overheating VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1990 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: VOLKSWAGEN, Model Year: 1990, Model line: CORRADO, Model: VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1990Pages: 906, PDF Size: 6.56 MB
Page 853 of 906
WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 9)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:52PM
The voltage controlled driver inside the computer operates
much like a simple switch because it does not need to worry about
limiting current flow. Recall, this driver typically requires injector
circuits with a total leg resistance of 12 or more ohms.
The driver is either ON, closing/completing the circuit
(eliminating the voltage-drop), or OFF, opening the circuit (causing a
total voltage drop).
Some manufacturers call it a "saturated switch" driver. This
is because when switched ON, the driver allows the magnetic field in
the injector to build to saturation. This is the same "saturation"
property that you are familiar with for an ignition coil.
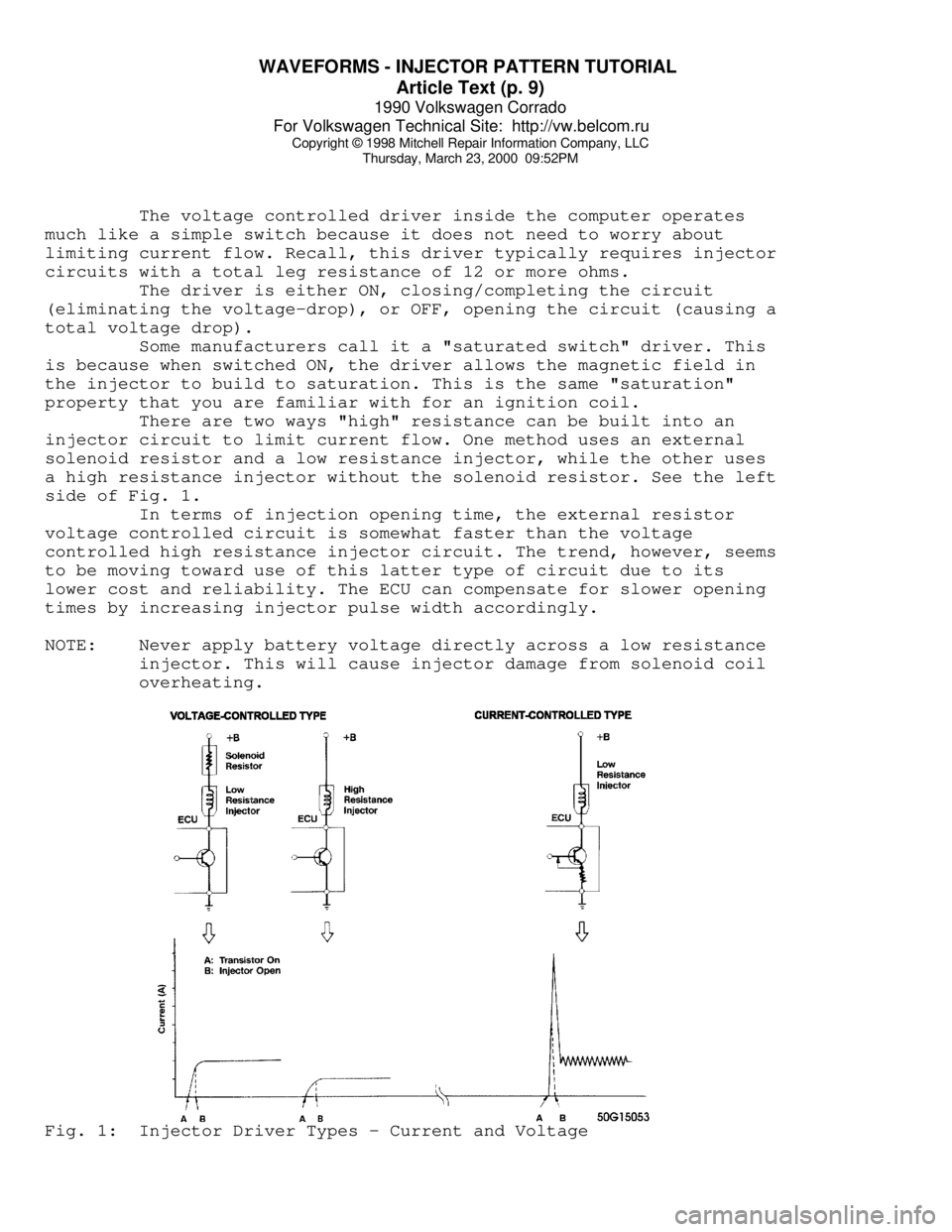
There are two ways "high" resistance can be built into an
injector circuit to limit current flow. One method uses an external
solenoid resistor and a low resistance injector, while the other uses
a high resistance injector without the solenoid resistor. See the left
side of Fig. 1.
In terms of injection opening time, the external resistor
voltage controlled circuit is somewhat faster than the voltage
controlled high resistance injector circuit. The trend, however, seems
to be moving toward use of this latter type of circuit due to its
lower cost and reliability. The ECU can compensate for slower opening
times by increasing injector pulse width accordingly.
NOTE: Never apply battery voltage directly across a low resistance
injector. This will cause injector damage from solenoid coil
overheating.Fig. 1: Injector Driver Types - Current and Voltage
Page 854 of 906

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 10)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:52PM
CURRENT CONTROLLED CIRCUIT ("PEAK & HOLD")
The current controlled driver inside the computer is more
complex than a voltage controlled driver because as the name implies,
it has to limit current flow in addition to its ON-OFF switching
function. Recall, this driver typically requires injector circuits
with a total leg resistance of less than 12 ohms.
Once the driver is turned ON, it will not limit current flow
until enough time has passed for the injector pintle to open. This
period is preset by the particular manufacturer/system based on the
amount of current flow needed to open their injector. This is
typically between two and six amps. Some manufacturers refer to this
as the "peak" time, referring to the fact that current flow is allowed
to "peak" (to open the injector).
Once the injector pintle is open, the amp flow is
considerably reduced for the rest of the pulse duration to protect the
injector from overheating. This is okay because very little amperage
is needed to hold the injector open, typically in the area of one amp
or less. Some manufacturers refer to this as the "hold" time, meaning
that just enough current is allowed through the circuit to "hold" the
already-open injector open.
There are a couple methods of reducing the current. The most
common trims back the available voltage for the circuit, similar to
turning down a light at home with a dimmer.
The other method involves repeatedly cycling the circuit ON-
OFF. It does this so fast that the magnetic field never collapses and
the pintle stays open, but the current is still significantly reduced.
See the right side of Fig. 1 for an illustration.
The advantage to the current controlled driver circuit is the
short time period from when the driver transistor goes ON to when the
injector actually opens. This is a function of the speed with which
current flow reaches its peak due to the low circuit resistance. Also,
the injector closes faster when the driver turns OFF because of the
lower holding current.
NOTE: Never apply battery voltage directly across a low resistance
injector. This will cause injector damage from solenoid coil
overheating.
THE TWO WAYS INJECTOR CIRCUITS ARE WIRED
Like other circuits, injector circuits can be wired in one of
two fundamental directions. The first method is to steadily power the
injectors and have the computer driver switch the ground side of the
circuit. Conversely, the injectors can be steadily grounded while the
driver switches the power side of the circuit.
There is no performance benefit to either method. Voltage
controlled and current controlled drivers have been successfully
implemented both ways.
However, 95% percent of the systems are wired so the driver
controls the ground side of the circuit. Only a handful of systems use
the drivers on the power side of the circuit. Some examples of the