YAMAHA YZ250F 2012 Repair Manual
Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2012, Model line: YZ250F, Model: YAMAHA YZ250F 2012Pages: 198, PDF Size: 11.78 MB
Page 61 of 198
3-11
ENGINE
b. Turn the throttle stop screw "1"
until the specified engine idling
speed.
Using a digital engine tachometer for
idle speed adjustment, detect the en-
gine idling speed by bringing the
sensing element "c" of the engine ta-
chometer close to the ignition coil "2".
ADJUSTING THE VALVE
CLEARANCE
• This section is intended for those
who have basic knowledge and skill
concerning the servicing of Yama-
ha motorcycles (e.g., Yamaha deal-
ers, service engineers, etc.) Those
who have little knowledge and skill
concerning servicing are requested
not to undertake inspection, adjust-
ment, disassembly, or reassembly
only by reference to this manual. It
may lead to servicing trouble and
mechanical damage.
• The valve clearance should be ad-
justed when the engine is cool to
the touch.
• The piston must be at Top Dead
Center (T.D.C.) on compression
stroke to check or adjust the valve
clearance.
1. Remove:
•Seat
•Fuel tank
Refer to "SEAT, FUEL TANK
AND SIDE COVERS" section in
the CHAPTER 4.
2. Remove:
• Spark plug
• Cylinder head cover
Refer to "CAMSHAFTS" section
in the CHAPTER 4.
3. Remove:
• Timing mark accessing screw "1"
• Crankshaft end accessing screw
"2"
• O-ring
4. Check:
• Valve clearance
Out of specification→Adjust.
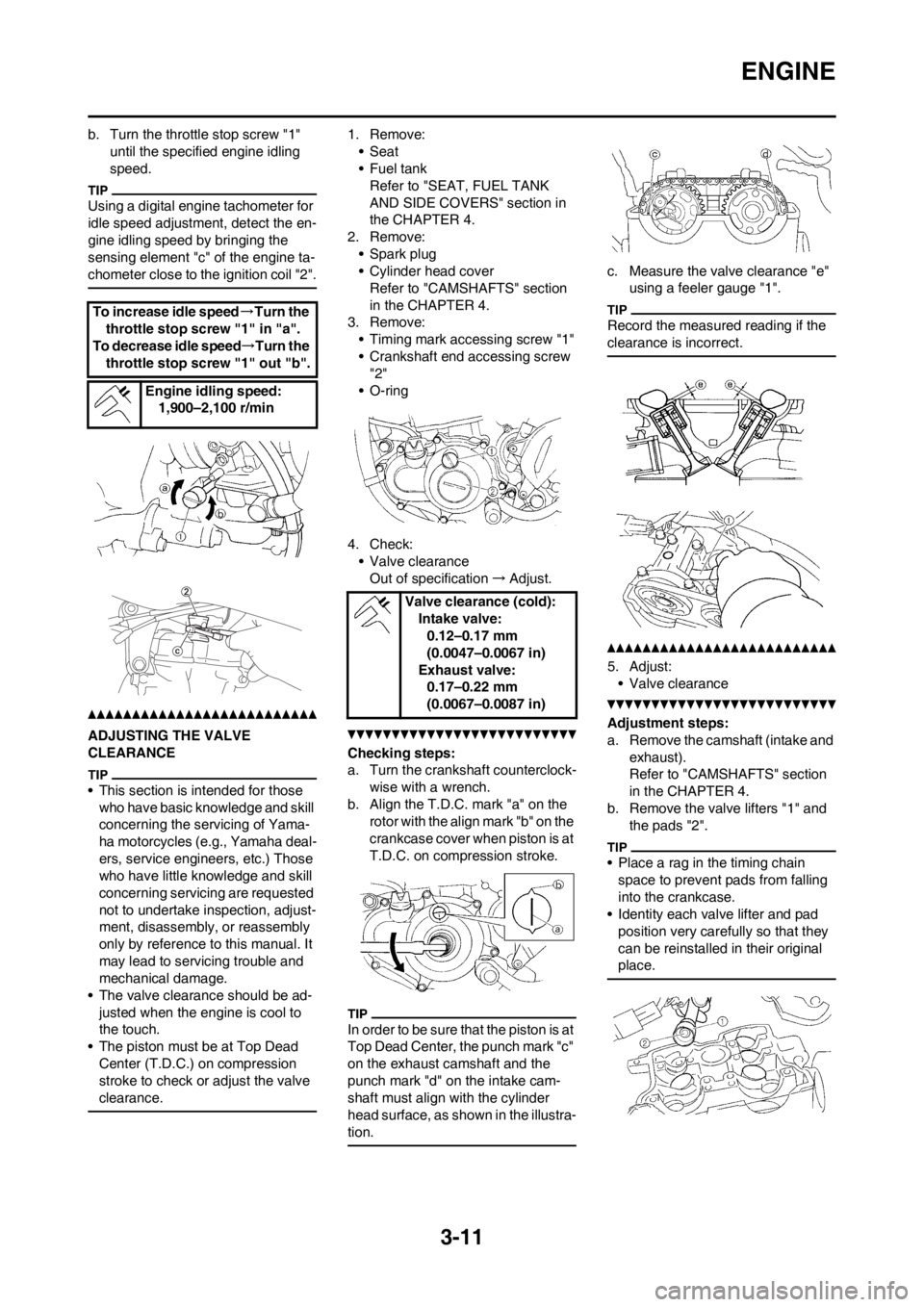
Checking steps:
a. Turn the crankshaft counterclock-
wise with a wrench.
b. Align the T.D.C. mark "a" on the
rotor with the align mark "b" on the
crankcase cover when piston is at
T.D.C. on compression stroke.
In order to be sure that the piston is at
Top Dead Center, the punch mark "c"
on the exhaust camshaft and the
punch mark "d" on the intake cam-
shaft must align with the cylinder
head surface, as shown in the illustra-
tion.
c. Measure the valve clearance "e"
using a feeler gauge "1".
Record the measured reading if the
clearance is incorrect.
5. Adjust:
• Valve clearance
Adjustment steps:
a. Remove the camshaft (intake and
exhaust).
Refer to "CAMSHAFTS" section
in the CHAPTER 4.
b. Remove the valve lifters "1" and
the pads "2".
• Place a rag in the timing chain
space to prevent pads from falling
into the crankcase.
• Identity each valve lifter and pad
position very carefully so that they
can be reinstalled in their original
place.
To increase idle speed→Turn the
throttle stop screw "1" in "a".
To decrease idle speed→Turn the
throttle stop screw "1" out "b".
