light YAMAHA YZ125LC 2013 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2013, Model line: YZ125LC, Model: YAMAHA YZ125LC 2013Pages: 168, PDF Size: 8.19 MB
Page 62 of 168
3-19
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL
CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG
1. Remove:
• Spark plug
2. Inspect:
• Electrode "1"
Wear/damage → Replace.
• Insulator color "2"
Normal condition is a medium to
light tan color.
Distinctly different color → Check
the engine condition.
When the engine runs for many hours
at low speeds, the spark plug insula-
tor will become sooty, even if the en-
gine and carburetor are in good
operating condition.
3. Measure:
• Plug gap "a"
Use a wire gauge or thickness
gauge.
Out of specification → Regap.
4. Clean the plug with a spark plug
cleaner if necessary.
5. Tighten:
• Spark plug
• Before installing a spark plug, clean
the gasket surface and plug sur-
face.
• Finger-tighten "a" the spark plug
before torquing to specification "b".
CHECKING THE IGNITION TIMING
1. Remove:
•Fuel tank
Refer to "SEAT, FUEL TANK
AND SIDE COVERS" section in
the CHAPTER 4.
• Spark plug
• Crankcase cover (left)
2. Attach:
• Dial gauge "1"
• Spark plug hole dial stand "2"
3. Rotate the magneto rotor "1" until
the piston reaches top dead cen-
ter (TDC). When this happens,
the needle on the dial gauge will
stop and reverse directions even
though the rotor is being turned in
the same direction.
4. Set the dial gauge to zero at TDC.
5. From TDC, rotate the rotor clock-
wise until the dial gauge indicates
that the piston is at a specified
distance from TDC.
6. Check:
• Ignition timing
Punch mark "a" on rotor should be
aligned with punch mark "b" on
stator.
Not aligned → Adjust.
7. Adjust:
• Ignition timing
Adjustment steps:
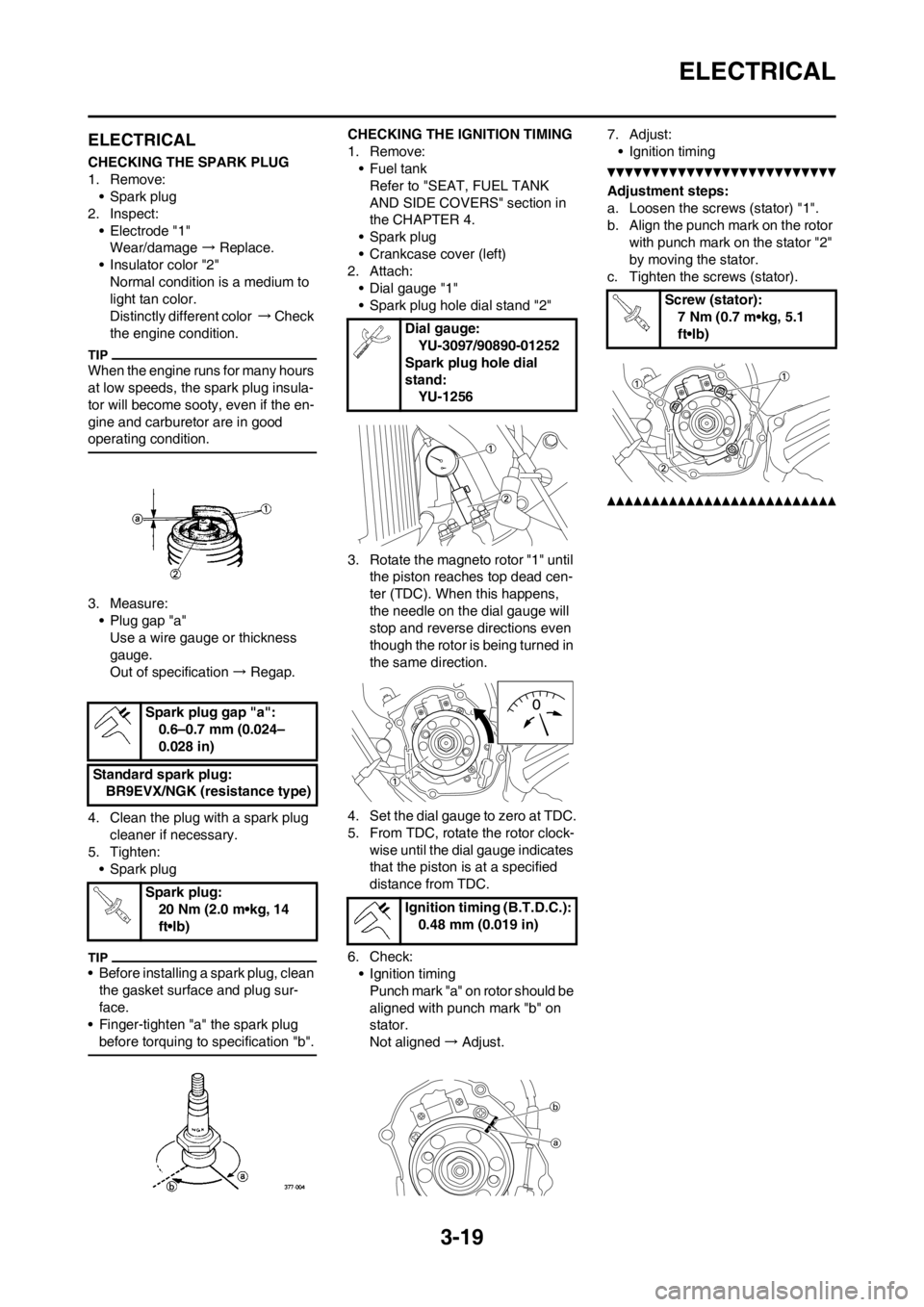
a. Loosen the screws (stator) "1".
