air filter TOYOTA CELICA 1987 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 1987, Model line: CELICA, Model: TOYOTA CELICA 1987Pages: 346, PDF Size: 35.13 MB
Page 23 of 346

. COOLING SYSTEM - Description
co;3
RESERVOIR TANK
The reservoir tank is used to catch coolant
which overflows the cooling systein as a result of
volumetric expansion when the coolant is heated.
The coolant in the reservoir tank returns to the
radiator when the coolant temperature drops, thus
keeping the radiator full at all times and avoiding
needless coolant loss. Check the reservoir tank
level to learn if the coolant needs to be rep-
lenished.
WATER PUMP
The water pump is used for forced circulation of
coolant through the cooling system. It is mounted
on the front of the cylinder block and driven by a
V-ribbed belt,
THERMOSTAT I The cooling system is composed of the water
jacket (inside the cylinder block and cylinder head),
radiator, water pump, thermostat, cooling fan,
hoses and other components.
Coolant which is heated in the water
jacket is
pumped to the radiator, through which a cooling
fan blows air to cool the coolant as it passes
through. Coolant which has been cooled is then
sent back to the engine by the water pump, where
it cools the engine.
The water jacket is a network of channels in the
shell of the cylinder block and cylinder head
through which coolant passes. It is designed to
provide adequate cooling of the cylinders are com-
bustion chambers which become the hottest dur-
ing engine operation.
F(/ “ IATOR
The radiator performs the function of cooling
the coolant which has passed through the water
jacket and become hot, and is mounted in the front
of the vehicle. The radiator consists of an upper
tank and ‘lower tank, and a core which connects
the two tanks. The upper tank contains the inlet for
coolant from the water jacket and the filter inlet. It
also has a hose attached through which excess
coolant or steam can flow. The lower tank contains
the outlet for coolant and the drain cock. The core
contains many tubes through which coolant flows
from the upper tank to the lower tank as well as
cooling fins which radiate heat away from the coo-
lant in the tubes. The air sucked through the radia-
tor by cooling fan, as well as the wind generated
by the vehicle’s travel, passes through the radia-
tor, cooling it. Models with automatic transmission
incrl*-le an automatic transmission fluid cooler built
in:.
.le lower tank of the radiator.
RADIATOR CAP
The radiator cap is a pressure type can which
seals the radiator, resulting in pressurization of the
radiator as the coolant expands. The pressuriza-
tion prevents the coolant from boiling even when
the coolant temperature exceeds 100°C. A relief
valve (pressurization valve) and a vacuum valve
(negative pressure valve) are built into the radiator
zap. The relief valve opens and lets steam escape
:hrough the overflow pipe when the pressure
3enerated inside the cooling system exceeds the
imit (coolant temperature:
110 - 1 20°C, (230
- 248”F), pressure; 0.3 - 1 .O kg/cmz, (4.3 - 14.2
)si, 29.4 - 98.1 kPa). The vacuum valve opens to
3ljeviate the vacuum which develops in the coolant
system after the engine is stopped and the coolant
emperature drops. The valve’s opening allows the
)ressure in the cooling system to return to the
Qclant in the reservoir tank. The thermostat has a wax type and is mounted
in the. water outlet housing. The thermostat
includes a type of automatic valve operated by
fluctuations in the coolant temperature. This valve
closes when the coolant temperature drops, pre-
venting the circulation of coolant through the
engine and thus permitting the engine to warm up
rapidly. The valve opens when the coolant tem-
perature has risen, allowing the circulation of coo-
lant. Wax inside the thermostat expands when
heated and contracts when cooled. Heating the
wax thus generates pressure which overpowers
the force of the spring which keeps the valve
closed, thus opening the valve. When the wax
cools, its contraction causes the force of the
spring to take effect once more, closing the valve.
The thermostat in this engine operates at a tem-
perature of 88”C(19O”F).
I
I
Page 46 of 346

1-12 EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting’
FlO48
TROUBLESH~~TI~~G
. .
TROUBLESHOOTING HlhJTS
1. Engine troubles are usually not caused by the EFI system.
When troubleshooting, always first check the condition of
the other systems.
(a) Electronic source
0 Battery
0 Fusible links
0 Fuses
(b) Body ground
(cl Fuel supply
0 Fuel leakage
0 Fuel filter
0 Fuel pump
(d) Ignition system
0 Spark plug
0 High-tension cord
l Distributor (7M-GE) or cam position sensor (7M-
GTE)
0 Igniter and ignition coil
(e) Air induction system
0 Vacuum leaks
(f) Emission control system
0 PCV system
0 EGR system (w/ EGR)
(g) Others
l Ignition timing (ESA system)
0 Idle speed (ISC system)
-r
2. The most frequent cause of problems is simply a bad don-
tact in wiring connectors. Always make sure that connec-
tions are secure.
When inspecting the connector, pay particular attention to
the following points:
(a) Check to see that the terminals are not bent.
(b) Check to see that the connector is pushed in com-
pletely and locked.
(c) Check to see that there is no signal change when the
connector is slightly tapped or wiggled.
3. Sufficiently troubleshoot for other causes before replac-
ing the ECU. The ECU is of high quality and it is expensive.
Page 49 of 346

EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
FI-1 E
CONTINUED FROM PAGE FI-14 ._
CHECK FUEL SUPPLY TO INJECTOR
1. Fuel in tank
2. Fuel pressure in fuel line
(1) Short terminals +B and FP of the
check connector.
(2) You can feel fuel pressure in fuel
return hose. BAD 1. Fuel line - leakage - deformation
2. Fuse
3. Fuel pump (See age FI-73)
4. Fuel filter
5. Fuel pressure regulator (See. page FI-84)
6. Circuit opening relay (See page FI-1 13)
3. Check circuit opening relay
(See page FI-1 13)
OK
CHECK FUEL PUMP SWITCH IN AIR
FLOW METER (7M-GE)
Check continuity between terminals FP and
El with measuring plate of,air flow meter
,,’
open.
L
I BAD c
Air flow meter (See page FL96)
I OK
CHECK IGNITION TIMING
1. Short terminals T(MA) or TEl (MS) and