Engine idling speed:
1,900–2,100 r/min
Valve clearance (cold):
Intake valve:
0.12–0.17 mm
(0.0047–0.0067 in)
Exhaust valve:
0.17–0.22 mm
(0.0067–0.0087 in)
Page 62 of 198
3-12
ENGINE
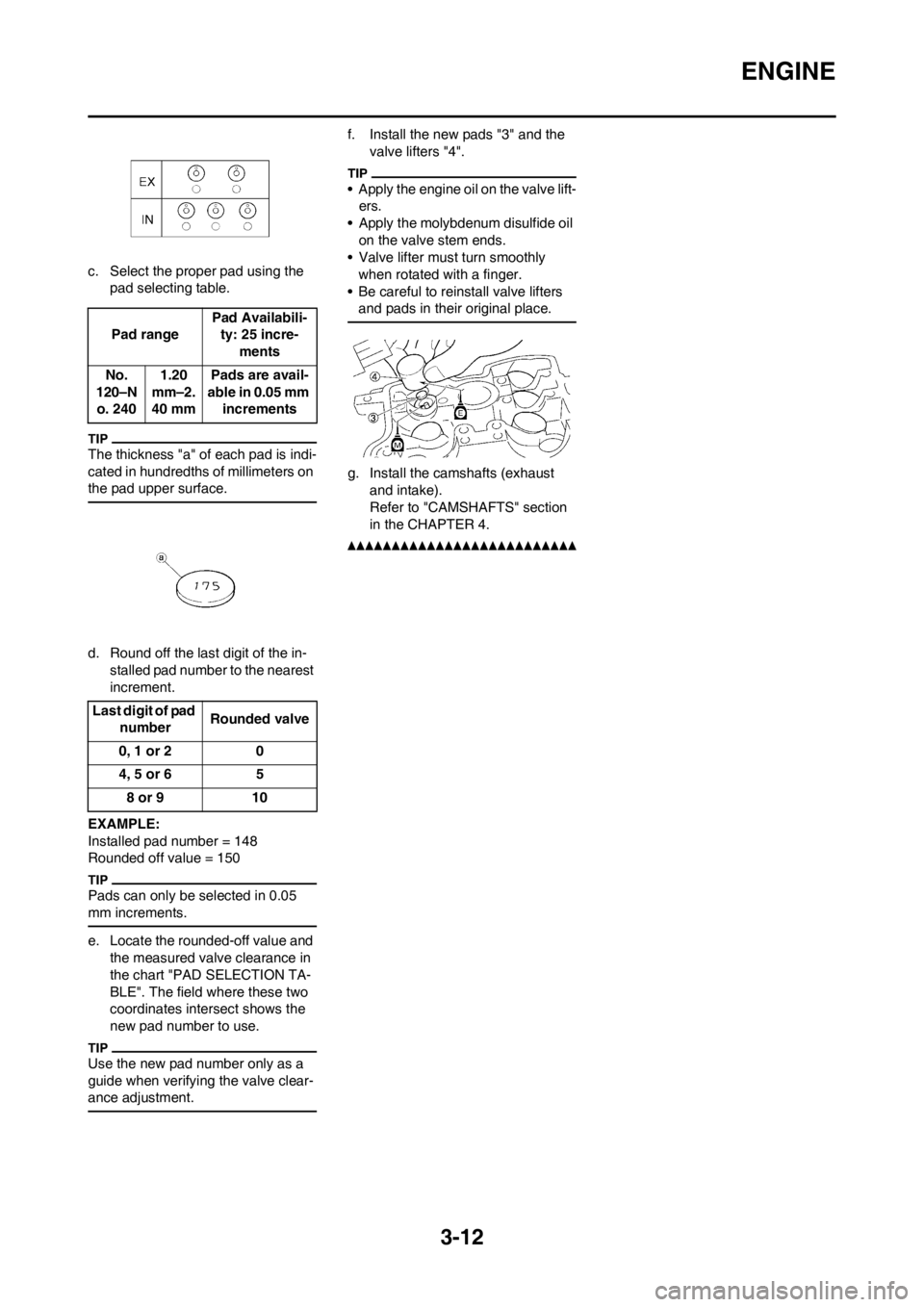
c. Select the proper pad using the
pad selecting table.
The thickness "a" of each pad is indi-
cated in hundredths of millimeters on
the pad upper surface.
d. Round off the last digit of the in-
stalled pad number to the nearest
increment.
EXAMPLE:
Installed pad number = 148
Rounded off value = 150
Pads can only be selected in 0.05
mm increments.
e. Locate the rounded-off value and
the measured valve clearance in
the chart "PAD SELECTION TA-
BLE". The field where these two
coordinates intersect shows the
new pad number to use.
Use the new pad number only as a
guide when verifying the valve clear-
ance adjustment.
f. Install the new pads "3" and the
valve lifters "4".
• Apply the engine oil on the valve lift-
ers.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide oil
on the valve stem ends.
• Valve lifter must turn smoothly
when rotated with a finger.
• Be careful to reinstall valve lifters
and pads in their original place.
g. Install the camshafts (exhaust
and intake).
Refer to "CAMSHAFTS" section
in the CHAPTER 4.
Pad rangePad Availabili-
ty: 25 incre-
ments
No.
120–N
o. 2401.20
mm–2.
40 mmPads are avail-
able in 0.05 mm
increments
Last digit of pad
numberRounded valve
0, 1 or 2 0
4, 5 or 6 5
8 or 9 10
Page 63 of 198

3-13
ENGINE
INTAKE
EXHAUST
120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155 160 165 170175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235 240
0.00 - 0.01
0.02 - 0.06
0.07 - 0.11
0.12 - 0.17
0.18 - 0.22
0.23 - 0.27
0.28 - 0.32
0.33 - 0.37
0.38 - 0.42
0.43 - 0.47
0.48 - 0.52
0.53 - 0.57
0.58 - 0.62
0.63 - 0.67
0.68 - 0.72
0.73 - 0.77
0.78 - 0.82
0.83 - 0.87
0.88 - 0.92
0.93 - 0.97
0.98 - 1.02
1.03 - 1.07
1.08 - 1.12
1.13 - 1.17
1.18 - 1.22
1.23 - 1.27
1.28 - 1.32
120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230120 125 130 135 140 145
150 155 160 165
170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235
125130135140145150155160165170175180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
130135140145150155160165170175180185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
135 140 145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
140 145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235 240
185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235
240
190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
205 210 215 220 225 230 235240
210 215 220 225 230 235240
215 220 225 230 235240
220 225 230 235240
225 230 235240
230 235240
235240
240
150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225
120 125 130 135 140 145
1.33 - 1.37
VALVE CLEARANCE (cold):
0.12 - 0.17 mm
Example: Installed is 175
Measured clearance is 0.23 mm
Replace 175 pad with 185 pad
MEASURED
CLEARANCEINSTALLED PAD NUMBER
STANDARD CLEARANCE
Pad number: (example)
Pad No. 175 = 1.75 mm
Pad No. 185 = 1.85 mm
MEASURED
CLEARANCEINSTALLED PAD NUMBER
120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155 160 165 170
175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230 235 240
0.00 - 0.04 120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155
160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225
0.05 - 0.09
120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155 160165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225 230
0.10 - 0.16
120125130135140145150155160165170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235
0.17 - 0.22STANDARD CLEARANCE
0.23 - 0.25 125 130 135 140 145 150 155 160 165 170 175
180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.26 - 0.30130135140145150155160165170175180185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.31 - 0.35 135 140 145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.36 - 0.40 140 145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.41 - 0.45 145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.46 - 0.50 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.51 - 0.55 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.56 - 0.60 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.61 - 0.65 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.66 - 0.70 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.71 - 0.75 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.76 - 0.80 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.81 - 0.85 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
VALVE CLEARANCE (cold):
0.17 - 0.22 mm
Example: Installed is 175
Measured clearance is 0.27 mm
Replace 175 pad with 185 pad
Pad number: (example)
Pad No. 175 = 1.75 mm
Pad No. 185 = 1.85 mm0.86 - 0.90 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.91 - 0.95 195 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
0.96 - 1.00 200 205 210 215 220 225230235240
1.01 - 1.05 205 210 215 220 225230235240
1.06 - 1.10 210 215 220 225230235240
1.11 - 1.15 215 220 225230235240
1.16 - 1.20 220 225230235240
1.21 - 1.25 225230235240
1.26 - 1.30 230235240
1.31 - 1.35 235240
1.36 - 1.40 240
Page 64 of 198
3-14
CHASSIS
CHASSIS
BLEEDING THE HYDRAULIC
BRAKE SYSTEM
Bleed the brake system if:
• The system has been disassem-
bled.
