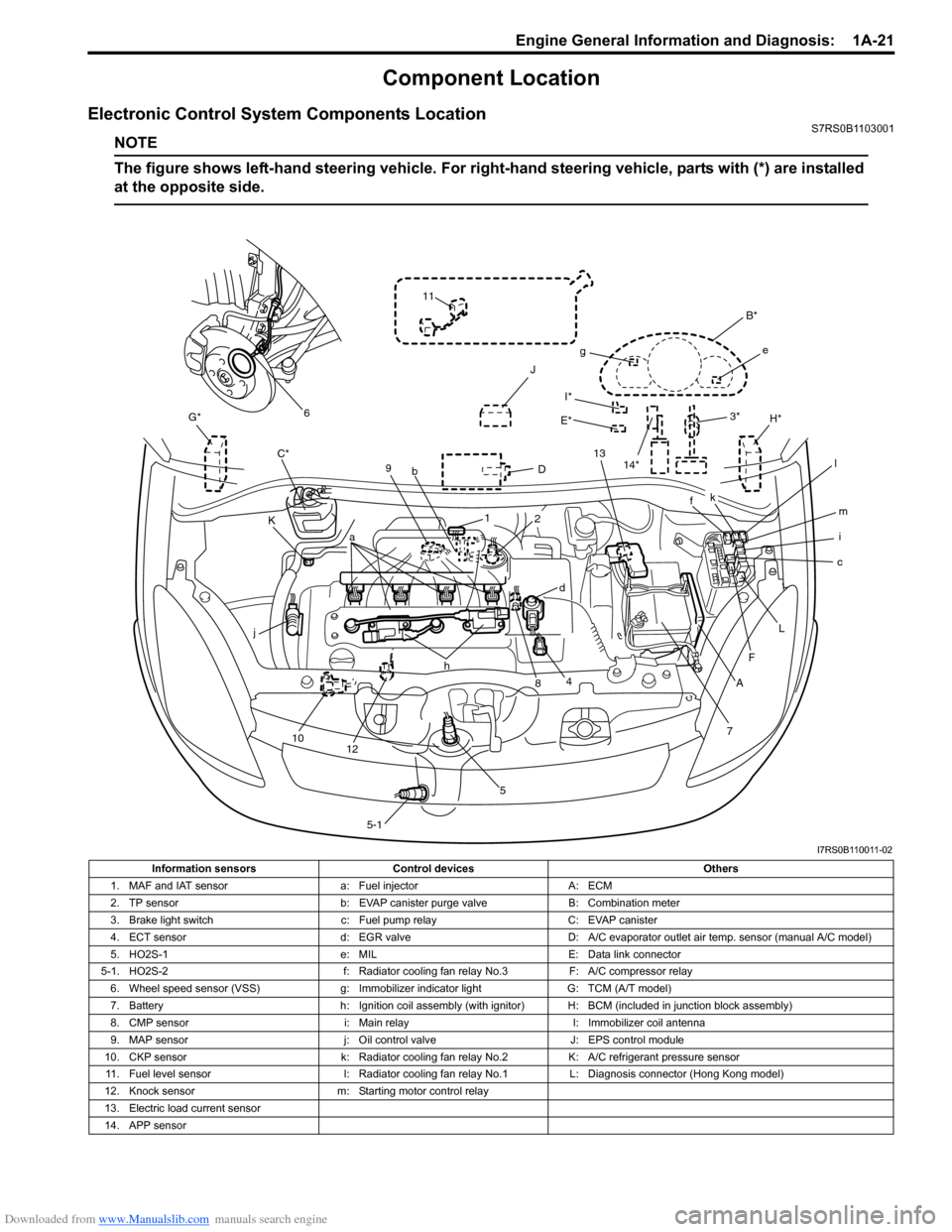
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-21
Component Location
Electronic Control System Components LocationS7RS0B1103001
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
I*
E*
G*
D
K H*
J
C*
7
A
F
c
L
i m
f
B*
e
g
k
l
13
3*
4
j
10 12 h
58
a
9
b
1
5-1
d
2
11
6
14*
I7RS0B110011-02
Information sensors Control devices Others
1. MAF and IAT sensor a: Fuel injectorA: ECM
2. TP sensor b: EVAP canister purge valve B: Combination meter
3. Brake light switch c: Fuel pump relayC: EVAP canister
4. ECT sensor d: EGR valveD: A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. HO2S-1 e: MILE: Data link connector
5-1. HO2S-2 f: Radiator cooling fan relay No.3F: A/C compressor relay
6. Wheel speed sensor (VSS) g: Immobilizer indicator lightG: TCM (A/T model)
7. Battery h: Ignition coil assembly (with ignitor) H: BCM (included in junction block assembly)
