Start BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 115 of 228
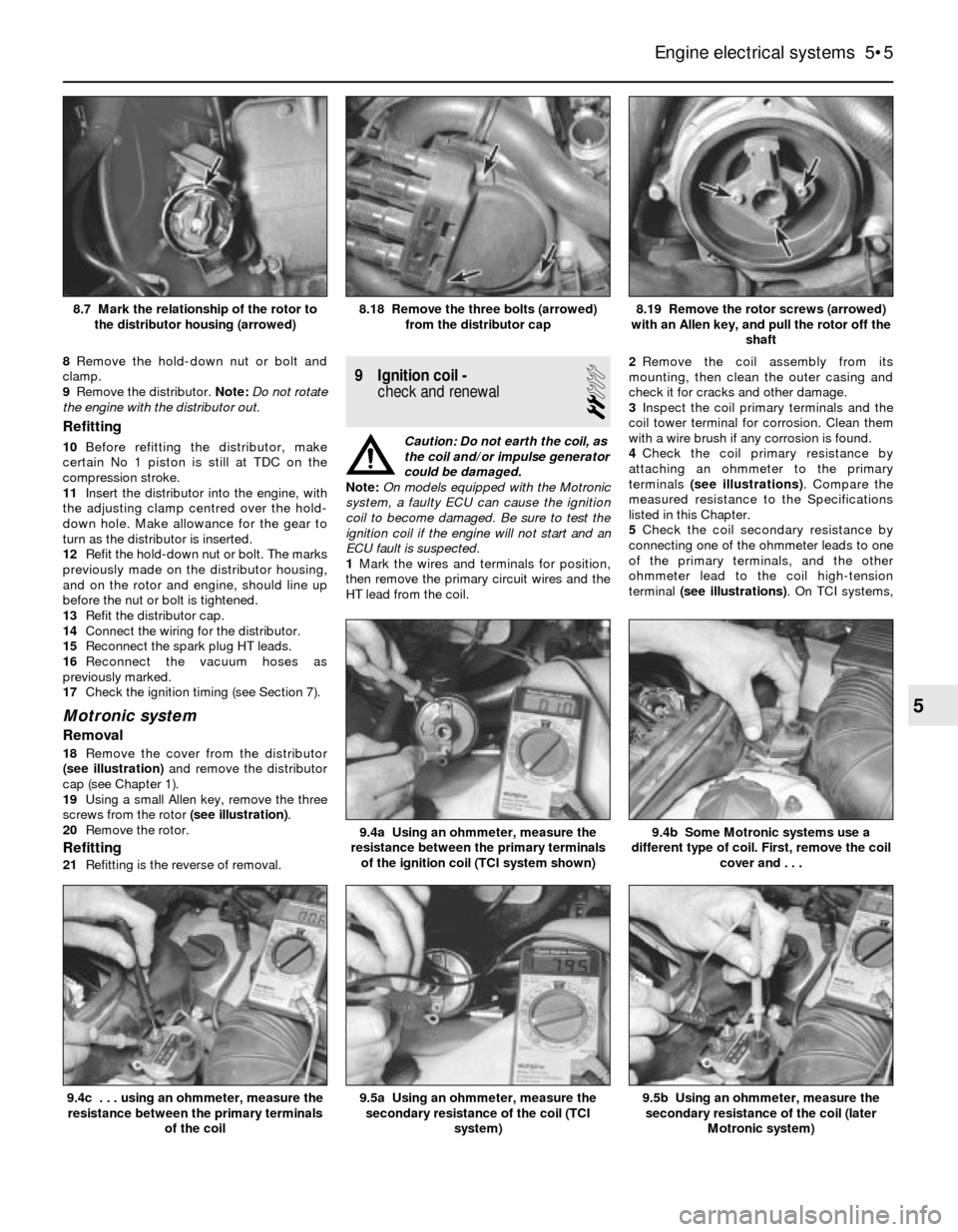
8Remove the hold-down nut or bolt and
clamp.
9Remove the distributor. Note:Do not rotate
the engine with the distributor out.
Refitting
10Before refitting the distributor, make
certain No 1 piston is still at TDC on the
compression stroke.
11Insert the distributor into the engine, with
the adjusting clamp centred over the hold-
down hole. Make allowance for the gear to
turn as the distributor is inserted.
12Refit the hold-down nut or bolt. The marks
previously made on the distributor housing,
and on the rotor and engine, should line up
before the nut or bolt is tightened.
13Refit the distributor cap.
14Connect the wiring for the distributor.
15Reconnect the spark plug HT leads.
16Reconnect the vacuum hoses as
previously marked.
17Check the ignition timing (see Section 7).
Motronic system
Removal
18Remove the cover from the distributor
(see illustration)and remove the distributor
cap (see Chapter 1).
19Using a small Allen key, remove the three
screws from the rotor (see illustration).
20Remove the rotor.
Refitting
21Refitting is the reverse of removal.
9 Ignition coil -
check and renewal
2
Caution: Do not earth the coil, as
the coil and/or impulse generator
could be damaged.
Note:On models equipped with the Motronic
system, a faulty ECU can cause the ignition
coil to become damaged. Be sure to test the
ignition coil if the engine will not start and an
ECU fault is suspected.
1Mark the wires and terminals for position,
then remove the primary circuit wires and the
HT lead from the coil.2Remove the coil assembly from its
mounting, then clean the outer casing and
check it for cracks and other damage.
3Inspect the coil primary terminals and the
coil tower terminal for corrosion. Clean them
with a wire brush if any corrosion is found.
4Check the coil primary resistance by
attaching an ohmmeter to the primary
terminals (see illustrations). Compare the
measured resistance to the Specifications
listed in this Chapter.
