temperature sensor SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 6 of 1496
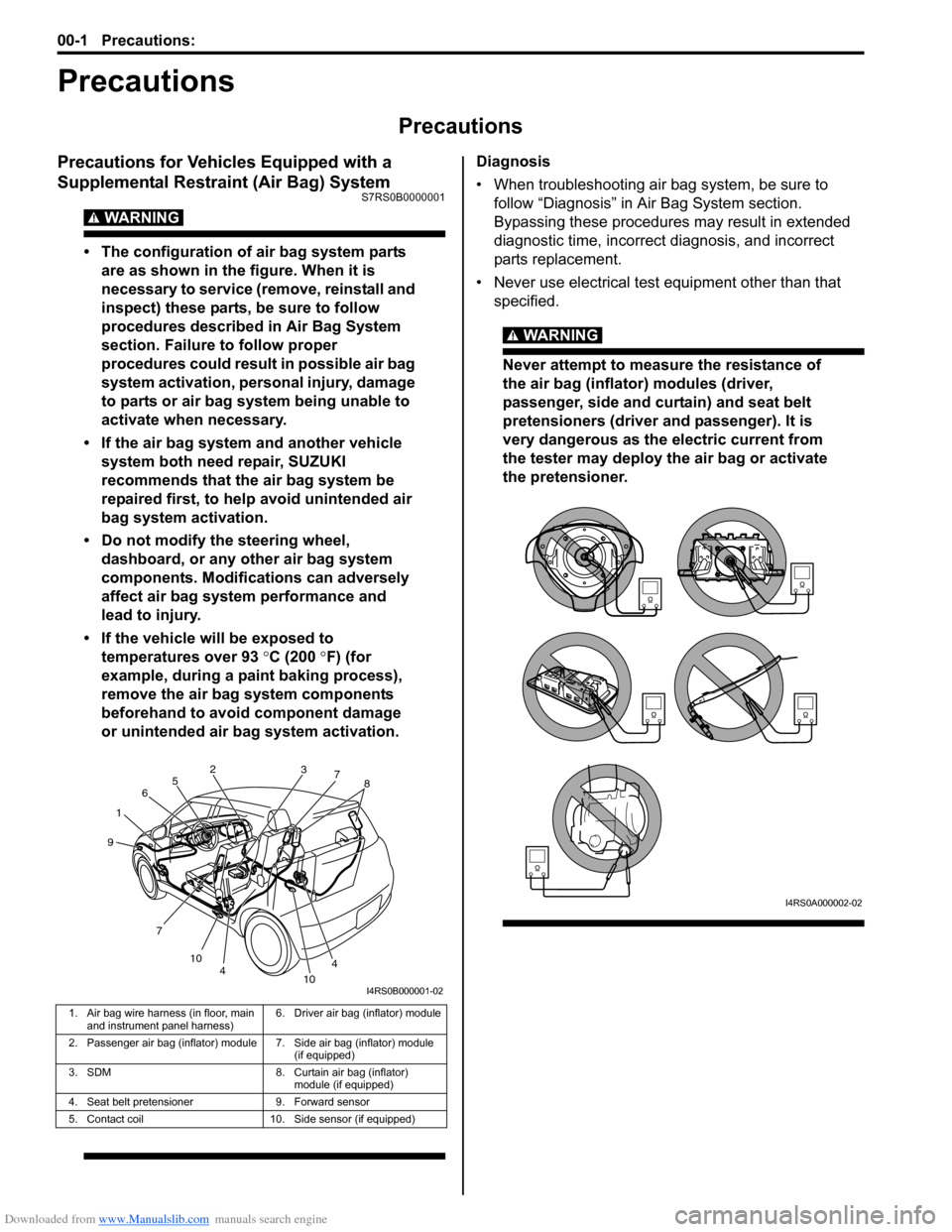
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-1 Precautions:
Precautions
Precautions
Precautions
Precautions for Vehicles Equipped with a
Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System
S7RS0B0000001
WARNING!
• The configuration of air bag system parts are as shown in the figure. When it is
necessary to service (remove, reinstall and
inspect) these parts, be sure to follow
procedures described in Air Bag System
section. Failure to follow proper
procedures could result in possible air bag
system activation, personal injury, damage
to parts or air bag system being unable to
activate when necessary.
• If the air bag system and another vehicle system both need repair, SUZUKI
recommends that the air bag system be
repaired first, to help avoid unintended air
bag system activation.
• Do not modify the steering wheel, dashboard, or any other air bag system
components. Modifications can adversely
affect air bag system performance and
lead to injury.
• If the vehicle will be exposed to temperatures over 93 °C (200 °F) (for
example, during a paint baking process),
remove the air bag system components
beforehand to avoid component damage
or unintended air bag system activation.
Diagnosis
• When troubleshooting air bag system, be sure to follow “Diagnosis” in Air Bag System section.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis, and incorrect
parts replacement.
• Never use electrical test equipment other than that specified.
WARNING!
Never attempt to measure the resistance of
the air bag (inflator) modules (driver,
passenger, side and curtain) and seat belt
pretensioners (driver and passenger). It is
very dangerous as the electric current from
the tester may deploy the air bag or activate
the pretensioner.
1. Air bag wire harness (in floor, main and instrument panel harness) 6. Driver air bag (inflator) module
2. Passenger air bag (inflator) module 7. Side air bag (inflator) module (if equipped)
3. SDM 8. Curtain air bag (inflator) module (if equipped)
4. Seat belt pretensioner 9. Forward sensor
5. Contact coil 10. Side sensor (if equipped)
1 2
3
4
4
5
6
7 7
8
9
10 10
I4RS0B000001-02
I4RS0A000002-02
Page 8 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-3 Precautions:
WARNING!
SDM
• For handling and storage of a SDM, select a place where the ambient temperature
below 65 °C (150 °F), without high humidity
and away from electric noise.
• During service procedures, be very careful when handling a Sensing and Diagnostic
Module (SDM). Never strike or jar the SDM.
• Never power up the air bag system when the SDM is not rigidly attached to the
vehicle. All SDM and mounting bracket
fasteners must be carefully torqued and
the arrow must be pointing toward the
front of the vehicle to ensure proper
operation of the air bag system.
