air suspension BMW 3 SERIES 1989 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1989, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1989 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 143 of 228

10
General
Power steering fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Tyres
Tyre sizes
3-Series, E30
316 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175/70x14
316i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175/70x14, 195/65x14
318i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175/70x14
320i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195/65x14
325i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195/65x14, 200/60x356, 205/55x15
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175x14
518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175x14
525i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175x14, 195/70x14
528i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195/70x14
535i and M535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220/55x390
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195/65x15
520i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195/65x15, 225/60x15
525i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195/65x15, 205/65x15, 225/65x15
530i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205/65x15, 225/60x15
535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225/60x15, 240/45x415
Tyre pressures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications
Chapter 10 Suspension and steering systems
Balljoints - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Control arm (3-Series) - inspection, removal and refitting,
and bush renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Control and thrust arms (5-Series) - inspection, removal and
refitting, and bush renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Front anti-roll bar - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Front hub and wheel bearing assembly - removal and refitting . . . . 8
Front strut assembly - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Power steering fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Power steering pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Power steering system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Rack-and-pinion steering gear (3-Series) - removal and refitting . . . 19
Rear anti-roll bar - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Rear coil springs (3-Series) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Rear shock absorbers (3-Series) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 9
Rear shock absorber/coil spring assembly (5-Series) - removal
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11Rear trailing arms (3-Series) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Rear trailing arms (5-Series) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Rear wheel bearings - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Steering and suspension check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Steering box (5-Series) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Steering gear boots (3-Series) - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Steering linkage (5-Series) - inspection, removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Steering system - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Steering wheel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Strut or shock absorber/coil spring - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Suspension and steering checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Track rod ends - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Tyre and tyre pressure checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Tyre rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Wheel alignment - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Wheels and tyres - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