• A brake hose has been loosened
or removed.
• The brake fluid is very low.
• The brake operation is faulty.
A dangerous loss of braking per-
formance may occur if the brake
system is not properly bled.
1. Remove:
• Brake master cylinder cap
• Diaphragm
• Reservoir float (front brake)
• Protector (rear brake)
2. Bleed:
• Brake fluid
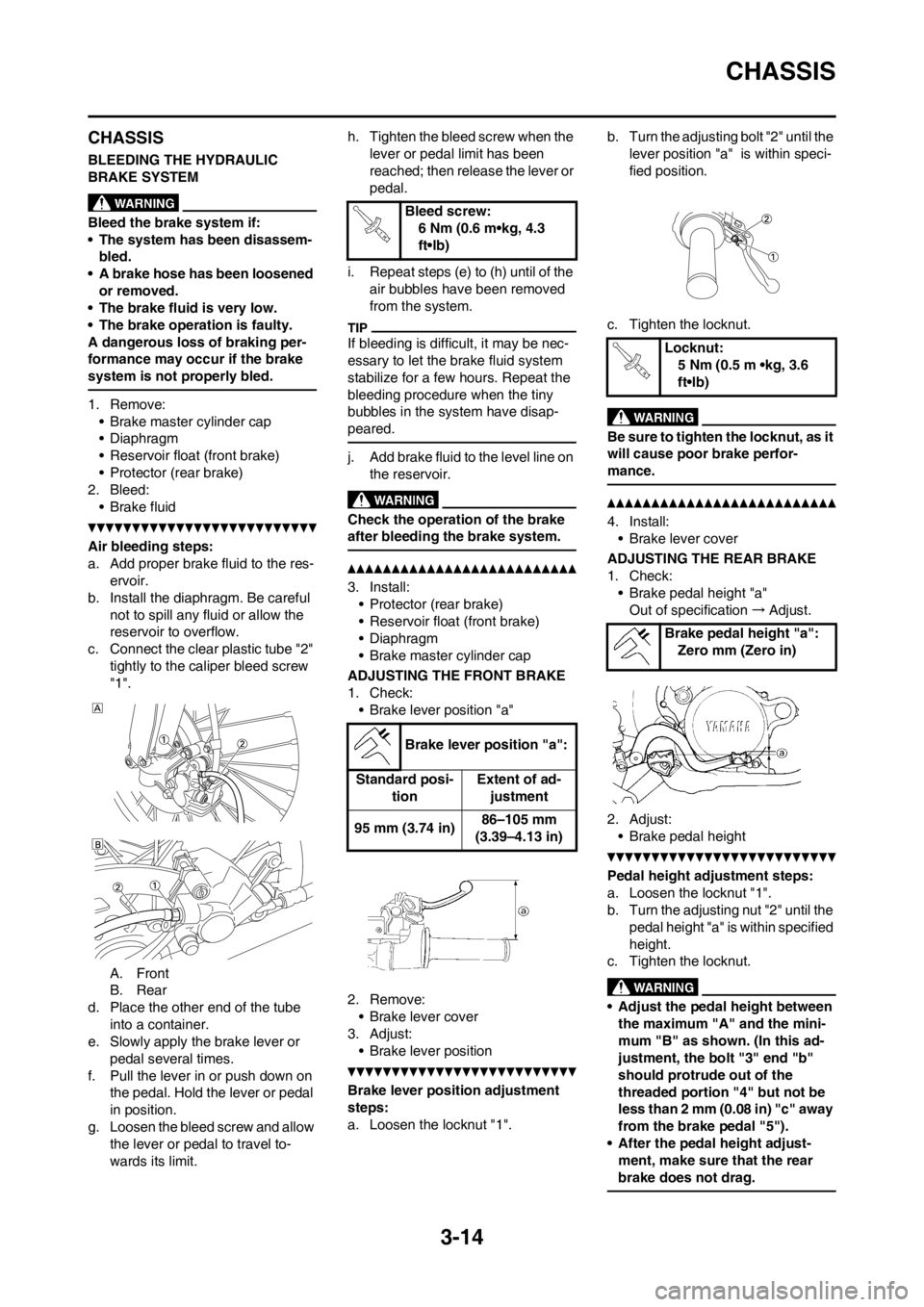
Air bleeding steps:
a. Add proper brake fluid to the res-
ervoir.
b. Install the diaphragm. Be careful
not to spill any fluid or allow the
reservoir to overflow.
c. Connect the clear plastic tube "2"
tightly to the caliper bleed screw
"1".
A. Front
B. Rear
d. Place the other end of the tube
into a container.
e. Slowly apply the brake lever or
pedal several times.
f. Pull the lever in or push down on
the pedal. Hold the lever or pedal
in position.
g. Loosen the bleed screw and allow
the lever or pedal to travel to-
wards its limit.h. Tighten the bleed screw when the
lever or pedal limit has been
reached; then release the lever or
pedal.
i. Repeat steps (e) to (h) until of the
air bubbles have been removed
from the system.
If bleeding is difficult, it may be nec-
essary to let the brake fluid system
stabilize for a few hours. Repeat the
bleeding procedure when the tiny
bubbles in the system have disap-
peared.
j. Add brake fluid to the level line on
the reservoir.
Check the operation of the brake
after bleeding the brake system.
3. Install:
• Protector (rear brake)
• Reservoir float (front brake)
• Diaphragm
• Brake master cylinder cap
ADJUSTING THE FRONT BRAKE
1. Check:
• Brake lever position "a"
2. Remove:
• Brake lever cover
3. Adjust:
• Brake lever position
Brake lever position adjustment
steps:
a. Loosen the locknut "1".b. Turn the adjusting bolt "2" until the
lever position "a" is within speci-
fied position.
c. Tighten the locknut.
Be sure to tighten the locknut, as it
will cause poor brake perfor-
mance.
4. Install:
• Brake lever cover
ADJUSTING THE REAR BRAKE
1. Check:
• Brake pedal height "a"
Out of specification→Adjust.
2. Adjust:
• Brake pedal height
Pedal height adjustment steps:
a. Loosen the locknut "1".
b. Turn the adjusting nut "2" until the
pedal height "a" is within specified
height.
c. Tighten the locknut.
• Adjust the pedal height between
the maximum "A" and the mini-
mum "B" as shown. (In this ad-
justment, the bolt "3" end "b"
should protrude out of the
threaded portion "4" but not be
less than 2 mm (0.08 in) "c" away
from the brake pedal "5").
• After the pedal height adjust-
ment, make sure that the rear
brake does not drag.
Bleed screw:
6 Nm (0.6 m•kg, 4.3
ft•lb)
Brake lever position "a":
Standard posi-
tionExtent of ad-
justment
95 mm (3.74 in)86–105 mm
(3.39–4.13 in)
Locknut:
5 Nm (0.5 m •kg, 3.6
ft•lb)
Brake pedal height "a":
Zero mm (Zero in)
Page 65 of 198
3-15
CHASSIS
CHECKING AND REPLACING THE
FRONT BRAKE PADS
1. Inspect:
• Brake pad thickness "a"
Out of specification→Replace as
a set.
2. Replace:
• Brake pad
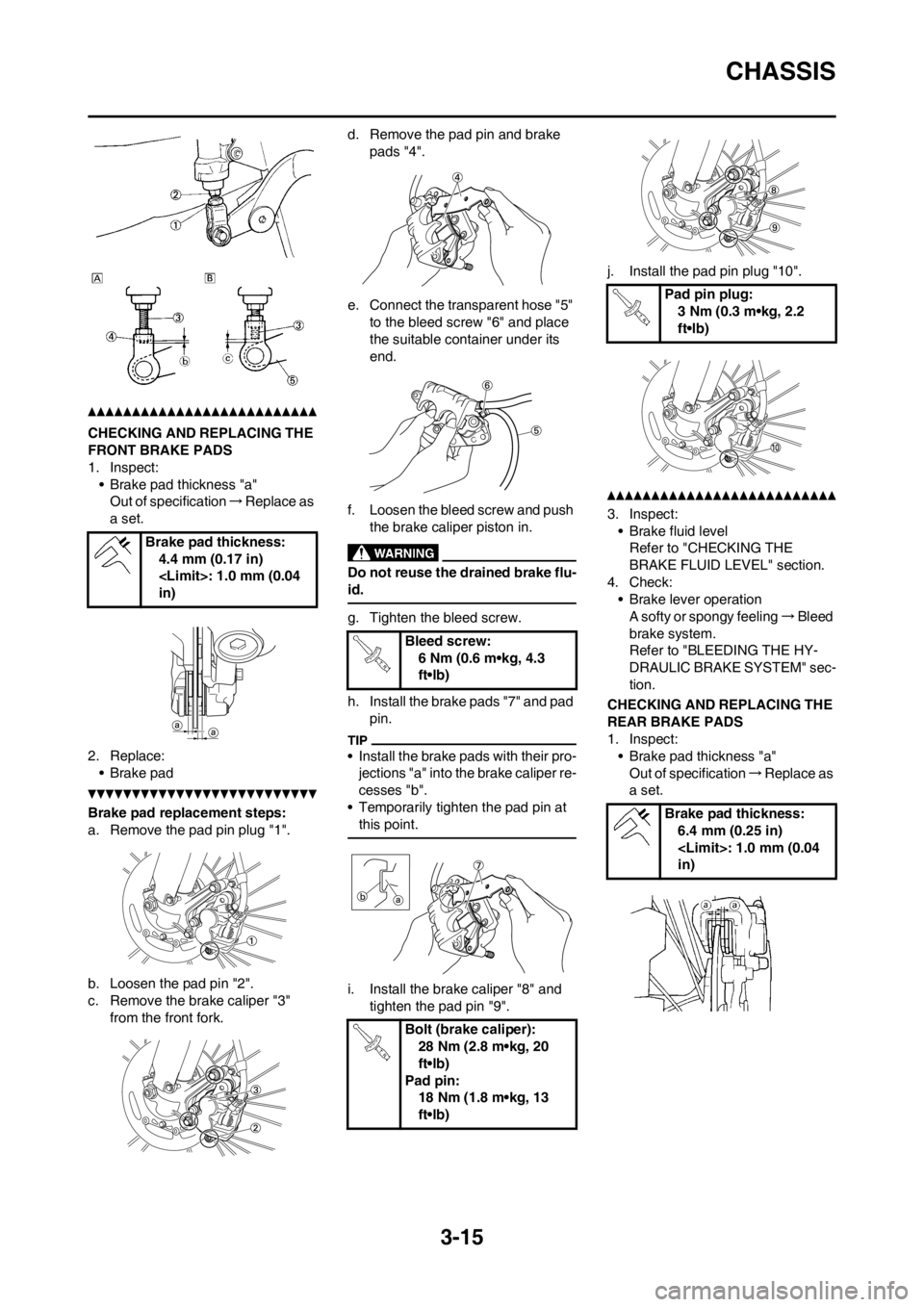
Brake pad replacement steps:
a. Remove the pad pin plug "1".
b. Loosen the pad pin "2".
c. Remove the brake caliper "3"
from the front fork.d. Remove the pad pin and brake
pads "4".
e. Connect the transparent hose "5"
to the bleed screw "6" and place
the suitable container under its
end.
f. Loosen the bleed screw and push
the brake caliper piston in.
Do not reuse the drained brake flu-
id.
g. Tighten the bleed screw.
h. Install the brake pads "7" and pad
pin.
• Install the brake pads with their pro-
jections "a" into the brake caliper re-
cesses "b".
• Temporarily tighten the pad pin at
this point.
i. Install the brake caliper "8" and
tighten the pad pin "9".j. Install the pad pin plug "10".
3. Inspect:
• Brake fluid level
Refer to "CHECKING THE
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL" section.
4. Check:
• Brake lever operation
A softy or spongy feeling→Bleed
brake system.
Refer to "BLEEDING THE HY-
DRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM" sec-
tion.