The SDM could be activated when powered
while not rigidly att ached to the vehicle
which could cause deployment and result
in personal injury.
WARNING!
Driver and Passenger Seat Belt
Pretensioners
• For handling and storage of a live seat belt pretensioner, select a place where the
ambient temperature below 65 °C (150 ° F),
without high humidity and away from
electric noise.
• Never carry seat belt pretensioner by wire or connector of pretensioner. When
placing a live seat belt pretensioner on the
workbench or some place like that, never
put something on seat belt pretensioner.
Otherwise, personal injury may result.
• Never dispose of live (inactivated) seat belt pretensioners (drive and passenger). If
disposal is necessary, be sure to activate
them according to activation procedures
described in “Air Bag (Inflator) Module and
Seat Belt Pretensioner Disposal in Section
8B” before disposal.
• The seat belt pretensioner immediately after activation is very hot. Wait for at least
half an hour to cool it off before
proceeding the work.
• With many service procedures, gloves and safety glasses should be worn to prevent
any possible irritation of the skin or eyes.
• Even when the accident was light enough not to cause air bags to activate, be sure to inspect system
parts and other related parts according to instructions
under “Repair and Inspection Required after Accident
in Section 8B”.
• When servicing parts other than air bag system, if shocks may be applied to air bag system component
parts, remove those parts beforehand.
• When handling the air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side and curtain), seat belt pretensioners
(driver and passenger), forward sensor, side sensors
or SDM, be careful not to drop it or apply an impact to
it. If an excessive impact was applied, never attempt
disassembly or repair but replace it with a new one.
• When grease, cleaning agent, oil, water, etc. has got onto air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side
and curtain) or seat belt pretensioners (drive and
passenger), wipe off immediately with a dry cloth.
• Air bag wire harness is included in floor and instrument panel wire harnesses. Air bag wire
harness branched off from floor and instrument panel
wire harnesses can be identifie d easily as it is covered
with a yellow protection tube and it has yellow
connectors. Be very ca reful when handling it.
• When an open in air bag wire harness, damaged wire harness, connector or terminal is found, replace wire
harness, connectors and terminals as an assembly.
• Do not apply power to the air bag system unless all components are connected or a diagnostic flow
requests it, as this will set a DTC.
• Never use air bag system component parts from another vehicle.
• When using electric welding, be sure to disconnect all air bag (inflator) module connectors and pretensioner
connectors from air bag wire harness respectively.
• Never expose air bag system component parts directly to hot air (drying or baking the vehicle after
painting) or flames.
• WARNING / CAUTION labels are attached on each
part of air bag system components. Be sure to follow
the instructions.
• After vehicle is completely repaired, perform “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check in Section 8B”.
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 45 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 1- i
1
Section 1
CONTENTS
Engine
Precautions ................................................. 1-1
Precautions............................................................. 1-1
Precautions for Engine .......................................... 1-1
Engine General Information and
Diagnosis ............. .................................... 1A-1
Precautions........................................................... 1A-1
Precautions on Engine Service ........................... 1A-1
Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System .............................................................. 1A-1
Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble ..................... 1A-1
Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection................ 1A-2
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration ......................................................... 1A-2
General Description ............................................. 1A-2 Statement on Cleanliness and Care ................... 1A-2
Engine Diagnosis General Description ............... 1A-3
On-Board Diagnostic System Description ........... 1A-3