5Check the coil secondary resistance by
connecting one of the ohmmeter leads to one
of the primary terminals, and the other
ohmmeter lead to the coil high-tension
terminal (see illustrations). On TCI systems,
Engine electrical systems 5•5
8.19 Remove the rotor screws (arrowed)
with an Allen key, and pull the rotor off the
shaft8.18 Remove the three bolts (arrowed)
from the distributor cap8.7 Mark the relationship of the rotor to
the distributor housing (arrowed)
9.5b Using an ohmmeter, measure the
secondary resistance of the coil (later
Motronic system)9.5a Using an ohmmeter, measure the
secondary resistance of the coil (TCI
system)
9.4b Some Motronic systems use a
different type of coil. First, remove the coil
cover and . . .9.4a Using an ohmmeter, measure the
resistance between the primary terminals
of the ignition coil (TCI system shown)
9.4c . . . using an ohmmeter, measure the
resistance between the primary terminals
of the coil
5
Page 117 of 228
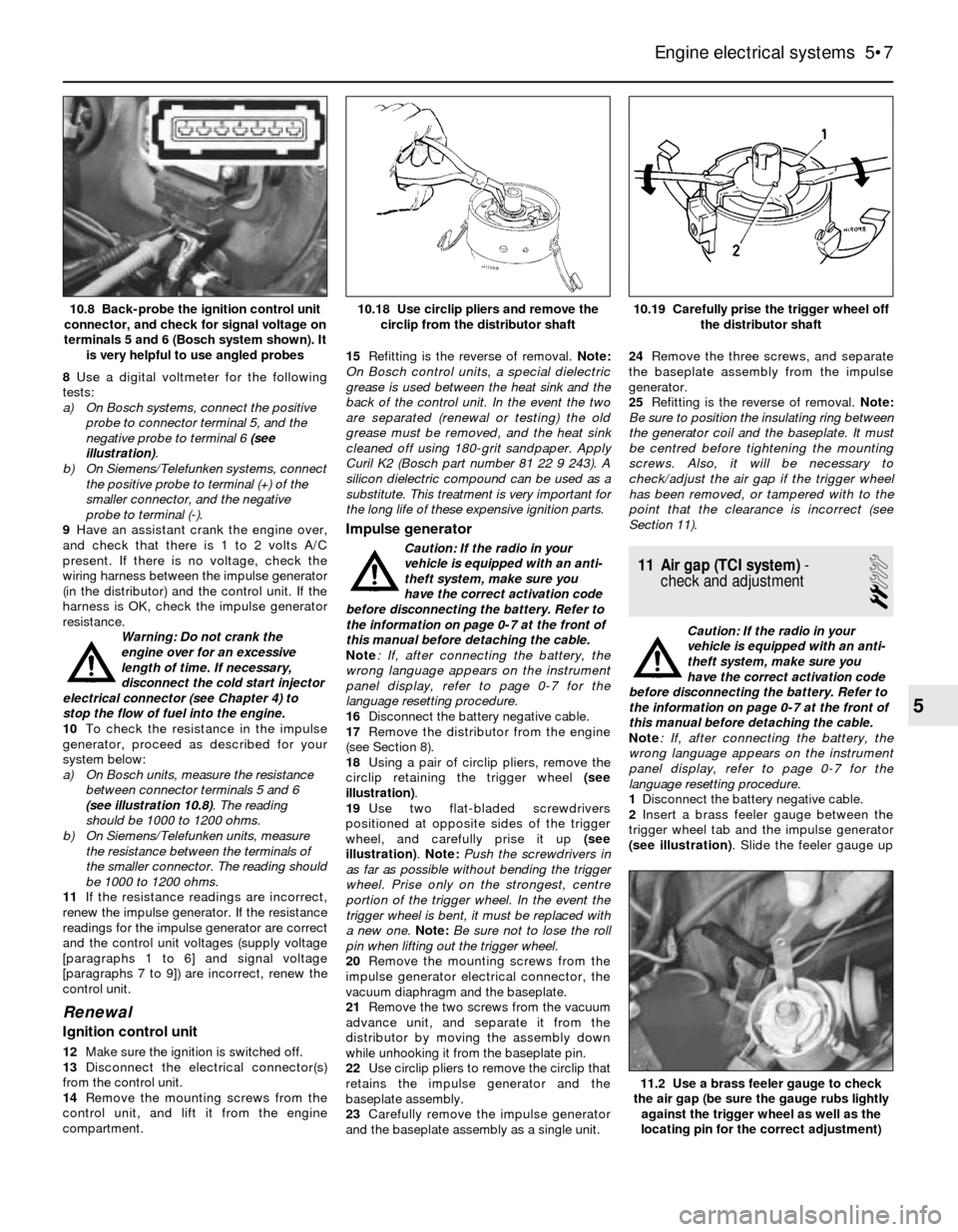
8Use a digital voltmeter for the following
tests:
a) On Bosch systems, connect the positive
probe to connector terminal 5, and the
negative probe to terminal 6 (see
illustration).
b) On Siemens/Telefunken systems, connect
the positive probe to terminal (+) of the
smaller connector, and the negative
probe to terminal (-).
9Have an assistant crank the engine over,
and check that there is 1 to 2 volts A/C
present. If there is no voltage, check the
wiring harness between the impulse generator
(in the distributor) and the control unit. If the
harness is OK, check the impulse generator
resistance.
Warning: Do not crank the
engine over for an excessive
length of time. If necessary,
disconnect the cold start injector
electrical connector (see Chapter 4) to
stop the flow of fuel into the engine.
10To check the resistance in the impulse
generator, proceed as described for your
system below:
a) On Bosch units, measure the resistance
between connector terminals 5 and 6
(see illustration 10.8). The reading
should be 1000 to 1200 ohms.
b) On Siemens/Telefunken units, measure
the resistance between the terminals of
the smaller connector. The reading should
be 1000 to 1200 ohms.
11If the resistance readings are incorrect,
renew the impulse generator. If the resistance
readings for the impulse generator are correct
and the control unit voltages (supply voltage
[paragraphs 1 to 6] and signal voltage
[paragraphs 7 to 9]) are incorrect, renew the
control unit.
Renewal
Ignition control unit
12Make sure the ignition is switched off.
13Disconnect the electrical connector(s)
from the control unit.
14Remove the mounting screws from the
control unit, and lift it from the engine
compartment.15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
On Bosch control units, a special dielectric
grease is used between the heat sink and the
back of the control unit. In the event the two
are separated (renewal or testing) the old
grease must be removed, and the heat sink
cleaned off using 180-grit sandpaper. Apply
Curil K2 (Bosch part number 81 22 9 243). A
silicon dielectric compound can be used as a
substitute. This treatment is very important for
the long life of these expensive ignition parts.
Impulse generator
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
16Disconnect the battery negative cable.
17Remove the distributor from the engine
(see Section 8).
18Using a pair of circlip pliers, remove the
circlip retaining the trigger wheel (see
illustration).
19Use two flat-bladed screwdrivers
positioned at opposite sides of the trigger
wheel, and carefully prise it up (see
illustration). Note: Push the screwdrivers in
as far as possible without bending the trigger
wheel. Prise only on the strongest, centre
portion of the trigger wheel. In the event the
trigger wheel is bent, it must be replaced with
a new one. Note:Be sure not to lose the roll
pin when lifting out the trigger wheel.
20Remove the mounting screws from the
impulse generator electrical connector, the
vacuum diaphragm and the baseplate.
21Remove the two screws from the vacuum
advance unit, and separate it from the
distributor by moving the assembly down
while unhooking it from the baseplate pin.
22Use circlip pliers to remove the circlip that
retains the impulse generator and the
baseplate assembly.
23Carefully remove the impulse generator
and the baseplate assembly as a single unit.24Remove the three screws, and separate
the baseplate assembly from the impulse
generator.
25Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
Be sure to position the insulating ring between
the generator coil and the baseplate. It must
be centred before tightening the mounting
screws. Also, it will be necessary to
check/adjust the air gap if the trigger wheel
has been removed, or tampered with to the
point that the clearance is incorrect (see
Section 11).
11 Air gap (TCI system)-
check and adjustment
2
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Insert a brass feeler gauge between the
trigger wheel tab and the impulse generator
(see illustration). Slide the feeler gauge up
Engine electrical systems 5•7
10.19 Carefully prise the trigger wheel off
the distributor shaft10.18 Use circlip pliers and remove the
circlip from the distributor shaft10.8 Back-probe the ignition control unit
connector, and check for signal voltage on
terminals 5 and 6 (Bosch system shown). It
is very helpful to use angled probes
11.2 Use a brass feeler gauge to check
the air gap (be sure the gauge rubs lightly
against the trigger wheel as well as the
locating pin for the correct adjustment)
5
Page 118 of 228

and down - you should feel a slight drag on
the feeler gauge as it is moved if the gap is
correct. The gap must be as given in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
3To adjust the gap, it is necessary to remove
the impulse generator and the baseplate
assembly from the distributor (see illus-
tration 10.1).
4Follow paragraphs 17 to 24 in Section 10
and loosen the screws that retain the impulse
generator to the baseplate assembly.
5Carefully insert the feeler gauge and tighten
the screws.
6Refit the assembly back into the distributor
and recheck the adjustment.12 Ignition sensors (Motronic
system)- check and renewal
2
Note:Some models are equipped with a TDC
sensor mounted on the front of the engine.
This sensor is strictly for the BMW service test
unit, and is not part of the Motronic ignition
system.
