engine YAMAHA YZ450F 2016 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2016, Model line: YZ450F, Model: YAMAHA YZ450F 2016Pages: 362, PDF Size: 10.49 MB
Page 331 of 362

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
8-39
1. Engine stop switch
2. Launch control switch
3. Neutral switch
Page 333 of 362
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
8-41
EASB111334CHECKING THE IGNITION SPARK GAP
1. Check:
• Ignition spark gap
Out of specification Perform the ignition
system troubleshooting.
Refer to “TROUBLESHOOTING” on page 8-
4.
TIP
If the ignition spark gap is within specification,
the ignition system circuit is operating normally.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
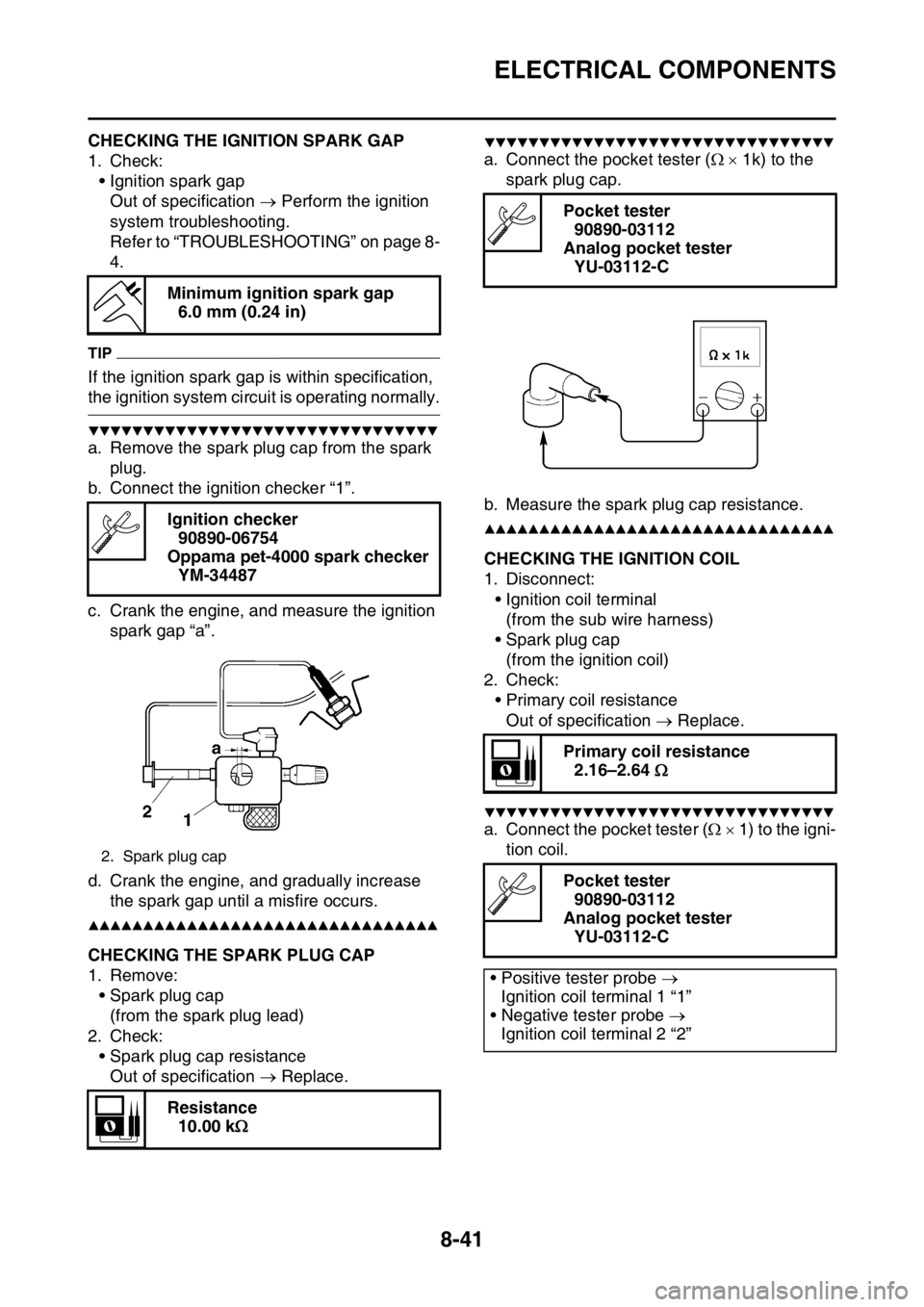
a. Remove the spark plug cap from the spark
plug.
b. Connect the ignition checker “1”.
c. Crank the engine, and measure the ignition
spark gap “a”.
d. Crank the engine, and gradually increase
the spark gap until a misfire occurs.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111335CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG CAP
1. Remove:
• Spark plug cap
(from the spark plug lead)
2. Check:
• Spark plug cap resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1k) to the
spark plug cap.
