head YAMAHA YZ250F 2015 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2015, Model line: YZ250F, Model: YAMAHA YZ250F 2015Pages: 356, PDF Size: 11.39 MB
Page 216 of 356
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
5-23
EAS1SM5221REMOVING THE VALVES
TIP
Before removing the internal parts of the cylin-
der head (e.g., valves, valve springs, valve
seats), make sure that the valves are properly
sealed.
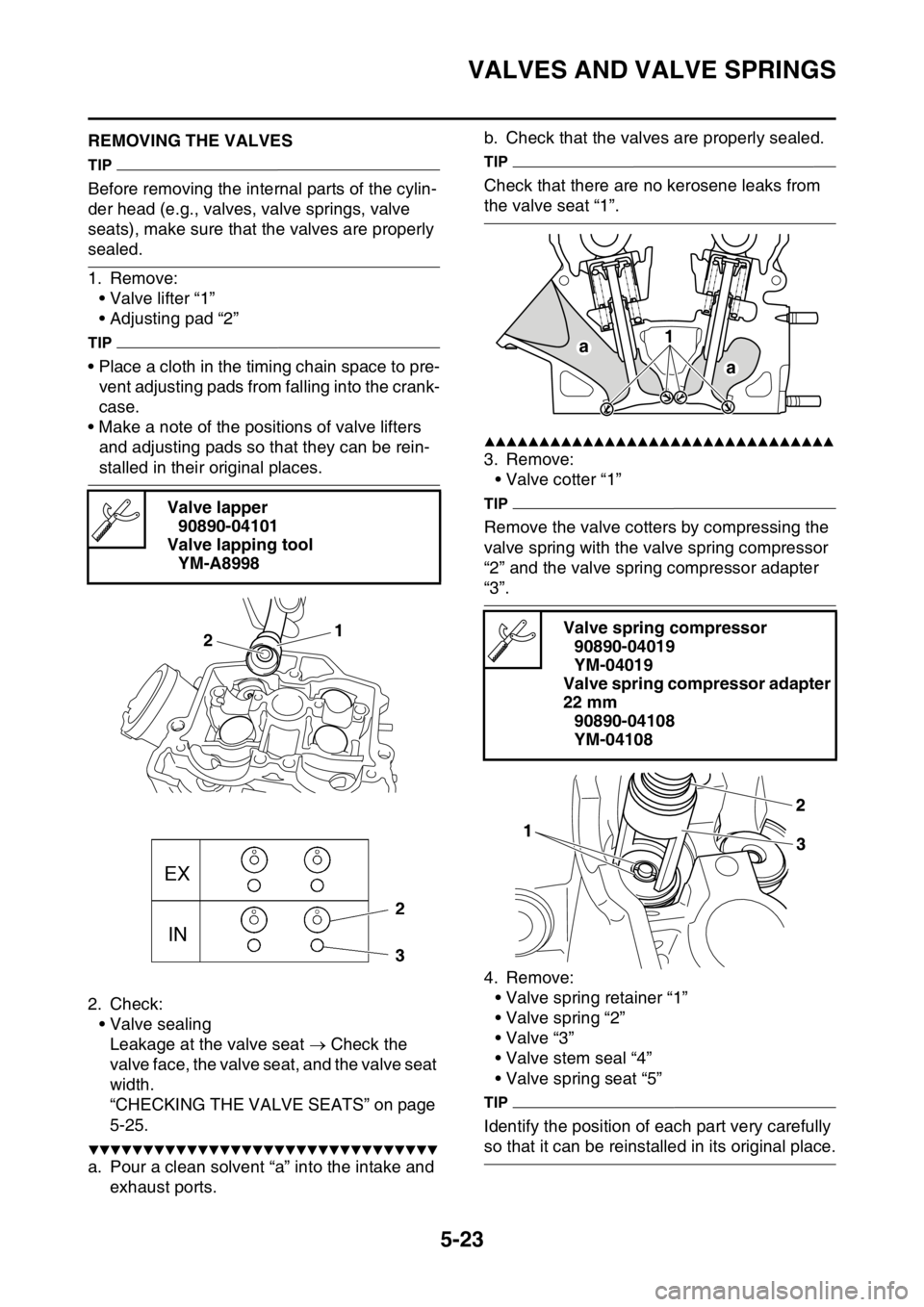
1. Remove:
• Valve lifter “1”
• Adjusting pad “2”
TIP
• Place a cloth in the timing chain space to pre-
vent adjusting pads from falling into the crank-
case.
• Make a note of the positions of valve lifters
and adjusting pads so that they can be rein-
stalled in their original places.
2. Check:
• Valve sealing
Leakage at the valve seat Check the
valve face, the valve seat, and the valve seat
width.
“CHECKING THE VALVE SEATS” on page
5-25.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Pour a clean solvent “a” into the intake and
exhaust ports.b. Check that the valves are properly sealed.
TIP
Check that there are no kerosene leaks from
the valve seat “1”.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
3. Remove:
• Valve cotter “1”
TIP
Remove the valve cotters by compressing the
valve spring with the valve spring compressor
“2” and the valve spring compressor adapter
“3”.
