spark plugs BMW 3 SERIES 1987 E30 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1987, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1987 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 12 of 228

Fuel system
Idle speed
3-Series, E30
316 with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
316i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 40 rpm
318i with M10/B18 engine (manual transmission) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
318i with M10/B18 engine (automatic transmission) . . . . . . . . . . . 750 ± 50 rpm
318i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 40 rpm
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 50 rpm
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 50 rpm
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
518i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 40 rpm
520i with M20/B20M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
525i with M20/B25M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
530i with M30/B30M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 50 rpm
535i with M30/B35M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
CO% at 3000 rpm
3-Series, E30
316 with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 to 1.0
316i and 318i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 ± 0.5
318i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 maximum
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 ± 0.5
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 maximum
525i with M30/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5
528i with M30/B28 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 maximum
535i with M30/B34 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 to 1.5
M535i with M30/B34 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 to 1.5
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 ± 0.5
Air filter element
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion W155 (round) or U504 (square)
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U504 or U527
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U504 or U527
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U527
Fuel filter (all fuel injection engines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion L206
Ignition system
Spark plug type
M10, M20 and M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion N9YCC
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion C9YCC
Spark plug gap* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.8 mm
Spark plug (HT) leads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
* The spark plug gap quoted is that recommended by Champion for their specified plugs listed above. If spark plugs of any other type are to be
fitted, refer to their manufacturer’s spark plug gap recommendations.
Brakes
Disc brake pad thickness (minimum) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Drum brake shoe lining thickness (minimum) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Wiper blades
Windscreen
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-5103
3-Series passenger side from 1991 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-5103 (20 inch) or Champion X-5303 (21 inch)
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-4503
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
Tailgate
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-4503
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
1•2Servicing Specifications
Page 13 of 228

Tyre pressures (cold) - bars (psi)Front Rear
3-Series, E30
316 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 (28) 2.1 (30)
316i
Saloon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.1 (30)
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.2 (32)
318i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.8 (26) 1.9 (28)
320i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 (28) 2.0 (29)
325i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.3 (33)
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.0 (29)
525i and 528i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.2 (32)
535i and M535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 (33) 2.5 (36)
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.0 (29)
520i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.1 (30)
525i, 530i and 535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.3 (33)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Automatic transmission sump bolts
Three-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 9
Four-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 to 7
Spark plugs
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 to 30
Except M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 33
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 33
Wheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Lubricants and fluids
Component or system Lubricant type/specification
Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multigrade engine oil, viscositySAE 10W/40 to 20W/50, to API SG
Cooling system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze with corrosion inhibitors
Manual transmission* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gear oil, viscosity SAE 80 to API-GL4, or single-grade mineral-based
engine oil, viscosity SAE 20, 30 or 40 to API-SG
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dexron ll type ATF
Final drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . BMW-approved hypoid gear oil, viscosity SAE 90**
Brake and clutch hydraulic systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic brake fluid to SAE J 1703 or DOT 4
Power steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dexron ll type ATF
* E34 520i & 525i with air conditioning, E34 530i & 535i - Dexron II type ATF)
** Only available in bulk; refer to your BMW dealer
Capacities*
1•3
1
Engine oil
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 litres
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.3 litres
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.8 litres
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 litres
Cooling system
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.5 litres
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.0 litres
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
Fuel tank
3-Series, E30
Saloon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 litres (early),
64 litres (later)
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63 litres (early),
70 litres (later)
5-Series
E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 litres
E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81 litresManual transmission
ZF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 litres
Getrag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.5 litres
Automatic transmission (refill)
3-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 litres
4-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 litres
Final drive capacity (drain and refill)
3-Series, E30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.9 litres
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.9 litres
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.7 litres
*All capacities approximate
Servicing Specifications
Page 14 of 228

Maintenance schedule
The following maintenance intervals are based on the assumption
that the vehicle owner will be doing the maintenance or service work,
as opposed to having a dealer service department do the work.
Although the time/mileage intervals are loosely based on factory rec-
ommendations, most have been shortened to ensure, for example, that
such items as lubricants and fluids are checked/changed at intervals
that promote maximum engine/driveline service life. Also, subject to
the preference of the individual owner interested in keeping his or her
vehicle in peak condition at all times, and with the vehicle’s ultimate
resale in mind, many of the maintenance procedures may be
performed more often than recommended in the following schedule.
We encourage such owner initiative.
When the vehicle is new, it should be serviced initially by a factory-
authorised dealer service department, to protect the factory warranty.
In many cases, the initial maintenance check is done at no cost to the
owner (check with your dealer service department for more
information).
1•4Maintenance and servicing
Every 250 miles or weekly, whichever
comes first
m mCheck the engine oil level (Section 4)
m mCheck the engine coolant level (Section 4)
m mCheck the brake fluid level (Section 4)
m mCheck the clutch fluid level (Section 4)
m mCheck the washer fluid level (Section 4)
m mCheck the tyres and tyre pressures (Section 5)
Every 6000 miles or 6 months,
whichever comes first
All items listed above, plus:
m mChange the engine oil and oil filter (Section 6)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level (Section 7)
m mCheck the tyres, and rotate if necessary (Section 9)
m mCheck the automatic transmission fluid level
(Section 8)
m mCheck the underbonnet hoses (Section 10)
m mCheck/adjust the drivebelts (Section 11)
m mCheck engine idle speed and CO (Section 12)
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months,
whichever comes first
All items listed above, plus:
m mCheck/service the battery (Section 13)
m mCheck the spark plugs (Section 14)
m mCheck/renew the HT leads, distributor cap and
rotor (Section 15)
m mCheck/top-up the manual transmission lubricant
(Section 16)
m mCheck the differential oil level (Section 17)
m mCheck the valve clearances, and adjust if
necessary - does not apply to M40 engines
(Section 18)
m mCheck and lubricate the throttle linkage (Section 19)
m mRenew the air filter (Section 20)
m mCheck the fuel system (Section 21)
m mInspect the cooling system (Section 22)
m mInspect the exhaust system (Section 23)
m mInspect the steering and suspension components
(Section 24)
m mCheck the driveshaft gaiter(s) (Section 25)
m mInspect the brakes (Section 26)
m mInspect/renew the windscreen wiper blades
(Section 27)
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years,
whichever comes first
All items listed above plus:
m mChange the automatic transmission fluid and filter
(Section 28)
m mDrain, flush and refill the cooling system (Section 29)
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 14)
m mCheck/renew the spark plug HT leads (Section 15)
m mRenew the fuel filter (Section 30)
m mChange the manual transmission lubricant (Section 31)
m mChange the differential oil (Section 32)
m mCheck the evaporative emissions system, where
applicable (Section 33)
m mReset the service indicator lights (Section 34)
m mRenew brake fluid by bleeding (see Chapter 9)
m mCheck the handbrake operation (see Chapter 9)
Every 60 000 miles
m
mRenew the timing belt (Section 35)
Page 17 of 228
1 Introduction
This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain his or her vehicle with the
goals of maximum performance, economy,
safety and reliability in mind. Included is a
master maintenance schedule, followed by
procedures dealing specifically with each item
on the schedule. Visual checks, adjustments,
component renewal and other helpful items
are included. Refer to the accompanying
illustrations of the engine compartment and
the underside of the vehicle for the locations
of various components. Servicing the vehicle,
in accordance with the mileage/time
maintenance schedule and the step-by-step
procedures, will result in a planned
maintenance programme that should produce
a long and reliable service life. Keep in mind
that it is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining
some items but not others at specified
intervals, will not produce the same results.