Speed and position sensors
Check
1Locate the two electrical connectors for the
sensors (see illustrations). The grey
connector is for the position sensor, and the
white connector is for the speed sensor.
2Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance
between terminal 1 (yellow wire) and terminal
2 (black wire) on the sensor side of each
connector. The resistance should be 860 to
1,060 ohms.
3Also check the resistance between terminal
3 and either terminal 1 or terminal 2. The
resistance should be approximately 100 000
ohms.
4If the reading(s) are incorrect, renew the
sensor(s).
Renewal
5Remove the sensor mounting screw(s),using an Allen key where necessary, and pull
the sensor(s) from the sockets. Disconnect
the wiring from one sensor at a time - be sure
the connectors are not interchanged when
fitting new sensors. The bellhousing is marked
with a B for the position sensor (grey
connector) and D for the speed sensor (black
connector) (see illustration). Note: It is a
good idea to check the condition of the raised
pin on the flywheel while the sensors are out
of the sockets. Turn the engine by hand as
necessary to bring the pin into view.
6Tighten the sensor mounting screw(s)
securely, but be careful not to overtighten.
Pulse sensor (later models)
Check
7Locate the two electrical connectors for the
sensor (see illustrations). Disconnect the
electrical connector from the front.
8Using an ohmmeter, check resistance
between terminal 1 (yellow wire) and terminal
2 (black wire) on the sensor side of each
connector (see illustration). The resistance
should be 500 to 600 ohms.
9If the reading is incorrect, renew the sensor.
Renewal
10Remove the pulse sensor mounting bolt
using a 5 mm hex spanner (see illustration).
5•8 Engine electrical systems
12.10 The pulse sensor itself (arrowed) is
located on the timing belt cover, to one
side of the pulley (later models)12.8 The resistance of the pulse sensor
should be 500 to 600 ohms (later models)12.7b On later 5-Series models, the pulse
sensor connector (arrowed) is located next
to the valve cover
12.7a On later 3-Series models, the pulse
sensor connector (arrowed) is located next
to the 20-pin diagnostic connector
12.5 Location of the position sensor (B) and
speed sensor (D) on the bellhousing on all
Motronic systems – do not interchange the
sensors, or the engine will not start12.1b Location of the position sensor
(grey connector) (A) and the speed sensor
(black connector) (B) on Motronic systems
(later models)12.1a Location of the position sensor (grey
connector) (A) and the speed sensor (black
connector) (B) on Motronic systems (early
models)
Page 119 of 228
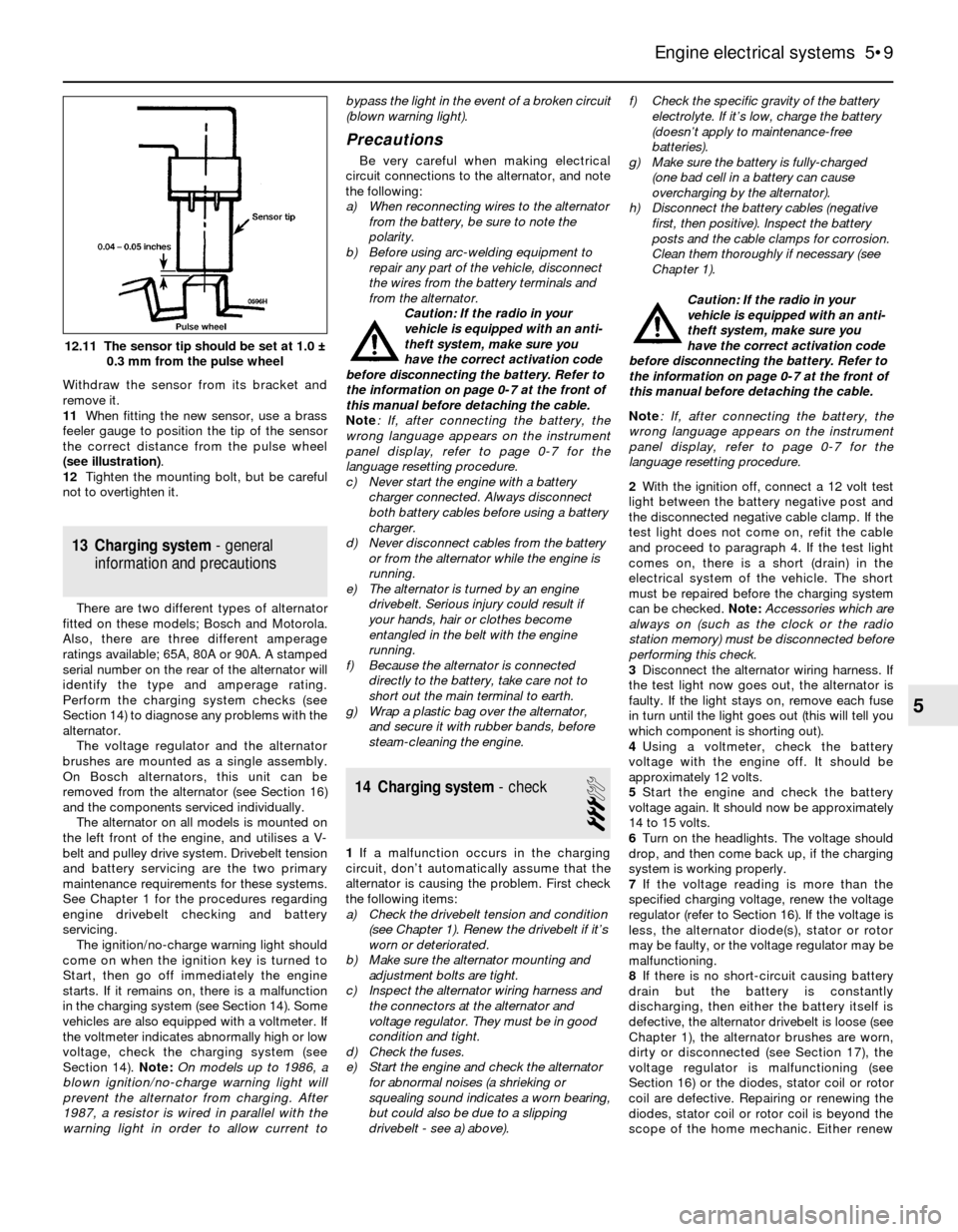
Withdraw the sensor from its bracket and
remove it.
11When fitting the new sensor, use a brass
feeler gauge to position the tip of the sensor
the correct distance from the pulse wheel
(see illustration).
12Tighten the mounting bolt, but be careful
not to overtighten it.
13 Charging system- general
information and precautions
There are two different types of alternator
fitted on these models; Bosch and Motorola.
Also, there are three different amperage
ratings available; 65A, 80A or 90A. A stamped
serial number on the rear of the alternator will
identify the type and amperage rating.
Perform the charging system checks (see
Section 14) to diagnose any problems with the
alternator.
The voltage regulator and the alternator
brushes are mounted as a single assembly.
On Bosch alternators, this unit can be
removed from the alternator (see Section 16)
and the components serviced individually.
The alternator on all models is mounted on
the left front of the engine, and utilises a V-
belt and pulley drive system. Drivebelt tension
and battery servicing are the two primary
maintenance requirements for these systems.
See Chapter 1 for the procedures regarding
engine drivebelt checking and battery
servicing.
The ignition/no-charge warning light should
come on when the ignition key is turned to
Start, then go off immediately the engine
starts. If it remains on, there is a malfunction
in the charging system (see Section 14). Some
vehicles are also equipped with a voltmeter. If
the voltmeter indicates abnormally high or low
voltage, check the charging system (see
Section 14). Note:On models up to 1986, a
blown ignition/no-charge warning light will
prevent the alternator from charging. After
1987, a resistor is wired in parallel with the
warning light in order to allow current tobypass the light in the event of a broken circuit
(blown warning light).
