air condition SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SX4, Model: SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.GPages: 1556, PDF Size: 37.31 MB
Page 34 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-3 Maintenance and Lubrication:
NOTE
• “I”: Inspect and correct or replace if necessary
• “R”: Replace or change
• *1: Inspect or replace more frequently if the vehicle is used under dusty conditions.
• *2: Clean or replace more frequently if the air from the air conditioning decreases.
Repair Instructions
Accessory Drive Belt InspectionS6RW0D0206001
WARNING!
All inspection and replacement are to be
performed with ENGINE NOT RUNNING.
Water Pump and Generator Drive Belt
Inspect belt for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and
cleanliness. If any defect exists, replace.
Check belt for tension referring to “Water Pump /
Generator Drive Belt Tension Inspection and Adjustment
in Section 1J”.
A/C Compressor Drive Belt (If Equipped)
Inspect belt for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and
cleanliness. If any defect exists, replace.
Check belt for tension referring to “Compressor Drive
Belt Inspection and Adjustment in Section 7B” or
“Compressor Drive Belt Inspection and Adjustment in
Section 7B”.
Accessory Drive Belt ReplacementS6RW0D0206002
Water Pump and Generator Drive Belt
Replace belt with new one referring to “Water Pump /
Generator Drive Belt Removal and Installation in Section
1J”.
A/C Compressor Drive Belt (If Equipped)
Replace belt with new one referring to “Compressor
Drive Belt Removal and Installation in Section 7B” or
“Compressor Drive Belt Removal and Installation in
Section 7B”.
Valve Lash (Clearance) InspectionS6RW0D0206003
Inspect intake and exhaust valve lash and adjust as
necessary.
Refer to “Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection in Section
1D” for valve lash inspection and adjustment procedure. – B – – E – – HManual transaxle oil
Transfer oil (4WD)
Differential oil (4WD)�) / �) / �) RFirst time only:
15,000 km (9,000 miles) or 12
months
Second time and after:
Every 30,000 km (18,000 miles) or
24 months reckoning from 0 km (0
mile) or 0 month
– B – – E – – H Automatic transaxle fluid�)R Every 30,000 km (18,000 miles) or
24 months
– – C D – – – – HVAC air filter (if equipped) *2�) IEvery 15,000 km (9,000 miles) or
12 months
�) REvery 45,000 km (27,000 miles) or
36 months Severe
condition codeMaintenanceMaintenance
operationMaintenance interval
1. Camshaft 2. Thickness gauge
I2RH0B020003-02
Page 38 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-7 Maintenance and Lubrication:
Brake Discs and Pads (Front) InspectionS6RW0D0206014
1) Remove wheel and caliper but don’t disconnect
brake hose from caliper.
2) Check front disc brake pads and discs for excessive
wear, damage and deflection. Replace parts as
necessary. For details, refer to “Front Disc Brake
Pad Inspection in Section 4B” and “Front Brake Disc
Inspection in Section 4B”.
Be sure to torque caliper pin bolts to specification.
Brake Drums and Shoes (Rear) InspectionS6RW0D0206015
1) Remove wheel and brake drum.
2) Check rear brake drums and brake linings for
excessive wear and damage, while wheels and
drums are removed. At the same time, check wheel
cylinders for leaks. Replace these parts as
necessary.
For details, refer to “Rear Brake Drum and Shoe
Inspection in Section 4C”.
Brake Hoses and Pipes InspectionS6RW0D0206016
Perform this inspection where these is enough light and
use a mirror as necessary.
• Check brake hoses and pipes for proper hookup,
leaks, cracks, chafing and other damage.
• Check that hoses and pipes are clear of sharp edges
and moving parts.
Repair or replace any of these parts as necessary.
CAUTION!
After replacing any brake pipe or hose, be
sure to carry out air purge operation.
Brake Fluid ReplacementS6RW0D0206017
Change brake fluid as follows.
Drain existing fluid from brake system completely, fill
system with specified fluid and carry out air purge
operation.
For air purging procedure, refer to “Air Bleeding of Brake
System in Section 4A”.
Brake Lever and Cable InspectionS6RW0D0206018
1) Inspect brake cable for damage and smooth
movement.
Replace cable if it is in deteriorated condition.
I3RM0A020006-01
I5RW0A020004-01
I4RS0A020008-01
I4RS0A020009-01
Page 39 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-8
2) Check tooth tip of each notch for damage or wear. If
any damage or wear is found, replace parking lever.
3) Check parking brake lever for proper operation and
stroke, and adjust it if necessary.
For checking and adjusting procedures, refer to
“Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment in Section
4D”.
