Alfa Romeo Stelvio 2018 Owner's Manual
Manufacturer: ALFA ROMEO, Model Year: 2018, Model line: Stelvio, Model: Alfa Romeo Stelvio 2018Pages: 276, PDF Size: 5.79 MB
Page 121 of 276

Warning!
Relying on the air bags alone could lead to
more severe injuries in a collision. The air
bags work with your seat belt to restrain
you properly. In some collisions, the air bags
won’t deploy at all. Always wear your seat
belt even though you have air bags.
In a collision, you and your passengers can
suffer much greater injuries if you are not
properly buckled up. You can strike the
interior of your vehicle or other passengers,
or you can be thrown out of the vehicle.
Always be sure you and others in your
vehicle are buckled up properly.
It is dangerous to ride in a cargo area,
inside or outside of a vehicle. In a collision,
people riding in these areas are more likely
to be seriously injured or killed.
Do not allow people to ride in any area of
your vehicle that is not equipped with seats
and seat belts.
Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a
seat and using a seat belt properly.
Occupants, including the driver, should
always wear their seat belts whether or not
an air bag is also provided at their seating
position to minimize the risk of severe injury
or death in the event of a crash.
Wearing your seat belt incorrectly could
make your injuries in a collision much worse.
You might suffer internal injuries, or you
could even slide out of the seat belt. Follow
these instructions to wear your seat belt
safely and to keep your passengers safe,
too.
Two people should never be belted into a
single seat belt. People belted together can
crash into one another in a collision, hurting
one another badly. Never use a lap/shoulder
belt or a lap belt for more than one person,
no matter what their size.
Warning!
A lap belt worn too high can increase the
risk of injury in a collision. The seat belt
forces won’t be at the strong hip and pelvic
bones, but across your abdomen. Always
wear the lap part of your seat belt as low as
possible and keep it snug.
A twisted seat belt may not protect you
properly. In a collision, it could even cut into you.
Be sure the seat belt is flat against your body,
without twists. If you can’t straighten a seat
belt in your vehicle, take it to your authorized
dealer immediately and have it fixed.
A seat belt that is buckled into the wrong
buckle will not protect you properly. The lap
portion could ride too high on your body,
possibly causing internal injuries. Always buckle
your seat belt into the buckle nearest you.
A seat belt that is too loose will not protect
you properly. In a sudden stop, you could move
too far forward, increasing the possibility of
injury. Wear your seat belt snugly.
A seat belt that is worn under your arm is
dangerous. Your body could strike the inside
surfaces of the vehicle in a collision,
increasing head and neck injury. A seat belt
worn under the arm can cause internal injuries. Ribs aren’t as strong as shoulder
bones. Wear the seat belt over your
shoulder so that your strongest bones will
take the force in a collision.
A shoulder belt placed behind you will not
protect you from injury during a collision.
You are more likely to hit your head in a
collision if you do not wear your shoulder
belt. The lap and shoulder belt are meant to
be used together.
A frayed or torn seat belt could rip apart
in a collision and leave you with no
protection. Inspect the seat belt system
periodically, checking for cuts, frays, or
loose parts. Damaged parts must be
replaced immediately. Do not disassemble
or modify the seat belt system. Seat belt
assemblies must be replaced after a
collision.
Lap/Shoulder Belt Operating
Instructions
1. Enter the vehicle and close the door.
Sit back and adjust the seat.
2. The seat belt latch plate is above the
back of the front seat, and next to your
arm in the rear seat (for vehicles
equipped with a rear seat). Grasp the
latch plate and pull out the seat belt.
Slide the latch plate up the webbing as
far as necessary to allow the seat belt to
go around your lap.
3. When the seat belt is long enough to
fit, insert the latch plate into the buckle
until you hear a “click.”
119
Page 122 of 276

4. Position the lap belt so that it is snug
and lies low across your hips, below your
abdomen. To remove slack in the lap belt
portion, pull up on the shoulder belt. To
loosen the lap belt if it is too tight, tilt the
latch plate and pull on the lap belt. A snug
seat belt reduces the risk of sliding under
the seat belt in a collision.
5. Position the shoulder belt across the
shoulder and chest with minimal, if any
slack so that it is comfortable and not
resting on your neck. The retractor will
withdraw any slack in the shoulder belt.