10•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
Page 146 of 228
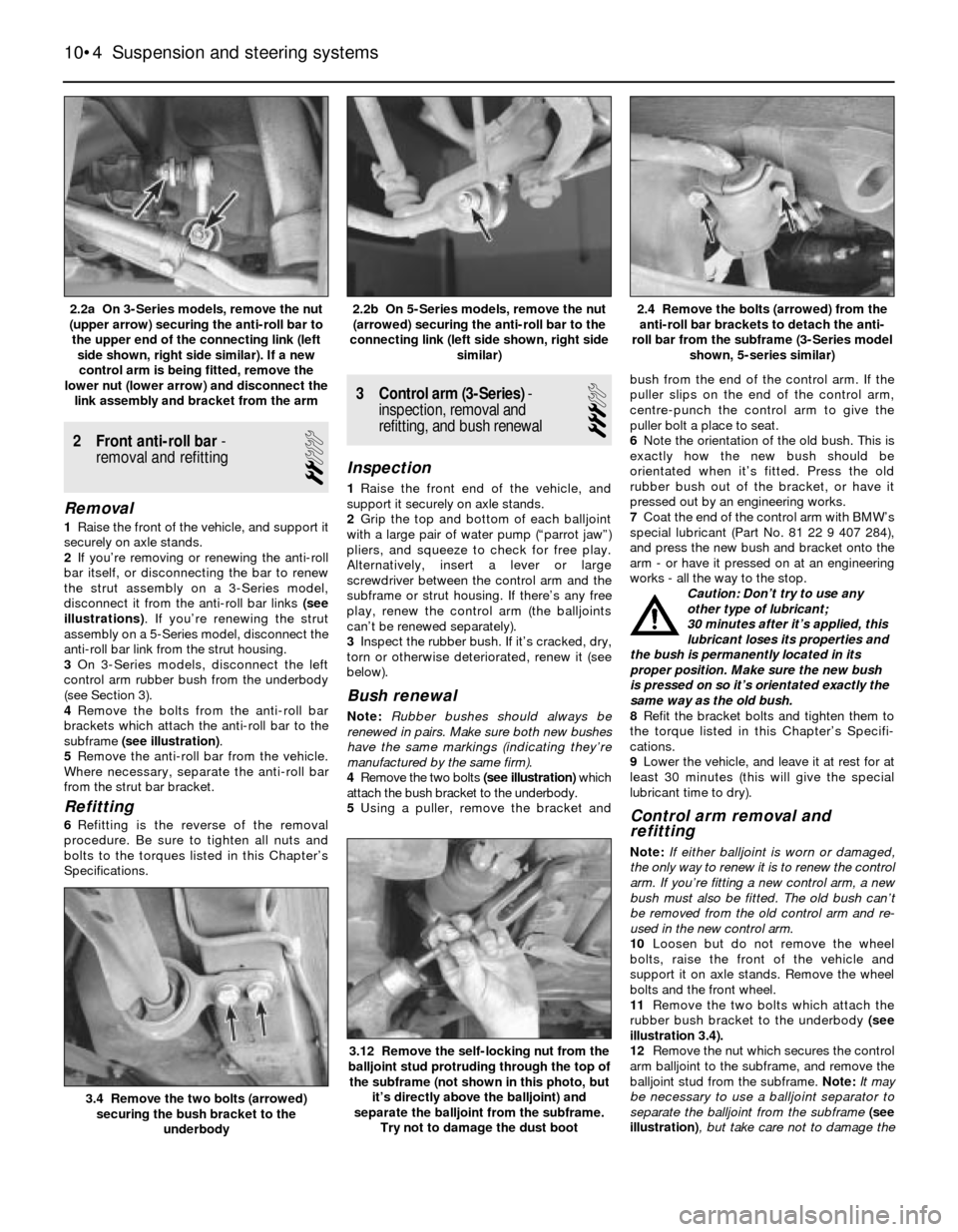
2 Front anti-roll bar-
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands.
2If you’re removing or renewing the anti-roll
bar itself, or disconnecting the bar to renew
the strut assembly on a 3-Series model,
disconnect it from the anti-roll bar links (see
illustrations). If you’re renewing the strut
assembly on a 5-Series model, disconnect the
anti-roll bar link from the strut housing.
3On 3-Series models, disconnect the left
control arm rubber bush from the underbody
(see Section 3).
4Remove the bolts from the anti-roll bar
brackets which attach the anti-roll bar to the
subframe (see illustration).
5Remove the anti-roll bar from the vehicle.
Where necessary, separate the anti-roll bar
from the strut bar bracket.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Be sure to tighten all nuts and
bolts to the torques listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
3 Control arm (3-Series)-
inspection, removal and
refitting, and bush renewal
3
Inspection
1Raise the front end of the vehicle, and
support it securely on axle stands.
2Grip the top and bottom of each balljoint
with a large pair of water pump (“parrot jaw”)
pliers, and squeeze to check for free play.
Alternatively, insert a lever or large
screwdriver between the control arm and the
subframe or strut housing. If there’s any free
play, renew the control arm (the balljoints
can’t be renewed separately).
3Inspect the rubber bush. If it’s cracked, dry,
torn or otherwise deteriorated, renew it (see
below).
Bush renewal
Note:Rubber bushes should always be
renewed in pairs. Make sure both new bushes
have the same markings (indicating they’re
manufactured by the same firm).
4Remove the two bolts (see illustration)which
attach the bush bracket to the underbody.
5Using a puller, remove the bracket andbush from the end of the control arm. If the
puller slips on the end of the control arm,
centre-punch the control arm to give the
puller bolt a place to seat.
6Note the orientation of the old bush. This is
exactly how the new bush should be
orientated when it’s fitted. Press the old
rubber bush out of the bracket, or have it
pressed out by an engineering works.
7Coat the end of the control arm with BMW’s
special lubricant (Part No. 81 22 9 407 284),
and press the new bush and bracket onto the
arm - or have it pressed on at an engineering
works - all the way to the stop.
Caution: Don’t try to use any
other type of lubricant;
30 minutes after it’s applied, this
lubricant loses its properties and
the bush is permanently located in its
proper position. Make sure the new bush
is pressed on so it’s orientated exactly the
same way as the old bush.
8Refit the bracket bolts and tighten them to
the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.
9Lower the vehicle, and leave it at rest for at
least 30 minutes (this will give the special
lubricant time to dry).