b. Measure the spark plug cap resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111336CHECKING THE IGNITION COIL
1. Disconnect:
• Ignition coil terminal
(from the sub wire harness)
• Spark plug cap
(from the ignition coil)
2. Check:
• Primary coil resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1) to the igni-
tion coil. Minimum ignition spark gap
6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Ignition checker
90890-06754
Oppama pet-4000 spark checker
YM-34487
2. Spark plug cap
Resistance
10.00 k
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
Primary coil resistance
2.16–2.64
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Ignition coil terminal 1 “1”
• Negative tester probe
Ignition coil terminal 2 “2”
Page 334 of 362
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
8-42
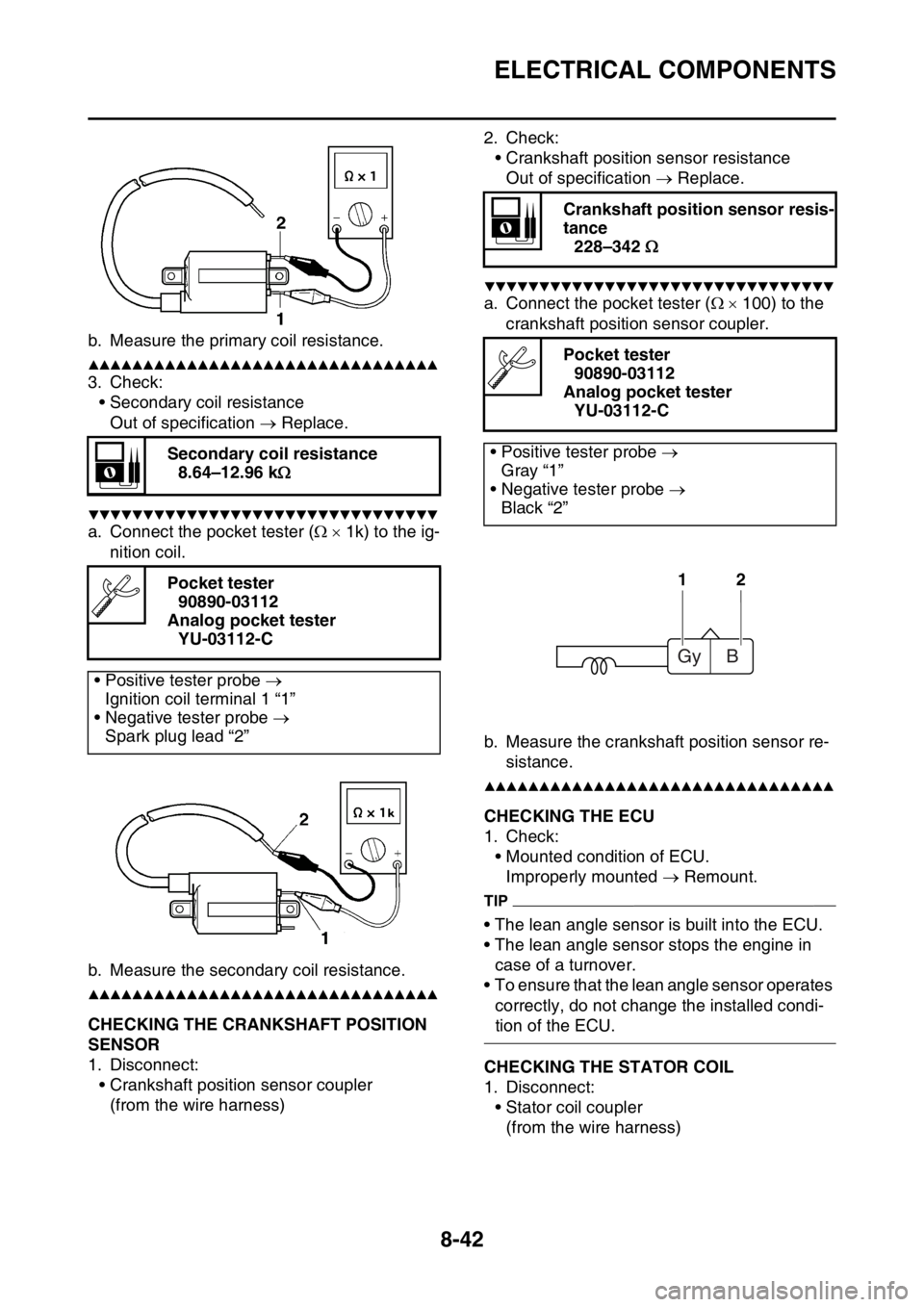
b. Measure the primary coil resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
3. Check:
• Secondary coil resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1k) to the ig-
nition coil.
b. Measure the secondary coil resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111337CHECKING THE CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
1. Disconnect:
• Crankshaft position sensor coupler
(from the wire harness)2. Check:
• Crankshaft position sensor resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 100) to the
crankshaft position sensor coupler.
b. Measure the crankshaft position sensor re-
sistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111338CHECKING THE ECU
1. Check:
• Mounted condition of ECU.
