weight TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 1 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – REPAIR INSTRUCTIONIN–25
IN
VEHICLE LIFT AND SUPPORT
LOCATIONS
1. NOTICE ABOUT VEHICLE CONDITION WHEN
JACKING UP VEHICLE
(a) The vehicle must be unloaded before jacking up/
lifting up the vehicle. Never jack up/lift up a heavily
loaded vehicle.
(b) When removing heavy parts such as the engine and
transmission, the center of gravity of the vehicle
may shift. To stabilize the vehicle, place a balance
weight in a location where it will not roll or shift, or
use a transmission jack to hold the jacking support.
2. NOTICE FOR USING 4 POST LIFT
(a) Follow the safety procedures outlined in the lift
instruction manual.
(b) Use precautionary measures to prevent the free
wheel beam from damaging tires or wheels.
(c) Use wheel chocks to secure the vehicle.
3. NOTICE FOR USING JACK AND SAFETY STAND
(a) Work on a level surface. Use wheel chocks at all
times.
(b) Set the jack and rigid racks to the specified
locations of the vehicle accurately.
(c) When jacking up the vehicle, first release the
parking brake and move the shift lever to N.
(d) When jacking up the entire vehicle:
(1) When jacking up the front wheels first, make
sure wheel chocks are behind the rear wheels.
(2) When jacking up the rear wheels first, make sure
wheel chocks are in front of the front wheels.
(e) When jacking up only the front or rear wheels of the
vehicle:
(1) Before jacking up the front wheels, place wheel
chocks on both sides of the rear wheels.
(2) Before jacking up the rear wheels, place wheel
chocks on both sides of the front wheels.
(f) When lowering a vehicle that only has its front or
rear wheels jacked up:
(1) Before lowering the front wheels, make sure
wheel chocks are in front of the rear wheels.
(2) Before lowering the rear wheels, make sure
wheel chocks are behind the front wheels.
Page 112 of 3000

DRIVE SHAFT – FRONT DRIVE SHAFTDS–7
DS
12. REMOVE FRONT DRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY RH (for
4WD)
(a) Using SST, remove the front drive shaft assembly
RH.
SST 09520-01010, 09520-24010 (09520-32040)
HINT:
Overhaul the side following the same procedures as
for the LH side.
NOTICE:
• When removing and installing the front drive
shaft assembly RH in 4WD vehicle, be sure to
first drain all the transaxle oil and transfer oil.
If removal and installation is carried out
without draining these oils, the transfer oil
will flow into the transaxle side. Extensive
cleaning will be required if the two oils mix.
• Do not damage the oil seal and dust cover.
• Move the drive shaft assembly while keeping
it level.
13. SECURE FRONT AXLE ASSEMBLY
NOTICE:
The hub bearing could be damaged if it is subjected
to the vehicle weight, such as when moving the
vehicle with the drive shaft removed. Therefore, if it
is absolutely necessary to place the vehicle weight
on the hub bearing, first support it with SST.
SST 09608-16042 (09608-02021, 09608-02041)
C108268E04
C054583E01
Page 174 of 3000
TW–4TIRE AND WHEEL – TIRE AND WHEEL SYSTEM
TW
4. INSPECT WHEEL BALANCE (for Non-steel Wheel)
(a) Check and adjust the off-the-car balance.
Imbalance after adjustment:
8.0 g (0.018 lb.) or less.
NOTICE:
• Use a cleaning detergent to remove dirt, oil
and water from the surface where the balance
weight is to be adhered.
• Do not touch the sticking surface of the tape.
• Adhere the sticking type balance weight to
the flat position shown in the illustration.
• Push the balance weight securely with a
finger to adhere it to the position.
• Do not reuse the balance weight.
HINT:
• The inner side balance weight should be installed
by clipping it to the rim.
• If necessary, check and adjust the on-the-car
balance.
5. INSPECT FRONT AXLE HUB BEARING LOOSENESS
HINT:
See page AH-5.
