fuel AUDI S4 1998 B5 / 1.G Engine Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: AUDI, Model Year: 1998, Model line: S4, Model: AUDI S4 1998 B5 / 1.GPages: 72, PDF Size: 3.25 MB
Page 48 of 72

49
Sensors
Charge pressure sender G31
The charge pressure sender is located
upstream of the throttle valve control part.
The Motronic supplies the sender with a
voltage of 5 volts and earth.
The signal which the sender generates is a
pressure- proportional voltage ranging from 0
to 5 volts.
At atmospheric pressure (at sea-level), the
voltage is approx. 2.5 volts.
The signal is used for charge pressure control.
The Motronic also needs information on
charge pressure so that it can take counter-
measures if the maximum permissible
pressure is exceeded.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
If sender G31 fails, the charge pressure is
controlled via the characteristic curve (engine
speed-dependent). This will result in a
deficiency of engine power.
SSP 198/29
Charge pressure sender G31
The altitude sender F96 ....
... is integrated in the engine control unit, as is
normally the case with turbocharged engines.
... is required to control the charge pressure. In
conditions of decreasing air pressure (lower
density), the charge pressure is reduced to
prevent the turbocharger overspeeding.
... influences the air/fuel mixture composition
at engine start-up. The starting mixture is
leaned down with rising altitude.Substitute function and self-diagnosis
If a signal fails, the charge pressure is reduced
to a safe level, which results in a deficiency of
engine power.
Adaption of the injection quantity at start-up
no longer takes place.
The fault message “Control unit defective“ is
displayed in the self-diagnosis.
The following chapter presents the new features of the sensors, provided that they have not
already been described in the chapter on Subsystems of Motronic.
Page 56 of 72
57
Additional signals/interfaces
Additional signals/interfaces to
Motronic ME 7.1
The Motronic receives a large number of
additional signals.
The following overview shows the signal
direction and meaning referred to the Motronic
control unit
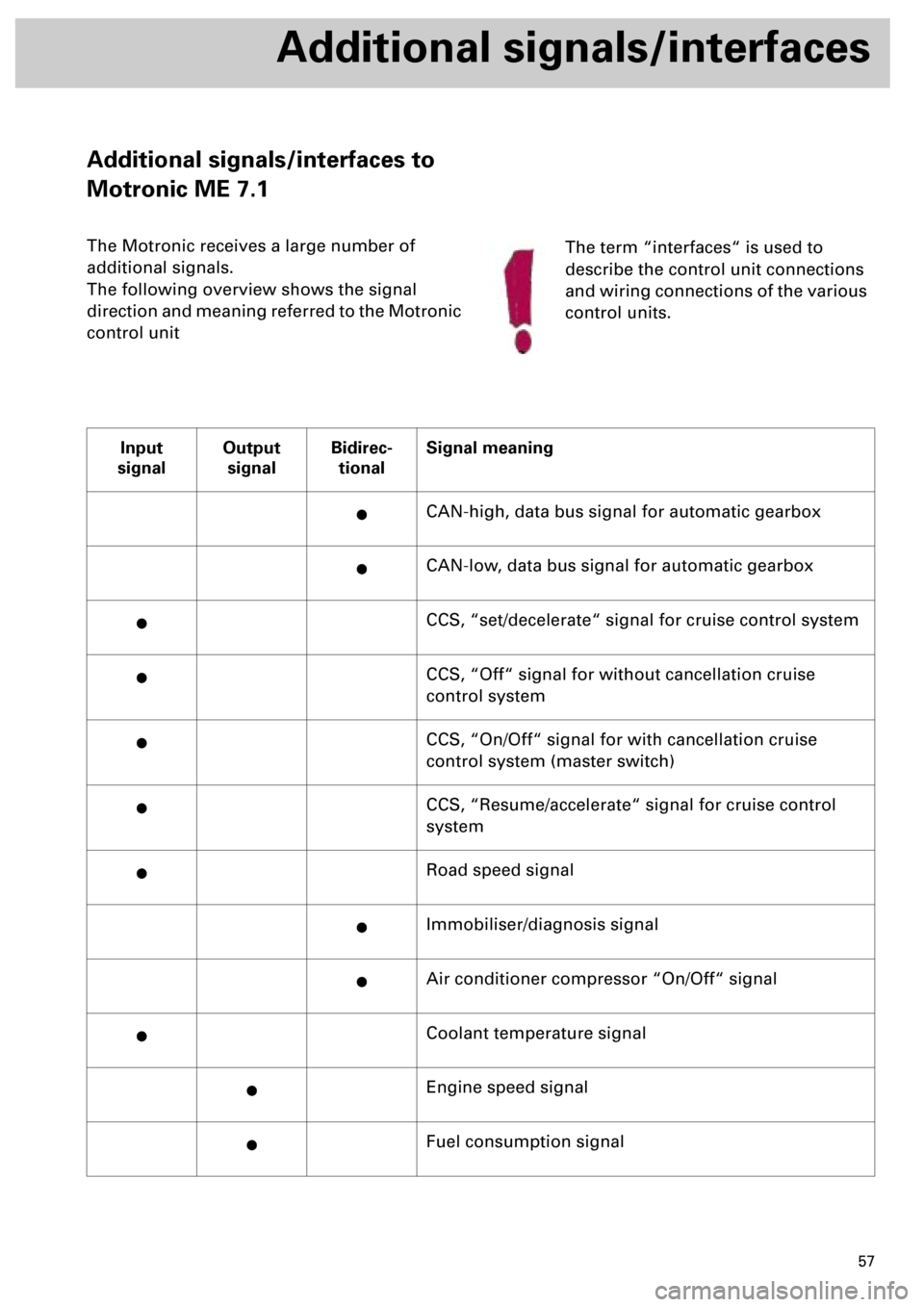
Input
signalOutput
signalBidirec-
tionalSignal meaning
·CAN-high, data bus signal for automatic gearbox
·CAN-low, data bus signal for automatic gearbox
·CCS, “set/decelerate“ signal for cruise control system
·CCS, “Off“ signal for without cancellation cruise
control system
·CCS, “On/Off“ signal for with cancellation cruise
control system (master switch)
·CCS, “Resume/accelerate“ signal for cruise control
system
·Road speed signal
·Immobiliser/diagnosis signal
·Air conditioner compressor “On/Off“ signal
·Coolant temperature signal
·Engine speed signal
·Fuel consumption signal
The term “interfaces“ is used to
describe the control unit connections
and wiring connections of the various
control units.
Page 60 of 72
61
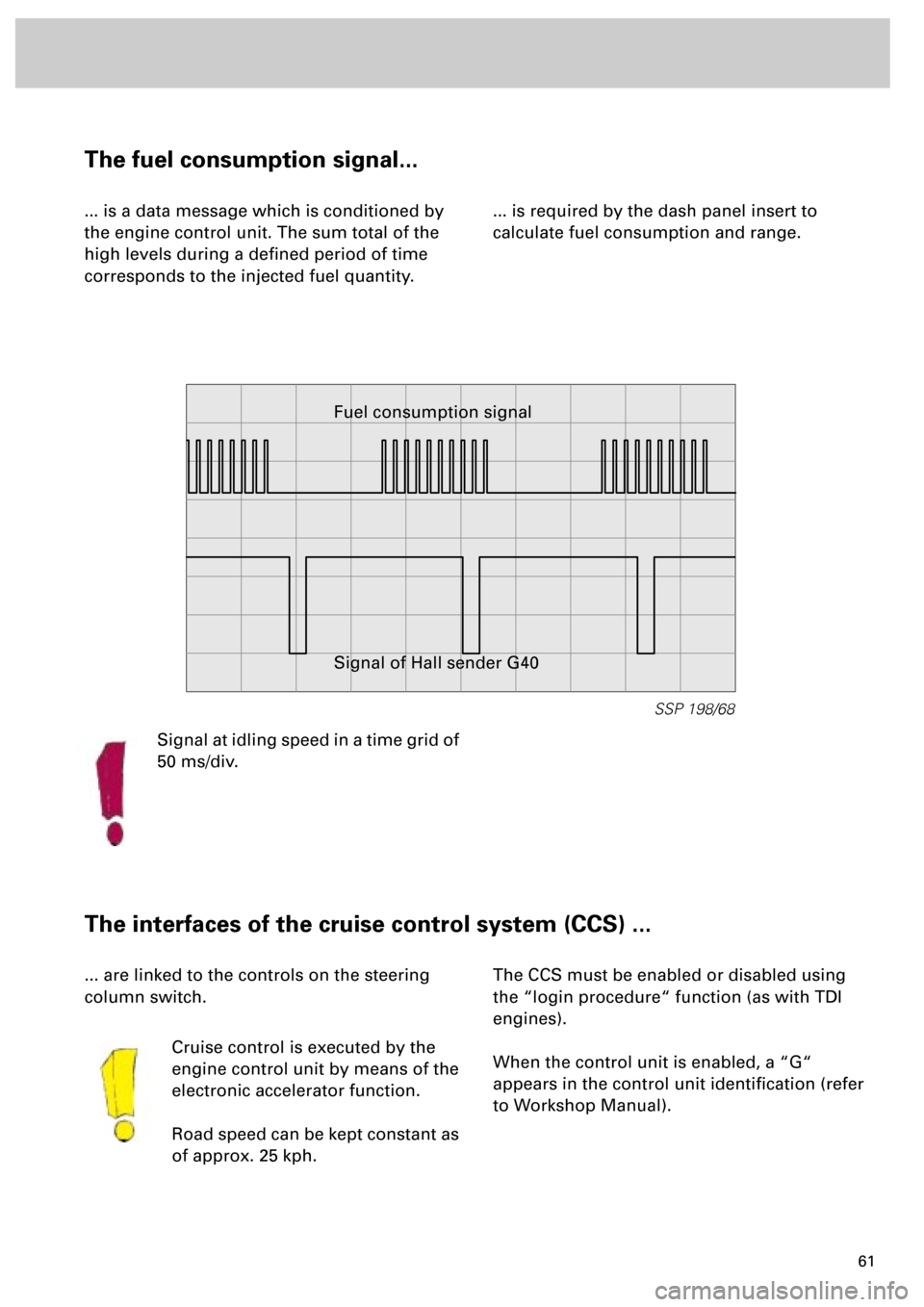
The fuel consumption signal...
... is a data message which is conditioned by
the engine control unit. The sum total of the
high levels during a defined period of time
corresponds to the injected fuel quantity.... is required by the dash panel insert to
calculate fuel consumption and range.
The interfaces of the cruise control system (CCS) ...
... are linked to the controls on the steering
column switch.
Cruise control is executed by the
engine control unit by means of the
electronic accelerator function.
Road speed can be kept constant as
of approx. 25 kph.The CCS must be enabled or disabled using
the “login procedure“ function (as with TDI
engines).
When the control unit is enabled, a “G“
appears in the control unit identification (refer
to Workshop Manual).
SSP 198/68
Fuel consumption signal
Signal of Hall sender G40
Signal at idling speed in a time grid of
50 ms/div.
Page 61 of 72
62
Functional diagram
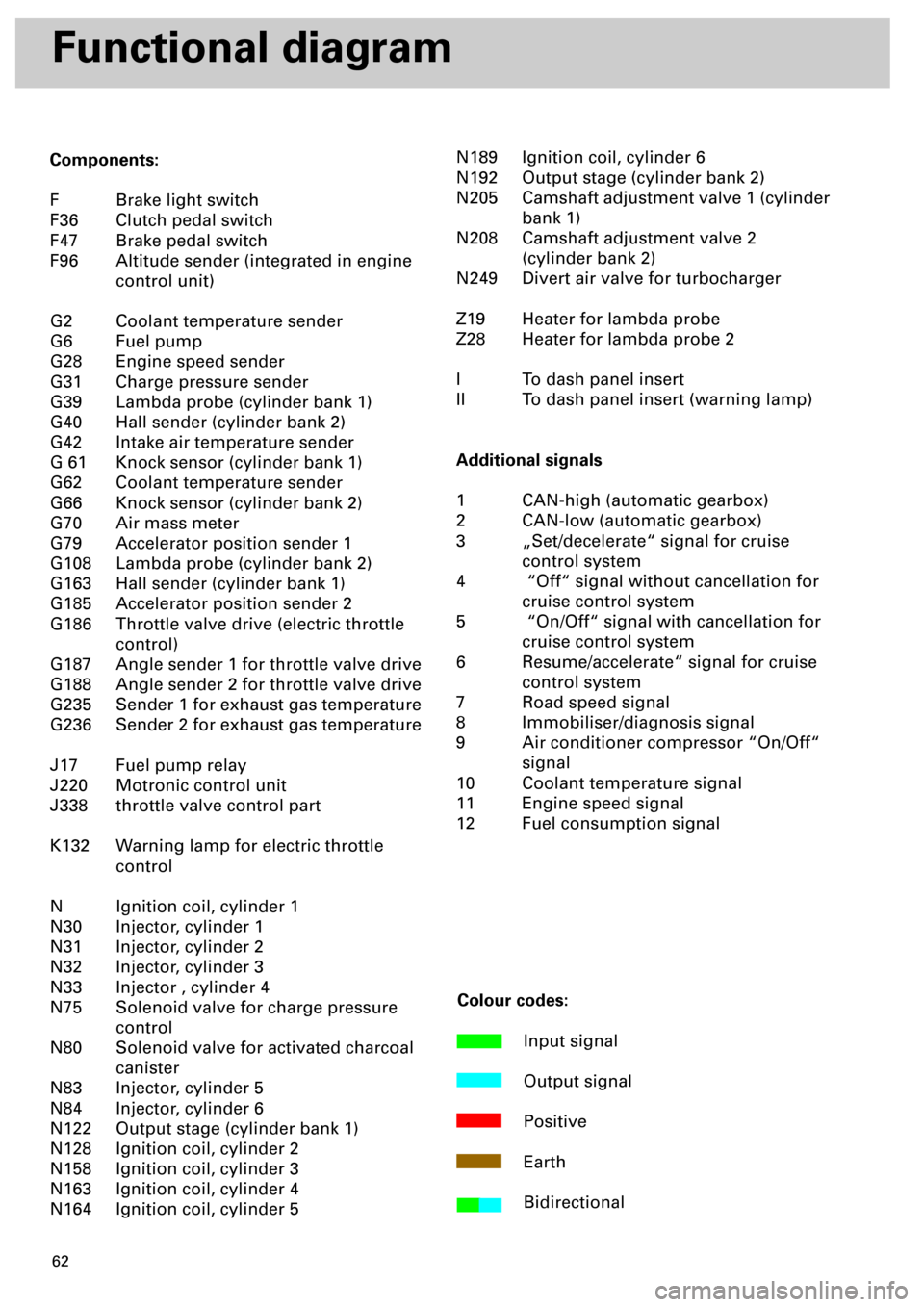
Components:
F Brake light switch
F36 Clutch pedal switch
F47 Brake pedal switch
F96 Altitude sender (integrated in engine
control unit)
G2 Coolant temperature sender
G6 Fuel pump
G28 Engine speed sender
G31 Charge pressure sender
G39 Lambda probe (cylinder bank 1)
G40 Hall sender (cylinder bank 2)
G42 Intake air temperature sender
G 61 Knock sensor (cylinder bank 1)
G62 Coolant temperature sender
G66 Knock sensor (cylinder bank 2)
G70 Air mass meter
G79 Accelerator position sender 1
G108 Lambda probe (cylinder bank 2)
G163 Hall sender (cylinder bank 1)
G185 Accelerator position sender 2
G186 Throttle valve drive (electric throttle
control)
G187 Angle sender 1 for throttle valve drive
G188 Angle sender 2 for throttle valve drive
G235 Sender 1 for exhaust gas temperature
G236 Sender 2 for exhaust gas temperature
J17 Fuel pump relay
J220 Motronic control unit
J338 throttle valve control part
K132 Warning lamp for electric throttle
control
N Ignition coil, cylinder 1
N30 Injector, cylinder 1
N31 Injector, cylinder 2
N32 Injector, cylinder 3
N33 Injector , cylinder 4
N75 Solenoid valve for charge pressure
control
N80 Solenoid valve for activated charcoal
canister
N83 Injector, cylinder 5
N84 Injector, cylinder 6
N122 Output stage (cylinder bank 1)
N128 Ignition coil, cylinder 2
N158 Ignition coil, cylinder 3
N163 Ignition coil, cylinder 4
N164 Ignition coil, cylinder 5N189 Ignition coil, cylinder 6
N192 Output stage (cylinder bank 2)
N205 Camshaft adjustment valve 1 (cylinder
bank 1)
N208 Camshaft adjustment valve 2
(cylinder bank 2)
N249 Divert air valve for turbocharger
Z19 Heater for lambda probe
Z28 Heater for lambda probe 2
I To dash panel insert
II To dash panel insert (warning lamp)
Additional signals
1 CAN-high (automatic gearbox)
2 CAN-low (automatic gearbox)
3 „Set/decelerate“ signal for cruise
control system
4 “Off“ signal without cancellation for
cruise control system
5 “On/Off“ signal with cancellation for
cruise control system
6 Resume/accelerate“ signal for cruise
control system
7 Road speed signal
8 Immobiliser/diagnosis signal
9 Air conditioner compressor “On/Off“
signal
10 Coolant temperature signal
11 Engine speed signal
12 Fuel consumption signal
Colour codes:
Input signal
Output signal
Positive
Earth
Bidirectional