stop start BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 141 of 228
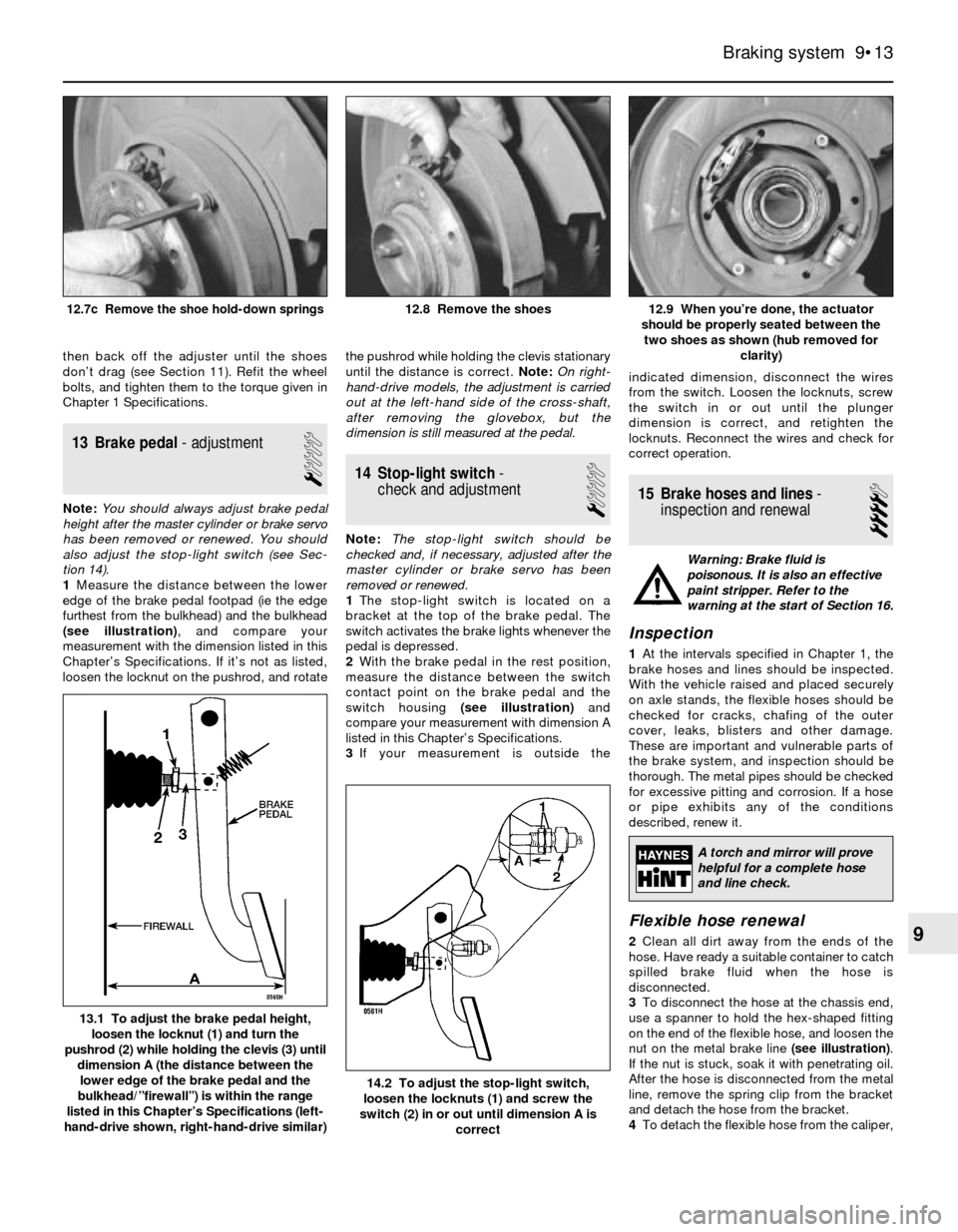
then back off the adjuster until the shoes
don’t drag (see Section 11). Refit the wheel
bolts, and tighten them to the torque given in
Chapter 1 Specifications.
13 Brake pedal- adjustment
1
Note:You should always adjust brake pedal
height after the master cylinder or brake servo
has been removed or renewed. You should
also adjust the stop-light switch (see Sec-
tion 14).