Improperly mounted Remount.
TIP
• The lean angle sensor is built into the ECU.
• The lean angle sensor stops the engine in
case of a turnover.
• To ensure that the lean angle sensor operates
correctly, do not change the installed condi-
tion of the ECU.
EASB111339CHECKING THE STATOR COIL
1. Disconnect:
• Stator coil coupler
(from the wire harness) Secondary coil resistance
8.64–12.96 k
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Ignition coil terminal 1 “1”
• Negative tester probe
Spark plug lead “2”
Crankshaft position sensor resis-
tance
228–342
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Gray “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black “2”
12
Gy B
Page 335 of 362
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
8-43
2. Check:
• Stator coil resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
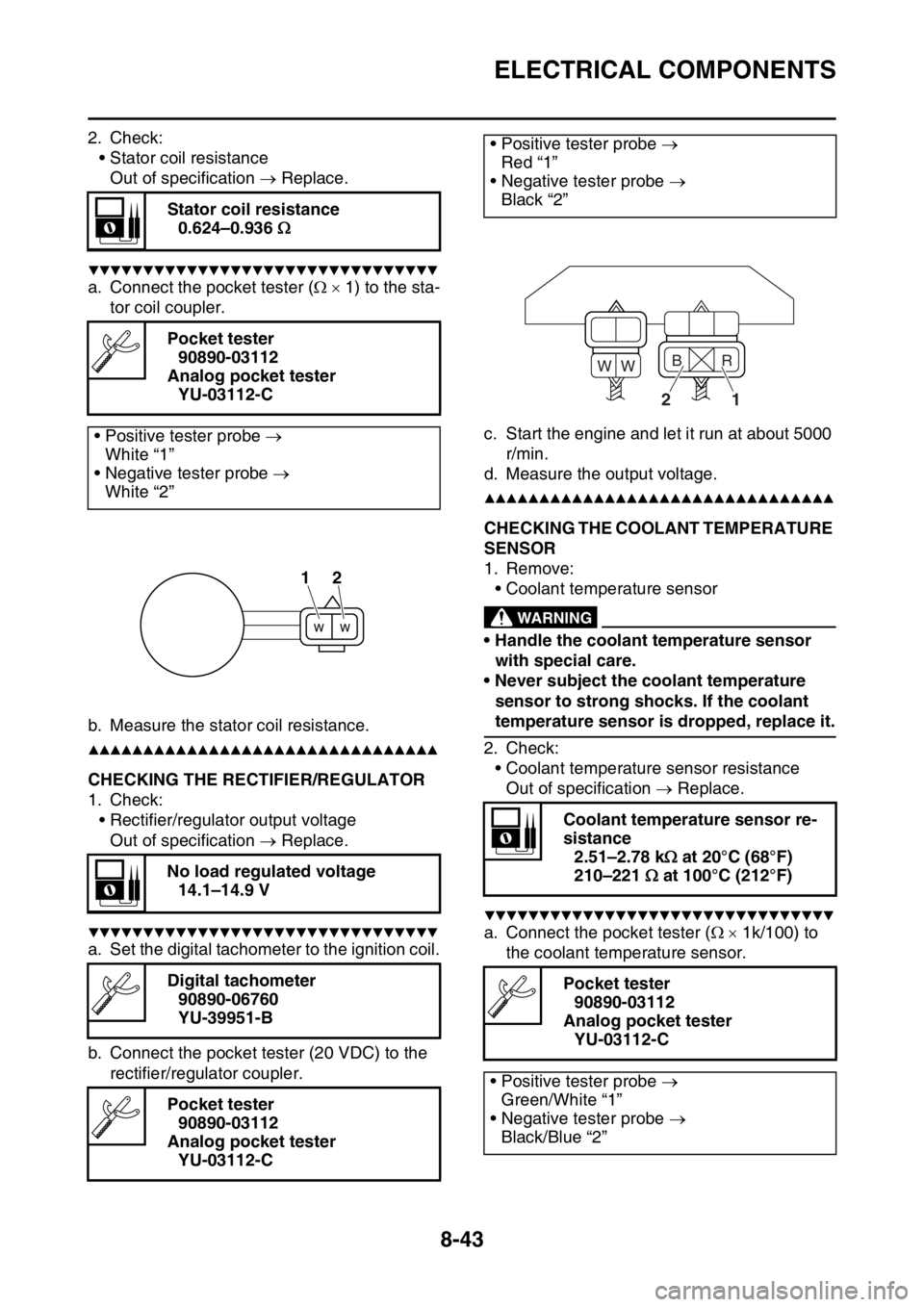
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1) to the sta-
tor coil coupler.
b. Measure the stator coil resistance.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111340CHECKING THE RECTIFIER/REGULATOR
1. Check:
• Rectifier/regulator output voltage
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Set the digital tachometer to the ignition coil.
b. Connect the pocket tester (20 VDC) to the
rectifier/regulator coupler.c. Start the engine and let it run at about 5000
r/min.
d. Measure the output voltage.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111341CHECKING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
1. Remove:
• Coolant temperature sensor
EWA
WARNING
• Handle the coolant temperature sensor
with special care.