Parking brake lever stroke
“a”: 4 – 9 notches (with 200 N (20 kg, 44 lbs) of pull
pressure)
Clutch Fluid InspectionS6RW0D0206019
1) Check clutch system for evidence of fluid leakage.
Repair leaky point if any.
2) Check reservoir for fluid level referring to “Clutch
Fluid Level Inspection in Section 5C”.
If fluid is lower than minimum level (1) of reservoir,
refill reservoir with specified brake fluid indicated on
reservoir cap (2).
Tires InspectionS6RW0D0206020
1) Check tires for uneven or excessive wear, or
damage. If defective, replace.
Refer to “Irregular and/or Premature Wear
Description in Section 2D” and “Wear Indicators
Description in Section 2D” for details.
2) Check inflating pressure of each tire and adjust
pressure to specification as necessary.
NOTE
• Tire inflation pressure should be checked
when tires are cool.
• Specified tire inflation pressure should be
found on tire placard or in owner’s manual
which came with the vehicle.
3) Rotate tires. For details, refer to “Tire Rotation in
Section 2D”.
Wheel Discs InspectionS6RW0D0206021
Inspect each wheel disc for dents, distortion and cracks.
A disc in badly damaged condition must be replaced.
Wheel Bearing InspectionS6RW0D0206022
1) Check front wheel bearing for wear, damage,
abnormal noise or rattles. For details, refer to “Front
Wheel Hub, Disc, Bolt and Bearing Check in Section
2B”.
2) Check rear wheel bearing for wear, damage,
abnormal noise or rattles. For details, refer to “Rear
Wheel Disc, Bolt and Bearing Inspection in Section
2C”.
I4RS0B020005-01
1
2
I5RW0A020005-01
1. Wear indicator
I2RH01020022-01
I2RH01020023-01
Page 41 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-10
Propeller Shaft (4WD) InspectionS6RW0D0206026
1) Check propeller shaft connecting bolts for
looseness. If looseness is found, tighten to specified
torque.
2) Check propeller shaft joints for wear, play and
damage. If any defect is found, replace.
3) Check propeller shaft center support for biting of
foreign matter, crank, abnormal noise and damage.
If any defect is found, replace.
Manual Transaxle Oil InspectionS6RW0D0206027
Check transaxle oil for leakage, contamination and level
referring to “Manual Transaxle Oil Level Check in
Section 5B”.
Manual Transaxle Oil ReplacementS6RW0D0206028
Change transaxle oil with new specified oil referring to
“Manual Transaxle Oil Change in Section 5B”.
Automatic Transaxle Fluid Level InspectionS6RW0D0206037
Check fluid for leakage, contamination and level
referring to“A/T Fluid Level Check in Section 5A”.
Automatic Transaxle Fluid ReplacementS6RW0D0206038
Change fluid referring to “A/T Fluid Change in Section
5A”.
Automatic Transaxle Fluid Cooler Hose
Inspection
S6RW0D0206039
Check automatic transaxle fluid cooler hose for fluid
leakage, cracks, damage and deterioration. Replace
hose and/or clamp if any faulty condition is found.
Transfer Oil Inspection (4WD)S6RW0D0206040
Check transfer oil for leakage, contamination and level
referring to “Transfer Oil Level Check in Section 3C”.
Transfer Oil Replacement (4WD)S6RW0D0206030
Change transfer oil with new specified oil referring to
“Transfer Oil Change in Section 3C”.
Rear Deferential Oil Inspection (4WD)S6RW0D0206031
Check differential oil for leakage, contamination and
level referring to “Rear Differential Oil Level Check in
Section 3B”.
Rear Deferential Oil Replacement (4WD)S6RW0D0206032
Change differential oil with new specified oil referring to
“Rear Differential Oil Change in Section 3B”.
All Latches, Hinges and Locks InspectionS6RW0D0206033
Doors
Check that each door of front, rear and back doors
opens and closes smoothly and locks securely when
closed.
If any malfunction is found, lubricate hinge and latch or
repair door lock system.
Engine Hood
Check that secondary latch operates properly (check
that secondary latch keeps hood from opening all the
way even when pulling hood release handle inside
vehicle.) Also check that hood opens and closes
smoothly and properly and hood locks securely when
closed.
If any malfunction is found, lubricate hinge and latch, or
repair hood lock system.I5RW0A020006-01
I5RW0C020001-01
I2RH01020033-01
Page 42 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-11 Maintenance and Lubrication:
HVAC Air Filter (If Equipped) InspectionS6RW0D0206034
Check HVAC air filter for dirt and dust referring to “HVAC
Air Filter Inspection (If Equipped) in Section 7A”. If air
filter is dirty, clean or replace air filter with new one.