CHECKING AND REPLACING THE
REAR BRAKE PADS
1. Inspect:
• Brake pad thickness "a"
Out of specification→Replace as
a set. Brake pad thickness:
4.4 mm (0.17 in)
in)
Bleed screw:
6 Nm (0.6 m•kg, 4.3
ft•lb)
Bolt (brake caliper):
28 Nm (2.8 m•kg, 20
ft•lb)
Pad pin:
18 Nm (1.8 m•kg, 13
ft•lb)
Pad pin plug:
3 Nm (0.3 m•kg, 2.2
ft•lb)
Brake pad thickness:
6.4 mm (0.25 in)
in)
Page 66 of 198
3-16
CHASSIS
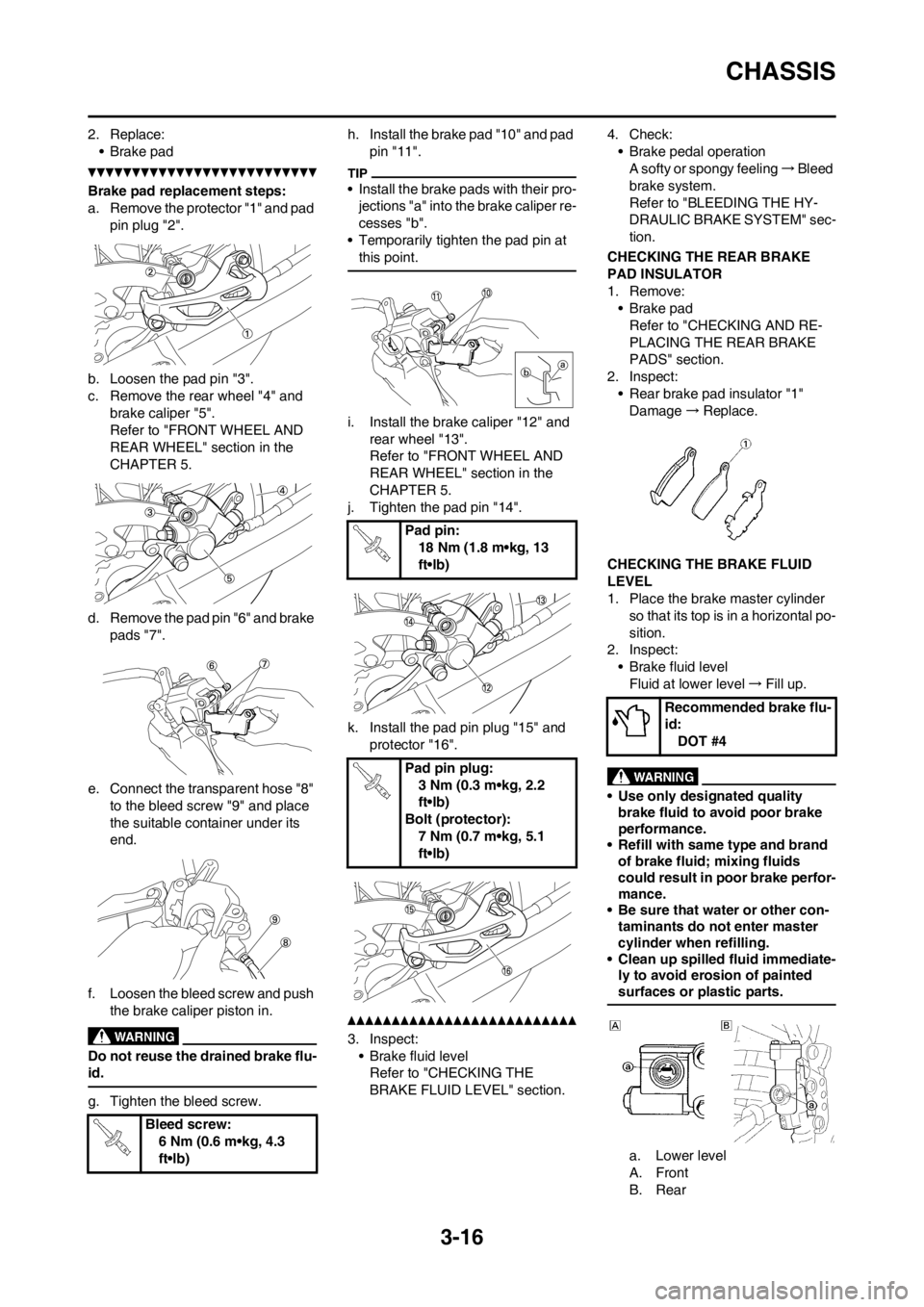
2. Replace:
• Brake pad
Brake pad replacement steps:
a. Remove the protector "1" and pad
pin plug "2".
b. Loosen the pad pin "3".
c. Remove the rear wheel "4" and
brake caliper "5".
Refer to "FRONT WHEEL AND
REAR WHEEL" section in the
CHAPTER 5.
d. Remove the pad pin "6" and brake
pads "7".
e. Connect the transparent hose "8"
to the bleed screw "9" and place
the suitable container under its
end.
f. Loosen the bleed screw and push
the brake caliper piston in.
Do not reuse the drained brake flu-
id.
g. Tighten the bleed screw.h. Install the brake pad "10" and pad
pin "11".
• Install the brake pads with their pro-
jections "a" into the brake caliper re-
cesses "b".
• Temporarily tighten the pad pin at
this point.
i. Install the brake caliper "12" and
rear wheel "13".
Refer to "FRONT WHEEL AND
REAR WHEEL" section in the
CHAPTER 5.
j. Tighten the pad pin "14".
k. Install the pad pin plug "15" and
protector "16".
3. Inspect:
• Brake fluid level
Refer to "CHECKING THE
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL" section.4. Check:
• Brake pedal operation
A softy or spongy feeling→Bleed
brake system.
Refer to "BLEEDING THE HY-
DRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM" sec-
tion.
CHECKING THE REAR BRAKE
PAD INSULATOR
1. Remove:
• Brake pad
Refer to "CHECKING AND RE-
PLACING THE REAR BRAKE
PADS" section.
2. Inspect:
• Rear brake pad insulator "1"
Damage→Replace.
CHECKING THE BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL
1. Place the brake master cylinder
so that its top is in a horizontal po-
sition.
2. Inspect:
• Brake fluid level
Fluid at lower level→Fill up.
• Use only designated quality
brake fluid to avoid poor brake
performance.
• Refill with same type and brand
of brake fluid; mixing fluids
could result in poor brake perfor-
mance.
• Be sure that water or other con-
taminants do not enter master
cylinder when refilling.