• Never subject the coolant temperature
sensor to strong shocks. If the coolant
temperature sensor is dropped, replace it.
2. Check:
• Coolant temperature sensor resistance
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester ( 1k/100) to
the coolant temperature sensor. Stator coil resistance
0.624–0.936
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
White “1”
• Negative tester probe
White “2”
No load regulated voltage
14.1–14.9 V
Digital tachometer
90890-06760
YU-39951-B
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
12
• Positive tester probe
Red “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black “2”
Coolant temperature sensor re-
sistance
2.51–2.78 k at 20°C (68°F)
210–221 at 100°C (212°F)
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Green/White “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black/Blue “2”
21
B
WWR
Page 337 of 362
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
8-45
EASB111343CHECKING THE THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR INPUT VOLTAGE
1. Check:
• Throttle position sensor input voltage
Out of specification Replace the ECU.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
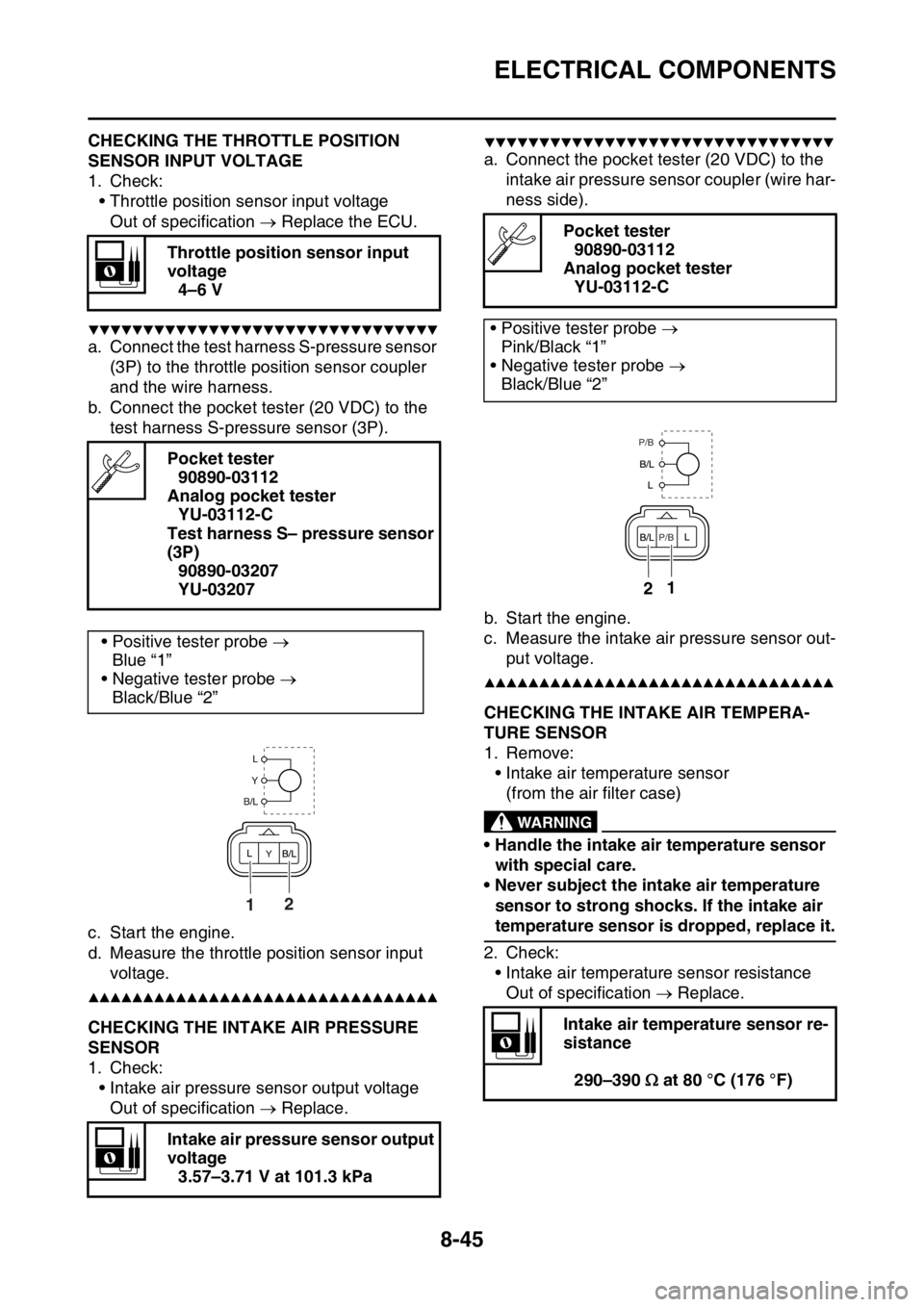
a. Connect the test harness S-pressure sensor
(3P) to the throttle position sensor coupler
and the wire harness.
