air condition BMW 3 SERIES 1987 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1987, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1987 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 28 of 228
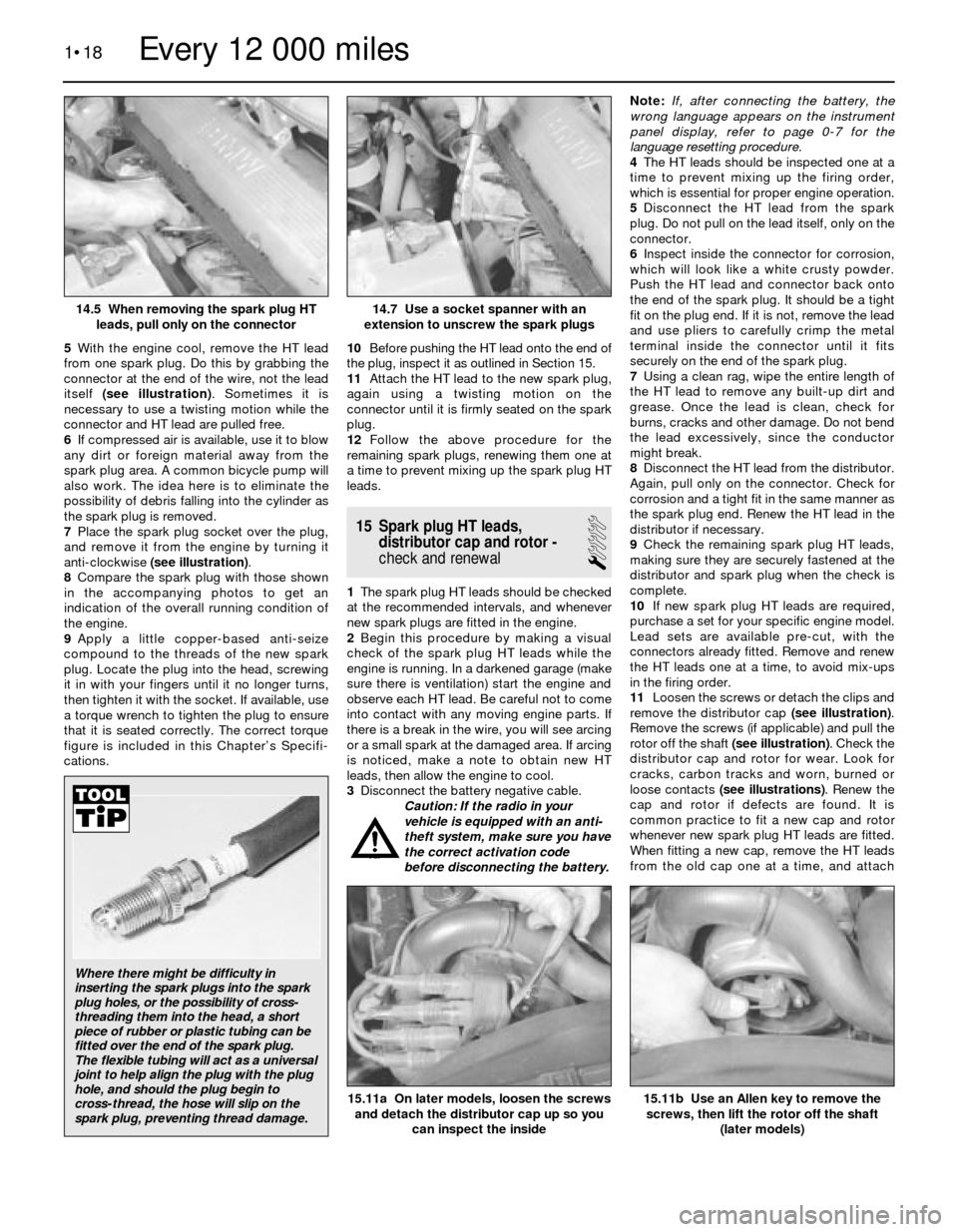
5With the engine cool, remove the HT lead
from one spark plug. Do this by grabbing the
connector at the end of the wire, not the lead
itself (see illustration). Sometimes it is
necessary to use a twisting motion while the
connector and HT lead are pulled free.
6If compressed air is available, use it to blow
any dirt or foreign material away from the
spark plug area. A common bicycle pump will
also work. The idea here is to eliminate the
possibility of debris falling into the cylinder as
the spark plug is removed.
7Place the spark plug socket over the plug,
and remove it from the engine by turning it
anti-clockwise (see illustration).
8Compare the spark plug with those shown
in the accompanying photos to get an
indication of the overall running condition of
the engine.
9Apply a little copper-based anti-seize
compound to the threads of the new spark
plug. Locate the plug into the head, screwing
it in with your fingers until it no longer turns,
then tighten it with the socket. If available, use
a torque wrench to tighten the plug to ensure
that it is seated correctly. The correct torque
figure is included in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.10Before pushing the HT lead onto the end of
the plug, inspect it as outlined in Section 15.
11Attach the HT lead to the new spark plug,
again using a twisting motion on the
connector until it is firmly seated on the spark
plug.
12Follow the above procedure for the
remaining spark plugs, renewing them one at
a time to prevent mixing up the spark plug HT
leads.
15 Spark plug HT leads,
distributor cap and rotor -
check and renewal
1
1The spark plug HT leads should be checked
at the recommended intervals, and whenever
new spark plugs are fitted in the engine.
2Begin this procedure by making a visual
check of the spark plug HT leads while the
engine is running. In a darkened garage (make
sure there is ventilation) start the engine and
observe each HT lead. Be careful not to come
into contact with any moving engine parts. If
there is a break in the wire, you will see arcing
or a small spark at the damaged area. If arcing
is noticed, make a note to obtain new HT
leads, then allow the engine to cool.
3Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
4The HT leads should be inspected one at a
time to prevent mixing up the firing order,
which is essential for proper engine operation.
5Disconnect the HT lead from the spark
plug. Do not pull on the lead itself, only on the
connector.
6Inspect inside the connector for corrosion,
which will look like a white crusty powder.
Push the HT lead and connector back onto
the end of the spark plug. It should be a tight
fit on the plug end. If it is not, remove the lead
and use pliers to carefully crimp the metal
terminal inside the connector until it fits
securely on the end of the spark plug.
7Using a clean rag, wipe the entire length of
the HT lead to remove any built-up dirt and
grease. Once the lead is clean, check for
burns, cracks and other damage. Do not bend
the lead excessively, since the conductor
might break.
8Disconnect the HT lead from the distributor.
Again, pull only on the connector. Check for
corrosion and a tight fit in the same manner as
the spark plug end. Renew the HT lead in the
distributor if necessary.
9Check the remaining spark plug HT leads,
making sure they are securely fastened at the
distributor and spark plug when the check is
complete.
10If new spark plug HT leads are required,
purchase a set for your specific engine model.
Lead sets are available pre-cut, with the
connectors already fitted. Remove and renew
the HT leads one at a time, to avoid mix-ups
in the firing order.
11Loosen the screws or detach the clips and
remove the distributor cap (see illustration).
Remove the screws (if applicable) and pull the
rotor off the shaft (see illustration). Check the
distributor cap and rotor for wear. Look for
cracks, carbon tracks and worn, burned or
loose contacts (see illustrations). Renew the
cap and rotor if defects are found. It is
common practice to fit a new cap and rotor
whenever new spark plug HT leads are fitted.
When fitting a new cap, remove the HT leads
from the old cap one at a time, and attach
1•18
15.11b Use an Allen key to remove the
screws, then lift the rotor off the shaft
(later models)15.11a On later models, loosen the screws
and detach the distributor cap up so you
can inspect the inside
14.7 Use a socket spanner with an
extension to unscrew the spark plugs14.5 When removing the spark plug HT
leads, pull only on the connector
Every 12 000 miles
Where there might be difficulty in
inserting the spark plugs into the spark
plug holes, or the possibility of cross-
threading them into the head, a short
piece of rubber or plastic tubing can be
fitted over the end of the spark plug.
The flexible tubing will act as a universal
joint to help align the plug with the plug
hole, and should the plug begin to
cross-thread, the hose will slip on the
spark plug, preventing thread damage.
Page 29 of 228
them to the new cap in the exact same
location - do not simultaneously remove all
the HT leads, or firing order mix-ups may
occur.