1Measure the distance between the lower
edge of the brake pedal footpad (ie the edge
furthest from the bulkhead) and the bulkhead
(see illustration), and compare your
measurement with the dimension listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. If it’s not as listed,
loosen the locknut on the pushrod, and rotatethe pushrod while holding the clevis stationary
until the distance is correct. Note:On right-
hand-drive models, the adjustment is carried
out at the left-hand side of the cross-shaft,
after removing the glovebox, but the
dimension is still measured at the pedal.
14 Stop-light switch-
check and adjustment
1
Note:The stop-light switch should be
checked and, if necessary, adjusted after the
master cylinder or brake servo has been
removed or renewed.
1The stop-light switch is located on a
bracket at the top of the brake pedal. The
switch activates the brake lights whenever the
pedal is depressed.
2With the brake pedal in the rest position,
measure the distance between the switch
contact point on the brake pedal and the
switch housing (see illustration)and
compare your measurement with dimension A
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
3If your measurement is outside theindicated dimension, disconnect the wires
from the switch. Loosen the locknuts, screw
the switch in or out until the plunger
dimension is correct, and retighten the
locknuts. Reconnect the wires and check for
correct operation.
15 Brake hoses and lines-
inspection and renewal
4
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Inspection
1At the intervals specified in Chapter 1, the
brake hoses and lines should be inspected.
With the vehicle raised and placed securely
on axle stands, the flexible hoses should be
checked for cracks, chafing of the outer
cover, leaks, blisters and other damage.
These are important and vulnerable parts of
the brake system, and inspection should be
thorough. The metal pipes should be checked
for excessive pitting and corrosion. If a hose
or pipe exhibits any of the conditions
described, renew it.
Flexible hose renewal
2Clean all dirt away from the ends of the
hose. Have ready a suitable container to catch
spilled brake fluid when the hose is
disconnected.
3To disconnect the hose at the chassis end,
use a spanner to hold the hex-shaped fitting
on the end of the flexible hose, and loosen the
nut on the metal brake line (see illustration).
If the nut is stuck, soak it with penetrating oil.
After the hose is disconnected from the metal
line, remove the spring clip from the bracket
and detach the hose from the bracket.
4To detach the flexible hose from the caliper,
Braking system 9•13
12.9 When you’re done, the actuator
should be properly seated between the
two shoes as shown (hub removed for
clarity)12.8 Remove the shoes12.7c Remove the shoe hold-down springs
14.2 To adjust the stop-light switch,
loosen the locknuts (1) and screw the
switch (2) in or out until dimension A is
correct
13.1 To adjust the brake pedal height,
loosen the locknut (1) and turn the
pushrod (2) while holding the clevis (3) until
dimension A (the distance between the
lower edge of the brake pedal and the
bulkhead/”firewall”) is within the range
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications (left-
hand-drive shown, right-hand-drive similar)
9
A torch and mirror will prove
helpful for a complete hose
and line check.
Page 162 of 228

it to the approximate size and shape required,
then pull off the backing paper (if used) and
stick the tape over the hole; it can be
overlapped if the thickness of one piece is
insufficient. Burnish down the edges of the
tape with the handle of a screwdriver or
similar, to ensure that the tape is securely
attached to the metal underneath.
Bodywork repairs - filling and
respraying
Before using this Section, see the Sections
on dent, deep scratch, rust holes and gash
repairs.
Many types of bodyfiller are available, but
generally speaking, those proprietary kits
which contain a tin of filler paste and a tube of
resin hardener are best for this type of repair. A
wide, flexible plastic or nylon applicator will be
found invaluable for imparting a smooth and
well-contoured finish to the surface of the filler.
Mix up a little filler on a clean piece of card
or board - measure the hardener carefully
(follow the maker’s instructions on the pack),
otherwise the filler will set too rapidly or too
slowly. Using the applicator, apply the filler
paste to the prepared area; draw the
applicator across the surface of the filler to
achieve the correct contour and to level the
surface. As soon as a contour that
approximates to the correct one is achieved,
stop working the paste - if you carry on too
long, the paste will become sticky and begin
to “pick-up” on the applicator. Continue to
add thin layers of filler paste at 20-minute
intervals, until the level of the filler is just
proud of the surrounding bodywork.
Once the filler has hardened, the excess
can be removed using a metal plane or file.
From then on, progressively-finer grades of
abrasive paper should be used, starting with a
40-grade production paper, and finishing with
a 400-grade wet-and-dry paper. Always wrap
the abrasive paper around a flat rubber, cork,
or wooden block - otherwise the surface of
the filler will not be completely flat. During the
smoothing of the filler surface, the wet-and-
dry paper should be periodically rinsed in
water. This will ensure that a very smooth
finish is imparted to the filler at the final stage.
