wheel torque Alfa Romeo MiTo 2014 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ALFA ROMEO, Model Year: 2014, Model line: MiTo, Model: Alfa Romeo MiTo 2014Pages: 280, PDF Size: 8.79 MB
Page 96 of 280
If the ABS system intervenes, this indicates that the
traction of the tyres on the road is nearing its limit.
Slow down to a speed compatible with the available
traction.The ABS gets the most from the available grip, but it
cannot improve it; you should therefore take every
care when driving on slippery surfaces and not take
unnecessary risks.When the ABS cuts in and you feel the brake pedal
pulsating, do not remove your foot, but keep the pedal
pushed down; in doing so you, will stop in the
shortest distance possible under the road conditions at the time.
ESC (Electronic Stability
Control) SYSTEMThis is an electronic system controlling car stability in the event of tyre
grip loss, helping to maintain directional control.
The system is capable of recognising potentially dangerous situations
in terms of the stability and intervenes automatically on the brakes in a
differentiated manner for the four wheels in order to provide a
stabilising torque.
The ESC system also includes the following systems:
❒Hill Holder
❒ASR
❒Brake Assist
❒MSR
❒CBC
❒“ELECTRONIC Q2” (“E-Q2”)
❒DSTSYSTEM ACTIVATIONThe ESC system switches on automatically when the engine is started
and cannot be switched off.SYSTEM INTERVENTIONIt is signalled by the blinking of the warning light
on the instrument
panel, to inform the driver that the car is in critical stability and grip
conditions.
92GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 97 of 280

HILL HOLDER SYSTEMThis system is an integral part of the ESC system and facilitates starting
on slopes.
It is automatically activated in the following conditions:
❒uphill: vehicle stationary on a road with a gradient higher than 5%,
engine running, brake pedal pressed and gearbox in neutral or
gear (other than reverse) engaged;
❒downhill: vehicle stationary on a road with a gradient higher than
5%, engine running, brake pedal pressed and reverse gear
engaged.
When setting off the ESC system control unit maintains the braking
pressure at the wheels until the engine torque required for departure is
reached or for approximately 2 seconds, allowing your right foot to
be moved easily from the brake pedal to the accelerator.
If the vehicle has not departed after this time, the system will deactivate
automatically by gradually releasing the brake force. A sound may
be heard during this stage: this indicates that the vehicle is about
to move off.
IMPORTANT The Hill Holder system is not a handbrake. Do not leave
the vehicle without having engaged the handbrake, switched off the
engine and engaged a gear.ASR (AntiSlip Regulation) SYSTEMIt is an integral part of the ESC system. It automatically operates in the
event of one or both drive wheels slipping, loss of grip on wet roads
(aquaplaning) and acceleration on slippery, snowy or icy roads, etc.Depending on the slipping conditions, two different control systems are
activated:
❒if the slipping involves both drive wheels, the ASR intervenes
reducing the power transmitted by the engine;
❒if the slipping only involves one of the drive wheels, the ASR
intervenes automatically braking the wheel that is slipping.
For the correct operation of the ESC and ASR systems,
the tyres must be the same make and type on all
wheels, in perfect condition and, above all, of the type,
make and size recommended.The ESC system operates even when the space-saver
wheel is being used. Always remember that the
space-saver wheel, being smaller than the original
wheel, provides less grip.Do not take unnecessary risks, even if your vehicle is
fitted with the ESC and ASR systems. Driving style must
always be adapted to road conditions, visibility and
traffic. The driver is always responsible for road safety.
93GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CARSAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 98 of 280
BRAKE ASSIST(assistance during emergency braking)
The system, which cannot be turned off, recognises emergency braking
(on the basis of the brake pedal operating speed) and speeding up
the response of the braking system. The Brake Assist device is
deactivated if there is a ESC system failure.MSR SYSTEM(Motor Schleppmoment Regelung)
This system is an integral part of the ABS, that intervenes, if there is a
sudden downshifting, restoring torque to the engine, thereby
preventing excessive drive at the drive wheels which, especially in poor
grip conditions, could lead to a loss in stability of the car.CBC (Cornering Brake Control)
SYSTEMThis function improves the distribution of the braking pressure at the
four wheels (to fully exploit the grip available on the ground) when
braking on bends if the ABS intervenes. This improves stopping
distances and above all vehicle stability when cornering.
“ELECTRONIC Q2” SYSTEM (“E-Q2”)The “Electronic Q2” system uses the braking system to create an effect
similar to a limited slip differential.
The front braking system, when accelerating around a curve, acts on
the inside wheel to increase the drive to the outside wheel (increased
load), dynamically and continuously distributing the torque between
the front drive wheels according to driving and road conditions.