16 Manual transmission
lubricant level check
1
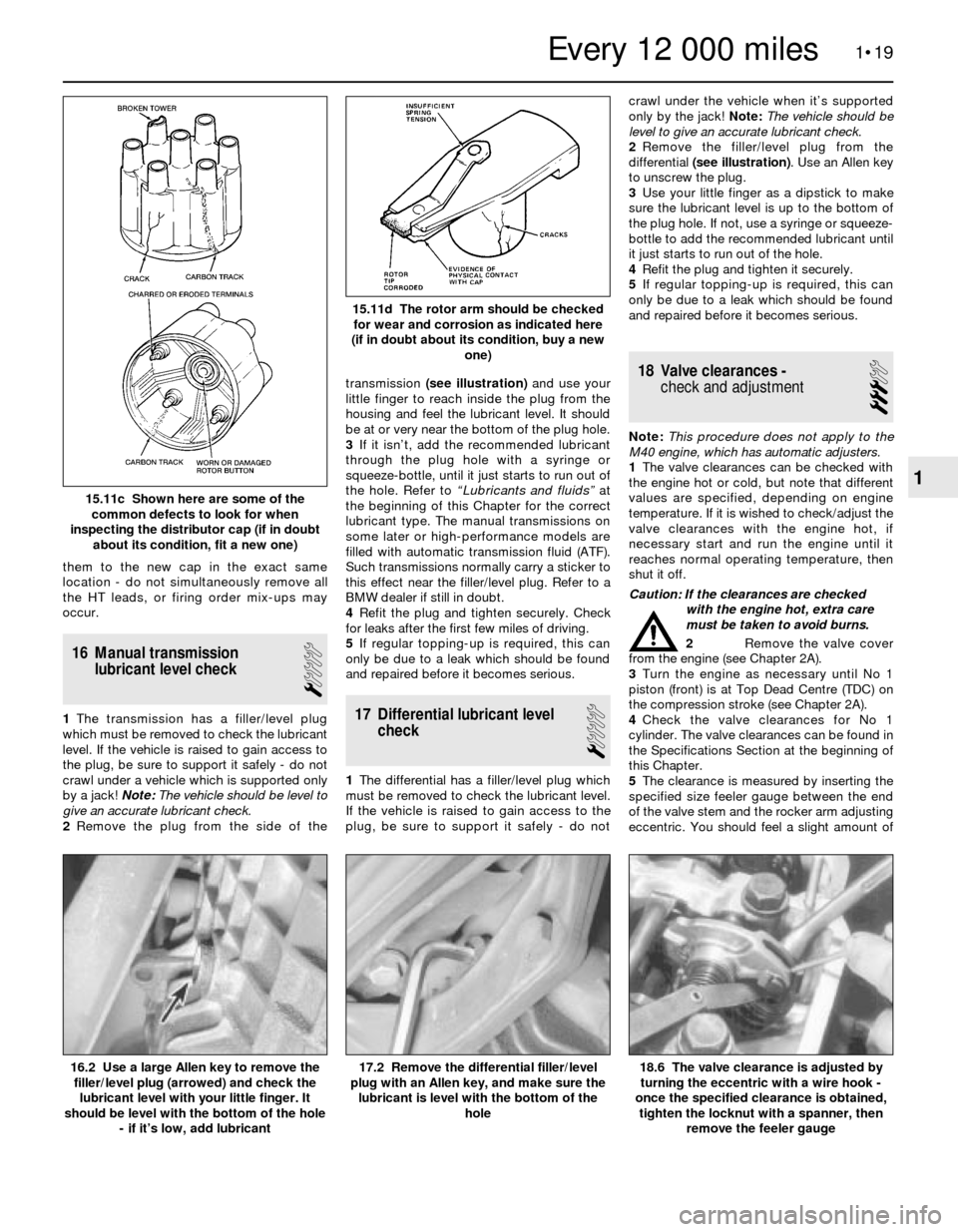
1The transmission has a filler/level plug
which must be removed to check the lubricant
level. If the vehicle is raised to gain access to
the plug, be sure to support it safely - do not
crawl under a vehicle which is supported only
by a jack!Note:The vehicle should be level to
give an accurate lubricant check.
2Remove the plug from the side of thetransmission (see illustration)and use your
little finger to reach inside the plug from the
housing and feel the lubricant level. It should
be at or very near the bottom of the plug hole.
3If it isn’t, add the recommended lubricant
through the plug hole with a syringe or
squeeze-bottle, until it just starts to run out of
the hole. Refer to “Lubricants and fluids” at
the beginning of this Chapter for the correct
lubricant type. The manual transmissions on
some later or high-performance models are
filled with automatic transmission fluid (ATF).
Such transmissions normally carry a sticker to
this effect near the filler/level plug. Refer to a
BMW dealer if still in doubt.
4Refit the plug and tighten securely. Check
for leaks after the first few miles of driving.
5If regular topping-up is required, this can
only be due to a leak which should be found
and repaired before it becomes serious.17 Differential lubricant level
check
1
1The differential has a filler/level plug which
must be removed to check the lubricant level.
If the vehicle is raised to gain access to the
plug, be sure to support it safely - do notcrawl under the vehicle when it’s supported
only by the jack! Note:The vehicle should be
level to give an accurate lubricant check.
2Remove the filler/level plug from the
differential (see illustration). Use an Allen key
to unscrew the plug.
3Use your little finger as a dipstick to make
sure the lubricant level is up to the bottom of
the plug hole. If not, use a syringe or squeeze-
bottle to add the recommended lubricant until
it just starts to run out of the hole.
4Refit the plug and tighten it securely.
5If regular topping-up is required, this can
only be due to a leak which should be found
and repaired before it becomes serious.
18 Valve clearances -
check and adjustment
3
Note:This procedure does not apply to the
M40 engine, which has automatic adjusters.
1The valve clearances can be checked with
the engine hot or cold, but note that different
values are specified, depending on engine
temperature. If it is wished to check/adjust the
valve clearances with the engine hot, if
necessary start and run the engine until it
reaches normal operating temperature, then
shut it off.
Caution: If the clearances are checked
with the engine hot, extra care
must be taken to avoid burns.
2Remove the valve cover
from the engine (see Chapter 2A).
3Turn the engine as necessary until No 1
piston (front) is at Top Dead Centre (TDC) on
the compression stroke (see Chapter 2A).
4Check the valve clearances for No 1
cylinder. The valve clearances can be found in
the Specifications Section at the beginning of
this Chapter.
5The clearance is measured by inserting the
specified size feeler gauge between the end
of the valve stem and the rocker arm adjusting
eccentric. You should feel a slight amount of
1•19
15.11d The rotor arm should be checked
for wear and corrosion as indicated here
(if in doubt about its condition, buy a new
one)
15.11c Shown here are some of the
common defects to look for when
inspecting the distributor cap (if in doubt
about its condition, fit a new one)
18.6 The valve clearance is adjusted by
turning the eccentric with a wire hook -
once the specified clearance is obtained,
tighten the locknut with a spanner, then
remove the feeler gauge17.2 Remove the differential filler/level
plug with an Allen key, and make sure the
lubricant is level with the bottom of the
hole16.2 Use a large Allen key to remove the
filler/level plug (arrowed) and check the
lubricant level with your little finger. It
should be level with the bottom of the hole
- if it’s low, add lubricant
1
Every 12 000 miles
Page 31 of 228

4Since some components of the fuel system
- the fuel tank and some of the fuel feed and
return lines, for example - are underneath the
vehicle, they can be inspected more easily
with the vehicle raised on a hoist. If that’s not
possible, raise the vehicle and support it on
axle stands or ramps.
5With the vehicle raised and safely
supported, inspect the fuel tank and filler neck
for punctures, cracks or other damage. The
connection between the filler neck and the
tank is particularly critical. Sometimes a
rubber filler neck will leak because of loose
clamps or deteriorated rubber. Inspect all fuel
tank mounting brackets and straps, to be sure
the tank is securely attached to the vehicle.
Warning: Do not, under any
circumstances, try to repair a fuel
tank (except rubber
components). A welding torch or
any naked flame can easily cause fuel
vapours inside the tank to explode.
6Carefully check all flexible hoses and metal
lines leading away from the fuel tank. Check
for loose connections, deteriorated hoses,
crimped lines, and other damage. Repair or
renew damaged sections as necessary (see
Chapter 4).
22 Cooling system check
1
1Many major engine failures can be
attributed to cooling system problems. If the
vehicle has automatic transmission, the
engine cooling system also plays an importantrole in prolonging transmission life, because it
cools the transmission fluid.
2The engine should be cold for the cooling
system check, so perform the following
procedure before the vehicle is driven for the
day, or after it has been switched off for at
leastthree hours.
3Remove the radiator cap, doing so slowly
and taking adequate precautions against
scalding if the engine is at all warm. Clean the
cap thoroughly, inside and out, with clean
water. Also clean the filler neck on the
radiator. The presence of rust or corrosion in
the filler neck means the coolant should be
changed (see Section 29). The coolant inside
the radiator should be relatively clean and
clear. If it’s rust-coloured, drain the system
and refill with new coolant.
4Carefully check the radiator hoses and the
smaller-diameter heater hoses. Inspect each
coolant hose along its entire length, renewing
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated (see illustration). Cracks will
show up better if the hose is squeezed. Pay
close attention to hose clamps that secure the
hoses to cooling system components. Hose
clamps can pinch and puncture hoses,
resulting in coolant leaks.
5Make sure all hose connections are tight. A
leak in the cooling system will usually show up
as white or rust-coloured deposits on the area
adjoining the leak. If wire-type clamps are
used on the hoses, it may be a good idea to
replace them with screw-type clamps.
6Clean the front of the radiator (and, where
applicable, the air conditioning condenser)
with compressed air if available, or a soft
brush. Remove all flies, leaves, etc,
embedded in the radiator fins. Be extremely
careful not to damage the cooling fins or to
cut your fingers on them.
7If the coolant level has been dropping
consistently and no leaks are detected, have
the radiator cap and cooling system pressure-
tested.
23 Exhaust system check
1
1The engine should be cold for this check,
so perform the following procedure before the
vehicle is driven for the day, or after it has
been switched off for at leastthree hours.
Check the complete exhaust system from the
engine to the end of the tailpipe. Ideally, the
inspection should be done with the vehicle on
a hoist, to give unrestricted access. If a hoist
isn’t available, raise the vehicle and support it
securely on axle stands or ramps.
2Check the exhaust pipes and connections
for evidence of leaks, severe corrosion, and
damage. Make sure that all brackets and
mountings are in good condition, and that
they are tight (see illustration).
3At the same time, inspect the underside of
the body for holes, corrosion, open seams,etc. which may allow exhaust gases to enter
the passenger compartment. Seal all body
openings with suitable sealant.
4Rattles and other noises can often be
traced to the exhaust system, especially the
mountings and heat shields. Try to move the
pipes, silencers (and, where applicable, the
catalytic converter). If the components can
come in contact with the body or suspension
parts, re-hang the exhaust system with new
mountings.
5The running condition of the engine may be
checked by inspecting inside the end of the
tailpipe. The exhaust deposits here are an
indication of the engine’s state of tune. If the
pipe is black and sooty, the engine may be
running too rich, indicating the need for a
thorough fuel system inspection.
24 Steering and suspension
check
1
Note: The steering linkage and suspension
components should be checked periodically.
Worn or damaged suspension and steering
linkage components can result in excessive
and abnormal tyre wear, poor ride quality and
vehicle handling, and reduced fuel economy.
For detailed illustrations of the steering and
suspension components, refer to Chapter 10.
Strut/shock absorber check
1Park the vehicle on level ground, turn the
engine off and apply the handbrake. Check
the tyre pressures.
2Push down at one corner of the vehicle,
then release it while noting the movement of
the body. It should stop moving and come to
rest in a level position with one or two
bounces.
3If the vehicle continues to move up and
down, or if it fails to return to its original
position, a worn or weak strut or shock
absorber is probably the reason.
4Repeat the above check at each of the
three remaining corners of the vehicle.
5Raise the vehicle and support it on axle
stands.
6Check the struts/shock absorbers for
evidence of fluid leakage. A light film of fluid is
1•21
22.4 Hoses, like drivebelts, have a habit of
failing at the worst possible time - to
prevent the inconvenience of a blown
radiator or heater hose, inspect them
carefully as shown here
23.2 Check the exhaust system rubber
mountings for cracks
1
Every 12 000 miles
Page 32 of 228
no cause for concern. Make sure that any fluid
noted is from the struts/shocks, and not from
any other source. If leakage is noted, renew
the struts or shock absorbers in axle pairs (or
as a full set).
7Check the struts/shock absorbers to be
sure that they are securely mounted and
undamaged. Check the upper mountings for
damage and wear. If damage or wear is
noted, renew the struts or shock absorbers.
8If the struts or shock absorbers must be
renewed, refer to Chapter 10 for the
procedure. Always renew both units on the
same axle, or the safety of the vehicle may be
compromised. If possible, renew all four as a
set.
Steering and suspension check
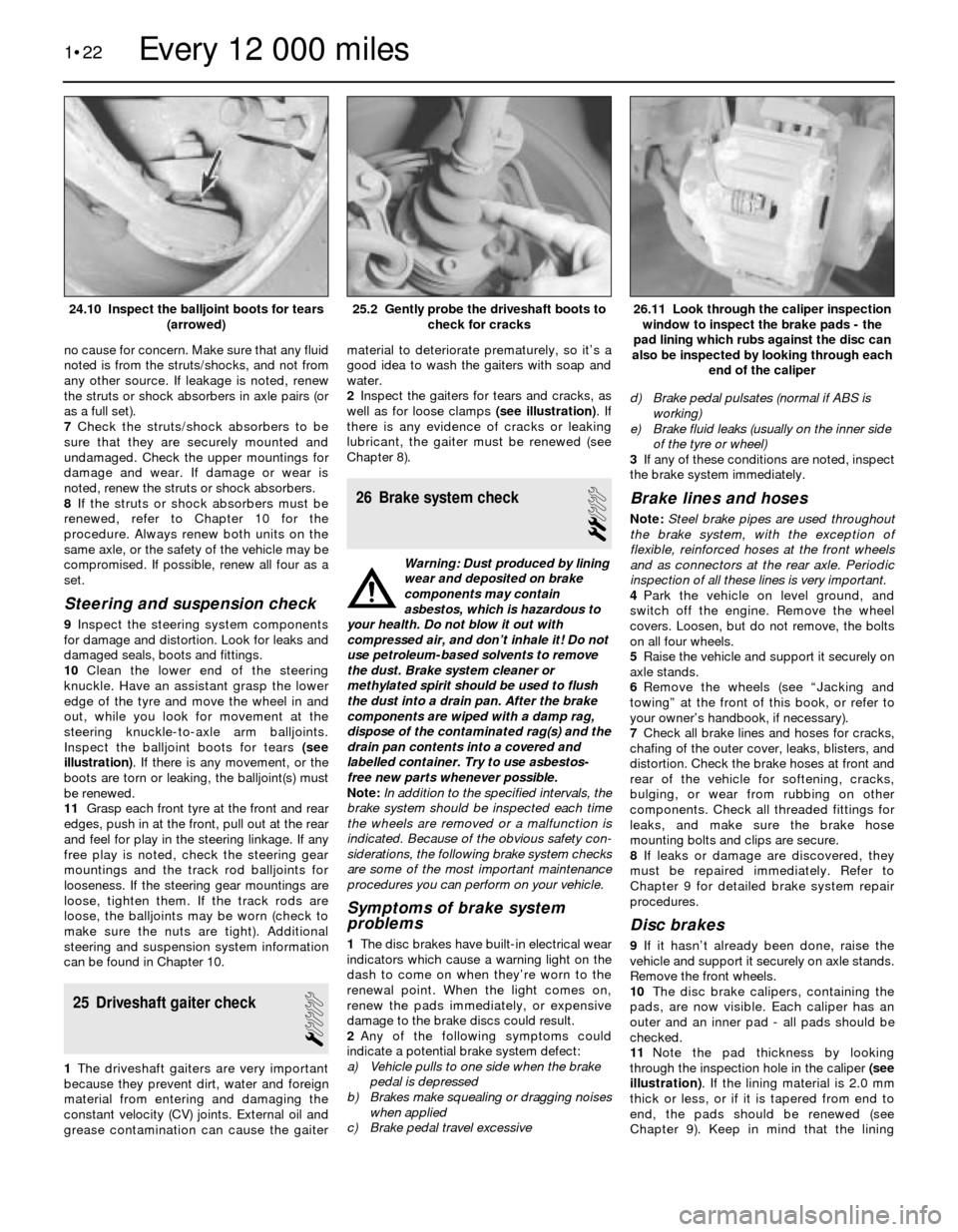
9Inspect the steering system components
for damage and distortion. Look for leaks and
damaged seals, boots and fittings.
10Clean the lower end of the steering
knuckle. Have an assistant grasp the lower
edge of the tyre and move the wheel in and
out, while you look for movement at the
steering knuckle-to-axle arm balljoints.