• Clean up spilled fluid immediate-
ly to avoid erosion of painted
surfaces or plastic parts.
a. Lower level
A. Front
B. Rear Bleed screw:
6 Nm (0.6 m•kg, 4.3
ft•lb)
Pad pin:
18 Nm (1.8 m•kg, 13
ft•lb)
Pad pin plug:
3 Nm (0.3 m•kg, 2.2
ft•lb)
Bolt (protector):
7 Nm (0.7 m•kg, 5.1
ft•lb)
Recommended brake flu-
id:
DOT #4
Page 67 of 198
3-17
CHASSIS
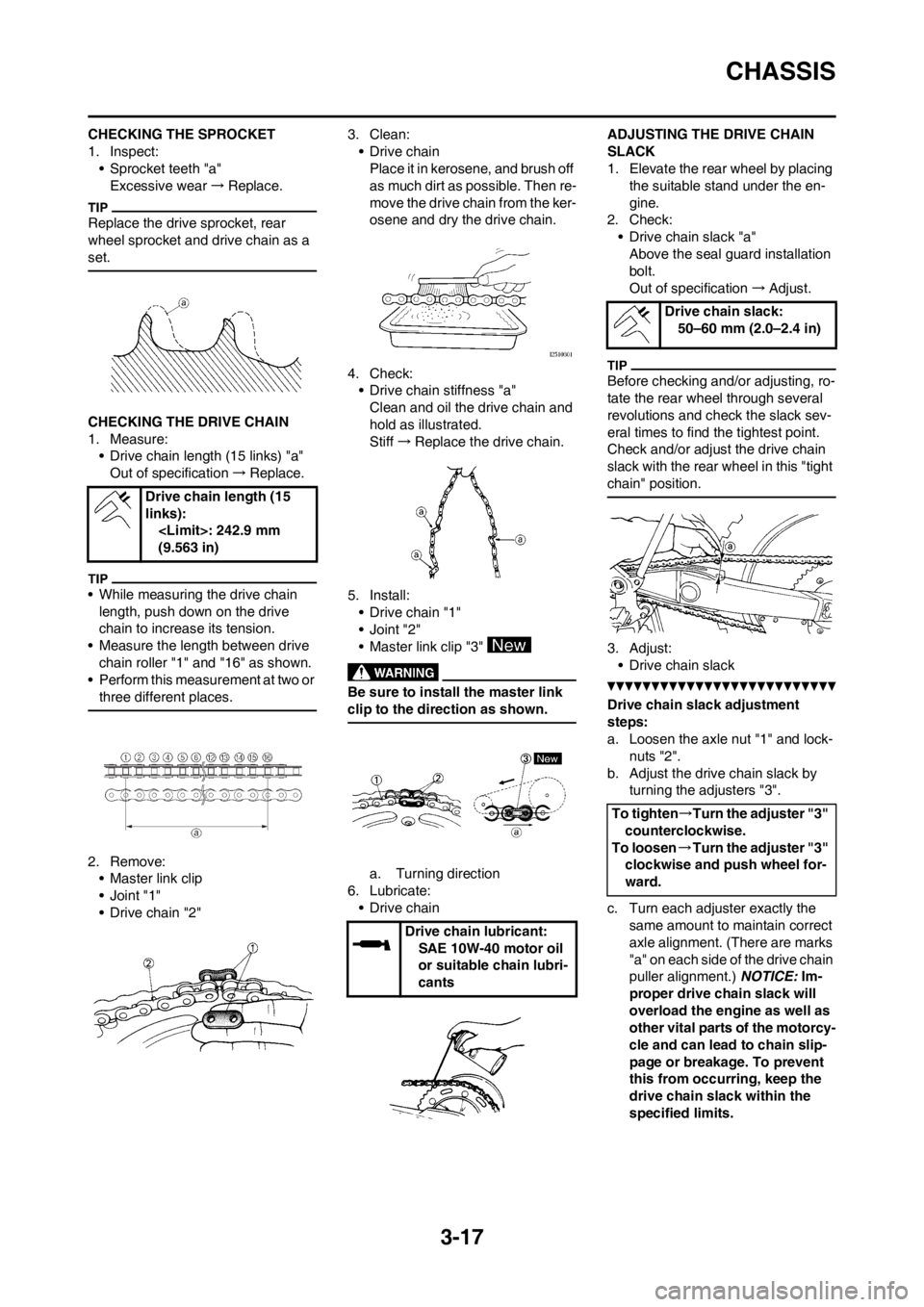
CHECKING THE SPROCKET
1. Inspect:
• Sprocket teeth "a"
Excessive wear→Replace.
Replace the drive sprocket, rear
wheel sprocket and drive chain as a
set.
CHECKING THE DRIVE CHAIN
1. Measure:
• Drive chain length (15 links) "a"
Out of specification→Replace.
• While measuring the drive chain
length, push down on the drive
chain to increase its tension.
• Measure the length between drive
chain roller "1" and "16" as shown.
• Perform this measurement at two or
three different places.
2. Remove:
• Master link clip
•Joint "1"
• Drive chain "2"3. Clean:
• Drive chain
Place it in kerosene, and brush off
as much dirt as possible. Then re-
move the drive chain from the ker-
osene and dry the drive chain.
4. Check:
• Drive chain stiffness "a"
Clean and oil the drive chain and
hold as illustrated.
Stiff→Replace the drive chain.
5. Install:
• Drive chain "1"
•Joint "2"
• Master link clip "3"
Be sure to install the master link
clip to the direction as shown.
a. Turning direction
6. Lubricate:
• Drive chainADJUSTING THE DRIVE CHAIN
SLACK
1. Elevate the rear wheel by placing
the suitable stand under the en-
gine.
2. Check:
• Drive chain slack "a"
Above the seal guard installation
bolt.
Out of specification→Adjust.
Before checking and/or adjusting, ro-
tate the rear wheel through several
revolutions and check the slack sev-
eral times to find the tightest point.
Check and/or adjust the drive chain
slack with the rear wheel in this "tight
chain" position.
3. Adjust:
• Drive chain slack
Drive chain slack adjustment
steps:
a. Loosen the axle nut "1" and lock-
nuts "2".
b. Adjust the drive chain slack by
turning the adjusters "3".
c. Turn each adjuster exactly the
same amount to maintain correct
axle alignment. (There are marks
"a" on each side of the drive chain
puller alignment.) NOTICE: Im-
proper drive chain slack will
overload the engine as well as
other vital parts of the motorcy-
cle and can lead to chain slip-
page or breakage. To prevent
this from occurring, keep the
drive chain slack within the
specified limits. Drive chain length (15
links):
(9.563 in)
Drive chain lubricant:
SAE 10W-40 motor oil
or suitable chain lubri-
cants
Drive chain slack:
50–60 mm (2.0–2.4 in)
To tighten→Turn the adjuster "3"
counterclockwise.
To loosen→Turn the adjuster "3"
clockwise and push wheel for-
ward.