4. Remove:
• Valve spring retainer “1”
• Valve spring “2”
•Valve “3”
• Valve stem seal “4”
• Valve spring seat “5”
TIP
Identify the position of each part very carefully
so that it can be reinstalled in its original place. Valve lapper
90890-04101
Valve lapping tool
YM-A8998
1
2Valve spring compressor
90890-04019
YM-04019
Valve spring compressor adapter
22 mm
90890-04108
YM-04108
a1
a
Page 217 of 356
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
5-24
EAS1SM5222CHECKING THE VALVES AND VALVE
GUIDES
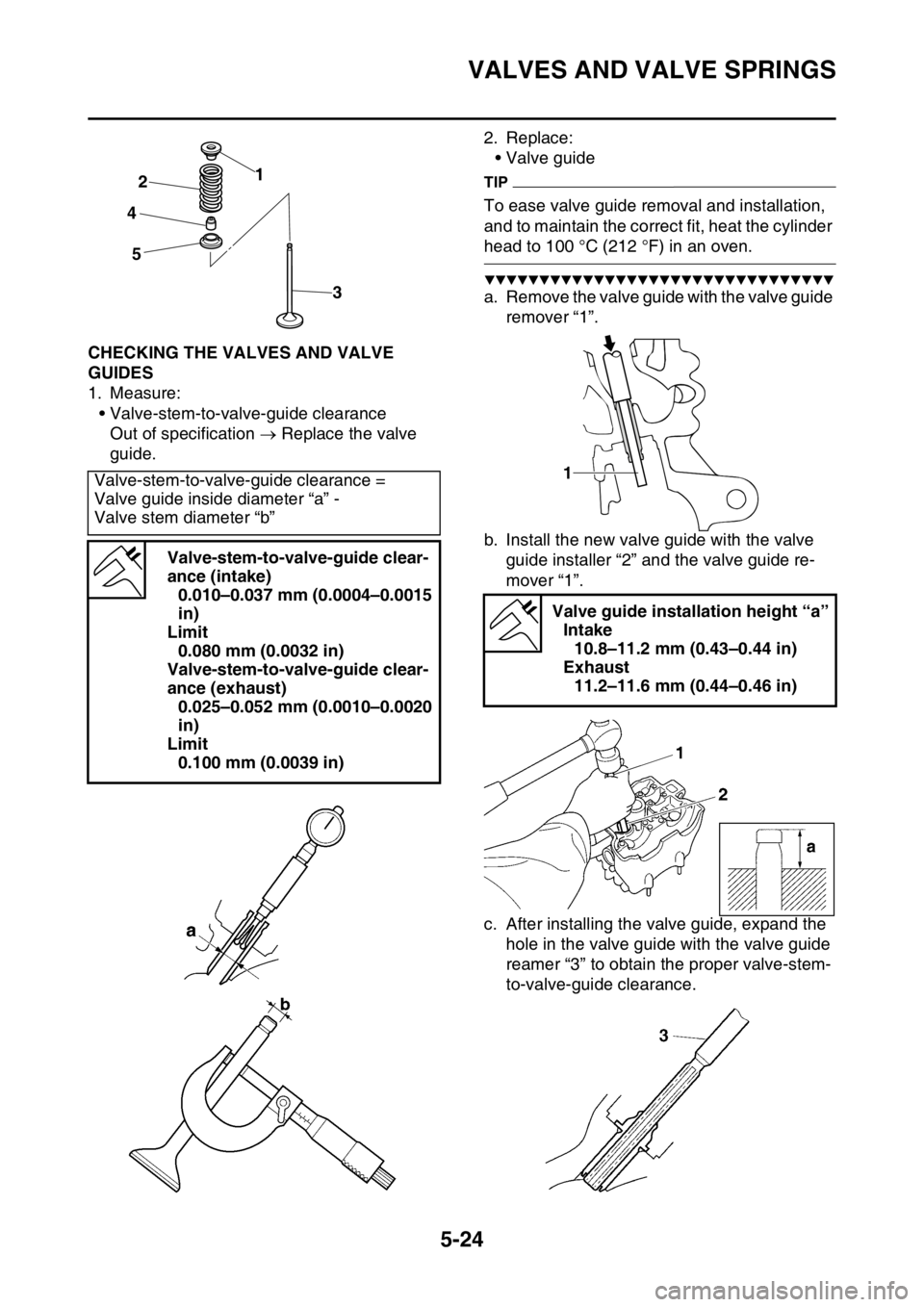
1. Measure:
• Valve-stem-to-valve-guide clearance
Out of specification Replace the valve
guide.2. Replace:
• Valve guide
TIP
To ease valve guide removal and installation,
and to maintain the correct fit, heat the cylinder
head to 100 °C (212 °F) in an oven.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Remove the valve guide with the valve guide
remover “1”.
b. Install the new valve guide with the valve
guide installer “2” and the valve guide re-
mover “1”.
c. After installing the valve guide, expand the
hole in the valve guide with the valve guide
reamer “3” to obtain the proper valve-stem-
to-valve-guide clearance. Valve-stem-to-valve-guide clearance =
Valve guide inside diameter “a” -
Valve stem diameter “b”
Valve-stem-to-valve-guide clear-
ance (intake)
0.010–0.037 mm (0.0004–0.0015
in)
Limit
0.080 mm (0.0032 in)
Valve-stem-to-valve-guide clear-
ance (exhaust)
0.025–0.052 mm (0.0010–0.0020
in)
Limit
0.100 mm (0.0039 in)
1
2
4
5
3
Valve guide installation height “a”
Intake
10.8–11.2 mm (0.43–0.44 in)
Exhaust
11.2–11.6 mm (0.44–0.46 in)
1
Page 218 of 356
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
5-25
TIP
After replacing the valve guide, reface the valve
seat.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
3. Eliminate:
• Carbon deposits
(from the valve face and valve seat)
4. Check:
• Valve face
Pitting/wear Grind the valve face.
• Valve stem end
Mushroom shape or diameter larger than
the body of the valve stem Replace the
valve.