At this stage, the “dent” should be
surrounded by a ring of bare metal, which in
turn should be encircled by the finely
“feathered” edge of the good paintwork.
Rinse the repair area with clean water, until all
of the dust produced by the rubbing-down
operation has gone.
Spray the whole area with a light coat of
primer - this will show up any imperfections in
the surface of the filler. Repair these
imperfections with fresh filler paste or
bodystopper, and once more smooth the
surface with abrasive paper. Repeat this
spray-and-repair procedure until you are
satisfied that the surface of the filler, and the
feathered edge of the paintwork, are perfect.
Clean the repair area with clean water, and
allow to dry fully.The repair area is now ready for final
spraying. Paint spraying must be carried out
in a warm, dry, windless and dust-free
atmosphere. This condition can be created
artificially if you have access to a large indoor
working area, but if you are forced to work in
the open, you will have to pick your day very
carefully. If you are working indoors, dousing
the floor in the work area with water will help
to settle the dust which would otherwise be in
the atmosphere. If the repair area is confined
to one body panel, mask off the surrounding
panels; this will help to minimise the effects of
a slight mis-match in paint colours. Bodywork
fittings (eg chrome strips, door handles etc)
will also need to be masked off. Use genuine
masking tape, and several thicknesses of
newspaper, for the masking operations.
Before commencing to spray, agitate the
aerosol can thoroughly, then spray a test area
(an old tin, or similar) until the technique is
mastered. Cover the repair area with a thick
coat of primer; the thickness should be built
up using several thin layers of paint, rather
than one thick one. Using 400-grade wet-and-
dry paper, rub down the surface of the primer
until it is really smooth. While doing this, the
work area should be thoroughly doused with
water, and the wet-and-dry paper periodically
rinsed in water. Allow to dry before spraying
on more paint.
Spray on the top coat, again building up the
thickness by using several thin layers of paint.
Start spraying at one edge of the repair area,
and then, using a side-to-side motion, work
until the whole repair area and about 2 inches
of the surrounding original paintwork is
covered. Remove all masking material 10 to
15 minutes after spraying on the final coat of
paint.
Allow the new paint at least two weeks to
harden, then, using a paintwork renovator, or
a very fine cutting paste, blend the edges of
the paint into the existing paintwork. Finally,
apply wax polish.
Plastic components
With the use of more and more plastic body
components by the vehicle manufacturers (eg
bumpers. spoilers, and in some cases major
body panels), rectification of more serious
damage to such items has become a matter
of either entrusting repair work to a specialist
in this field, or renewing complete
components. Repair of such damage by the
DIY owner is not really feasible, owing to the
cost of the equipment and materials required
for effecting such repairs. The basic technique
involves making a groove along the line of the
crack in the plastic, using a rotary burr in a
power drill. The damaged part is then weldedback together, using a hot-air gun to heat up
and fuse a plastic filler rod into the groove.
Any excess plastic is then removed, and the
area rubbed down to a smooth finish. It is
important that a filler rod of the correct plastic
is used, as body components can be made of
a variety of different types (eg polycarbonate,
ABS, polypropylene).
Damage of a less serious nature (abrasions,
minor cracks etc) can be repaired by the DIY
owner using a two-part epoxy filler repair
material. Once mixed in equal proportions,
this is used in similar fashion to the bodywork
filler used on metal panels. The filler is usually
cured in twenty to thirty minutes, ready for
sanding and painting.
If the owner is renewing a complete
component himself, or if he has repaired it
with epoxy filler, he will be left with the
problem of finding a suitable paint for finishing
which is compatible with the type of plastic
used. At one time, the use of a universal paint
was not possible, owing to the complex range
of plastics encountered in body component
applications. Standard paints, generally
speaking, will not bond to plastic or rubber
satisfactorily. However, it is now possible to
obtain a plastic body parts finishing kit which
consists of a pre-primer treatment, a primer
and coloured top coat. Full instructions are
normally supplied with a kit, but basically, the
method of use is to first apply the pre-primer
to the component concerned, and allow it to
dry for up to 30 minutes. Then the primer is
applied, and left to dry for about an hour
before finally applying the special-coloured
top coat. The result is a correctly-coloured
component, where the paint will flex with the
plastic or rubber, a property that standard
paint does not normally possess.