Page 68 of 198
3-18
CHASSIS
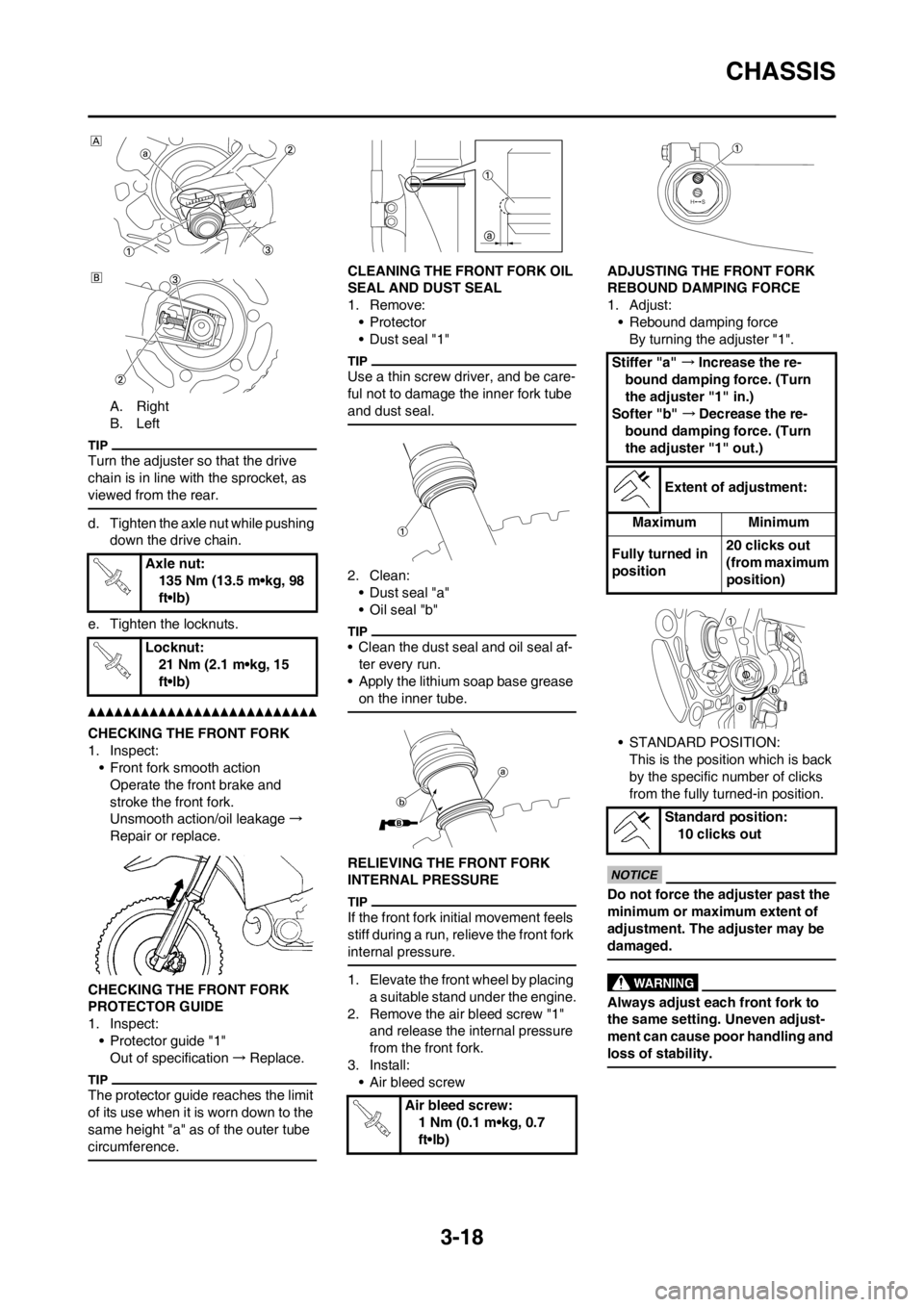
A. Right
B. Left
Turn the adjuster so that the drive
chain is in line with the sprocket, as
viewed from the rear.
d. Tighten the axle nut while pushing
down the drive chain.
e. Tighten the locknuts.
CHECKING THE FRONT FORK
1. Inspect:
• Front fork smooth action
Operate the front brake and
stroke the front fork.
Unsmooth action/oil leakage→
Repair or replace.
CHECKING THE FRONT FORK
PROTECTOR GUIDE
1. Inspect:
• Protector guide "1"
Out of specification→Replace.
The protector guide reaches the limit
of its use when it is worn down to the
same height "a" as of the outer tube
circumference.
CLEANING THE FRONT FORK OIL
SEAL AND DUST SEAL
1. Remove:
•Protector
• Dust seal "1"
Use a thin screw driver, and be care-
ful not to damage the inner fork tube
and dust seal.
2. Clean:
• Dust seal "a"
• Oil seal "b"
• Clean the dust seal and oil seal af-
ter every run.
• Apply the lithium soap base grease
on the inner tube.
RELIEVING THE FRONT FORK
INTERNAL PRESSURE
If the front fork initial movement feels
stiff during a run, relieve the front fork
internal pressure.
1. Elevate the front wheel by placing
a suitable stand under the engine.
2. Remove the air bleed screw "1"
and release the internal pressure
from the front fork.
3. Install:
• Air bleed screwADJUSTING THE FRONT FORK
REBOUND DAMPING FORCE
1. Adjust:
• Rebound damping force
By turning the adjuster "1".
• STANDARD POSITION:
This is the position which is back
by the specific number of clicks
from the fully turned-in position.
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
Always adjust each front fork to
the same setting. Uneven adjust-
ment can cause poor handling and
loss of stability.
Axle nut:
135 Nm (13.5 m•kg, 98
ft•lb)
Locknut:
21 Nm (2.1 m•kg, 15
ft•lb)
Air bleed screw:
1 Nm (0.1 m•kg, 0.7
ft•lb)
Stiffer "a" →Increase the re-
bound damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" →Decrease the re-
bound damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position20 clicks out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position:
10 clicks out
Page 69 of 198
3-19
CHASSIS
ADJUSTING THE FRONT FORK
COMPRESSION DAMPING FORCE
2. Adjust:
• Compression damping force
By turning the adjuster "1".
• STANDARD POSITION:
This is the position which is back
by the specific number of clicks
from the fully turned-in position.
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
Always adjust each front fork to
the same setting. Uneven adjust-
ment can cause poor handling and
loss of stability.