Inspect the balljoint boots for tears (see
illustration). If there is any movement, or the
boots are torn or leaking, the balljoint(s) must
be renewed.
11Grasp each front tyre at the front and rear
edges, push in at the front, pull out at the rear
and feel for play in the steering linkage. If any
free play is noted, check the steering gear
mountings and the track rod balljoints for
looseness. If the steering gear mountings are
loose, tighten them. If the track rods are
loose, the balljoints may be worn (check to
make sure the nuts are tight). Additional
steering and suspension system information
can be found in Chapter 10.
25 Driveshaft gaiter check
1
1The driveshaft gaiters are very important
because they prevent dirt, water and foreign
material from entering and damaging the
constant velocity (CV) joints. External oil and
grease contamination can cause the gaitermaterial to deteriorate prematurely, so it’s a
good idea to wash the gaiters with soap and
water.
2Inspect the gaiters for tears and cracks, as
well as for loose clamps (see illustration). If
there is any evidence of cracks or leaking
lubricant, the gaiter must be renewed (see
Chapter 8).
26 Brake system check
2
Warning: Dust produced by lining
wear and deposited on brake
components may contain
asbestos, which is hazardous to
your health. Do not blow it out with
compressed air, and don’t inhale it! Do not
use petroleum-based solvents to remove
the dust. Brake system cleaner or
methylated spirit should be used to flush
the dust into a drain pan. After the brake
components are wiped with a damp rag,
dispose of the contaminated rag(s) and the
drain pan contents into a covered and
labelled container. Try to use asbestos-
free new parts whenever possible.
Note:In addition to the specified intervals, the
brake system should be inspected each time
the wheels are removed or a malfunction is
indicated. Because of the obvious safety con-
siderations, the following brake system checks
are some of the most important maintenance
procedures you can perform on your vehicle.
Symptoms of brake system
problems
1The disc brakes have built-in electrical wear
indicators which cause a warning light on the
dash to come on when they’re worn to the
renewal point. When the light comes on,
renew the pads immediately, or expensive
damage to the brake discs could result.
2Any of the following symptoms could
indicate a potential brake system defect:
a) Vehicle pulls to one side when the brake
pedal is depressed
b) Brakes make squealing or dragging noises
when applied
c) Brake pedal travel excessived) Brake pedal pulsates (normal if ABS is
working)
e) Brake fluid leaks (usually on the inner side
of the tyre or wheel)
3If any of these conditions are noted, inspect
the brake system immediately.
Brake lines and hoses
Note: Steel brake pipes are used throughout
the brake system, with the exception of
flexible, reinforced hoses at the front wheels
and as connectors at the rear axle. Periodic
inspection of all these lines is very important.
4Park the vehicle on level ground, and
switch off the engine. Remove the wheel
covers. Loosen, but do not remove, the bolts
on all four wheels.
5Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
6Remove the wheels (see “Jacking and
towing” at the front of this book, or refer to
your owner’s handbook, if necessary).
7Check all brake lines and hoses for cracks,
chafing of the outer cover, leaks, blisters, and
distortion. Check the brake hoses at front and
rear of the vehicle for softening, cracks,
bulging, or wear from rubbing on other
components. Check all threaded fittings for
leaks, and make sure the brake hose
mounting bolts and clips are secure.
8If leaks or damage are discovered, they
must be repaired immediately. Refer to
Chapter 9 for detailed brake system repair
procedures.
Disc brakes
9If it hasn’t already been done, raise the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the front wheels.
10The disc brake calipers, containing the
pads, are now visible. Each caliper has an
outer and an inner pad - all pads should be
checked.
11Note the pad thickness by looking
through the inspection hole in the caliper (see
illustration). If the lining material is 2.0 mm
thick or less, or if it is tapered from end to
end, the pads should be renewed (see
Chapter 9). Keep in mind that the lining
1•22
26.11 Look through the caliper inspection
window to inspect the brake pads - the
pad lining which rubs against the disc can
also be inspected by looking through each
end of the caliper25.2 Gently probe the driveshaft boots to
check for cracks24.10 Inspect the balljoint boots for tears
(arrowed)
Every 12 000 miles
Page 33 of 228
material is bonded to a metal plate or shoe -
the metal portion is not included in this
measurement. Always renew the pads on
both sides of the vehicle (in axle sets), even if
only one pad of the four is worn, or uneven
braking may result.
12Remove the calipers without
disconnecting the brake hoses (see Chap-
ter 9).
13Check the condition of the brake disc.
Look for score marks, deep scratches and
overheated areas (they will appear blue or
discoloured). If damage or wear is noted, the
disc can be removed and resurfaced by an
engineering workshop; otherwise, it will have
to be renewed. In either case, both discs
should be involved, even if only one is worn.
Refer to Chapter 9 for more detailed
inspection and repair procedures.
Drum brakes
14Refer to Chapter 9 and remove the rear
brake drums.
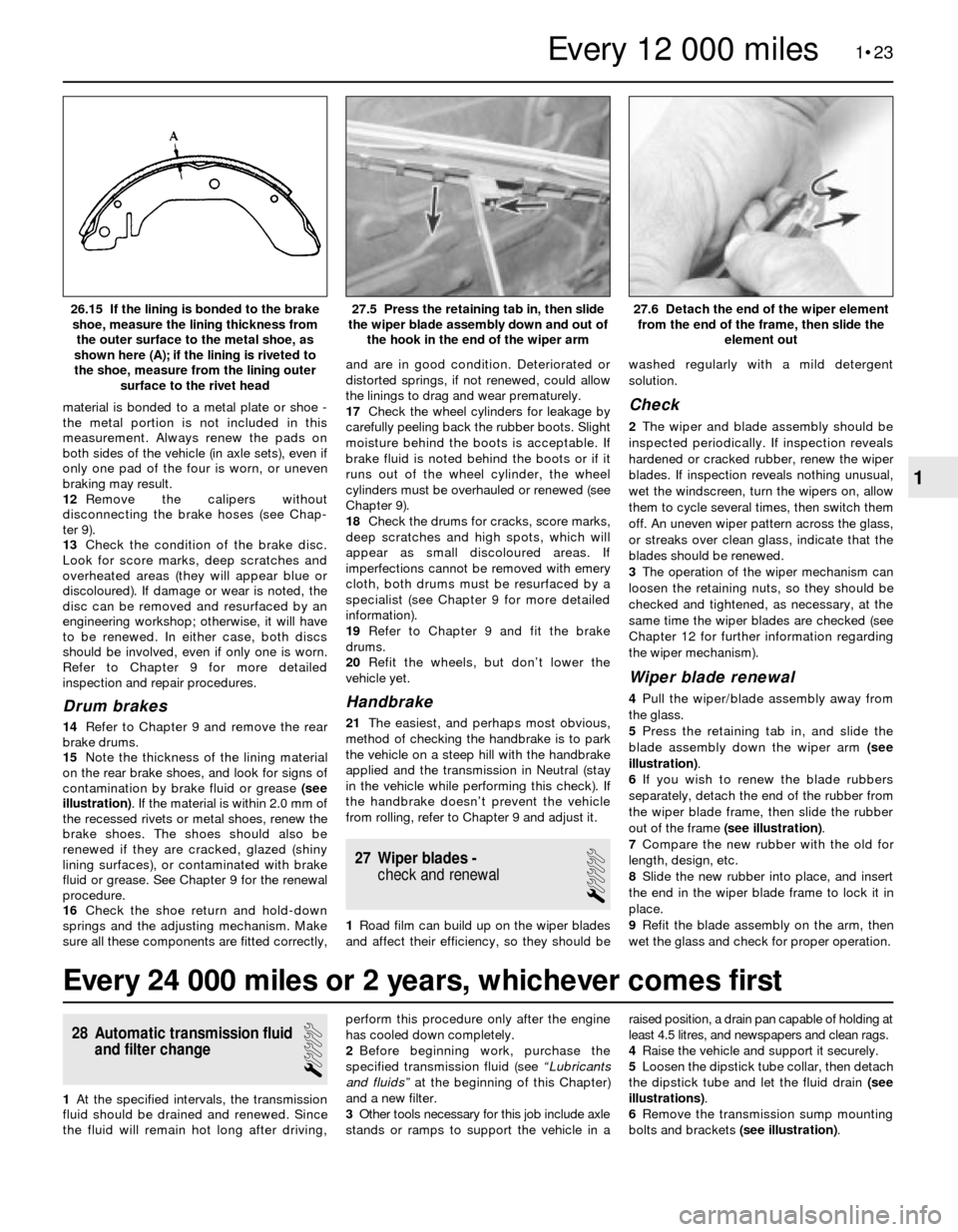
15Note the thickness of the lining material
on the rear brake shoes, and look for signs of
contamination by brake fluid or grease (see
illustration). If the material is within 2.0 mm of
the recessed rivets or metal shoes, renew the
brake shoes. The shoes should also be
renewed if they are cracked, glazed (shiny
lining surfaces), or contaminated with brake
fluid or grease. See Chapter 9 for the renewal
procedure.