b. Connect the pocket tester (20 VDC) to the
test harness S-pressure sensor (3P).
c. Start the engine.
d. Measure the throttle position sensor input
voltage.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111344CHECKING THE INTAKE AIR PRESSURE
SENSOR
1. Check:
• Intake air pressure sensor output voltage
Out of specification Replace.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester (20 VDC) to the
intake air pressure sensor coupler (wire har-
ness side).
b. Start the engine.
c. Measure the intake air pressure sensor out-
put voltage.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EASB111345CHECKING THE INTAKE AIR TEMPERA-
TURE SENSOR
1. Remove:
• Intake air temperature sensor
(from the air filter case)
EWA
WARNING
• Handle the intake air temperature sensor
with special care.
• Never subject the intake air temperature
sensor to strong shocks. If the intake air
temperature sensor is dropped, replace it.
2. Check:
• Intake air temperature sensor resistance
Out of specification Replace. Throttle position sensor input
voltage
4–6 V
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
Test harness S– pressure sensor
(3P)
90890-03207
YU-03207
• Positive tester probe
Blue “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black/Blue “2”
Intake air pressure sensor output
voltage
3.57–3.71 V at 101.3 kPa
21
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
• Positive tester probe
Pink/Black “1”
• Negative tester probe
Black/Blue “2”
Intake air temperature sensor re-
sistance
290–390 at 80 °C (176 °F)
12
P/B
P/B
Page 341 of 362

9
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING...................................................................................... 9-1
GENERAL INFORMATION ........................................................................ 9-1
STARTING FAILURES ............................................................................... 9-1
INCORRECT ENGINE IDLING SPEED ..................................................... 9-1
POOR MEDIUM-AND-HIGH-SPEED PERFORMANCE ............................ 9-2
SHIFTING IS DIFFICULT ........................................................................... 9-2
SHIFT PEDAL DOES NOT MOVE ............................................................. 9-2
JUMPS OUT OF GEAR.............................................................................. 9-2
CLUTCH SLIPS .......................................................................................... 9-2
CLUTCH DRAGS ....................................................................................... 9-2
OVERHEATING ......................................................................................... 9-2
OVERCOOLING ......................................................................................... 9-3
POOR BRAKING PERFORMANCE ........................................................... 9-3
FRONT FORK OIL LEAKING ..................................................................... 9-3
FAULTY FRONT FORK LEGS ................................................................... 9-3
UNSTABLE HANDLING ............................................................................. 9-3
LIST OF SELF-DIAGNOSTIC AND FAIL-SAFE ACTIONS............................. 9-4
Page 342 of 362

TROUBLESHOOTING
9-1
EASB111348
TROUBLESHOOTING
EASB111349GENERAL INFORMATION
TIP
The following guide for troubleshooting does
not cover all the possible causes of trouble. It
should be helpful, however, as a guide to basic
troubleshooting. Refer to the relative procedure
in this manual for checks, adjustments, and re-
placement of parts.
EASB111350STARTING FAILURES
Engine
1. Cylinder and cylinder head
• Loose spark plug
• Loose cylinder head or cylinder
• Damaged cylinder head gasket
• Damaged cylinder gasket
• Worn or damaged cylinder
• Incorrect valve clearance
• Improperly sealed valve
• Incorrect valve-to-valve-seat contact
• Incorrect valve timing
• Faulty valve spring
• Seized valve
2. Piston and piston ring(s)
• Improperly installed piston ring
• Damaged, worn or fatigued piston ring
• Seized piston ring
• Seized or damaged piston
3. Air filter
• Improperly installed air filter
• Clogged air filter element
4. Crankcase and crankshaft
• Improperly assembled crankcase
• Seized crankshaft
Fuel system
1. Fuel tank
• Empty fuel tank
• Clogged fuel tank breather hose
• Deteriorated or contaminated fuel
• Clogged or damaged fuel hose
2. Fuel pump
• Faulty fuel pump
3. Throttle body
• Deteriorated or contaminated fuel
• Sucked-in airElectrical system
1. Spark plug
• Incorrect spark plug gap
• Incorrect spark plug heat range
• Fouled spark plug
• Worn or damaged electrode
• Worn or damaged insulator
2. Ignition coil
• Cracked or broken ignition coil body
• Broken or shorted primary or secondary
coils
3. Ignition system
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty crankshaft position sensor
• Broken generator rotor woodruff key
4. Switches and wiring
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty engine stop switch
• Broken or shorted wiring
• Faulty neutral switch
• Improperly grounded circuit
• Loose connections
EASB111351INCORRECT ENGINE IDLING SPEED
Engine
1. Cylinder and cylinder head
• Incorrect valve clearance
• Damaged valve train components
2. Air filter
• Clogged air filter element
Fuel system
1. Throttle body
• Damaged or loose throttle body joint
• Improperly synchronized throttle bodies
• Improper throttle cable free play
• Flooded throttle body
Electrical system
1. Spark plug
• Incorrect spark plug gap
• Incorrect spark plug heat range
• Fouled spark plug
• Worn or damaged electrode
• Worn or damaged insulator
• Faulty spark plug cap
2. Ignition coil
• Broken or shorted primary or secondary
coils
• Cracked or broken ignition coil
Page 343 of 362

TROUBLESHOOTING
9-2
3. Ignition system
• Faulty ECU
• Faulty crankshaft position sensor
• Broken generator rotor woodruff key
EASB111352POOR MEDIUM-AND-HIGH-SPEED PER-
FORMANCE
Refer to “STARTING FAILURES” on page 9-1.