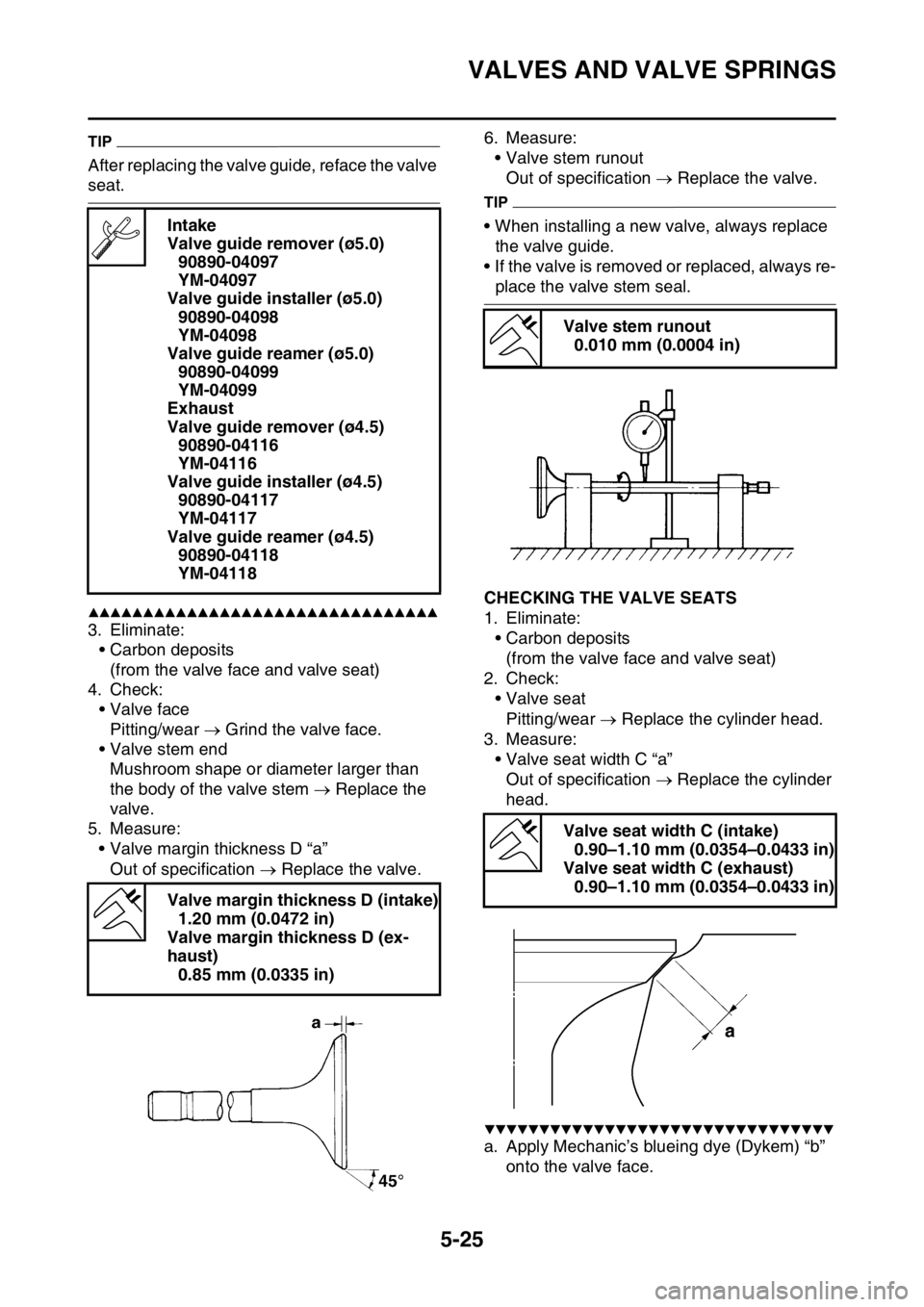
5. Measure:
• Valve margin thickness D “a”
Out of specification Replace the valve.6. Measure:
• Valve stem runout
Out of specification Replace the valve.
TIP
• When installing a new valve, always replace
the valve guide.
• If the valve is removed or replaced, always re-
place the valve stem seal.
EAS1SM5223CHECKING THE VALVE SEATS
1. Eliminate:
• Carbon deposits
(from the valve face and valve seat)
2. Check:
• Valve seat
Pitting/wear Replace the cylinder head.
3. Measure:
• Valve seat width C “a”
Out of specification Replace the cylinder
head.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Apply Mechanic’s blueing dye (Dykem) “b”
onto the valve face. Intake
Valve guide remover (ø5.0)
90890-04097
YM-04097
Valve guide installer (ø5.0)
90890-04098
YM-04098
Valve guide reamer (ø5.0)
90890-04099
YM-04099
Exhaust
Valve guide remover (ø4.5)
90890-04116
YM-04116
Valve guide installer (ø4.5)
90890-04117
YM-04117
Valve guide reamer (ø4.5)
90890-04118
YM-04118
Valve margin thickness D (intake)
1.20 mm (0.0472 in)
Valve margin thickness D (ex-
haust)
0.85 mm (0.0335 in)
Valve stem runout
0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
Valve seat width C (intake)
0.90–1.10 mm (0.0354–0.0433 in)
Valve seat width C (exhaust)
0.90–1.10 mm (0.0354–0.0433 in)
Page 219 of 356
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
5-26
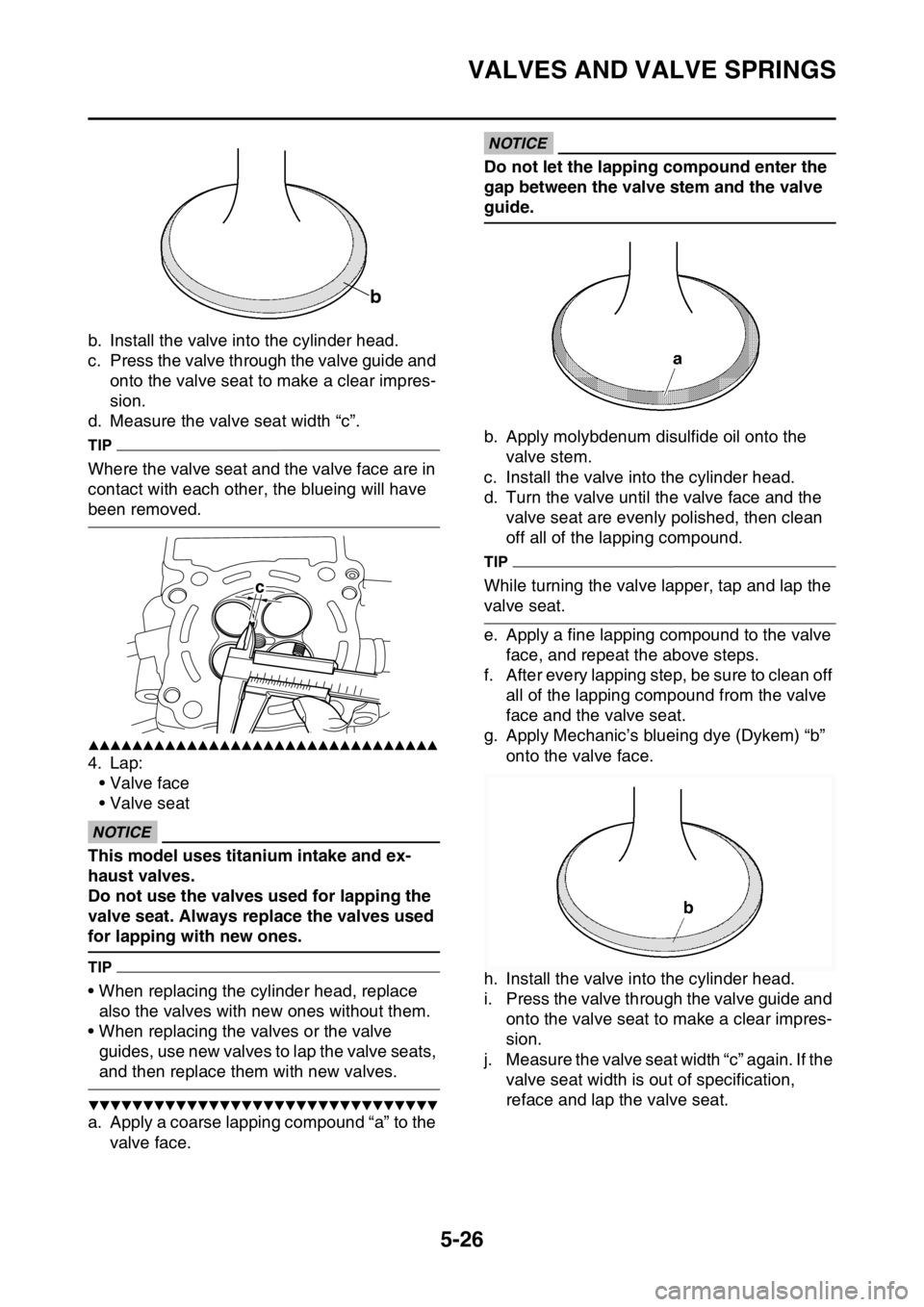
b. Install the valve into the cylinder head.
c. Press the valve through the valve guide and
onto the valve seat to make a clear impres-
sion.
d. Measure the valve seat width “c”.
TIP
Where the valve seat and the valve face are in
contact with each other, the blueing will have
been removed.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
4. Lap:
• Valve face
• Valve seat
ECA1DX1018
NOTICE
This model uses titanium intake and ex-
haust valves.
Do not use the valves used for lapping the
valve seat. Always replace the valves used
for lapping with new ones.
TIP
• When replacing the cylinder head, replace
also the valves with new ones without them.
• When replacing the valves or the valve
guides, use new valves to lap the valve seats,
and then replace them with new valves.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Apply a coarse lapping compound “a” to the
valve face.
ECA13790
NOTICE
Do not let the lapping compound enter the
gap between the valve stem and the valve
guide.
b. Apply molybdenum disulfide oil onto the
valve stem.
c. Install the valve into the cylinder head.
d. Turn the valve until the valve face and the
valve seat are evenly polished, then clean
off all of the lapping compound.
TIP
While turning the valve lapper, tap and lap the
valve seat.
e. Apply a fine lapping compound to the valve
face, and repeat the above steps.
f. After every lapping step, be sure to clean off
all of the lapping compound from the valve
face and the valve seat.
g. Apply Mechanic’s blueing dye (Dykem) “b”
onto the valve face.
h. Install the valve into the cylinder head.
i. Press the valve through the valve guide and
onto the valve seat to make a clear impres-
sion.
j. Measure the valve seat width “c” again. If the
valve seat width is out of specification,
reface and lap the valve seat.
c
Page 220 of 356
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
5-27
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
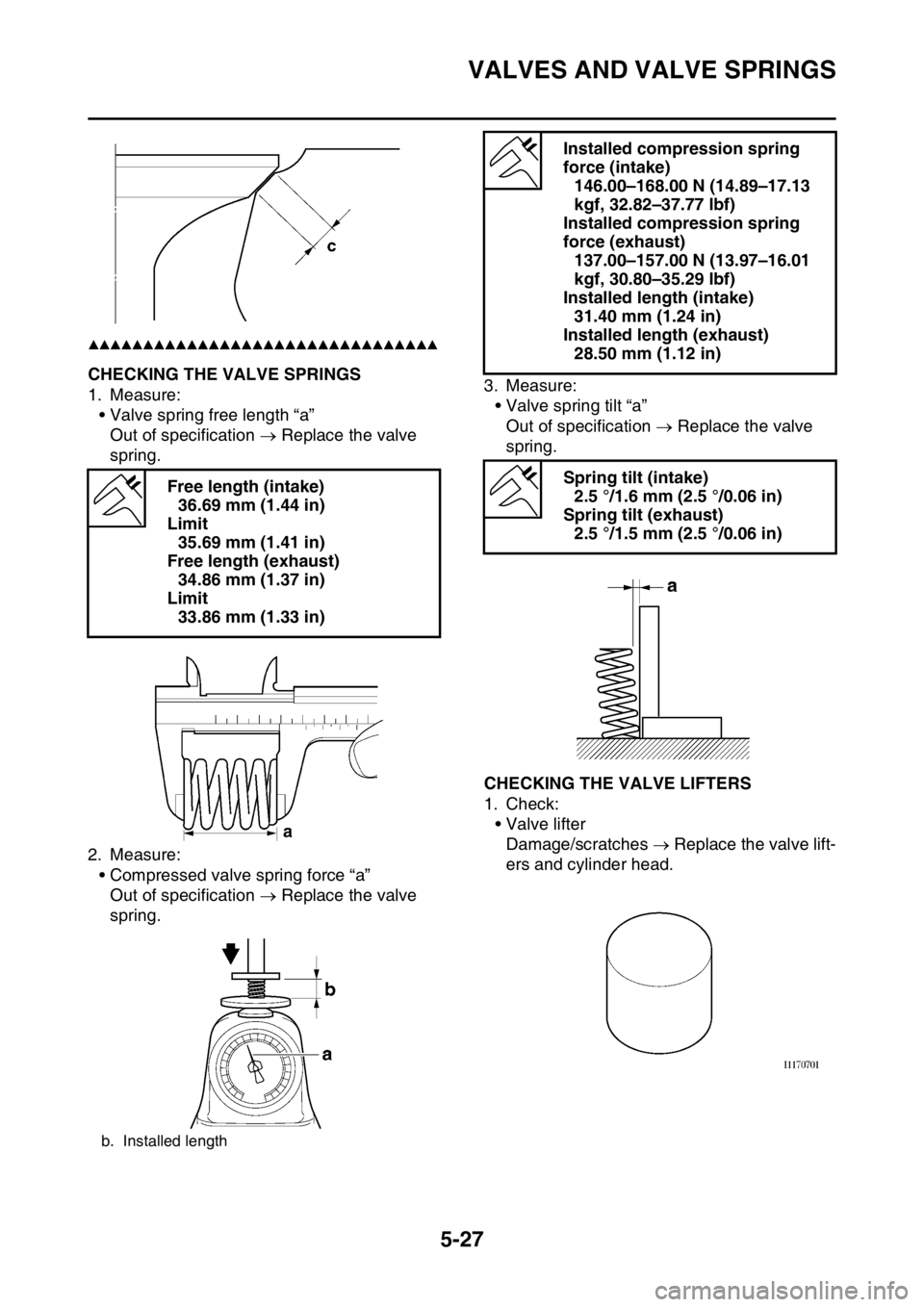
EAS1SM5224CHECKING THE VALVE SPRINGS
1. Measure:
• Valve spring free length “a”
Out of specification Replace the valve
spring.