16Check the shoe return and hold-down
springs and the adjusting mechanism. Make
sure all these components are fitted correctly,and are in good condition. Deteriorated or
distorted springs, if not renewed, could allow
the linings to drag and wear prematurely.
17Check the wheel cylinders for leakage by
carefully peeling back the rubber boots. Slight
moisture behind the boots is acceptable. If
brake fluid is noted behind the boots or if it
runs out of the wheel cylinder, the wheel
cylinders must be overhauled or renewed (see
Chapter 9).
18Check the drums for cracks, score marks,
deep scratches and high spots, which will
appear as small discoloured areas. If
imperfections cannot be removed with emery
cloth, both drums must be resurfaced by a
specialist (see Chapter 9 for more detailed
information).
19Refer to Chapter 9 and fit the brake
drums.
20Refit the wheels, but don’t lower the
vehicle yet.
Handbrake
21The easiest, and perhaps most obvious,
method of checking the handbrake is to park
the vehicle on a steep hill with the handbrake
applied and the transmission in Neutral (stay
in the vehicle while performing this check). If
the handbrake doesn’t prevent the vehicle
from rolling, refer to Chapter 9 and adjust it.
27 Wiper blades -
check and renewal
1
1Road film can build up on the wiper blades
and affect their efficiency, so they should bewashed regularly with a mild detergent
solution.
Check
2The wiper and blade assembly should be
inspected periodically. If inspection reveals
hardened or cracked rubber, renew the wiper
blades. If inspection reveals nothing unusual,
wet the windscreen, turn the wipers on, allow
them to cycle several times, then switch them
off. An uneven wiper pattern across the glass,
or streaks over clean glass, indicate that the
blades should be renewed.
3The operation of the wiper mechanism can
loosen the retaining nuts, so they should be
checked and tightened, as necessary, at the
same time the wiper blades are checked (see
Chapter 12 for further information regarding
the wiper mechanism).
Wiper blade renewal
4Pull the wiper/blade assembly away from
the glass.
5Press the retaining tab in, and slide the
blade assembly down the wiper arm (see
illustration).
6If you wish to renew the blade rubbers
separately, detach the end of the rubber from
the wiper blade frame, then slide the rubber
out of the frame (see illustration).
7Compare the new rubber with the old for
length, design, etc.
8Slide the new rubber into place, and insert
the end in the wiper blade frame to lock it in
place.
9Refit the blade assembly on the arm, then
wet the glass and check for proper operation.
1•23
27.6 Detach the end of the wiper element
from the end of the frame, then slide the
element out27.5 Press the retaining tab in, then slide
the wiper blade assembly down and out of
the hook in the end of the wiper arm26.15 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here (A); if the lining is riveted to
the shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
1
Every 12 000 miles
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years, whichever comes first
28 Automatic transmission fluid
and filter change
1
1At the specified intervals, the transmission
fluid should be drained and renewed. Since
the fluid will remain hot long after driving,perform this procedure only after the engine
has cooled down completely.
2Before beginning work, purchase the
specified transmission fluid (see “Lubricants
and fluids”at the beginning of this Chapter)
and a new filter.
3Other tools necessary for this job include axle
stands or ramps to support the vehicle in araised position, a drain pan capable of holding at
least 4.5 litres, and newspapers and clean rags.
4Raise the vehicle and support it securely.
5Loosen the dipstick tube collar, then detach
the dipstick tube and let the fluid drain (see
illustrations).
6Remove the transmission sump mounting
bolts and brackets (see illustration).
Page 34 of 228

7Detach the sump from the transmission and
lower it, being careful not to spill the
remaining fluid (see illustration).
8Carefully clean the sump-to-transmission
contact surface.
9Pour the fluid from the sump into a suitable
container, then clean the sump with solvent
and dry it with compressed air. Be sure to
clean any metal filings from the magnet, if
applicable.
10Remove the filter from inside the
transmission (see illustrations).
11Fit the O-ring and a new filter, being sure
to tighten the bolts securely.
12Make sure that the sump gasket contact
surfaces are clean, then fit the new gasket.
Offer the sump up to the transmission, and
refit the brackets and bolts. Working aroundthe sump, tighten each bolt a little at a time
until the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations is reached. Don’t overtighten the
bolts! Connect the dipstick tube, and tighten
the collar securely.
13Lower the vehicle, and add the specified
amount of fluid through the filler tube (see
Section 8).
14With the transmission in Park and the
handbrake applied, run the engine at fast idle,
but don’t race it.
15Move the gear selector through each
position, and back to Park. Check the fluid
level.
16Check under the vehicle for leaks after the
first few trips.
29 Cooling system -draining,
flushing and refilling
1
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin,
or with the painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. Antifreeze
is highly toxic if ingested. Never leave
antifreeze lying around in an open container
or in puddles on the floor; children and pets
are attracted by its sweet smell, and may
drink it. Check with local authorities about
disposing of used antifreeze. Local
collection centres may exist to see that
antifreeze is disposed of safely.1Periodically, the cooling system should be
drained, flushed and refilled. This will restore
the effectiveness of the antifreeze mixture and
prevent formation of rust and corrosion, which
can impair the performance of the cooling
system and cause engine damage. When the
cooling system is serviced, all hoses and the
radiator cap should be checked and renewed
if necessary.
Draining
2If the vehicle has just been driven, wait
several hours to allow the engine to cool down
before beginning this procedure.
3Once the engine is completely cool, remove
the expansion tank cap or radiator cap. If the
cap must be removed while the engine is still
warm, unscrew it slowly, and take adequate
precautions to avoid scalding.
4Move a large container under the radiator to
catch the coolant. Where a drain plug is fitted,
unscrew it (a pair of pliers or screwdriver may
be required to turn it, depending on the
model) (see illustration). Where there is no
drain plug, it will be necessary to disconnect
the bottom hose from the radiator.
5While the coolant is draining, check the
condition of the radiator hoses, heater hoses
and clamps (see Section 21 if necessary).
6Renew any damaged clamps or hoses (see
Chapter 3 for detailed renewal procedures).
1•24
28.10c Remove the O-ring from the
transmission. If it is in good condition,
clean it and transfer it to the new fluid
filter; otherwise, renew it
28.10b . . . then remove the fluid filter from
the transmission28.10a Use a Torx key to remove the filter
bolts . . .
28.7 Lower the sump from the
transmission
28.6 Use a socket and extension to
remove the bolts and brackets28.5b Detach the tube and let the fluid
drain28.5a Unscrew the dipstick tube collar
Every 24 000 miles
Page 40 of 228
12After the No 1 piston has been positioned
at TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for
any of the remaining pistons can be located
by turning the crankshaft and following the
firing order. Mark the remaining spark plug
lead terminal locations just like you did for the
No 1 terminal, then number the marks to
correspond with the cylinder numbers. As you
turn the crankshaft, the rotor will also turn.
When it’s pointing directly at one of the marks
on the distributor, the piston for that particular
cylinder is at TDC on the compression stroke.
4 Valve cover-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Detach the breather hose from the valve
cover.
3On M20 engines, unbolt and remove the
intake manifold support bracket and, if
applicable, the bracket for the engine sensors
or idle air stabiliser (it will probably be
necessary to disconnect the electrical
connectors from the sensors and stabiliser).
4On M30 engines, disconnect the electrical
connector for the airflow sensor. Unclip the
electrical harness, moving it out of the way.
5Where necessary on M30 engines, remove
the hoses and fittings from the intake air hose,
then loosen the clamp and separate the hose
from the throttle body. Unscrew the mounting
nuts for the air cleaner housing, and remove
the housing together with the air hose and
airflow sensor.