2 Routine maintenance
As you service the vehicle, you will discover
that many of the procedures can - and should
- be grouped together, because of the nature
of the particular procedure you’re performing,
or because of the close proximity of two
otherwise-unrelated components to one
another. For example, if the vehicle is raised
for chassis lubrication, you should inspect the
exhaust, suspension, steering and fuelsystems while you’re under the vehicle. When
the wheels are removed for other work, it
makes good sense to check the brakes, since
the wheels are already removed. Finally, let’s
suppose you have to borrow a torque wrench.
Even if you only need it to tighten the spark
plugs, you might as well check the torque of
as many critical nuts and bolts as time allows.
The first step in this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
procedures you’re planning to do, then gather
up all the parts and tools needed. If it looks
like you might run into problems during a
particular job, seek advice from a mechanic or
an experienced do-it-yourselfer.
3 Engine “tune-up”-
general information
The term “tune-up” is used in this manual to
represent a combination of individual
operations rather than one specific procedure.
If, from the time the vehicle is new, the
routine maintenance schedule is followed
closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid
levels and high-wear items, as suggested
throughout this manual, the engine will be
kept in relatively good running condition, and
the need for additional work will be minimised.
More likely than not, however, there will be
times when the engine is running poorly due
to a lack of regular maintenance. This is even
more likely if a used vehicle, which has not
received regular and frequent maintenance
checks, is purchased. In such cases, an
engine tune-up will be needed outside of the
regular maintenance intervals. The first step in any tune-up or diagnostic
procedure to help correct a poor-running
engine is a cylinder compression check. A
compression check (see Chapter 2B) will help
determine the condition of internal engine
components, and should be used as a guide
for tune-up and repair procedures. If, for
instance, a compression check indicates
serious internal engine wear, a conventional
tune-up will not improve the performance of
the engine, and would be a waste of time and
money. Because of its importance, the
compression check should be done by
someone with the right equipment, and the
knowledge to use it properly.
The following procedures are those most
often needed to bring a generally poor-
running engine back into a proper state of
tune.
Minor tune-up
Check all engine-related fluids (Section 4)
Check all underbonnet hoses (Section 10)
Check and adjust the drivebelts (Sec-
tion 11)
Clean, inspect and test the battery (Sec-
tion 13)
Renew the spark plugs (Section 14)
Inspect the spark plug HT leads, distributor
cap and rotor (Section 15)
Check the air filter (Section 20)
Check the cooling system (Section 22)
Major tune-up
All items listed under minor tune-up, plus . . .
Check the ignition system (see Chapter 5)
Check the charging system (see Chapter 5)
Check the fuel system (see Chapter 4)
Renew the spark plug HT leads, distributor
cap and rotor (Section 15)
1•7
1
Routine Maintenance
Weekly checks
4 Fluid level checks
1
Note:The following are fluid level checks to
be done on a 250-mile or weekly basis.
Additional fluid level checks can be found in
specific maintenance procedures which
follow. Regardless of intervals, be alert to fluid
leaks under the vehicle, which would indicate
a fault to be corrected immediately.
1Fluids are an essential part of the
lubrication, cooling, brake and windscreen
washer systems. Because the fluids gradually
become depleted and/or contaminated during
normal operation of the vehicle, they must be
periodically replenished. See “Lubricants and
fluids”at the beginning of this Chapter before
adding fluid to any of the following
components. Note:The vehicle must be on
level ground when any fluid levels are
checked.
Engine oil
2Engine oil is checked with a dipstick, which
is located on the side of the engine (refer to
the underbonnet illustrations in this Chapter
for dipstick location). The dipstick extends
through a metal tube down into the sump.
3The engine oil should be checked before
the vehicle has been driven, or at least
15 minutes after the engine has been shut off.
4Pull the dipstick out of the tube, and wipe
all of the oil away from the end with a clean
rag or paper towel. Insert the clean dipstick all
the way back into the tube, and pull it out
again. Note the oil at the end of the dipstick.
At its highest point, the oil should be betweenthe two notches or marks (see illustration).
5It takes one litre of oil to raise the level from
the lower mark to the upper mark on the
dipstick. Do not allow the level to drop below
the lower mark, or oil starvation may cause
4.4 The oil level should be kept between
the two marks, preferably at or near the
upper one - if it isn’t, add enough oil to
bring the level to the upper mark
If the oil is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the upper part of
the engine, resulting in an inaccurate
reading on the dipstick.
Page 18 of 228

engine damage. Conversely, overfilling the
engine (adding oil above the upper mark) may
cause oil-fouled spark plugs, oil leaks, or oil
seal failures.
6To add oil, remove the filler cap located on
the valve cover (see illustrations). After
adding oil, wait a few minutes to allow the
level to stabilise, then pull the dipstick out and
check the level again. Add more oil if required.
Refit the filler cap, tightening it by hand only.
7Checking the oil level is an important
preventive maintenance step. A consistently
low oil level indicates oil leakage through
damaged seals or defective gaskets, or oil
burning (internal leakage past worn rings or
valve guides). The condition of the oil should
also be noted. If the oil looks milky in colour or
has water droplets in it, the cylinder head
gasket may be blown, or the head or block
may be cracked. The engine should be
repaired immediately. Whenever you check
the oil level, slide your thumb and index finger
up the dipstick before wiping off the oil. If you
see small dirt or metal particles clinging to the
dipstick, the oil should be changed (see
Section 6).
Engine coolant
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your
skin, or with the vehiclepaintwork. Rinse off spills immediately
with plenty of water. Antifreeze is highly
toxic if ingested. Never leave antifreeze
lying around in an open container, or in
puddles on the floor; children and pets are
attracted by its sweet smell, and may drink
it. Check with local authorities about
disposing of used antifreeze. Local
collection centres may exist, to see that
antifreeze is disposed of safely.
8All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with a pressurised coolant recovery
system. On most models, a white plastic
expansion tank (or coolant reservoir) located
in the engine compartment is connected by a
hose to the radiator. As the engine heats up
during operation, the expanding coolant fills
the tank. As the engine cools, the coolant is
automatically drawn back into the cooling
system, to maintain the correct level.