Precautions
Be very careful when making electrical
circuit connections to the alternator, and note
the following:
a) When reconnecting wires to the alternator
from the battery, be sure to note the
polarity.
b) Before using arc-welding equipment to
repair any part of the vehicle, disconnect
the wires from the battery terminals and
from the alternator.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
c) Never start the engine with a battery
charger connected. Always disconnect
both battery cables before using a battery
charger.
d) Never disconnect cables from the battery
or from the alternator while the engine is
running.
e) The alternator is turned by an engine
drivebelt. Serious injury could result if
your hands, hair or clothes become
entangled in the belt with the engine
running.
f) Because the alternator is connected
directly to the battery, take care not to
short out the main terminal to earth.
g) Wrap a plastic bag over the alternator,
and secure it with rubber bands, before
steam-cleaning the engine.
14 Charging system- check
3
1If a malfunction occurs in the charging
circuit, don’t automatically assume that the
alternator is causing the problem. First check
the following items:
a) Check the drivebelt tension and condition
(see Chapter 1). Renew the drivebelt if it’s
worn or deteriorated.
b) Make sure the alternator mounting and
adjustment bolts are tight.
c) Inspect the alternator wiring harness and
the connectors at the alternator and
voltage regulator. They must be in good
condition and tight.
d) Check the fuses.
e) Start the engine and check the alternator
for abnormal noises (a shrieking or
squealing sound indicates a worn bearing,
but could also be due to a slipping
drivebelt - see a) above).f) Check the specific gravity of the battery
electrolyte. If it’s low, charge the battery
(doesn’t apply to maintenance-free
batteries).
g) Make sure the battery is fully-charged
(one bad cell in a battery can cause
overcharging by the alternator).
h) Disconnect the battery cables (negative
first, then positive). Inspect the battery
posts and the cable clamps for corrosion.
Clean them thoroughly if necessary (see
Chapter 1).
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2With the ignition off, connect a 12 volt test
light between the battery negative post and
the disconnected negative cable clamp. If the
test light does not come on, refit the cable
and proceed to paragraph 4. If the test light
comes on, there is a short (drain) in the
electrical system of the vehicle. The short
must be repaired before the charging system
can be checked. Note: Accessories which are
always on (such as the clock or the radio
station memory) must be disconnected before
performing this check.
3Disconnect the alternator wiring harness. If
the test light now goes out, the alternator is
faulty. If the light stays on, remove each fuse
in turn until the light goes out (this will tell you
which component is shorting out).
4Using a voltmeter, check the battery
voltage with the engine off. It should be
approximately 12 volts.
5Start the engine and check the battery
voltage again. It should now be approximately
14 to 15 volts.
6Turn on the headlights. The voltage should
drop, and then come back up, if the charging
system is working properly.
7If the voltage reading is more than the
specified charging voltage, renew the voltage
regulator (refer to Section 16). If the voltage is
less, the alternator diode(s), stator or rotor
may be faulty, or the voltage regulator may be
malfunctioning.
8If there is no short-circuit causing battery
drain but the battery is constantly
discharging, then either the battery itself is
defective, the alternator drivebelt is loose (see
Chapter 1), the alternator brushes are worn,
dirty or disconnected (see Section 17), the
voltage regulator is malfunctioning (see
Section 16) or the diodes, stator coil or rotor
coil are defective. Repairing or renewing the
diodes, stator coil or rotor coil is beyond the
scope of the home mechanic. Either renew
Engine electrical systems 5•9
12.11 The sensor tip should be set at 1.0 ±
0.3 mm from the pulse wheel
5
Page 121 of 228
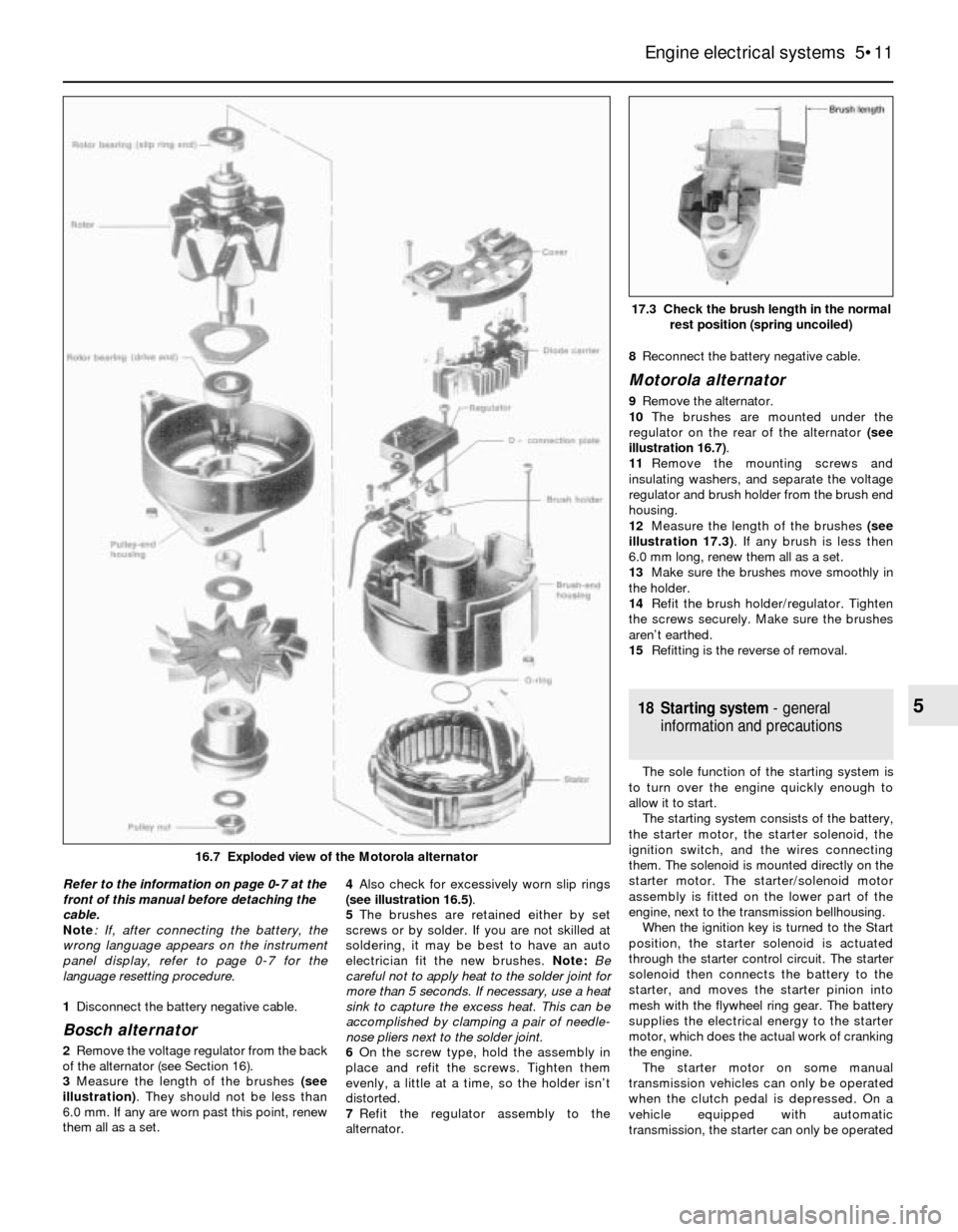
Refer to the information on page 0-7 at the
front of this manual before detaching the
cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Bosch alternator
2Remove the voltage regulator from the back
of the alternator (see Section 16).