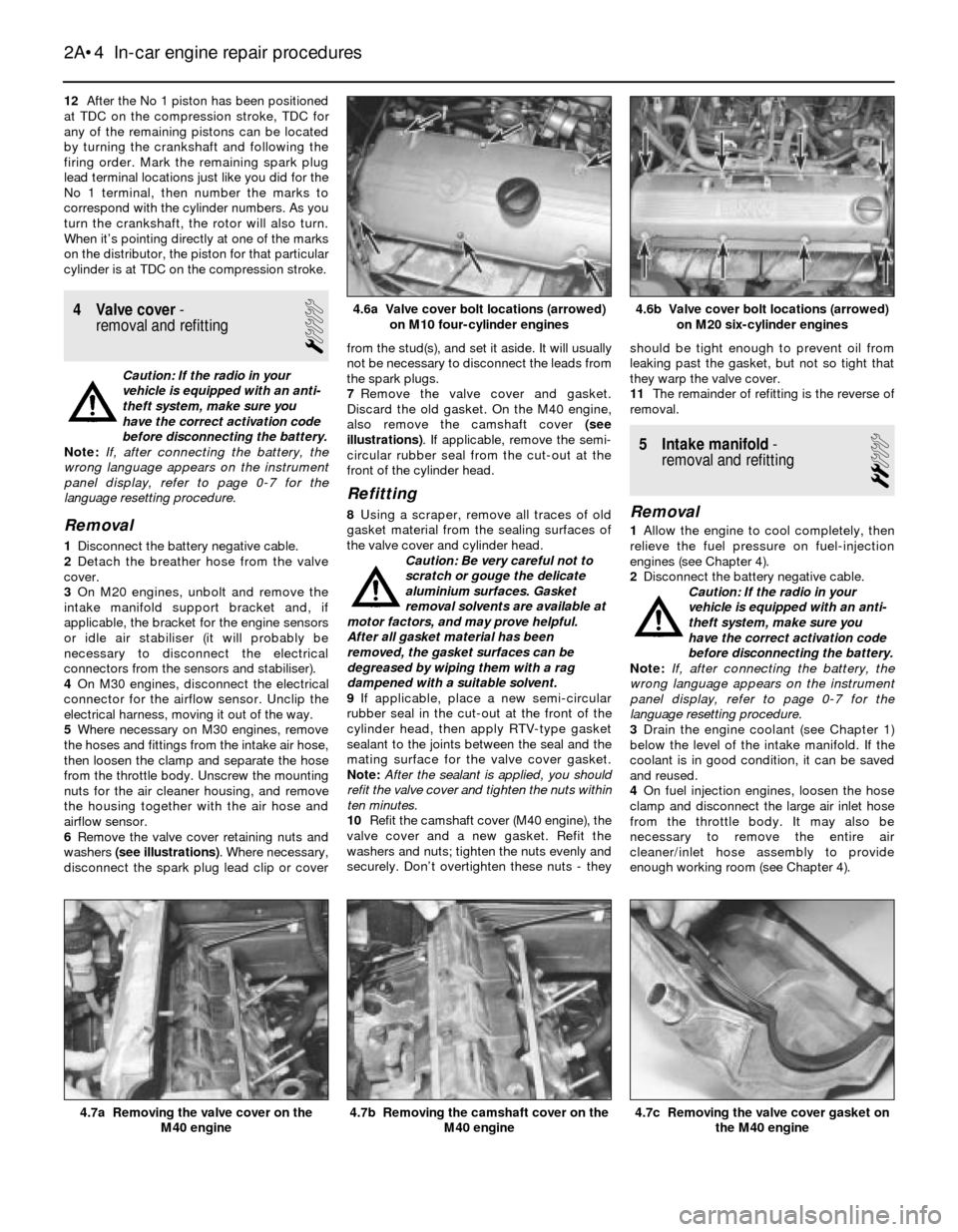
6Remove the valve cover retaining nuts and
washers (see illustrations). Where necessary,
disconnect the spark plug lead clip or coverfrom the stud(s), and set it aside. It will usually
not be necessary to disconnect the leads from
the spark plugs.
7Remove the valve cover and gasket.
Discard the old gasket. On the M40 engine,
also remove the camshaft cover (see
illustrations). If applicable, remove the semi-
circular rubber seal from the cut-out at the
front of the cylinder head.
Refitting
8Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the valve cover and cylinder head.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Gasket
removal solvents are available at
motor factors, and may prove helpful.
After all gasket material has been
removed, the gasket surfaces can be
degreased by wiping them with a rag
dampened with a suitable solvent.
9If applicable, place a new semi-circular
rubber seal in the cut-out at the front of the
cylinder head, then apply RTV-type gasket
sealant to the joints between the seal and the
mating surface for the valve cover gasket.
Note:After the sealant is applied, you should
refit the valve cover and tighten the nuts within
ten minutes.
10Refit the camshaft cover (M40 engine), the
valve cover and a new gasket. Refit the
washers and nuts; tighten the nuts evenly and
securely. Don’t overtighten these nuts - theyshould be tight enough to prevent oil from
leaking past the gasket, but not so tight that
they warp the valve cover.
11The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
5 Intake manifold-
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Allow the engine to cool completely, then
relieve the fuel pressure on fuel-injection
engines (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Drain the engine coolant (see Chapter 1)
below the level of the intake manifold. If the
coolant is in good condition, it can be saved
and reused.
4On fuel injection engines, loosen the hose
clamp and disconnect the large air inlet hose
from the throttle body. It may also be
necessary to remove the entire air
cleaner/inlet hose assembly to provide
enough working room (see Chapter 4).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
4.7b Removing the camshaft cover on the
M40 engine4.7a Removing the valve cover on the
M40 engine4.7c Removing the valve cover gasket on
the M40 engine
4.6b Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M20 six-cylinder engines4.6a Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M10 four-cylinder engines
Page 42 of 228
6 Exhaust manifold-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Make sure the engine is
completely cool before beginning
work on the exhaust system.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2On models where the air cleaner is on the
exhaust manifold side of the engine, remove
the air cleaner housing assembly and/or
airflow sensor to provide sufficient working
area (see Chapter 4, if necessary).
3Unplug the HT leads and set the spark plug
lead harness aside (see Chapter 1).
4Clearly label, then disconnect or remove, all
wires, hoses, fittings, etc. that are in the way.
Be sure to disconnect the oxygen sensor,
where fitted.
5Raise the vehicle, and support it securely
on axle stands. Working from under the
vehicle, separate the exhaust downpipe from
the manifold. Use penetrating oil on the
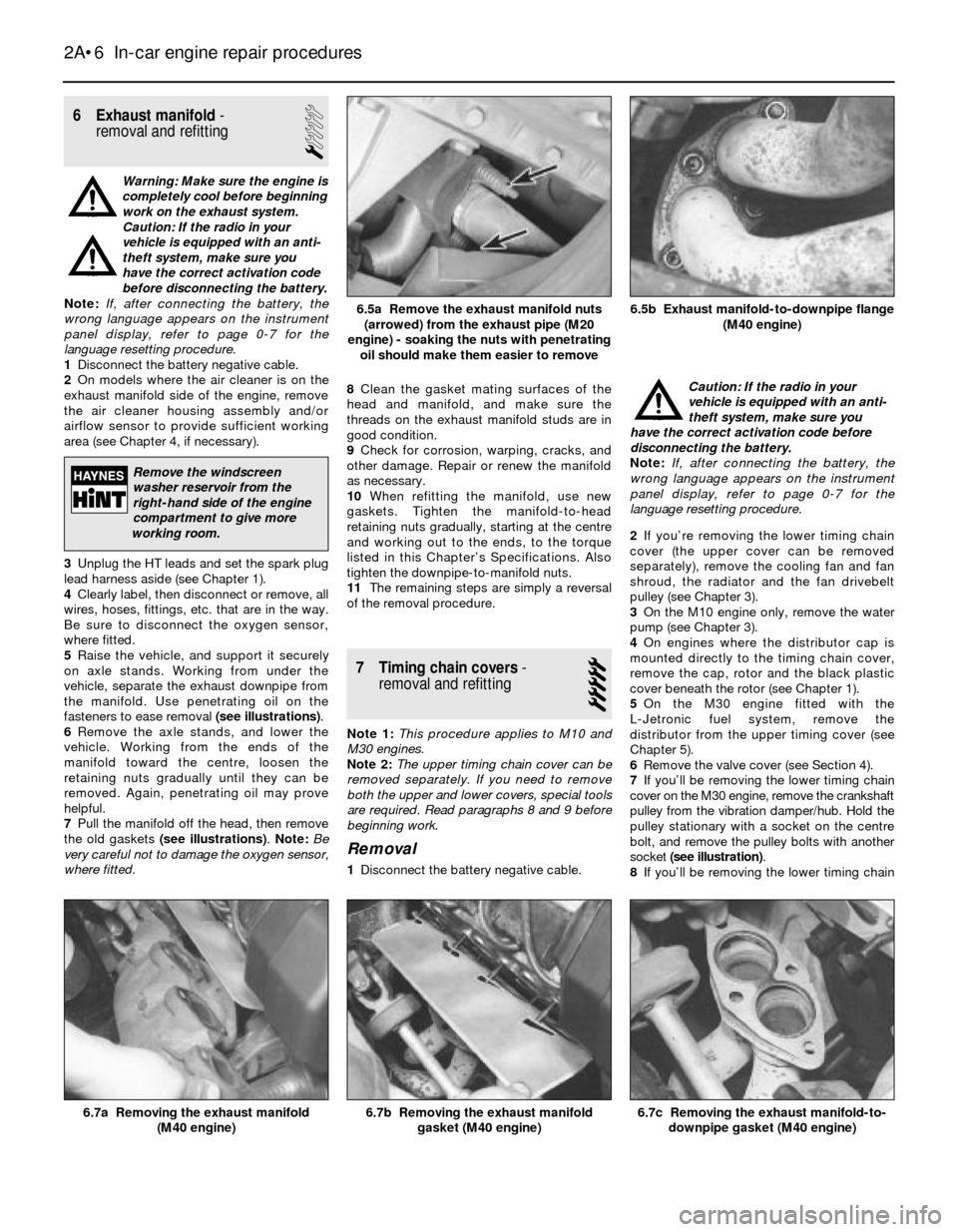
fasteners to ease removal (see illustrations).