9The coolant level in the reservoir (see
illustrations)should be checked regularly.
Add a 40%/60% mixture of ethylene glycol-
based antifreeze to water (see illustration).
Warning: Do not remove the
expansion tank cap or radiator
cap to check the coolant level,
unless the engine is completely
cold! The level in the reservoir varies with
the temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should beabove the LOW mark on the reservoir.
Once the engine has warmed up, the level
should be at or near the FULL mark. If it
isn’t, allow the engine to cool, then remove
the cap from the reservoir.
10Drive the vehicle and recheck the coolant
level. If only a small amount of coolant is
required to bring the system up to the proper
level, plain water can be used. However,
repeated additions of water will dilute the
antifreeze. In order to maintain the proper
ratio of antifreeze and water, always top-up
the coolant level with the correct mixture.
11If the coolant level drops consistently,
there must be a leak in the system. Inspect
the radiator, hoses, filler cap, drain plugs and
water pump (see Section 29). If no leaks are
noted, have the expansion tank cap or
radiator cap pressure-tested by a BMW
dealer.
12If you have to remove the cap, wait until
the engine has cooled completely, then wrap
a thick cloth around the cap and turn it to the
first stop. If coolant or steam escapes, let the
engine cool down longer, then remove the
cap.
13Check the condition of the coolant as
well. It should be relatively clear. If it’s brown
or rust-coloured, the system should be
drained, flushed and refilled. Even if the
coolant appears to be normal, the corrosion
1•8
4.9d Adding antifreeze mixture4.9c On some 5-Series models, the
expansion tank (coolant reservoir) is
located on the bulkhead4.9b On other models, the expansion tank
(coolant reservoir) is located on the side of
the engine compartment - remove the cap
to add coolant
4.9a On some models, the expansion tank
(coolant reservoir) is mounted on the
radiator - make sure the level is kept at or
near the FULL mark (arrowed)4.6b Topping-up the engine oil4.6a The threaded oil filler cap is located
in the valve cover - always make sure the
area around the opening is clean before
unscrewing the cap
Weekly Checks
Page 27 of 228

terminals and cable clamps after they are
assembled.
9Make sure that the battery carrier is in good
condition, and that the hold-down clamp bolt
is tight. If the battery is removed (see Chap-
ter 5 for the removal and refitting procedure),
make sure that no parts remain in the bottom
of the carrier when it’s refitted. When refitting
the hold-down clamp, don’t overtighten the
bolt.
10Corrosion on the carrier, battery case and
surrounding areas can be removed with a
solution of water and baking soda. Apply the
mixture with a small brush, let it work, then
rinse it off with plenty of clean water.
11Any metal parts of the vehicle damaged
by corrosion should be coated with a zinc-
based primer, then painted.
12Additional information on the battery and
jump starting can be found in Chapter 5 and
the front of this manual.
Charging
Note: The manufacturer recommends the
battery be removed from the vehicle for
charging, because the gas which escapes
during this procedure can damage the paint or
interior, depending on the location of the
battery. Fast charging with the battery cables
connected can result in damage to the
electrical system.
13Remove all of the cell caps (if applicable),
and cover the holes with a clean cloth to
prevent spattering electrolyte. Disconnect thebattery negative cable, and connect the
battery charger leads to the battery posts
(positive to positive, negative to negative),
then plug in the charger. Make sure it is set at
12 volts if it has a selector switch.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Note: If,
after connecting the battery, the wrong
language appears on the instrument panel
display, refer to page 0-7 for the language
resetting procedure.
14If you’re using a charger with a rate higher
than two amps, check the battery regularly
during charging to make sure it doesn’t
overheat. If you’re using a trickle charger, you
can safely let the battery charge overnight
after you’ve checked it regularly for the first
couple of hours. Where a maintenance-free
battery is fitted, special precautions may be
necessary when charging it (for example, the
charge rate is normally very low). There may
be a warning label on the battery, but if not,
consult a BMW dealer or auto-electrician.
15If the battery has removable cell caps,
measure the specific gravity with a
hydrometer every hour during the last few
hours of the charging cycle. Hydrometers are
available inexpensively from car accessory
shops - follow the instructions that come with
the hydrometer. Consider the battery charged
when there’s no change in the specific gravity
reading for two hours, and the electrolyte in
the cells is gassing (bubbling) freely. The
specific gravity reading from each cell should
be very close to the others. If not, the battery
probably has a bad cell(s), and a new one
should be fitted.
16Some maintenance-free (sealed) batteries
have built-in hydrometers on the top,
indicating the state of charge by the colour
displayed in the hydrometer window.
Normally, a bright-coloured hydrometer
indicates a full charge, and a dark hydrometer
indicates the battery still needs charging.
Check the battery manufacturer’s instructions
to be sure you know what the colours mean.17If the battery is sealed and has no built-in
hydrometer, you can connect a digital
voltmeter across the battery terminals to
check the charge. A fully-charged battery
should read 12.6 volts or higher.
18Further information on the battery and
jump starting can be found in Chapter 5 and
at the front of this manual.
14 Spark plug check and
renewal
1
1Before beginning, obtain the necessary
tools, which will include a spark plug socket
and a set of feeler blades. Special spark plug
gap gauges can be obtained from certain
spark plug manufacturers (see illustration).
2The best procedure to follow when
renewing the spark plugs is to purchase the
new spark plugs beforehand, adjust them to
the proper gap, and then renew each plug one
at a time. When buying the new spark plugs, it
is important to obtain the correct plugs for
your specific engine. This information can be
found in the Specifications section in the front
of this Chapter.
3With the new spark plugs at hand, allow the
engine to cool completely before attempting
plug removal. During this time, each of the
new spark plugs can be inspected for defects
and the gaps can be checked.
4The gap is checked by inserting the proper
thickness gauge between the electrodes at the
tip of the plug (see illustration). The gap
between the electrodes should be the same as
that given in the Specifications. The wire
should just touch each of the electrodes. If the
gap is incorrect, use the notched adjuster to
bend the curved side of the electrode slightly
until the proper gap is achieved (see
illustration). Note: When adjusting the gap of a
new plug, bend only the base of the earth
electrode, do not touch the tip. If the earth
electrode is not exactly over the centre
electrode, use the notched adjuster to align the
two. Check for cracks in the porcelain insulator,
indicating the spark plug should not be used.
1•17
14.4b To change the gap, bend the earth
electrode only, as indicated by the arrows,
and be very careful not to crack or chip the
porcelain insulator surrounding the centre
electrode14.4a Spark plug manufacturers
recommend using a wire-type gauge when
checking the gap - if the wire does not
slide between the electrodes with a slight
drag, adjustment is required
14.1 Tools required for changing spark
plugs
1 Spark plug socket- This will have special
padding inside to protect the spark plug’s
porcelain insulator
2 Torque wrench - Although not mandatory,
using this tool is the best way to ensure the
plugs are tightened properly
3 Ratchet - Standard hand tool to fit the
spark plug socket
4 Extension - Depending on model and
accessories, you may need special
extensions and universal joints to reach one
or more of the plugs
5 Spark plug gap gauge- This gauge for
checking the gap comes in a variety of
styles. Make sure the gap for your engine is
included. Feeler blades may be used
instead
1
Every 12 000 miles
Page 28 of 228
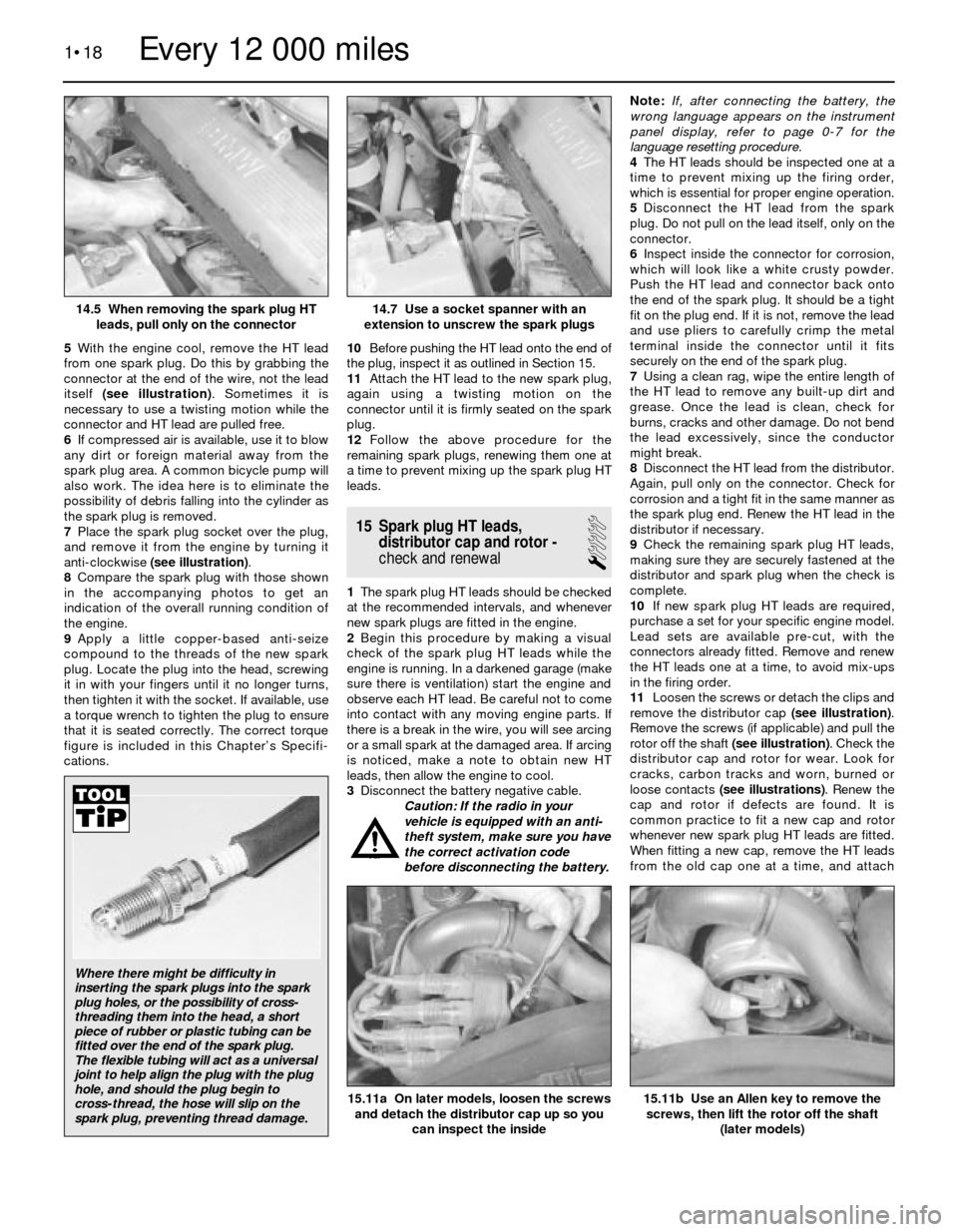
5With the engine cool, remove the HT lead
from one spark plug. Do this by grabbing the
connector at the end of the wire, not the lead
itself (see illustration). Sometimes it is
necessary to use a twisting motion while the
connector and HT lead are pulled free.
6If compressed air is available, use it to blow
any dirt or foreign material away from the
spark plug area. A common bicycle pump will
also work. The idea here is to eliminate the
possibility of debris falling into the cylinder as
the spark plug is removed.
7Place the spark plug socket over the plug,
and remove it from the engine by turning it
anti-clockwise (see illustration).
8Compare the spark plug with those shown
in the accompanying photos to get an
indication of the overall running condition of
the engine.
9Apply a little copper-based anti-seize
compound to the threads of the new spark
plug. Locate the plug into the head, screwing
it in with your fingers until it no longer turns,
then tighten it with the socket. If available, use
a torque wrench to tighten the plug to ensure
that it is seated correctly. The correct torque
figure is included in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.10Before pushing the HT lead onto the end of
the plug, inspect it as outlined in Section 15.
11Attach the HT lead to the new spark plug,
again using a twisting motion on the
connector until it is firmly seated on the spark
plug.
12Follow the above procedure for the
remaining spark plugs, renewing them one at
a time to prevent mixing up the spark plug HT
leads.
15 Spark plug HT leads,
distributor cap and rotor -
check and renewal
1
1The spark plug HT leads should be checked
at the recommended intervals, and whenever
new spark plugs are fitted in the engine.
2Begin this procedure by making a visual
check of the spark plug HT leads while the
engine is running. In a darkened garage (make
sure there is ventilation) start the engine and
observe each HT lead. Be careful not to come
into contact with any moving engine parts. If
there is a break in the wire, you will see arcing
or a small spark at the damaged area. If arcing
is noticed, make a note to obtain new HT
leads, then allow the engine to cool.
3Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
4The HT leads should be inspected one at a
time to prevent mixing up the firing order,
which is essential for proper engine operation.
5Disconnect the HT lead from the spark
plug. Do not pull on the lead itself, only on the
connector.
6Inspect inside the connector for corrosion,
which will look like a white crusty powder.
Push the HT lead and connector back onto
the end of the spark plug. It should be a tight
fit on the plug end. If it is not, remove the lead
and use pliers to carefully crimp the metal
terminal inside the connector until it fits
securely on the end of the spark plug.
7Using a clean rag, wipe the entire length of
the HT lead to remove any built-up dirt and
grease. Once the lead is clean, check for
burns, cracks and other damage. Do not bend
the lead excessively, since the conductor
might break.
8Disconnect the HT lead from the distributor.
Again, pull only on the connector. Check for
corrosion and a tight fit in the same manner as
the spark plug end. Renew the HT lead in the
distributor if necessary.
9Check the remaining spark plug HT leads,
making sure they are securely fastened at the
distributor and spark plug when the check is
complete.
10If new spark plug HT leads are required,
purchase a set for your specific engine model.
Lead sets are available pre-cut, with the
connectors already fitted. Remove and renew
the HT leads one at a time, to avoid mix-ups
in the firing order.
11Loosen the screws or detach the clips and
remove the distributor cap (see illustration).
Remove the screws (if applicable) and pull the
rotor off the shaft (see illustration). Check the
distributor cap and rotor for wear. Look for
cracks, carbon tracks and worn, burned or
loose contacts (see illustrations). Renew the
cap and rotor if defects are found. It is
common practice to fit a new cap and rotor
whenever new spark plug HT leads are fitted.
When fitting a new cap, remove the HT leads
from the old cap one at a time, and attach
1•18
15.11b Use an Allen key to remove the
screws, then lift the rotor off the shaft
(later models)15.11a On later models, loosen the screws
and detach the distributor cap up so you
can inspect the inside
14.7 Use a socket spanner with an
extension to unscrew the spark plugs14.5 When removing the spark plug HT
leads, pull only on the connector
Every 12 000 miles
Where there might be difficulty in
inserting the spark plugs into the spark
plug holes, or the possibility of cross-
threading them into the head, a short
piece of rubber or plastic tubing can be
fitted over the end of the spark plug.
The flexible tubing will act as a universal
joint to help align the plug with the plug
hole, and should the plug begin to
cross-thread, the hose will slip on the
spark plug, preventing thread damage.
Page 39 of 228
1 General information
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to in-
vehicle engine repair procedures. All
information concerning engine removal and
refitting and engine block and cylinder head
overhaul can be found in Chapter 2B.
The following repair procedures are based
on the assumption that the engine is still fitted
in the vehicle. If the engine has been removed
from the vehicle and mounted on a stand,
many of the steps outlined in this Part of
Chapter 2 will not apply.
The Specifications included in this Part of
Chapter 2 apply only to the procedures
contained in this Part. Chapter 2B contains
the Specifications necessary for cylinder head
and engine block rebuilding.
The single overhead camshaft four- and
six-cylinder engines covered in this manual
are very similar in design. Where there are
differences, they will be pointed out.
The means by which the overhead
camshaft is driven varies according to engine
type; M10 and M30 engines use a timing
chain, while M20 and M40 engines have a
timing belt.
2 Repair operations possible
with the engine in the vehicle
Many major repair operations can be
accomplished without removing the engine
from the vehicle.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and help keep dirt out of
the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (see Chapter 11 if necessary).
Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint. Special pads are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for gasket or seal
renewal, the repairs can generally be made
with the engine in the vehicle. The intake and
exhaust manifold gaskets, sump gasket,
crankshaft oil seals and cylinder head gasket
are all accessible with the engine in place.
Exterior components, such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator, the distributor and the fuel system
components, can be removed for repair with
the engine in place.
The cylinder head can be removed without
removing the engine, so this procedure is
covered in this Part of Chapter 2. Camshaft,
rocker arm and valve component servicing ismost easily accomplished with the cylinder
head removed; these procedures are covered
in Part B of this Chapter. Note, however, that
the camshaft on the M40 engine may be
removed with the engine in the vehicle since it
is retained by bearing caps.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine in
the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved.
3 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
No 1 piston- locating
2
Note 1:The following procedure is based on
the assumption that the distributor (if
applicable) is correctly fitted. If you are trying
to locate TDC to refit the distributor correctly,
piston position must be determined by feeling
for compression at the No 1 spark plug hole,
then aligning the ignition timing marks or
inserting the timing tool in the flywheel, as
applicable.
Note 2:The No 1 cylinder is the one closest to
the radiator.
1Top Dead Centre (TDC) is the highest point
in the cylinder that each piston reaches as it
travels up and down when the crankshaft
turns. Each piston reaches TDC on the
compression stroke and again on the exhaust
stroke, but TDC generally refers to piston
position on the compression stroke.
2Positioning the piston at TDC is an essential
part of many procedures, such as timing belt
or chain removal and distributor removal.
3Before beginning this procedure, be sure to
place the transmission in Neutral, and apply
the handbrake or chock the rear wheels. Also,
disable the ignition system by detaching the
coil wire from the centre terminal of the
distributor cap, and earthing it on the engine
block with a jumper wire. Remove the spark
plugs (see Chapter 1).
4In order to bring any piston to TDC, the
crankshaft must be turned using one of the
methods outlined below. When looking at the
front of the engine, normal crankshaft rotation
is clockwise.
(a) The preferred method is to turn the
crankshaft with a socket and ratchet
attached to the bolt threaded into the
front of the crankshaft.
(b) A remote starter switch, which may save
some time, can also be used. Follow the
instructions included with the switch.
Once the piston is close to TDC, use a
socket and ratchet as described in the
previous paragraph.
(c) If an assistant is available to turn the
ignition switch to the Start position in
short bursts, you can get the piston close
to TDC without a remote starter switch.Make sure your assistant is out of the
vehicle, away from the ignition switch,
then use a socket and ratchet as
described in (a) to complete the
procedure.
5Note the position of the terminal for the
No 1 spark plug lead on the distributor cap. If
the terminal isn’t marked, follow the plug lead
from the No 1 cylinder spark plug to the cap
(No 1 cylinder is nearest the radiator).
6Use a felt-tip pen or chalk to make a mark
directly below the No 1 terminal on the
distributor body or timing cover.
7Detach the distributor cap, and set it aside
(see Chapter 1 if necessary).