Control arm removal and
refitting
Note:If either balljoint is worn or damaged,
the only way to renew it is to renew the control
arm. If you’re fitting a new control arm, a new
bush must also be fitted. The old bush can’t
be removed from the old control arm and re-
used in the new control arm.
10Loosen but do not remove the wheel
bolts, raise the front of the vehicle and
support it on axle stands. Remove the wheel
bolts and the front wheel.
11Remove the two bolts which attach the
rubber bush bracket to the underbody (see
illustration 3.4).
12Remove the nut which secures the control
arm balljoint to the subframe, and remove the
balljoint stud from the subframe. Note:It may
be necessary to use a balljoint separator to
separate the balljoint from the subframe (see
illustration), but take care not to damage the
10•4 Suspension and steering systems
3.12 Remove the self-locking nut from the
balljoint stud protruding through the top of
the subframe (not shown in this photo, but
it’s directly above the balljoint) and
separate the balljoint from the subframe.
Try not to damage the dust boot
3.4 Remove the two bolts (arrowed)
securing the bush bracket to the
underbody
2.4 Remove the bolts (arrowed) from the
anti-roll bar brackets to detach the anti-
roll bar from the subframe (3-Series model
shown, 5-series similar)2.2b On 5-Series models, remove the nut
(arrowed) securing the anti-roll bar to the
connecting link (left side shown, right side
similar)2.2a On 3-Series models, remove the nut
(upper arrow) securing the anti-roll bar to
the upper end of the connecting link (left
side shown, right side similar). If a new
control arm is being fitted, remove the
lower nut (lower arrow) and disconnect the
link assembly and bracket from the arm
Page 147 of 228
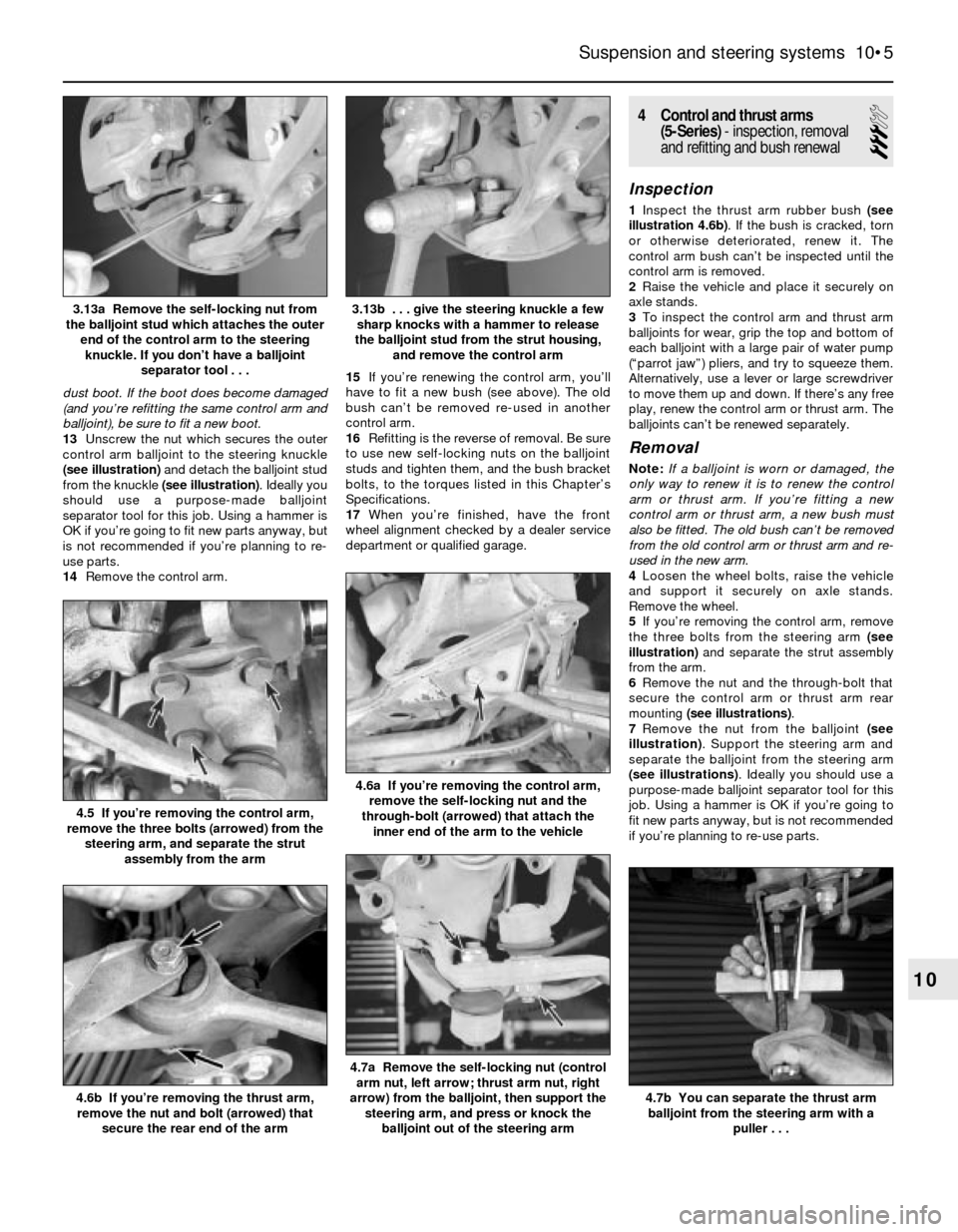
dust boot. If the boot does become damaged
(and you’re refitting the same control arm and
balljoint), be sure to fit a new boot.
13Unscrew the nut which secures the outer
control arm balljoint to the steering knuckle
(see illustration)and detach the balljoint stud
from the knuckle (see illustration). Ideally you
should use a purpose-made balljoint
separator tool for this job. Using a hammer is
OK if you’re going to fit new parts anyway, but