8. CMP sensor i: Main relayI: Immobilizer coil antenna
9. MAP sensor j: Oil control valveJ: EPS control module
10. CKP sensor k: Radiator cooling fan relay No.2K: A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
11. Fuel level sensor l: Radiator cooling fan relay No.1L: Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model)
12. Knock sensor m: Starting motor control relay
13. Electric load current sensor
14. APP sensor
Page 72 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-22 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Engine and Emission Control System CheckS7RS0B1104001
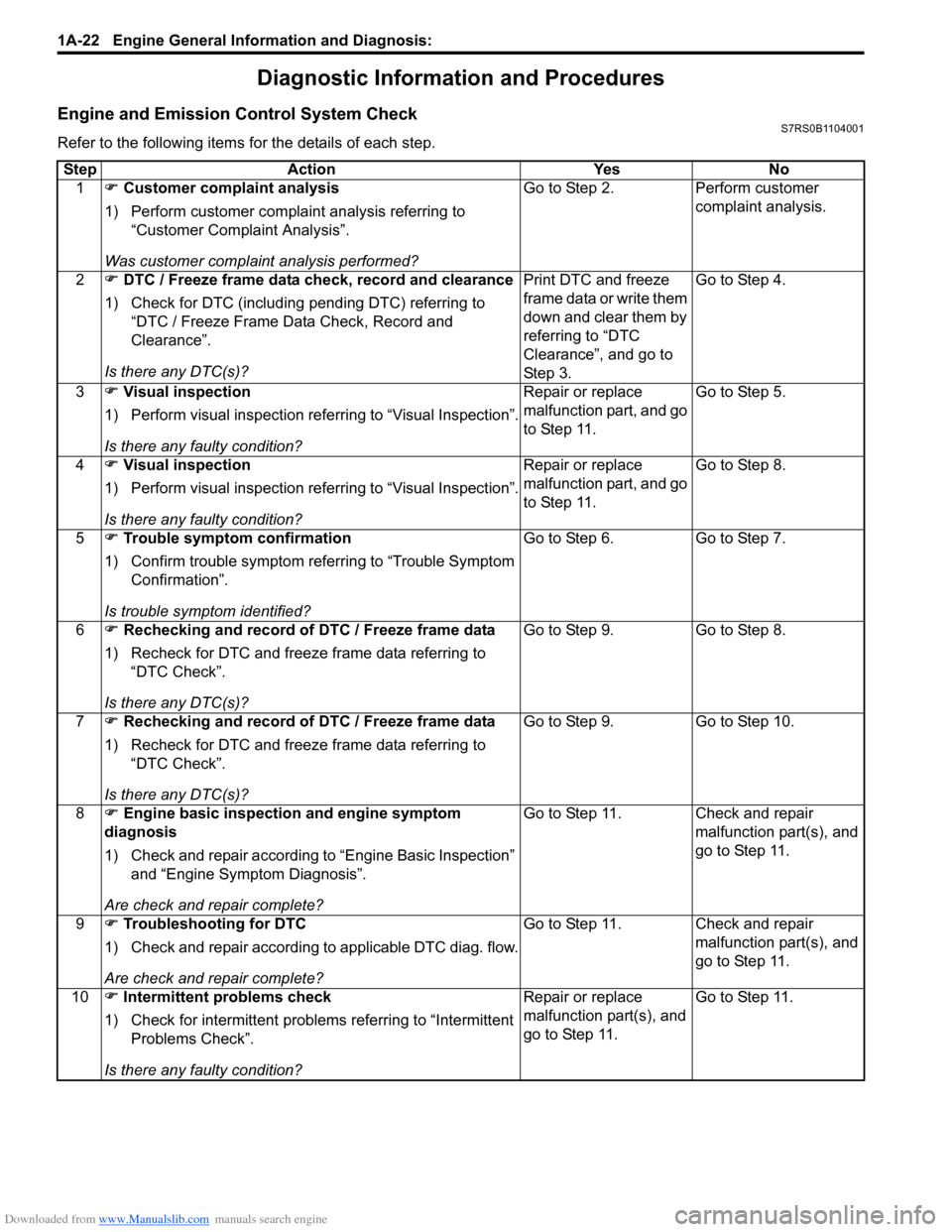
Refer to the following items for the details of each step.Step Action Yes No 1 �) Customer complaint analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis referring to “Customer Complaint Analysis”.
Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to Step 2. Perform customer
complaint analysis.
2 �) DTC / Freeze frame data check, record and clearance
1) Check for DTC (including pending DTC) referring to “DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Print DTC and freeze
frame data or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC
Clearance”, and go to
St ep 3 .Go to Step 4.
3 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 5.
4 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 8.
5 �) Trouble symptom confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom referring to “Trouble Symptom Confirmation”.
Is trouble symptom identified? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 7.
6 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / Freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 8.
7 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / Freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 10.
8 �) Engine basic inspection and engine symptom
diagnosis
1) Check and repair according to “Engine Basic Inspection”
and “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
9 �) Troubleshooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable DTC diag. flow.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
10 �) Intermittent problems check
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to “Intermittent Problems Check”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
Go to Step 11.
Page 75 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-25
Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to
“DTC Check”. If DTC is indicated, print it and freeze
frame data or write them down and then clear them by
referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates malfunction
that occurred in the system but does not indicate
whether it exists now or it occurred in the past and the
normal condition has been restored now. To check which
case applies, check the sy mptom in question according
to Step 5 and recheck DTC according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame
Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble
symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC
Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC diag.
flow.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC /
Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Engine Basic Inspection and Engine
Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic engine check according to “Engine Basic
Inspection” first. When the end of the flow has been
reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a
possible cause referring to “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”
and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle
(symptoms obtained through steps of customer
complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or
basic engine check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, ECM or other part and repair or
replace faulty parts. Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermit
tent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connec tion Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the
engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is re lated to the DTC, clear the DTC once,
perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that no
DTC is indicated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) CheckS7RS0B1104002
1) Turn ON ignition switch (with engine at stop) and check that MIL (1) lights.
If MIL does not light up (or MIL dims) but engine can
be starting, go to “MIL Does Not Come ON with
Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can
Be Started)” for troubleshooting.
If MIL does not light with ignition switch ON and
engine does not start though it is cranked up, go to
“ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”.
2) Start engine and check that MIL turns OFF. If MIL remains ON and no DTC is stored in ECM, go
to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after
Engine Starts” for troubleshooting.
1
I4RS0A110012-01
Page 76 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-26 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
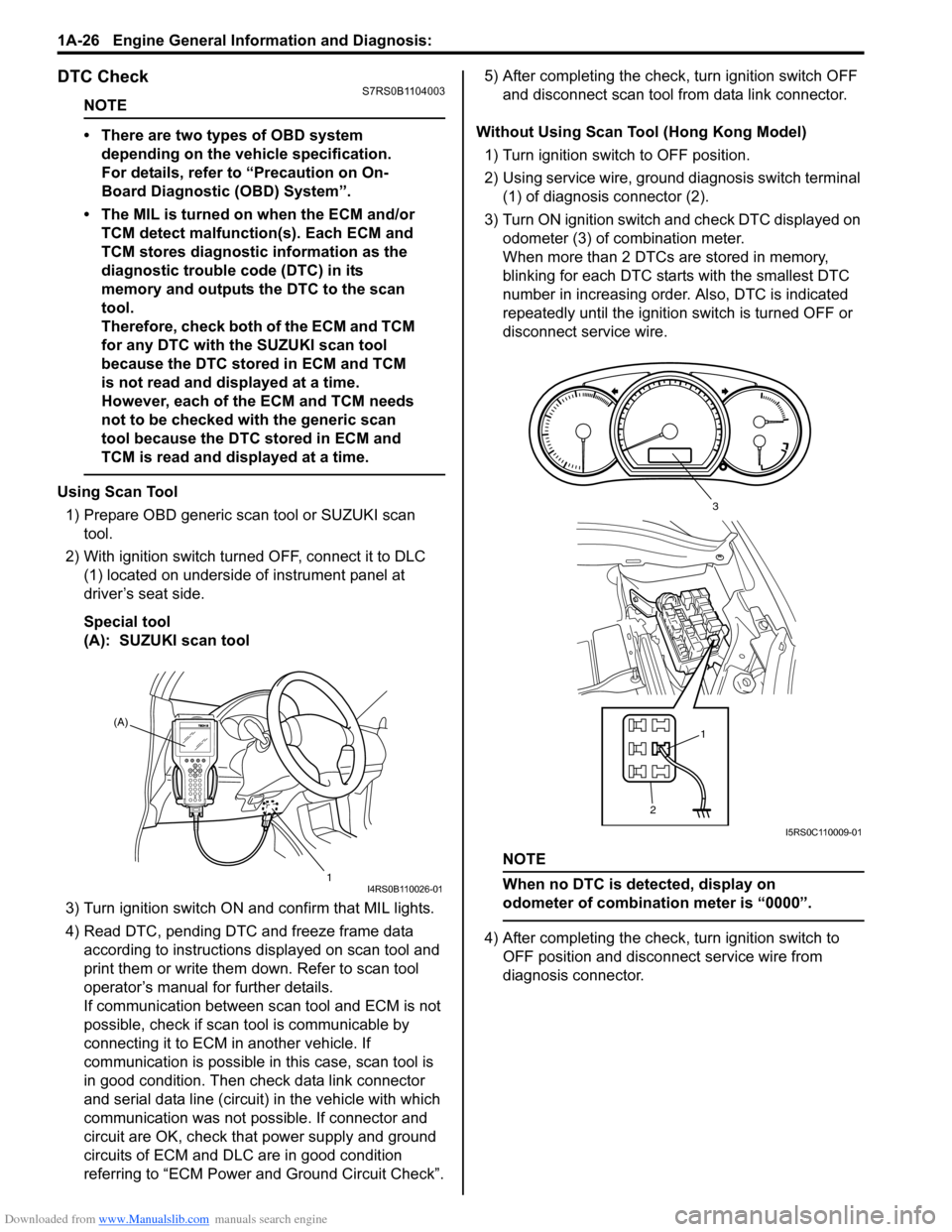
DTC CheckS7RS0B1104003
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-
Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• The MIL is turned on when the ECM and/or TCM detect malfunction(s). Each ECM and
TCM stores diagnostic information as the
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its
memory and outputs th e DTC to the scan
tool.
Therefore, check both of the ECM and TCM
for any DTC with the SUZUKI scan tool
because the DTC stored in ECM and TCM
is not read and displayed at a time.
However, each of the ECM and TCM needs
not to be checked with the generic scan
tool because the DTC stored in ECM and
TCM is read and displayed at a time.
Using Scan Tool
1) Prepare OBD generic scan tool or SUZUKI scan tool.
2) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect it to DLC (1) located on underside of instrument panel at
driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch ON and confirm that MIL lights.
4) Read DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data according to instructions displayed on scan tool and
print them or write them down. Refer to scan tool
operator’s manual for further details.
If communication between scan tool and ECM is not
possible, check if scan tool is communicable by
connecting it to ECM in another vehicle. If
communication is possible in this case, scan tool is
in good condition. Then check data link connector
and serial data line (circuit) in the vehicle with which
communication was not possible. If connector and
circuit are OK, check that power supply and ground
circuits of ECM and DLC are in good condition
referring to “ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”. 5) After completing the check,
turn ignition switch OFF
and disconnect scan tool from data link connector.
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model) 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Using service wire, ground diagnosis switch terminal (1) of diagnosis connector (2).
3) Turn ON ignition switch and check DTC displayed on
odometer (3) of combination meter.
When more than 2 DTCs are stored in memory,
blinking for each DTC star ts with the smallest DTC
number in increasing order. Also, DTC is indicated
repeatedly until the ignition switch is turned OFF or
disconnect service wire.
NOTE
When no DTC is detected, display on
odometer of combinatio n meter is “0000”.
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect service wire from
diagnosis connector.
(A)
1
I4RS0B110026-01
21
3
I5RS0C110009-01
Page 77 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-27
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B1104004
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Using Scan Tool1) Connect OBD generic scan to ol or SUZUKI scan tool
to data link connector in the same manner as when
making this connection for DTC check.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and then ON.
3) Erase DTC and pending DTC according to instructions displayed on scan tool. Refer to scan
tool operator’s manual for further details.
4) After completing the clear ance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
NOTE
DTC and freeze frame data stored in ECM
memory are also cleared in the following
cases. Be careful not to clear them before
keeping their record.
• When power to ECM is cut off (by disconnecting battery cable, removing
fuse or disconnecting ECM connectors).
• When the same malfunction (DTC) is not detected again during 40 engine warm-up
cycles. (See “Warm-Up Cycle” of “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description”.)
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model)
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect battery negative cable for specified time below to erase diagnostic trouble code stored in
ECM memory and reconnect it.
Time required to erase DTC
DTC TableS7RS0B1104005
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
• For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• For non-Euro-OBD model, some of DTC No. with delta ( �U) mark in the following table can not be
detected by ECM depending on vehicl e specification and local regulation.
• DTC with square ( �†) mark in the following table can be detected only for Hong Kong model.
• DTC with circle ( �{) mark in the following table can be detected only for Euro OBD model and Hong
Kong model.
• For Euro OBD model, with the generic scan tool, onl y star (*) marked DTC No. in the following table
can be read.
• 1 driving cycle: MIL lights up when DTC is detected during 1 driving cycle.
• 2 driving cycles: MIL lights up when the same DTC is detected also in the next driving cycle after DTC is detected and stored temporarily in the first driving cycle.
• *2 driving cycles: MIL blinks or lights up. Refer to “DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304: Random / Multiple
Cylinder Misfire Detected / Cylinder 1 / Cylinder 2 / Cylinder 3 / Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected” for
details.
Ambient temperature Time to cut power to ECM
Over 0 °C (32 ° F) 30 sec. or longer
Under 0 °C (32 °F) Not specifiable.
Select a place with higher
than 0 °C (32 °F)
temperature.
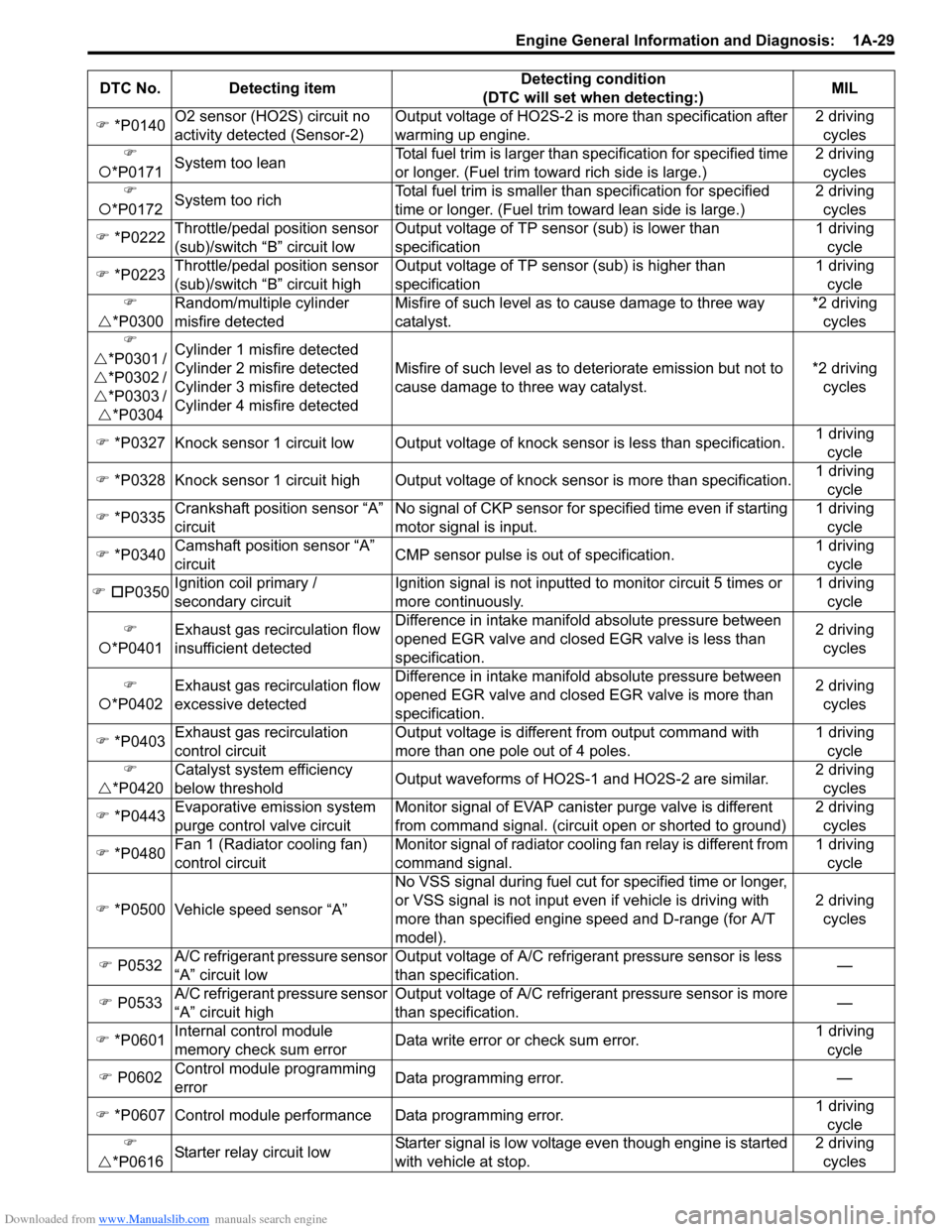
DTC No. Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL
�) *P0010 “A” camshaft position actuator
circuit Oil control valve circuit open or short. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0011 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-advanced or system
performance Actual value of advanced va
lve timing does not reach
target value, or valve timi ng is advanced although ECM
command is most retarding. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0012 “A” camshaft position – timing
over-retarded 2 driving
cycles
Page 79 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-29
�) *P0140 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit no
activity detected (Sensor-2) Output voltage of HO2S-2 is more than specification after
warming up engine. 2 driving
cycles
�)
�{ *P0171 System too lean Total fuel trim is larger than
specification for specified time
or longer. (Fuel trim towa rd rich side is large.) 2 driving
cycles
�)
�{ *P0172 System too rich Total fuel trim is smaller th
an specification for specified
time or longer. (Fue l trim toward lean side is large.) 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0222 Throttle/pedal position sensor
(sub)/switch “B” circuit low Output voltage of TP sensor (sub) is lower than
specification 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0223 Throttle/pedal position sensor
(sub)/switch “B” circuit high Output voltage of TP sensor (sub) is higher than
specification 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P0300 Random/multiple cylinder
misfire detected Misfire of such level as to cause damage to three way
catalyst. *2 driving