6Remove the axle stands, and lower the
vehicle. Working from the ends of the
manifold toward the centre, loosen the
retaining nuts gradually until they can be
removed. Again, penetrating oil may prove
helpful.
7Pull the manifold off the head, then remove
the old gaskets (see illustrations). Note:Be
very careful not to damage the oxygen sensor,
where fitted.8Clean the gasket mating surfaces of the
head and manifold, and make sure the
threads on the exhaust manifold studs are in
good condition.
9Check for corrosion, warping, cracks, and
other damage. Repair or renew the manifold
as necessary.
10When refitting the manifold, use new
gaskets. Tighten the manifold-to-head
retaining nuts gradually, starting at the centre
and working out to the ends, to the torque
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications. Also
tighten the downpipe-to-manifold nuts.
11The remaining steps are simply a reversal
of the removal procedure.
7 Timing chain covers-
removal and refitting
5
Note 1:This procedure applies to M10 and
M30 engines.
Note 2:The upper timing chain cover can be
removed separately. If you need to remove
both the upper and lower covers, special tools
are required. Read paragraphs 8 and 9 before
beginning work.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code before
disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2If you’re removing the lower timing chain
cover (the upper cover can be removed
separately), remove the cooling fan and fan
shroud, the radiator and the fan drivebelt
pulley (see Chapter 3).
3On the M10 engine only, remove the water
pump (see Chapter 3).
4On engines where the distributor cap is
mounted directly to the timing chain cover,
remove the cap, rotor and the black plastic
cover beneath the rotor (see Chapter 1).
5On the M30 engine fitted with the
L-Jetronic fuel system, remove the
distributor from the upper timing cover (see
Chapter 5).
6Remove the valve cover (see Section 4).
7If you’ll be removing the lower timing chain
cover on the M30 engine, remove the crankshaft
pulley from the vibration damper/hub. Hold the
pulley stationary with a socket on the centre
bolt, and remove the pulley bolts with another
socket (see illustration).
8If you’ll be removing the lower timing chain
2A•6 In-car engine repair procedures
6.7c Removing the exhaust manifold-to-
downpipe gasket (M40 engine)6.7b Removing the exhaust manifold
gasket (M40 engine)6.7a Removing the exhaust manifold
(M40 engine)
6.5b Exhaust manifold-to-downpipe flange
(M40 engine)6.5a Remove the exhaust manifold nuts
(arrowed) from the exhaust pipe (M20
engine) - soaking the nuts with penetrating
oil should make them easier to remove
Remove the windscreen
washer reservoir from the
right-hand side of the engine
compartment to give more
working room.
Page 44 of 228

8 Timing chain and
sprockets- removal,
inspection and refitting
5
Note:This procedure applies to M10 and M30
engines.
Caution: Once the engine is set
at TDC, do not rotate the
camshaft or crankshaft until the
timing chain is reinstalled. If the
crankshaft or camshaft is rotated with the
timing chain removed, the valves could hit
the pistons, causing expensive internal
engine damage.
Removal
1Position the No 1 cylinder at Top Dead
Centre (TDC) on the compression stroke (see
Section 3).
2Remove the valve cover (see Section 4).
Double-check that the No 1 cylinder is at TDC
on the compression stroke by making sure the
No 1 cylinder rocker arms are loose (not
compressing their valve springs).
3Remove the upper timing chain cover (see
Section 7). Note the location of the camshaft
timing marks, which should now be aligned.
On four-cylinder (M10) engines, there’s
usually a stamped line on the camshaft flange
that aligns with a cast mark on the top of the
cylinder head; also, the camshaft sprocket
dowel pin hole will be at its lowest point. On
six-cylinder (M30) engines, a line drawn
through two of the camshaft sprocket bolts
opposite each other would be exactly vertical,
while a line drawn through the other two bolts
would be horizontal. Additionally, the locating
pin should be in the lower left corner (between
the 7 and 8 o’clock positions). Be sure you’ve
identified the correct camshaft TDC position
before dismantling, because correct valve
timing depends on you aligning them exactly
on reassembly. Note:As the engine is
mounted in the engine compartment at anangle, all references to horizontal and vertical
whilst timing the camshafts are in relation to
the crankshaft, and not the ground.
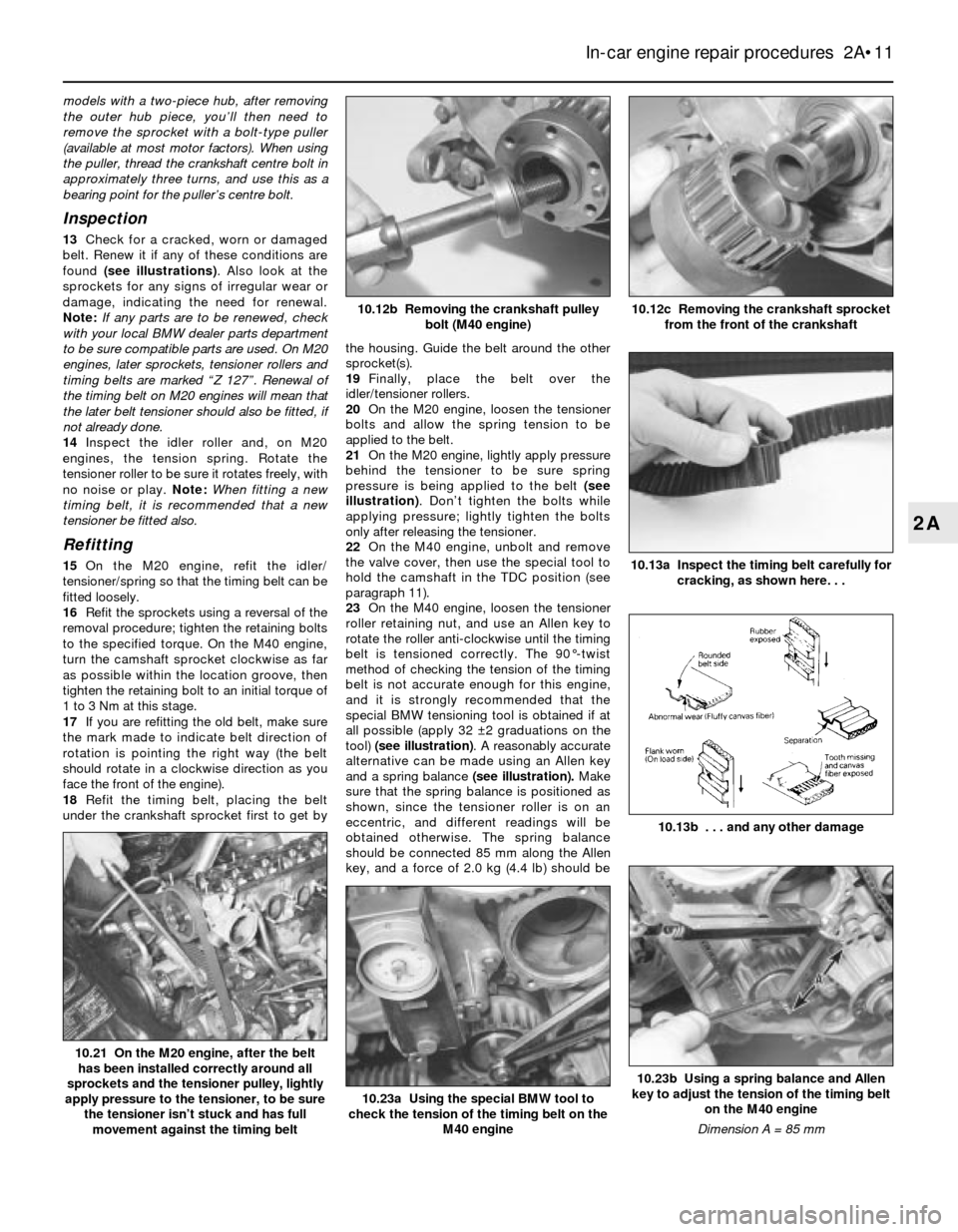
4Hold the crankshaft stationary with a socket
and ratchet on the vibration damper centre bolt,
then loosen (but don’t unscrew completely) the
four bolts attaching the camshaft sprocket to
the camshaft. Be very careful not to rotate the
camshaft or crankshaft. Note:Some earlier
models may have locking tabs for the camshaft
sprocket bolts. Bend the tabs down before
loosening the bolts. The tabs are no longer
available from the manufacturer, and do not
have to be used on refitting.
5Remove the lower timing chain cover (see
Section 7).
6Unscrew and remove the four camshaft
sprocket bolts, then disengage the chain from
the crankshaft sprocket and carefully remove
the chain and camshaft sprocket from the
engine. It may be necessary to gently prise
the camshaft sprocket loose from the
camshaft with a screwdriver.
Inspection
Timing sprockets
7Examine the teeth on both the crankshaft
sprocket and the camshaft sprocket for wear.
Each tooth forms an inverted V. If worn, the
side of each tooth under tension will be
slightly concave in shape when compared
with the other side of the tooth (i.e. one side of
the inverted V will be concave when
compared with the other, giving the teeth a
hooked appearance). If the teeth appear to be
worn, the sprockets must be renewed. Note:
The crankshaft sprocket is a press fit on the
crankshaft, and can be removed with a jaw-
type puller after the Woodruff key and oil
pump are removed (see Section 14). However,
BMW recommends the new sprocket be
pressed onto the crankshaft after being
heated to 80°C (175°F) on the M10 engine, or
to 200°C(390°F) on the M30 engine. For this
reason, if the crankshaft sprocket requires
renewal, we recommend removing the
crankshaft (see Part B of this Chapter) and
taking it to an engineering works to have the
old sprocket pressed off and a new one
pressed on.
Timing chain
8The chain should be renewed if the
sprockets are worn or if the chain is loose
(indicated by excessive noise in operation).
It’s a good idea to renew the chain anyway if
the engine is stripped down for overhaul. The
rollers on a very badly worn chain may be
slightly grooved. To avoid future problems, if
there’s any doubt at all about the chain’s
condition, renew it.
Chain rail and tensioner
9Inspect the chain guide rail and tensioner
rail for deep grooves caused by chain contact.
Renew them if they are excessively worn. The
rails can be renewed after removing the
circlips with a pointed tool or needle-nose
pliers (see illustration).10Shake the tensioner plunger, and listen for
a rattling sound from the check ball. If you
can’t hear the ball rattling, renew the plunger.
11To further check the tensioner plunger,
blow through it first from the closed end, then
from the slotted (guide) end. No air should
flow through the plunger when you blow
through the closed end, and air should flow
through it freely when you blow through the
slotted end. If the tensioner fails either test,
renew it.
Refitting
12Refit the tensioner rail and chain guide
rail, if removed.
13Temporarily refit the lower timing chain
cover and vibration damper, so you can check
the crankshaft timing marks. Once you’ve
verified the TDC marks are aligned, remove
the damper and cover.
14Loop the timing chain over the crankshaft
sprocket, then loop it over the camshaft
sprocket and, guiding the chain between the
chain guide and tensioner rail, refit the
camshaft sprocket on the camshaft. Make
sure the camshaft timing marks are aligned.
15The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal. Be sure to tighten the fasteners to
the correct torques (see this Chapter’s Speci-
fications).
9 Timing belt covers-
removal and refitting
2
Note:This procedure applies to M20 and M40
engines.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the fan clutch and fan shroud (see
Chapter 3).
3On the M20 engine, remove the radiator
(see Chapter 3).
4Remove the fan drivebelt pulley.
2A•8 In-car engine repair procedures
9.6a Unbolt the distributor cap
(M40 engine) . . .
8.9 To remove the tensioner or chain guide
rail, remove the circlips with a pointed tool
or needle-nose pliers - the circlips tend to
fly off when they’re released, so make sure
you catch them or they’ll get lost (or,
worse, wind up in the engine!)
Page 47 of 228
models with a two-piece hub, after removing
the outer hub piece, you’ll then need to
remove the sprocket with a bolt-type puller
(available at most motor factors). When using
the puller, thread the crankshaft centre bolt in
approximately three turns, and use this as a
bearing point for the puller’s centre bolt.
Inspection
13Check for a cracked, worn or damaged
belt. Renew it if any of these conditions are
found (see illustrations). Also look at the
sprockets for any signs of irregular wear or
damage, indicating the need for renewal.
Note:If any parts are to be renewed, check
with your local BMW dealer parts department
to be sure compatible parts are used. On M20
engines, later sprockets, tensioner rollers and
timing belts are marked “Z 127”. Renewal of
the timing belt on M20 engines will mean that
the later belt tensioner should also be fitted, if
not already done.
14Inspect the idler roller and, on M20
engines, the tension spring. Rotate the
tensioner roller to be sure it rotates freely, with
no noise or play. Note:When fitting a new
timing belt, it is recommended that a new
tensioner be fitted also.
Refitting
15On the M20 engine, refit the idler/
tensioner/spring so that the timing belt can be
fitted loosely.
16Refit the sprockets using a reversal of the
removal procedure; tighten the retaining bolts
to the specified torque. On the M40 engine,
turn the camshaft sprocket clockwise as far
as possible within the location groove, then
tighten the retaining bolt to an initial torque of
1 to 3 Nm at this stage.
17If you are refitting the old belt, make sure
the mark made to indicate belt direction of
rotation is pointing the right way (the belt
should rotate in a clockwise direction as you
face the front of the engine).
18Refit the timing belt, placing the belt
under the crankshaft sprocket first to get bythe housing. Guide the belt around the other
sprocket(s).
19Finally, place the belt over the
idler/tensioner rollers.
20On the M20 engine, loosen the tensioner
bolts and allow the spring tension to be
applied to the belt.
21On the M20 engine, lightly apply pressure
behind the tensioner to be sure spring
pressure is being applied to the belt (see
illustration). Don’t tighten the bolts while
applying pressure; lightly tighten the bolts
only after releasing the tensioner.
22On the M40 engine, unbolt and remove
the valve cover, then use the special tool to
hold the camshaft in the TDC position (see
paragraph 11).
23On the M40 engine, loosen the tensioner
roller retaining nut, and use an Allen key to
rotate the roller anti-clockwise until the timing
belt is tensioned correctly. The 90°-twist
method of checking the tension of the timing
belt is not accurate enough for this engine,
and it is strongly recommended that the
special BMW tensioning tool is obtained if at
all possible (apply 32 ±2 graduations on the
tool) (see illustration). A reasonably accurate
alternative can be made using an Allen key
and a spring balance (see illustration).Make
sure that the spring balance is positioned as
shown, since the tensioner roller is on an
eccentric, and different readings will be
obtained otherwise. The spring balance
should be connected 85 mm along the Allen
key, and a force of 2.0 kg (4.4 lb) should be
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•11
10.13a Inspect the timing belt carefully for
cracking, as shown here. . .
10.13b . . . and any other damage
10.12c Removing the crankshaft sprocket
from the front of the crankshaft10.12b Removing the crankshaft pulley
bolt (M40 engine)
10.23b Using a spring balance and Allen
key to adjust the tension of the timing belt
on the M40 engine
Dimension A = 85 mm
10.23a Using the special BMW tool to
check the tension of the timing belt on the
M40 engine
10.21 On the M20 engine, after the belt
has been installed correctly around all
sprockets and the tensioner pulley, lightly
apply pressure to the tensioner, to be sure
the tensioner isn’t stuck and has full
movement against the timing belt
2A