weight Alfa Romeo Giulietta 2014 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ALFA ROMEO, Model Year: 2014, Model line: Giulietta, Model: Alfa Romeo Giulietta 2014Pages: 280, PDF Size: 6.65 MB
Page 70 of 280

System intervention
A slight pulsing of the brake pedal and
noise indicates the intervention of the
ABS: this is completely normal when
the system intervenes.
35) 36) 37) 38) 39) 40) 41)
CBC (Cornering Brake
Control) SYSTEM
The system acts when braking on
corners, optimising the distribution of
brake pressure on the four wheels: the
system prevents the wheels on the
inside of the corner (less affected by the
weight of the car) from locking,
ensuring better stability and direction
for the car.ASR (Anti-Slip
Regulation) SYSTEM
42) 43) 44)
This is an integral part of the ESC
system and automatically operates in
the event of one or both drive wheels
slipping, loss of grip on wet roads
(aquaplaning) and acceleration
on slippery, snowy or icy roads, etc.
Depending on the slipping conditions,
two different control systems are
activated:
❒if the slipping involves both drive
wheels, the ASR system intervenes,
reducing the power transmitted by
the engine;
❒if the slipping only involves one of the
drive wheels, it also intervenes
automatically, braking the wheel that
is slipping.
System intervention
This is indicated by the flashing of the
warning light on the instrument
panel, to inform the driver that the car is
in critical stability and grip conditions.HILL HOLDER SYSTEM
This is an integral part of the ESC
system and facilitates starting on
slopes, activating automatically in the
following cases:
❒uphill: car stationary on a road with a
gradient higher than 5%, engine
running, brake pressed and gearbox
in neutral or gear (other than reverse)
engaged;
❒downhill: car stationary on a road
with a gradient higher than 5%,
engine running, brake pressed and
reverse gear engaged.
When setting off, the ESC system
control unit maintains the braking
pressure on the wheels until the engine
torque necessary for starting is
reached, or in any case for a maximum
of 2 seconds, allowing your right foot
to be moved easily from the brake
pedal to the accelerator.
66
GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
Page 72 of 280

“ELECTRONIC Q2”
SYSTEM (“E-Q2”)
The "Electronic Q2" system intervenes
during acceleration on corners, braking
the inner drive wheel and thus
increasing the traction of the outer
wheel (which bears more of the car’s
weight): the torque is thus distributed
optimally between the drive wheels
in accordance with the driving
conditions and road surface, permitting
particularly effective, sporty driving.
"PRE-FILL" SYSTEM
(RAB - Ready Alert
Brake)
(only with 'Dynamic" mode activated)
This function activates automatically
if the accelerator pedal is released
rapidly, reducing the brake pad travel
(both at front and back), with the aim of
preparing the braking system and
enhancing its responsiveness, thus
reducing the stopping distance in the
event of subsequent braking.
WARNING
30) The ESC system can’t alter the
natural laws of physics, and can’t
increase grip which depends on
the condition of the road.
31) The ESC system cannot prevent
accidents, including those due to
excessive speed on corners,
driving on low-grip surfaces or
aquaplaning.
32) The capability of the ESC system
must never be tested irresponsibly
and dangerously, in such a way
as to compromise personal safety
and the safety of others.
33) For the correct operation of the
ASR system, the tyres must of
necessity be the same make and
type on all wheels, in perfect
condition and, above all, of the
prescribed type and dimensions.
34) The performance of the ESC
and ASR systems must not
encourage the driver to take
unnecessary risks. Your driving
style must always be suited to the
road conditions, visibility and
traffic. The driver is always
responsible for road safety.35) When the ABS intervenes and
you feel the brake pedal pulsating,
do not reduce the pressure, but
hold it down firmly and
confidently; in doing so you will
brake in the shortest distance
possible, depending on the
current road conditions.
36) For maximum efficiency of the
braking system, a bedding-in
period of about 500 km is
required: during this period it is
advisable to avoid sharp, repeated
and prolonged braking.