2. Measure:
• Compressed valve spring force “a”
Out of specification Replace the valve
spring.3. Measure:
• Valve spring tilt “a”
Out of specification Replace the valve
spring.
EAS1SM5225CHECKING THE VALVE LIFTERS
1. Check:
• Valve lifter
Damage/scratches Replace the valve lift-
ers and cylinder head. Free length (intake)
36.69 mm (1.44 in)
Limit
35.69 mm (1.41 in)
Free length (exhaust)
34.86 mm (1.37 in)
Limit
33.86 mm (1.33 in)
b. Installed length
Installed compression spring
force (intake)
146.00–168.00 N (14.89–17.13
kgf, 32.82–37.77 lbf)
Installed compression spring
force (exhaust)
137.00–157.00 N (13.97–16.01
kgf, 30.80–35.29 lbf)
Installed length (intake)
31.40 mm (1.24 in)
Installed length (exhaust)
28.50 mm (1.12 in)
Spring tilt (intake)
2.5 °/1.6 mm (2.5 °/0.06 in)
Spring tilt (exhaust)
2.5 °/1.5 mm (2.5 °/0.06 in)
Page 221 of 356
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
5-28
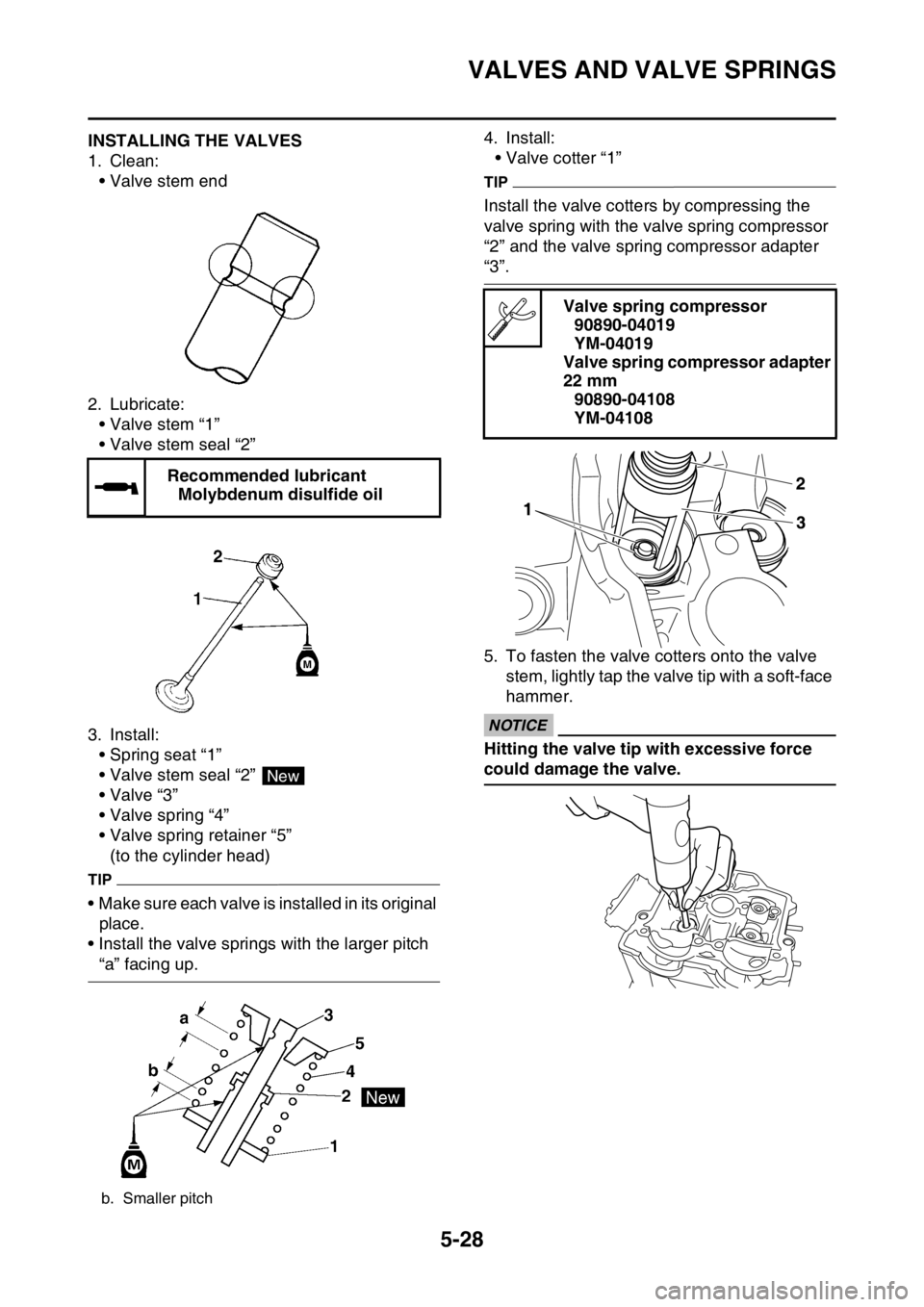
EAS1SM5226INSTALLING THE VALVES
1. Clean:
• Valve stem end
2. Lubricate:
• Valve stem “1”
• Valve stem seal “2”
3. Install:
• Spring seat “1”
• Valve stem seal “2”
•Valve “3”
• Valve spring “4”
• Valve spring retainer “5”
(to the cylinder head)
TIP
• Make sure each valve is installed in its original
place.