Engine
1. Air filter
• Clogged air filter element
Fuel system
1. Fuel pump
• Faulty fuel pump
2. Throttle body
• Defective throttle body
3. ECU
• Faulty ECU
EASB111353SHIFTING IS DIFFICULT
Refer to “CLUTCH” on page 5-38.
EASB111354SHIFT PEDAL DOES NOT MOVE
Engine
1. Shift shaft
• Bent shift shaft
2. Shift drum and shift forks
• Foreign object in a shift drum groove
• Seized shift fork
• Bent shift fork guide bar
3. Transmission
• Seized transmission gear
• Foreign object between transmission gears
• Improperly assembled transmission
EASB111355JUMPS OUT OF GEAR
Engine
1. Shift shaft
• Incorrect shift pedal position
• Improperly returned stopper lever
2. Shift forks
• Worn shift fork
3. Shift drum
• Incorrect axial play
• Worn shift drum groove
4. Transmission
• Worn gear dog
EASB111356
CLUTCH SLIPS
Engine
1. Clutch
• Improperly assembled clutch
• Loose or fatigued clutch spring
• Worn friction plate
• Worn clutch plate
2. Engine oil
• Incorrect oil level
• Incorrect oil viscosity (low)
• Deteriorated oil
EASB111357CLUTCH DRAGS
Engine
1. Clutch
• Unevenly tensioned clutch springs
• Warped pressure plate
• Bent clutch plate
• Swollen friction plate
• Bent clutch push rod
• Damaged clutch boss
• Burnt primary driven gear bushing
2. Engine oil
• Incorrect oil level
• Incorrect oil viscosity (high)
• Deteriorated oil
EASB111358OVERHEATING
Engine
1. Cylinder head and piston
• Heavy carbon buildup
• Clogged coolant passages
2. Engine oil
• Incorrect oil level
• Incorrect oil viscosity
• Inferior oil quality
Cooling system
1. Coolant
• Low coolant level
2. Radiator
• Damaged or leaking radiator
• Faulty radiator cap
• Bent or damaged radiator fin
3. Water pump
• Damaged or faulty water pump
• Damaged hose
• Improperly connected hose
• Damaged pipe
• Improperly connected pipe