37) If the ABS intervenes, this
indicates that the grip of the tyres
on the road is nearing its limit:
you must slow down to a speed
compatible with the available grip.
38) The ABS can’t overrule the
natural laws of physics, and can’t
increase the grip available
according to the condition of the
road.
39) The ABS cannot prevent
accidents, including those due to
excessive speed on corners,
driving on low-grip surfaces or
aquaplaning.
40) The capability of the ABS must
never be tested irresponsibly and
dangerously, in such a way as
to compromise personal safety
and the safety of others.
68
GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
Page 143 of 280
76) If the belt has been subjected to
heavy strain, for example after an
accident, it must changed
completely together with the
anchors, anchor fastening screws
and the pretensioner. Even if the
belt has no visible defects, it could
have lost its resilience.
IMPORTANT
15) Operations which lead to
impacts, vibrations or localised
heating (over 100°C for a
maximum of six hours) in the area
around the pretensioner may
damage or deploy it. Contact an
Alfa Romeo Dealership should
intervention be necessary on
these components.
CARRYING
CHILDREN SAFELYFor optimal protection in the event of an
impact, all occupants must be seated
and wearing adequate restraint
systems, including newborn and other
children!
This prescription is compulsory in all EC
countries according to EC Directive
2003/20/EC.
Compared with an adult, a child's head
is larger and heavier in proportion to
his/her body and the child's muscular
and bone structures are not fully
developed. Therefore, correct restraint
systems other than adult seat belts
are necessary to reduce as much as
possible the risk of injuries in case
of accident, braking or sudden
manoeuvre.
Children must be seated safely and
comfortably. As far as the
characteristics of the child restraint
systems used allow, you are advised to
keep children in rear facing restraint
systems for as long as possible (at least
until 3–4 years old), since this is the
most protected position in the event of
an impact.
77) 78)
The choice of the most suitable child
restraint device depends on the weight
of the child; there are various types of
child restraint systems and you are
advised always to choose the one that
is most suitable for the child.
When over 1.50 m in height, from the
point of view of restraint systems,
children are considered as adults and
wear seat belts normally.
In Europe the characteristics of children
restraint systems are ruled by the
regulation ECE-R44, dividing them into
five weight groups:Group Weight groupsGroup0 upto10kg
Group 0+ up to 13 kg
Group 1 9-18 kg
Group 2 15-25 kg
Group 3 22-36 kg
139
Page 144 of 280

All restraint devices must bear the
type-approval data along with
the control mark on a label firmly
secured to the child seat which must
never be removed.
Lineaccessori Alfa Romeo includes
child restraint systems for each weight
group. These devices are
recommended having been specifically
tested for Alfa Romeo cars.
WARNING
77) SEVERE DANGER. When an
active passenger airbag is fitted,
DO NOT install rear facing child
restraint systems on the front
seat. Deployment of the airbag in
an accident could cause fatal
injuries to the baby regardless of
the severity of the impact. It is
advisable to always carry children
in a child restraint system on the
rear seat, which is the most
protected position in the event of
a collision.
78) On the sun visor there is a label
with suitable symbols
remembering that it is compulsory
to deactivate the airbag if a rear
facing child restraint system is
fitted. Always comply with the
instructions on the passenger's
side sun visor (see the "Front
airbag" paragraph).
FITTING
“UNIVERSAL” CHILD
SEAT (with seat
belts)GROUP 0 and 0+
80)
Infants up to 13 kg must be carried with
a child seat facing backwards of a
type as shown in fig. 113 which,
supporting the head, does not induce
stress on the neck in the event of
sudden decelerations.