6. INSPECT REAR AXLE HUB BEARING LOOSENESS
(for 2WD)
HINT:
See page AH-16.
7. INSPECT REAR AXLE HUB BEARING LOOSENESS
(for 4WD)
HINT:
See page AH-19.
8. INSPECT FRONT AXLE HUB RUNOUT
HINT:
See page AH-5.
9. INSPECT REAR AXLE HUB RUNOUT (for 2WD)
HINT:
See page AH-16.
10. INSPECT REAR AXLE HUB RUNOUT (for 4WD)
HINT:
See page AH-19.
C144018E01
Page 196 of 3000
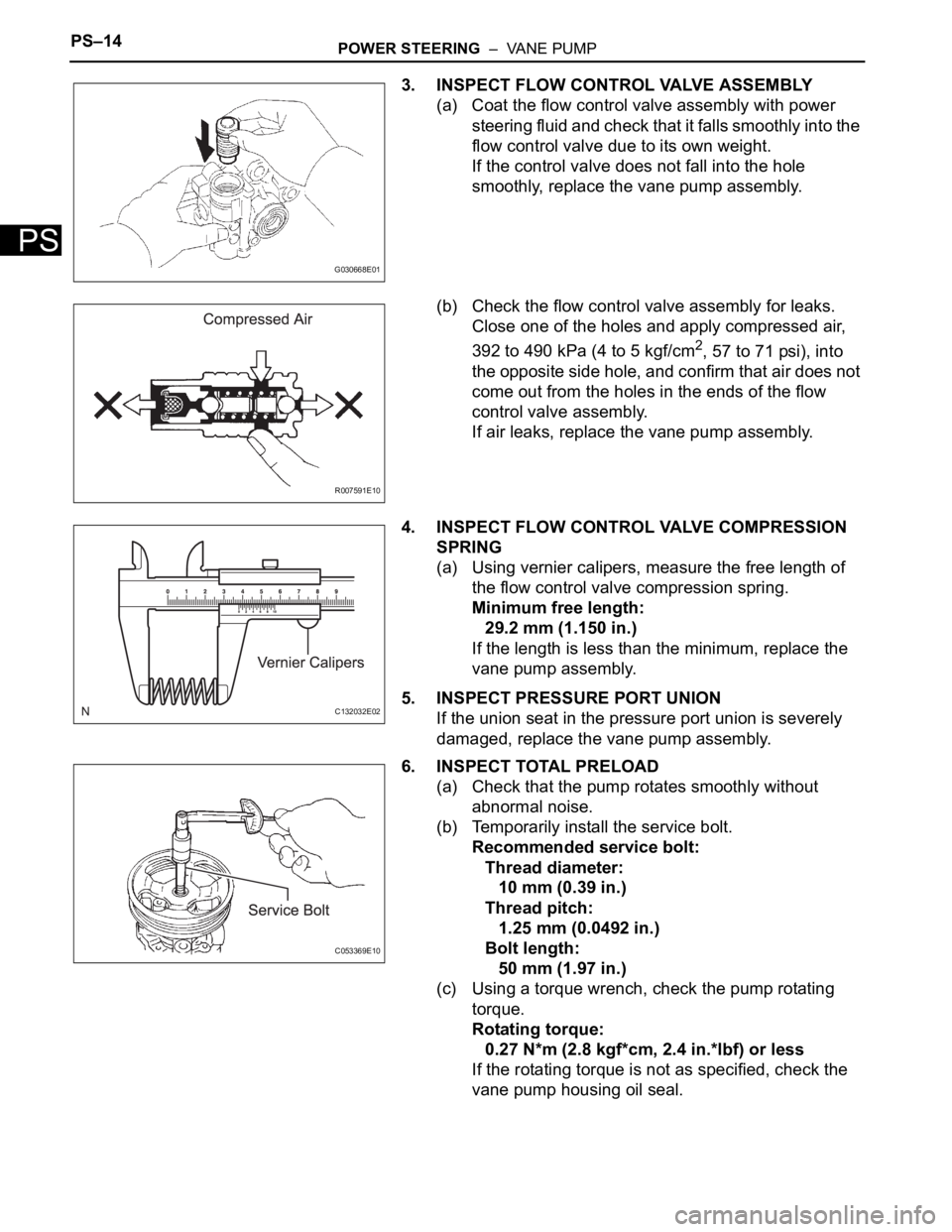
PS–14POWER STEERING – VANE PUMP
PS
3. INSPECT FLOW CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY
(a) Coat the flow control valve assembly with power
steering fluid and check that it falls smoothly into the
flow control valve due to its own weight.