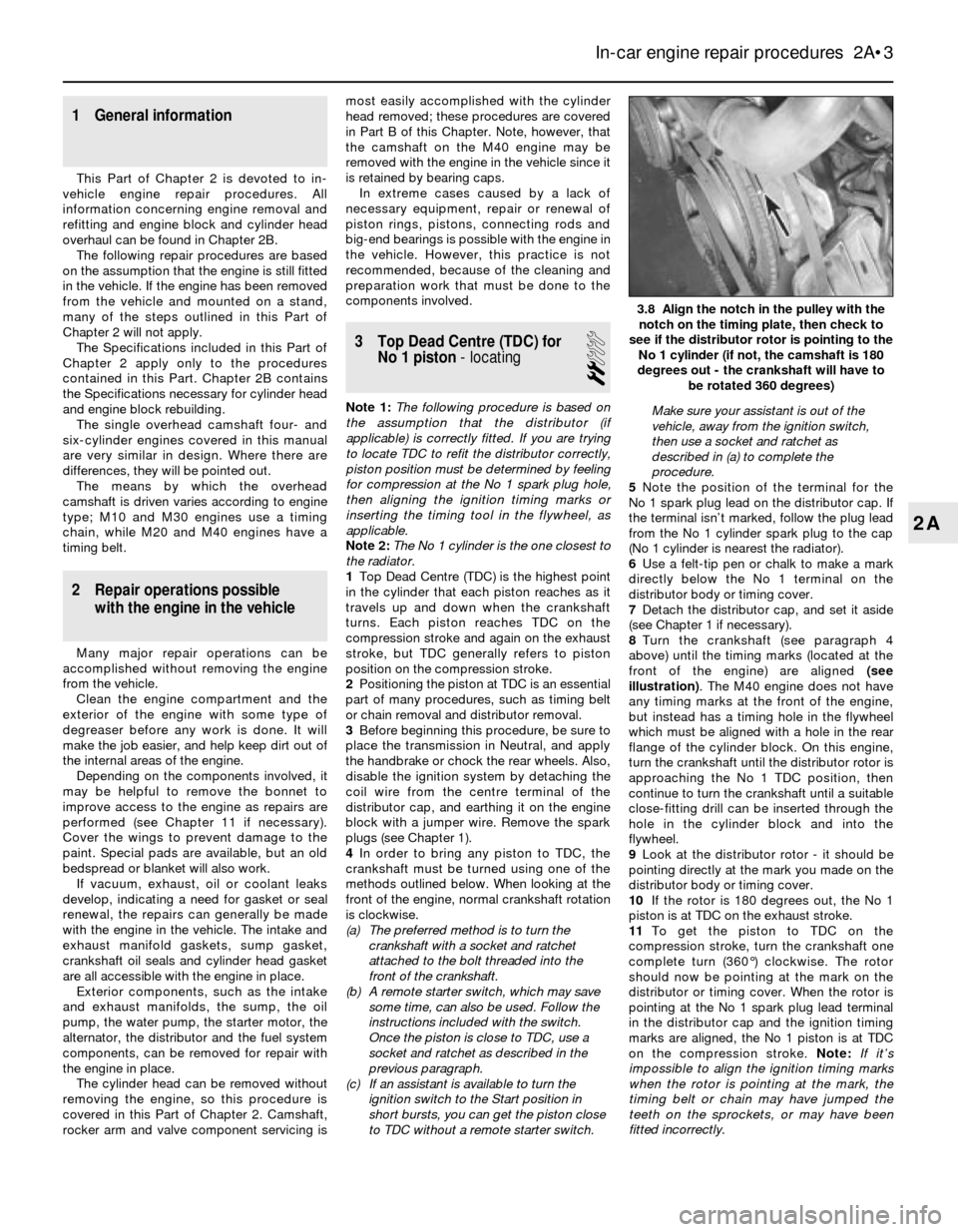
8Turn the crankshaft (see paragraph 4
above) until the timing marks (located at the
front of the engine) are aligned (see
illustration). The M40 engine does not have
any timing marks at the front of the engine,
but instead has a timing hole in the flywheel
which must be aligned with a hole in the rear
flange of the cylinder block. On this engine,
turn the crankshaft until the distributor rotor is
approaching the No 1 TDC position, then
continue to turn the crankshaft until a suitable
close-fitting drill can be inserted through the
hole in the cylinder block and into the
flywheel.
9Look at the distributor rotor - it should be
pointing directly at the mark you made on the
distributor body or timing cover.
10If the rotor is 180 degrees out, the No 1
piston is at TDC on the exhaust stroke.
11To get the piston to TDC on the
compression stroke, turn the crankshaft one
complete turn (360°) clockwise. The rotor
should now be pointing at the mark on the
distributor or timing cover. When the rotor is
pointing at the No 1 spark plug lead terminal
in the distributor cap and the ignition timing
marks are aligned, the No 1 piston is at TDC
on the compression stroke. Note:If it’s
impossible to align the ignition timing marks
when the rotor is pointing at the mark, the
timing belt or chain may have jumped the
teeth on the sprockets, or may have been
fitted incorrectly.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•3
3.8 Align the notch in the pulley with the
notch on the timing plate, then check to
see if the distributor rotor is pointing to the
No 1 cylinder (if not, the camshaft is 180
degrees out - the crankshaft will have to
be rotated 360 degrees)
2A
Page 40 of 228
12After the No 1 piston has been positioned
at TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for
any of the remaining pistons can be located
by turning the crankshaft and following the
firing order. Mark the remaining spark plug
lead terminal locations just like you did for the
No 1 terminal, then number the marks to
correspond with the cylinder numbers. As you
turn the crankshaft, the rotor will also turn.
When it’s pointing directly at one of the marks
on the distributor, the piston for that particular
cylinder is at TDC on the compression stroke.
4 Valve cover-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Detach the breather hose from the valve
cover.
3On M20 engines, unbolt and remove the
intake manifold support bracket and, if
applicable, the bracket for the engine sensors
or idle air stabiliser (it will probably be
necessary to disconnect the electrical
connectors from the sensors and stabiliser).
4On M30 engines, disconnect the electrical
connector for the airflow sensor. Unclip the
electrical harness, moving it out of the way.
5Where necessary on M30 engines, remove
the hoses and fittings from the intake air hose,
then loosen the clamp and separate the hose
from the throttle body. Unscrew the mounting
nuts for the air cleaner housing, and remove
the housing together with the air hose and
airflow sensor.