b. Align the punch mark on the rotor
with punch mark on the stator "2"
by moving the stator.
c. Tighten the screws (stator).
Spark plug gap "a":
0.6–0.7 mm (0.024–
0.028 in)
Standard spark plug:
BR9EVX/NGK (resistance type)
Spark plug:
20 Nm (2.0 m•kg, 14
ft•lb)
Dial gauge:
YU-3097/90890-01252
Spark plug hole dial
stand:
YU-1256
Ignition timing (B.T.D.C.):
0.48 mm (0.019 in)
Screw (stator):
7 Nm (0.7 m•kg, 5.1
ft•lb)
Page 72 of 168
4-10
CARBURETOR AND REED VALVE
d. Measure the fuel level with the
fuel level gauge.
Keep the carburetor and fuel level
gauge vertically when measuring the
fuel level.
e. If the fuel level is not within speci-
fication, inspect the valve seat
and needle valve.
f. If either is worn, replace them
both.
g. If both are fine, adjust the fuel lev-
el by bending the float tab "b" on
the float.
h. Recheck the fuel level.
CHECKING THE FLOAT
1. Inspect:
• Float "1"
Damage → Replace.
CHECKING THE REED VALVE
1. Measure:
• Reed valve bending "a"
Out of specification → R e p l a c e . 2. Measure:
• Valve stopper height "a"
Out of specification → Adjust
stopper/Replace valve stopper.
INSTALLING THE REED VALVE
1. Install:
• Reed valve "1"
• Stopper (reed valve) "2"
• Screw (reed valve) "3"
• Install the reed valve with the reed
valve bending as shown.
• Note the cut "a" in the lower corner
of the reed and stopper plate.
Tighten each screw gradually to
avoid warping.
2. Install:
• Reed valve assembly "1"
• Reed valve spacer "2"
3. Install:
• Carburetor joint "1"
• Bolt (carburetor joint) "2"ASSEMBLING THE CARBURETOR
1. Install:
• Throttle stop screw "1"
• Locknut "2"
• Pilot air screw "3"
Note the following installation
points:
a. Screw in the pilot air screw until it
is lightly seated.
b. Back out it by the specified num-
ber of turns.
2. Install:
• Starter plunger "1"
3. Install:
• Main jet holder "1"
•Main jet "2"
• Pilot jet "3"
• Valve seat "4"
• Screw (valve seat) "5"
4. Install:
• Needle valve "1"
• Float "2"
• Float pin "3"
• Screw (float pin) "4"
• Needle jet cover "5" Reed valve bending limit
"a":
0.2 mm (0.008 in)
Valve stopper height "a":
8.2–8.6 mm (0.323–
0.339 in)
Screw (reed valve):
1 Nm (0.1 m•kg, 0.7
ft•lb)
Bolt (carburetor joint):
10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Pilot air screw:
2-1/4 turns out
Page 103 of 168
4-41
CRANKCASE AND CRANKSHAFT
REMOVING THE SEGMENT
1. Remove:
• Bolt (segment) "1"
• Segment "2"
Turn the segment counterclockwise
until it stops and loosen the bolt.
If the segment gets an impact, it
may be damaged. Take care not to
give an impact to the segment
when removing the bolt.
DISASSEMBLING THE
CRANKCASE
1. Remove:
• Crankcase (right) "1"
Use the flywheel puller "2".
• Make appropriate bolts "3" as
shown available by yourself and at-
tach the tool with them.
• Fully tighten the tool holding bolts,
but make sure the tool body is par-
allel with the case. If necessary,
one screw may be backed out
slightly to level tool body.
• As pressure is applied, alternately
tap on the engine mounting boss
and transmission shafts.
Use soft hammer to tap on the
case half. Tap only on reinforced
portions of case. Do not tap on
gasket mating surface. Work slow-
ly and carefully. Make sure the
case halves separate evenly. If one
end "hangs up", take pressure off
the push screw, realign, and start
over. If the cases do not separate,
check for a remaining case bolt or
fitting. Do not force.