Page 352 of 362
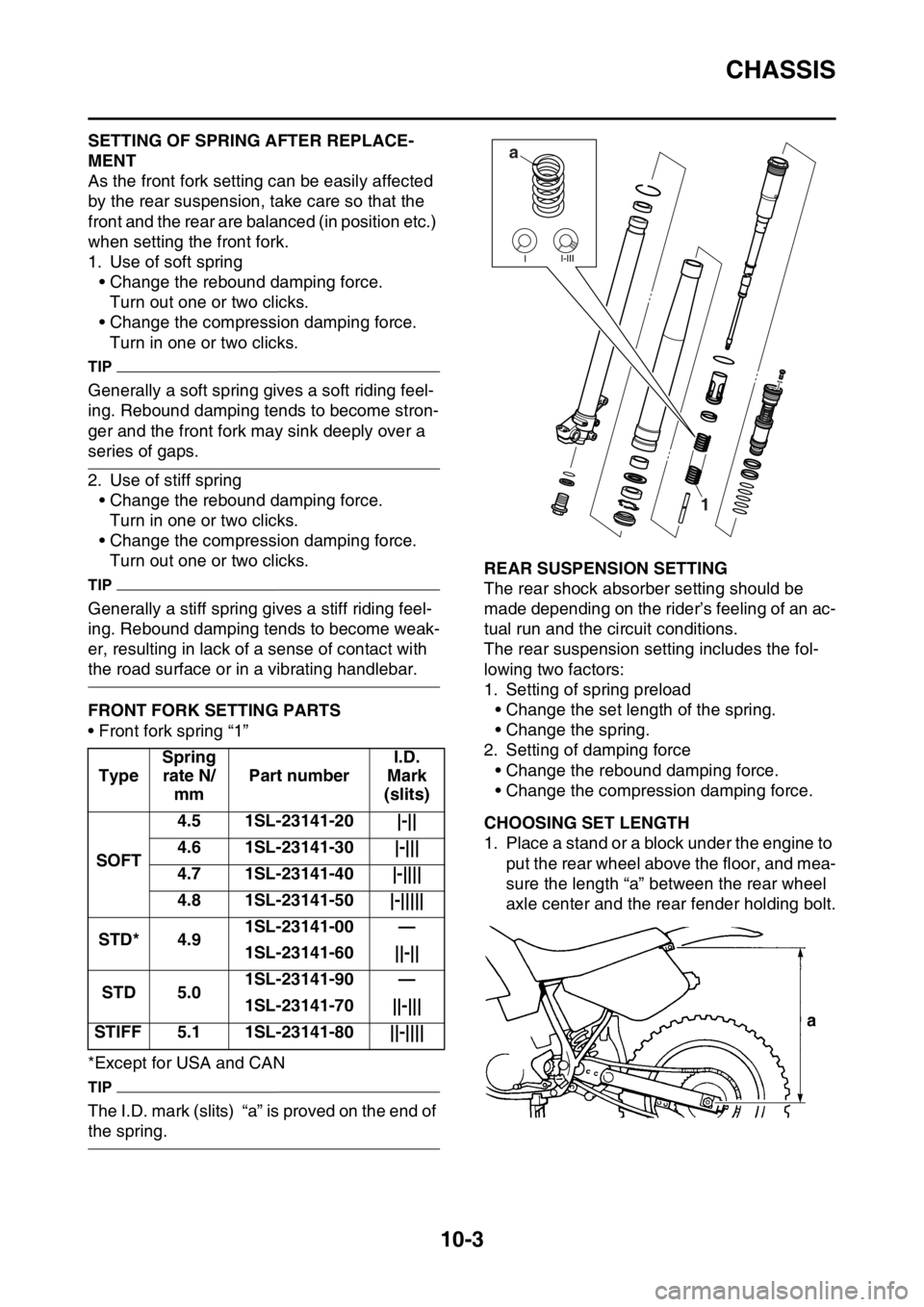
CHASSIS
10-3
EASB111372SETTING OF SPRING AFTER REPLACE-
MENT
As the front fork setting can be easily affected
by the rear suspension, take care so that the
front and the rear are balanced (in position etc.)
when setting the front fork.
1. Use of soft spring
• Change the rebound damping force.
Turn out one or two clicks.
• Change the compression damping force.
Turn in one or two clicks.
TIP
Generally a soft spring gives a soft riding feel-
ing. Rebound damping tends to become stron-
ger and the front fork may sink deeply over a
series of gaps.
2. Use of stiff spring
• Change the rebound damping force.
Turn in one or two clicks.
• Change the compression damping force.
Turn out one or two clicks.
TIP
Generally a stiff spring gives a stiff riding feel-
ing. Rebound damping tends to become weak-
er, resulting in lack of a sense of contact with
the road surface or in a vibrating handlebar.
EASB111373FRONT FORK SETTING PARTS
• Front fork spring “1”
*Except for USA and CAN
TIP
The I.D. mark (slits) “a” is proved on the end of
the spring.
EASB111374REAR SUSPENSION SETTING
The rear shock absorber setting should be
made depending on the rider’s feeling of an ac-
tual run and the circuit conditions.
The rear suspension setting includes the fol-
lowing two factors:
1. Setting of spring preload
• Change the set length of the spring.
• Change the spring.
2. Setting of damping force
• Change the rebound damping force.
• Change the compression damping force.
EASB111375CHOOSING SET LENGTH
1. Place a stand or a block under the engine to
put the rear wheel above the floor, and mea-
sure the length “a” between the rear wheel
axle center and the rear fender holding bolt. TypeSpring
rate N/
mmPart numberI.D.
Mark
(slits)
SOFT4.5 1SL-23141-20 |-||
4.6 1SL-23141-30 |-|||
4.7 1SL-23141-40 |-||||
4.8 1SL-23141-50 |-|||||
STD* 4.91SL-23141-00 —
1SL-23141-60 ||-||
STD 5.01SL-23141-90 —
1SL-23141-70 ||-|||
STIFF 5.1 1SL-23141-80 ||-||||
a
1
Page 353 of 362
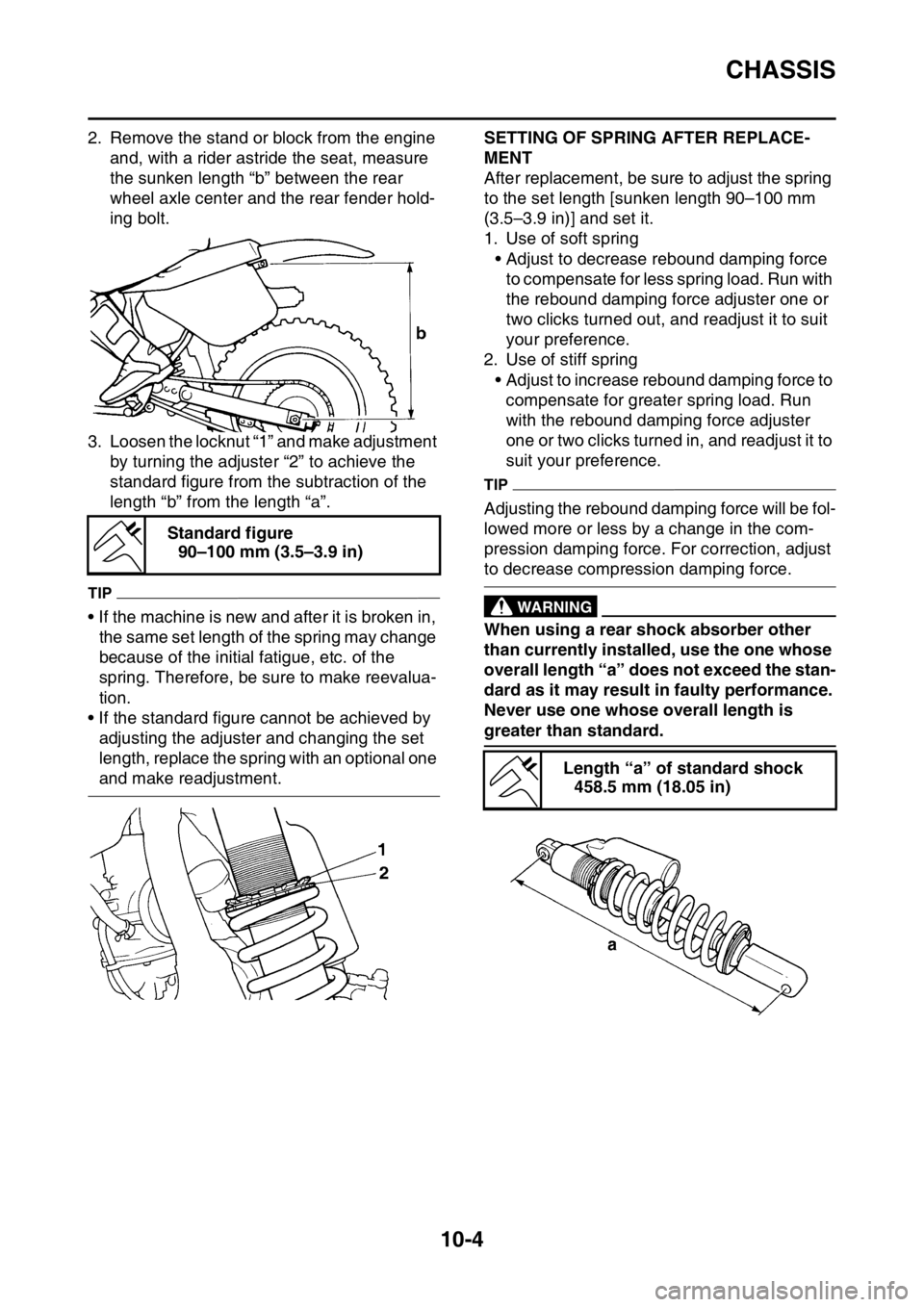
CHASSIS
10-4
2. Remove the stand or block from the engine
and, with a rider astride the seat, measure
the sunken length “b” between the rear
wheel axle center and the rear fender hold-
ing bolt.
3. Loosen the locknut “1” and make adjustment
by turning the adjuster “2” to achieve the
standard figure from the subtraction of the
length “b” from the length “a”.
TIP
• If the machine is new and after it is broken in,
the same set length of the spring may change
because of the initial fatigue, etc. of the
spring. Therefore, be sure to make reevalua-
tion.
• If the standard figure cannot be achieved by
adjusting the adjuster and changing the set
length, replace the spring with an optional one
and make readjustment.
EASB111376
SETTING OF SPRING AFTER REPLACE-
MENT
After replacement, be sure to adjust the spring
to the set length [sunken length 90–100 mm
(3.5–3.9 in)] and set it.
1. Use of soft spring
• Adjust to decrease rebound damping force
to compensate for less spring load. Run with
the rebound damping force adjuster one or
two clicks turned out, and readjust it to suit
your preference.
2. Use of stiff spring
• Adjust to increase rebound damping force to
compensate for greater spring load. Run
with the rebound damping force adjuster
one or two clicks turned in, and readjust it to
suit your preference.
TIP
Adjusting the rebound damping force will be fol-
lowed more or less by a change in the com-
pression damping force. For correction, adjust
to decrease compression damping force.
EWA1DX4002
WARNING
When using a rear shock absorber other
than currently installed, use the one whose
overall length “a” does not exceed the stan-
dard as it may result in faulty performance.
Never use one whose overall length is
greater than standard. Standard figure
90–100 mm (3.5–3.9 in)
Length “a” of standard shock
458.5 mm (18.05 in)