is not recommended if you’re planning to re-
use parts.
14Remove the control arm.15If you’re renewing the control arm, you’ll
have to fit a new bush (see above). The old
bush can’t be removed re-used in another
control arm.
16Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to use new self-locking nuts on the balljoint
studs and tighten them, and the bush bracket
bolts, to the torques listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
17When you’re finished, have the front
wheel alignment checked by a dealer service
department or qualified garage.
4 Control and thrust arms
(5-Series)- inspection, removal
and refitting and bush renewal
3
Inspection
1Inspect the thrust arm rubber bush (see
illustration 4.6b). If the bush is cracked, torn
or otherwise deteriorated, renew it. The
control arm bush can’t be inspected until the
control arm is removed.
2Raise the vehicle and place it securely on
axle stands.
3To inspect the control arm and thrust arm
balljoints for wear, grip the top and bottom of
each balljoint with a large pair of water pump
(“parrot jaw”) pliers, and try to squeeze them.
Alternatively, use a lever or large screwdriver
to move them up and down. If there’s any free
play, renew the control arm or thrust arm. The
balljoints can’t be renewed separately.
Removal
Note:If a balljoint is worn or damaged, the
only way to renew it is to renew the control
arm or thrust arm. If you’re fitting a new
control arm or thrust arm, a new bush must
also be fitted. The old bush can’t be removed
from the old control arm or thrust arm and re-
used in the new arm.
4Loosen the wheel bolts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel.
5If you’re removing the control arm, remove
the three bolts from the steering arm (see
illustration)and separate the strut assembly
from the arm.
6Remove the nut and the through-bolt that
secure the control arm or thrust arm rear
mounting (see illustrations).
7Remove the nut from the balljoint (see
illustration). Support the steering arm and
separate the balljoint from the steering arm
(see illustrations). Ideally you should use a
purpose-made balljoint separator tool for this
job. Using a hammer is OK if you’re going to
fit new parts anyway, but is not recommended
if you’re planning to re-use parts.