The child seat is secured by the car
seat belts, as shown in fig. 113 and it
must restrain the child in turn with
its own belts.113
A0K0014
140
SAFETY
Page 145 of 280
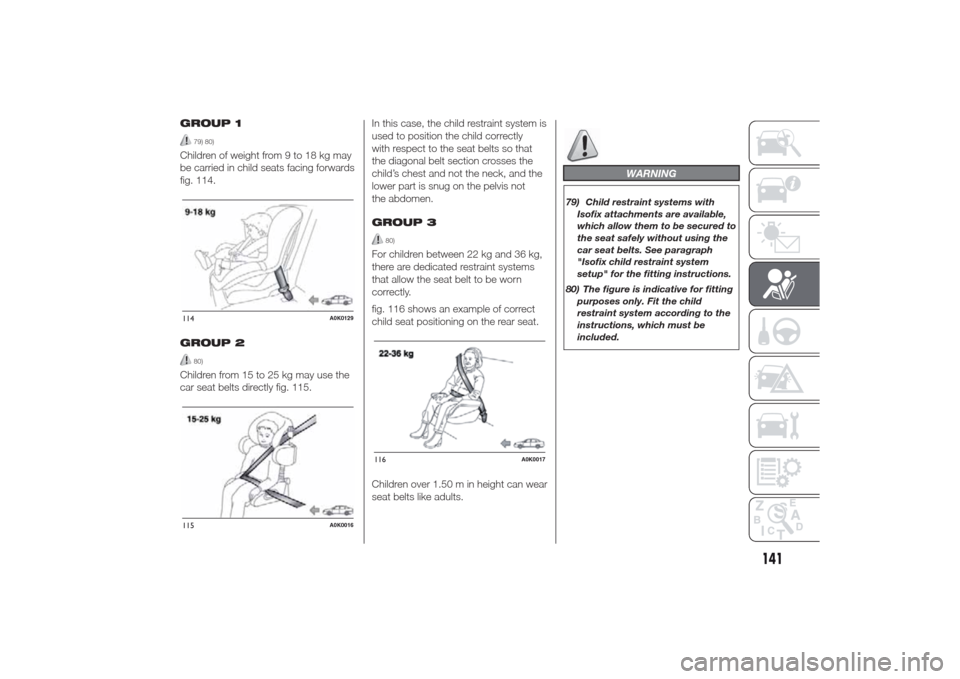
GROUP 1
79) 80)
Children of weight from 9 to 18 kg may
be carried in child seats facing forwards
fig. 114.
GROUP 2
80)
Children from 15 to 25 kg may use the
car seat belts directly fig. 115.In this case, the child restraint system is
used to position the child correctly
with respect to the seat belts so that
the diagonal belt section crosses the
child’s chest and not the neck, and the
lower part is snug on the pelvis not
the abdomen.
GROUP 3
80)
For children between 22 kg and 36 kg,
there are dedicated restraint systems
that allow the seat belt to be worn
correctly.
fig. 116 shows an example of correct
child seat positioning on the rear seat.
Children over 1.50 m in height can wear
seat belts like adults.
WARNING
79) Child restraint systems with
Isofix attachments are available,
which allow them to be secured to
the seat safely without using the
car seat belts. See paragraph
"Isofix child restraint system
setup" for the fitting instructions.
80) The figure is indicative for fitting
purposes only. Fit the child
restraint system according to the
instructions, which must be
included.