Data Link Connector (DLC) ................................. 1A-6
Engine and Emission Control System Description ........................................................ 1A-6
CAN Communication System Description........... 1A-7
Air Intake System Description ............................. 1A-9
Description of Electric Throttle Body System ...... 1A-9
Description of Electric Throttle Body System Calibration ....................................................... 1A-10
Fuel Cut Control Description ............................. 1A-10
Generator Control System Description ............. 1A-11
Electronic Control System Description .............. 1A-12
Engine and Emission Control Input / Output Table ............................................................... 1A-18
Schematic and Routing Diagram ...................... 1A-19 Engine and Emission Control System Diagram .......................................................... 1A-19
Component Locatio n ......................................... 1A-21
Electronic Control System Components Location .......................................................... 1A-21
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 1A-22 Engine and Emission Control System Check.... 1A-22
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check .......... 1A-25
DTC Check ....................................................... 1A-26
DTC Clearance ................................................. 1A-27
DTC Table ......................................................... 1A-27
Fail-Safe Table ................ .................................. 1A-31 Scan Tool Data ................................................. 1A-33
Visual Inspection ............................................... 1A-37
Engine Basic Inspection .................................... 1A-38
Engine Symptom Diagnosis .............................. 1A-41
MIL Does Not Come ON with Ignition Switch
ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can Be
Started) ........................................................... 1A-47
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after Engine Starts................................................... 1A-48
DTC P0010: “A” Camshaft Position Actuator Circuit .............................................................. 1A-49
DTC P0011 / P0012: “A” Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System
Performance / -Retarded................................. 1A-52
DTC P0031 / P0032: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High (Sensor-1) .......................... 1A-54
DTC P0037 / P0038: HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low / High (Sensor-2) .......................... 1A-56
DTC P0101: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range / Performance ...................................... 1A-58
DTC P0102: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input......................................................... 1A-61
DTC P0103: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit High Input ........................................................ 1A-63
DTC P0106: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circuit Range /
Performance.................................................... 1A-64
DTC P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circ uit Low Input............ 1A-66
DTC P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure /
Barometric Pressure Circ uit High Input ........... 1A-67
DTC P0111: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Range / Performance ........................... 1A-69
DTC P0112: Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Low ...................................................... 1A-72
DTC P0113: Intake Air Temperature 1 Sensor Circuit High...................................................... 1A-74
DTC P0116: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range / Performance ........................... 1A-76
DTC P0117: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low ...................................................... 1A-79
DTC P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High...................................................... 1A-81
DTC P0122: Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch “A” (Main) Circuit Low ........................ 1A-83
Page 58 of 1496
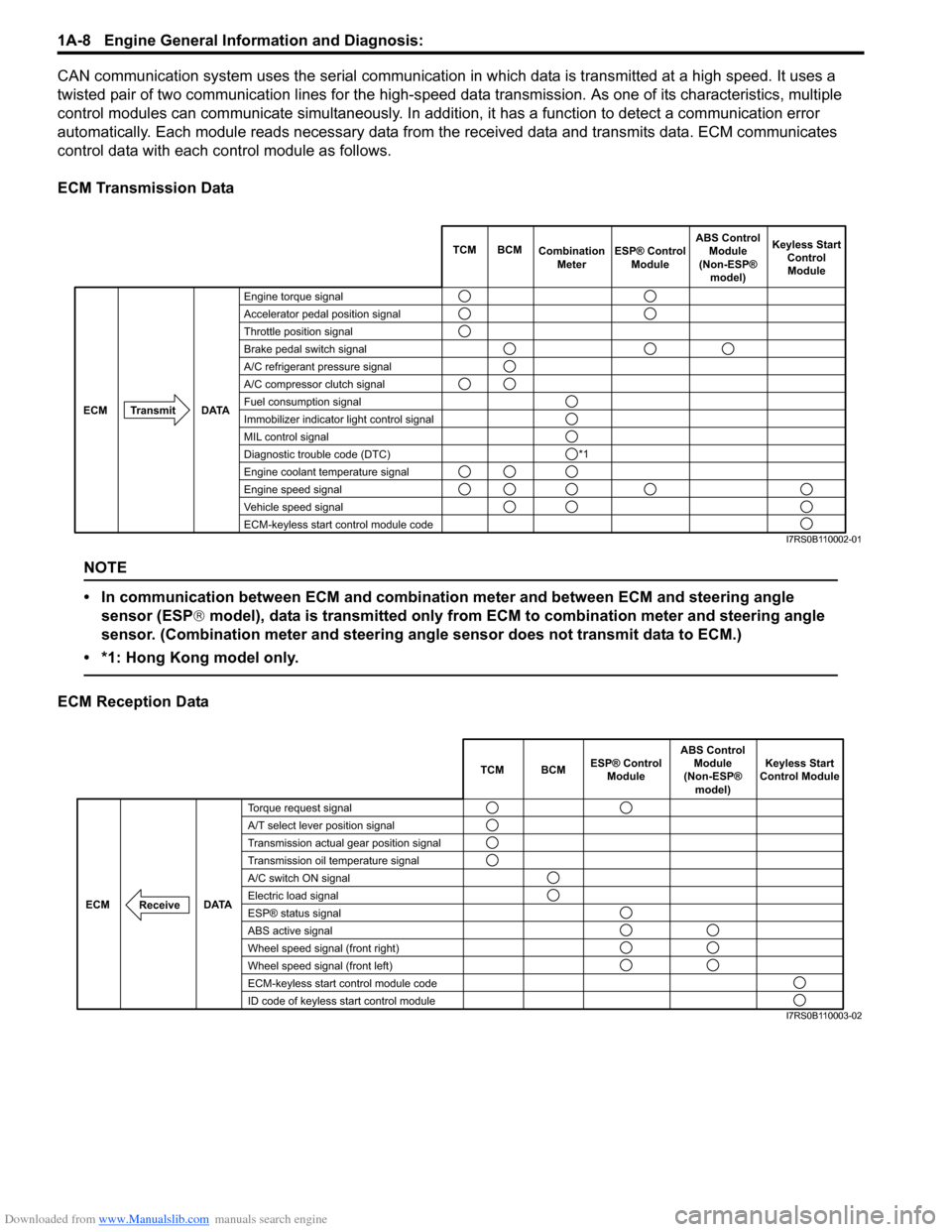
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
CAN communication system uses the serial communication in which data is transmitted at a high speed. It uses a