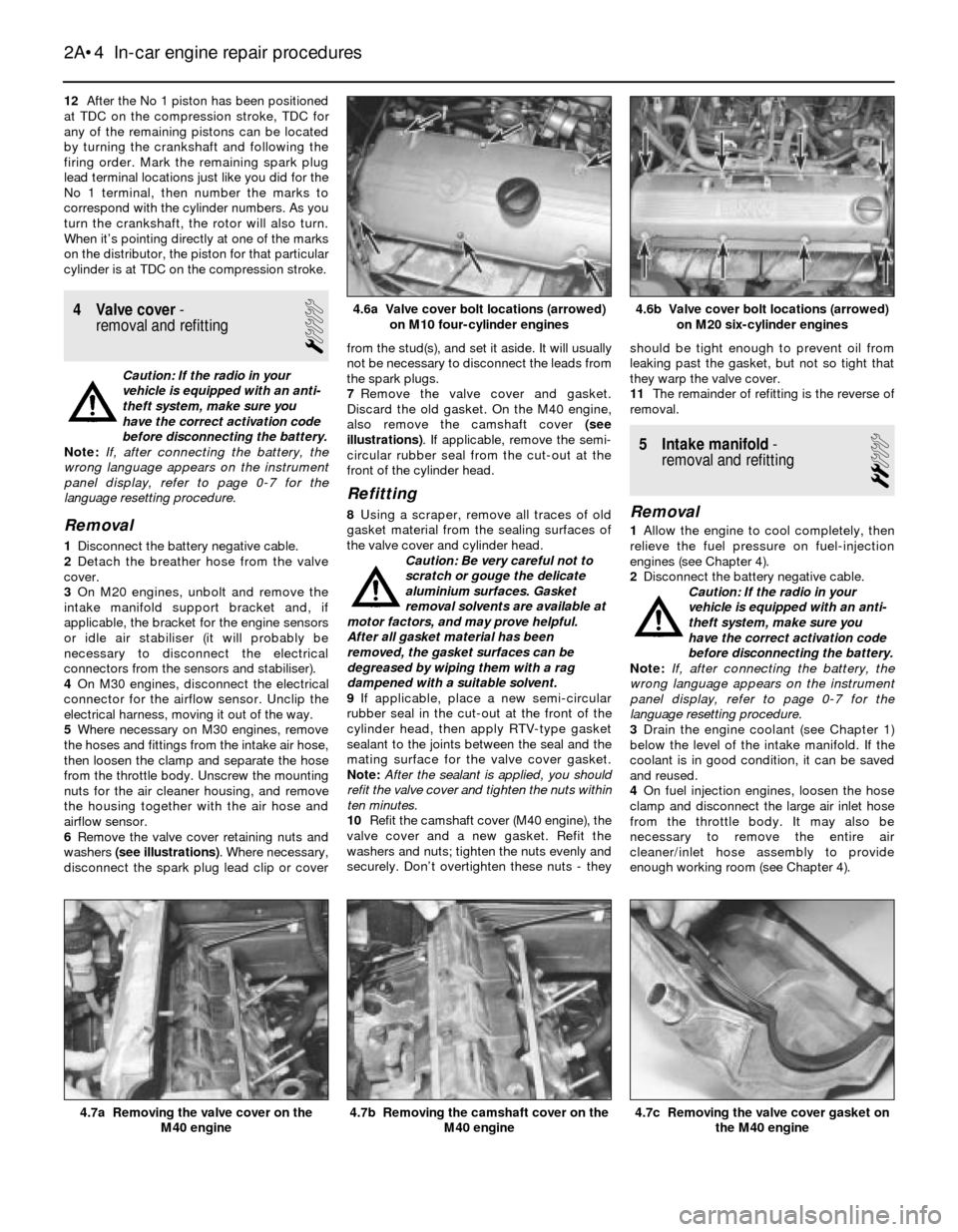
6Remove the valve cover retaining nuts and
washers (see illustrations). Where necessary,
disconnect the spark plug lead clip or coverfrom the stud(s), and set it aside. It will usually
not be necessary to disconnect the leads from
the spark plugs.
7Remove the valve cover and gasket.
Discard the old gasket. On the M40 engine,
also remove the camshaft cover (see
illustrations). If applicable, remove the semi-
circular rubber seal from the cut-out at the
front of the cylinder head.
Refitting
8Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the valve cover and cylinder head.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Gasket
removal solvents are available at
motor factors, and may prove helpful.
After all gasket material has been
removed, the gasket surfaces can be
degreased by wiping them with a rag
dampened with a suitable solvent.
9If applicable, place a new semi-circular
rubber seal in the cut-out at the front of the
cylinder head, then apply RTV-type gasket
sealant to the joints between the seal and the
mating surface for the valve cover gasket.
Note:After the sealant is applied, you should
refit the valve cover and tighten the nuts within
ten minutes.
10Refit the camshaft cover (M40 engine), the
valve cover and a new gasket. Refit the
washers and nuts; tighten the nuts evenly and
securely. Don’t overtighten these nuts - theyshould be tight enough to prevent oil from
leaking past the gasket, but not so tight that
they warp the valve cover.
11The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
5 Intake manifold-
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Allow the engine to cool completely, then
relieve the fuel pressure on fuel-injection
engines (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Drain the engine coolant (see Chapter 1)
below the level of the intake manifold. If the
coolant is in good condition, it can be saved
and reused.
4On fuel injection engines, loosen the hose
clamp and disconnect the large air inlet hose
from the throttle body. It may also be
necessary to remove the entire air
cleaner/inlet hose assembly to provide
enough working room (see Chapter 4).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
4.7b Removing the camshaft cover on the
M40 engine4.7a Removing the valve cover on the
M40 engine4.7c Removing the valve cover gasket on
the M40 engine
4.6b Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M20 six-cylinder engines4.6a Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M10 four-cylinder engines
Page 60 of 228
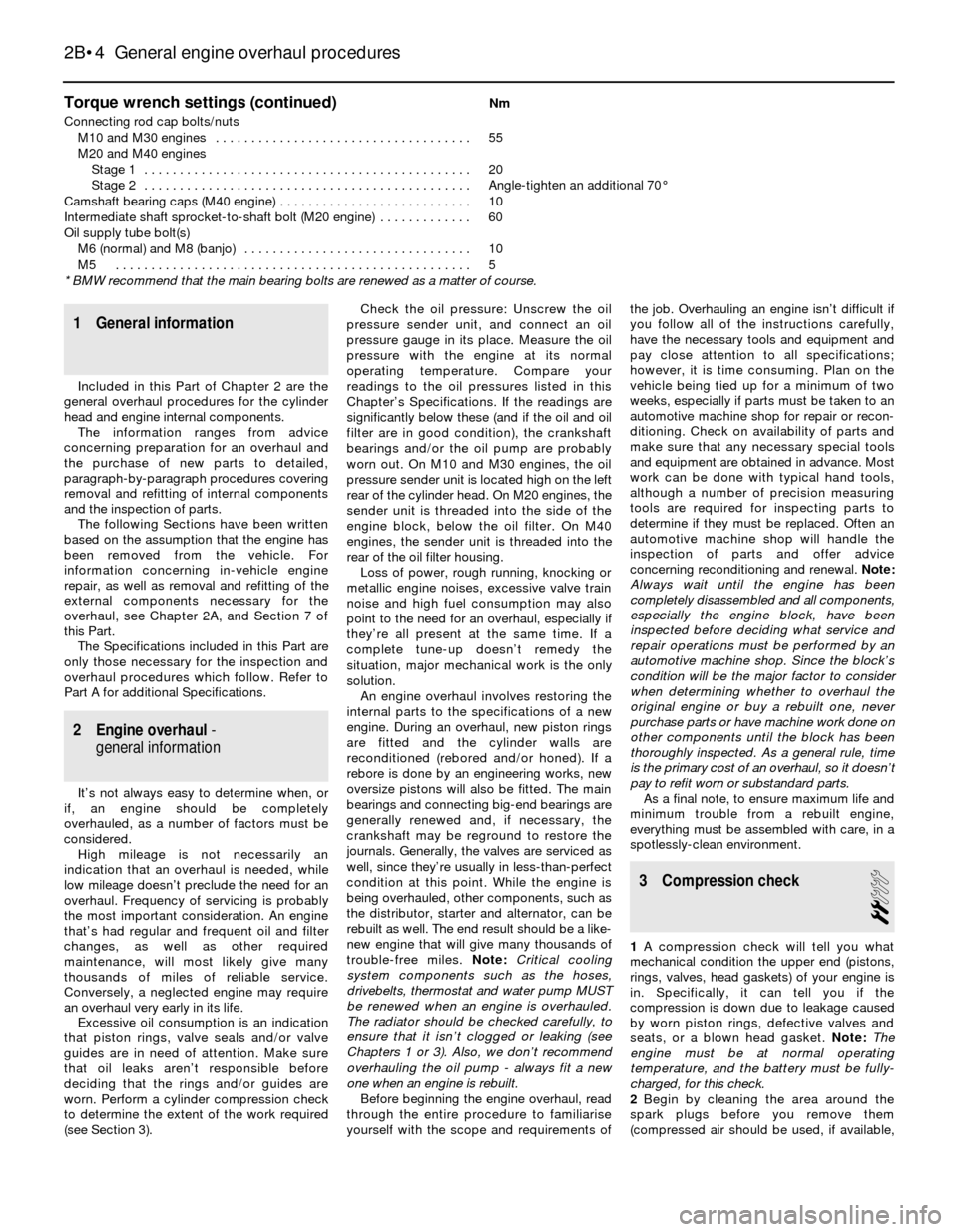
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nm
Connecting rod cap bolts/nuts
M10 and M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
M20 and M40 engines
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 70°
Camshaft bearing caps (M40 engine) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Intermediate shaft sprocket-to-shaft bolt (M20 engine) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Oil supply tube bolt(s)
M6 (normal) and M8 (banjo) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
M5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
* BMW recommend that the main bearing bolts are renewed as a matter of course.