3Measure the length of the brushes (see
illustration). They should not be less than
6.0 mm. If any are worn past this point, renew
them all as a set. 4Also check for excessively worn slip rings
(see illustration 16.5).
5The brushes are retained either by set
screws or by solder. If you are not skilled at
soldering, it may be best to have an auto
electrician fit the new brushes. Note: Be
careful not to apply heat to the solder joint for
more than 5 seconds. If necessary, use a heat
sink to capture the excess heat. This can be
accomplished by clamping a pair of needle-
nose pliers next to the solder joint.
6On the screw type, hold the assembly in
place and refit the screws. Tighten them
evenly, a little at a time, so the holder isn’t
distorted.
7Refit the regulator assembly to the
alternator.8Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Motorola alternator
9Remove the alternator.
10The brushes are mounted under the
regulator on the rear of the alternator (see
illustration 16.7).
11Remove the mounting screws and
insulating washers, and separate the voltage
regulator and brush holder from the brush end
housing.
12Measure the length of the brushes (see
illustration 17.3). If any brush is less then
6.0 mm long, renew them all as a set.
13Make sure the brushes move smoothly in
the holder.
14Refit the brush holder/regulator. Tighten
the screws securely. Make sure the brushes
aren’t earthed.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal.
18 Starting system- general
information and precautions
The sole function of the starting system is
to turn over the engine quickly enough to
allow it to start.
The starting system consists of the battery,
the starter motor, the starter solenoid, the
ignition switch, and the wires connecting
them. The solenoid is mounted directly on the
starter motor. The starter/solenoid motor
assembly is fitted on the lower part of the
engine, next to the transmission bellhousing.
When the ignition key is turned to the Start
position, the starter solenoid is actuated
through the starter control circuit. The starter
solenoid then connects the battery to the
starter, and moves the starter pinion into
mesh with the flywheel ring gear. The battery
supplies the electrical energy to the starter
motor, which does the actual work of cranking
the engine.
The starter motor on some manual
transmission vehicles can only be operated
when the clutch pedal is depressed. On a
vehicle equipped with automatic
transmission, the starter can only be operated
Engine electrical systems 5•11
17.3 Check the brush length in the normal
rest position (spring uncoiled)
5
16.7 Exploded view of the Motorola alternator
Page 122 of 228

when the transmission selector lever is in Park
or Neutral.
Always detach the battery negative cable
before working on the starting system.
19 Starter motor-
in-vehicle check
2
Note:Before diagnosing starter problems,
make sure the battery is fully charged.
1If the starter motor does not turn at all when
the switch is operated, make sure that the
gear lever is in Neutral or Park (automatic
transmission) or, where applicable, that the
clutch pedal is depressed (manual
transmission).
2Make sure that the battery is charged, and
that all cables, both at the battery and starter
solenoid terminals, are clean and secure.
3If the starter motor spins but the engine is
not cranking, the overrun clutch in the starter
motor is slipping, and the starter motor must
be renewed.
4If, when the switch is actuated, the starter
motor does not operate at all but the solenoid
clicks, then the problem lies either in the
battery, the main solenoid contacts, or the
starter motor itself (or the engine is seized).
5If the solenoid plunger cannot be heard
when the switch is actuated, the battery is
faulty, the switch is defective, the fusible link
is burned-out (the circuit is open), or the
solenoid itself is defective.
6To check the solenoid, connect a jumper
lead between the battery (+) and the ignition
switch wire terminal (the small terminal) on the
solenoid. If the starter motor now operates,
the solenoid is OK and the problem is in the
ignition switch, starter inhibitor switch
(automatic transmission models), clutch
switch (some manual transmission models), or
the wiring.
7If the starter motor still does not operate,
remove the starter/solenoid assembly for
dismantling, testing and repair.
8If the starter motor cranks the engine at an
abnormally-slow speed, first make sure that
the battery is charged, and that all terminal
connections are tight. If the engine is partially-
seized, or has the wrong viscosity oil in it, it
will crank slowly.
9Run the engine until normal operating
temperature is reached, then disconnect the
coil HT lead from the distributor cap and earth
it on the engine.
10Connect a voltmeter positive lead to the
battery positive post, and connect the
negative lead to the negative post.11Crank the engine, and take the voltmeter
readings as soon as a steady figure is
indicated. Do not allow the starter motor to
turn for more than 10 seconds at a time. A
reading of 9 volts or more, with the starter
motor turning at normal cranking speed, is
normal. If the reading is 9 volts or more but
the cranking speed is slow, the solenoid
contacts are burned, there is a bad
connection, or the starter motor itself is faulty.
If the reading is less than 9 volts and the
cranking speed is slow, the starter motor is
faulty or the battery is responsible (defective
or discharged).
20 Starter motor-
removal and refitting
1
Note:If the starter motor is defective, it should
be renewed, or taken to an auto electrical
specialist for repair. Overhaul of the starter
motor is unlikely to be a practical proposition
for the home mechanic, even if spare parts are
available. However, the solenoid can be
renewed separately (see Section 21).
Removal
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Detach the battery negative cable.
2Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Clearly label the wires from the terminals onthe starter motor and solenoid, then
disconnect them. Note: On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the air cleaner
(see Chapter 4), coolant expansion tank (see
Chapter 3) and the heater hoses to gain
access to the top of the starter. Carefully label
any hoses or components that need to be
removed from the engine compartment, to
avoid confusion when reassembling.
4Unscrew the mounting bolts and detach the
starter (see illustrations).
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
21 Starter solenoid-
removal and refitting
1
Removal
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the starter motor (see Section 20).
3Disconnect the cable from the solenoid to
the starter motor terminal.
4Remove the screws which secure the
solenoid to the starter motor.
5Detach the solenoid from the starter body.
6Remove the plunger and plunger spring.
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5•12 Engine electrical systems
20.4b Withdrawing the starter motor from
the M40 engine20.4a Working under the vehicle, remove
the starter lower mounting bolt and nut
(arrowed)
Page 124 of 228

4 Information sensors
2
Note:Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for additional
information on the location and diagnosis of
the information sensors that are not covered in
this Section.
Coolant temperature sensor
General description
1The coolant temperature sensor (see
illustration)is a thermistor (a resistor which
varies its resistance value in accordance with
temperature changes). The change in the
resistance value regulates the amount of
voltage that can pass through the sensor. At
low temperatures, the sensor’s resistance is
high. As the sensor temperature increases, its
resistance will decrease. Any failure in this
sensor circuit will in most cases be due to a
loose or shorted-out wire; if no wiring
problems are evident, check the sensor as
described below.
Check
2To check the sensor, first check its
resistance (see illustration)when it is
completely cold (typically 2100 to 2900 ohms).
Next, start the engine and warm it up until it
reaches operating temperature. The resistance
should be lower (typically 270 to 400 ohms).
Note: If restricted access to the coolant
temperature sensor makes it difficult to attach
electrical probes to the terminals, remove the
sensor as described below, and perform the
tests in a container of heated water to simulate
the conditions.
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.
Renewal
3To remove the sensor, depress the spring
lock, unplug the electrical connector, then
carefully unscrew the sensor. Be prepared for
some coolant spillage; to reduce this, have
the new sensor ready for fitting as quickly as
possible.Caution: Handle the coolant
sensor with care. Damage to this
sensor will affect the operation of
the entire fuel injection system.
Note: It may be necessary to drain a small
amount of coolant from the radiator before
removing the sensor.