HVAC Air Filter (If Equipped) ReplacementS6RW0D0206035
Replace HVAC air filter with new one referring to “HVAC
Air Filter Removal and Installation (If Equipped) in
Section 7A”.
Final Inspection for Maintenance ServiceS6RW0D0206036
WARNING!
When carrying out road tests, select a safe
place where no man or no running vehicle is
seen so as to prevent any accident.
Seats
Check that seat slides smoothly and locks securely at
any position. Also check that reclining mechanism of
front seat back allows it to be locked at any angle.
Seat Belt
Inspect belt system including webbing, buckles, latch
plates, retractors and anchors for damage or wear.
Check that seat belt is securely locked. If “REPLACE
BELT” label on seat belt is visible, replace belt.
Battery Electrolyte Level Check
Check that the electrolyte level of all battery cells is
between the upper and lower level lines on the case. If
battery is equipped with built-in indicator, check battery
condition by the indicator.
Accelerator Pedal Operation
Check that pedal operates smoothly without getting
caught or interfered by any other part.
Engine Start
Check engine start for readiness.
WARNING!
Before performing the following check, be
sure to have enough room around the
vehicle. Then, firmly apply both the parking
brake and the regular brakes. Do not use the
accelerator pedal. If the engine starts, be
ready to turn off the ignition promptly. Take
these precautions because the vehicle could
move without warning and possibly cause
personal injury or property damage.
On automatic transaxle vehicles, try to start the engine in
each select lever position. The starting motor should
crank only in “P” (Park) or “N” (Neutral).
On manual transaxle vehicles, place the shift lever in
“Neutral,” depress clutch pedal fully and try to start.
Exhaust System Check
Check for leakage, cracks or loose supports.
Clutch (for Manual Transaxle)
Check for the following.
• Clutch is completely released when depressing clutch
pedal,
• No slipping clutch occurs when releasing pedal and
accelerating.
• Clutch itself is free from any abnormal condition.
Gearshift or Select Lever
Check gear shift or select lever for smooth shifting to all
positions and for good performance of transaxle in any
position.
With automatic transaxle equipped vehicle, also check
that shift indicator indicates properly according to which
position select lever is shifted to.
With automatic transaxle equipped vehicle, make sure
that vehicle is at complete stop when shifting select lever
to “P” range position and release all brakes.
Brake
Foot brake
Check the following:
• that brake pedal has proper travel,
• that brake works properly,
• that it is free from noise,
• that vehicle does not pull to one side when brake is
applied.
• and that brake do not drag.
Parking brake
Check that lever has proper travel.
WARNING!
With vehicle parked on a fairly steep slope,
make sure nothing is in the way downhill to
avoid any personal injury or property
damage. Be prepared to apply regular brake
quickly even if vehicle should start to move.
Check to ensure that parking brake is fully effective
when the vehicle is stopped on the safe slope and brake
lever is pulled all the way.
Page 43 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance and Lubrication: 0B-12
Steering
• Check to ensure that steering wheel is free from
instability, or abnormally heavy feeling.
• Check that the vehicle does not wander or pull to one
side.
Engine
• Check that engine responds readily at all speeds.
• Check that engine is free from abnormal noise and
abnormal vibration.
Body, Wheels and Power Transmitting System
Check that body, wheels and power transmitting system
are free from abnormal noise and abnormal vibration or
any other abnormal condition.Meters and Gauge
Check that speedometer, odometer, fuel meter,
temperature gauge, etc. are operating accurately.
Lights
Check that all lights operate properly.
Windshield Defroster
Periodically check that air comes out from defroster
outlet when operating heater or air conditioning.
Set mode control lever to defroster position and fan
switch lever to highest position for this check.
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS6RW0D0207001
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Fluids and LubricantsS6RW0D0208001
Special ToolS6RW0D0208002
Fastening partTightening torque
Note
N⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Engine oil drain plug 35 3.5 25.5�)
Oil filter 14 1.4 10.5 for reference �)
Engine oil SG, SH, SJ, SL or SM grade (Refer to “Engine Oil and Filter Change” for engine
oil viscosity.)
Engine coolant
(Ethylene glycol base coolant)“Antifreeze/Anticorrosion coolant”
Brake fluid Refer to reservoir cap of brake master cylinder.
Manual transaxle oil Refer to “Manual Transaxle Oil Change in Section 5B”.
Automatic transaxle fluid Refer to “A/T Fluid Change in Section 5A”.
Transfer oil (4WD) Refer to “Transfer Oil Change in Section 3C”.
Rear differential (4WD) Refer to “Rear Differential Oil Change in Section 3B”.
Door hinges Engine oil or water resistance chassis grease
Hood latch assembly Engine oil or water resistance chassis grease
Key lock cylinder Spray lubricant
09915–47331
Oil filter wrench
�)
Page 52 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– CAN communication OBD generic scan tool
displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM
(for A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instruction in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel
system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too
rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304
(Misfire detected)
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit
Service in Section 00” before inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement:
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as
specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor (if
equipped with A/C), accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor and TP sensor are in good condition
and none of power circuits of these sensors is
shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, combination meter,
keyless start control module (if equipped with keyless
start control system), 4WD control module (if
equipped), TCM (for A/T model) and ABS control
module, is established by CAN (Controller Area
Network). (For more detail of CAN communication for
ECM, refer to “CAN Communication System
Description”). Therefore, handle CAN communication
line with care referring to “Precaution for CAN
Communication System in Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM (Immobilizer model)
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions for DTC TroubleshootingS6RW0D1100003
• Before performed trouble shooting, be sure to read
the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection”.
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or
pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referring to
“Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work,
perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm
that the trouble has been corrected.
Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS6RW0D1100004
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of
the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring circuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into the sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are
different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S6RW0D1100005
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of
battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2119 and/or P2135
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal
position (APP) sensor assembly
Page 56 of 1556
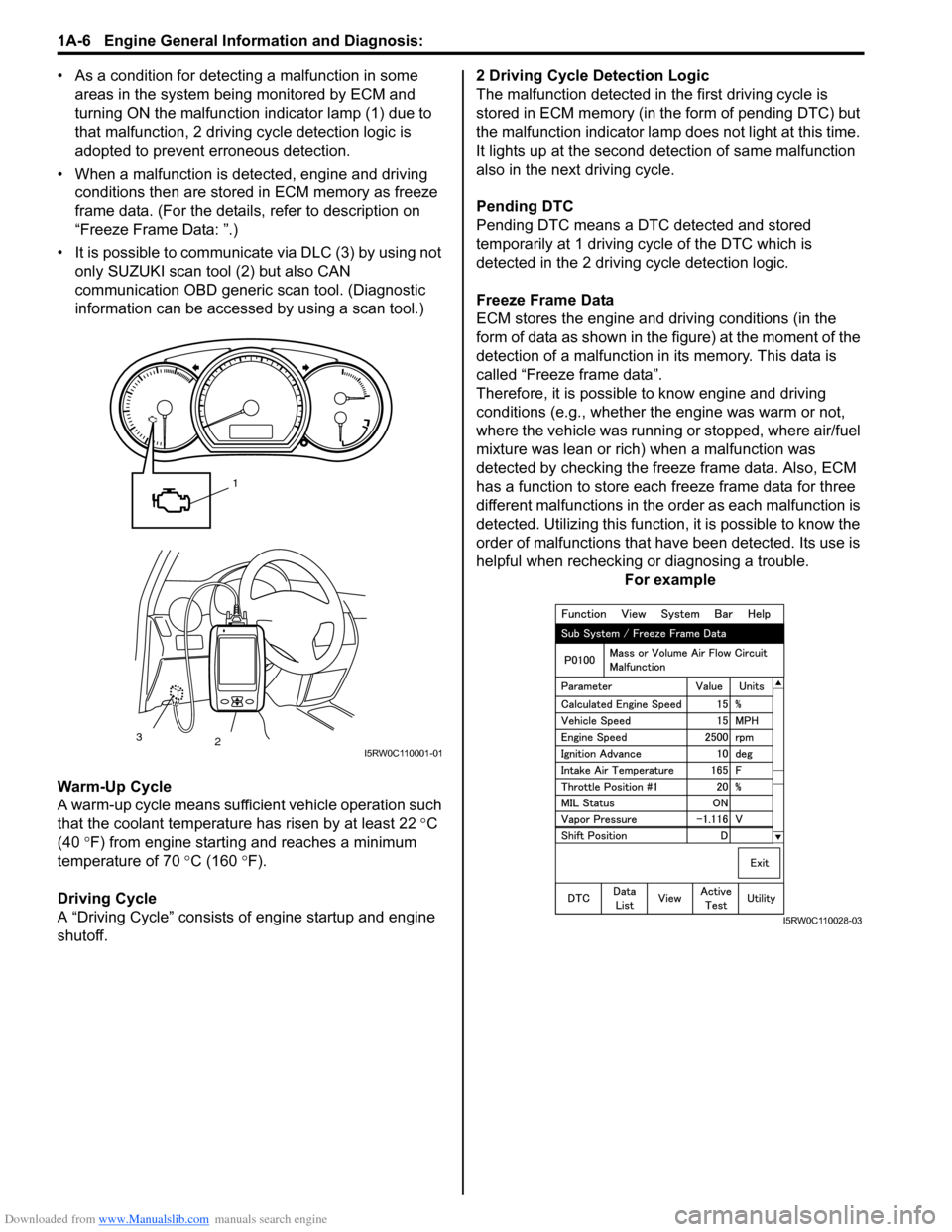
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-6 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some
areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving
conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data: ”.)
