headlights VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1990 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: VOLKSWAGEN, Model Year: 1990, Model line: CORRADO, Model: VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1990Pages: 906, PDF Size: 6.56 MB
Page 293 of 906

1.8L 4-CYL 8-VALVE & 1.8L 4-CYL 16-VALVE
Article Text (p. 2)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:40PM
NOTE: Match mark engine mounts to ensure original alignment is
achieved after installation. On vehicles with A/C and power
steering, remove components with hoses attached and secure
out of way.
ENGINE R & I (EXCEPT FOX)
REMOVAL (EXCEPT FOX)
1) Disconnect and remove battery. Open fuel tank fill cap and
radiator cap. Remove intake air duct. On 16-valve engines, remove
intake manifold assembly. On vehicles with A/C, remove trim panel and
lower apron. Remove condenser from crossmember and radiator. Remove
all duct work. Mark and disconnect A/C and cooling fan electrical
connectors. Remove accessory belts.
2) On Golf, GTI and Jetta models, leave A/C hoses attached
and remove A/C compressor. Pivot A/C condenser and compressor to side
of vehicle and secure.
3) On Cabriolet and Scirocco models, remove alternator and
timing belt cover. Remove 3 A/C bracket Allen head bolts behind timing
belt cover. Remove A/C bracket support brace. Remove A/C compressor
bracket bolts. Leave hoses attached and secure A/C compressor with
bracket out of way.
4) On all models, open heater controls. Remove cooling hose
from thermostat housing flange and drain coolant. Remove flange. Mark
and remove all cooling system hoses (as necessary).
5) On Golf, GTI and Jetta models, remove grille from radiator
support. Disconnect electrical connectors at radiator support. Remove
radiator-to-support bolts. Remove radiator support using care not
damage headlights. Remove radiator, fan and shroud assembly.
6) On all models, remove axle shafts from transaxle. See FWD
AXLE SHAFTS article in the DRIVE AXLES section. Mark and disconnect
shift linkage and speedometer cable. Mark and remove electrical
connectors and vacuum hoses (as necessary). Disconnect throttle,
cruise and kickdown cables (if equipped). Leave fuel lines connected
and remove cold start injector and warm-up regulator.
7) Remove fuel injectors and install protective caps and
plugs. Remove rear engine mount. Remove complete transaxle mount. On
Cabriolet models, remove right front tire assembly. Remove right and
left engine mount through bolts.
8) On all models, install engine sling on engine lift hooks.
Carefully raise engine and transaxle out of vehicle. Separate
transaxle from engine (if necessary).
INSTALLATION
1) To install, reverse removal procedure. Engine alignment
adjustment is necessary whenever engine is removed or mounts are
loosened. To adjust, loosen through bolt on engine mount "A". Loosen
transmission transaxle mount "B" bolts. Loosen front engine mount and
bracket. See Fig. 2.
2) Lightly rock engine and transaxle to allow position to
Page 822 of 906

TROUBLE SHOOTING - BASIC PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 46)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:52PM
in the section(s) you are accessing.
BASIC STARTER TROUBLE SHOOTING CHARTÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄCONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄStarter Fails Dead battery or bad Check battery charge
to Operate connections between and all wires and
starter and battery connections to starter
Ignition switch faulty Adjust or replace
or misadjusted ignition switch
Open circuit between Check and repair wires
starter switch ignition and connections as
terminal on starter relay necessary
Starter relay or starter See Testing in STARTER
defective article
Open solenoid pull-in See Testing in STARTER
wire article
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄStarter Does Not Weak battery or dead Charge or replace
Operate and cell battery as necessary
Headlights Dim
Loose or corroded battery Check that battery
connections connections are clean
and tight
Internal ground in See Testing in STARTER
starter windings article
Grounded starter fields See Testing in STARTERS
Armature rubbing on pole See STARTER article
shoes
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄStarter Turns Starter clutch slipping See STARTER article
but Engine
Does Not Rotate
Broken clutch housing See STARTER article
Pinion shaft rusted or See STARTER article
dry
Engine basic timing See Ignition Timing in
incorrect TUNE-UP article
Broken teeth on engine Replace flywheel and
flywheel check for starter pinion
gear damage
Page 847 of 906