114
A0K0129
115
A0K0016
116
A0K0017
141
Page 146 of 280
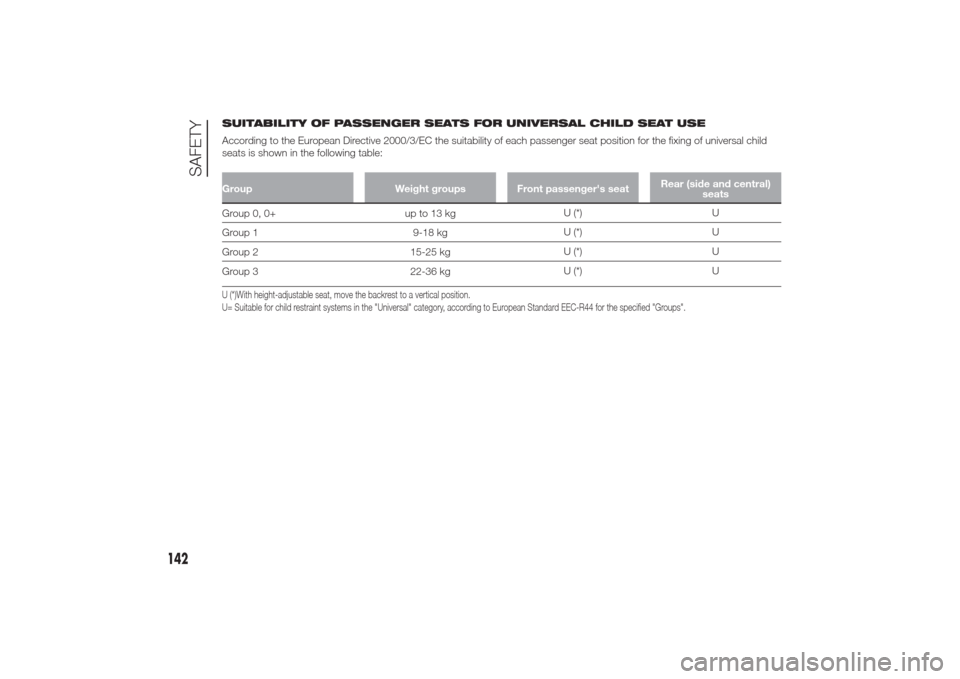
SUITABILITY OF PASSENGER SEATS FOR UNIVERSAL CHILD SEAT USE
According to the European Directive 2000/3/EC the suitability of each passenger seat position for the fixing of universal child
seats is shown in the following table:Group Weight groups Front passenger's seatRear (side and central)
seatsGroup 0, 0+ up to 13 kgU (*) U
Group 1 9-18 kgU (*) U
Group 2 15-25 kgU (*) U
Group 3 22-36 kgU (*) UU (*)With height-adjustable seat, move the backrest to a vertical position.
U= Suitable for child restraint systems in the "Universal" category, according to European Standard EEC-R44 for the specified "Groups".
142
SAFETY
Page 147 of 280
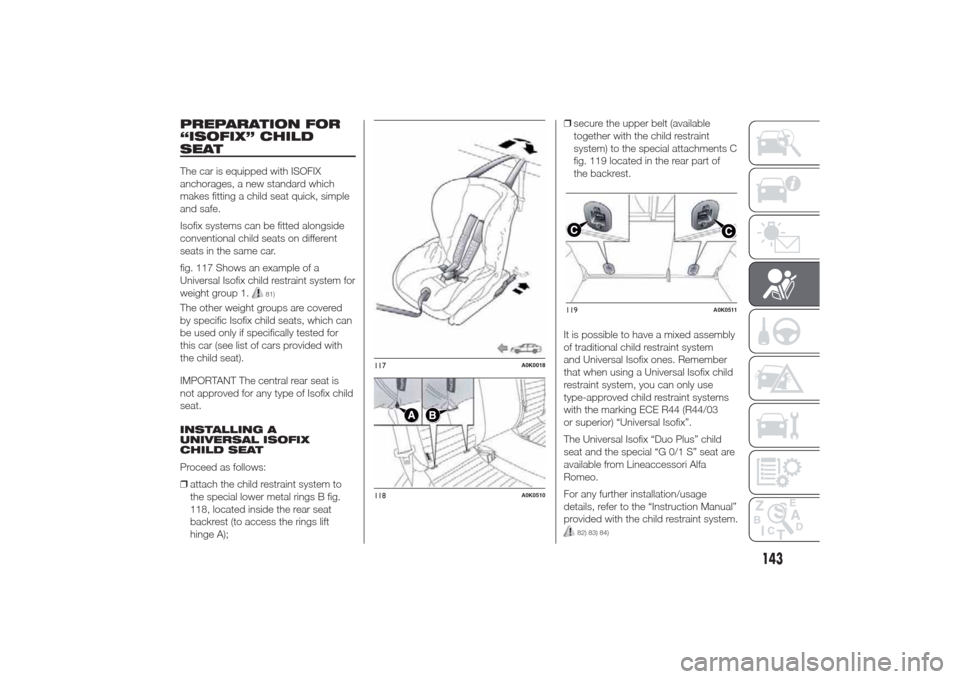
PREPARATION FOR
“ISOFIX” CHILD
SEATThe car is equipped with ISOFIX
anchorages, a new standard which
makes fitting a child seat quick, simple
and safe.
Isofix systems can be fitted alongside
conventional child seats on different
seats in the same car.
fig. 117 Shows an example of a
Universal Isofix child restraint system for
weight group 1.
81)
The other weight groups are covered
by specific Isofix child seats, which can
be used only if specifically tested for
this car (see list of cars provided with
the child seat).
IMPORTANT The central rear seat is
not approved for any type of Isofix child
seat.
INSTALLING A
UNIVERSAL ISOFIX
CHILD SEAT
Proceed as follows:
❒attach the child restraint system to
the special lower metal rings B fig.
118, located inside the rear seat
backrest (to access the rings lift
hinge A);❒secure the upper belt (available
together with the child restraint
system) to the special attachments C
fig. 119 located in the rear part of
the backrest.
It is possible to have a mixed assembly
of traditional child restraint system
and Universal Isofix ones. Remember
that when using a Universal Isofix child
restraint system, you can only use
type-approved child restraint systems
with the marking ECE R44 (R44/03
or superior) “Universal Isofix”.
The Universal Isofix “Duo Plus” child
seat and the special “G 0/1 S” seat are
available from Lineaccessori Alfa
Romeo.
For any further installation/usage
details, refer to the “Instruction Manual”
provided with the child restraint system.
82) 83) 84)
117
A0K0018
118
A0K0510
119
A0K0511
143
Page 148 of 280
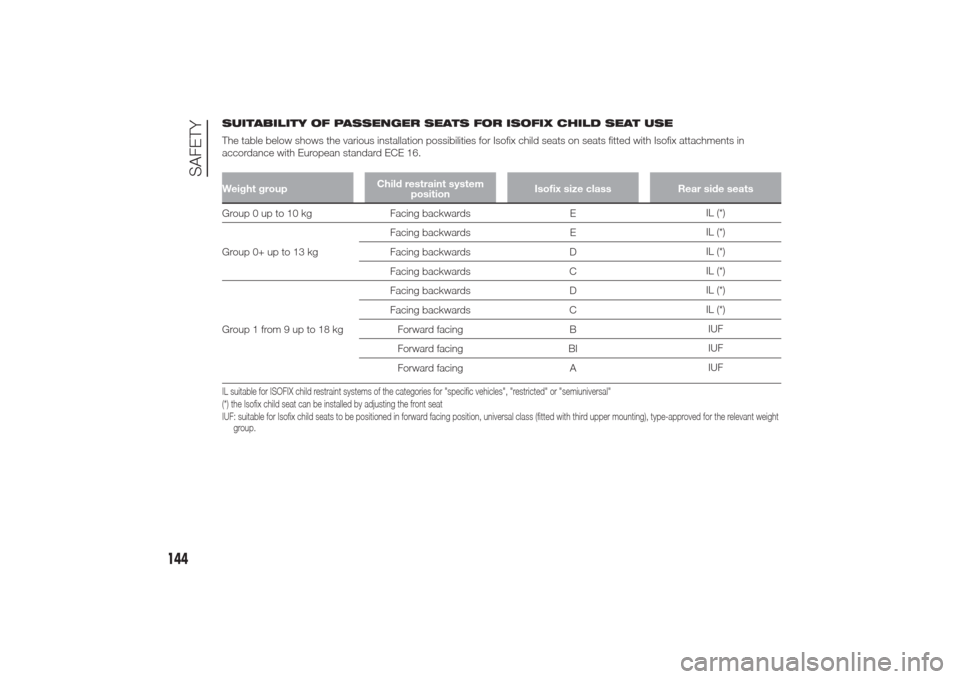
SUITABILITY OF PASSENGER SEATS FOR ISOFIX CHILD SEAT USE
The table below shows the various installation possibilities for Isofix child seats on seats fitted with Isofix attachments in
accordance with European standard ECE 16.Weight groupChild restraint system
positionIsofix size class Rear side seatsGroup 0 up to 10 kg Facing backwards EIL (*)
Group 0+ up to 13 kgFacing backwards EIL (*)
Facing backwards DIL (*)
Facing backwards CIL (*)
Group1from9upto18kgFacing backwards DIL (*)
Facing backwards CIL (*)
Forward facing BIUF
Forward facing BIIUF
Forward facing AIUFIL suitable for ISOFIX child restraint systems of the categories for "specific vehicles", "restricted" or "semiuniversal"
(*) the Isofix child seat can be installed by adjusting the front seat
IUF: suitable for Isofix child seats to be positioned in forward facing position, universal class (fitted with third upper mounting), type-approvedfor the relevant weight
group.