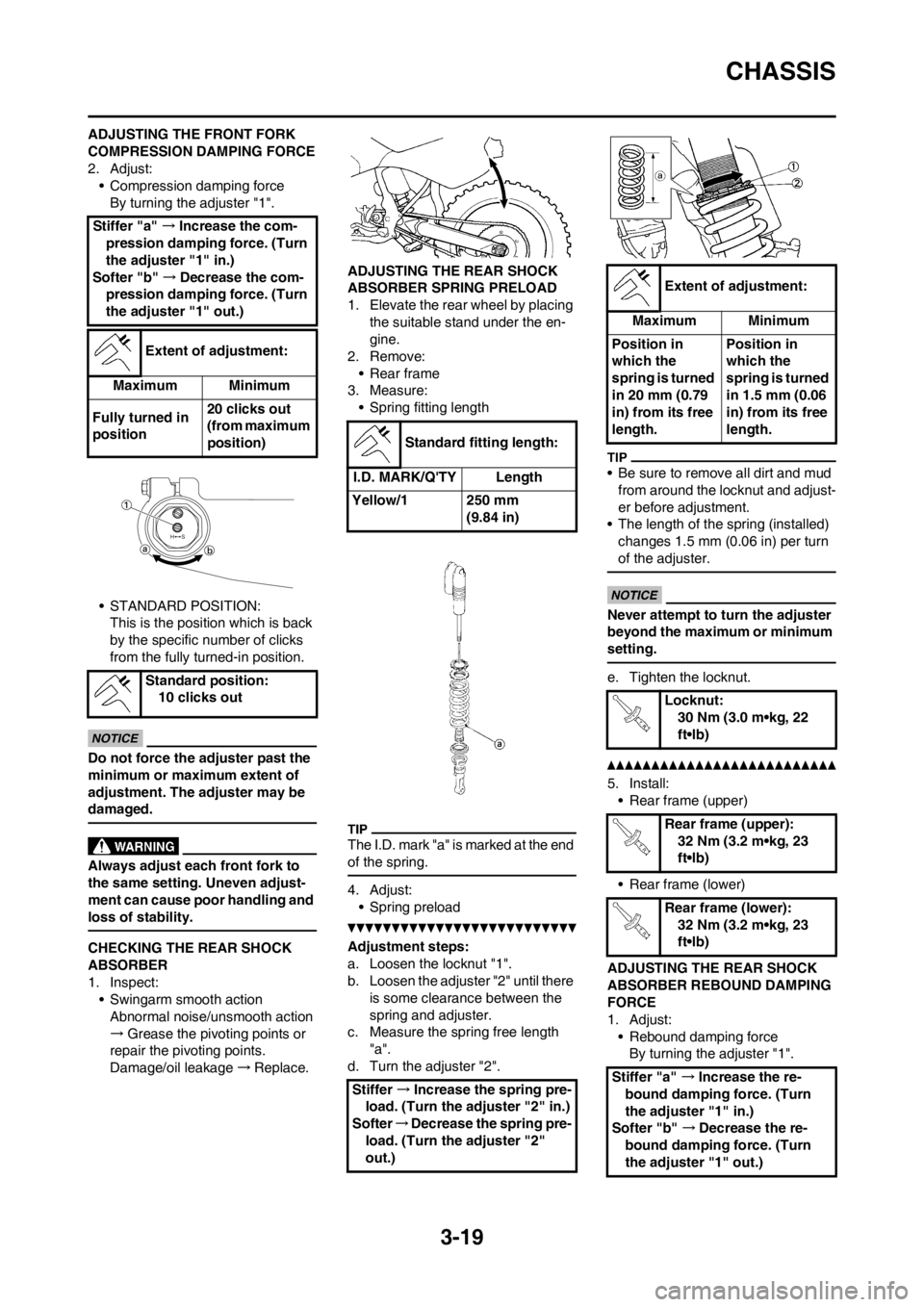
CHECKING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER
1. Inspect:
• Swingarm smooth action
Abnormal noise/unsmooth action
→Grease the pivoting points or
repair the pivoting points.
Damage/oil leakage→Replace.ADJUSTING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER SPRING PRELOAD
1. Elevate the rear wheel by placing
the suitable stand under the en-
gine.
2. Remove:
• Rear frame
3. Measure:
• Spring fitting length
The I.D. mark "a" is marked at the end
of the spring.
4. Adjust:
• Spring preload
Adjustment steps:
a. Loosen the locknut "1".
b. Loosen the adjuster "2" until there
is some clearance between the
spring and adjuster.
c. Measure the spring free length
"a".
d. Turn the adjuster "2".
• Be sure to remove all dirt and mud
from around the locknut and adjust-
er before adjustment.
• The length of the spring (installed)
changes 1.5 mm (0.06 in) per turn
of the adjuster.
Never attempt to turn the adjuster
beyond the maximum or minimum
setting.
e. Tighten the locknut.
5. Install:
• Rear frame (upper)
• Rear frame (lower)
ADJUSTING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER REBOUND DAMPING
FORCE
1. Adjust:
• Rebound damping force
By turning the adjuster "1". Stiffer "a" →Increase the com-
pression damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" →Decrease the com-
pression damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position20 clicks out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position:
10 clicks out
Standard fitting length:
I.D. MARK/Q'TY Length
Yellow/1 250 mm
(9.84 in)
Stiffer →Increase the spring pre-
load. (Turn the adjuster "2" in.)
Softer→Decrease the spring pre-
load. (Turn the adjuster "2"
out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Position in
which the
spring is turned
in 20 mm (0.79
in) from its free
length.Position in
which the
spring is turned
in 1.5 mm (0.06
in) from its free
length.
Locknut:
30 Nm (3.0 m•kg, 22
ft•lb)
Rear frame (upper):
32 Nm (3.2 m•kg, 23
ft•lb)
Rear frame (lower):
32 Nm (3.2 m•kg, 23
ft•lb)
Stiffer "a" →Increase the re-
bound damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" →Decrease the re-
bound damping force. (Turn
the adjuster "1" out.)
Page 70 of 198
3-20
CHASSIS
• STANDARD POSITION:
This is the position which is back
by the specific number of clicks
from the fully turned-in position.
(Which align the punch mark "a"
on the adjuster with the punch
mark "b" on the bracket.)
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
ADJUSTING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER LOW COMPRESSION
DAMPING FORCE
1. Adjust:
• Low compression damping force
By turning the adjuster "1".• STANDARD POSITION:
This is the position which is back
by the specific number of clicks
from the fully turned-in position.
(Which align the punch mark "a"
on the adjuster with the punch
mark "b" on the high compression
damping adjuster.)
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
ADJUSTING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER HIGH COMPRESSION
DAMPING FORCE
1. Adjust:
• High compression damping force
By turning the adjuster "1".• STANDARD POSITION:
This is the position which is back
by the specific number of turns
from the fully turned-in position.
(Which align the punch mark "a"
on the adjuster with the punch
mark "b" on the adjuster body.)
Do not force the adjuster past the
minimum or maximum extent of
adjustment. The adjuster may be
damaged.
CHECKING THE TIRE PRESSURE
1. Measure:
• Tire pressure
Out of specification→Adjust.
• Check the tire while it is cold.
• Loose bead stoppers allow the tire
to slip off its position on the rim
when the tire pressure is low.
• A tilted tire valve stem indicates that
the tire slips off its position on the
rim.
• If the tire valve stem is found tilted,
the tire is considered to be slipping
off its position. Correct the tire posi-
tion.
CHECKING AND TIGHTENING THE
SPOKES
The following procedure applies to all
of the spokes.
1. Check:
• Spokes
Bend/damage→Replace.
Loose spoke→Retighten.
Tap the spokes with a screw-
driver. Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position20 clicks out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position:
13–16 clicks out
Stiffer "a" →Increase the low
compression damping force.
(Turn the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" →Decrease the low
compression damping force.
(Turn the adjuster "1" out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position20 clicks out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position
7–10 clicks out
Stiffer "a" →Increase the high
compression damping force.
(Turn the adjuster "1" in.)
Softer "b" →Decrease the high
compression damping force.
(Turn the adjuster "1" out.)
Extent of adjustment:
Maximum Minimum
Fully turned in
position2 turns out
(from maximum
position)
Standard position:
1-3/4 ± 1/6 turns out
Standard tire pressure:
100 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm
2,
15 psi)