twisted pair of two communication lines for the high-speed da ta transmission. As one of its characteristics, multiple
control modules can communicate simultaneously. In addition, it has a function to detect a communication error
automatically. Each module reads necessary data from the received data and transmits data. ECM communicates
control data with each control module as follows.
ECM Transmission Data
NOTE
• In communication between ECM and combination meter and between ECM and steering angle sensor (ESP ® model), data is transmitted only from ECM to combination meter and steering angle
sensor. (Combination meter and steering angle sensor does not transmit data to ECM.)
• *1: Hong Kong model only.
ECM Reception Data
Engine torque signal
Accelerator pedal position signal
Throttle position signal
Brake pedal switch signal
A/C refrigerant pressure signal
A/C compressor clutch signal
Fuel consumption signal
Immobilizer indicator light control signal
MIL control signal
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Engine coolant temperature signal
Engine speed signal
Vehicle speed signal
ECM-keyless start control module code TCM BCM
Combination
Meter Keyless Start
ControlModule
Transmit DATA
ECM
ESP® Control
Module ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
*1
I7RS0B110002-01
TCM BCM Keyless Start
Control Module
DATA
ECM
Torque request signal
A/T select lever position signal
Transmission actual gear position signal
Transmission oil temperature signal
A/C switch ON signal
Electric load signal
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ECM-keyless start control module code
ID code of keyless start control module
Receive
ABS Control
Module
(Non-ESP® model)
ESP® Control
Module
I7RS0B110003-02
Page 78 of 1496
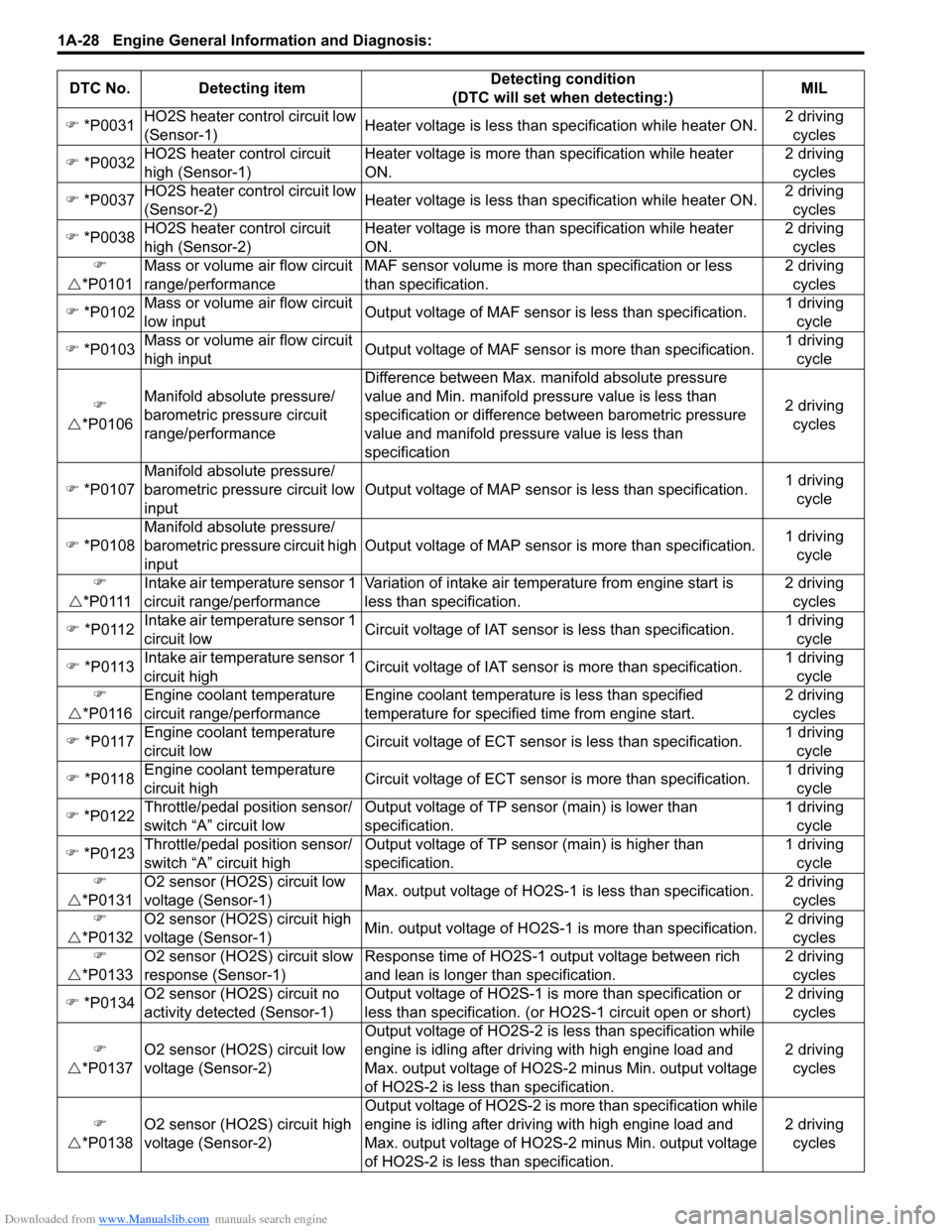
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-28 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
�) *P0031 HO2S heater control circuit low
(Sensor-1) Heater voltage is less than specification while heater ON. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0032 HO2S heater control circuit
high (Sensor-1) Heater voltage is more than
specification while heater
ON. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0037 HO2S heater control circuit low
(Sensor-2) Heater voltage is less than specification while heater ON. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0038 HO2S heater control circuit
high (Sensor-2) Heater voltage is more than
specification while heater
ON. 2 driving
cycles
�)
�U *P0101 Mass or volume air flow circuit
range/performance MAF sensor volume is more
than specification or less
than specification. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0102 Mass or volume air flow circuit
low input Output voltage of MAF sensor is less than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0103 Mass or volume air flow circuit
high input Output voltage of MAF sensor is more than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P0106 Manifold absolute pressure/
barometric pressure circuit
range/performance Difference between Max. manifold absolute pressure
value and Min. manifold pressure value is less than
specification or difference between barometric pressure
value and manifold pressure value is less than
specification
2 driving
cycles
�) *P0107 Manifold absolute pressure/
barometric pressure circuit low
input Output voltage of MAP sensor
is less than specification.1 driving
cycle
�) *P0108 Manifold absolute pressure/
barometric pressure circuit high
input Output voltage of MAP sensor is more than specification.
1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P0111 Intake air temperature sensor 1
circuit range/performance Variation of intake air temperature from engine start is
less than specification. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0112 Intake air temperature sensor 1
circuit low Circuit voltage of IAT sensor is less than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0113 Intake air temperature sensor 1
circuit hig
h Circuit voltage of IAT sensor
is more than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P0116 Engine coolant temperature
circuit range/performance Engine coolant temperature is less than specified
temperature for specified time from engine start. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0117 Engine coolant temperature
circuit low Circuit voltage of ECT sensor
is less than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0118 Engine coolant temperature
circuit high Circuit voltage of ECT sensor
