engine VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1993 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: VOLKSWAGEN, Model Year: 1993, Model line: CORRADO, Model: VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1993Pages: 920, PDF Size: 6.92 MB
Page 855 of 920

TROUBLE SHOOTING - BASIC PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 64)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
Carburetor setting too lean Readjust mixture
setting, see ENGINE
PERFORMANCE
Vacuum leak Eliminate vacuum leak
EGR valve malfunction Replace EGR valveÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄPoor Gasoline Cracked or broken vacuum Replace vacuum hoses
Mileage hoses
Vacuum leaks Repair vacuum leaks
Defective ignition wires Replace wires
Incorrect choke setting Readjust setting, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Defective vacuum advance Replace vacuum advance
Defective spark plugs Replace spark plugs
Binding carburetor power Eliminate binding
piston
Dirt in carburetor jets Clean and/or replace
jets
Incorrect float adjustment Readjust float
setting, see FUEL
Defective power valve Replace power valve,
see ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Incorrect idle speed Readjust idle speed
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄEngine Stalls Improper float level Readjust float level
Leaking needle valve and Replace needle valve
seat and seat
Vacuum leaks Eliminate vacuum
leaks
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ VACUUM PUMP - DIESEL TROUBLE SHOOTING
WARNING: This is GENERAL information. This article is not intended
to be specific to any unique situation or individual vehicle
configuration. The purpose of this Trouble Shooting
information is to provide a list of common causes to
Page 856 of 920

TROUBLE SHOOTING - BASIC PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 65)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
problem symptoms. For model-specific Trouble Shooting,
refer to SUBJECT, DIAGNOSTIC, or TESTING articles available
in the section(s) you are accessing.
NOTE: Diesel engines mechanical diagnosis is the same as gasoline
engines for items such as noisy valves, bearings, pistons,
etc. The following trouble shooting covers only items
pertaining to diesel engines.
VACUUM PUMP (DIESEL) TROUBLE SHOOTING CHARTÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄCONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄExcessive Noise Loose pump-to-drive Tighten screws
assembly screws
Loose tube on pump assembly Tighten tube
Valves not functioning Replace valves
properly
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄOil Leakage Loose end plug Tighten end plug
Bad seal crimp Remove and re-crimp
seal
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ WHEEL ALIGNMENT TROUBLE SHOOTING
WARNING: This is GENERAL information. This article is not intended
to be specific to any unique situation or individual vehicle
configuration. The purpose of this Trouble Shooting
information is to provide a list of common causes to
problem symptoms. For model-specific Trouble Shooting,
refer to SUBJECT, DIAGNOSTIC, or TESTING articles available
in the section(s) you are accessing.
BASIC WHEEL ALIGNMENT TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄCONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄPremature Tire Improper tire inflation Check tire pressure
Wear
Front alignment out of See ALIGNMENT SPECS in
tolerance WHEEL ALIGNMENT section
Suspension components worn See SUSPENSION section
Steering system components See STEERING section
worn
Improper standing height See WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Uneven or sagging springs See SUSPENSION section
Page 860 of 920

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
ARTICLE BEGINNING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Waveforms - Injector Pattern Tutorial
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
NOTE: This article is intended for general information purposes
only. This information may not apply to all makes and models.
PURPOSE OF THIS ARTICLE
Learning how to interpret injector drive patterns from a Lab
Scope can be like learning ignition patterns all over again. This
article exists to ease you into becoming a skilled injector pattern
interpreter.
You will learn:
* How a DVOM and noid light fall short of a lab scope.
* The two types of injector driver circuits, voltage controlled
& current controlled.
* The two ways injector circuits can be wired, constant
ground/switched power & constant power/switched ground.
* The two different pattern types you can use to diagnose with,
voltage & current.
* All the valuable details injector patterns can reveal.
SCOPE OF THIS ARTICLE
This is NOT a manufacturer specific article. All different
types of systems are covered here, regardless of the specific
year/make/model/engine.
The reason for such broad coverage is because there are only
a few basic ways to operate a solenoid-type injector. By understanding
the fundamental principles, you will understand all the major points
of injector patterns you encounter. Of course there are minor
differences in each specific system, but that is where a waveform
library helps out.
