charging BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 120 of 228
the alternator complete, or take it to an
automotive electrician, who may be able to
overhaul it. Note:On models up to 1986, a
blown ignition/no-charge warning light bulb
will prevent the alternator from charging. After
1987, a resistor is wired in parallel with the
warning light, in order to allow current to
bypass the light in the event of a broken circuit
(blown warning light).
15 Alternator-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Detach the battery negative cable.2Detach the electrical connectors from the
alternator, noting their locations for refitting
(see illustration). Note: On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the air cleaner
assembly and airflow meter to gain access to
the alternator.
3Loosen the alternator adjustment and pivot
bolts, and slip off the drivebelt (see Chap-
ter 1).
4Remove the adjustment and pivot bolts,
and separate the alternator from the engine.
Refitting
5If you are renewing the alternator, take the
old one with you when purchasing a new or
reconditioned unit. Make sure the new unit
looks identical to the old alternator. Look at
the terminals - they should be the same in
number, size and location as the terminals on
the old alternator. Finally, look at the identifi-
cation numbers - they will be stamped into the
housing, or printed on a tag attached to the
housing. Make sure the numbers are the same
on both alternators.
6Many new alternators do not come with a
pulley fitted, so you may have to transfer the
pulley from the old unit to the new one.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
8After the alternator is fitted, adjust the
drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1).
9Check the charging voltage to verify
proper operation of the alternator (see Sec-
tion 14).
16 Voltage regulator- renewal
1
1The voltage regulator controls the charging
system voltage by limiting the alternator
output. The regulator is a sealed unit, and isn’t
adjustable.
2If the voltmeter indicates that the alternator
is not charging (or if the ignition/no-charge
warning light comes on) and the alternator,
battery, drivebelt tension and electrical
connections seem to be fine, have theregulator checked by a dealer service
department or electrical specialist.
3Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Bosch alternator
4The voltage regulator is mounted externally
on the alternator housing. To renew the
regulator, remove the mounting screws (see
illustration)and lift it off the alternator (see
illustration). Note: Some Bosch alternators
have an integral voltage regulator which is part
of the brush assembly.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
Before refitting the regulator, check the
condition of the slip rings(see illustration).
Use a torch and check for any scoring or deep
wear grooves. Renew the alternator if
necessary.
Motorola alternator
6Remove the alternator from the engine
compartment (see Section 15).
7Remove the rear cover and diode carrier,
remove the voltage regulator mounting
screws (see illustration)and lift the regulator
off the alternator body.
8Refitting is the reverse of removal.
17 Alternator brushes-
check and renewal
3
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
5•10 Engine electrical systems
16.5 Use a torch to check the slip rings for
scoring or deep grooves16.4b The regulator can be withdrawn
easily on Bosch alternators. This type of
regulator is integral with the brush
assembly16.4a Remove the nuts and lift off the
small terminal protector from the
alternator cover, then remove the nuts and
the cover
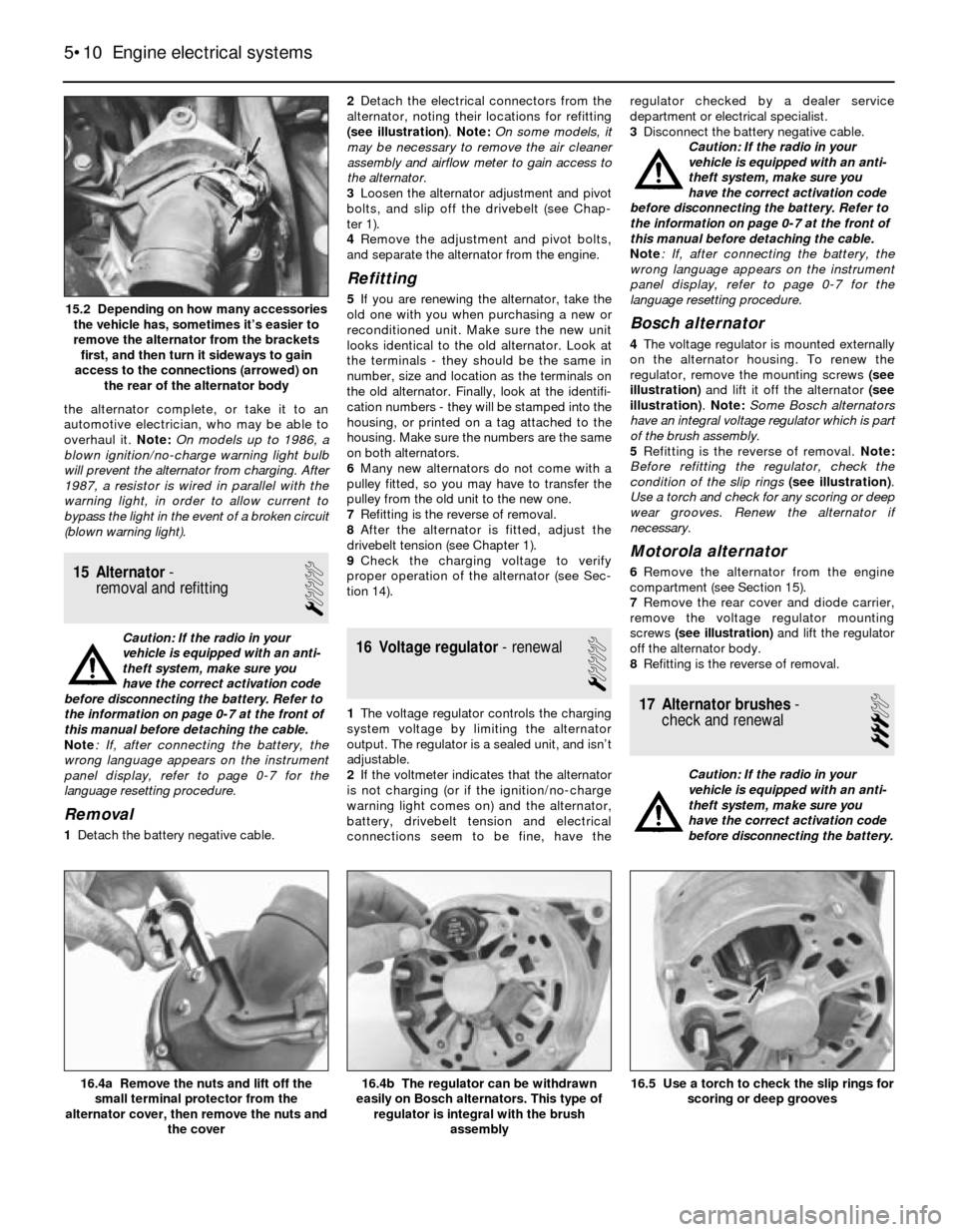
15.2 Depending on how many accessories
the vehicle has, sometimes it’s easier to
remove the alternator from the brackets
first, and then turn it sideways to gain
access to the connections (arrowed) on
the rear of the alternator body
Page 173 of 228
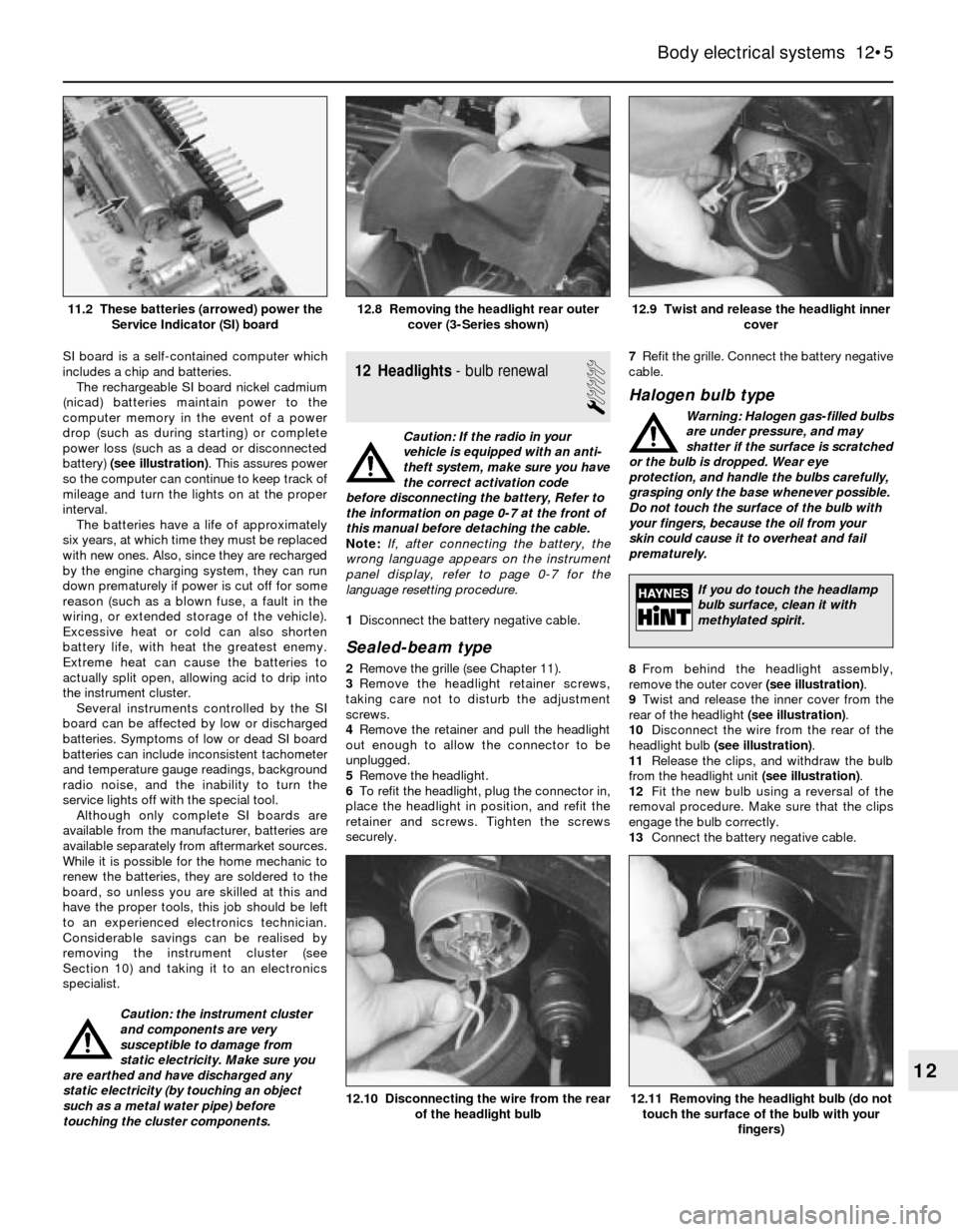
SI board is a self-contained computer which
includes a chip and batteries.
The rechargeable SI board nickel cadmium
(nicad) batteries maintain power to the
computer memory in the event of a power
drop (such as during starting) or complete
power loss (such as a dead or disconnected
battery) (see illustration). This assures power
so the computer can continue to keep track of
mileage and turn the lights on at the proper
interval.
The batteries have a life of approximately
six years, at which time they must be replaced
with new ones. Also, since they are recharged
by the engine charging system, they can run
down prematurely if power is cut off for some
reason (such as a blown fuse, a fault in the
wiring, or extended storage of the vehicle).
Excessive heat or cold can also shorten
battery life, with heat the greatest enemy.
Extreme heat can cause the batteries to
actually split open, allowing acid to drip into
the instrument cluster.
Several instruments controlled by the SI
board can be affected by low or discharged
batteries. Symptoms of low or dead SI board
batteries can include inconsistent tachometer
and temperature gauge readings, background
radio noise, and the inability to turn the
service lights off with the special tool.
Although only complete SI boards are
available from the manufacturer, batteries are
available separately from aftermarket sources.
While it is possible for the home mechanic to
renew the batteries, they are soldered to the
board, so unless you are skilled at this and
have the proper tools, this job should be left
to an experienced electronics technician.
Considerable savings can be realised by
removing the instrument cluster (see
Section 10) and taking it to an electronics
specialist.
Caution: the instrument cluster
and components are very
susceptible to damage from
static electricity. Make sure you
are earthed and have discharged any
static electricity (by touching an object
such as a metal water pipe) before
touching the cluster components.12 Headlights- bulb renewal
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Sealed-beam type
2Remove the grille (see Chapter 11).
3Remove the headlight retainer screws,
taking care not to disturb the adjustment
screws.
4Remove the retainer and pull the headlight
out enough to allow the connector to be
unplugged.
5Remove the headlight.
6To refit the headlight, plug the connector in,
place the headlight in position, and refit the
retainer and screws. Tighten the screws
securely.7Refit the grille. Connect the battery negative
cable.
Halogen bulb type
Warning: Halogen gas-filled bulbs
are under pressure, and may
shatter if the surface is scratched
or the bulb is dropped. Wear eye
protection, and handle the bulbs carefully,
grasping only the base whenever possible.
Do not touch the surface of the bulb with
your fingers, because the oil from your
skin could cause it to overheat and fail
prematurely.
8From behind the headlight assembly,
remove the outer cover (see illustration).
9Twist and release the inner cover from the
rear of the headlight (see illustration).
10Disconnect the wire from the rear of the
headlight bulb (see illustration).
11Release the clips, and withdraw the bulb
from the headlight unit (see illustration).
12Fit the new bulb using a reversal of the
removal procedure. Make sure that the clips
engage the bulb correctly.
13Connect the battery negative cable.
Body electrical systems 12•5
12.9 Twist and release the headlight inner
cover12.8 Removing the headlight rear outer
cover (3-Series shown)11.2 These batteries (arrowed) power the
Service Indicator (SI) board
12.11 Removing the headlight bulb (do not
touch the surface of the bulb with your
fingers)12.10 Disconnecting the wire from the rear
of the headlight bulb
12
If you do touch the headlamp
bulb surface, clean it with
methylated spirit.
Page 178 of 228
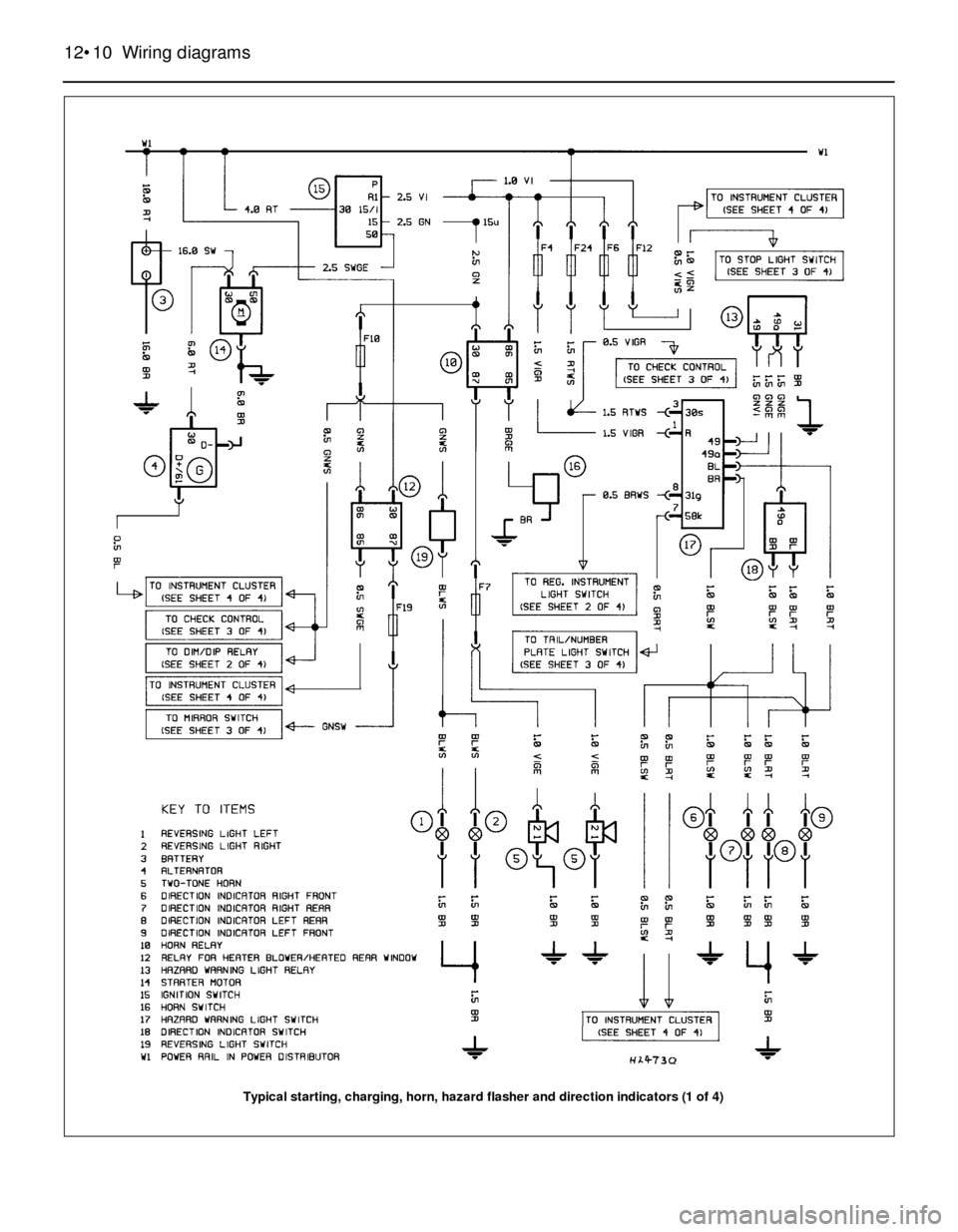
12•10 Wiring diagrams
Typical starting, charging, horn, hazard flasher and direction indicators (1 of 4)
Page 212 of 228

REF•11
REF
Fault Finding
Engine misses at idle speed
m mSpark plugs worn or incorrectly-gapped (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leaks (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mUneven or low compression (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6).
Engine misses throughout driving speed range
m
mFuel filter clogged and/or impurities in the fuel system (Chapter 1).
m mLow fuel output at the injectors, or partially-blocked carburettor
jets (Chapter 4).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mCracked distributor cap, disconnected distributor HT leads, or
damaged distributor components (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty emission system components (Chapter 6).
m mLow or uneven cylinder compression pressures (Chapter 2).
m mWeak or faulty ignition system (Chapter 5).
m mVacuum leak in fuel injection system, intake manifold or vacuum
hoses (Chapter 4).
Engine misfires on acceleration
m mSpark plugs fouled (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mFuel filter clogged (Chapters 1 and 4).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mIntake manifold air leak (Chapter 4).
Engine surges while holding accelerator steady
m
mIntake air leak (Chapter 4).
m mFuel pump faulty (Chapter 4).
m mLoose fuel injector harness connections (Chapters 4 and 6).
m mDefective ECU (Chapter 5).
Engine lacks power
m
mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mExcessive play in distributor shaft (Chapter 5).
m mWorn rotor, distributor cap or HT leads (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mFaulty coil (Chapter 5).
m mBrakes binding (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission fluid level incorrect (Chapter 1).
m mClutch slipping (Chapter 8).
m mFuel filter clogged and/or impurities in the fuel system (Chapter 1).
m mEmission control system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mLow or uneven cylinder compression pressures (Chapter 2).
Engine stalls
m
mIdle speed incorrect (Chapter 1).
m mFuel filter clogged and/or water and impurities in the fuel system
(Chapter 1).
m mDistributor components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty emissions system components (Chapter 6).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leak in the fuel injection system, intake manifold or
vacuum hoses (Chapter 4).
Engine backfires
m mEmissions system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty secondary ignition system (cracked spark plug insulator,
faulty plug HT leads, distributor cap and/or rotor) (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mVacuum leak at fuel injector(s), intake manifold or vacuum hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mValve clearances incorrect (Chapter 1), or valve(s) sticking or
damaged (Chapter 2).
Pinking or knocking engine sounds when
accelerating or driving uphill
m mIncorrect grade of fuel.
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor in need of adjustment (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDamaged spark plugs or HT leads, or incorrect type fitted (Chapter 1).
m mWorn or damaged distributor components (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty emission system (Chapter 6).
m mVacuum leak (Chapter 4).
Engine runs with oil pressure light on
Caution: Stop the engine immediately if the oil
pressure light comes on and establish the cause.
Running the engine while the oil pressure is low can
cause severe damage.
m mLow oil level (Chapter 1).
m mIdle speed too low (Chapter 1).
m mShort-circuit in wiring (Chapter 12).
m mFaulty oil pressure sender unit (Chapter 2).
m mWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2).
Engine runs-on after switching off
m
mIdle speed too high (Chapter 1).
m mExcessive engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
m mIncorrect fuel octane grade.
m mSpark plugs defective or incorrect grade (Chapter 1).
Engine electrical system
Battery will not hold charge
m
mAlternator drivebelt defective or not adjusted properly (Chapter 1).
m mElectrolyte level low (Chapter 1).
m mBattery terminals loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mAlternator not charging properly (Chapter 5).
m mLoose, broken or faulty wiring in the charging circuit (Chapter 5).
m mShort in vehicle wiring (Chapters 5 and 12).
m mInternally-defective battery (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light bulb blown - on some early
models (Chapter 5)
Ignition (no-charge) warning light fails to go out
m mFaulty alternator or charging circuit (Chapter 5).
m mAlternator drivebelt defective or out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mAlternator voltage regulator inoperative (Chapter 5).
Ignition (no-charge) warning light fails to come on
when key is turned
m mWarning light bulb defective (Chapter 12).
m mFault in the printed circuit, wiring or bulbholder (Chapter 12).
Page 225 of 228

REF•25
REF
Index
Note: References throughout this index relate to Chapter•page number
A
ABS - 9•2
Accelerator cable - 4•9
Acknowledgements - 0•4
Aerial - 12•4
Air bags - 0•5
Air cleaner - 4•8
Air conditioning system - 3•2, 3•7, 3•8,
3•9, 3•10
Air filter - 1•20
Air gap - 5•7
Air intake system - 4•2, 4•14
Airflow meter - 4•15, 6•4
Alternator - 5•10
Anti-lock Braking system (ABS) - 9•2
Anti-roll bar - 10•4, 10•9
Anti-theft audio system - 0•7
Antifreeze - 1•3, 1-8, 3•2
Asbestos - 0•5
ATF - 1•3, 1•13, 1•23
Automatic choke - 4•13
Automatic transmission- 7B•1et seq
Automatic transmission fault finding -
7B•4, REF•13
Automatic transmission fluid - 1•3, 1•13,
1•23
B
Backfire - REF•11
Balljoints - 10•7
Battery - 0•5, 1•16, 5•2
Battery fault - REF•11
Big-end bearings - 2B•17, 2B•21
Bleeding brakes - 9•14
Bleeding clutch - 8•4
Bleeding power steering - 10•16Block - 2B•14, 2B•15
Blower motor - 3•7
Body corrosion - REF•4
Body electrical systems- 12•1et seq
Bodywork and fittings- 11•1et seq
Bonnet - 11•4
Boot lid - 11•6
Boots - 8•9, 10•13
Brake fluid - 1•3, 1•9
Brake lines and hoses - 1•22, 9•13
Braking system- 1•22, 9•1et seq,REF•1,
REF•2, REF•3
Braking system fault finding - REF•14
Bulbs - 12•6
Bumpers - 11•6
Burning - 0•5
C
Cables - 4•9, 5•2, 7B•3, 9•12
Calipers - 9•4
Cam followers - 2B•11
Camshaft - 2A•12, 2B•11
Carburettor - 4•10, 4•11
Carpets - 11•2
Catalytic converter - 4•20, 6•6
Central locking - 12•8
Charging - 1•17, 5•9
Chemicals - REF•18
Choke - 4•13
Clutch and driveline- 8•1et seq
Clutch fault finding - REF•12
Clutch fluid - 1•3, 1•9
CO level adjustment - 1•15, REF•4
Coil - 5•5
Coil springs - 10•7, 10•9
Cold start injectors - 4•17, 4•18
Compression check - 2B•4Compressor - 3•8
Condenser - 3•9
Connecting rods -2B•12, 2B•16, 2B•21
Constant velocity (CV) joint - 8•2, 8•8, 8•9
Continuity check - 12•2
Control arm - 10•4, 10•5
Conversion factors - REF•17
Coolant - 1•3, 1•8
Coolant pump - 3•5
Coolant temperature sender unit - 3•6
Coolant temperature sensor - 6•2
Cooling fan - 3•4
Cooling, heating and air conditioning
systems- 1•21, 1•24, 3•1et seq
Cooling system fault finding - REF•12
Crankshaft - 2A•12, 2A•13, 2A•19, 2B•13,
2B•17, 2B•19, 2B•20
Cruise control - 12•3, 12•8
Crushing - 0•5
Cushion - 11•9
CV joints - 8•2, 8•8, 8•9
Cylinder head - 2A•13, 2B•7, 2B•10, 2B•12
Cylinder honing - 2B•15
D
Dents in bodywork - 11•2
Differential (final drive) - 8•2, 8•10, 8•11
Differential oil -1•3, 1•19, 1•26
Direction indicators - 12•2, 12•3
Discs - 1•22, 9•5
Distributor - 1•18, 5•4
Door - 11•6, 11•8, REF•2
Drivebelts - 1•14
Driveplate - 2A•18
Driveshafts - 1•22, 8•2, 8•9
Drums - 1•23