is more than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0122 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “A” circuit low Output voltage of TP sensor (main) is lower than
specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P0123 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “A” circuit high Output voltage of TP sensor (main) is higher than
specification. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P0131 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit low
voltage (Sensor-1)
Max. output voltage of HO2S-1
is less than specification.2 driving
cycles
�)
�U *P0132 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit high
voltage (Sensor-1)
Min. output voltage of HO2S-1
is more than specification. 2 driving
cycles
�)
�U *P0133 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit slow
response (Sensor-1) Response time of HO2S-1 output voltage between rich
and lean is longer than specification. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P0134 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit no
activity detected (Sensor-1) Output voltage of HO2S-1 is
more than specification or
less than specification. (or HO2S-1 circuit open or short) 2 driving
cycles
�)
�U *P0137 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit low
voltage (Sensor-2) Output voltage of HO2S-2 is
less than specification while
engine is idling after driving with high engine load and
Max. output voltage of HO2S-2 minus Min. output voltage
of HO2S-2 is less than specification. 2 driving
cycles
�)
�U *P013
8 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit high
voltage (Sensor-2) Output voltage of HO2S-2 is
more than specification while
engine is idling after driving with high engine load and
Max. output voltage of HO2S-2 minus Min. output voltage
of HO2S-2 is less than specification. 2 driving
cycles
DTC No. Detecting item
Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL
Page 81 of 1496
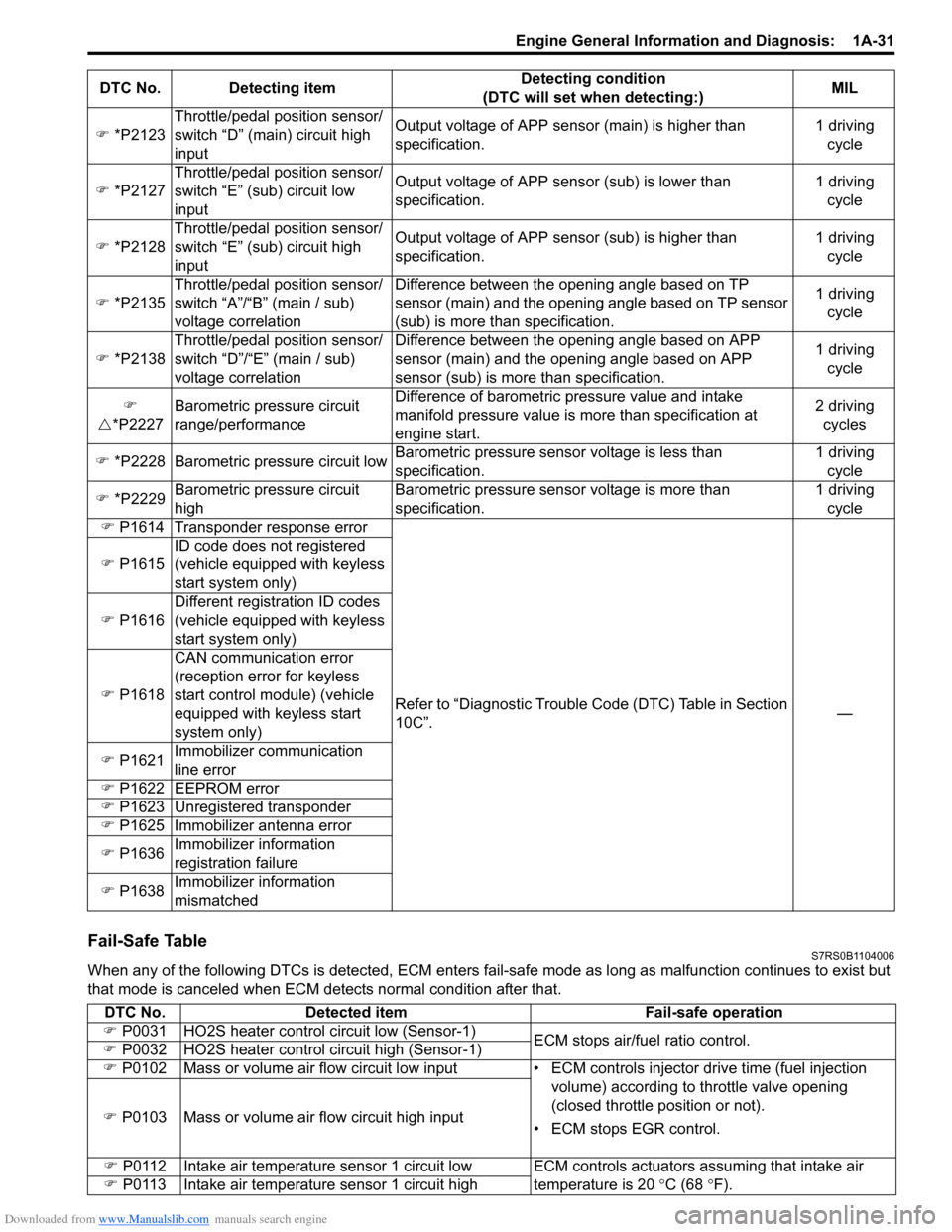
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-31
Fail-Safe TableS7RS0B1104006
When any of the following DTCs is detected, ECM enters fail-safe mode as long as malfunction continues to exist but
that mode is canceled when ECM de tects normal condition after that.
�)
*P2123 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “D” (main) circuit high
input Output voltage of APP sensor (main) is higher than
specification.
1 driving
cycle
�) *P2127 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “E” (sub) circuit low
input Output voltage of APP sens
or (sub) is lower than
specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P2128 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “E” (sub) circuit high
input Output voltage of APP sensor (sub) is higher than
specification.
1 driving
cycle
�) *P2135 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “A”/“B” (main / sub)
voltage correlation Difference between the opening angle based on TP
sensor (main) and the opening angle based on TP sensor
(sub) is more than specification.
1 driving
cycle
�) *P2138 Throttle/pedal position sensor/
switch “D”/“E” (main / sub)
voltage correlation Difference between the opening angle based on APP
sensor (main) and the opening angle based on APP
sensor (sub) is more
than specification. 1 driving
cycle
�)
�U *P2227 Barometric pressure circuit
range/performance Difference of barometric pressure value and intake
manifold pressure value is
more than specification at
engine start. 2 driving
cycles
�) *P2228 Barometric pressure circuit low Barometric pressure sens
or voltage is less than
specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) *P2229 Barometric pressure circuit
high Barometric pressure sensor voltage is more than
specification. 1 driving
cycle
�) P1614 Transponder response error
Refer to “Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Table in Section
10C”. —
�) P1615 ID code does not registered
(vehicle equipped with keyless
start system only)
�) P1616 Different registration ID codes
(vehicle equipped with keyless
start system only)
�) P1618 CAN communication error
(reception error for keyless
start control module) (vehicle
equipped with keyless start
system only)
�) P1621 Immobilizer communication
line error
�) P1622
EEPROM error
�) P1623 Unregistered transponder
�) P1625 Immobilizer antenna error
�) P1636 Immobilizer information
registration failure
�) P1638 Immobilizer information
mismatched
DTC No. Detecting item
Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting:) MIL
DTC No.