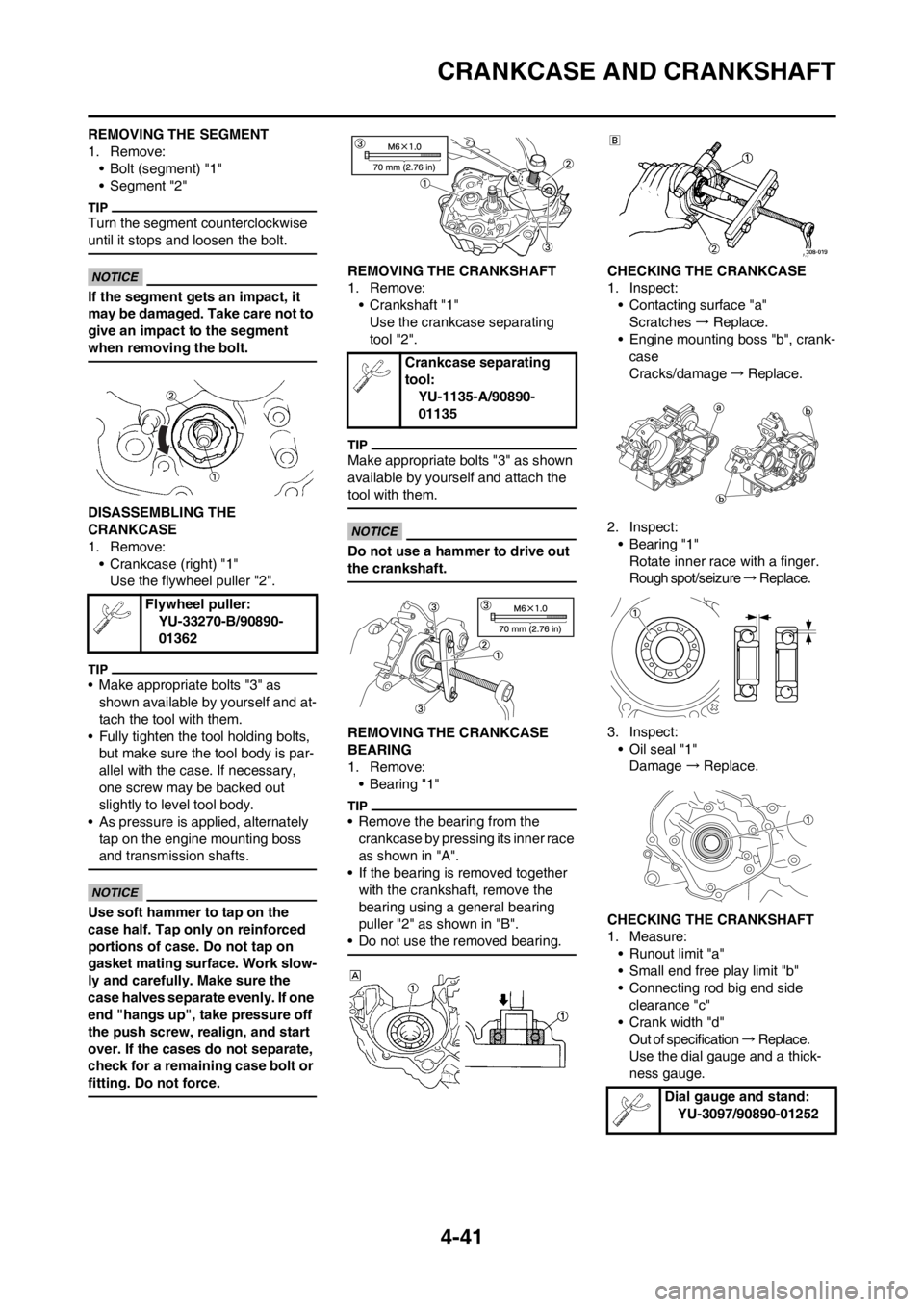
REMOVING THE CRANKSHAFT
1. Remove:
• Crankshaft "1"
Use the crankcase separating
tool "2".
Make appropriate bolts "3" as shown
available by yourself and attach the
tool with them.
Do not use a hammer to drive out
the crankshaft.
REMOVING THE CRANKCASE
BEARING
1. Remove:
•Bearing "1"
• Remove the bearing from the
crankcase by pressing its inner race
as shown in "A".
• If the bearing is removed together
with the crankshaft, remove the
bearing using a general bearing
puller "2" as shown in "B".
• Do not use the removed bearing.
CHECKING THE CRANKCASE
1. Inspect:
• Contacting surface "a"
Scratches → Replace.
• Engine mounting boss "b", crank-
case
Cracks/damage → Replace.
2. Inspect:
• Bearing "1"
Rotate inner race with a finger.
Rough spot/seizure → R e p l a c e .
3. Inspect:
• Oil seal "1"
Damage →Replace.
CHECKING THE CRANKSHAFT
1. Measure:
• Runout limit "a"
• Small end free play limit "b"
• Connecting rod big end side
clearance "c"
• Crank width "d"
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
Use the dial gauge and a thick-
ness gauge. Flywheel puller:
YU-33270-B/90890-
01362
Crankcase separating
tool:
YU-1135-A/90890-
01135
Dial gauge and stand:
YU-3097/90890-01252
Page 107 of 168
4-45
TRANSMISSION, SHIFT CAM AND SHIFT FORK
REMOVING THE TRANSMISSION
1. Remove:
• Main axle "1"
• Drive axle "2"
• Tap lightly on the transmission drive
axle with a soft hammer to remove.