El of the check connector.
2. Check ignition timing.
STD: 10’ BTDC @ Idle
short circuited TIMA) or
3
I OK NO Adjust ignition timing (See page EM-l 7)
BAD 1. Wiring connection
2. Power to ECU
(1) .Fusible links
(2) Fuses
(3) EFI main relay
3. Air flow meter
4. Water temp. sensor
5. Air temp. sensor
6. Injection signal circuit
(1) Injector wiring
Page 50 of 346
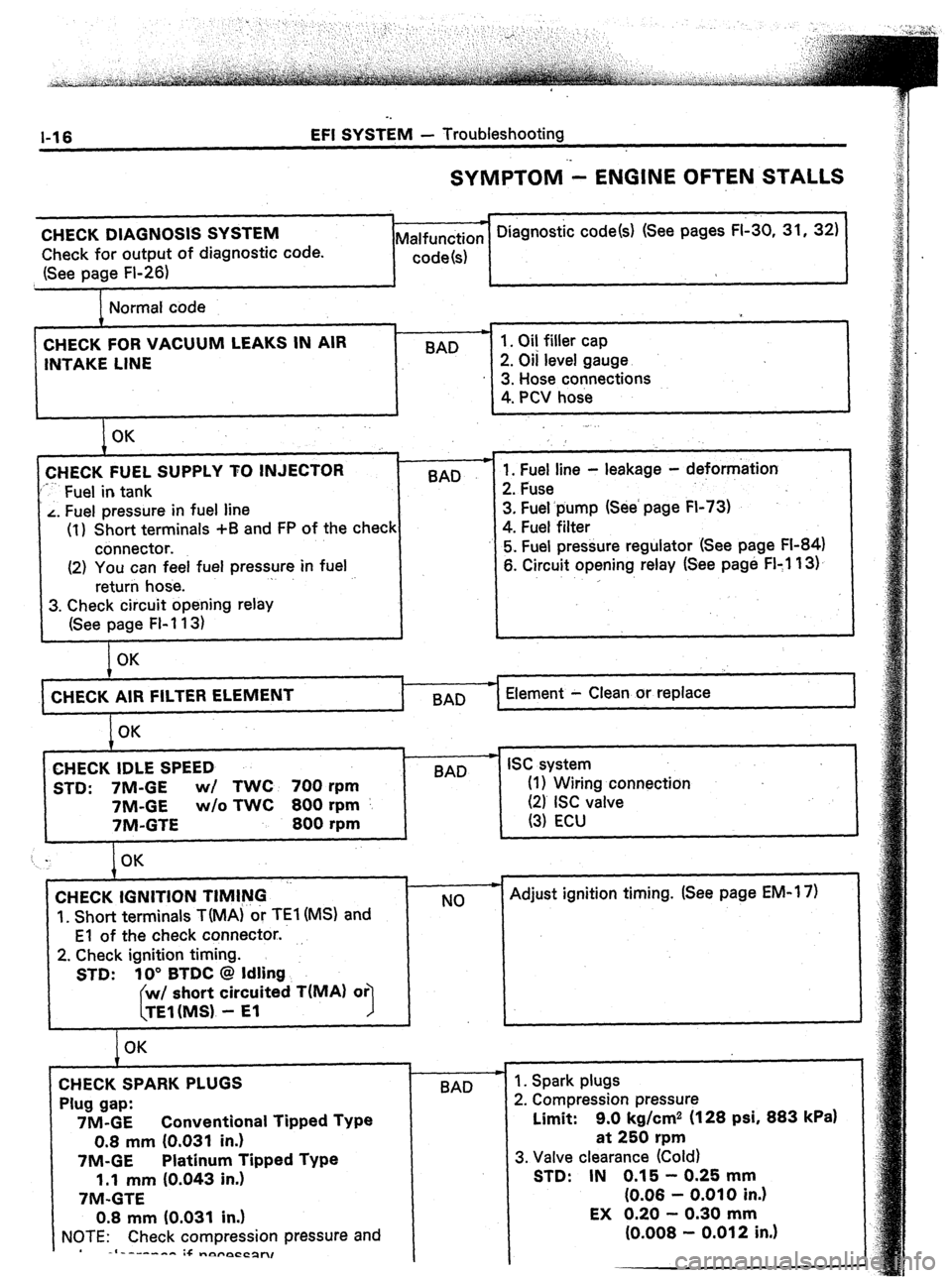
l-16 EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
SYMPTOM - ENGINE OFTEN STALLS
CHECK DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
Check for output of diagnostic code.
(See page Fl-26) * Diagnostic code(s) (See pages FI-30, 31, 32)
Malfunction
code(s)
Normal code
CHECK FOR VACUUM LEAKS IN AIR
INTAKE LINE BAD 1. Oil filler cap
2. Oil level gauge
3. Hose connections
4. PCV hose
I OK
CHECK FUEL SUPPLY TO INJECTOR
‘*-- Fuel in tank BAD
L. Fuel pressure in fuel line
(1) Short terminals +B and FP of the check
connector.
(2) You can feel fuel pressure in fuel
return hose. .
3. Check circuit opening relay
(See page FI-113) .
1. Fuel line - leakage - deformation
2. Fuse
3. Fuel.pump (See’ page FI-73)
4. Fuel filter
5. Fuel pressure regulator (See page FI-84)
6. Circuit opening relay (See page FI:1 13).
,
OK
CHECK AIR FILTER
I BAD Element - Clean or replace
OK
CHECK IDLE SPEED
STD: 7M-GE wl TWC 700 rpm
7M-GE w/o TWC 800 rpm
7M-GTE 800 rpm
t w
BAD ISC system
(I 1 Wiring connection
(21 ISC valve
(3) ECU
CHECK IGNITION TIMING ‘-
‘I. Short terminals TiMA) or TEl (MS) and
El of the check connector..
2. Check ignition timing.
STD: 10” BTDC @ Idling
short circuited T(MA) or
1
OK
CHECK SPARK PLUGS
Plug gap:
7M-GE Conventional Tipped Type
0.8 mm (0.031 in.)
7M-GE Platinum Tipped Type
1.1 mm (0.043 in.)
7M-GTE
0.8 mm (0.031 in.)