cycles
�)
�U *P0301 /
�U *P0302 /
�U *P0303 /
�U *P0304 Cylinder 1 misfire detected
Cylinder 2 misfire detected
Cylinder 3 misfire detected
Cylinder 4 misfire detected
Misfire of such level as to deteriorate emission but not to
cause damage to three way catalyst.
*2 driving
cycles
�) *P0327 Knock sensor 1 circuit low Output voltage of knock sensor is less than specification.1 driving
cycle
�) *P0328 Knock sensor 1 circuit high Output volta ge of knock sensor is more than specification.1 driving
cycle
�) *P0335 Crankshaft position sensor “A”
circuit No signal of CKP sensor for sp
ecified time even if starting
motor signal is input. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0340 Camshaft position sensor “A”
circuit CMP sensor pulse is out of specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) �† P0350 Ignition c
oil primary /
secondary circuit Ignition signal is not inputted to monitor circuit 5 times or
more continuously. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�{ *P0401 Exhaust gas recirculation flow
insufficient detected Difference in intake manifold absolute pressure between
opened EGR valve and closed EGR valve is less than
specification. 2 driving
cycles
�)
�{ *P0402 Exhaust gas recirculation flow
excessive detected Difference in intake manifold absolute pressure between
opened EGR valve and closed EGR valve is more than
specification. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0403 Exhaust gas recirculation
control circuit Output voltage is different from output command with
more than one pole out of 4 poles. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P0420 Catalyst system efficiency
below threshold
Output waveforms of HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 are similar. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0443 Evaporative emission system
purge control valve circuit Monitor signal of EVAP canister purge valve is different
from command signal. (circuit open or shorted to ground) 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0480 Fan 1 (Radiator cooling fan)
control circuit Monitor signal of radiator cooling fan relay is different from
command signal. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0500 Vehicle speed sensor “A” No VSS signal during fuel cut fo
r specified time or longer,
or VSS signal is not input even if vehicle is driving with
more than specified engine speed and D-range (for A/T
model). 2 driving
cycles
�) P0532 A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
“A” circuit low Output voltage of A/C refrigerant pressure sensor is less
than specification.
—
�) P0533 A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
“A” circuit high Output voltage of A/C refrigerant pressure sensor is more
than specification.
—
�) *P0601 Internal control module
memory check sum error Data write error or check sum error. 1 driving
cycle
�) P0602 Control module programming
error Data programming error.
—
�) *P0607 Control module performance Data programming error. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P061
6Starter relay circuit low Starter signal is low voltage even though engine is started
with vehicle at stop. 2 driving
cycles
DTC No. Detecting item
Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL