fuel filter BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 127 of 228
filtered with a flame trap like most
conventional systems. There are no
conventional PCV valves fitted on these
systems - just a hose (see illustration).
3The main components of the PCV system
are the hoses that connect the valve cover to
the throttle body or air cleaner. If abnormal
operating conditions (such as piston ring
problems) arise, the system is designed to
allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to
flow back through the crankcase vent tube
into the intake system, to be consumed by
normal combustion. Note: Since these
models don’t use a filtering element, it’s a
good idea to check the PCV system
passageways for clogging from sludge and
combustion residue(see illustration).
6 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system
2
General description
Note:This system is normally only fitted to
those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter.
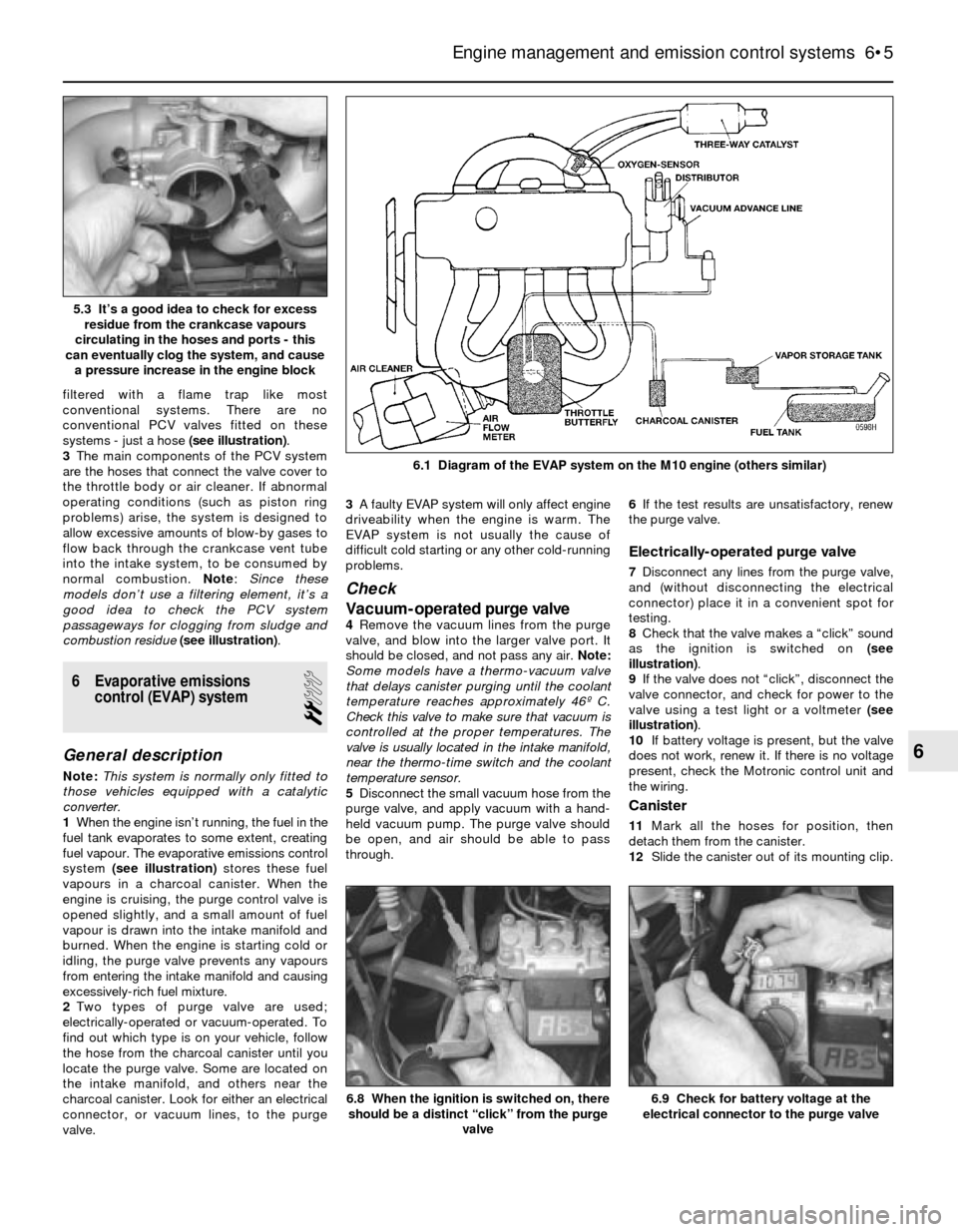
1When the engine isn’t running, the fuel in the
fuel tank evaporates to some extent, creating
fuel vapour. The evaporative emissions control
system (see illustration)stores these fuel
vapours in a charcoal canister. When the
engine is cruising, the purge control valve is
opened slightly, and a small amount of fuel
vapour is drawn into the intake manifold and
burned. When the engine is starting cold or
idling, the purge valve prevents any vapours
from entering the intake manifold and causing
excessively-rich fuel mixture.
2Two types of purge valve are used;
electrically-operated or vacuum-operated. To
find out which type is on your vehicle, follow
the hose from the charcoal canister until you
locate the purge valve. Some are located on
the intake manifold, and others near the
charcoal canister. Look for either an electrical
connector, or vacuum lines, to the purge
valve.3A faulty EVAP system will only affect engine
driveability when the engine is warm. The
EVAP system is not usually the cause of
difficult cold starting or any other cold-running
problems.
Check
Vacuum-operated purge valve
4Remove the vacuum lines from the purge
valve, and blow into the larger valve port. It
should be closed, and not pass any air. Note:
Some models have a thermo-vacuum valve
that delays canister purging until the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 46º C.
Check this valve to make sure that vacuum is
controlled at the proper temperatures. The
valve is usually located in the intake manifold,
near the thermo-time switch and the coolant
temperature sensor.
5Disconnect the small vacuum hose from the
purge valve, and apply vacuum with a hand-
held vacuum pump. The purge valve should
be open, and air should be able to pass
through.6If the test results are unsatisfactory, renew
the purge valve.
Electrically-operated purge valve
7Disconnect any lines from the purge valve,
and (without disconnecting the electrical
connector) place it in a convenient spot for
testing.
8Check that the valve makes a “click” sound
as the ignition is switched on (see
illustration).
9If the valve does not “click”, disconnect the
valve connector, and check for power to the
valve using a test light or a voltmeter (see
illustration).
10If battery voltage is present, but the valve
does not work, renew it. If there is no voltage
present, check the Motronic control unit and
the wiring.
Canister
11Mark all the hoses for position, then
detach them from the canister.
12Slide the canister out of its mounting clip.
Engine management and emission control systems 6•5
6.1 Diagram of the EVAP system on the M10 engine (others similar)
6.9 Check for battery voltage at the
electrical connector to the purge valve6.8 When the ignition is switched on, there
should be a distinct “click” from the purge
valve
6
5.3 It’s a good idea to check for excess
residue from the crankcase vapours
circulating in the hoses and ports - this
can eventually clog the system, and cause
a pressure increase in the engine block
Page 128 of 228
On some models, it will be necessary to
release the retaining clip (see illustration).
13Visually examine the canister for leakage
or damage.
14Renew the canister if you find evidence of
damage or leakage.
7 Catalytic converter
1
General description
1To reduce emissions of unburnt
hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), the later
vehicles covered by this manual are equipped
with a catalytic converter (see illustration).
The converter contains a ceramic honeycomb
coated with precious metals, which speed up
the reaction between the pollutants listed
previously and the oxygen in the exhaust gas.
The pollutants are oxidised to produce water
(H
2O), nitrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Check
2Visually examine the converter(s) for cracks
or damage. Make sure all nuts and bolts are
tight.
3Inspect the insulation cover (if applicable)
welded onto the converter - it should not be
loose.
Caution: If an insulation cover is
dented so that it touches the
converter housing inside,
excessive heat may be
transferred to the floor.
4Start the engine and run it at idle speed.
5Check for exhaust gas leakage from the
converter flanges. Check the body of each
converter for holes.
Component renewal
6See Chapter 4 for removal and refitting
procedures.
Precautions
7The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware, if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded (eg UK “4-star”)
petrol in a car equipped with a catalytic
converter - the lead will coat the precious
metals, reducing their converting
efficiency, and will eventually destroy the
converter.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule, as given in
Chapter 1. In particular, ensure that the air
cleaner filter element, the fuel filter (where
fitted) and the spark plugs are renewed at
the correct interval. If the intake air/fuel
mixture is allowed to become too rich due
to neglect, unburned fuel will enter the
catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
(d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see (b) or (c)
above.
(e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - ie do not “blip” the
throttle immediately before switching offthe engine. If the ignition is switched off
at anything above idle speed, unburned
fuel will enter the (very hot) catalytic
converter, with the possible risk of its
igniting on the element and damaging the
converter.
(f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
(g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages, and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody - and the casing will become
hot enough to ignite combustible
materials which brush against it. DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry
undergrowth, or over long grass or piles
of dead leaves.
(i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, and take great care
when working on the exhaust system.
Ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car, and do not drive the car over
rough ground, road humps, etc, in such a
way as to “ground” the exhaust system.
(j) In some cases, particularly when the car
is new and/or is used for stop/start
driving, a sulphurous smell (like that of
rotten eggs) may be noticed from the
exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped cars, and
seems to be due to the small amount of
sulphur found in some petrols reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust, to produce
hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) gas; while this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the car
has covered a few thousand miles, the
problem should disappear - in the
meanwhile, a change of driving style, or of
the brand of petrol used, may effect a
solution.
(k) The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for 50 000 to 100 000 miles - from
this point on, the CO level should be
carefully checked regularly, to ensure that
the converter is still operating efficiently. If
the converter is no longer effective, it
must be renewed.
6•6 Engine management and emission control systems
7.1 Typical catalytic converter (M10
engine type shown, others similar)6.12 EVAP system charcoal canister
viewed from under the vehicle (316i model)
Page 205 of 228

REF•4MOT Test Checks
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test can
be carried out later to check that the vehicle
pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-bearing
areas. (These include chassis box sections,
side sills, cross-members, pillars, and all
suspension, steering, braking system and
seat belt mountings and anchorages.) Any
corrosion which has seriously reduced the
thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allowthe engine speed to return to idle, and watch
for smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000 rpm;
if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less, this
counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
Page 211 of 228

REF•10Fault Finding
Engine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission not completely engaged in Park (Chap-
ter 7B) or (on models with a clutch switch) clutch not completely
depressed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapters 5 and 12).
m mStarter motor pinion jammed in flywheel ring gear (Chapter 5).
m mStarter solenoid faulty (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor faulty (Chapter 5).
m mIgnition switch faulty (Chapter 12).
m mStarter pinion or flywheel teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mEngine internal problem (Chapter 2B).
Engine rotates, but will not start
m
mFuel tank empty.
m mBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mLeaking fuel injector(s), faulty fuel pump, pressure regulator, etc
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel not reaching fuel injection system or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injector stuck open (Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapter 5).
m mLoose distributor mounting bolts causing ignition timing to wander
(Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wires at the ignition coil, or faulty
coil (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when cold
m mBattery discharged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel system malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mInjector(s) leaking or carburettor automatic choke faulty (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDistributor rotor carbon-tracked (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when hot
m
mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel not reaching the fuel injection system or carburettor (Chap-
ter 4).
m mCorroded battery connections, especially earth (negative)
connection (Chapter 1).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
m mPinion or flywheel gear teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
m
mLoose or faulty electrical connections at distributor, coil or
alternator (Chapter 5).
m mInsufficient fuel reaching the fuel injector(s) or carburettor
(Chapters 1 and 4).
m mDamaged fuel injection system speed sensors (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty fuel injection relays (Chapter 5).
Oil puddle under engine
m
mOil sump gasket and/or sump drain plug seal leaking (Chapter 2).
m mOil pressure sender unit leaking (Chapter 2).
m mValve cover gaskets leaking (Chapter 2).
m mEngine oil seals leaking (Chapter 2).
Engine idles erratically
m
mVacuum leakage (Chapter 4).
m mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump not delivering sufficient fuel to the fuel injection system
or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mTiming belt/chain and/or sprockets worn (Chapter 2).
m mCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6). This Section provides an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of your
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. They also refer you to the Chapter and/or
Section which deals with the problem.
Remember that successful fault diagnosis is not a mysterious
black art practised only by professional mechanics. It is simply the
result of the right knowledge combined with an intelligent, systematic
approach to the problem. Always work by a process of elimination,
starting with the simplest solution and working through to the mostcomplex - and never overlook the obvious. Anyone can run the fuel
tank dry or leave the lights on overnight, so don’t assume that you are
exempt from such oversights.
Finally, always establish a clear idea of why a problem has
occurred, and take steps to ensure that it doesn’t happen again. If the
electrical system fails because of a poor connection, check all other
connections in the system to make sure that they don’t fail as well. If a
particular fuse continues to blow, find out why - don’t just renew one
fuse after another. Remember, failure of a small component can often
be indicative of potential failure or incorrect functioning of a more
important component or system.
Engine
Page 212 of 228

REF•11
REF
Fault Finding
Engine misses at idle speed
m mSpark plugs worn or incorrectly-gapped (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leaks (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mUneven or low compression (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6).
Engine misses throughout driving speed range
m
mFuel filter clogged and/or impurities in the fuel system (Chapter 1).
m mLow fuel output at the injectors, or partially-blocked carburettor
jets (Chapter 4).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mCracked distributor cap, disconnected distributor HT leads, or
damaged distributor components (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty emission system components (Chapter 6).
m mLow or uneven cylinder compression pressures (Chapter 2).
m mWeak or faulty ignition system (Chapter 5).
m mVacuum leak in fuel injection system, intake manifold or vacuum
hoses (Chapter 4).
Engine misfires on acceleration
m mSpark plugs fouled (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mFuel filter clogged (Chapters 1 and 4).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mIntake manifold air leak (Chapter 4).
Engine surges while holding accelerator steady
m
mIntake air leak (Chapter 4).
m mFuel pump faulty (Chapter 4).
m mLoose fuel injector harness connections (Chapters 4 and 6).
m mDefective ECU (Chapter 5).
Engine lacks power
m
mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mExcessive play in distributor shaft (Chapter 5).
m mWorn rotor, distributor cap or HT leads (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mFaulty coil (Chapter 5).
m mBrakes binding (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission fluid level incorrect (Chapter 1).
m mClutch slipping (Chapter 8).
m mFuel filter clogged and/or impurities in the fuel system (Chapter 1).
m mEmission control system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mLow or uneven cylinder compression pressures (Chapter 2).
Engine stalls
m
mIdle speed incorrect (Chapter 1).
m mFuel filter clogged and/or water and impurities in the fuel system
(Chapter 1).
m mDistributor components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty emissions system components (Chapter 6).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leak in the fuel injection system, intake manifold or
vacuum hoses (Chapter 4).
Engine backfires
m mEmissions system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty secondary ignition system (cracked spark plug insulator,
faulty plug HT leads, distributor cap and/or rotor) (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mVacuum leak at fuel injector(s), intake manifold or vacuum hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mValve clearances incorrect (Chapter 1), or valve(s) sticking or
damaged (Chapter 2).
Pinking or knocking engine sounds when
accelerating or driving uphill
m mIncorrect grade of fuel.
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor in need of adjustment (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDamaged spark plugs or HT leads, or incorrect type fitted (Chapter 1).
m mWorn or damaged distributor components (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty emission system (Chapter 6).
m mVacuum leak (Chapter 4).
Engine runs with oil pressure light on
Caution: Stop the engine immediately if the oil
pressure light comes on and establish the cause.
Running the engine while the oil pressure is low can
cause severe damage.
m mLow oil level (Chapter 1).
m mIdle speed too low (Chapter 1).
m mShort-circuit in wiring (Chapter 12).
m mFaulty oil pressure sender unit (Chapter 2).
m mWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2).
Engine runs-on after switching off
m
mIdle speed too high (Chapter 1).
m mExcessive engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
m mIncorrect fuel octane grade.
m mSpark plugs defective or incorrect grade (Chapter 1).
Engine electrical system
Battery will not hold charge
m
mAlternator drivebelt defective or not adjusted properly (Chapter 1).
m mElectrolyte level low (Chapter 1).
m mBattery terminals loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mAlternator not charging properly (Chapter 5).
m mLoose, broken or faulty wiring in the charging circuit (Chapter 5).
m mShort in vehicle wiring (Chapters 5 and 12).
m mInternally-defective battery (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light bulb blown - on some early
models (Chapter 5)
Ignition (no-charge) warning light fails to go out
m mFaulty alternator or charging circuit (Chapter 5).
m mAlternator drivebelt defective or out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mAlternator voltage regulator inoperative (Chapter 5).
Ignition (no-charge) warning light fails to come on
when key is turned
m mWarning light bulb defective (Chapter 12).
m mFault in the printed circuit, wiring or bulbholder (Chapter 12).
Page 213 of 228

REF•12Fault Finding
Fuel system
Excessive fuel consumption
m mDirty or clogged air filter element (Chapter 1).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mEmissions system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mFuel injection internal parts or carburettor jets excessively worn or
damaged (Chapter 4).
m mLow tyre pressure or incorrect tyre size (Chapter 1).
m mUnsympathetic driving style, or unfavourable conditions.
Fuel leakage and/or fuel odour
Warning: Don’t drive the vehicle if a fuel leak is
suspected. Leaking fuel in the engine compartment
could catch fire.
m mLeak in a fuel feed or vent line (Chapter 4).
m mTank overfilled.
m mFuel injector or carburettor parts excessively worn, or fuel system
gaskets leaking (Chapter 4).
Cooling system
Overheating
m mInsufficient coolant in system (Chapter 1).
m mWater pump drivebelt defective or out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mRadiator matrix blocked, or grille restricted (Chapter 3).
m mThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
m mRadiator cap not maintaining proper pressure (Chapter 3).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
Overcooling
m
mFaulty thermostat (Chapter 3).
External coolant leakage
m
mDeteriorated/damaged hoses; loose clamps (Chapters 1 and 3).
m mWater pump seal defective (Chapters 1 and 3).
m mLeakage from radiator matrix, heater matrix or header tank
(Chapter 3).
m mRadiator/engine block drain plugs or water jacket core plugs
leaking (Chapters 2 and 3).
Internal coolant leakage
m mLeaking cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mCracked cylinder bore or cylinder head (Chapter 2).
Coolant loss
m
mToo much coolant in system (Chapter 1).
m mCoolant boiling away because of overheating (see above).
m mInternal or external leakage (see above).
m mFaulty radiator cap (Chapter 3).
Poor coolant circulation
m
mInoperative water pump (Chapter 3).
m mRestriction in cooling system (Chapters 1 and 3).
m mWater pump drivebelt defective/out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mThermostat sticking (Chapter 3).
Clutch
Pedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little
resistance
m mMaster or slave cylinder faulty (Chapter 8).
m mFluid line burst or leaking (Chapter 8).
m mConnections leaking (Chapter 8).
m mNo fluid in reservoir (Chapter 1).
m mIf fluid is present in master cylinder dust cover, master cylinder rear
seal has failed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken release bearing or fork (Chapter 8).
Fluid in area of master cylinder dust cover, and on
pedal
m mRear seal failure in master cylinder (Chapter 8).
Fluid on slave cylinder
m
mSlave cylinder plunger seal faulty (Chapter 8).
Pedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m
mAir in system (Chapter 8).
Unable to select gears
m
mFaulty transmission (Chapter 7).
m mFaulty clutch plate (Chapter 8).
m mFork and bearing not assembled properly (Chapter 8).
m mFaulty pressure plate (Chapter 8).
m mPressure plate-to-flywheel bolts loose (Chapter 8).
Clutch slips (engine speed increases with no
increase in vehicle speed)
m mClutch plate worn (Chapter 8).
m mClutch plate is oil-soaked by leaking rear main seal (Chapter 8).
m mWarped pressure plate or flywheel (Chapter 8).
m mWeak diaphragm spring (Chapter 8).
m mClutch plate overheated.
Grabbing (chattering) as clutch is engaged
m
mOil on clutch plate lining, burned or glazed facings (Chapter 8).
m mWorn or loose engine or transmission mountings (Chapters 2
and 7A).
m mWorn splines on clutch plate hub (Chapter 8).
m mWarped pressure plate or flywheel (Chapter 8).
Noise in clutch area
m
mFork improperly fitted (Chapter 8).
m mFaulty release bearing (Chapter 8).
Clutch pedal stays on floor
m
mFork binding in housing (Chapter 8).
m mBroken release bearing or fork (Chapter 8).
High pedal effort
m
mFork binding in housing (Chapter 8).
m mPressure plate faulty (Chapter 8).
m mIncorrect-size master or slave cylinder fitted (Chapter 8).
Page 226 of 228

REF•26Index
E
Earth check - 12•2
Electric fan - 3•4
Electric shock - 0•5
Electric windows - 12•9
Electrical equipment - REF•2
Electrical system fault finding - 12•1
Electronic control system - 4•3, 4•14
Electronic control unit (ECU) - 6•1
Engine fault finding - REF•10
Engine tune-up - 1•7
Engine electrical systems- 5•1et seq
Engine electrical systems fault finding -
REF•11
Engine management and emission control
systems- 6•1et seq
Engine oil - 1•3, 1•7, 1•11
Environmental considerations - REF•8
Evaporative emissions control (EVAP)
system - 1•26, 6•5
Evaporator - 3•10
Exhaust emission checks - REF•4
Exhaust manifold - 2A•6
Exhaust system - 1•21, 4•20, REF•3
F
Fan - 3•4, 3•5
Fault finding- REF•9et seq
Fault finding - automatic transmission -
7B•2, REF•13
Fault finding - braking system - REF•14
Fault finding - clutch - REF•12
Fault finding - cooling system - REF•12
Fault finding - electrical system - 12•1,
REF•11
Fault finding - engine - REF•10
Fault finding - fuel system - 4•21, REF•12
Fault finding - manual transmission -
REF•13
Fault finding - suspension and steering -
REF•15
Filling - 11•3
Final drive - 8•2, 8•10, 8•11
Final drive oil - 1•3, 1•19, 1•26
Fire - 0•5
Flexible coupling - 8•7
Fluid level checks - 1•7
Fluid seals - 7B•5
Flywheel - 2A•18
Fuel and exhaust systems- 1•20, 4•1et
seq,REF•4
Fuel system fault finding - REF•12
Fuel filter - 1•25
Fuel hoses - 1•14
Fuel injection system - 4•3, 4•14