NOTE: Check compression pressure and
-I------- :+ -nyrpCCpn, c
NO
-I-
BAD - Adjust ignition timing. (See page EM-1 7)
1. Spark plugs
2. Compression pressure
Limit: 9.0 kg/cm2 (128 psi, 883
kPa)
at 250 rpm
3. Valve clearance (Cold)
STD: IN 0.15 - 0.25 mm
(0.06 - 0.010 in.)
Page 51 of 346

EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
OK ‘. .CONTINUED FROM PAGE FI-I 6
m
CHECK COLD START INJECTOR
1. Cold start injector
(See page FI-80) BAD
2. Cold start injector time switch
(See page FL11 5)
OK FI-17
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
(See page FI-74) BAD p 1. Fuel pump (See page FL73)
2. Fuel filter
3. Fuel pressure regulator (See page FI-84)
OK
CHECK INJECTORS
(See page FI-86) c
-
BAD Injection condition
I OK
..I
’ CHECK EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT
USING VOLT/OHMMETER
(See pages FI-34, 57) BAD 1. Wiring connection
2. Power to ECU
(I) Fusible links
(2) Fuses
(3) EFI main relay
3. Air flow meter
4. Water temp. sensor
5. Air temp. sensor
6. Injection signal circuit
(I 1 Injector wiring
SYMPTOM - ENGINE SOMETIMES STALLS
I
CHECK DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
Check for output of diagnostic code.
‘I ,. ,dSee page FI-26)
I Normal code
I
CHECK AIR FLOW METER’
Air flow meter
(See pages .Fl-96, 98)
I
OK
CHECK WIRING CONNECTORS AND
RELAYS 1 BAD --
2’ EFI main relay (See page FI 112)
Check for a signal change when the connec- 3. Circuit opening relay (See page FI-113)