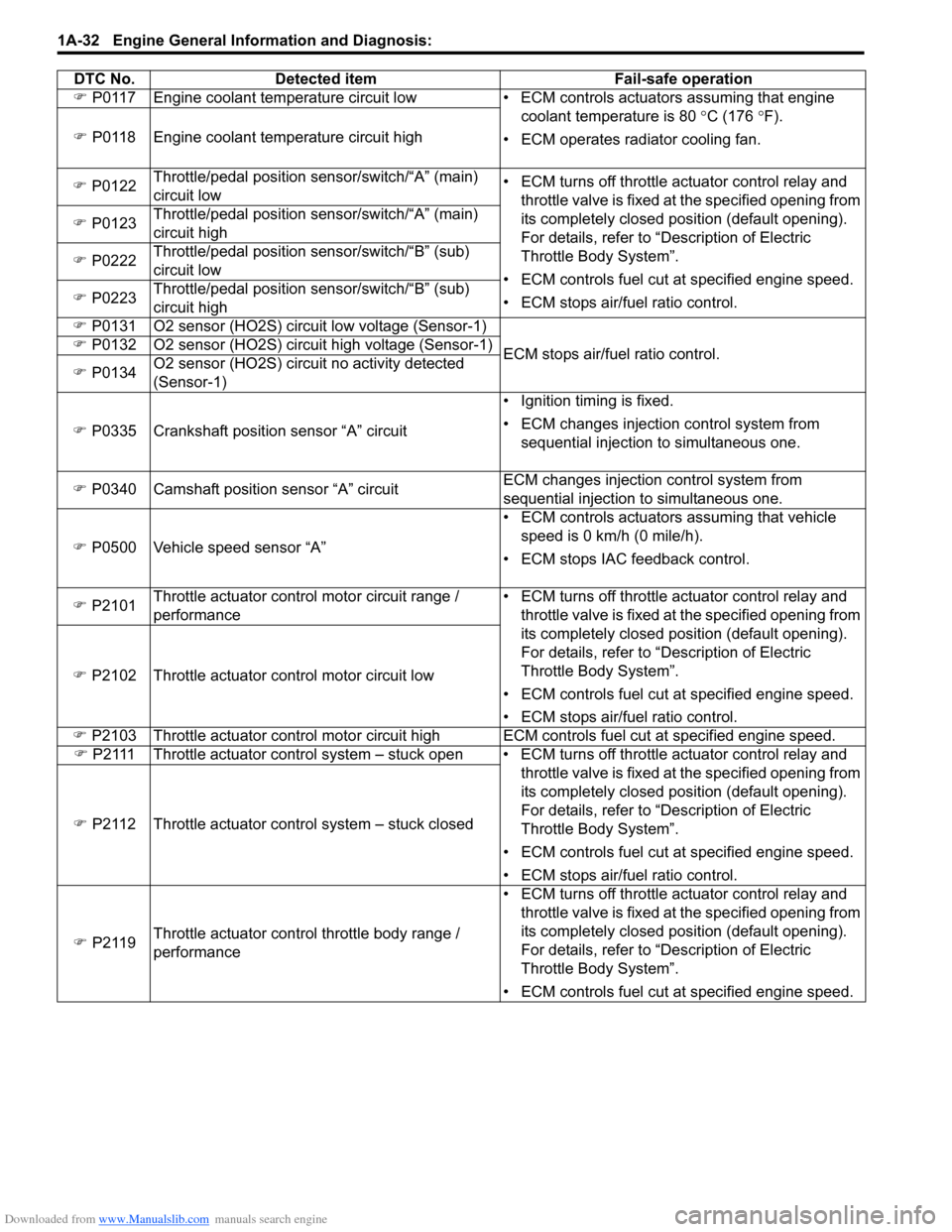
Detected item Fail-safe operation
�) P0031 HO2S heater control circuit low (Sensor-1)
ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�) P0032 HO2S heater control circuit high (Sensor-1)
�) P0102 Mass or volume air flow circuit low input • ECM controls injector drive time (fuel injection
volume) according to throttle valve opening
(closed throttle position or not).
• ECM stops EGR control.
�)
P0103 Mass or volume air flow circuit high input
�) P0112 Intake air temperature sensor 1 circuit low ECM controls actuators assuming that intake air
temperature is 20 °C (68 ° F).
�) P0113 Intake air temperature sensor 1 circuit high
Page 82 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-32 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
�) P0117 Engine coolant temperature circuit low • EC M controls actuators assuming that engine
coolant temperature is 80 °C (176 °F).
• ECM operates radiator cooling fan.
�)
P0118 Engine coolant temperature circuit high
�) P0122 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“A” (main)
circuit low • ECM turns off throttle actuator control relay and
throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
• ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P0123 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“A” (main)
circuit high
�) P0222 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“B” (sub)
circuit low
�) P0223 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“B” (sub)
circuit high
�) P0131 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit low voltage (Sensor-1)
ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P0132 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit high voltage (Sensor-1)
�) P0134 O2 sensor (HO2S) circuit no activity detected
(Sensor-1)
�) P0335 Crankshaft position sensor “A” circuit • Ignition timing is fixed.
• ECM changes injection control system from
sequential injection to simultaneous one.
�) P0340 Camshaft position sensor “A” circuit ECM changes injection
control system from
sequential injection to simultaneous one.
�) P0500 Vehicle speed sensor “A” • ECM controls actuators assuming that vehicle
speed is 0 km/h (0 mile/h).
• ECM stops IAC feedback control.
�) P2101 Throttle actuator control motor circuit range /
performance • ECM turns off throttle actuator control relay and
throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
• ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P2102 Throttle actuator control motor circuit low
�) P2103 Throttle actuator control motor circuit high ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
�) P2111 Throttle actuator control system – stuck open • EC M turns off throttle actuator control relay and
throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
• ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P2112 Throttle actuator control system – stuck closed
�) P2119 Throttle actuator control throttle body range /
performance • ECM turns off throttle actuator control relay and
throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
DTC No.