If the control valve does not fall into the hole
smoothly, replace the vane pump assembly.
(b) Check the flow control valve assembly for leaks.
Close one of the holes and apply compressed air,
392 to 490 kPa (4 to 5 kgf/cm
2, 57 to 71 psi), into
the opposite side hole, and confirm that air does not
come out from the holes in the ends of the flow
control valve assembly.
If air leaks, replace the vane pump assembly.
4. INSPECT FLOW CONTROL VALVE COMPRESSION
SPRING
(a) Using vernier calipers, measure the free length of
the flow control valve compression spring.
Minimum free length:
29.2 mm (1.150 in.)
If the length is less than the minimum, replace the
vane pump assembly.
5. INSPECT PRESSURE PORT UNION
If the union seat in the pressure port union is severely
damaged, replace the vane pump assembly.
6. INSPECT TOTAL PRELOAD
(a) Check that the pump rotates smoothly without
abnormal noise.
(b) Temporarily install the service bolt.
Recommended service bolt:
Thread diameter:
10 mm (0.39 in.)
Thread pitch:
1.25 mm (0.0492 in.)
Bolt length:
50 mm (1.97 in.)
(c) Using a torque wrench, check the pump rotating
torque.
Rotating torque:
0.27 N*m (2.8 kgf*cm, 2.4 in.*lbf) or less
If the rotating torque is not as specified, check the
vane pump housing oil seal.
G030668E01
R007591E10
C132032E02
C053369E10
Page 350 of 3000

ES–242GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HO2S Bank 2 Sensor 2
Catalyst-Bank 1
Catalyst-Bank 2
EVAP
Misfire
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$06 $07 Multiply by 0.001 V Minimum sensor voltage
$06 $08 Multiply by 0.001 V Maximum sensor voltage
$06 $8F Multiply by 0.003 g Maximum oxygen storage capacity
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$21 $A9 Multiply by 0.003 No dimension Oxygen storage capacity of catalyst-bank 1
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$22 $A9 Multiply by 0.003 No dimension Oxygen storage capacity of catalyst-bank 2
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$3D $C9 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for small leak (P0456)
$3D $CA Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for gross leak (P0455)
$3D $CB Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for leak detection pump OFF stuck (P2401)
$3D $CD Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for leak detection pump ON stuck (P2402)
$3D $CE Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for vent valve OFF stuck (P2420)
$3D $CF Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for vent valve ON stuck (P2419)
$3D $D0 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for reference orifice low flow (P043E)
$3D $D1 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for reference orifice high flow (P043F)
$3D $D4 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for purge VSV close stuck (P0441)
$3D $D5 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for purge VSV open stuck (P0441)
$3D $D7 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for purge flow insufficient (P0441)
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$A1 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeExponential Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) misfire for all
cylinders: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-Total
$A1 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for all cylinders: Misfire counts for last/current driving
cycles-Total
$A2 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 1: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A2 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 1: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A3 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 2: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A3 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 2: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A4 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 3: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A4 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 3: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A5 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 4: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A5 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 4: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A6 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 5: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A6 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 5: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A7 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 6: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
Page 705 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–419
ES
Cut-off valve Located in fuel tank. Valve floats and closes when fuel tank is 100% full.