tor or relay is slightly tapped or wiggled.
Page 52 of 346
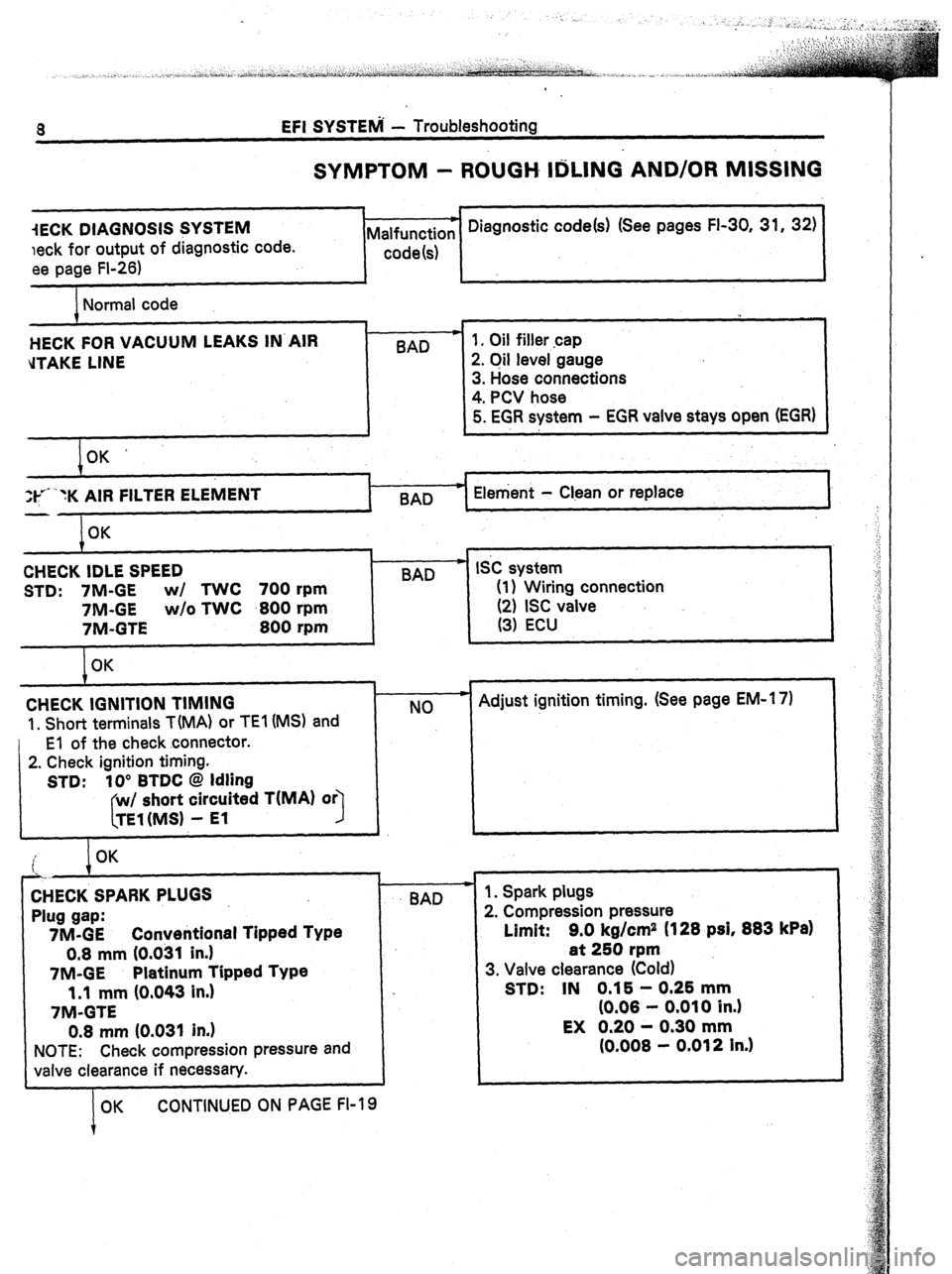
a EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
SYMPTOM - ROUGH IrIiLlNG AND/OR MISSING
iECK DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
leek for output of diagnostic code.
ee page FI-26)
1 -c Diagnostic code(s) (See pages FI-30, 31, 32)
Malfunction
code(s)
Normal code
HECK FOR VACUUM LEAKS IN’AIR
d-FAKE LINE
I OK’
If* “K AIR FILTER
ELEMENT Element - Clean or replace
I
I 1, Oil filler cap
2. Oil level gauge
3. Hose connections
4. PCV hose
5. EGR system - EGR vaive stays open (EGR)
OK
CHECK IDLE SPEED
STD: 7M-GE w/ TWC 700 rpm
7M-GE w/o TWC 800 rpm
7M-GTE
800 rpm
OK
,
BAD SC system
(1) Wiring connection
(2) ISC valve
(3) ECU
CHECK IGNITION TIMING
1, Short terminals T(MA) or TEI (MS) and
El of the check connector.
2. Check ignition timing.
STD: IO” BTDC @ Idling
w/ short circuited T(MA)
I TEl(MS1 - El NO F Adjust ignition timing. (See page EM-l 7)
i OK
‘.
7
I
CHECK SPARK PLUGS
Plug gap:
7M-GE Converitional Tipped Type
0.8 mm (0.031 in.)
7M-GE Platinum Tipped Type
1.1 mm (0,043 in.)
7M-GTE
0.8 mm (0.031 in.)
NOTE: Check compression pressure and
valve clearance if necessary.
OK CONTINUED ON PAGE FI-19 BAD 1. Spark plugs
2. Compression pressure
Limit: 9.0 kg/cm2 (128 psi, 883
kPa)
at 250 rpm
3. Valve clearance (Cold)
STD: IN 0.15 - 0.25 mm
(0.08 - 0.010 in.)
EX 0.20 - 0.30 mm
(0.008 - 0.012 in.)