6 Bodywork repair-
major damage
5
1Major damage must be repaired by a
qualified bodywork repair specialist, or
preferably by a BMW dealer. Specialised
equipment is required to do the job properly.
2If the damage is extensive, the bodyshell
must be checked for proper alignment, or the
vehicle’s handling characteristics may be
adversely affected and other components
may wear at an accelerated rate.
3Due to the fact that all of the major body
components (bonnet, wings, etc.) are
separate units, any seriously damaged
components should be replaced with new
ones rather than repaired.
Bodywork and fittings 11•3
11
If bodystopper is used, it can
be mixed with cellulose
thinners to form a really thin
paste which is ideal for filling
small holes
Sometimes bodywork
components can be found in
a scrapyard that specialises
in used vehicle components,
often at a considerable saving over the
cost of new parts.
Page 168 of 228
19 Steering column shrouds -
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
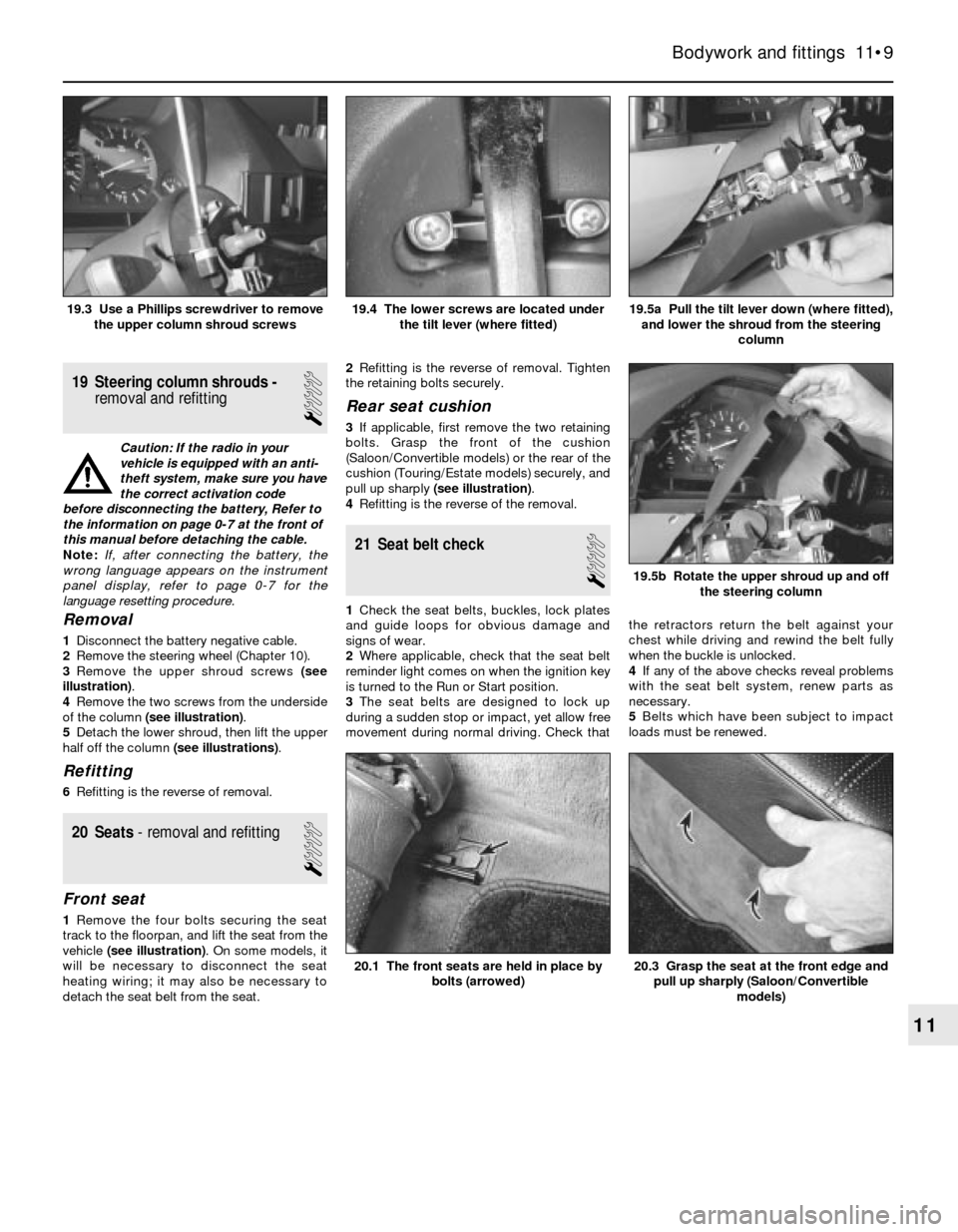
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the steering wheel (Chapter 10).