• It is possible to communicate via DLC (3) by using not
only SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also CAN
communication OBD generic scan tool. (Diagnostic
information can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 °F).
Driving Cycle
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup and engine
shutoff.2 Driving Cycle Detection Logic
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is
stored in ECM memory (in the form of pending DTC) but
the malfunction indicator lamp does not light at this time.
It lights up at the second detection of same malfunction
also in the next driving cycle.
Pending DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored
temporarily at 1 driving cycle of the DTC which is
detected in the 2 driving cycle detection logic.
Freeze Frame Data
ECM stores the engine and driving conditions (in the
form of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the
detection of a malfunction in its memory. This data is
called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving
conditions (e.g., whether the engine was warm or not,
where the vehicle was running or stopped, where air/fuel
mixture was lean or rich) when a malfunction was
detected by checking the freeze frame data. Also, ECM
has a function to store each freeze frame data for three
different malfunctions in the order as each malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the
order of malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is
helpful when rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
For example
1
2 3
I5RW0C110001-01
I5RW0C110028-03
Page 72 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-22 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Engine and Emission Control System CheckS6RW0D1104001
Refer to the following items for the details of each step.
Step Action Yes No
1�) Customer complaint analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis referring to
“Customer Complaint Analysis”.
Was customer complaint analysis performed?Go to Step 2. Perform customer
complaint analysis.
2�) DTC / Freeze frame data check, record and clearance
1) Check for DTC (including pending DTC) referring to
“DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance”.
Is there any DTC(s)?Print DTC and freeze
frame data or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC
Clearance”, and go to
St ep 3 .Go to Step 4.
3�) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.Go to Step 5.
4�) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.Go to Step 8.
5�) Trouble symptom confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom referring to “Trouble Symptom
Confirmation”.
Is trouble symptom identified?Go to Step 6. Go to Step 7.
6�) Rechecking and record of DTC / Freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to
“DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 8.
7�) Rechecking and record of DTC / Freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC and freeze frame data referring to
“DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 9. Go to Step 10.
8�) Engine basic inspection and engine symptom
diagnosis
1) Check and repair according to “Engine Basic Inspection”
and “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
9�) Troubleshooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable DTC diag. flow.
Are check and repair complete?Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.
10�) Intermittent problems check
1) Check for intermittent problems referring to “Intermittent
Problems Check”.
Is there any faulty condition?Repair or replace
malfunction part(s), and
go to Step 11.Go to Step 11.
Page 75 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-25
Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to
“DTC Check”. If DTC is indicated, print it and freeze
frame data or write them down and then clear them by
referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates malfunction
that occurred in the system but does not indicate
whether it exists now or it occurred in the past and the
normal condition has been restored now. To check which
case applies, check the symptom in question according
to Step 5 and recheck DTC according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame
Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble
symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC
Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC diag.
flow.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC /
Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Engine Basic Inspection and Engine
Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic engine check according to “Engine Basic
Inspection” first. When the end of the flow has been
reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a
possible cause referring to “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”
and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle
(symptoms obtained through steps of customer
complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or
basic engine check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, ECM or other part and repair or
replace faulty parts.Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the
engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is related to the DTC, clear the DTC once,
perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that no
DTC is indicated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) CheckS6RW0D1104002
1) Turn ON ignition switch (with engine at stop) and
check that MIL (1) lights.
If MIL does not light up (or MIL dims) but engine can
be starting, go to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Does
Not Come ON with Ignition Switch ON and Engine
Stop (but Engine Can Be Started)” for
troubleshooting.
If MIL does not light with ignition switch ON and
engine does not start though it is cranked up, go to
“ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”.
2) Start engine and check that MIL turns OFF.
If MIL remains ON and no DTC is stored in ECM, go
to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after
Engine Starts” for troubleshooting.
DTC CheckS6RW0D1104085
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For identification, refer to “Precaution on
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
1
I4RS0A110012-01