• Remove assembly carefully. Note
the position of each part. Pay partic-
ular attention to the location and di-
rection of shift forks.
CHECKING THE GEARS
1. Inspect:
• Matching dog "a"
• Gear teeth "b"
• Shift fork groove "c"
Wear/damage → Replace.
2. Check:
• Gears movement
Unsmooth movement → Repair
or replace.
CHECKING THE BEARING
1. Inspect:
• Bearing "1"
Rotate inner race with a finger.
Rough spot/seizure → R e p l a c e . CHECKING THE SHIFT FORK,
SHIFT CAM AND SEGMENT
1. Inspect:
• Shift fork "1"
Wear/damage/scratches → Re-
place.
2. Inspect:
• Shift cam "1"
• Segment "2"
• Guide bar "3"
Wear/damage →Replace.
3. Check:
• Shift fork movement
On its guide bar.
Unsmooth operation → Replace
shift fork and/or guide bar.
For a malfunctioning shift fork, re-
place not only the shift fork itself but
the two gears each adjacent to the
shift fork.
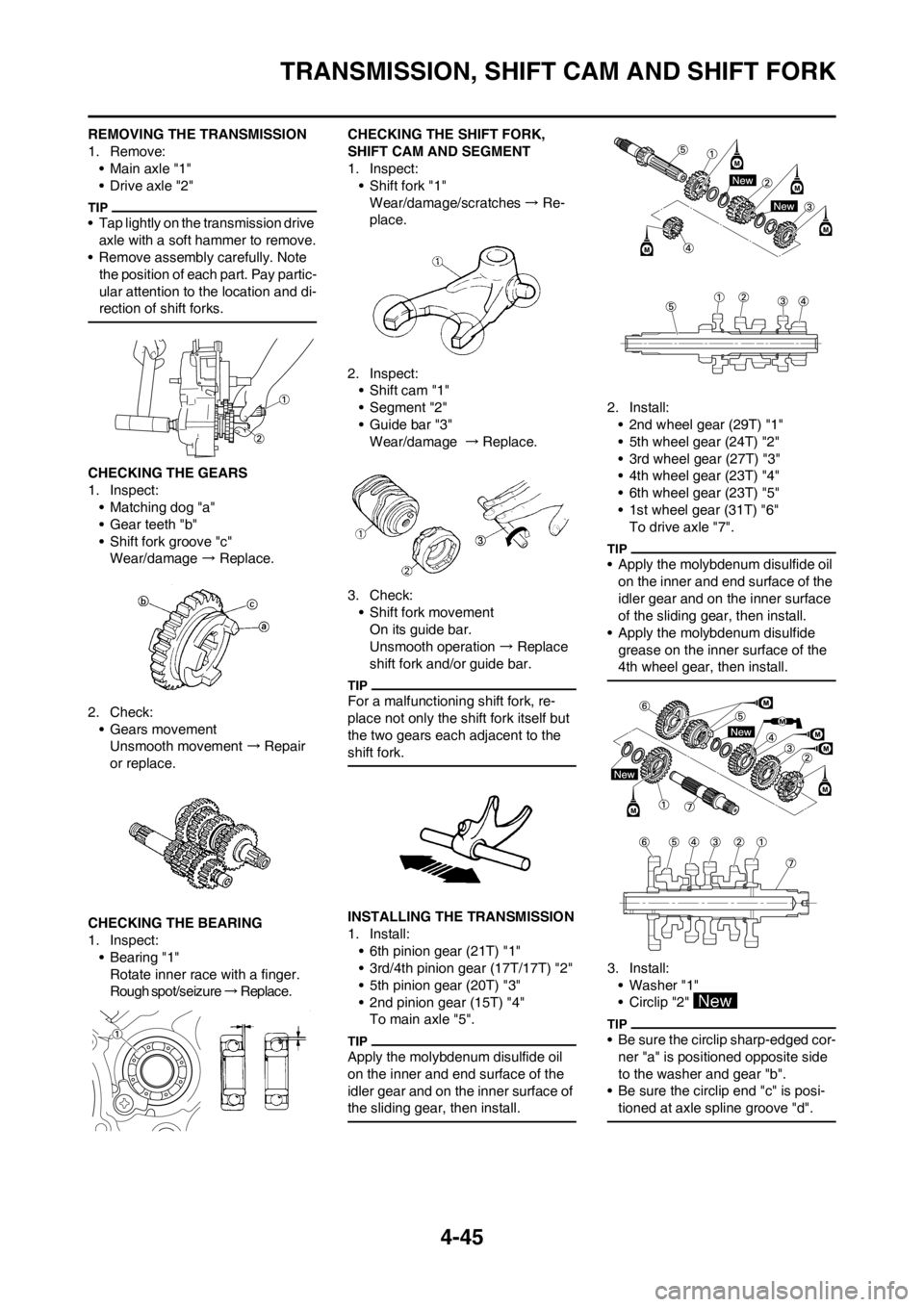
INSTALLING THE TRANSMISSION
1. Install:
• 6th pinion gear (21T) "1"
• 3rd/4th pinion gear (17T/17T) "2"
• 5th pinion gear (20T) "3"
• 2nd pinion gear (15T) "4"
To main axle "5".