The system, combined with MacPherson front suspension, allows
particularly effective and sports driving to be achieved.DST SYSTEM
(Dynamic Steering Torque)This function integrates Dual Pinion active steering into the operation of
ESC. For particular manoeuvres, the ESC system controls the steering
to actuate a steering torque and assist the driver in the best possible
way.
The system operates the brakes and steering in a coordinated manner
to increase the suspension and safety level of the car as a whole.
The steering provides additional torque on the steering wheel.
94GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
Page 100 of 280
Steering wheel tuning:functions aimed at comfort in normal
conditions of use.
DST:braking standard control coordinated with ABS/ESC. Standard
control over lateral acceleration. Oversteer compensation: a slight
pulse on the steering wheel encourages the driver to carry out the most
appropriate manoeuvre.
Engine:standard response.ENGAGEMENT/DISENGAGEMENT OF
“Dynamic” MODEEngagement
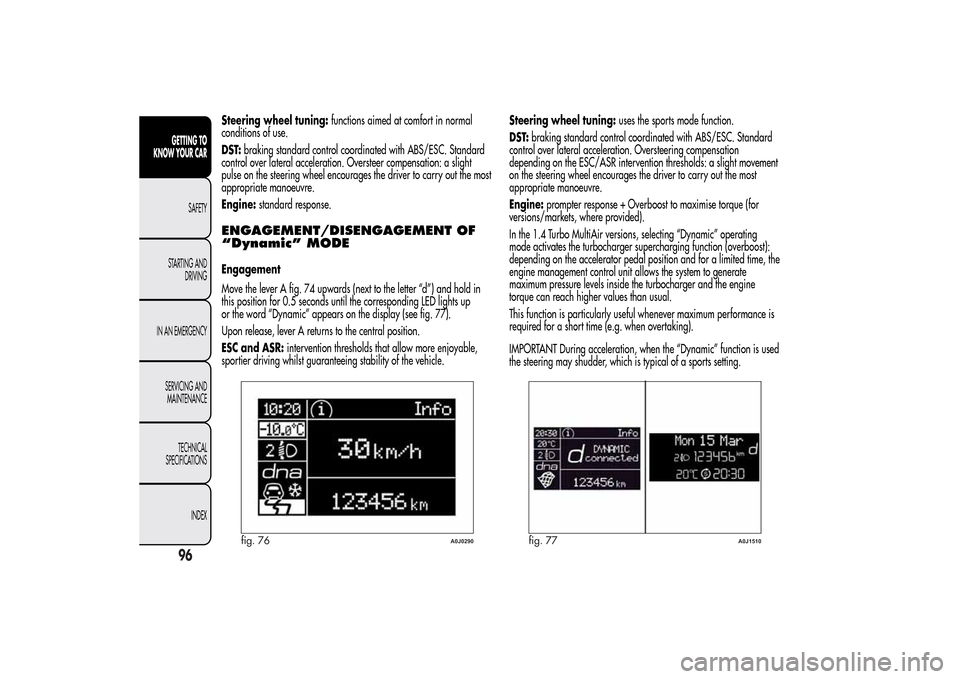
Move the lever A fig. 74 upwards (next to the letter “d”) and hold in
this position for 0.5 seconds until the corresponding LED lights up
or the word “Dynamic” appears on the display (see fig. 77).
Upon release, lever A returns to the central position.
ESC and ASR:intervention thresholds that allow more enjoyable,
sportier driving whilst guaranteeing stability of the vehicle.Steering wheel tuning:uses the sports mode function.
DST:braking standard control coordinated with ABS/ESC. Standard
control over lateral acceleration. Oversteering compensation
depending on the ESC/ASR intervention thresholds: a slight movement
on the steering wheel encourages the driver to carry out the most
appropriate manoeuvre.
Engine:prompter response + Overboost to maximise torque (for
versions/markets, where provided).
In the 1.4 Turbo MultiAir versions, selecting “Dynamic” operating
mode activates the turbocharger supercharging function (overboost):
depending on the accelerator pedal position and for a limited time, the
engine management control unit allows the system to generate
maximum pressure levels inside the turbocharger and the engine
torque can reach higher values than usual.
This function is particularly useful whenever maximum performance is
required for a short time (e.g. when overtaking).
IMPORTANT During acceleration, when the “Dynamic” function is used
the steering may shudder, which is typical of a sports setting.
fig. 76
A0J0290
fig. 77
A0J1510
96GETTING TO
KNOW YOUR CAR
SAFETY
STARTING AND
DRIVING
IN AN EMERGENCY
SERVICING AND
MAINTENANCE
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX