dashboard BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 80 of 228

Warning: Do not remove the
pressure cap from the radiator or
expansion tank until the engine
has cooled completely and
there’s no pressure remaining in the
cooling system. Removing the cap from a
hot engine risks personal injury by
scalding.
Heating system
The heating system consists of a blower fan
and heater matrix located in the heater box,
with hoses connecting the heater matrix to the
engine cooling system, and the heater/air
conditioning control head on the dashboard.
Hot engine coolant is circulated through the
heater matrix passages all the time the engine
is running. Switching the heater on opens a
flap door to direct air through the heater
matrix, and the warmed air enters the
passenger compartment. A fan switch on the
control head activates the blower motor,
which forces more air through the heater
matrix, giving additional heater output for
demisting, etc.
Air conditioning system
The air conditioning system consists of a
condenser mounted in front of the radiator, an
evaporator mounted adjacent to the heater
matrix, a compressor mounted on the engine,
a filter-drier (receiver-drier) which contains a
high-pressure relief valve, and the plumbing
connecting all of the above components.
A blower fan forces the warmer air of the
passenger compartment through the
evaporator matrix (a radiator-in-reverse),
transferring the heat from the air to the
refrigerant. The liquid refrigerant boils off into
low-pressure vapour, taking the heat with it
when it leaves the evaporator.
Note: Refer to the precautions at the start
of Section 12 concerning the potential
dangers associated with the air conditioning
system.
2 Antifreeze-
general information
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. If
consumed, antifreeze can be fatal;
children and pets are attracted by its
sweet taste, so wipe up garage floor and
drip pan coolant spills immediately. Keep
antifreeze containers covered, and repair
leaks in your cooling system as soon as
they are noticed.
The cooling system should be filled with a
60/40% water/ethylene-glycol-based anti-
freeze solution, which will prevent freezing
down to approximately -27°C (-17°F). The
antifreeze also raises the boiling point of thecoolant, and (if of good quality) provides
protection against corrosion.
The cooling system should be drained,
flushed and refilled at the specified intervals
(see Chapter 1). Old or contaminated
antifreeze solutions are likely to cause
damage, and encourage the formation of rust
and scale in the system. Use distilled water
with the antifreeze, if available, or clean
rainwater. Tap water will do, but not if the
water in your area is at all “hard”.
Before adding antifreeze, check all hose
connections, because antifreeze tends to
search out and leak through very minute
openings. Engines don’t normally consume
coolant, so if the level goes down, find the
cause and correct it.
The antifreeze mixture should be
maintained at its correct proportions; adding
too much antifreeze reduces the efficiency of
the cooling system. If necessary, consult the
mixture ratio chart on the antifreeze container
before adding coolant. Hydrometers are
available at most car accessory shops to test
the coolant. Use antifreeze which meets the
vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
3 Thermostat-
check and renewal
1
Warning: Do not remove the
radiator cap, drain the coolant, or
renew the thermostat until the
engine has cooled completely.
Check
1Before assuming the thermostat is to blame
for a cooling system problem, check the
coolant level, drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1)
and temperature gauge (or warning light)
operation.
2If the engine seems to be taking a long time
to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the
thermostat.
3If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the upper radiator
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,preventing the coolant inside the engine from
circulating to the radiator. Renew the
thermostat.
Caution: Don’t drive the vehicle
without a thermostat. The engine
will be very slow to warm-up in
cold conditions, resulting in poor
fuel economy and driveability. A new
thermostat is normally an inexpensive
component anyway.
4If the upper radiator hose is hot, it means
that the coolant is flowing and the thermostat
is at least partly open. Consult the “Fault
finding” Section at the rear of this manual for
cooling system diagnosis.
Renewal
All models
5Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
6Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
M10 engines
7The thermostat is located in the bottom
hose. First remove the cooling fan.
8Note the fitted position of the thermostat,
then unscrew the hose clamps and withdraw
the thermostat from the hose connections
(see illustration).
9Refit the thermostat-to-hose connections,
and tighten the hose clamps.
10Refit the cooling fan.
M20 and M30 engines
11Loosen the hose clamp (see illustration),
then detach the hose(s) from the thermostat
cover.
3•2 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
3.11 On M20 and M30 engine models,
loosen the hose clamp (A) and disconnect
the hose from the thermostat housing
cover - note that the coolant temperature
sender unit (barely visible behind the fuel
pressure regulator) is located at the top of
the thermostat housing (B)
3.8 On the M10 (four-cylinder) engine, the
thermostat (arrowed) is connected in-line
in the radiator hose
Page 130 of 228

Torque wrench settingsNm
Front disc brake caliper
Caliper guide (mounting) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 35
Caliper bracket-to-strut housing bolts
3-Series, E30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Rear disc brake caliper
Caliper guide (mounting) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 35
Carrier-to-trailing arm bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Brake hose-to-caliper fitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 to 17
Master cylinder-to-brake servo nuts
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 to 29
Brake servo mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 24
Hydraulic line-to-hydraulic brake servo threaded
fittings - 5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Wheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
9•2 Braking system
1 General information
All 3-Series models, and 5-Series E28 (“old-
shape”) models, are equipped with front disc
brakes and either rear drum or rear disc
brakes. 5-Series E34 (“new-shape”) models
have disc brakes front and rear. Front and
rear brakes are self-adjusting on all models.
Some later models are equipped with an Anti-
lock Braking System (ABS); this is described
in Section 2.
Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system consists of two
separate circuits. The master cylinder has
separate reservoirs for the two circuits; in the
event of a leak or failure in one hydraulic
circuit, the other circuit will remain operative.
Brake servo
The vacuum brake servo, utilising engine
manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure
to provide assistance to the hydraulically
operated brakes, is mounted on the bulkhead
in the engine compartment.
A hydraulic brake servo system is used on
5-Series E28 models. This system uses
hydraulic pressure from the power steering
pump to assist braking.
Handbrake
The handbrake operates the rear brakes,
and is cable-operated via a lever mounted in
the centre console. The handbrake assembly
on rear drum brake models is part of the rear
drum brake assembly, and is self-adjusting.
On rear disc brake models, the handbrake
uses a pair of brake shoes located inside the
centre portion of the rear brake disc, and is
manually-adjusted.
Brake pad wear warning system
The brake pad wear warning system is
linked to a red warning light in the instrumentcluster, which comes on when the brake pads
have worn down to the point at which they
require renewal. DO NOT ignore this reminder.
If you don’t renew the pads shortly after the
brake pad wear warning light comes on, the
brake discs will be damaged.
On some models, the brake pad wear
warning system also includes an early
warning light that comes on only when the
brake pedal is depressed, letting you know in
advance that the pads need to be renewed.
The wear sensor is attached to the brake
pads. The sensor is located at the left front
wheel; on some models, there is another
sensor at the right rear wheel. The wear
sensor is part of a closed circuit. Once the
pads wear down to the point at which they’re
flush with the sensor, the disc grinds away the
side of the sensor facing the disc. Thus, the
wire inside the sensor is broken, and the red
light on the instrument panel comes on.
Always check the sensor(s) when renewing
the pads. If you change the pads before the
warning light comes on, the sensor(s) may still
be good; once the light has come on, renew
the sensor.
Service
After completing any operation involving
dismantling of any part of the brake system,
always test drive the vehicle to check for
proper braking performance before resuming
normal driving. When testing the brakes, try to
select a clean, dry, road with no camber (ie as
flat as possible) and with no other traffic.
Conditions other than these can lead to
inaccurate test results.
Test the brakes at various speeds with both
light and heavy pedal pressure. The vehicle
should stop evenly, without pulling to one side
or the other. Avoid locking the brakes,
because this slides the tyres and diminishes
braking efficiency and control of the vehicle.
Tyres, vehicle load and wheel alignment are
factors which also affect braking
performance.
2 Anti-lock Braking system
(ABS)- general information
The Anti-lock Braking System is designed
to maintain vehicle control, directional stability
and optimum deceleration under severe
braking conditions on most road surfaces. It
does so by monitoring the rotational speed of
each wheel and controlling the brake line
pressure to each wheel during braking. This
prevents the wheels from locking up.
The ABS system has three main
components - the wheel speed sensors, the
electronic control unit, and the hydraulic
control unit. The sensors - one at each wheel
since 1985, but at both front wheels and one
at the rear differential on earlier models - send
a variable voltage signal to the control unit,
which monitors these signals, compares them
to its program information, and determines
whether a wheel is about to lock up. When a
wheel is about to lock up, the control unit
signals the hydraulic unit to reduce hydraulic
pressure (or not increase it further) at that
wheel’s brake caliper. Pressure modulation is
handled by electrically-operated solenoid
valves.
If a problem develops within the system, an
“ABS” warning light will glow on the
dashboard. Sometimes, a visual inspection of
the ABS system can help you locate the
problem. Carefully inspect the ABS wiring
harness. Pay particularly close attention to the
harness and connections near each wheel.
Look for signs of chafing and other damage
caused by incorrectly-routed wires. If a wheel
sensor harness is damaged, the sensor
should be renewed (the harness and sensor
are integral).
Warning: DO NOT try to repair an
ABS wiring harness. The ABS
system is sensitive to even the
smallest changes in resistance. Repairing
the harness could alter resistance values
Page 131 of 228
and cause the system to malfunction. If
the ABS wiring harness is damaged in any
way, it must be renewed.
Caution: Make sure the ignition is
turned off before unplugging or
re-making any electrical
connections.
Diagnosis and repair
If the dashboard warning light comes on
and stays on while the vehicle is in operation,
the ABS system requires attention. Although
special electronic ABS diagnostic testing
tools are necessary to properly diagnose the
system, you can perform a few preliminary
checks before taking the vehicle to a dealer
service department.
a) Check the brake fluid level in the
reservoir.
b) Verify that the electronic control unit
connectors are securely connected.
c) Check the electrical connectors at the
hydraulic control unit.
d) Check the fuses.
e) Follow the wiring harness to each front
and rear wheel, and verify that all
connections are secure and that the
wiring is undamaged.
If the above preliminary checks do not
rectify the problem, the vehicle should bediagnosed by a dealer service department.
Due to the complex nature of this system, all
actual repair work must be done by a dealer
service department.
3 Disc brake pads- renewal
2
Warning: Disc brake pads must
be renewed on both front wheels
or both rear wheels at the same
time - NEVER renew the pads on
only one wheel. Also, the dust created by
the brake system may contain asbestos,
which is harmful to your health. Never
blow it out with compressed air, and don’t
inhale any of it. An approved filtering mask
should be worn when working on the
brakes. Do not, under any circumstances,
use petroleum-based solvents to clean
brake parts. Use brake system cleaner
only! When servicing the disc brakes, use
only original-equipment or high-quality
brand-name pads.
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Note:This procedure applies to both the front
and rear disc brakes.
1Remove the cap(s) from the brake fluid
reservoir, and syphon off about two-thirds of
the fluid from the reservoir. Failing to do thiscould result in the reservoir overflowing when
the caliper pistons are pressed back into their
bores.
2Loosen the wheel bolts, raise the front or
rear of the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Remove the front or rear wheels, as
applicable. Work on one brake assembly at a
time, using the assembled brake for reference
if necessary.
4Inspect the brake disc carefully as outlined
in Section 5. If machining is necessary, follow
the information in that Section to remove the
disc, at which time the pads can be removed
from the calipers as well.
5Follow the accompanying photos,
beginning with illustration 3.5a, for the pad
removal procedure. Be sure to stay in order,
and read the caption under each illustration.
Note 1:Different types of front calipers are
used on 3 and 5-Series models. Illustrations
3.5a to 3.5e are for the front calipers on 3-
Series models.Illustrations 3.5f to 3.5m are
for the front calipers on 5-Series models.
There’s no photo sequence for rear calipers;
although slightly different in size, they’re
identical in design to the front brake calipers
used on 5-Series models.Note 2: Some
models may have different numbers and types
of anti-squeal shims and other hardware than
what is shown in this Chapter. It’s best to note
how the hardware is fitted on the vehicle
before dismantling, so you can duplicate it on
reassembly.
Braking system 9•3
3.5c Hold the guide pins while loosening
the caliper mounting bolts (3-Series)3.5b Unplug the electrical connector for
the brake pad wear sensor (3-Series)
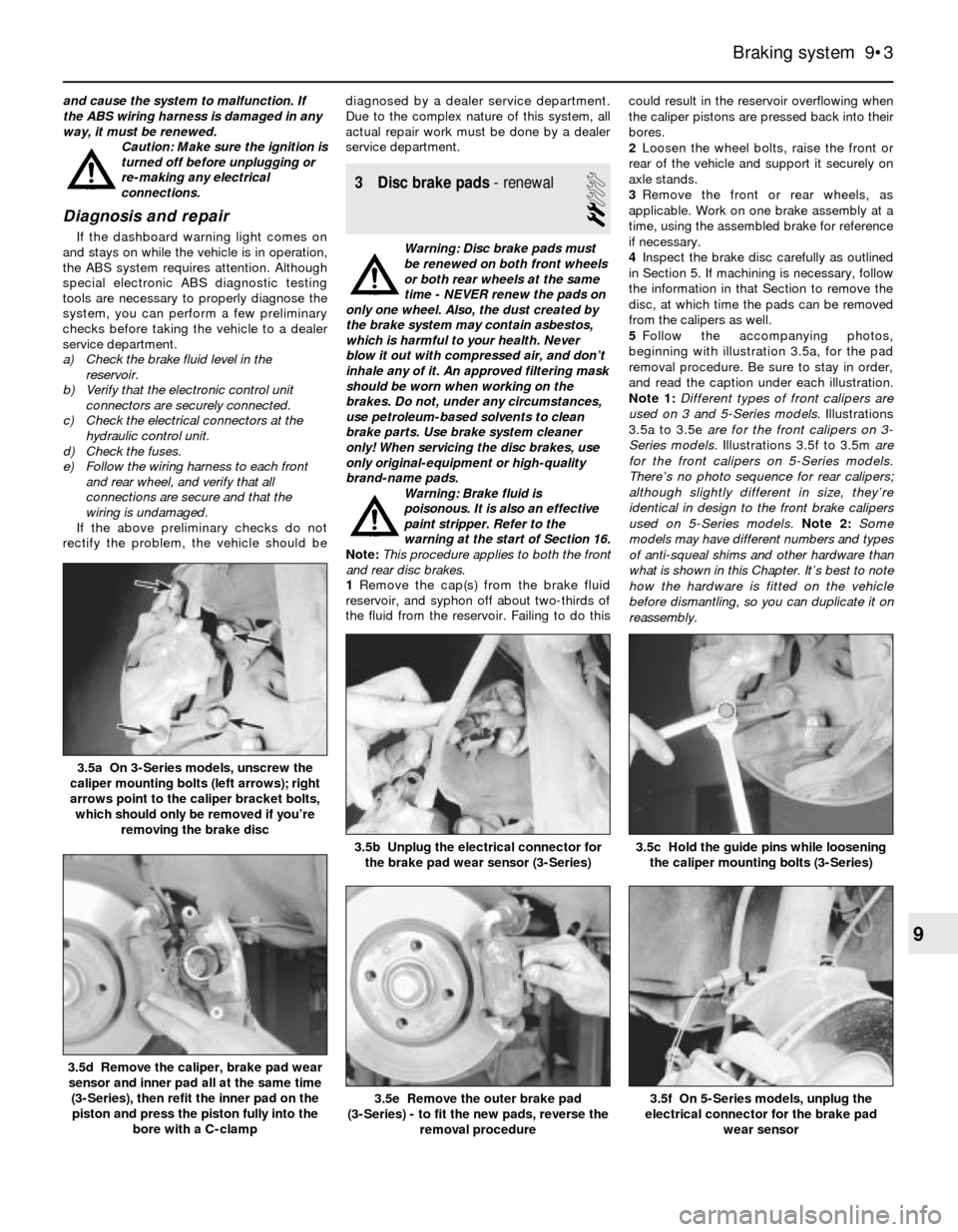
3.5a On 3-Series models, unscrew the
caliper mounting bolts (left arrows); right
arrows point to the caliper bracket bolts,
which should only be removed if you’re
removing the brake disc
3.5f On 5-Series models, unplug the
electrical connector for the brake pad
wear sensor3.5e Remove the outer brake pad
(3-Series) - to fit the new pads, reverse the
removal procedure
3.5d Remove the caliper, brake pad wear
sensor and inner pad all at the same time
(3-Series), then refit the inner pad on the
piston and press the piston fully into the
bore with a C-clamp
9