Apply the molybdenum disulfide oil
on the inner and end surface of the
idler gear and on the inner surface of
the sliding gear, then install.
2. Install:
• 2nd wheel gear (29T) "1"
• 5th wheel gear (24T) "2"
• 3rd wheel gear (27T) "3"
• 4th wheel gear (23T) "4"
• 6th wheel gear (23T) "5"
• 1st wheel gear (31T) "6"
To drive axle "7".
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide oil
on the inner and end surface of the
idler gear and on the inner surface
of the sliding gear, then install.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the inner surface of the
4th wheel gear, then install.
3. Install:
• Washer "1"
• Circlip "2"
• Be sure the circlip sharp-edged cor-
ner "a" is positioned opposite side
to the washer and gear "b".
• Be sure the circlip end "c" is posi-
tioned at axle spline groove "d".
Page 121 of 168

5-13
FRONT BRAKE AND REAR BRAKE
2. Install:
• Brake lever "1"
• Bolt (brake lever) "2"
• Nut (brake lever) "3"
Apply the silicone grease on the
brake lever sliding surface, bolt and
tip of the push rod.
INSTALLING THE REAR BRAKE
MASTER CYLINDER
1. Install:
• Copper washer "1"
• Brake hose "2"
• Union bolt "3"
Always use new copper washers.
Install the brake hose so that its
pipe portion "a" directs as shown
and lightly touches the projection
"b" on the brake master cylinder.
2. Install:
• Brake master cylinder "1"
• Bolt (brake master cylinder) "2"
3. Install:
• Spring "1"
• Brake pedal "2"
• O-ring "3"
• Bolt (brake pedal) "4"
• Clip "5"
Apply the lithium soap base grease
on the bolt, O-rings and brake pedal
bracket.
4. Install:
•Pin "1"
• Washer "2"
• Cotter pin "3"
After installing, check the brake pedal
height. Refer to "ADJUSTING THE
REAR BRAKE" section in the CHAP-
TER 3.
INSTALLING THE FRONT BRAKE
HOSE
1. Install:
• Copper washer "1"
• Brake hose "2"
• Union bolt "3"
Always use new copper washers.
Install the brake hose so that its
pipe portion "a" directs as shown
and lightly touches the projection
"b" on the brake caliper.
2. Install:
• Brake hose holder "1"
• Bolt (brake hose holder) "2"
Align the top "a" of the brake hose
holder with the paint "b" of the brake
hose.
3. Pass the brake hose through the
cable guide "1". Bolt (brake lever):
6 Nm (0.6 m•kg, 4.3
ft•lb)
Nut (brake lever):
6 Nm (0.6 m•kg, 4.3
ft•lb)
Union bolt:
30 Nm (3.0 m•kg, 22
ft•lb)
Bolt (brake master cylin-
der):
10 Nm (1.0 m•kg, 7.2
ft•lb)
Bolt (brake pedal):
26 Nm (2.6 m•kg, 19
ft•lb)
Union bolt:
30 Nm (3.0 m•kg, 22
ft•lb)
Bolt (brake hose holder):
8 Nm (0.8 m•kg, 5.8
ft •lb)
Page 122 of 168

5-14
FRONT BRAKE AND REAR BRAKE
4. Install:
• Copper washer "1"
• Brake hose "2"
• Union bolt "3"
Always use new copper washers.
Install the brake hose so that its
pipe portion "a" directs as shown
and lightly touches the projection
"b" on the brake master cylinder.
INSTALLING THE REAR BRAKE
HOSE
1. Install:
• Copper washer "1"
• Brake hose "2"
• Union bolt "3"
Always use new copper washers.
Install the brake hose so that its
pipe portion "a" directs as shown
and lightly touches the projection
"b" on the brake caliper.
2. Install:
• Brake hose holder "1"
• Screw (brake hose holder) "2"
After installing the brake hose
holders, make sure the brake hose
does not contact the spring (rear
shock absorber). If it does, correct
its twist.
FILLING THE BRAKE FLUID
1. Fill:
•Brake fluid
Until the fluid level reaches
"LOWER" level line "a".
• Use only the designated quality
brake fluid:
otherwise, the rubber seals may
deteriorate, causing leakage and
poor brake performance.
• Refill with the same type of brake
fluid;
mixing fluids may result in a
harmful chemical reaction and
lead to poor performance.
• Be careful that water does not
enter the master cylinder when
refilling. Water will significantly
lower the boiling point of the flu-
id and may result in vapor lock.
Brake fluid may erode painted sur-
faces or plastic parts. Always
clean up spilled fluid immediately.
A. Front
B. Rear
2. Air bleed:
• Brake system
Refer to "BLEEDING THE HY-
DRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM" sec-
tion in the CHAPTER 3.
3. Inspect:
• Brake fluid level
Fluid at lower level → Fill up.