Suspension and steering systems 10•5
4.5 If you’re removing the control arm,
remove the three bolts (arrowed) from the
steering arm, and separate the strut
assembly from the arm
3.13b . . . give the steering knuckle a few
sharp knocks with a hammer to release
the balljoint stud from the strut housing,
and remove the control arm3.13a Remove the self-locking nut from
the balljoint stud which attaches the outer
end of the control arm to the steering
knuckle. If you don’t have a balljoint
separator tool . . .
4.7b You can separate the thrust arm
balljoint from the steering arm with a
puller . . .
4.6a If you’re removing the control arm,
remove the self-locking nut and the
through-bolt (arrowed) that attach the
inner end of the arm to the vehicle
4.7a Remove the self-locking nut (control
arm nut, left arrow; thrust arm nut, right
arrow) from the balljoint, then support the
steering arm, and press or knock the
balljoint out of the steering arm
4.6b If you’re removing the thrust arm,
remove the nut and bolt (arrowed) that
secure the rear end of the arm
10
Page 148 of 228
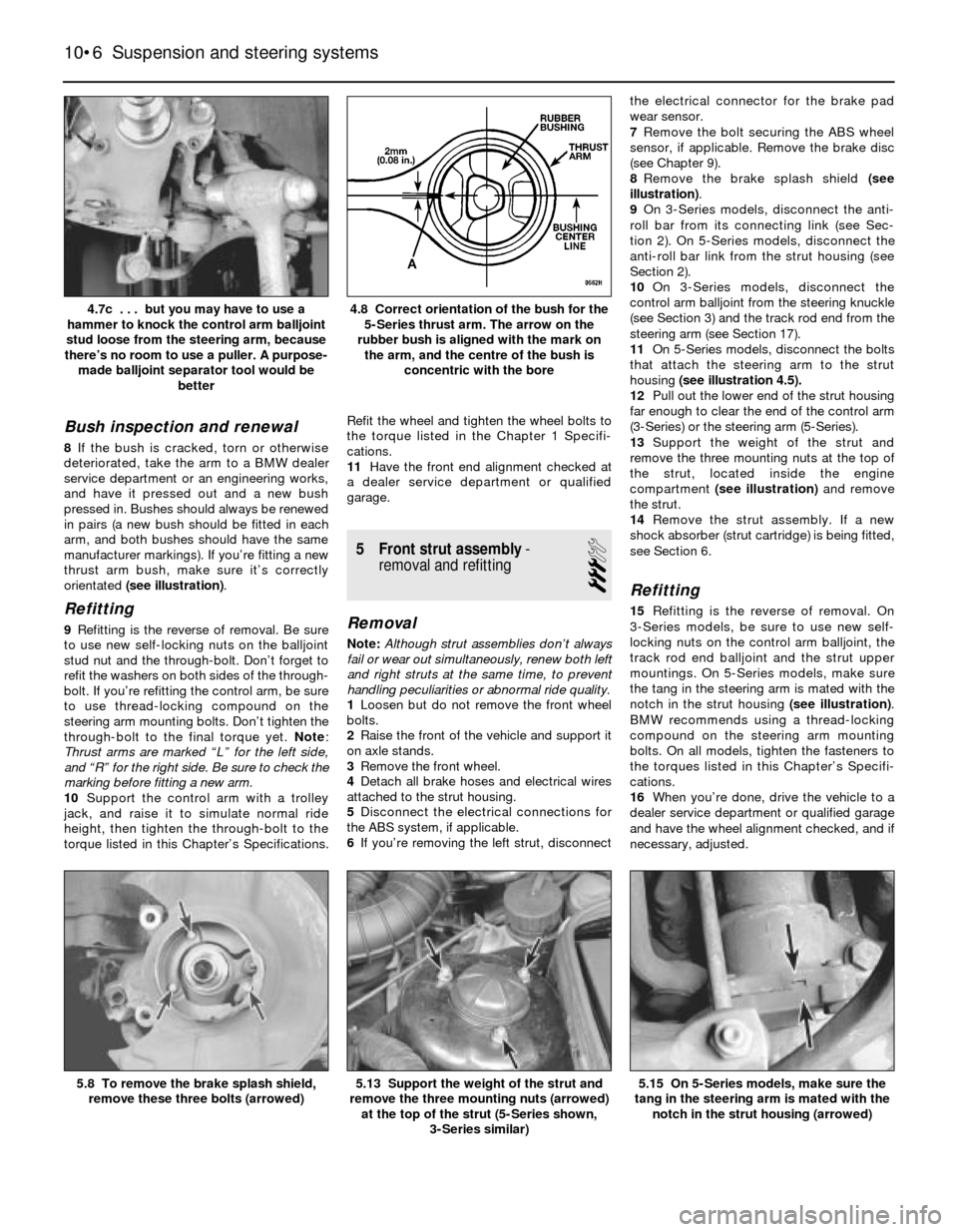
Bush inspection and renewal
8If the bush is cracked, torn or otherwise
deteriorated, take the arm to a BMW dealer
service department or an engineering works,
and have it pressed out and a new bush
pressed in. Bushes should always be renewed
in pairs (a new bush should be fitted in each
arm, and both bushes should have the same
manufacturer markings). If you’re fitting a new
thrust arm bush, make sure it’s correctly
orientated (see illustration).
Refitting
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to use new self-locking nuts on the balljoint
stud nut and the through-bolt. Don’t forget to
refit the washers on both sides of the through-
bolt. If you’re refitting the control arm, be sure
to use thread-locking compound on the
steering arm mounting bolts. Don’t tighten the
through-bolt to the final torque yet. Note:
Thrust arms are marked “L” for the left side,
and “R” for the right side. Be sure to check the
marking before fitting a new arm.
10Support the control arm with a trolley
jack, and raise it to simulate normal ride
height, then tighten the through-bolt to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.Refit the wheel and tighten the wheel bolts to
the torque listed in the Chapter 1 Specifi-
cations.
11Have the front end alignment checked at
a dealer service department or qualified
garage.
5 Front strut assembly-
removal and refitting
3
Removal
Note:Although strut assemblies don’t always
fail or wear out simultaneously, renew both left
and right struts at the same time, to prevent
handling peculiarities or abnormal ride quality.
1Loosen but do not remove the front wheel
bolts.
2Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on axle stands.
3Remove the front wheel.
4Detach all brake hoses and electrical wires
attached to the strut housing.
5Disconnect the electrical connections for
the ABS system, if applicable.
6If you’re removing the left strut, disconnectthe electrical connector for the brake pad
wear sensor.
7Remove the bolt securing the ABS wheel
sensor, if applicable. Remove the brake disc
(see Chapter 9).
8Remove the brake splash shield (see
illustration).
9On 3-Series models, disconnect the anti-
roll bar from its connecting link (see Sec-
tion 2). On 5-Series models, disconnect the
anti-roll bar link from the strut housing (see
Section 2).
10On 3-Series models, disconnect the
control arm balljoint from the steering knuckle
(see Section 3) and the track rod end from the
steering arm (see Section 17).
11On 5-Series models, disconnect the bolts
that attach the steering arm to the strut
housing (see illustration 4.5).
12Pull out the lower end of the strut housing
far enough to clear the end of the control arm
(3-Series) or the steering arm (5-Series).
13Support the weight of the strut and
remove the three mounting nuts at the top of
the strut, located inside the engine
compartment (see illustration)and remove
the strut.
14Remove the strut assembly. If a new
shock absorber (strut cartridge) is being fitted,
see Section 6.
Refitting
15Refitting is the reverse of removal. On
3-Series models, be sure to use new self-
locking nuts on the control arm balljoint, the
track rod end balljoint and the strut upper
mountings. On 5-Series models, make sure
the tang in the steering arm is mated with the
notch in the strut housing (see illustration).
BMW recommends using a thread-locking
compound on the steering arm mounting
bolts. On all models, tighten the fasteners to
the torques listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.
16When you’re done, drive the vehicle to a
dealer service department or qualified garage
and have the wheel alignment checked, and if
necessary, adjusted.