Purge VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve)Opens or closes line between canister and intake manifold. ECM uses purge VSV to control EVAP
purge flow. In order to discharge EVAP absorbed by canister to intake manifold, ECM opens purge
VSV. EVAP discharge volume to intake manifold is controlled by purge VSV duty cycle ratio
(current-carrying time). (Open: ON, Close: OFF)
Refueling valveControls EVAP pressure from fuel tank to canister. Valve consists of diaphragm, spring and
restrictor (diameter: 0.08 inch). When fuel vapor and pressure inside fuel tank increase, valve
opens. While EVAP is purged, valve closes and restrictor prevents a large amount of vacuum from
affecting pressure in fuel tank. Valve is opened while refueling. When valve is open, adding fuel into
fuel tank is possible.
Roll-over valveLocated in fuel tank. Valve closes by its own weight when vehicle overturns to prevent fuel from
spilling out.
Service port Used for connecting vacuum gauge for inspecting EVAP system.
Soak timerBuilt into ECM. To ensure accurate EVAP monitor, measures 5 hours (+/- 15 min.) after ignition
switch is turned off. This allows fuel to cool down, stabilizing Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP). When
approx. 5 hours elapsed, ECM activates.
Canister pump module Consists of (a) to (d) below. Pump module cannot be disassembled.
(a) Vent valveVents and closes EVAP system. When ECM turns valve ON, EVAP system is closed. When ECM
turns valve OFF, EVAP system is vented. Negative pressure (vacuum) is created in EVAP system
to check for EVAP leaks by closing purge VSV and vent valve (closed), and operating vacuum
pump are turned on (refer to fig. 1).
(b) Canister pressure sensorIndicates pressure as voltages. ECM supplies regulated 5 V to pressure sensor, and uses feedback
from sensor to monitor EVAP system pressure (refer to fig 2).
(c) Vacuum pump Creates negative pressure (vacuum) in EVAP system for leak check.
(d) 0.02 inch orificeHas an opening with 0.02 inch diameter. Vacuum is produced through orifice by closing purge VSV,
turning off vent valve and operating vacuum pump, to monitor 0.02 inch leak pressure. 0.02 inch
leak pressure indicates a small leak of EVAP. Component Operation
Page 796 of 3000

ES–242GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HO2S Bank 2 Sensor 2
Catalyst-Bank 1
Catalyst-Bank 2
EVAP
Misfire
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$06 $07 Multiply by 0.001 V Minimum sensor voltage
$06 $08 Multiply by 0.001 V Maximum sensor voltage
$06 $8F Multiply by 0.003 g Maximum oxygen storage capacity
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$21 $A9 Multiply by 0.003 No dimension Oxygen storage capacity of catalyst-bank 1
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$22 $A9 Multiply by 0.003 No dimension Oxygen storage capacity of catalyst-bank 2