Refer to "CHECKING THE
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL" section in
the CHAPTER 3. Union bolt:
30 Nm (3.0 m•kg, 22
ft•lb)
Union bolt:
30 Nm (3.0 m•kg, 22
ft•lb)
Screw (brake hose hold-
er):
3 Nm (0.3 m•kg, 2.2
ft•lb)
Recommended brake flu-
id:
DOT #4
Page 159 of 168
7-4
ENGINE
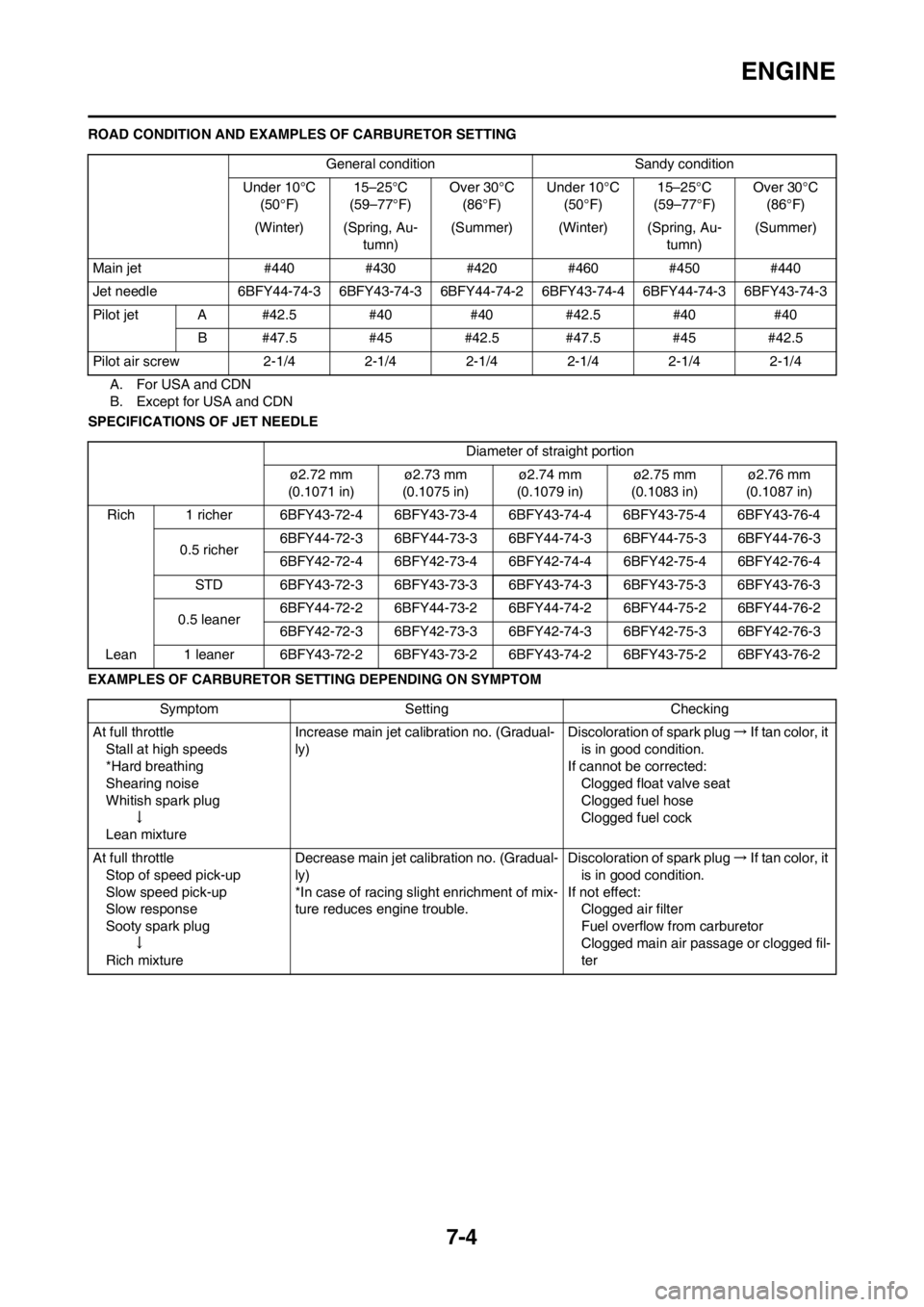
ROAD CONDITION AND EXAMPLES OF CARBURETOR SETTING
A. For USA and CDN
B. Except for USA and CDN
SPECIFICATIONS OF JET NEEDLE
EXAMPLES OF CARBURETOR SETTING DEPENDING ON SYMPTOMGeneral condition Sandy condition
Under 10°C
(50°F)15–25°C
(59–77°F)Over 30°C
(86°F)Under 10°C
(50°F)15–25°C
(59–77°F)Over 30°C
(86°F)
(Winter) (Spring, Au-
tumn)(Summer) (Winter) (Spring, Au-
tumn)(Summer)
Main jet #440 #430 #420 #460 #450 #440
Jet needle 6BFY44-74-3 6BFY43-74-3 6BFY44-74-2 6BFY43-74-4 6BFY44-74-3 6BFY43-74-3
Pilot jet A #42.5 #40 #40 #42.5 #40 #40
B #47.5 #45 #42.5 #47.5 #45 #42.5
Pilot air screw 2-1/4 2-1/4 2-1/4 2-1/4 2-1/4 2-1/4
Diameter of straight portion
ø2.72 mm
(0.1071 in)ø2.73 mm
(0.1075 in)ø2.74 mm
(0.1079 in)ø2.75 mm
(0.1083 in)ø2.76 mm
(0.1087 in)
Rich 1 richer 6BFY43-72-4 6BFY43-73-4 6BFY43-74-4 6BFY43-75-4 6BFY43-76-4
0.5 richer6BFY44-72-3 6BFY44-73-3 6BFY44-74-3 6BFY44-75-3 6BFY44-76-3
6BFY42-72-4 6BFY42-73-4 6BFY42-74-4 6BFY42-75-4 6BFY42-76-4
STD 6BFY43-72-3 6BFY43-73-3 6BFY43-74-3 6BFY43-75-3 6BFY43-76-3
0.5 leaner6BFY44-72-2 6BFY44-73-2 6BFY44-74-2 6BFY44-75-2 6BFY44-76-2
6BFY42-72-3 6BFY42-73-3 6BFY42-74-3 6BFY42-75-3 6BFY42-76-3
Lean 1 leaner 6BFY43-72-2 6BFY43-73-2 6BFY43-74-2 6BFY43-75-2 6BFY43-76-2
Symptom Setting Checking
At full throttle
Stall at high speeds
*Hard breathing
Shearing noise
Whitish spark plug
↓
Lean mixtureIncrease main jet calibration no. (Gradual-
ly)Discoloration of spark plug → If tan color, it
is in good condition.
If cannot be corrected:
Clogged float valve seat
Clogged fuel hose
Clogged fuel cock
At full throttle
Stop of speed pick-up
Slow speed pick-up
Slow response
Sooty spark plug
↓
Rich mixtureDecrease main jet calibration no. (Gradual-
ly)
*In case of racing slight enrichment of mix-
ture reduces engine trouble.Discoloration of spark plug → If tan color, it
is in good condition.
If not effect:
Clogged air filter
Fuel overflow from carburetor
Clogged main air passage or clogged fil-
ter
Page 161 of 168
7-6
CHASSIS
CHANGE OF THE HEAT RANGE
OF SPARK PLUGS
Judging from the discoloration of
spark plugs, if they are found improp-
er, it can be corrected by the following
two methods; changing carburetor
settings and changing the heat range
of spark plug.
• In principle, it is advisable to first
use spark plugs of standard heat
range, and judging from the discol-
oration of spark plugs, adjust carbu-
retor settings.
• If the calibration No. of the main jet
must be changed by ±30, it is advis-
able to change the heat range of
spark plugs and newly select the
proper main jet.
• When checking the discoloration of
spark plugs, be sure to stop the en-
gine immediately after a run and
check.
• Avoid racing.
• When changing the heat range of
spark plugs, never attempt to
change it more than ±1 rank.
• When using a spark plug other than
standard, check its heat range
against the standard and check that
it is a resistance type.
• Note that even if the discoloration
seems proper, it may slightly vary
with the spark plug maker and oil in
use.
CHASSIS
SELECTION OF THE SECONDARY
REDUCTION RATIO (SPROCKET)
• It is generally said that the second-
ary gear ratio should be reduced for
a longer straight portion of a speed
course and should be increased for
a course with many corners. Actual-
ly, however, as the speed depends
on the ground condition of the day
of the race, be sure to run through
the circuit to set the machine suit-
able for the entire course.
• In actuality, it is very difficult to
achieve settings suitable for the en-
tire course and some settings may
be sacrificed. Thus, the settings
should be matched to the portion of
the course that has the greatest ef-
fect on the race result. In such a
case, run through the entire course
while making notes of lap times to
find the best balance; then, deter-
mine the secondary reduction ratio.
• If a course has a long straight por-
tion where a machine can run at
maximum speed, the machine is
generally set such that it can devel-
op its maximum revolutions toward
the end of the straight line, with care
taken to avoid the engine over-rev-
ving.
Riding technique varies from rider to
rider and the performance of a ma-
chine also vary from machine to ma-
chine. Therefore, do not imitate other
rider's settings from the beginning but
choose your own setting according to
the level of your riding technique.