Detected item Fail-safe operation
Page 84 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-34 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
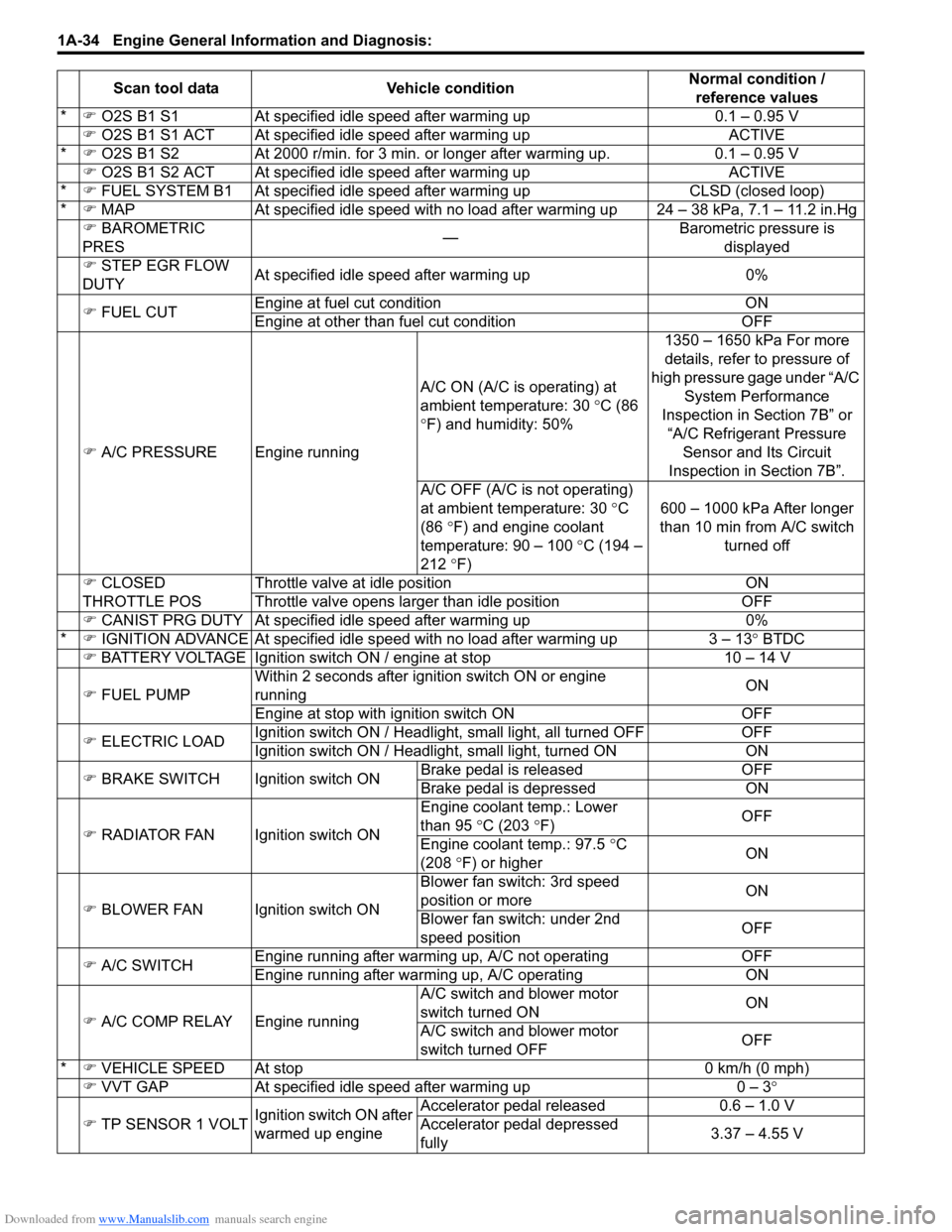
*�) O2S B1 S1 At specified idle speed after warming up 0.1 – 0.95 V
�) O2S B1 S1 ACT At specified id le speed after warming up ACTIVE
* �) O2S B1 S2 At 2000 r/min. for 3 min. or longer after warming up. 0.1 – 0.95 V
�) O2S B1 S2 ACT At specified id le speed after warming up ACTIVE
* �) FUEL SYSTEM B1 At specif ied idle speed after warming up CLSD (closed loop)
* �) MAP At specified idle speed with no load after warming up 24 – 38 kPa, 7.1 – 11.2 in.Hg
�) BAROMETRIC
PRES —Barometric pressure is
displayed
�) STEP EGR FLOW
DUTY At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
�) FUEL CUT Engine at fuel cut condition ON
Engine at other than fuel cut condition OFF
�) A/C PRESSURE Engine running A/C ON (A/C is operating) at
ambient temperature: 30
°C (86
° F) and humidity: 50% 1350 – 1650 kPa For more
details, refer to pressure of
high pressure gage under “A/C System Performance
Inspection in Section 7B” or “A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor and Its Circuit
Inspection in Section 7B”.
A/C OFF (A/C is not operating)
at ambient temperature: 30 ° C
(86 °F) and engine coolant
temperature: 90 – 100 °C (194 –
212 °F) 600 – 1000 kPa After longer
than 10 min from A/C switch turned off
�) CLOSED
THROTTLE POS Throttle valve at idle position ON
Throttle valve opens larger than idle position OFF
�) CANIST PRG DUTY At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
* �) IGNITION ADVANCE At specified idle s peed with no load after warming up 3 – 13 ° BTDC
�) BATTERY VOLTAGE Ignition switch ON / engine at stop 10 – 14 V
�) FUEL PUMP Within 2 seconds after ignition switch ON or engine
running
ON
Engine at stop with ignition switch ON OFF
�) ELECTRIC LOAD Ignition switch ON / Headligh
t, small light, all turned OFF OFF
Ignition switch ON / Headli ght, small light, turned ON ON
�) BRAKE SWITCH Igni tion switch ONBrake pedal is released OFF
Brake pedal is depressed ON
�) RADIATOR FAN Ignition switch ON Engin
e coolant temp.: Lower
than 95 °C (203 °F) OFF
Engine coolant temp.: 97.5 °C
(208 °F) or higher ON
�) BLOWER FAN Ignition switch ON Blower fan switch: 3rd speed
position or more
ON
Blower fan switch: under 2nd
speed position OFF
�) A/C SWITCH Engine running after warming up, A/C not operating
OFF
Engine running after warming up, A/C operating ON
�) A/C COMP RELAY Engine running A/C switch and blower motor
switch turned ON
ON
A/C switch and blower motor
switch turned OFF OFF
* �) VEHICLE SPEED At stop 0 km/h (0 mph)
�) VVT GAP At specified idle speed after warming up 0 – 3°
�) TP SENSOR 1 VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
0.6 – 1.0 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.37 – 4.55 V
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
Page 85 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-35
Scan Tool Data Definitions
COOLANT TEMP (ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE, °C, °F)
It is detected by engine coolant temp. sensor.
INTAKE AIR TEMP. ( °C, °F)
It is detected by intake air temp. sensor.
ENGINE SPEED (rpm)
It is computed by reference pulses from the camshaft
position sensor.
INJ PULSE WIDTH (FUEL INJECTION PULSE WIDTH,
msec.)
This parameter indicates time of the injector drive (valve
opening) pulse which is output from ECM (but injector
drive time of NO.1 cylinder fo r multiport fuel injection).