4Before the sensor is fitted, ensure its
threads are clean, and apply a little sealant to
them.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Oxygen sensor
General description
Note:Oxygen sensors are normally only fitted
to those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter. Most oxygen sensors are located in
the exhaust pipe, downstream from the
exhaust manifold. On 535 models, the oxygen
sensor is mounted in the catalytic converter.
The sensor’s electrical connector is located
near the bulkhead (left side) for easy access.
6The oxygen sensor, which is located in the
exhaust system (see illustration), monitors
the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The
oxygen content in the exhaust reacts with the
oxygen sensor, to produce a voltage output
which varies from 0.1 volts (high oxygen, lean
mixture) to 0.9 volts (low oxygen, rich
mixture). The ECU constantly monitors this
variable voltage output to determine the ratio
of oxygen to fuel in the mixture. The ECU
alters the air/fuel mixture ratio by controlling
the pulse width (open time) of the fuel
injectors. A mixture ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1
part fuel is the ideal mixture ratio for
minimising exhaust emissions, thus allowing
the catalytic converter to operate at maximum
efficiency. It is this ratio of 14.7 to 1 which the
ECU and the oxygen sensor attempt to
maintain at all times.
7The oxygen sensor produces no voltage
when it is below its normal operating
temperature of about 320º C. During this initial
period before warm-up, the ECU operates in
“open-loop” mode (ie without the information
from the sensor).
8If the engine reaches normal operating
temperature and/or has been running for two
or more minutes, and if the oxygen sensor is
producing a steady signal voltage below 0.45 volts at 1500 rpm or greater, the ECU
fault code memory will be activated.
9When there is a problem with the oxygen
sensor or its circuit, the ECU operates in the
“open-loop” mode - that is, it controls fuel
delivery in accordance with a programmed
default value instead of with feedback
information from the oxygen sensor.
10The proper operation of the oxygen
sensor depends on four conditions:
a) Electrical - The low voltages generated by
the sensor depend upon good, clean
connections, which should be checked
whenever a malfunction of the sensor is
suspected or indicated.
b) Outside air supply - The sensor is
designed to allow air circulation to the
internal portion of the sensor. Whenever
the sensor is disturbed, make sure the air
passages are not restricted.
c) Proper operating temperature - The ECU
will not react to the sensor signal until the
sensor reaches approximately 320º C.
This factor must be taken into
consideration when evaluating the
performance of the sensor.
d) Unleaded fuel - The use of unleaded fuel
is essential for proper operation of the
sensor. Make sure the fuel you are using
is of this type.
11In addition to observing the above
conditions, special care must be taken
whenever the sensor is serviced.
a) The oxygen sensor has a permanently-
attached pigtail and electrical connector,
which should not be removed from the
sensor. Damage or removal of the pigtail
or electrical connector can adversely
affect operation of the sensor.
b) Grease, dirt and other contaminants
should be kept away from the electrical
connector and the louvered end of the
sensor.
c) Do not use cleaning solvents of any kind
on the oxygen sensor.
d) Do not drop or roughly handle the sensor.
e) The silicone boot must be fitted in the
correct position, to prevent the boot from
being melted and to allow the sensor to
operate properly.
6•2 Engine management and emission control systems
4.6 The oxygen sensor (arrowed) is usually
located in the exhaust pipe, downstream
from the exhaust manifold4.2 Check the resistance of the coolant
temperature sensor at different
temperatures4.1 The coolant temperature sensor
(arrowed) is usually located next to the
temperature sender unit, near the fuel
pressure regulator
Page 125 of 228
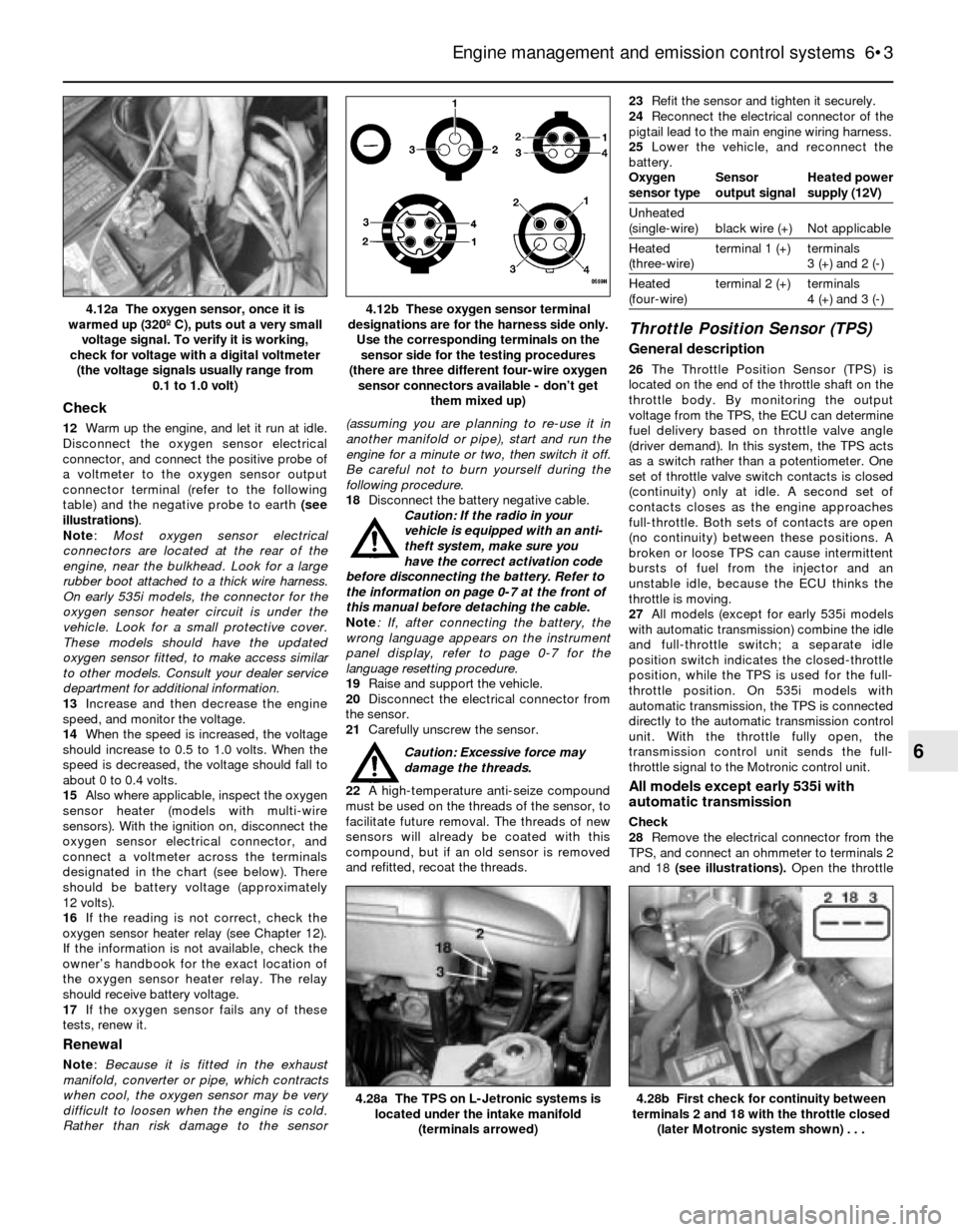
Check
12Warm up the engine, and let it run at idle.
Disconnect the oxygen sensor electrical
connector, and connect the positive probe of
a voltmeter to the oxygen sensor output
connector terminal (refer to the following
table) and the negative probe to earth (see
illustrations).
Note:Most oxygen sensor electrical
connectors are located at the rear of the
engine, near the bulkhead. Look for a large
rubber boot attached to a thick wire harness.
On early 535i models, the connector for the
oxygen sensor heater circuit is under the
vehicle. Look for a small protective cover.
These models should have the updated
oxygen sensor fitted, to make access similar
to other models. Consult your dealer service
department for additional information.
13Increase and then decrease the engine
speed, and monitor the voltage.
14When the speed is increased, the voltage
should increase to 0.5 to 1.0 volts. When the
speed is decreased, the voltage should fall to
about 0 to 0.4 volts.
15Also where applicable, inspect the oxygen
sensor heater (models with multi-wire
sensors). With the ignition on, disconnect the
oxygen sensor electrical connector, and
connect a voltmeter across the terminals
designated in the chart (see below). There
should be battery voltage (approximately
12 volts).
16If the reading is not correct, check the
oxygen sensor heater relay (see Chapter 12).
If the information is not available, check the
owner’s handbook for the exact location of
the oxygen sensor heater relay. The relay
should receive battery voltage.
17If the oxygen sensor fails any of these
tests, renew it.
Renewal
Note: Because it is fitted in the exhaust
manifold, converter or pipe, which contracts
when cool, the oxygen sensor may be very
difficult to loosen when the engine is cold.
Rather than risk damage to the sensor(assuming you are planning to re-use it in
another manifold or pipe), start and run the
engine for a minute or two, then switch it off.
Be careful not to burn yourself during the
following procedure.
18Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
19Raise and support the vehicle.
20Disconnect the electrical connector from
the sensor.
21Carefully unscrew the sensor.
Caution: Excessive force may
damage the threads.
22A high-temperature anti-seize compound
must be used on the threads of the sensor, to
facilitate future removal. The threads of new
sensors will already be coated with this
compound, but if an old sensor is removed
and refitted, recoat the threads.23Refit the sensor and tighten it securely.
24Reconnect the electrical connector of the
pigtail lead to the main engine wiring harness.
25Lower the vehicle, and reconnect the
battery.
Oxygen Sensor Heated power
sensor type output signal supply (12V)
Unheated
(single-wire) black wire (+) Not applicable
Heated terminal 1 (+) terminals
(three-wire) 3 (+) and 2 (-)
Heated terminal 2 (+) terminals
(four-wire) 4 (+) and 3 (-)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
General description
26The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is
located on the end of the throttle shaft on the
throttle body. By monitoring the output
voltage from the TPS, the ECU can determine
fuel delivery based on throttle valve angle
(driver demand). In this system, the TPS acts
as a switch rather than a potentiometer. One
set of throttle valve switch contacts is closed
(continuity) only at idle. A second set of
contacts closes as the engine approaches
full-throttle. Both sets of contacts are open
(no continuity) between these positions. A
broken or loose TPS can cause intermittent
bursts of fuel from the injector and an
unstable idle, because the ECU thinks the
throttle is moving.
27All models (except for early 535i models
with automatic transmission) combine the idle
and full-throttle switch; a separate idle
position switch indicates the closed-throttle
position, while the TPS is used for the full-
throttle position. On 535i models with
automatic transmission, the TPS is connected
directly to the automatic transmission control
unit. With the throttle fully open, the
transmission control unit sends the full-
throttle signal to the Motronic control unit.
All models except early 535i with
automatic transmission
Check
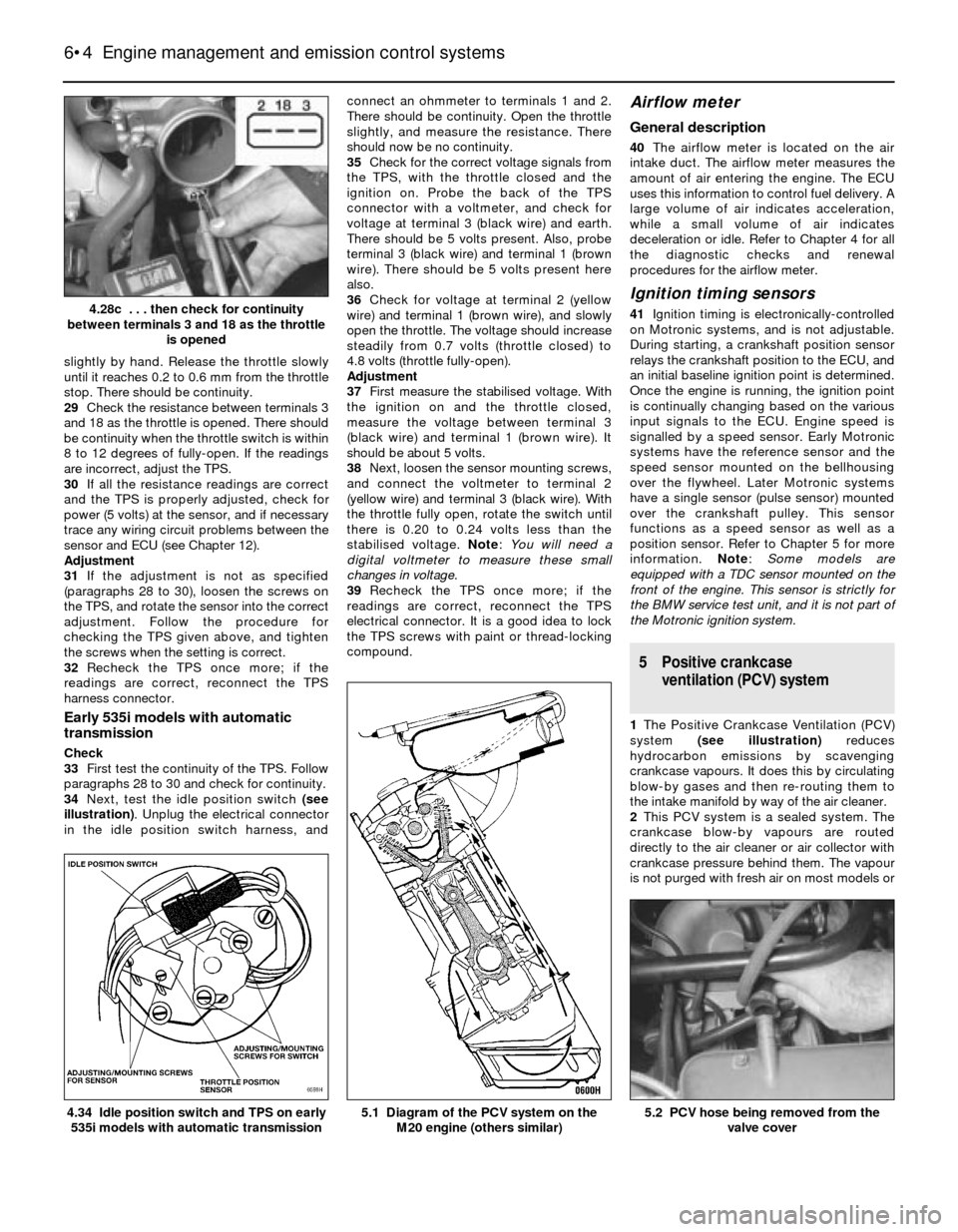
28Remove the electrical connector from the
TPS, and connect an ohmmeter to terminals 2
and 18 (see illustrations). Open the throttle
Engine management and emission control systems 6•3
4.12b These oxygen sensor terminal
designations are for the harness side only.
