change wheel AUDI S4 1998 B5 / 1.G Engine Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: AUDI, Model Year: 1998, Model line: S4, Model: AUDI S4 1998 B5 / 1.GPages: 72, PDF Size: 3.25 MB
Page 26 of 72
27
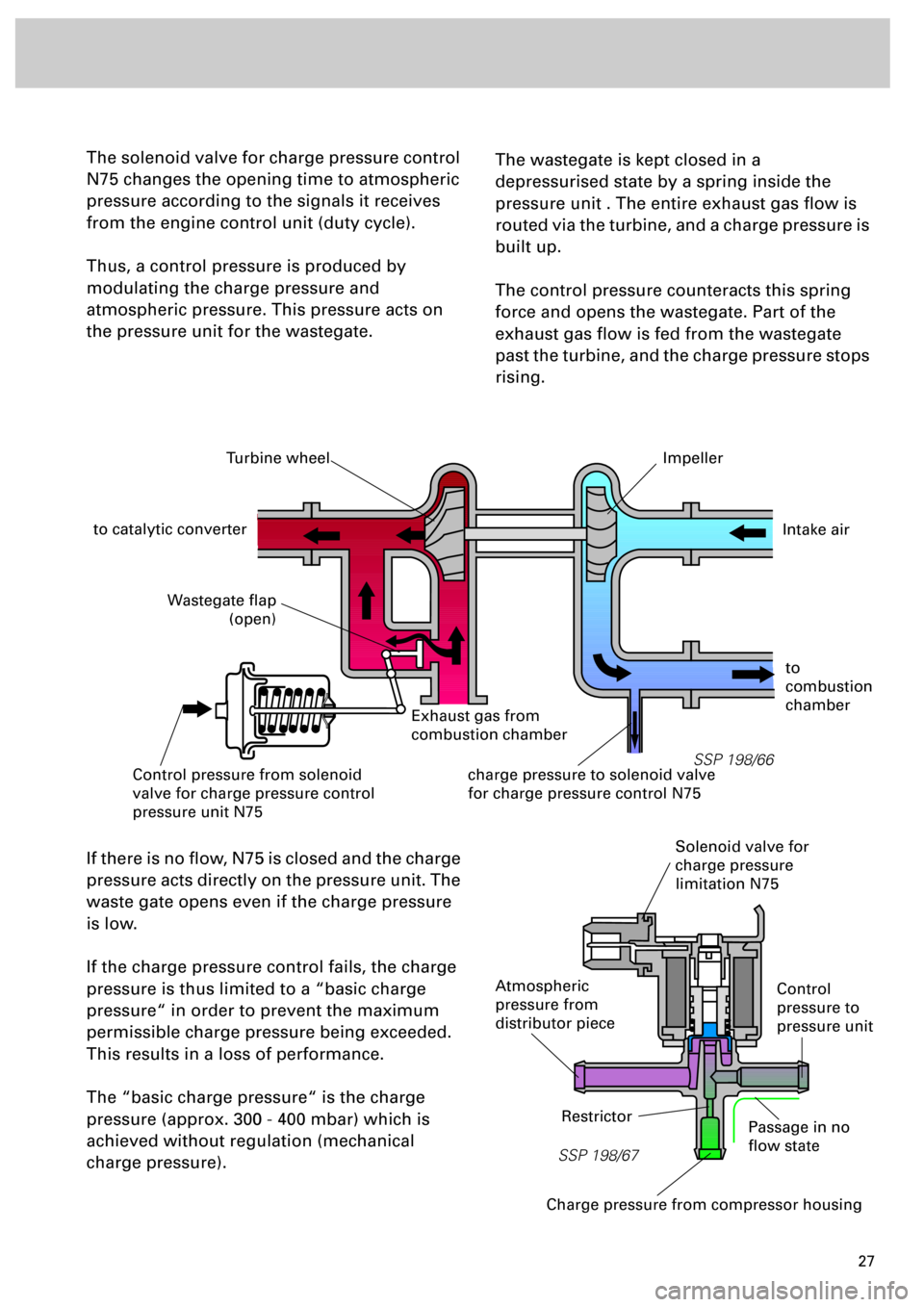
The solenoid valve for charge pressure control
N75 changes the opening time to atmospheric
pressure according to the signals it receives
from the engine control unit (duty cycle).
Thus, a control pressure is produced by
modulating the charge pressure and
atmospheric pressure. This pressure acts on
the pressure unit for the wastegate.
The wastegate is kept closed in a
depressurised state by a spring inside the
pressure unit . The entire exhaust gas flow is
routed via the turbine, and a charge pressure is
built up.
The control pressure counteracts this spring
force and opens the wastegate. Part of the
exhaust gas flow is fed from the wastegate
past the turbine, and the charge pressure stops
rising.
If there is no flow, N75 is closed and the charge
pressure acts directly on the pressure unit. The
waste gate opens even if the charge pressure
is low.
If the charge pressure control fails, the charge
pressure is thus limited to a “basic charge
pressure“ in order to prevent the maximum
permissible charge pressure being exceeded.
This results in a loss of performance.
The “basic charge pressure“ is the charge
pressure (approx. 300 - 400 mbar) which is
achieved without regulation (mechanical
charge pressure).
SSP 198/66
Turbine wheel
to catalytic converter
Impeller
Exhaust gas from
combustion chamber
Wastegate flap
(open)
Control pressure from solenoid
valve for charge pressure control
pressure unit N75charge pressure to solenoid valve
for charge pressure control N75
Intake air
to
combustion
chamber
SSP 198/67
Atmospheric
pressure from
distributor piece
Solenoid valve for
charge pressure
limitation N75
Charge pressure from compressor housing
RestrictorPassage in no
flow state
Control
pressure to
pressure unit
Page 27 of 72
28
SSP 198/05
Engine
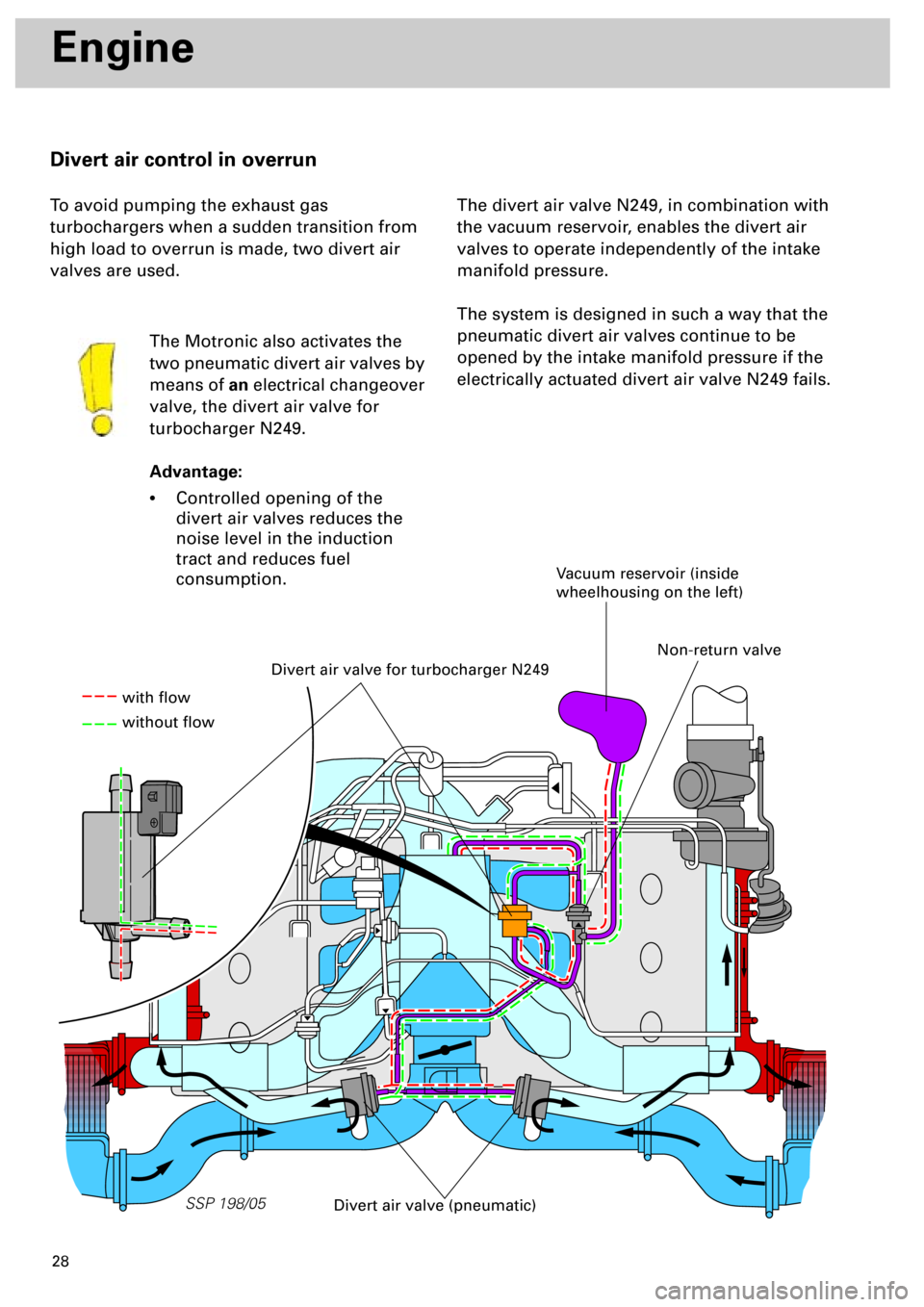
Divert air control in overrun
To avoid pumping the exhaust gas
turbochargers when a sudden transition from
high load to overrun is made, two divert air
valves are used.
The Motronic also activates the
two pneumatic divert air valves by
means of
an
electrical changeover
valve, the divert air valve for
turbocharger N249.
Advantage:
•
Controlled opening of the
divert air valves reduces the
noise level in the induction
tract and reduces fuel
consumption.
The divert air valve N249, in combination with
the vacuum reservoir, enables the divert air
valves to operate independently of the intake
manifold pressure.
The system is designed in such a way that the
pneumatic divert air valves continue to be
opened by the intake manifold pressure if the
electrically actuated divert air valve N249 fails.
Divert air valve for turbocharger N249
Vacuum reservoir (inside
wheelhousing on the left)
Divert air valve (pneumatic)
with flow
without flow
Non-return valve
Page 53 of 72
54
Sensors
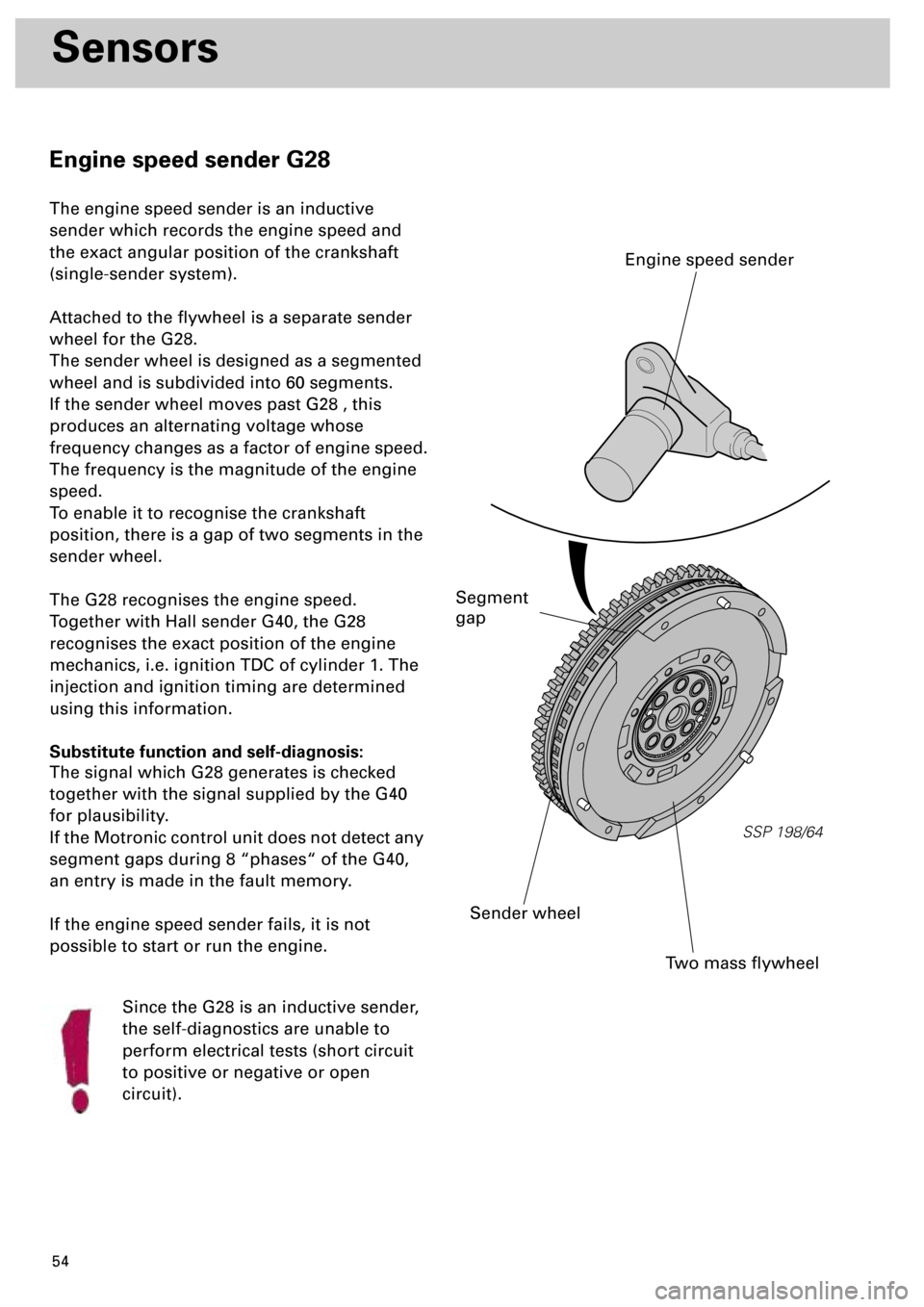
Engine speed sender G28
The engine speed sender is an inductive
sender which records the engine speed and
the exact angular position of the crankshaft
(single-sender system).
Attached to the flywheel is a separate sender
wheel for the G28.
The sender wheel is designed as a segmented
wheel and is subdivided into 60 segments.
If the sender wheel moves past G28 , this
produces an alternating voltage whose
frequency changes as a factor of engine speed.
The frequency is the magnitude of the engine
speed.
To enable it to recognise the crankshaft
position, there is a gap of two segments in the
sender wheel.
The G28 recognises the engine speed.
Together with Hall sender G40, the G28
recognises the exact position of the engine
mechanics, i.e. ignition TDC of cylinder 1. The
injection and ignition timing are determined
using this information.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
The signal which G28 generates is checked
together with the signal supplied by the G40
for plausibility.
If the Motronic control unit does not detect any
segment gaps during 8 “phases“ of the G40,
an entry is made in the fault memory.
If the engine speed sender fails, it is not
possible to start or run the engine.
Since the G28 is an inductive sender,
the self-diagnostics are unable to
perform electrical tests (short circuit
to positive or negative or open
circuit).
SSP 198/64
Two mass flywheel
Sender wheel
Engine speed sender
Segment
gap
Page 57 of 72
58
Additional signals/interfaces
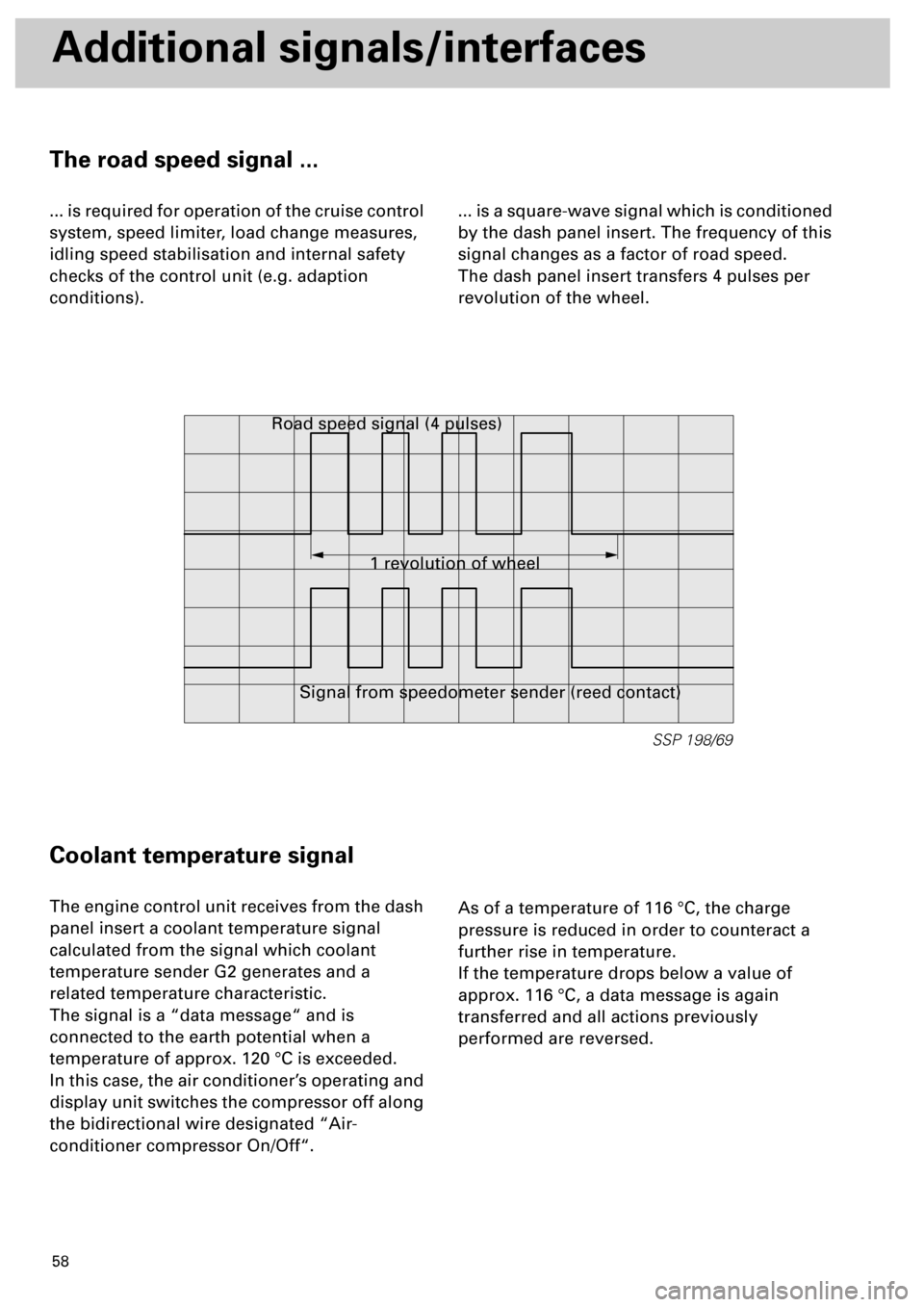
The road speed signal ...
... is required for operation of the cruise control
system, speed limiter, load change measures,
idling speed stabilisation and internal safety
checks of the control unit (e.g. adaption
conditions).... is a square-wave signal which is conditioned
by the dash panel insert. The frequency of this
signal changes as a factor of road speed.
The dash panel insert transfers 4 pulses per
revolution of the wheel.
Coolant temperature signal
The engine control unit receives from the dash
panel insert a coolant temperature signal
calculated from the signal which coolant
temperature sender G2 generates and a
related temperature characteristic.
The signal is a “data message“ and is
connected to the earth potential when a
temperature of approx. 120 °C is exceeded.
In this case, the air conditioner’s operating and
display unit switches the compressor off along
the bidirectional wire designated “Air-
conditioner compressor On/Off“.As of a temperature of 116 °C, the charge
pressure is reduced in order to counteract a
further rise in temperature.
If the temperature drops below a value of
approx. 116 °C, a data message is again
transferred and all actions previously
performed are reversed.
SSP 198/69
1 revolution of wheel Road speed signal (4 pulses)
Signal from speedometer sender (reed contact)