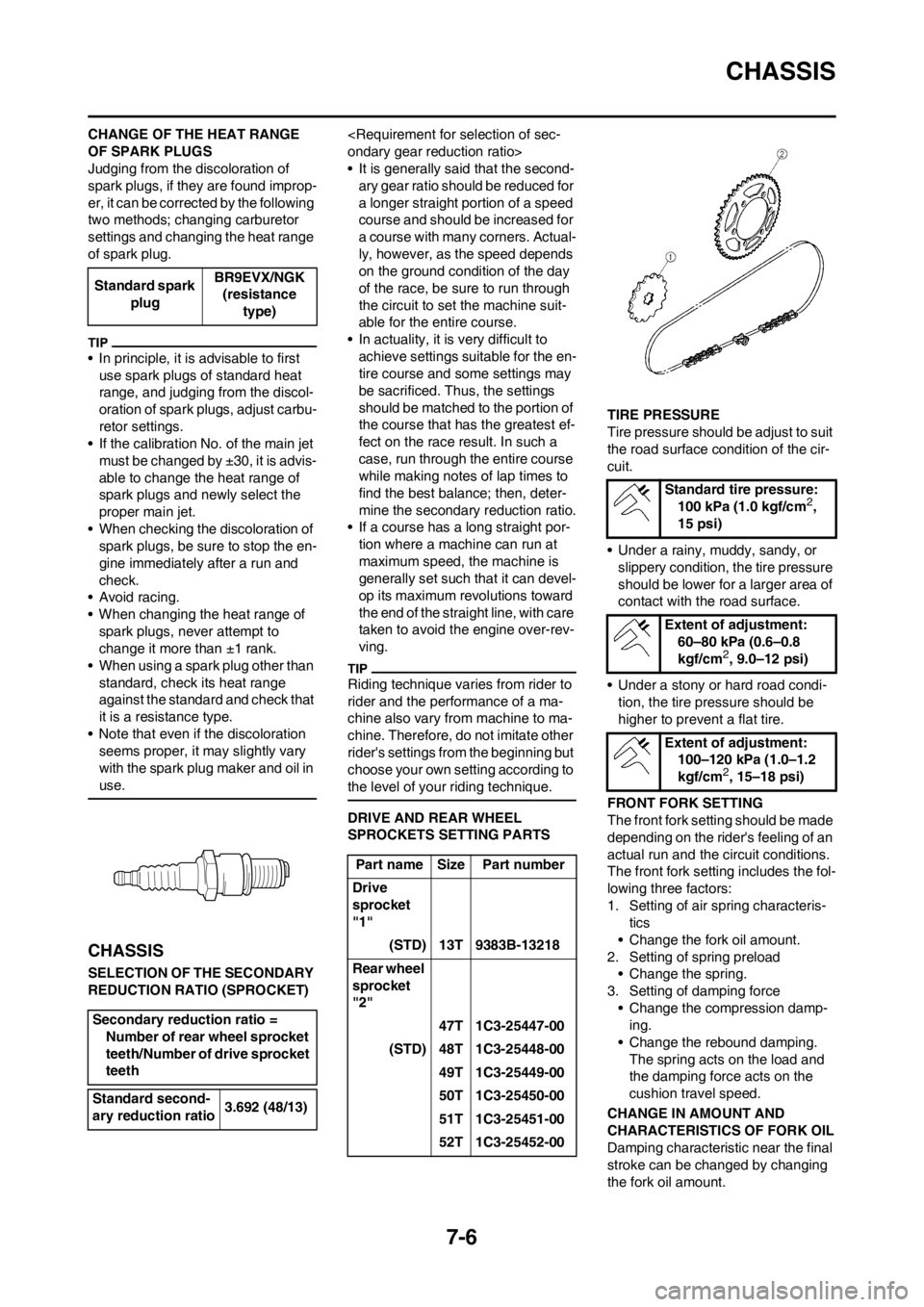
DRIVE AND REAR WHEEL
SPROCKETS SETTING PARTSTIRE PRESSURE
Tire pressure should be adjust to suit
the road surface condition of the cir-
cuit.
• Under a rainy, muddy, sandy, or
slippery condition, the tire pressure
should be lower for a larger area of
contact with the road surface.
• Under a stony or hard road condi-
tion, the tire pressure should be
higher to prevent a flat tire.
FRONT FORK SETTING
The front fork setting should be made
depending on the rider's feeling of an
actual run and the circuit conditions.
The front fork setting includes the fol-
lowing three factors:
1. Setting of air spring characteris-
tics
• Change the fork oil amount.
2. Setting of spring preload
• Change the spring.
3. Setting of damping force
• Change the compression damp-
ing.
• Change the rebound damping.
The spring acts on the load and
the damping force acts on the
cushion travel speed.
CHANGE IN AMOUNT AND
CHARACTERISTICS OF FORK OIL
Damping characteristic near the final
stroke can be changed by changing
the fork oil amount. Standard spark
plugBR9EVX/NGK
(resistance
type)
Secondary reduction ratio =
Number of rear wheel sprocket
teeth/Number of drive sprocket
teeth
Standard second-
ary reduction ratio3.692 (48/13)
Part name Size Part number
Drive
sprocket
"1"
(STD) 13T 9383B-13218
Rear wheel
sprocket
"2"
47T 1C3-25447-00
(STD) 48T 1C3-25448-00
49T 1C3-25449-00
50T 1C3-25450-00
51T 1C3-25451-00
52T 1C3-25452-00
Standard tire pressure:
100 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm2,
15 psi)
Extent of adjustment:
60–80 kPa (0.6–0.8
kgf/cm
2, 9.0–12 psi)
Extent of adjustment:
100–120 kPa (1.0–1.2
kgf/cm
2, 15–18 psi)