144
SAFETY
Page 168 of 280

If reverse (R) is engaged, only engage
the 1
stgear (or vice versa) when the car
is completely stopped.
Although it is highly inadvisable, if you
are driving downhill and, for unexpected
reasons, you let the car move forward
with the transmission in neutral (N),
when there is a request to engage
a gear, depending on the speed of the
car, the system will automatically
engage the best gear for the correct
transmission of drive torque to the
wheels.
107)IMPORTANT
21) If the car is on a gradient, always
pull the handbrake BEFORE
placing the gear lever in P.
22) Engage reverse only with the car
stationary, engine at idling speed
and accelerator fully released.
WARNING
106) Using the levers incorrectly
(levers pushed towards the
dashboard, see fig. 137) could
break them.
107) Never leave children
unattended in the car. Always
remove the ignition key when
leaving the car and take the key
with you.
SAVING FUELHere are some suggestions which can
help you to save fuel and lower harmful
emissions.
GENERAL
CONSIDERATIONS
Car maintenance
Checks and adjustments should be
carried out in accordance with the
“Scheduled Servicing Plan” (see
chapter “Maintenance and care”).
Tyres
Check the tyre pressures at least once
every four weeks: if the pressure is
too low, consumption levels increase as
resistance to rolling is higher.
Unnecessary loads
Do not travel with an overloaded boot.
The weight of the car and its
arrangement greatly affect fuel
consumption and stability.
164
STARTING AND DRIVING
Page 170 of 280

CONDITIONS OF USE
Cold starting
Short distances and frequent cold
start-ups will prevent the engine from
reaching optimal running temperature.
This results in a significant increase
in consumption levels (from +15 to
+30% on the urban cycle) and
emissions.
Traffic and road
conditions
High fuel consumption is caused by
heavy traffic, for instance when
travelling in a queue with frequent use
of low gears or in large towns with
many traffic lights. Winding mountain
roads and rough road surfaces also
adversely affect consumption.
Stops in traffic
During prolonged hold-ups (e.g. level
crossings) switch off the engine.
TOWING TRAILERSIMPORTANT
The vehicle must be provided with a
type-approved tow hook and adequate
electrical system to tow caravans or
trailers. Installation must be carried out
by a specialist.
Fit any specific and/or additional rear
view mirrors as specified by the
Highway Code.
Remember that when towing a trailer,
steep hills are harder to climb, the
braking spaces increase and overtaking
takes longer depending on the overall
weight.
Engage a low gear when driving
downhill, rather than constantly using
the brake.
The weight of the trailer reduces the
load capacity of the car by the same
amount. Consider the weight at full
load, including accessories and
luggage, to make sure you do not
exceed the maximum towable weight
(shown in the registration document).
Do not exceed the speed limits specific
to each country you are driving in, in
the case of vehicles towing trailers.
In any case do not exceed 100 km/h.INSTALLING A TOW
HOOK
Contact an Alfa Romeo Dealership to
install a tow hook.
108) 109)
WARNING
108) The ABS with which the car is
equipped will not control the
braking system of the trailer.
Particular caution is therefore
required when travelling on
slippery roads.
109) Never modify the braking
system of the car to control the
trailer brake. The trailer braking
system must be fully independent
from the hydraulic system of the
car.
166
STARTING AND DRIVING