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$3D $C9 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for small leak (P0456)
$3D $CA Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for gross leak (P0455)
$3D $CB Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for leak detection pump OFF stuck (P2401)
$3D $CD Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for leak detection pump ON stuck (P2402)
$3D $CE Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for vent valve OFF stuck (P2420)
$3D $CF Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for vent valve ON stuck (P2419)
$3D $D0 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for reference orifice low flow (P043E)
$3D $D1 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for reference orifice high flow (P043F)
$3D $D4 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for purge VSV close stuck (P0441)
$3D $D5 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for purge VSV open stuck (P0441)
$3D $D7 Multiply by 0.001 kPa Test value for purge flow insufficient (P0441)
Monitor ID Test ID Scaling Unit Description
$A1 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeExponential Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) misfire for all
cylinders: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-Total
$A1 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for all cylinders: Misfire counts for last/current driving
cycles-Total
$A2 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 1: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A2 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 1: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A3 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 2: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A3 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 2: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A4 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 3: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A4 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 3: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A5 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 4: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A5 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 4: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A6 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 5: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
$A6 $0C Multiply by 1 TimeMisfire rate for cylinder 5: Misfire counts for last/current driving cycle-
To t a l
$A7 $0B Multiply by 1 TimeEWMA misfire for cylinder 6: Misfire counts for last ten driving cycles-
To t a l
Page 1292 of 3000
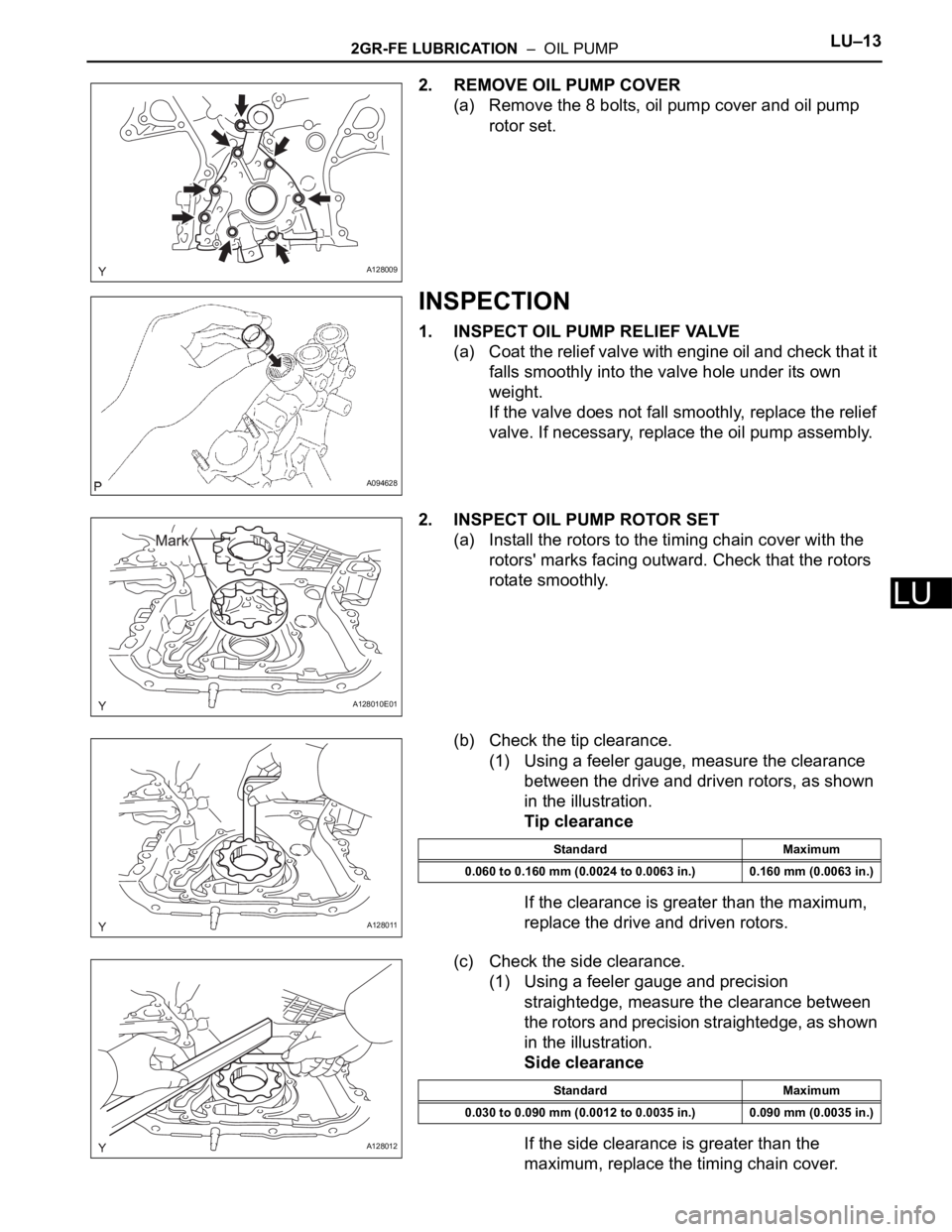
2GR-FE LUBRICATION – OIL PUMPLU–13
LU
2. REMOVE OIL PUMP COVER
(a) Remove the 8 bolts, oil pump cover and oil pump
rotor set.