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 3)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:52PM
Let's move to the other situation where a noid light flashes
normally when it should be dim. This could occur if a more sensitive
noid light is used on a higher voltage/amperage circuit that was
weakened enough to cause problems (but not outright broken). A circuit
with an actual problem would thus appear normal.
Let's look at why. A noid light does not come close to
consuming as much amperage as an injector solenoid. If there is a
partial driver failure or a minor voltage drop in the injector
circuit, there can be adequate amperage to fully operate the noid
light BUT NOT ENOUGH TO OPERATE THE INJECTOR.
If this is not clear, picture a battery with a lot of
corrosion on the terminals. Say there is enough corrosion that the
starter motor will not operate; it only clicks. Now imagine turning on
the headlights (with the ignition in the RUN position). You find they
light normally and are fully bright. This is the same idea as noid
light: There is a problem, but enough amp flow exists to operate the
headlights ("noid light"), but not the starter motor ("injector").
How do you identify and avoid all these situations? By using
the correct type of noid light. This requires that you understanding
the types of injector circuits that your noid lights are designed for.
There are three. They are:
* Systems with a voltage controlled injector driver. Another
way to say it: The noid light is designed for a circuit with
a "high" resistance injector (generally 12 ohms or above).
* Systems with a current controlled injector driver. Another
way to say it: The noid light is designed for a circuit with
a low resistance injector (generally less than 12 ohms)
without an external injector resistor.
* Systems with a voltage controlled injector driver and an
external injector resistor. Another way of saying it: The
noid light is designed for a circuit with a low resistance
injector (generally less than 12 ohms) and an external
injector resistor.
NOTE: Some noid lights can meet both the second and third
categories simultaneously.
If you are not sure which type of circuit your noid light is
designed for, plug it into a known good car and check out the results.
If it flashes normally during cranking, determine the circuit type by
finding out injector resistance and if an external injector resistor
is used. You now know enough to identify the type of injector circuit.
Label the noid light appropriately.
Next time you need to use a noid light for diagnosis,
determine what type of injector circuit you are dealing with and
select the appropriate noid light.
Of course, if you suspect a no-pulse condition you could plug
in any one whose connector fit without fear of misdiagnosis. This is
because it is unimportant if the flashing light is dim or bright. It
is only important that it flashes.
Page 898 of 906
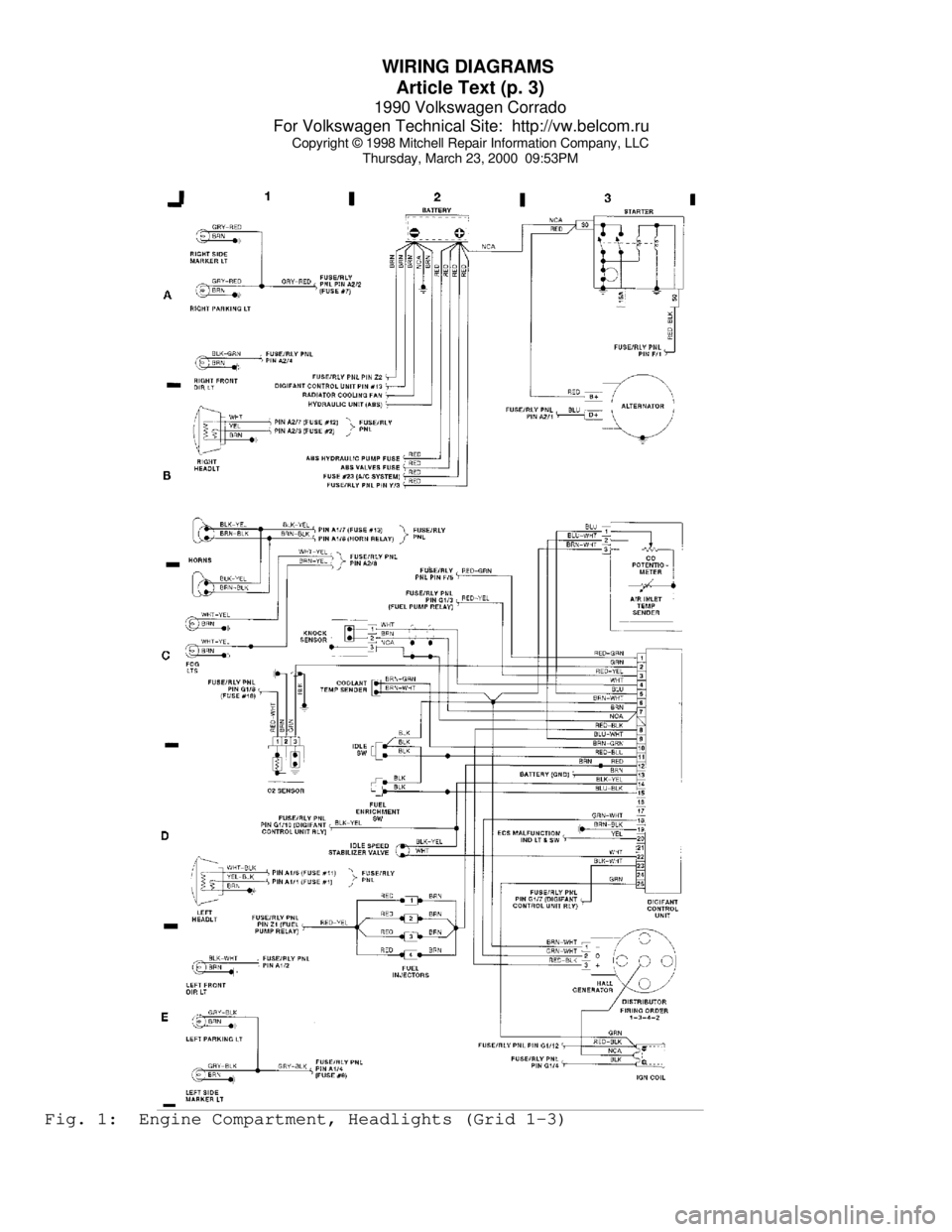
WIRING DIAGRAMS
Article Text (p. 3)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:53PMFig. 1: Engine Compartment, Headlights (Grid 1-3)