Page 53 of 346

EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
FI-19
CONTINUED FROM PAGE Fl-18 ._
t
CHECK COLD START INJECTOR *
(See page FI-80) BAD 1. Cold start injector
2. Cold start injector time switch
(See page FL11 5)
CHECK FUEL PRES$URE
(See page FL74) BAD c 1. Fuel pump (See page FI-73)
2. Fuel filter
.3. Fuel pressure regulator (See page FI-84)
I
I 1 c 4
/OK
I
CHECK INJECTORS
(See page FI-86) 8AD * Injection condition
I OK
L 1
ZHECK EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT
USING VOLT/OHMMETER
(See pages FL34, 57) c
BAD 1. Wiring connection
2. Power to ECU
\‘l’, F;t;e links
(3) EFI main relay
3. Air flow meter
4. Water temp. sensor
5. Air temp. sensor
6. Throttle position sensor
7. Injection signal circuit
(1) injector wiring
Page 55 of 346
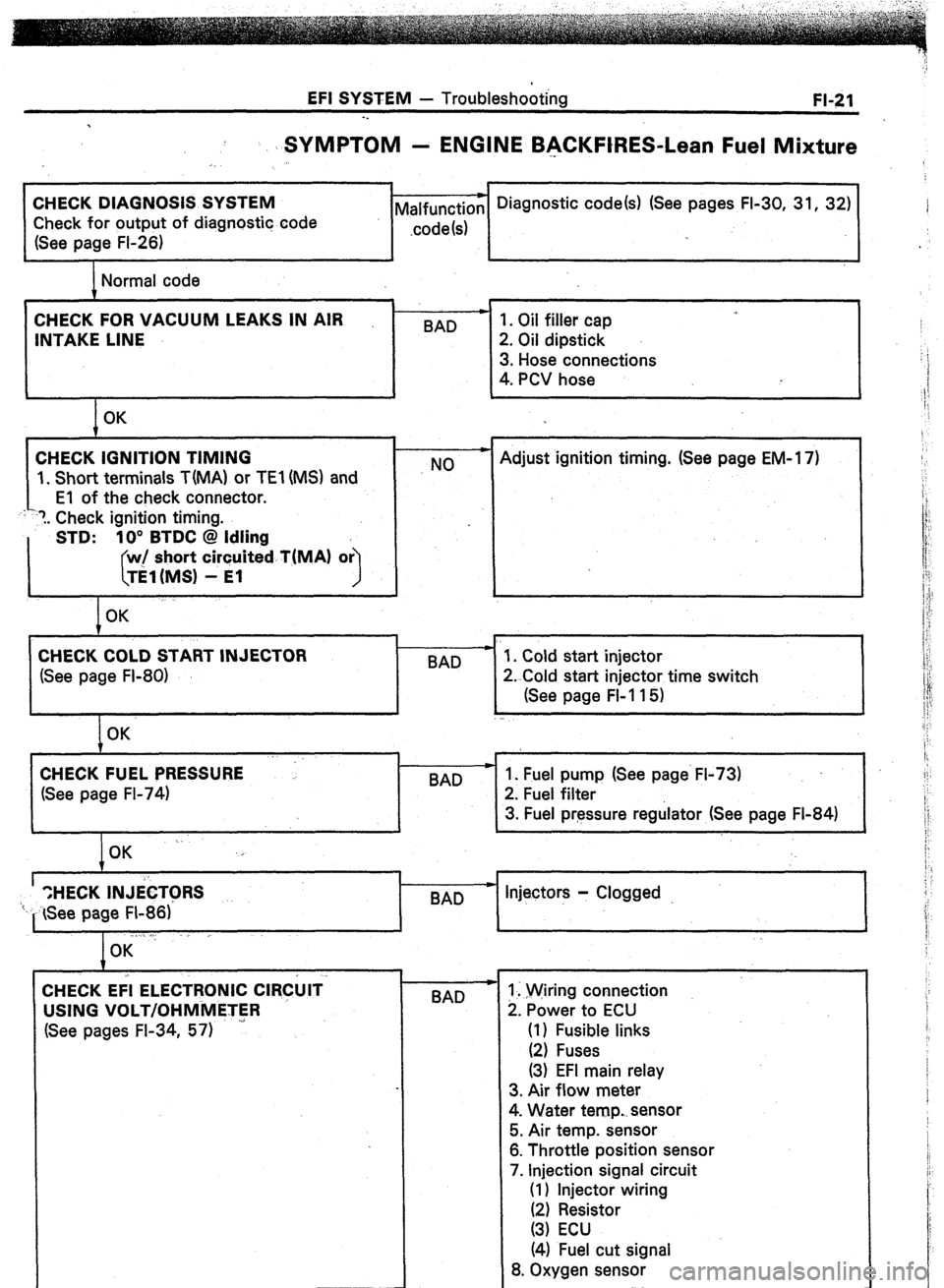
EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
FI-21
-.