INSPECTION
1. INSPECT OIL PUMP RELIEF VALVE
(a) Coat the relief valve with engine oil and check that it
falls smoothly into the valve hole under its own
weight.
If the valve does not fall smoothly, replace the relief
valve. If necessary, replace the oil pump assembly.
2. INSPECT OIL PUMP ROTOR SET
(a) Install the rotors to the timing chain cover with the
rotors' marks facing outward. Check that the rotors
rotate smoothly.
(b) Check the tip clearance.
(1) Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance
between the drive and driven rotors, as shown
in the illustration.
Tip clearance
If the clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the drive and driven rotors.
(c) Check the side clearance.
(1) Using a feeler gauge and precision
straightedge, measure the clearance between
the rotors and precision straightedge, as shown
in the illustration.
Side clearance
If the side clearance is greater than the
maximum, replace the timing chain cover.
A128009
A094628
A128010E01
A128011
Standard Maximum
0.060 to 0.160 mm (0.0024 to 0.0063 in.) 0.160 mm (0.0063 in.)
A128012
Standard Maximum
0.030 to 0.090 mm (0.0012 to 0.0035 in.) 0.090 mm (0.0035 in.)
Page 1305 of 3000
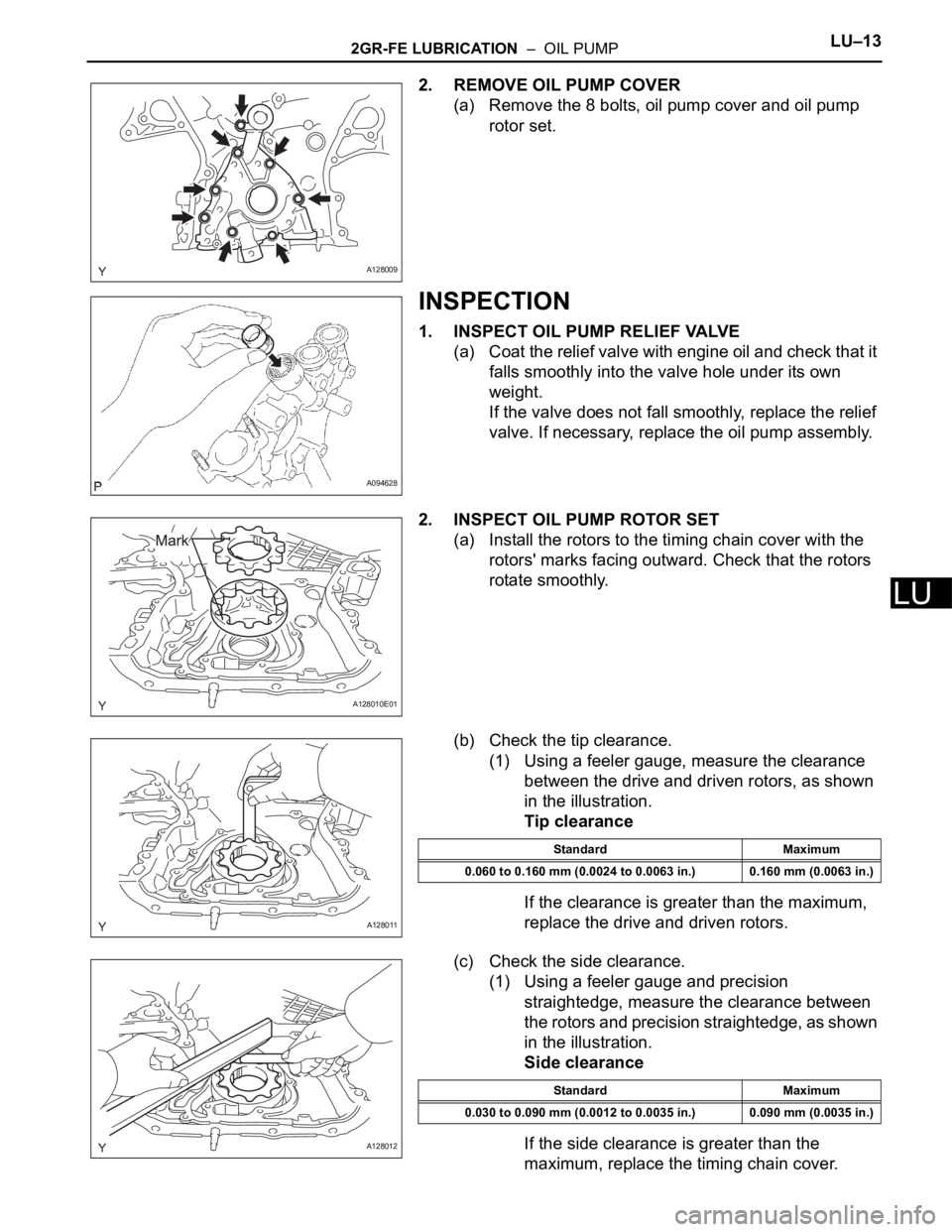
2GR-FE LUBRICATION – OIL PUMPLU–13
LU
2. REMOVE OIL PUMP COVER
(a) Remove the 8 bolts, oil pump cover and oil pump