DESIRED IDLE (DESIRED IDLE SPEED, rpm)
The Desired Idle Speed is an ECM internal parameter
which indicates the ECM requested idle. If the engine is
not running, this number is not valid.
SHORT FT B1 (SHORT TERM FUEL TRIM, %)
Short term fuel trim valu e represents short term
corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value
of 0 indicates no correction, a value greater than 0
means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0
implies an enleanment correction. LONG FT B1 (LONG TERM FUEL TRIM, %)
Long term fuel trim value represents long term
corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value
of 0 indicates no correction, a value greater than 0
means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0
implies an enleanment correction.
TOTAL FUEL TRIM B1 (%)
The value of Total Fuel Trim is obtained by calculating
based on values of Short Term Fuel Trim and Long Term
Fuel Trim. This value indica
tes how much correction is
necessary to keep the air/fuel mixture stoichiometrical.
MAF (MASS AIR FLOW RATE, g/s, lb/min.)
It represents total mass of air entering intake manifold
which is measured by mass air flow sensor.
CALC LOAD (CALCULATED LOAD VALUE, %)
Engine load displayed as a percentage of maximum
possible load. Value is calculated mathematically using
the formula: actual (current) intake air volume ÷
maximum possible intake air volume × 100%
THROTTLE POS (ABSOLUTE THROTTLE POSITION,
%)
When throttle position sensor is at fully closed position,
throttle opening is indicated as 0 – 5% and 90 – 100%
full open position.
O2S SENSOR B1 S1 (HEA TED OXYGEN SENSOR-1,
V)
It indicates output voltage of HO2S-1 installed on
exhaust manifold (pre-catalyst).
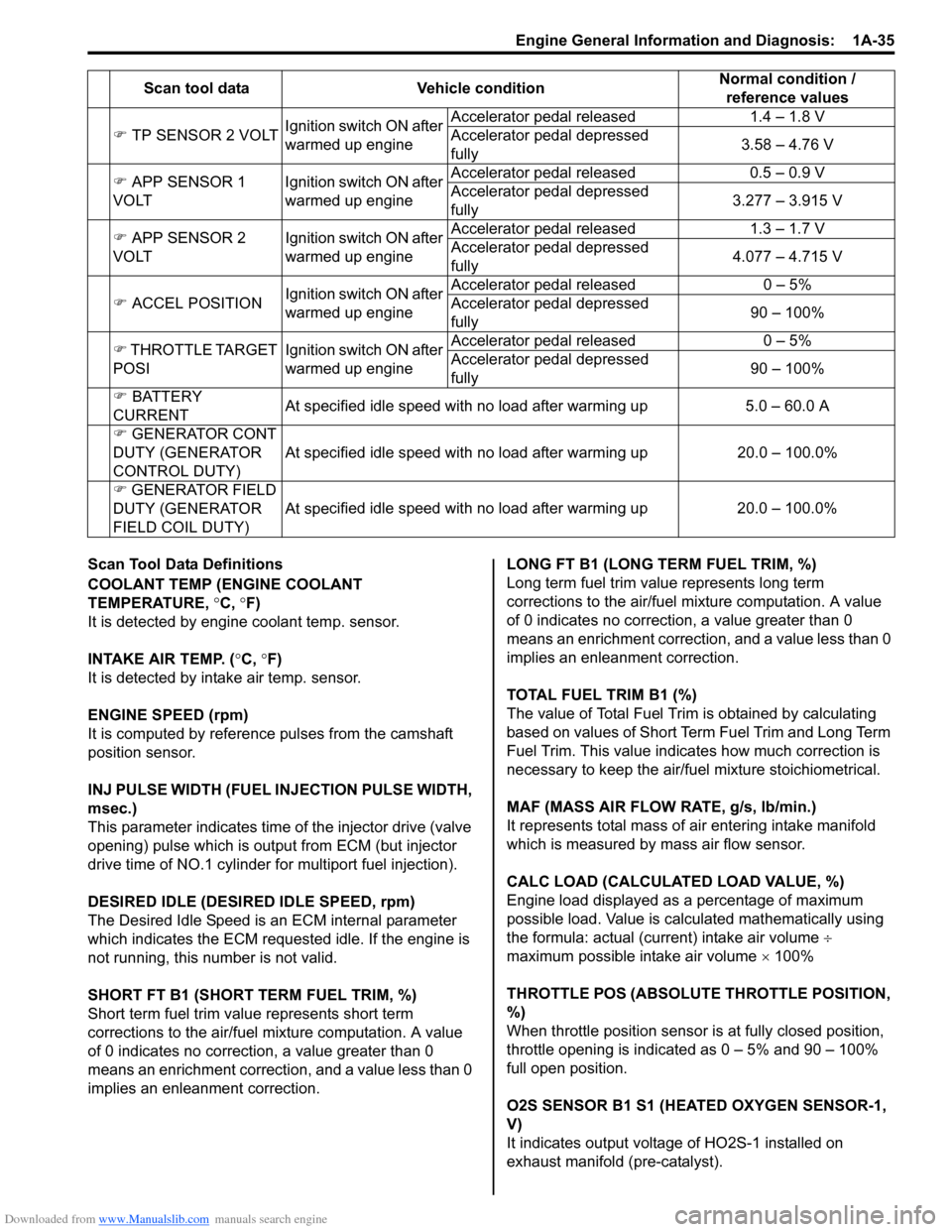
�)
TP SENSOR 2 VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
1.4 – 1.8 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.58 – 4.76 V
�) APP SENSOR 1
VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engineAccelerator pedal released
0.5 – 0.9 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 3.277 – 3.915 V
�) APP SENSOR 2
VOLT Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engineAccelerator pedal released
1.3 – 1.7 V
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 4.077 – 4.715 V
�) ACCEL POSITION Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engine Accelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
�) THROTTLE TARGET
POSI Ignition switch ON after
warmed up engineAccelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
�) BATTERY
CURRENT At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
5.0 – 60.0 A
�) GENERATOR CONT
DUTY (GENERATOR
CONTROL DUTY) At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
20.0 – 100.0%
�) GENERATOR FIELD
DUTY (GENERATOR
FIELD COIL DUTY) At spe
cified idle speed with no load after warming up
20.0 – 100.0%
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values