Fuel injection system - fault finding - 4•21
Fuel injectors - 4•18
Fuel level sender unit - 4•5, 4•6
Fuel lines and fittings - 4•7
Fuel pressure - 4•3
Fuel pressure regulator - 4•16
Fuel pump - 4•3, 4•4, 4•5
Fuel tank - 4•7, 4•8
Fume or gas intoxication - 0•5
Fuses - 12•2
G
Gaiters - 1•22, 8•9, 10•13
Gashes in bodywork - 11•2
Gaskets - REF•8
Gear lever - 7A•1
Gearbox - SeeManual transmission
Gearbox oil - 1•3, 1•19, 1•25
General engine overhaul procedures-
2B•1et seq
Glass - 11•4, 11•8
Glossary of technical terms - REF•20
Grille - 11•4
H
Handbrake - 1•23, 9•2, 9•12, REF•1
Handbrake fault - REF•14
Handles - 11•8
Hazard warning flasher - 12•2
HC emissions - REF•4
Headlights - 12•3, 12•5, 12•6
Heated rear window - 12•8
Heater - 3•2, 3•7, 3•8
Hinges - 11•4
HT leads - 1•18
Hubs - 10•8, 10•11, REF•3
Hydraulic servo - 9•11
Hydraulic tappets - 2B•11
Hydrofluoric acid - 0•5
I
Idle air stabiliser valve - 4•18
Idle speed adjustment - 1•15
Ignition coil - 5•5
Ignition control unit - 5•6, 5•7
Ignition sensors - 5•8
Ignition switch - 12•3
Ignition system - 5•3
Ignition timing - 5•4
Ignition timing sensors - 6•4
Impulse generator - 5•6, 5•7
In-car engine repair procedures- 2A•1et
seq
Indicators - 12•2, 12•3
Information sensors - 6•2
Injectors - 4•18
Input shaft - 7A•2
Instrument cluster - 12•4
Instrument panel language display - 0•7
Intake manifold - 2A•4
Intermediate shaft - 2A•12, 2B•14, 2B•19
Introduction to the BMW 3- and 5-Series -
0•4
J
Jacking - 0•8
Joint mating faces - REF•8
Jump starting - 0•9
K
Kickdown cable - 7B•3
L
L-Jetronic fuel injection system - 4•14,
4•19
Language display - 0•7
Latch - 11•8
Leaks - 0•10, 7B•3, REF•12, REF•13
Locknuts, locktabs and washers - REF•8
Locks - 11•4, 11•8
Lubricants - REF•18
M
Main bearings - 2B•17, 2B•19
Manifolds - 2A•4, 2A•6
Manual transmission- 7A•1et seq
Manual transmission fault finding - REF•13
Manual transmission oil - 1•3, 1•19, 1•25
Master cylinder - 8•3, 9•9
Mechanical fan - 3•4, 3•5
Mirrors - 11•8, REF•1
Misfire - REF•11
Mixture - REF•4
MOT test checks- REF•1 et seq
Motronic engine management system -
6•1
Motronic fuel injection system - 4•14, 4•19
Mountings - 2A•19, 7A•3
O
Oil - differential - 1•19, 1•26
Oil - engine - 1•3, 1•7, 1•11
Oil - final drive - 1•3
Oil - manual transmission - 1•3, 1•19, 1•25
Oil filter - 1•11, 1•12
Oil pump - 2A•16
Oil seals - 2A•12, 2A•13, 2A•19, 2B•20,
7A•2, 7B•5, 8•10, 8•12, REF•8
Open-circuit - 12•2
Output shaft - 7A•2, 7B•5
Overcooling - REF•12
Overheating - REF•12
Oxygen sensor - 6•2
P
Pads - 9•2, 9•3
Pedals - 8•3, 9•13
Pinion oil - 8•12
Pinking - REF•11
Piston rings - 2B•18
Pistons - 2B•12, 2B•16, 2B•21
Plastic components - 11•3
Poisonous or irritant substances - 0•5
Position sensors - 5•8
Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
system - 6•4
Power steering - 1•14, 10•15, 10•16
Power steering fluid - 1•12
Propeller shaft - 8•2, 8•6, 8•8
Pulse sensor - 5•8
Purge valve - 6•5