10•6 Suspension and steering systems
5.15 On 5-Series models, make sure the
tang in the steering arm is mated with the
notch in the strut housing (arrowed)5.13 Support the weight of the strut and
remove the three mounting nuts (arrowed)
at the top of the strut (5-Series shown,
3-Series similar)5.8 To remove the brake splash shield,
remove these three bolts (arrowed)
4.8 Correct orientation of the bush for the
5-Series thrust arm. The arrow on the
rubber bush is aligned with the mark on
the arm, and the centre of the bush is
concentric with the bore4.7c . . . but you may have to use a
hammer to knock the control arm balljoint
stud loose from the steering arm, because
there’s no room to use a puller. A purpose-
made balljoint separator tool would be
better
Page 153 of 228

the longer side of the sleeve facing towards
the centre of the vehicle.
Refitting
12Refitting is the reverse of removal. Refit
the inner pivot bolt first. Don’t fully tighten the
nuts on the pivot bolts or the shock absorber
yet.
13Bleed the brakes as described in Chap-
ter 9.
14Support the trailing arm with a trolley jack,
and raise it to simulate normal ride height.
Tighten the bolts and nuts to the torques
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
15 Rear wheel bearings-
renewal
4
3-Series models
1Loosen the driveshaft nut and the rear
wheel bolts, then chock the front wheels.
Raise the rear of the vehicle and place it
securely on axle stands. Remove the rear
wheel. Note: Depending on the type of rear
wheel, it may be necessary to remove the
wheel first, remove the hubcap, then refit the
wheel and loosen the driveshaft nut.
2Remove the driveshaft (see Chapter 8).3On models with rear brake drums, remove
the drum. On models with rear disc brakes,
remove the brake caliper and mounting
bracket. Don’t disconnect the hose. Hang the
caliper out of the way with a piece of wire.
Remove the brake disc (see Chapter 9).
Working from behind, drive the wheel hub out
of the wheel bearing with a large socket or a
piece of pipe.
4Remove the large circlip (see illustration)
that holds the wheel bearing in the wheel
bearing housing, then drive out the bearing
with a large socket or piece of pipe.
5Refitting is basically the reverse of removal,
bearing in mind the following points:
a) Be extremely careful where you place the
socket or piece of pipe when you drive
the new bearing into the housing. It
should be butted up against the outer
race of the bearing. Driving in the new
bearing using the inner race will ruin the
bearing.
b) Refit the wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground before attempting to tighten
the driveshaft nut to the torque listed in
the Chapter 8 Specifications.
5-Series models
6Chock the front wheels, then raise the rear
of the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands. Disconnect the outer CV joint from the
drive flange (see Chapter 8). Support the outer
end of the driveshaft with a piece of wire -
don’t let it hang, as this could damage the
inner CV joint.
7Prise out the lockplate that secures the
drive flange nut (see illustration). Once
you’ve prised out an edge of the lockplate,
pull it out with a pair of needle-nose pliers.
8Lower the vehicle and unscrew the drive
flange nut, but don’t remove it yet. You’ll need
a long bar (see illustration).
Warning: Don’t attempt to loosen
this nut with the vehicle on axle
stands. The force required to
loosen the nut could topple the
vehicle from the stands.
9Loosen the rear wheel bolts, raise the rear
of the vehicle again, place it securely on axle
stands and remove the wheel.
10Remove the brake caliper and the brake
disc (see Chapter 9). Hang the caliper out of
the way with a piece of wire.
11Remove the drive flange nut. Using a
suitable puller, remove the drive flange (see
illustration).
12Using a soft-faced hammer, drive the stub
axle out of the bearing (see illustration). If the
bearing inner race comes off with the stub
Suspension and steering systems 10•11
15.7 Prise out the lockplate that secures
the drive flange nut - once you’ve prised
out an edge of the lockplate, pull it out
with a pair of needle-nose pliers15.4 An exploded view of the 3-Series rear
wheel bearing assembly14.8 On 1983 and later models, remove
one of these trailing arm-to-axle carrier
bolts (it doesn’t matter which one you
remove - one attaches the link to the
trailing arm, and the other attaches the link
to the axle carrier)
15.12 Using a soft-faced hammer, drive
the stub axle out of the bearing15.11 Remove the drive flange with a
puller15.8 Lower the vehicle and loosen the
drive flange nut
10
If the bearing inner race
sticks to the hub (it probably
will), use a puller to remove
the race from the hub.