3Remove the upper shroud screws (see
illustration).
4Remove the two screws from the underside
of the column (see illustration).
5Detach the lower shroud, then lift the upper
half off the column (see illustrations).
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
20 Seats- removal and refitting
1
Front seat
1Remove the four bolts securing the seat
track to the floorpan, and lift the seat from the
vehicle (see illustration). On some models, it
will be necessary to disconnect the seat
heating wiring; it may also be necessary to
detach the seat belt from the seat.2Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the retaining bolts securely.
Rear seat cushion
3If applicable, first remove the two retaining
bolts. Grasp the front of the cushion
(Saloon/Convertible models) or the rear of the
cushion (Touring/Estate models) securely, and
pull up sharply (see illustration).
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal.
21 Seat belt check
1
1Check the seat belts, buckles, lock plates
and guide loops for obvious damage and
signs of wear.
2Where applicable, check that the seat belt
reminder light comes on when the ignition key
is turned to the Run or Start position.
3The seat belts are designed to lock up
during a sudden stop or impact, yet allow free
movement during normal driving. Check thatthe retractors return the belt against your
chest while driving and rewind the belt fully
when the buckle is unlocked.
4If any of the above checks reveal problems
with the seat belt system, renew parts as
necessary.
5Belts which have been subject to impact
loads must be renewed.
Bodywork and fittings 11•9
19.5a Pull the tilt lever down (where fitted),
and lower the shroud from the steering
column19.4 The lower screws are located under
the tilt lever (where fitted)19.3 Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove
the upper column shroud screws
20.3 Grasp the seat at the front edge and
pull up sharply (Saloon/Convertible
models)20.1 The front seats are held in place by
bolts (arrowed)
19.5b Rotate the upper shroud up and off
the steering column
11
Page 210 of 228

REF•9
REF
Fault Finding
Engine
m mEngine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mEngine rotates, but will not start
m mEngine hard to start when cold
m mEngine hard to start when hot
m mStarter motor noisy or excessively-rough in engagement
m mEngine starts, but stops immediately
m mOil puddle under engine
m mEngine idles erratically
m mEngine misses at idle speed
m mEngine misses throughout driving speed range
m mEngine misfires on acceleration
m mEngine surges while holding accelerator steady
m mEngine stalls
m mEngine lacks power
m mEngine backfires
m mPinking or knocking engine sounds when accelerating
or driving uphill
m mEngine runs with oil pressure light on
m mEngine runs-on after switching off
Engine electrical system
m
mBattery will not hold charge
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light fails to go out
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light fails to come on
when key is turned
Fuel system
m mExcessive fuel consumption
m mFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
Cooling system
m
mOverheating
m mOvercooling
m mExternal coolant leakage
m mInternal coolant leakage
m mCoolant loss
m mPoor coolant circulation
Clutch
m
mPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
m mFluid in area of master cylinder dust cover and on pedal
m mFluid on slave cylinder
m mPedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m mUnable to select gears
m mClutch slips (engine speed increases with no increase in
vehicle speed)
m mGrabbing (chattering) as clutch is engaged
m mNoise in clutch area
m mClutch pedal stays on floor
m mHigh pedal effort
Manual transmission
m
mVibration
m mNoisy in neutral with engine running
m mNoisy in one particular gear
m mNoisy in all gears
m mSlips out of gear
m mLeaks lubricant
Automatic transmission
m
mFluid leakage
m mTransmission fluid brown, or has a burned smell
m mGeneral shift mechanism problems
m mTransmission will not kickdown with accelerator pedal
pressed to the floor
m mEngine will start in gears other than Park or Neutral
m mTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no drive
in forward or reverse gears
Brakes
m mVehicle pulls to one side during braking
m mNoise (high-pitched squeal) when the brakes are applied
m mBrake vibration (pedal pulsates)
m mExcessive pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m mExcessive brake pedal travel
m mDragging brakes
m mGrabbing or uneven braking action
m mBrake pedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m mBrake pedal travels to the floor with little resistance
m mHandbrake does not hold
Suspension and steering
m
mVehicle pulls to one side
m mAbnormal or excessive tyre wear
m mWheel makes a “thumping” noise
m mShimmy, shake or vibration
m mHigh steering effort
m mPoor steering self-centring
m mAbnormal noise at the front end
m mWandering or poor steering stability
m mErratic steering when braking
m mExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners or
during braking
m mSuspension bottoms
m mUnevenly-worn tyres
m mExcessive tyre wear on outside edge
m mExcessive tyre wear on inside edge
m mTyre tread worn in one place
m mExcessive play or looseness in steering system
m mRattling or clicking noise in steering gear
Page 211 of 228

REF•10Fault Finding
Engine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission not completely engaged in Park (Chap-
ter 7B) or (on models with a clutch switch) clutch not completely
depressed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapters 5 and 12).
m mStarter motor pinion jammed in flywheel ring gear (Chapter 5).
m mStarter solenoid faulty (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor faulty (Chapter 5).
m mIgnition switch faulty (Chapter 12).
m mStarter pinion or flywheel teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mEngine internal problem (Chapter 2B).
Engine rotates, but will not start
m
mFuel tank empty.
m mBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mLeaking fuel injector(s), faulty fuel pump, pressure regulator, etc
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel not reaching fuel injection system or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injector stuck open (Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapter 5).
m mLoose distributor mounting bolts causing ignition timing to wander
(Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wires at the ignition coil, or faulty
coil (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when cold
m mBattery discharged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel system malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mInjector(s) leaking or carburettor automatic choke faulty (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDistributor rotor carbon-tracked (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when hot
m
mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel not reaching the fuel injection system or carburettor (Chap-
ter 4).
m mCorroded battery connections, especially earth (negative)
connection (Chapter 1).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
m mPinion or flywheel gear teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
m
mLoose or faulty electrical connections at distributor, coil or
alternator (Chapter 5).
m mInsufficient fuel reaching the fuel injector(s) or carburettor
(Chapters 1 and 4).
m mDamaged fuel injection system speed sensors (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty fuel injection relays (Chapter 5).
Oil puddle under engine
m
mOil sump gasket and/or sump drain plug seal leaking (Chapter 2).
m mOil pressure sender unit leaking (Chapter 2).
m mValve cover gaskets leaking (Chapter 2).
m mEngine oil seals leaking (Chapter 2).
Engine idles erratically
m
mVacuum leakage (Chapter 4).
m mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump not delivering sufficient fuel to the fuel injection system
or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mTiming belt/chain and/or sprockets worn (Chapter 2).
m mCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6). This Section provides an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of your
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. They also refer you to the Chapter and/or
Section which deals with the problem.
Remember that successful fault diagnosis is not a mysterious
black art practised only by professional mechanics. It is simply the
result of the right knowledge combined with an intelligent, systematic
approach to the problem. Always work by a process of elimination,
starting with the simplest solution and working through to the mostcomplex - and never overlook the obvious. Anyone can run the fuel
tank dry or leave the lights on overnight, so don’t assume that you are
exempt from such oversights.
Finally, always establish a clear idea of why a problem has
occurred, and take steps to ensure that it doesn’t happen again. If the
electrical system fails because of a poor connection, check all other
connections in the system to make sure that they don’t fail as well. If a
particular fuse continues to blow, find out why - don’t just renew one
fuse after another. Remember, failure of a small component can often
be indicative of potential failure or incorrect functioning of a more
important component or system.
Engine
Page 223 of 228

REF•23
REF
Glossary of Technical Terms
JJump startStarting the engine of a vehicle
with a discharged or weak battery by
attaching jump leads from the weak battery to
a charged or helper battery.
LLoad Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV)A
brake hydraulic system control valve that
works like a proportioning valve, but also
takes into consideration the amount of weight
carried by the rear axle.
LocknutA nut used to lock an adjustment
nut, or other threaded component, in place.
For example, a locknut is employed to keep
the adjusting nut on the rocker arm in
position.
LockwasherA form of washer designed to
prevent an attaching nut from working loose.
MMacPherson strutA type of front
suspension system devised by Earle
MacPherson at Ford of England. In its original
form, a simple lateral link with the anti-roll bar
creates the lower control arm. A long strut - an
integral coil spring and shock absorber - is
mounted between the body and the steering
knuckle. Many modern so-called MacPherson
strut systems use a conventional lower A-arm
and don’t rely on the anti-roll bar for location.
MultimeterAn electrical test instrument with
the capability to measure voltage, current and
resistance.
NNOxOxides of Nitrogen. A common toxic
pollutant emitted by petrol and diesel engines
at higher temperatures.
OOhmThe unit of electrical resistance. One
volt applied to a resistance of one ohm will
produce a current of one amp.
OhmmeterAn instrument for measuring
electrical resistance.
O-ringA type of sealing ring made of a
special rubber-like material; in use, the O-ring
is compressed into a groove to provide the
sealing action.Overhead cam (ohc) engineAn engine with
the camshaft(s) located on top of the cylinder
head(s).
Overhead valve (ohv) engineAn engine with
the valves located in the cylinder head, but
with the camshaft located in the engine block.
Oxygen sensorA device installed in the
engine exhaust manifold, which senses the
oxygen content in the exhaust and converts
this information into an electric current. Also
called a Lambda sensor.
PPhillips screwA type of screw head having a
cross instead of a slot for a corresponding
type of screwdriver.
PlastigageA thin strip of plastic thread,
available in different sizes, used for measuring
clearances. For example, a strip of Plastigage
is laid across a bearing journal. The parts are
assembled and dismantled; the width of the
crushed strip indicates the clearance between
journal and bearing.
Propeller shaftThe long hollow tube with
universal joints at both ends that carries
power from the transmission to the differential
on front-engined rear wheel drive vehicles.
Proportioning valveA hydraulic control
valve which limits the amount of pressure to
the rear brakes during panic stops to prevent
wheel lock-up.
RRack-and-pinion steeringA steering system
with a pinion gear on the end of the steering
shaft that mates with a rack (think of a geared
wheel opened up and laid flat). When the
steering wheel is turned, the pinion turns,
moving the rack to the left or right. This
movement is transmitted through the track
rods to the steering arms at the wheels.
RadiatorA liquid-to-air heat transfer device
designed to reduce the temperature of the
coolant in an internal combustion engine
cooling system.
RefrigerantAny substance used as a heat
transfer agent in an air-conditioning system.
R-12 has been the principle refrigerant for
many years; recently, however, manufacturers
have begun using R-134a, a non-CFC
substance that is considered less harmful tothe ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Rocker armA lever arm that rocks on a shaft
or pivots on a stud. In an overhead valve
engine, the rocker arm converts the upward
movement of the pushrod into a downward
movement to open a valve.
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.
SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
O-ring
Serpentine drivebelt
Plastigage
Page 224 of 228

REF•24Glossary of Technical Terms
automatic transmission, a switch that
prevents starting if the vehicle is not in Neutral
or Park.
StrutSee MacPherson strut.
TTappetA cylindrical component which
transmits motion from the cam to the valve
stem, either directly or via a pushrod and
rocker arm. Also called a cam follower.
ThermostatA heat-controlled valve that
regulates the flow of coolant between the
cylinder block and the radiator, so maintaining
optimum engine operating temperature. A
thermostat is also used in some air cleaners in
which the temperature is regulated.
Thrust bearingThe bearing in the clutch
assembly that is moved in to the release levers
by clutch pedal action to disengage the
clutch. Also referred to as a release bearing.
Timing beltA toothed belt which drives the
camshaft. Serious engine damage may result
if it breaks in service.
Timing chainA chain which drives the
camshaft.
Toe-inThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the front than at the rear. On
rear wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-in is usually specified to keep the front
wheels running parallel on the road by
offsetting other forces that tend to spread the
wheels apart.
Toe-outThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the rear than at the front. Onfront wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-out is usually specified.
ToolsFor full information on choosing and
using tools, refer to the Haynes Automotive
Tools Manual.
TracerA stripe of a second colour applied to
a wire insulator to distinguish that wire from
another one with the same colour insulator.
Tune-upA process of accurate and careful
adjustments and parts replacement to obtain
the best possible engine performance.
TurbochargerA centrifugal device, driven by
exhaust gases, that pressurises the intake air.
Normally used to increase the power output
from a given engine displacement, but can
also be used primarily to reduce exhaust
emissions (as on VW’s “Umwelt” Diesel
engine).
UUniversal joint or U-jointA double-pivoted
connection for transmitting power from a
driving to a driven shaft through an angle. A U-
joint consists of two Y-shaped yokes and a
cross-shaped member called the spider.
VValveA device through which the flow of
liquid, gas, vacuum, or loose material in bulk
may be started, stopped, or regulated by a
movable part that opens, shuts, or partiallyobstructs one or more ports or passageways.
A valve is also the movable part of such a
device.
Valve clearanceThe clearance between the
valve tip (the end of the valve stem) and the
rocker arm or tappet. The valve clearance is
measured when the valve is closed.
Vernier caliperA precision measuring
instrument that measures inside and outside
dimensions. Not quite as accurate as a
micrometer, but more convenient.
ViscosityThe thickness of a liquid or its
resistance to flow.
VoltA unit for expressing electrical “pressure”
in a circuit. One volt that will produce a current
of one ampere through a resistance of one
ohm.
WWeldingVarious processes used to join metal
items by heating the areas to be joined to a
molten state and fusing them together. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Welding Manual.
Wiring diagramA drawing portraying the
components and wires in a vehicle’s electrical
system, using standardised symbols. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Electrical and Electronic Systems
Manual.
Page 227 of 228

REF•27
REF
Index
R
Radiator - 3•3, 11•4
Radio - 12•4
Receiver-drier - 3•9
Regulator (voltage) - 5•10
Regulator (window) - 11•8
Relays - 12•2
Repair procedures - REF•8
Respraying - 11•3
Reversing light switch - 7B•4
Rocker arms - 2B•11
Rotor - 1•18
Routine maintenance and servicing- 1•1
et seq
Routine maintenance - air conditioning
system - 3•8
Routine maintenance - bodywork and
underframe - 11•1
Routine maintenance - hinges and locks -
11•4
Routine maintenance - interior trim - 11•2
Routine maintenance - upholstery and
carpets - 11•2
Rust holes in bodywork - 11•2
S
Safety first! - 0•5
Scalding - 0•5
Scratches in bodywork - 11•2
Screw threads and fastenings - REF•8
Seat belt - 11•9, REF•2
Seats - 11•9, REF•2
Selector lever - 7B•3, 7B•5
Selector shaft - 7A•2
Service Indicator (SI) board - 12•4
Service indicator light - 1•26
Servo - 9•2, 9•10, 9•11
Shock absorber - 1•21, 10•7, 10•8, 10•9,
REF•2, REF•3
Shoes - 9•7
Short-circuit - 12•2Silencer - 4•20
Slave cylinder - 8•3
Spares - REF•19
Spark plug - 1•17, 1•18
Speed sensors - 5•8
Springs - 10•7, 10•9, REF•3
Starter inhibitor - 7B•4
Starter motor - 5•12
Starter motor fault - REF•10
Starting system - 5•11
Steering box - 10•15
Steering column - 11•9, 12•3, REF•1
Steering gear - 10•12, 10•13, REF•3
Steering linkage - 10•14
Steering wheel - 10•16, REF•1
Stop-light switch - 9•13
Struts - 1•21, 10•6, 10•7
Sump - 2A•15
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) -
12•8
Suspension and steering systems- 1•21,
1•22, 10•1et seq, REF•2, REF•3
Suspension and steering fault finding -
REF•15
Switches - 7B•4, 9•13, 12•3
T
Tailgate - 11•6
Tappets - 2B•11
Thermostat - 3•2
Thermotime switch - 4•17, 4•18
Throttle body - 4•16
Throttle linkage - 1•20
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) - 6•3
Throttle positioner - 4•13, 4•14
Thrust arm - 10•5
Timing - 5•4
Timing belt - 1•26, 2A•8, 2A•9
Timing chain - 2A•6, 2A•8
Timing sensors - 6•4
Tools - REF•5, REF•7, REF•8
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston -
2A•3Torque converter - 7B•5
Towing - 0•8
Track rod ends - 10•13
Trailing arms - 10•10
Transmission - SeeManual transmission or
Automatic transmission
Trim - 11•2, 11•6
Tyres - 1•9, 1•14, 10•16, REF•4, REF•15
U
Underframe - 11•1
Universal joints - 8•8
Upholstery - 11•2
V
Vacuum hoses - 1•14
Vacuum servo - 9•10
Valve clearances - 1•19
Valve cover - 2A•4
Valves - 2B•10, 2B•11
Vehicle identification - REF•2, REF•19
Voltage checks - 12•1
Voltage regulator - 5•10
W
Washer fluid - 1•9
Water pump - 3•5
Weekly checks- 1•7et seq
Wheel alignment - 10•17
Wheel bearings - 10•8, 10•11, REF•3
Wheel changing - 0•8
Wheels - 10•16, REF•4
Windows - 11•8, 12•9
Windscreen - REF•1
Wiper blades - 1•23
Wiper motor - 12•7
Wiring diagrams- 12•9et seq
Working faclities - REF•7