6. To release the seat belt, push the red
button on the buckle. The seat belt will
automatically retract to its stowed
position. If necessary, slide the latch
plate down the webbing to allow the seat
belt to retract fully.
Lap/Shoulder Belt Untwisting
Procedure
Use the following procedure to untwist a
twisted lap/shoulder belt.
1. Position the latch plate as close as
possible to the anchor point.
2. At about 6 to 12 inches (15 to 30 cm)
above the latch plate, grasp and twist the
seat belt webbing 180 degrees to create
a fold that begins immediately above the
latch plate.
3. Slide the latch plate upward over the
folded webbing. The folded webbing
must enter the slot at the top of the latch
plate.
4. Continue to slide the latch plate up
until it clears the folded webbing and the
seat belt is no longer twisted.
Adjustable Upper Shoulder Belt
Anchorage
In the driver and front passenger seats,
the top of the shoulder belt can be
adjusted upward or downward to position
the seat belt away from your neck. Push
or squeeze the anchorage button to
release the anchorage, and move it up or
down to the position that serves you
best.As a guide, if you are shorter than
average, you will prefer the shoulder belt
anchorage in a lower position, and if you
are taller than average, you will prefer the
shoulder belt anchorage in a higher
position. After you release the anchorage
button, try to move it up or down to make
sure that it is locked in position.
Note:
The adjustable upper shoulder belt
anchorage is equipped with an Easy Up
feature. This feature allows the shoulder
belt anchorage to be adjusted in the
upward position without pushing or
squeezing the release button. To verify
the shoulder belt anchorage is latched,
pull downward on the shoulder belt
anchorage until it is locked into position.
0101132150USSeat Belt Latch Plate Inserted Into Seat Belt Buckle0101132173USAdjustable Upper Shoulder BeltAnchorage
4 — Adjustable Anchorage
120
SAFETY
Page 123 of 276

Warning!
Wearing your seat belt incorrectly could
make your injuries in a collision much worse.
You might suffer internal injuries, or you
could even slide out of the seat belt. Follow
these instructions to wear your seat belt
safely and to keep your passengers safe,
too.
Position the shoulder belt across the
shoulder and chest with minimal, if any slack
so that it is comfortable and not resting on
your neck. The retractor will withdraw any
slack in the shoulder belt.
Misadjustment of the seat belt could
reduce the effectiveness of the safety belt
in a crash.
Seat Belts And Pregnant Women
Seat belts must be worn by all occupants
including pregnant women: the risk of
injury in the event of an accident is reduced for the mother and the unborn
child if they are wearing a seat belt.
Position the lap belt snug and low below
the abdomen and across the strong
bones of the hips. Place the shoulder belt
across the chest and away from the neck.
Never place the shoulder belt behind the
back or under the arm.
Seat Belt Pretensioner
The front seat belt system is equipped
with pretensioning devices that are
designed to remove slack from the seat
belt in the event of a collision. These
devices may improve the performance of
the seat belt by removing slack from the
seat belt early in a collision.
Pretensioners work for all size
occupants, including those in child
restraints.
Note:
These devices are not a substitute
for proper seat belt placement by the
occupant. The seat belt still must be worn
snugly and positioned properly.
The pretensioners are triggered by the
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC).
Like the air bags, the pretensioners are
single use items. A deployed
pretensioner or a deployed air bag must
be replaced immediately.
Energy Management Feature
The front seat belt system is equipped
with an Energy Management feature that
may help further reduce the risk of injury
in the event of a collision. The seat belt system has a retractor assembly that is
designed to release webbing in a
controlled manner.
Switchable Automatic Locking
Retractors (ALR)
The seat belts in the passenger seating
positions are equipped with a Switchable
Automatic Locking Retractor (ALR) which
is used to secure a child restraint system.
For additional information, refer to
“Installing Child Restraints Using The
Vehicle Seat Belt” under the “Child
Restraints” section of this manual. The
figure below illustrates the locking
feature for each seating position.
If the passenger seating position is
equipped with an ALR and is being used
for normal usage, only pull the seat belt
webbing out far enough to comfortably
wrap around the occupant’s mid-section
so as to not activate the ALR. If the ALR
is activated, you will hear a clicking sound
as the seat belt retracts. Allow the
0226075266Pregnant Women And Seat Belts
16086V0101NAALR — Switchable Automatic Locking
Retractor
121
Page 124 of 276

webbing to retract completely in this
case and then carefully pull out only the
amount of webbing necessary to
comfortably wrap around the occupant’s
mid-section. Slide the latch plate into the
buckle until you hear a "click."
In Automatic Locking Mode, the shoulder
belt is automatically pre-locked. The seat
belt will still retract to remove any slack
in the shoulder belt. Use the Automatic
Locking Mode anytime a child restraint is
installed in a seating position that has a
seat belt with this feature. Children
12 years old and under should always be
properly restrained in the rear seat of a
vehicle with a rear seat.
Warning!
Never place a rear-facing child restraint in
front of an air bag. A deploying passenger
front air bag can cause death or serious
injury to a child 12 years or younger,
including a child in a rear-facing child
restraint.
Only use a rear-facing child restraint in
the rear seat of a vehicle with a rear seat.
How To Engage The Automatic Locking
Mode
1. Buckle the combination lap and
shoulder belt. 2. Grasp the shoulder portion and pull
downward until the entire seat belt is
extracted.
3. Allow the seat belt to retract. As the
seat belt retracts, you will hear a clicking
sound. This indicates the seat belt is now
in the Automatic Locking Mode.
How To Disengage The Automatic
Locking Mode
Unbuckle the combination lap/shoulder
belt and allow it to retract completely to
disengage the Automatic Locking Mode
and activate the vehicle sensitive
(emergency) locking mode.
Warning!
The seat belt assembly must be replaced
if the switchable Automatic Locking
Retractor (ALR) feature or any other seat
belt function is not working properly when
checked according to the procedures in the
Service Manual.
Failure to replace the seat belt assembly
could increase the risk of injury in collisions.
Do not use the Automatic Locking Mode
to restrain occupants who are wearing the
seat belt or children who are using booster
seats. The locked mode is only used to
install rear-facing or forward-facing child
restraints that have a harness for
restraining the child.
Supplemental Restraint Systems
(SRS)
Some of the safety features described in
this section may be standard equipment
on some models, or may be optional
equipment on others. If you are not sure,
ask your authorized dealer.
The air bag system must be ready to
protect you in a collision. The Occupant
Restraint Controller (ORC) monitors the
internal circuits and interconnecting
wiring associated with the electrical Air
Bag System Components. Your vehicle
may be equipped with the following Air
Bag System Components:
Air Bag System Components
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
Air Bag Warning Light
Steering Wheel and Column
Instrument Panel
Knee Impact Bolsters
Driver and Front Passenger Air Bags
Seat Belt Buckle Switch
Supplemental Side Air Bags
Supplemental Knee Air Bags
Front and Side Impact Sensors
Seat Belt Pretensioners
Seat Track Position Sensors
122
SAFETY
Page 125 of 276

Air Bag Warning Light
The ORC monitors the readiness of the
electronic parts of the air bag system
whenever the ignition switch is in the
START or ON/RUN position. If the ignition
switch is in the OFF position or in the ACC
position, the air bag system is not on and
the air bags will not inflate.
The ORC contains a backup power supply
system that may deploy the air bag
system even if the battery loses power or
it becomes disconnected prior to
deployment.
The ORC turns on the Air Bag Warning
Light in the instrument panel for
approximately four to eight seconds for a
self-check when the ignition switch is
first in the ON/RUN position. After the
self-check, the Air Bag Warning Light will
turn off. If the ORC detects a malfunction
in any part of the system, it turns on the
Air Bag Warning Light, either
momentarily or continuously. A single
chime will sound to alert you if the light
comes on again after initial startup.
The ORC also includes diagnostics that
will illuminate the instrument panel Air
Bag Warning Light if a malfunction is
detected that could affect the air bag
system. The diagnostics also record the
nature of the malfunction. While the air
bag system is designed to be
maintenance free, if any of the followingoccurs, have an authorized dealer service
the air bag system immediately.
The Air Bag Warning Light does not
come on during the four to eight seconds
when the ignition switch is first in the
ON/RUN position.
The Air Bag Warning Light remains on
after the four to eight-second interval.
The Air Bag Warning Light comes on
intermittently or remains on while
driving.
Note: If the speedometer, tachometer,
or any engine related gauges are not
working, the Occupant Restraint
Controller (ORC) may also be disabled. In
this condition the air bags may not be
ready to inflate for your protection. Have
an authorized dealer service the air bag
system immediately.
Warning!
Ignoring the Air Bag Warning Light in your
instrument panel could mean you won’t have
the air bag system to protect you in a
collision. If the light does not come on as a
bulb check when the ignition is first turned
on, stays on after you start the vehicle, or if
it comes on as you drive, have an authorized
dealer service the air bag system
immediately.
Redundant Air Bag Warning Light
If a fault with the Air Bag Warning Light is
detected, which could affect the
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS),
the Redundant Air Bag Warning Light will
illuminate on the instrument panel. The
Redundant Air Bag Warning Light will
stay on until the fault is cleared. In
addition, a single chime will sound to alert
you that the Redundant Air Bag Warning
Light has come on and a fault has been
detected. If the Redundant Air Bag
Warning Light comes on intermittently or
remains on while driving have an
authorized dealer service the vehicle
immediately. For additional information
regarding the Redundant Air Bag Warning
Light refer to “Getting To Know Your
Instrument Panel” section of this manual.
Front Air Bags
This vehicle has front air bags and
lap/shoulder belts for both the driver and
front passenger. The front air bags are a
supplement to the seat belt restraint
systems. The driver front air bag is
mounted in the center of the steering
wheel. The passenger front air bag is
mounted in the instrument panel, above
the glove compartment. The words “SRS
AIRBAG” or “AIRBAG” are embossed on
the air bag covers.
123
Page 126 of 276
Warning!
Being too close to the steering wheel or
instrument panel during front air bag
deployment could cause serious injury,
including death. Air bags need room to
inflate. Sit back, comfortably extending
your arms to reach the steering wheel or
instrument panel.
Never place a rear-facing child restraint in
front of an air bag. A deploying passenger
front air bag can cause death or serious
injury to a child 12 years or younger,
including a child in a rear-facing child
restraint.
Only use a rear-facing child restraint in
the rear seat of a vehicle with a rear seat.
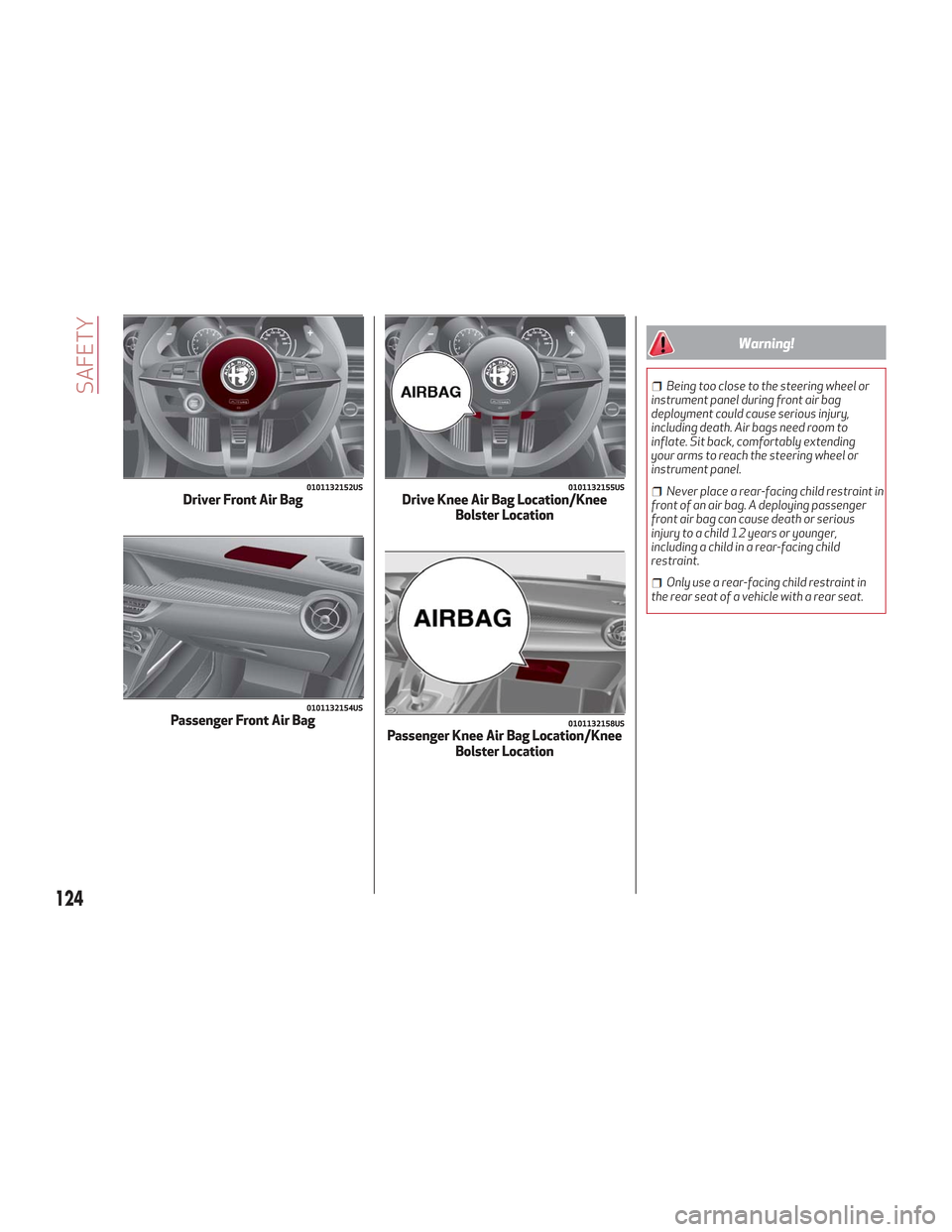
0101132152USDriver Front Air Bag
0101132154USPassenger Front Air Bag
0101132155USDrive Knee Air Bag Location/Knee Bolster Location
0101132158USPassenger Knee Air Bag Location/Knee Bolster Location
124
SAFETY
Page 127 of 276

Driver And Passenger Front Air Bag
Features
The Advanced Front Air Bag system has
multistage driver and front passenger air
bags. This system provides output
appropriate to the severity and type of
collision as determined by the Occupant
Restraint Controller (ORC), which may
receive information from the front
impact sensors (if equipped) or other
system components.
The first stage inflator is triggered
immediately during an impact that
requires air bag deployment. A low
energy output is used in less severe
collisions. A higher energy output is used
for more severe collisions.
This vehicle may be equipped with a
driver and/or front passenger seat belt
buckle switch that detects whether the
driver or front passenger seat belt is
buckled. The seat belt buckle switch may
adjust the inflation rate of the Advanced
Front Air Bags.
This vehicle may be equipped with driver
and/or front passenger seat track
position sensors that may adjust the
inflation rate of the Advanced Front Air
Bags based upon seat position.
Warning!
No objects should be placed over or near
the air bag on the instrument panel or
steering wheel because any such objects
could cause harm if the vehicle is in a
collision severe enough to cause the air bag
to inflate.
Do not put anything on or around the air
bag covers or attempt to open them
manually. You may damage the air bags and
you could be injured because the air bags
may no longer be functional. The protective
covers for the air bag cushions are designed
to open only when the air bags are inflating.
Relying on the air bags alone could lead to
more severe injuries in a collision. The air
bags work with your seat belt to restrain
you properly. In some collisions, air bags
won’t deploy at all. Always wear your seat
belts even though you have air bags.
Front Air Bag Operation
Front Air Bags are designed to provide
additional protection by supplementing
the seat belts. Front air bags are not
expected to reduce the risk of injury in
rear, side, or rollover collisions. The front
air bags will not deploy in all frontal
collisions, including some that may
produce substantial vehicle damage —
for example, some pole collisions, truck
underrides, and angle offset collisions.
On the other hand, depending on the type and location of impact, front air bags may
deploy in crashes with little vehicle
front-end damage but that produce a
severe initial deceleration.
Because air bag sensors measure vehicle
deceleration over time, vehicle speed and
damage by themselves are not good
indicators of whether or not an air bag
should have deployed.
Seat belts are necessary for your
protection in all collisions, and also are
needed to help keep you in position, away
from an inflating air bag.
When the ORC detects a collision
requiring the front air bags, it signals the
inflator units. A large quantity of
non-toxic gas is generated to inflate the
front air bags.
The steering wheel hub trim cover and
the upper passenger side of the
instrument panel separate and fold out of
the way as the air bags inflate to their full
size. The front air bags fully inflate in less
time than it takes to blink your eyes. The
front air bags then quickly deflate while
helping to restrain the driver and front
passenger.
Knee Impact Bolsters
The Knee Impact Bolsters help protect
the knees of the driver and front
passenger, and position the front
occupants for improved interaction with
the front air bags.
125
Page 128 of 276

Warning!
Do not drill, cut, or tamper with the knee
impact bolsters in any way.
Do not mount any accessories to the knee
impact bolsters such as alarm lights,
stereos, citizen band radios, etc.
Supplemental Driver And Front
Passenger Knee Air Bags
This vehicle is equipped with a
Supplemental Driver Knee Air Bag
mounted in the instrument panel below
the steering column and a Supplemental
Passenger Knee Air Bag mounted in the
instrument panel below the glove
compartment. The Supplemental Knee
Air Bags provide enhanced protection
during a frontal impact by working
together with the seat belts,
pretensioners, and front air bags.
Supplemental Side Air Bags
Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side Air
Bags (SABs)
This vehicle is equipped with
Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side Air
Bags (SABs).
Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side Air
Bags (SABs) are located in the outboard
side of the front seats. The SABs are
marked with “SRS AIRBAG” or “AIRBAG” on a label or on the seat trim on the
outboard side of the seats.
The SABs may help to reduce the risk of
occupant injury during certain side
impacts, in addition to the injury
reduction potential provided by the seat
belts and body structure.
When the SAB deploys, it opens the seam
on the outboard side of the seatback’s
trim cover. The inflating SAB deploys
through the seat seam into the space
between the occupant and the door. The
SAB moves at a very high speed and with
such a high force that it could injure
occupants if they are not seated
properly, or if items are positioned in the
area where the SAB inflates. Children are
at an even greater risk of injury from a
deploying air bag.
Warning!
Do not use accessory seat covers or place
objects between you and the Side Air Bags;
the performance could be adversely
affected and/or objects could be pushed into
you, causing serious injury.
Supplemental Side Air Bag Inflatable
Curtains (SABICs)
This vehicle is equipped with
Supplemental Side Air Bag Inflatable
Curtains (SABICs).
Supplemental Side Air Bag Inflatable
Curtains (SABICs) are located above the
side windows. The trim covering the
SABICs is labeled “SRS AIRBAG” or
“AIRBAG.”
0101132163USFront Supplemental Seat-Mounted Side
Air Bag
0101132180USSupplemental Side Air Bag InflatableCurtain (SABIC) Location
126
SAFETY
Page 129 of 276

SABICs may help reduce the risk of head
and other injuries to front and rear seat
outboard occupants in certain side
impacts, in addition to the injury
reduction potential provided by the seat
belts and body structure.
The SABIC deploys downward, covering
the side windows. An inflating SABIC
pushes the outside edge of the headliner
out of the way and covers the window.
The SABICs inflate with enough force to
injure occupants if they are not belted
and seated properly, or if items are
positioned in the area where the SABICs
inflate. Children are at an even greater
risk of injury from a deploying air bag.
The SABICs may help reduce the risk of
partial or complete ejection of vehicle
occupants through side windows in
certain side impact events.
Warning!
Do not mount equipment, or stack
luggage or other cargo up high enough to
block the deployment of the SABICs. The
trim covering above the side windows where
the SABIC and its deployment path are
located should remain free from any
obstructions.
In order for the SABICs to work as
intended, do not install any accessory items
in your vehicle which could alter the roof. Do
not add an aftermarket sunroof to your
vehicle. Do not add roof racks that require
permanent attachments (bolts or screws) for installation on the vehicle roof. Do not
drill into the roof of the vehicle for any
reason.
Side Impacts
The Side Air Bags are designed to
activate in certain side impacts. The
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
determines whether the deployment of
the Side Air Bags in a particular impact
event is appropriate, based on the
severity and type of collision. The side
impact sensors aid the ORC in
determining the appropriate response to
impact events. The system is calibrated
to deploy the Side Air Bags on the impact
side of the vehicle during impacts that
require Side Air Bag occupant protection.