rotor set.
INSPECTION
1. INSPECT OIL PUMP RELIEF VALVE
(a) Coat the relief valve with engine oil and check that it
falls smoothly into the valve hole under its own
weight.
If the valve does not fall smoothly, replace the relief
valve. If necessary, replace the oil pump assembly.
2. INSPECT OIL PUMP ROTOR SET
(a) Install the rotors to the timing chain cover with the
rotors' marks facing outward. Check that the rotors
rotate smoothly.
(b) Check the tip clearance.
(1) Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance
between the drive and driven rotors, as shown
in the illustration.
Tip clearance
If the clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the drive and driven rotors.
(c) Check the side clearance.
(1) Using a feeler gauge and precision
straightedge, measure the clearance between
the rotors and precision straightedge, as shown
in the illustration.
Side clearance
If the side clearance is greater than the
maximum, replace the timing chain cover.
A128009
A094628
A128010E01
A128011
Standard Maximum
0.060 to 0.160 mm (0.0024 to 0.0063 in.) 0.160 mm (0.0063 in.)
A128012
Standard Maximum
0.030 to 0.090 mm (0.0012 to 0.0035 in.) 0.090 mm (0.0035 in.)
Page 2075 of 3000
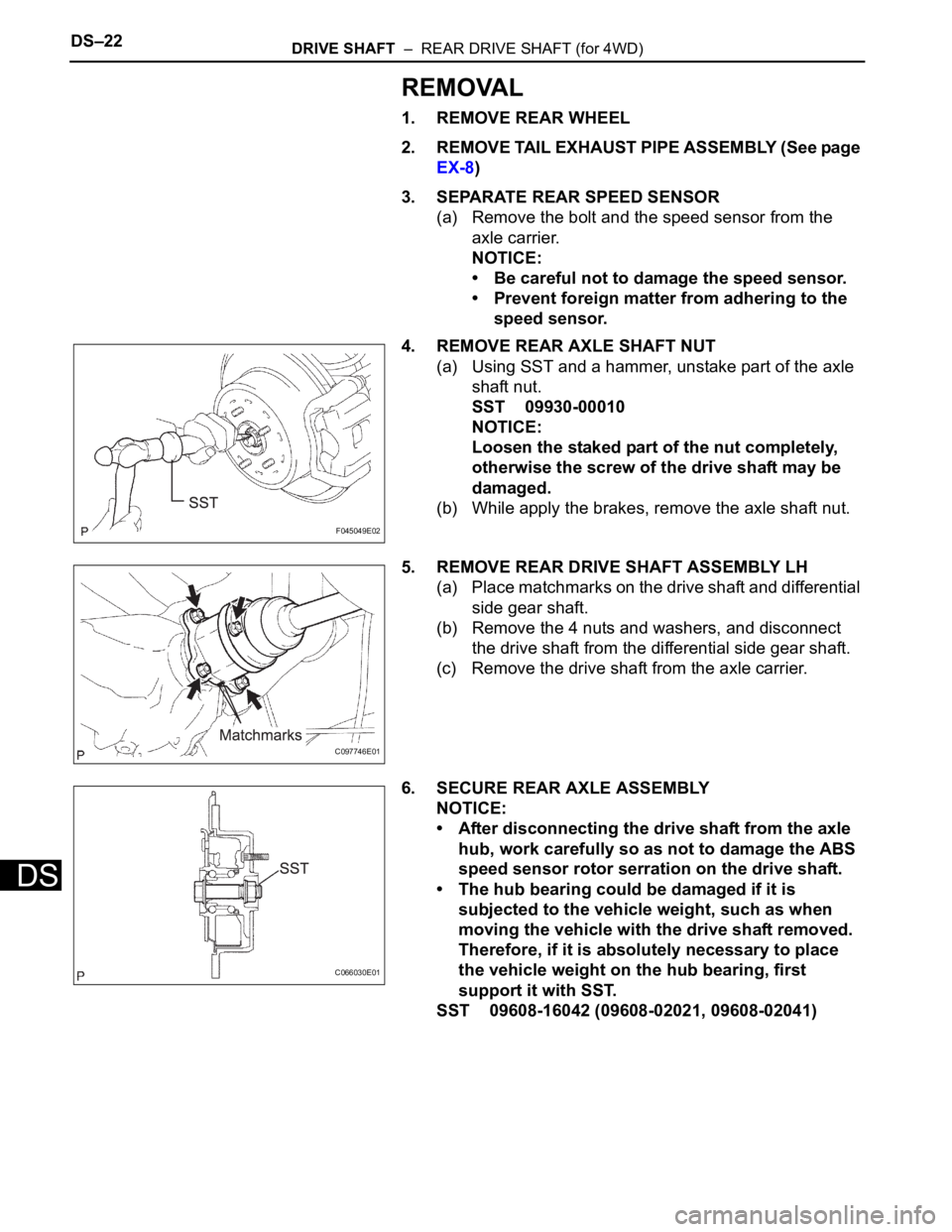
DS–22DRIVE SHAFT – REAR DRIVE SHAFT (for 4WD)
DS
REMOVAL
1. REMOVE REAR WHEEL
2. REMOVE TAIL EXHAUST PIPE ASSEMBLY (See page
EX-8)
3. SEPARATE REAR SPEED SENSOR
(a) Remove the bolt and the speed sensor from the
axle carrier.
NOTICE:
• Be careful not to damage the speed sensor.
• Prevent foreign matter from adhering to the
speed sensor.
4. REMOVE REAR AXLE SHAFT NUT
(a) Using SST and a hammer, unstake part of the axle
shaft nut.
SST 09930-00010
NOTICE:
Loosen the staked part of the nut completely,
otherwise the screw of the drive shaft may be
damaged.
(b) While apply the brakes, remove the axle shaft nut.
5. REMOVE REAR DRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Place matchmarks on the drive shaft and differential
side gear shaft.
(b) Remove the 4 nuts and washers, and disconnect
the drive shaft from the differential side gear shaft.
(c) Remove the drive shaft from the axle carrier.
6. SECURE REAR AXLE ASSEMBLY
NOTICE:
• After disconnecting the drive shaft from the axle
hub, work carefully so as not to damage the ABS
speed sensor rotor serration on the drive shaft.
• The hub bearing could be damaged if it is
subjected to the vehicle weight, such as when
moving the vehicle with the drive shaft removed.
Therefore, if it is absolutely necessary to place
the vehicle weight on the hub bearing, first
support it with SST.
SST 09608-16042 (09608-02021, 09608-02041)
F045049E02
C097746E01
C066030E01