• Install the valve springs with the larger pitch
“a” facing up.4. Install:
• Valve cotter “1”
TIP
Install the valve cotters by compressing the
valve spring with the valve spring compressor
“2” and the valve spring compressor adapter
“3”.
5. To fasten the valve cotters onto the valve
stem, lightly tap the valve tip with a soft-face
hammer.
ECA13800
NOTICE
Hitting the valve tip with excessive force
could damage the valve. Recommended lubricant
Molybdenum disulfide oil
b. Smaller pitch
New
Valve spring compressor
90890-04019
YM-04019
Valve spring compressor adapter
22 mm
90890-04108
YM-04108
Page 223 of 356
CYLINDER AND PISTON
5-30
EAS1SM5227
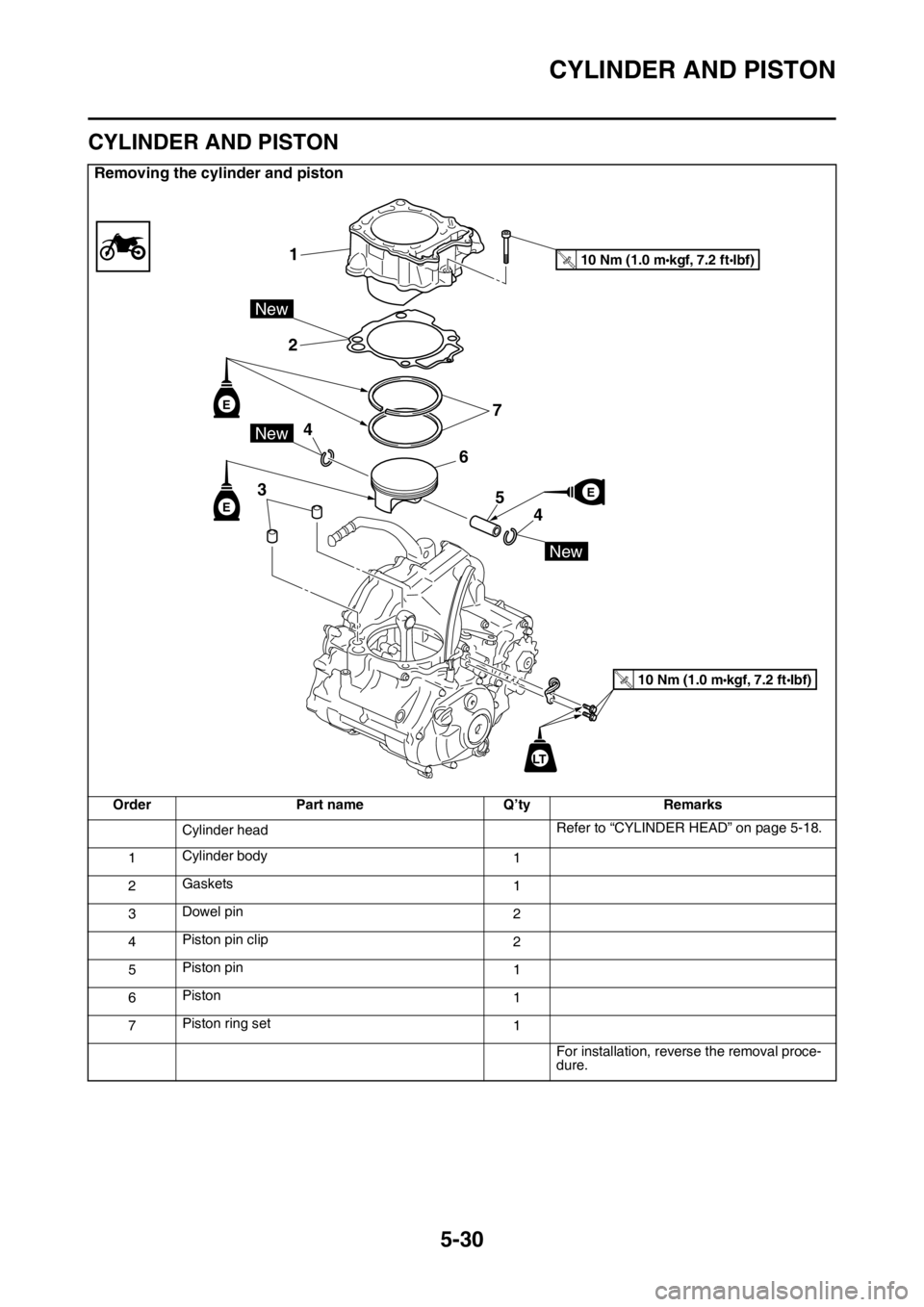
CYLINDER AND PISTON
Removing the cylinder and piston
Order Part name Q’ty Remarks
Cylinder headRefer to “CYLINDER HEAD” on page 5-18.
1Cylinder body
1
2Gaskets
1
3Dowel pin
2
4Piston pin clip
2
5Piston pin
1
6Piston
1
7Piston ring set
1
For installation, reverse the removal proce-
dure.
1
2
3
4
4
5
6
7
10 Nm (1.0 mkgf, 7.2 ftIbf)T.R.
10 Nm (1.0 mkgf, 7.2 ftIbf)T.R.
E
E
New
New
New
LT
E
Page 258 of 356
CRANKCASE
5-65
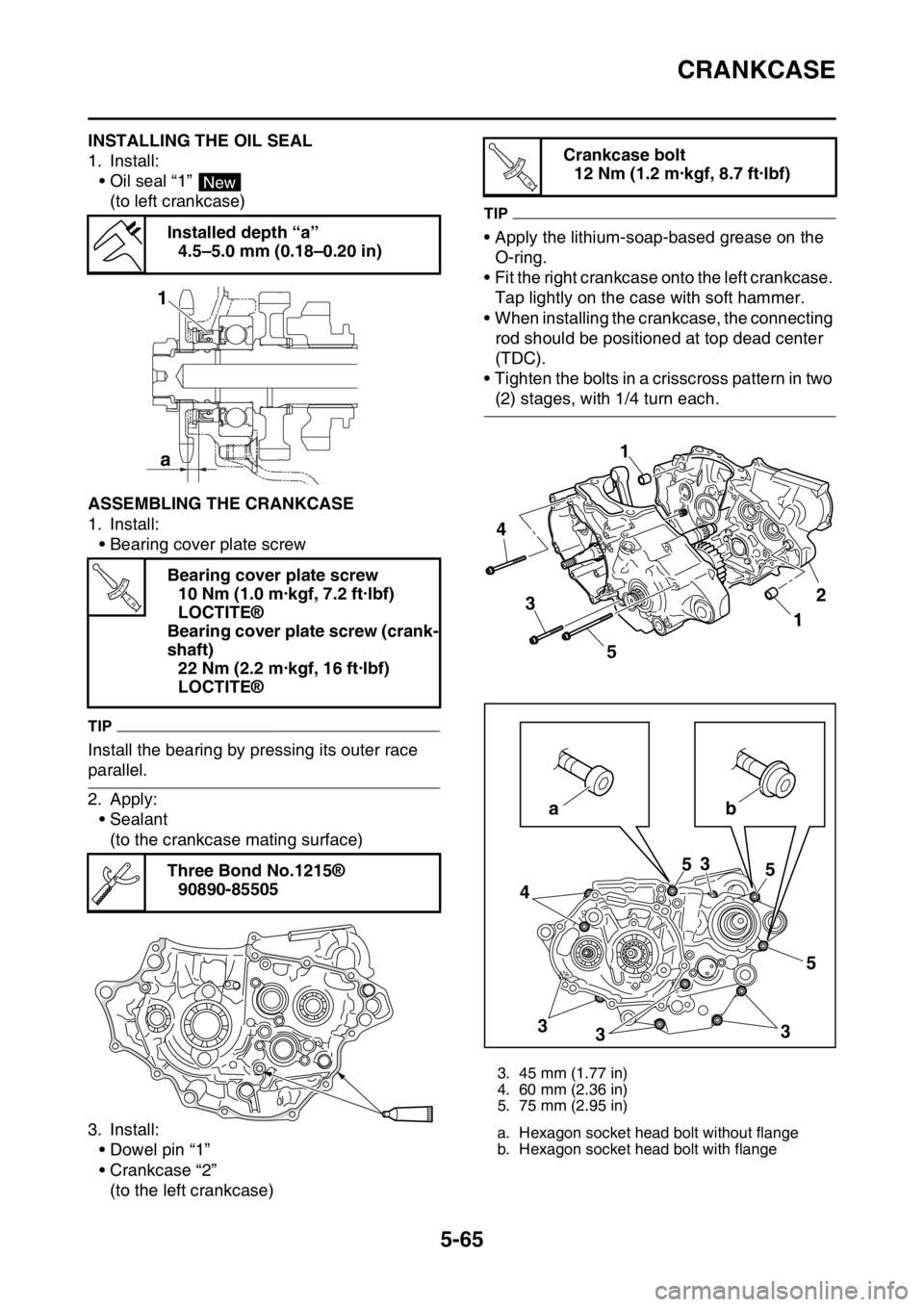
EAS1SM5283INSTALLING THE OIL SEAL
1. Install:
• Oil seal “1”
(to left crankcase)
EAS1SM5284ASSEMBLING THE CRANKCASE
1. Install:
• Bearing cover plate screw
TIP
Install the bearing by pressing its outer race
parallel.
2. Apply:
• Sealant
(to the crankcase mating surface)
3. Install:
• Dowel pin “1”
• Crankcase “2”
(to the left crankcase)
TIP
• Apply the lithium-soap-based grease on the
O-ring.
• Fit the right crankcase onto the left crankcase.
Tap lightly on the case with soft hammer.
• When installing the crankcase, the connecting
rod should be positioned at top dead center
(TDC).
• Tighten the bolts in a crisscross pattern in two
(2) stages, with 1/4 turn each. Installed depth “a”
4.5–5.0 mm (0.18–0.20 in)
Bearing cover plate screw
10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
LOCTITE®
Bearing cover plate screw (crank-
shaft)
22 Nm (2.2 m·kgf, 16 ft·lbf)
LOCTITE®
Three Bond No.1215®
90890-85505
New
a 1
T R..
Crankcase bolt
12 Nm (1.2 m·kgf, 8.7 ft·lbf)
3. 45 mm (1.77 in)
4. 60 mm (2.36 in)
5. 75 mm (2.95 in)
a. Hexagon socket head bolt without flange
b. Hexagon socket head bolt with flange
T R..
4
5
3
43
335 5 5
3
ab1
1
2
Page 270 of 356
RADIATOR
6-3
EAS1SM5298HANDLING NOTEEWA1DX1007
WARNING
If coolant seems hot, do not remove the ra-
diator cap.
EAS1SM5299CHECKING THE RADIATOR
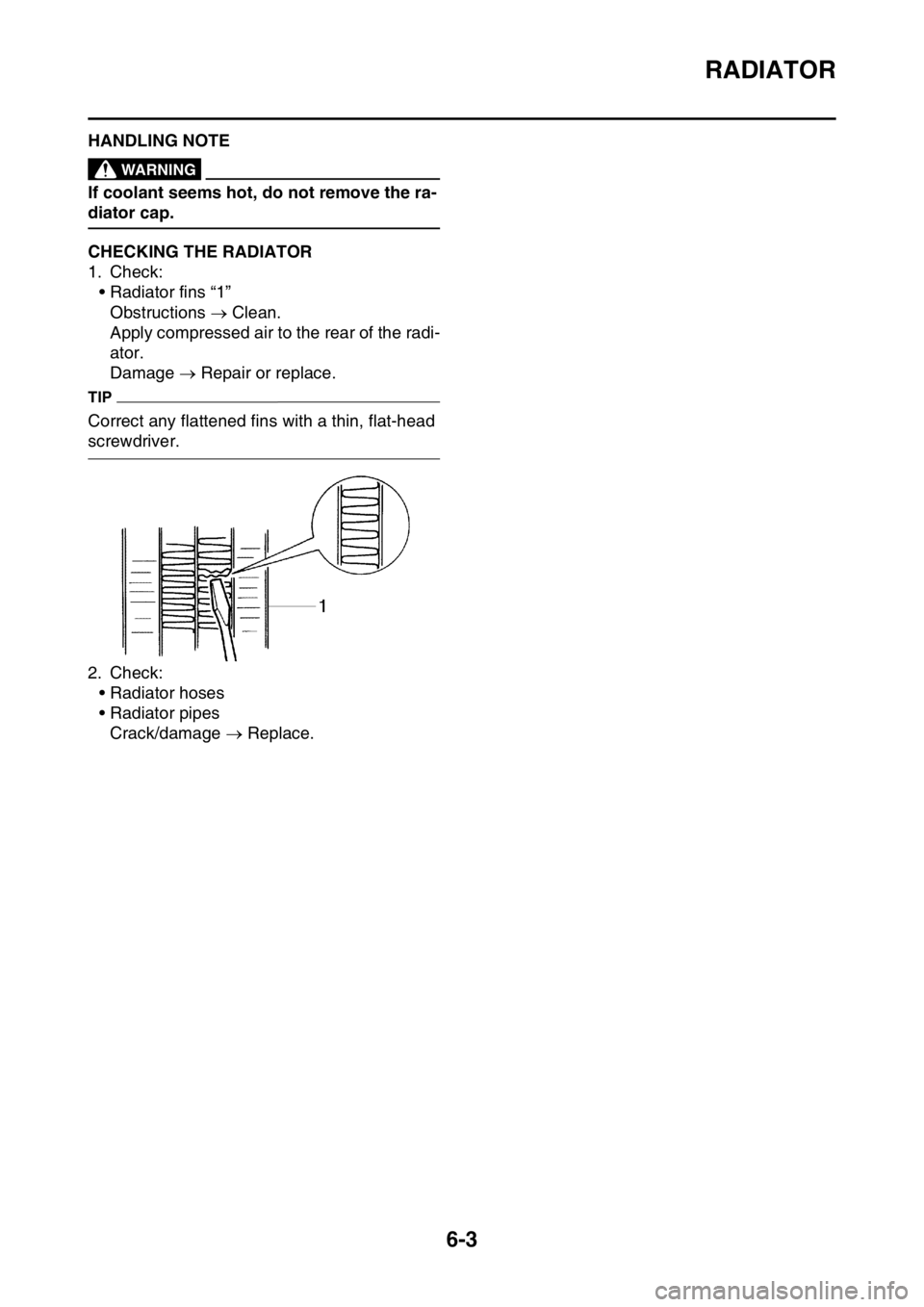
1. Check:
• Radiator fins “1”
Obstructions Clean.
Apply compressed air to the rear of the radi-
ator.
Damage Repair or replace.
TIP
Correct any flattened fins with a thin, flat-head
screwdriver.
2. Check:
• Radiator hoses
• Radiator pipes
Crack/damage Replace.
Page 336 of 356

TROUBLESHOOTING
9-1
EAS1SM5351
TROUBLESHOOTING
EAS1SM5352GENERAL INFORMATION
TIP
The following guide for troubleshooting does
not cover all the possible causes of trouble. It
should be helpful, however, as a guide to basic
troubleshooting. Refer to the relative procedure
in this manual for checks, adjustments, and re-
placement of parts.
EAS1SM5353STARTING FAILURES
Engine
1. Cylinder and cylinder head
• Loose spark plug
• Loose cylinder head or cylinder
• Damaged cylinder head gasket
• Damaged cylinder gasket
• Worn or damaged cylinder
• Incorrect valve clearance
• Improperly sealed valve
• Incorrect valve-to-valve-seat contact
• Incorrect valve timing
• Faulty valve spring
• Seized valve
2. Piston and piston ring(s)
• Improperly installed piston ring
• Damaged, worn or fatigued piston ring
• Seized piston ring
• Seized or damaged piston
3. Air filter
• Improperly installed air filter
• Clogged air filter element
4. Crankcase and crankshaft
• Improperly assembled crankcase
• Seized crankshaft
Fuel system
1. Fuel tank
• Empty fuel tank
• Clogged fuel tank breather hose
• Deteriorated or contaminated fuel
• Clogged or damaged fuel hose
2. Fuel pump
• Faulty fuel pump
3. Throttle body
• Deteriorated or contaminated fuel
• Sucked-in airElectrical system
1. Spark plug
• Incorrect spark plug gap
• Incorrect spark plug heat range
• Fouled spark plug
• Worn or damaged electrode
• Worn or damaged insulator
2. Ignition coil
• Cracked or broken ignition coil body
• Broken or shorted primary or secondary
coils
3. Ignition system
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty crankshaft position sensor
• Broken generator rotor woodruff key
4. Switches and wiring
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty engine stop switch
• Broken or shorted wiring
• Faulty neutral switch
• Improperly grounded circuit
• Loose connections
EAS1SM5354INCORRECT ENGINE IDLING SPEED
Engine
1. Cylinder and cylinder head
• Incorrect valve clearance
• Damaged valve train components
2. Air filter
• Clogged air filter element
Fuel system
1. Throttle body
• Damaged or loose throttle body joint
• Improperly synchronized throttle bodies
• Improper throttle cable free play
• Flooded throttle body
Electrical system
1. Spark plug
• Incorrect spark plug gap
• Incorrect spark plug heat range
• Fouled spark plug
• Worn or damaged electrode
• Worn or damaged insulator
• Faulty spark plug cap
2. Ignition coil
• Broken or shorted primary or secondary
coils
• Cracked or broken ignition coil