In side impacts, the Side Air Bags deploy
independently; a left side impact deploys
the left Side Air Bags only and a
right-side impact deploys the right Side
Air Bags only. Vehicle damage by itself is
not a good indicator of whether or not
Side Air Bags should have deployed.
The Side Air Bags will not deploy in all
side collisions, including some collisions
at certain angles, or some side collisions
that do not impact the area of the
passenger compartment. The Side Air
Bags may deploy during angled or offset
frontal collisions where the front air bags
deploy.
Side Air Bags are a supplement to the
seat belt restraint system. Side Air Bags
deploy in less time than it takes to blink
your eyes.
Warning!
Occupants, including children, who are up
against or very close to Side Air Bags can be
seriously injured or killed. Occupants,
including children, should never lean on or
sleep against the door, side windows, or
area where the side air bags inflate, even if
they are in an infant or child restraint.
Seat belts (and child restraints where
appropriate) are necessary for your
protection in all collisions. They also help
keep you in position, away from an inflating
Side Air Bag. To get the best protection
from the Side Air Bags, occupants must
wear their seat belts properly and sit
upright with their backs against the seats.
Children must be properly restrained in a
child restraint or booster seat that is
appropriate for the size of the child.
Warning!
Side Air Bags need room to inflate. Do not
lean against the door or window. Sit upright
in the center of the seat.
Being too close to the Side Air Bags
during deployment could cause you to be
severely injured or killed.
127
Page 130 of 276

Relying on the Side Air Bags alone could
lead to more severe injuries in a collision.
The Side Air Bags work with your seat belt
to restrain you properly. In some collisions,
Side Air Bags won’t deploy at all. Always
wear your seat belt even though you have
Side Air Bags.
Note: Air bag covers may not be obvious
in the interior trim, but they will open
during air bag deployment.
Rollover Events
Side Air Bags are designed to activate in
certain rollover events. The ORC
determines whether the deployment of
the Side Air Bags in a particular rollover
event is appropriate, based on the
severity and type of collision. Vehicle
damage by itself is not a good indicator
of whether or not Side Air Bags should
have deployed.
The Side Air Bags will not deploy in all
rollover events. The rollover sensing
system determines if a rollover event
may be in progress and whether
deployment is appropriate. In the event
the vehicle experiences a rollover or near
rollover event, and deployment of the
Side Air Bags is appropriate, the rollover
sensing system will also deploy the seat
belt pretensioners on both sides of the
vehicle.
The SABICs may help reduce the risk of
partial or complete ejection of vehicle
occupants through side windows in
certain rollover or side impact events.
Air Bag System Components
Note: The Occupant Restraint Controller
(ORC) monitors the internal circuits and
interconnecting wiring associated with
electrical Air Bag System Components
listed below:
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
Air Bag Warning Light
Steering Wheel and Column
Instrument Panel
Knee Impact Bolsters
Driver and Front Passenger Air Bags
Seat Belt Buckle Switch
Supplemental Side Air Bags
Supplemental Knee Air Bags
Front and Side Impact Sensors
Seat Belt Pretensioners
Seat Track Position Sensors
If A Deployment Occurs
The front air bags are designed to deflate
immediately after deployment.
Note: Front and/or side air bags will not
deploy in all collisions. This does not
mean something is wrong with the air bag
system. If you do have a collision which deploys
the air bags, any or all of the following
may occur:
The air bag material may sometimes
cause abrasions and/or skin reddening to
the occupants as the air bags deploy and
unfold. The abrasions are similar to
friction rope burns or those you might get
sliding along a carpet or gymnasium floor.
They are not caused by contact with
chemicals. They are not permanent and
normally heal quickly. However, if you
haven’t healed significantly within a few
days, or if you have any blistering, see
your doctor immediately.
As the air bags deflate, you may see
some smoke-like particles. The particles
are a normal by-product of the process
that generates the non-toxic gas used for
air bag inflation. These airborne particles
may irritate the skin, eyes, nose, or
throat. If you have skin or eye irritation,
rinse the area with cool water. For nose
or throat irritation, move to fresh air. If
the irritation continues, see your doctor.
If these particles settle on your clothing,
follow the garment manufacturer’s
instructions for cleaning.
Do not drive your vehicle after the air
bags have deployed. If you are involved in
another collision, the air bags will not be
in place to protect you.
128
SAFETY