If this is confusing, consider a secondary ignition pattern.
Even though there are many different implementations, each still has
a primary voltage turn-on, firing line, spark line, etc.
If specific waveforms are available in On Demand for the
engine and vehicle you are working on, you will find them in the
Engine Performance section under the Engine Performance category.
IS A LAB SCOPE NECESSARY?
INTRODUCTION
You probably have several tools at your disposal to diagnose
injector circuits. But you might have questioned "Is a lab scope
Page 864 of 920

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 5)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
second, all measurements in between are averaged. Because a potential
voltage drop is visible for such a small amount of time, it gets
"averaged out", causing you to miss it.
Only a DVOM that has a "min-max" function that checks EVERY
MILLISECOND will catch this fault consistently (if used in that mode).
The Fluke 87 among others has this capability.
A "min-max" DVOM with a lower frequency of checking (100
millisecond) can miss the fault because it will probably check when
the injector is not on. This is especially true with current
controlled driver circuits. The Fluke 88, among others fall into this
category.
Outside of using a Fluke 87 (or equivalent) in the 1 mS "min-
max" mode, the only way to catch a voltage drop fault is with a lab
scope. You will be able to see a voltage drop as it happens.
One final note. It is important to be aware that an injector
circuit with a solenoid resistor will always show a voltage drop when
the circuit is energized. This is somewhat obvious and normal; it is a
designed-in voltage drop. What can be unexpected is what we already
covered--a voltage drop disappears when the circuit is unloaded. The
unloaded injector circuit will show normal battery voltage at the
injector. Remember this and do not get confused.
Checking Injector On-Time With Built-In Function
Several DVOMs have a feature that allows them to measure
injector on-time (mS pulse width). While they are accurate and fast to
hookup, they have three limitations you should be aware of:
* They only work on voltage controlled injector drivers (e.g
"Saturated Switch"), NOT on current controlled injector
drivers (e.g. "Peak & Hold").
* A few unusual conditions can cause inaccurate readings.
* Varying engine speeds can result in inaccurate readings.
Regarding the first limitation, DVOMs need a well-defined
injector pulse in order to determine when the injector turns ON and
OFF. Voltage controlled drivers provide this because of their simple
switch-like operation. They completely close the circuit for the
entire duration of the pulse. This is easy for the DVOM to interpret.
The other type of driver, the current controlled type, start
off well by completely closing the circuit (until the injector pintle
opens), but then they throttle back the voltage/current for the
duration of the pulse. The DVOM understands the beginning of the pulse
but it cannot figure out the throttling action. In other words, it
cannot distinguish the throttling from an open circuit (de-energized)
condition.
Yet current controlled injectors will still yield a
millisecond on-time reading on these DVOMs. You will find it is also
always the same, regardless of the operating conditions. This is
because it is only measuring the initial completely-closed circuit on-
time, which always takes the same amount of time (to lift the injector
pintle off its seat). So even though you get a reading, it is useless.
The second limitation is that a few erratic conditions can
Page 865 of 920

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 6)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
cause inaccurate readings. This is because of a DVOM's slow display
rate; roughly two to five times a second. As we covered earlier,
measurements in between display updates get averaged. So conditions
like skipped injector pulses or intermittent long/short injector
pulses tend to get "averaged out", which will cause you to miss
important details.
The last limitation is that varying engine speeds can result
in inaccurate readings. This is caused by the quickly shifting
injector on-time as the engine load varies, or the RPM moves from a
state of acceleration to stabilization, or similar situations. It too
is caused by the averaging of all measurements in between DVOM display
periods. You can avoid this by checking on-time when there are no RPM
or load changes.
A lab scope allows you to overcome each one of these
limitations.
Checking Injector On-Time With Dwell Or Duty
If no tool is available to directly measure injector
millisecond on-time measurement, some techs use a simple DVOM dwell or
duty cycle functions as a replacement.
While this is an approach of last resort, it does provide
benefits. We will discuss the strengths and weaknesses in a moment,
but first we will look at how a duty cycle meter and dwell meter work.