Use the corresponding terminals on the
sensor side for the testing procedures
(there are three different four-wire oxygen
sensor connectors available - don’t get
them mixed up)4.12a The oxygen sensor, once it is
warmed up (320º C), puts out a very small
voltage signal. To verify it is working,
check for voltage with a digital voltmeter
(the voltage signals usually range from
0.1 to 1.0 volt)
4.28b First check for continuity between
terminals 2 and 18 with the throttle closed
(later Motronic system shown) . . .4.28a The TPS on L-Jetronic systems is
located under the intake manifold
(terminals arrowed)
6
Page 126 of 228
slightly by hand. Release the throttle slowly
until it reaches 0.2 to 0.6 mm from the throttle
stop. There should be continuity.
29Check the resistance between terminals 3
and 18 as the throttle is opened. There should
be continuity when the throttle switch is within
8 to 12 degrees of fully-open. If the readings
are incorrect, adjust the TPS.
30If all the resistance readings are correct
and the TPS is properly adjusted, check for
power (5 volts) at the sensor, and if necessary
trace any wiring circuit problems between the
sensor and ECU (see Chapter 12).
Adjustment
31If the adjustment is not as specified
(paragraphs 28 to 30), loosen the screws on
the TPS, and rotate the sensor into the correct
adjustment. Follow the procedure for
checking the TPS given above, and tighten
the screws when the setting is correct.
32Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
harness connector.
Early 535i models with automatic
transmission
Check
33First test the continuity of the TPS. Follow
paragraphs 28 to 30 and check for continuity.
34Next, test the idle position switch (see
illustration). Unplug the electrical connector
in the idle position switch harness, andconnect an ohmmeter to terminals 1 and 2.
There should be continuity. Open the throttle
slightly, and measure the resistance. There
should now be no continuity.
35Check for the correct voltage signals from
the TPS, with the throttle closed and the
ignition on. Probe the back of the TPS
connector with a voltmeter, and check for
voltage at terminal 3 (black wire) and earth.
There should be 5 volts present. Also, probe
terminal 3 (black wire) and terminal 1 (brown
wire). There should be 5 volts present here
also.
36Check for voltage at terminal 2 (yellow
wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire), and slowly
open the throttle. The voltage should increase
steadily from 0.7 volts (throttle closed) to
4.8 volts (throttle fully-open).
Adjustment
37First measure the stabilised voltage. With
the ignition on and the throttle closed,
measure the voltage between terminal 3
(black wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire). It
should be about 5 volts.
38Next, loosen the sensor mounting screws,
and connect the voltmeter to terminal 2
(yellow wire) and terminal 3 (black wire). With
the throttle fully open, rotate the switch until
there is 0.20 to 0.24 volts less than the
stabilised voltage. Note: You will need a
digital voltmeter to measure these small
changes in voltage.
39Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
electrical connector. It is a good idea to lock
the TPS screws with paint or thread-locking
compound.
Airflow meter
General description
40The airflow meter is located on the air
intake duct. The airflow meter measures the
amount of air entering the engine. The ECU
uses this information to control fuel delivery. A
large volume of air indicates acceleration,
while a small volume of air indicates
deceleration or idle. Refer to Chapter 4 for all
the diagnostic checks and renewal
procedures for the airflow meter.
Ignition timing sensors
41Ignition timing is electronically-controlled
on Motronic systems, and is not adjustable.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
relays the crankshaft position to the ECU, and
an initial baseline ignition point is determined.
Once the engine is running, the ignition point
is continually changing based on the various
input signals to the ECU. Engine speed is
signalled by a speed sensor. Early Motronic
systems have the reference sensor and the
speed sensor mounted on the bellhousing
over the flywheel. Later Motronic systems
have a single sensor (pulse sensor) mounted
over the crankshaft pulley. This sensor
functions as a speed sensor as well as a
position sensor. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. Note: Some models are
equipped with a TDC sensor mounted on the
front of the engine. This sensor is strictly for
the BMW service test unit, and it is not part of
the Motronic ignition system.
5 Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) system
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system (see illustration)reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
blow-by gases and then re-routing them to
the intake manifold by way of the air cleaner.
2This PCV system is a sealed system. The
crankcase blow-by vapours are routed
directly to the air cleaner or air collector with
crankcase pressure behind them. The vapour
is not purged with fresh air on most models or
6•4 Engine management and emission control systems
5.2 PCV hose being removed from the
valve cover5.1 Diagram of the PCV system on the
M20 engine (others similar)4.34 Idle position switch and TPS on early
535i models with automatic transmission
4.28c . . . then check for continuity
between terminals 3 and 18 as the throttle
is opened
Page 127 of 228
filtered with a flame trap like most
conventional systems. There are no
conventional PCV valves fitted on these
systems - just a hose (see illustration).
3The main components of the PCV system
are the hoses that connect the valve cover to
the throttle body or air cleaner. If abnormal
operating conditions (such as piston ring
problems) arise, the system is designed to
allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to
flow back through the crankcase vent tube
into the intake system, to be consumed by
normal combustion. Note: Since these
models don’t use a filtering element, it’s a
good idea to check the PCV system
passageways for clogging from sludge and
combustion residue(see illustration).
6 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system
2
General description
Note:This system is normally only fitted to
those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter.
1When the engine isn’t running, the fuel in the
fuel tank evaporates to some extent, creating
fuel vapour. The evaporative emissions control
system (see illustration)stores these fuel
vapours in a charcoal canister. When the
engine is cruising, the purge control valve is
opened slightly, and a small amount of fuel
vapour is drawn into the intake manifold and
burned. When the engine is starting cold or
idling, the purge valve prevents any vapours
from entering the intake manifold and causing
excessively-rich fuel mixture.
2Two types of purge valve are used;
electrically-operated or vacuum-operated. To
find out which type is on your vehicle, follow
the hose from the charcoal canister until you
locate the purge valve. Some are located on
the intake manifold, and others near the
charcoal canister. Look for either an electrical
connector, or vacuum lines, to the purge
valve.3A faulty EVAP system will only affect engine
driveability when the engine is warm. The
EVAP system is not usually the cause of
difficult cold starting or any other cold-running
problems.
Check
Vacuum-operated purge valve
4Remove the vacuum lines from the purge
valve, and blow into the larger valve port. It
should be closed, and not pass any air. Note:
Some models have a thermo-vacuum valve
that delays canister purging until the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 46º C.
Check this valve to make sure that vacuum is
controlled at the proper temperatures. The
valve is usually located in the intake manifold,
near the thermo-time switch and the coolant
temperature sensor.
5Disconnect the small vacuum hose from the
purge valve, and apply vacuum with a hand-
held vacuum pump. The purge valve should
be open, and air should be able to pass
through.6If the test results are unsatisfactory, renew
the purge valve.
Electrically-operated purge valve
7Disconnect any lines from the purge valve,
and (without disconnecting the electrical
connector) place it in a convenient spot for
testing.
8Check that the valve makes a “click” sound
as the ignition is switched on (see
illustration).
9If the valve does not “click”, disconnect the
valve connector, and check for power to the
valve using a test light or a voltmeter (see
illustration).
10If battery voltage is present, but the valve
does not work, renew it. If there is no voltage
present, check the Motronic control unit and
the wiring.
Canister
11Mark all the hoses for position, then
detach them from the canister.
12Slide the canister out of its mounting clip.
Engine management and emission control systems 6•5
6.1 Diagram of the EVAP system on the M10 engine (others similar)
6.9 Check for battery voltage at the
electrical connector to the purge valve6.8 When the ignition is switched on, there
should be a distinct “click” from the purge
valve
6
5.3 It’s a good idea to check for excess
residue from the crankcase vapours
circulating in the hoses and ports - this
can eventually clog the system, and cause
a pressure increase in the engine block