2B•4 General engine overhaul procedures
1 General information
Included in this Part of Chapter 2 are the
general overhaul procedures for the cylinder
head and engine internal components.
The information ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of new parts to detailed,
paragraph-by-paragraph procedures covering
removal and refitting of internal components
and the inspection of parts.
The following Sections have been written
based on the assumption that the engine has
been removed from the vehicle. For
information concerning in-vehicle engine
repair, as well as removal and refitting of the
external components necessary for the
overhaul, see Chapter 2A, and Section 7 of
this Part.
The Specifications included in this Part are
only those necessary for the inspection and
overhaul procedures which follow. Refer to
Part A for additional Specifications.
2 Engine overhaul-
general information
It’s not always easy to determine when, or
if, an engine should be completely
overhauled, as a number of factors must be
considered.
High mileage is not necessarily an
indication that an overhaul is needed, while
low mileage doesn’t preclude the need for an
overhaul. Frequency of servicing is probably
the most important consideration. An engine
that’s had regular and frequent oil and filter
changes, as well as other required
maintenance, will most likely give many
thousands of miles of reliable service.
Conversely, a neglected engine may require
an overhaul very early in its life.
Excessive oil consumption is an indication
that piston rings, valve seals and/or valve
guides are in need of attention. Make sure
that oil leaks aren’t responsible before
deciding that the rings and/or guides are
worn. Perform a cylinder compression check
to determine the extent of the work required
(see Section 3).Check the oil pressure: Unscrew the oil
pressure sender unit, and connect an oil
pressure gauge in its place. Measure the oil
pressure with the engine at its normal
operating temperature. Compare your
readings to the oil pressures listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. If the readings are
significantly below these (and if the oil and oil
filter are in good condition), the crankshaft
bearings and/or the oil pump are probably
worn out. On M10 and M30 engines, the oil
pressure sender unit is located high on the left
rear of the cylinder head. On M20 engines, the
sender unit is threaded into the side of the
engine block, below the oil filter. On M40
engines, the sender unit is threaded into the
rear of the oil filter housing.
Loss of power, rough running, knocking or
metallic engine noises, excessive valve train
noise and high fuel consumption may also
point to the need for an overhaul, especially if
they’re all present at the same time. If a
complete tune-up doesn’t remedy the
situation, major mechanical work is the only
solution.
An engine overhaul involves restoring the
internal parts to the specifications of a new
engine. During an overhaul, new piston rings
are fitted and the cylinder walls are
reconditioned (rebored and/or honed). If a
rebore is done by an engineering works, new
oversize pistons will also be fitted. The main
bearings and connecting big-end bearings are
generally renewed and, if necessary, the
crankshaft may be reground to restore the
journals. Generally, the valves are serviced as
well, since they’re usually in less-than-perfect
condition at this point. While the engine is
being overhauled, other components, such as
the distributor, starter and alternator, can be
rebuilt as well. The end result should be a like-
new engine that will give many thousands of
trouble-free miles. Note: Critical cooling
system components such as the hoses,
drivebelts, thermostat and water pump MUST
be renewed when an engine is overhauled.
The radiator should be checked carefully, to
ensure that it isn’t clogged or leaking (see
Chapters 1 or 3). Also, we don’t recommend
overhauling the oil pump - always fit a new
one when an engine is rebuilt.
Before beginning the engine overhaul, read
through the entire procedure to familiarise
yourself with the scope and requirements ofthe job. Overhauling an engine isn’t difficult if
you follow all of the instructions carefully,
have the necessary tools and equipment and
pay close attention to all specifications;
however, it is time consuming. Plan on the
vehicle being tied up for a minimum of two
weeks, especially if parts must be taken to an
automotive machine shop for repair or recon-
ditioning. Check on availability of parts and
make sure that any necessary special tools
and equipment are obtained in advance. Most
work can be done with typical hand tools,
although a number of precision measuring
tools are required for inspecting parts to
determine if they must be replaced. Often an
automotive machine shop will handle the
inspection of parts and offer advice
concerning reconditioning and renewal. Note:
Always wait until the engine has been
completely disassembled and all components,
especially the engine block, have been
inspected before deciding what service and
repair operations must be performed by an
automotive machine shop. Since the block’s
condition will be the major factor to consider
when determining whether to overhaul the
original engine or buy a rebuilt one, never
purchase parts or have machine work done on
other components until the block has been
thoroughly inspected. As a general rule, time
is the primary cost of an overhaul, so it doesn’t
pay to refit worn or substandard parts.
As a final note, to ensure maximum life and
minimum trouble from a rebuilt engine,
everything must be assembled with care, in a
spotlessly-clean environment.
3 Compression check
2
1A compression check will tell you what
mechanical condition the upper end (pistons,
rings, valves, head gaskets) of your engine is
in. Specifically, it can tell you if the
compression is down due to leakage caused
by worn piston rings, defective valves and
seats, or a blown head gasket. Note:The
engine must be at normal operating
temperature, and the battery must be fully-
charged, for this check.
2Begin by cleaning the area around the
spark plugs before you remove them
(compressed air should be used, if available,