How A Duty Cycle Meter and Dwell Meter Work
All readings are obtained by comparing how long something has
been OFF to how long it has been ON in a fixed time period. A dwell
meter and duty cycle meter actually come up with the same answers
using different scales. You can convert freely between them. See
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DWELL & DUTY CYCLE READINGS TABLE.
The DVOM display updates roughly one time a second, although
some DVOMs can be a little faster or slower. All measurements during
this update period are tallied inside the DVOM as ON time or OFF time,
and then the total ratio is displayed as either a percentage (duty
cycle) or degrees (dwell meter).
For example, let's say a DVOM had an update rate of exactly 1
second (1000 milliseconds). Let's also say that it has been
measuring/tallying an injector circuit that had been ON a total of 250
mS out of the 1000 mS. That is a ratio of one-quarter, which would be
displayed as 25% duty cycle or 15ø dwell (six-cylinder scale). Note
that most duty cycle meters can reverse the readings by selecting the
positive or negative slope to trigger on. If this reading were
reversed, a duty cycle meter would display 75%.
Strengths of Dwell/Duty Meter
The obvious strength of a dwell/duty meter is that you can
compare injector on-time against a known-good reading. This is the
only practical way to use a dwell/duty meter, but requires you to have
known-good values to compare against.
Another strength is that you can roughly convert injector mS
on-time into dwell reading with some computations.
A final strength is that because the meter averages
Page 866 of 920

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 7)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
everything together it does not miss anything (though this is also a
severe weakness that we will look at later). If an injector has a
fault where it occasionally skips a pulse, the meter registers it and
the reading changes accordingly.
Let's go back to figuring out dwell/duty readings by using
injector on-time specification. This is not generally practical, but
we will cover it for completeness. You NEED to know three things:
* Injector mS on-time specification.
* Engine RPM when specification is valid.
* How many times the injectors fire per crankshaft revolution.
The first two are self-explanatory. The last one may require
some research into whether it is a bank-fire type that injects every
360ø of crankshaft rotation, a bank-fire that injects every 720ø, or
an SFI that injects every 720
ø. Many manufacturers do not release this
data so you may have to figure it out yourself with a frequency meter.
Here are the four complete steps to convert millisecond on-
time:
1) Determine the injector pulse width and RPM it was obtained
at. Let's say the specification is for one millisecond of on-time at a
hot idle of 600 RPM.
2) Determine injector firing method for the complete 4 stroke
cycle. Let's say this is a 360
ø bank-fired, meaning an injector fires
each and every crankshaft revolution.
3) Determine how many times the injector will fire at the
specified engine speed (600 RPM) in a fixed time period. We will use
100 milliseconds because it is easy to use.
Six hundred crankshaft Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) divided
by 60 seconds equals 10 revolutions per second.
Multiplying 10 times .100 yields one; the crankshaft turns
one time in 100 milliseconds. With exactly one crankshaft rotation in
100 milliseconds, we know that the injector fires exactly one time.
4) Determine the ratio of injector on-time vs. off-time in
the fixed time period, then figure duty cycle and/or dwell. The
injector fires one time for a total of one millisecond in any given
100 millisecond period.
One hundred minus one equals 99. We have a 99% duty cycle. If
we wanted to know the dwell (on 6 cylinder scale), multiple 99% times
.6; this equals 59.4
ø dwell.
Weaknesses of Dwell/Duty Meter
The weaknesses are significant. First, there is no one-to-one
correspondence to actual mS on-time. No manufacturer releases
dwell/duty data, and it is time-consuming to convert the mS on-time
readings. Besides, there can be a large degree of error because the
conversion forces you to assume that the injector(s) are always firing
at the same rate for the same period of time. This can be a dangerous
assumption.
Second, all level of detail is lost in the averaging process.
This is the primary weakness. You cannot see the details you need to
make a confident diagnosis.
Page 867 of 920

WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 8)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
Here is one example. Imagine a vehicle that has a faulty
injector driver that occasionally skips an injector pulse. Every
skipped pulse means that that cylinder does not fire, thus unburned O2
gets pushed into the exhaust and passes the O2 sensor. The O2 sensor
indicates lean, so the computer fattens up the mixture to compensate
for the supposed "lean" condition.
A connected dwell/duty meter would see the fattened pulse
width but would also see the skipped pulses. It would tally both and
likely come back with a reading that indicated the "pulse width" was
within specification because the rich mixture and missing pulses
offset each other.
This situation is not a far-fetched scenario. Some early GM
3800 engines were suffering from exactly this. The point is that a
lack of detail could cause misdiagnosis.
As you might have guessed, a lab scope would not miss this.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DWELL & DUTY CYCLE READINGS TABLE (1)ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄDwell Meter (2) Duty Cycle Meter
1
ø .................................................... 1%
15
ø .................................................. 25%
30
ø .................................................. 50%
45
ø .................................................. 75%
60
ø ................................................. 100%
(1) - These are just some examples for your understanding.
It is okay to fill in the gaps.
(2) - Dwell meter on the six-cylinder scale.
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ THE TWO TYPES OF INJECTOR DRIVERS
OVERVIEW
There are two types of transistor driver circuits used to
operate electric fuel injectors: voltage controlled and current
controlled. The voltage controlled type is sometimes called a
"saturated switch" driver, while the current controlled type is
sometimes known as a "peak and hold" driver.
The basic difference between the two is the total resistance
of the injector circuit. Roughly speaking, if a particular leg in an
injector circuit has total resistance of 12 or more ohms, a voltage
control driver is used. If less than 12 ohms, a current control driver
is used.
It is a question of what is going to do the job of limiting
the current flow in the injector circuit; the inherent "high"
resistance in the injector circuit, or the transistor driver. Without
some form of control, the current flow through the injector would
cause the solenoid coil to overheat and result in a damaged injector.
VOLTAGE CONTROLLED CIRCUIT ("SATURATED SWITCH")
Page 875 of 920
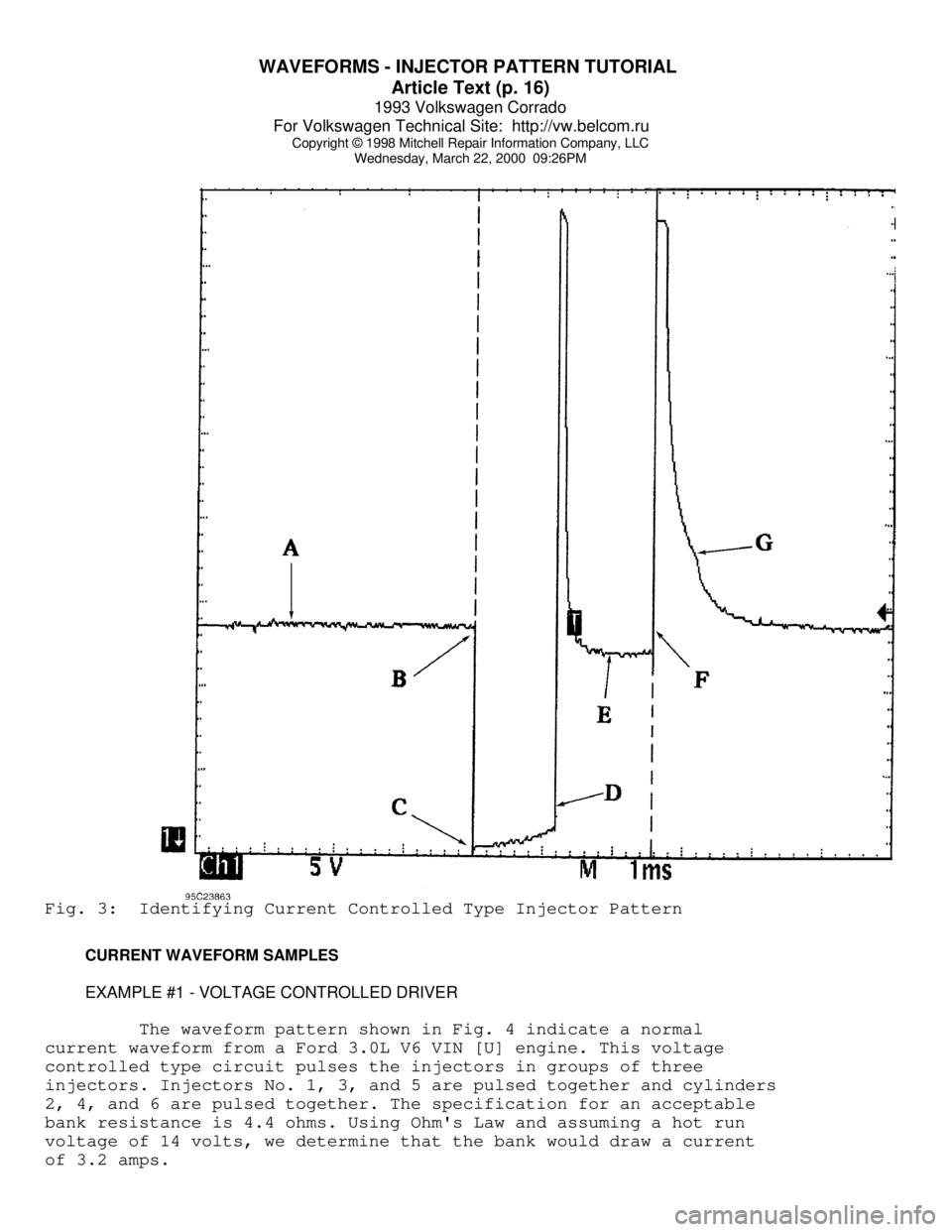
WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 16)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PMFig. 3: Identifying Current Controlled Type Injector Pattern
CURRENT WAVEFORM SAMPLES
EXAMPLE #1 - VOLTAGE CONTROLLED DRIVER
The waveform pattern shown in Fig. 4 indicate a normal
current waveform from a Ford 3.0L V6 VIN [U] engine. This voltage
controlled type circuit pulses the injectors in groups of three
injectors. Injectors No. 1, 3, and 5 are pulsed together and cylinders
2, 4, and 6 are pulsed together. The specification for an acceptable
bank resistance is 4.4 ohms. Using Ohm's Law and assuming a hot run
voltage of 14 volts, we determine that the bank would draw a current
of 3.2 amps.
Page 878 of 920
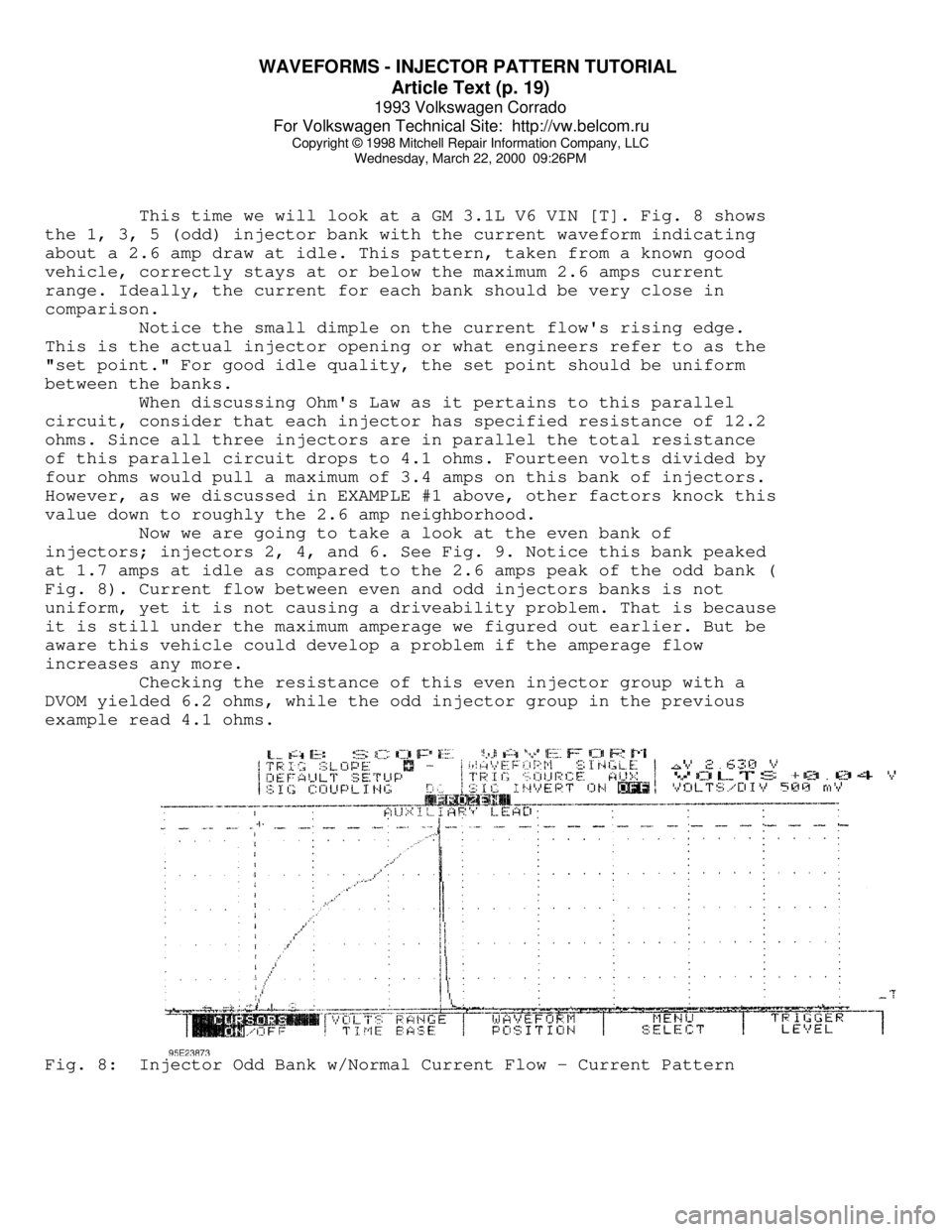
WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 19)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PM
This time we will look at a GM 3.1L V6 VIN [T]. Fig. 8 shows
the 1, 3, 5 (odd) injector bank with the current waveform indicating
about a 2.6 amp draw at idle. This pattern, taken from a known good
vehicle, correctly stays at or below the maximum 2.6 amps current
range. Ideally, the current for each bank should be very close in
comparison.
Notice the small dimple on the current flow's rising edge.
This is the actual injector opening or what engineers refer to as the
"set point." For good idle quality, the set point should be uniform
between the banks.
When discussing Ohm's Law as it pertains to this parallel
circuit, consider that each injector has specified resistance of 12.2
ohms. Since all three injectors are in parallel the total resistance
of this parallel circuit drops to 4.1 ohms. Fourteen volts divided by
four ohms would pull a maximum of 3.4 amps on this bank of injectors.
However, as we discussed in EXAMPLE #1 above, other factors knock this
value down to roughly the 2.6 amp neighborhood.
Now we are going to take a look at the even bank of
injectors; injectors 2, 4, and 6. See Fig. 9. Notice this bank peaked
at 1.7 amps at idle as compared to the 2.6 amps peak of the odd bank (
Fig. 8). Current flow between even and odd injectors banks is not
uniform, yet it is not causing a driveability problem. That is because
it is still under the maximum amperage we figured out earlier. But be
aware this vehicle could develop a problem if the amperage flow
increases any more.