SYMPTOM - ENGINE BACKFtRES-Lean Fuel Mixture
CHECK DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
Check for output of diagnostic code
(See page FI-26) Malfunction --) Diagnostic code(s) (See pages FI-30, 31, 32)
.code 1s) j
,
Normal code
CHECK FOR VACUUM LEAKS IN AIR
INTAKE LINE
1. Short terminals T(MA) or TEl (MS) and BAD -
NO 1. Oil filler cap
2. Oil dipstick
3. Hose connections
4. PCV hose
Adjust ignition timing. (See page EM-1 7)
1. Cold start injector
2. Cold start injector time switch
(See page FI-115)
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
(See page FI-74)
I
I
BAD 1. Fuel pump (See page‘ FI-73)
2. Fuel filter
3. Fuel pressure regulator (See page Fl-84)
I
’ “,HECK INJib
‘I- See page FI-86)’ - Injectors - Clogged
BAD
. ., .l
I OK
CHECK Eii ELECTRONIC ClR&lT
USING VOLT/OHMMETER
(See pages FI-34, 57)
4
BAD 1. Wiring connection
2. Power to ECU
(1) Fusible links
(2) Fuses
(3) EFI main relay
3. Air flow meter
4. Water temp. sensor
5. Air temp. sensor
6. Throttle position sensor
7. Injection signal circuit
(1) Injector wiring
Ii, zesstor
(4) Fuel cut signal
8. Oxygen sensor
Page 57 of 346
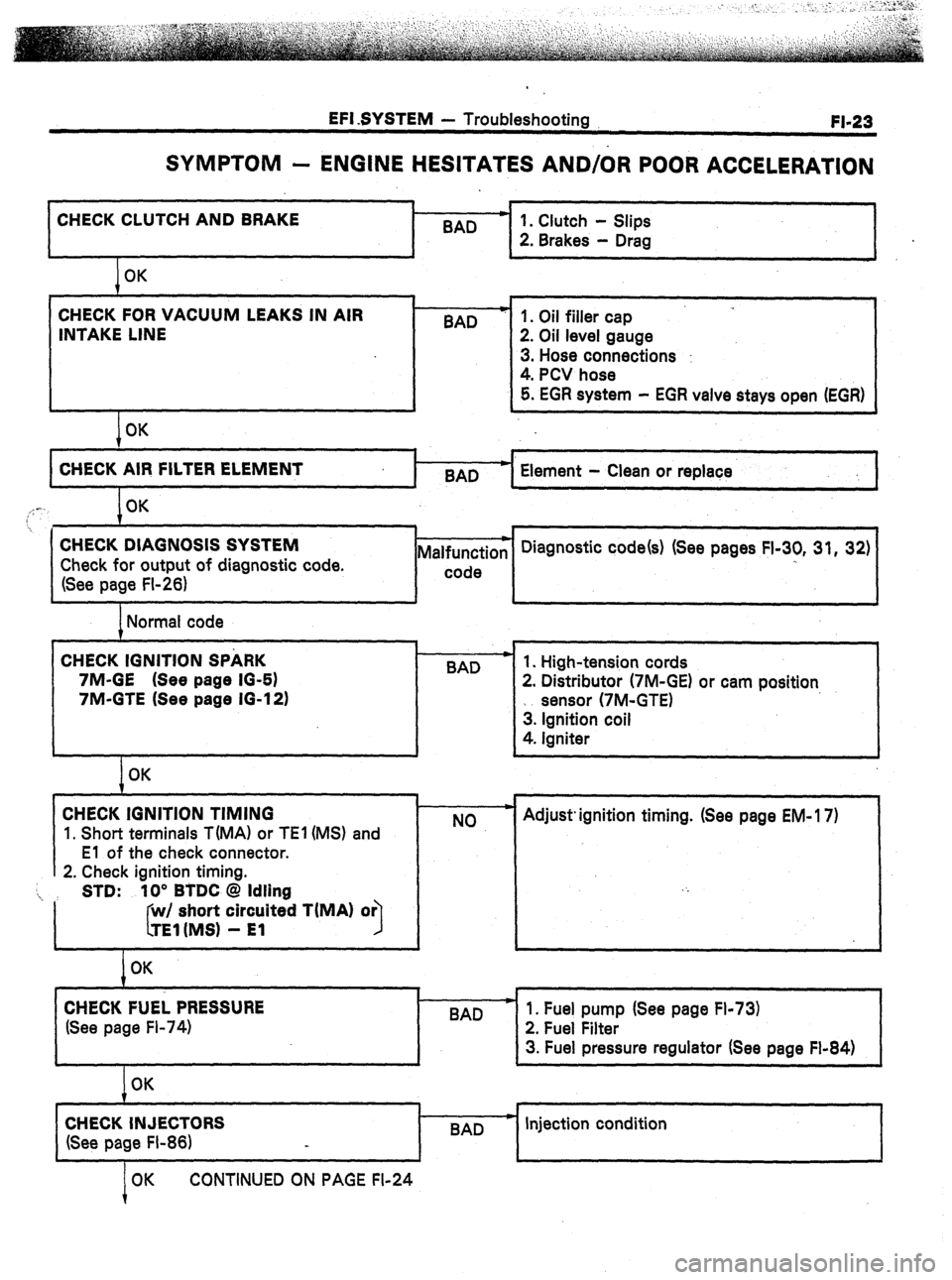
EFI SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
FI-23
SYMPTOM - ENGINE HESITATES AND/OR POOR ACCELERATION
CHECK CLUTCH AND BRAKE .
BAD
I
I 1
1 OK
CHECK FOR VACUUM LEAKS IN AIR
INTAKE LINE
I OK BAD
I-
1. Clutch - Slips
2. Brakes - Drag
1. Oil filler cap
2. Oil level gauge
3. Hose connections :
4. PCV hose
5. EGR system - EGR valve stays open (EGR)
4
CHECK AIR FILTER ELEMENT
BAD Element - Clean or replace
I
,,: -. OK
7
. . 1 i , 1
CHECK DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
Check for output of diagnostic code.
(See page FI-26) Malfunction
I-- code Diagnostic code(s) (See pages FI-30, 31, 32)
I
I I I J
1 Normal code
CHECK IGNITION SPARK
7M-GE (See page IO-61
7M-GTE (See page 16-12) .
BAD
I
I OK
CHECK IGNITION TIMING
1. Short terminals T(MA1 or TEl (MS) and
El of the check connector.
2. Check ignition timing.
‘i, STD: 10” BTDC @ Idling
I short circuited TiMA) or
I
I OK
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
(See page Fl-74) 1. High-tension cords
2. Distributor (7M-GE) or cam position
sensor (7M-GTE)
3. Ignition coil
4. Igniter
NO Adjust. ignition timing. (See page EM- 17)
I
I
BAD
I
1. Fuel pump (See page Fl-73)
2. Fuel Filter
3. Fuel pressure regulator (See page Fl-84)
1
OK
CHECK INJECTORS
(See page FI-86) BAD c Injection condition
OK CONTINUED ON PAGE FI-24
Page 107 of 346

EFI SYSTEM - Fuel System FI-73
FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel Pump
Check Valve-------,
n!
Relief Valved
Bearing
Brush OUTLET INLET
Armature
I Filter I
Rubber Cushion
ECU
Fusible Link Ignition Switch
1 G S/W
3ATT
tB1 (B’l
I-B (B)
WREL
FPR
9’
FM-CT
El 1 AM2 30A 1 AM2-IG2 IGN
(MA)
Fusible Link Fuse
‘Q-p
I EFI Main Relay
fc4 r
MAIN I%? (MS) EFi 15A
Ignition
Fusible Link Switch 1
‘El
I
m AM1 ST1
AM1 40A
” (MA)
(MS) Check
Connector
Circuit
usible
ink
IAIN 2.0
I
F
L
(Air Flow Meter) (MA)
Battery1
T
ALT ,,A#, w
(M/T)
1
(MA/7M-GTE)
1 OOA
(MS)
= 1 OOA
FlO491 Fl14