Checking the resistance of this even injector group with a
DVOM yielded 6.2 ohms, while the odd injector group in the previous
example read 4.1 ohms.Fig. 8: Injector Odd Bank w/Normal Current Flow - Current Pattern
Page 879 of 920
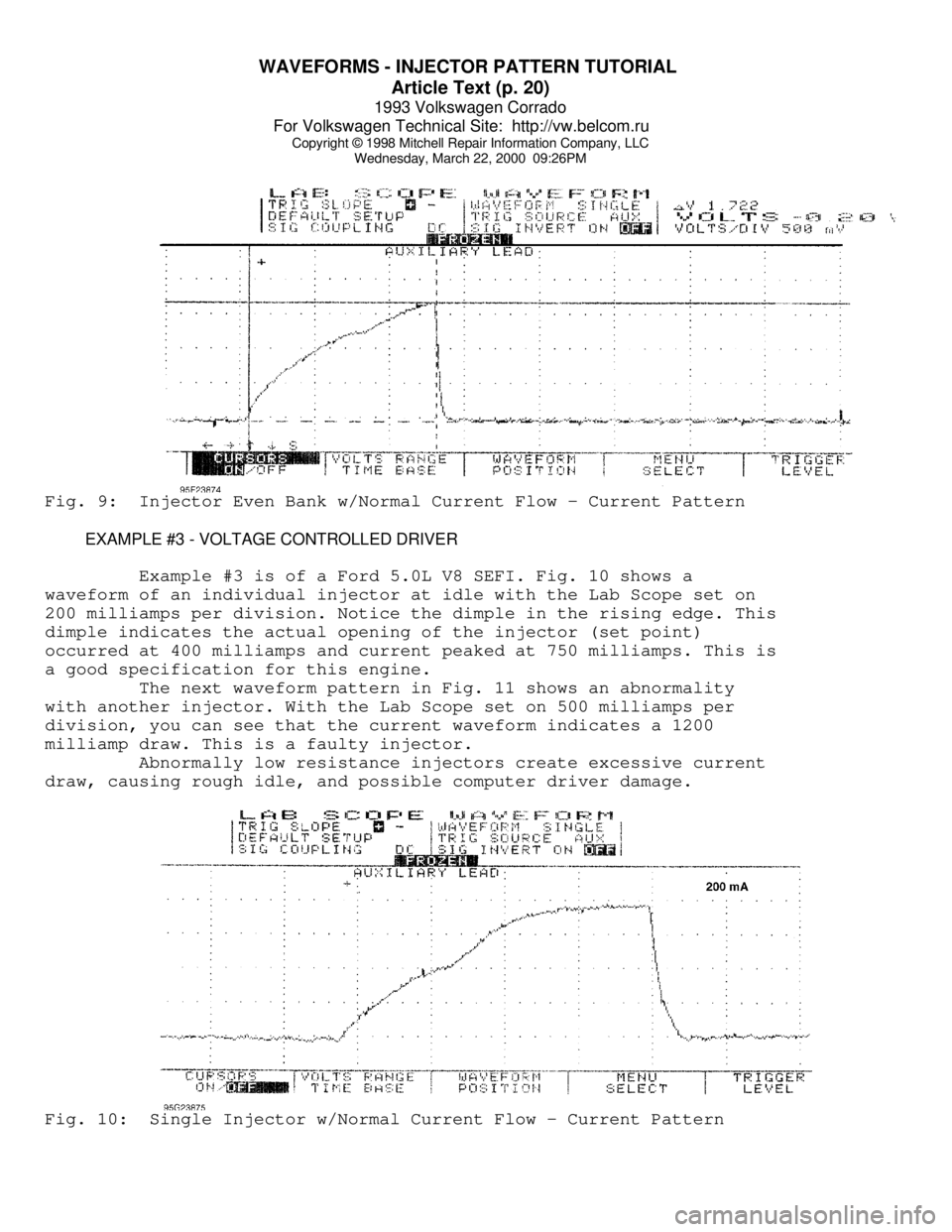
WAVEFORMS - INJECTOR PATTERN TUTORIAL
Article Text (p. 20)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:26PMFig. 9: Injector Even Bank w/Normal Current Flow - Current Pattern
EXAMPLE #3 - VOLTAGE CONTROLLED DRIVER
Example #3 is of a Ford 5.0L V8 SEFI. Fig. 10 shows a
waveform of an individual injector at idle with the Lab Scope set on
200 milliamps per division. Notice the dimple in the rising edge. This
dimple indicates the actual opening of the injector (set point)
occurred at 400 milliamps and current peaked at 750 milliamps. This is
a good specification for this engine.
The next waveform pattern in Fig. 11 shows an abnormality
with another injector. With the Lab Scope set on 500 milliamps per
division, you can see that the current waveform indicates a 1200
milliamp draw. This is a faulty injector.
Abnormally low resistance injectors create excessive current
draw, causing rough idle, and possible computer driver damage.Fig. 10: Single Injector w/Normal Current Flow - Current Pattern