Page 154 of 228
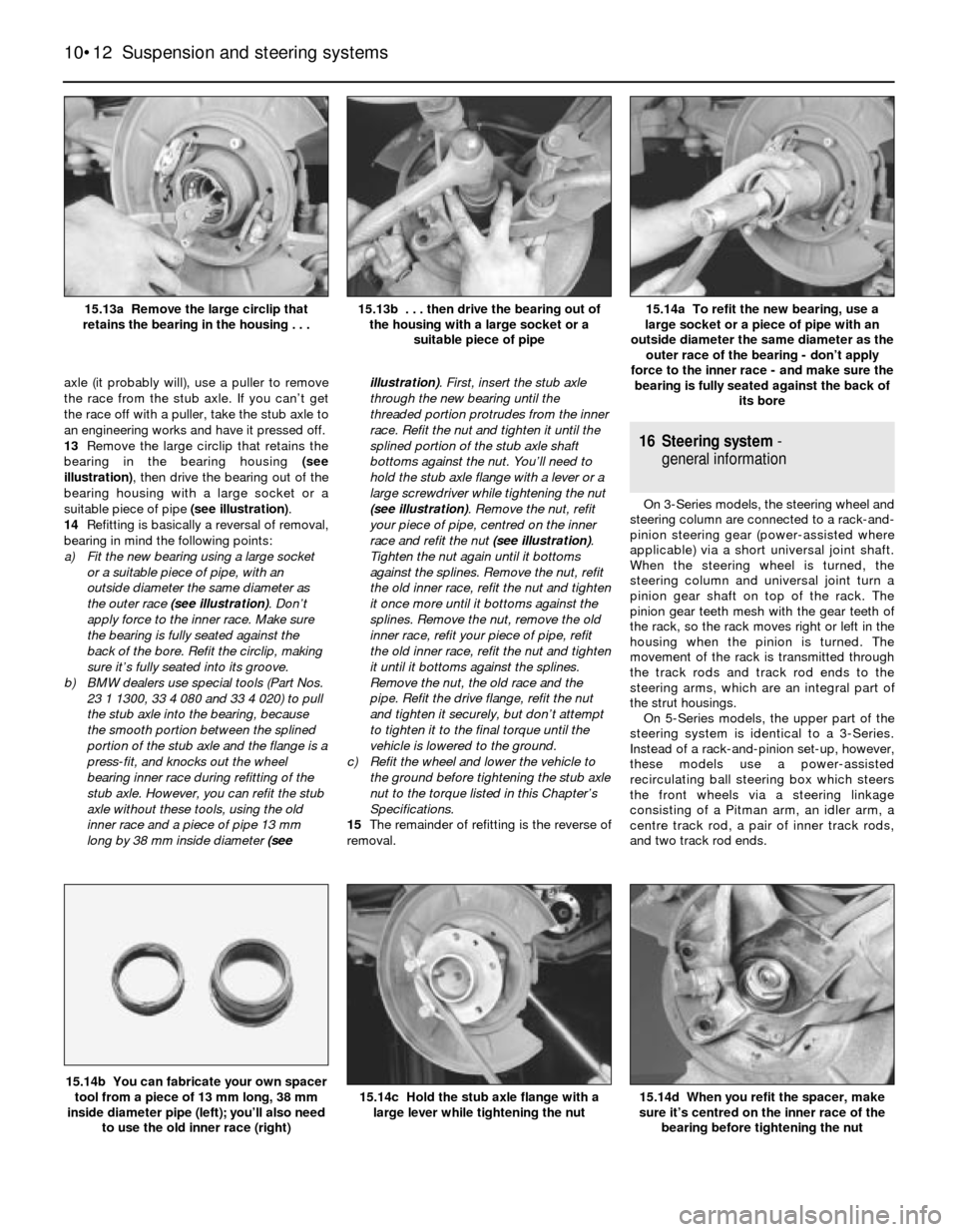
axle (it probably will), use a puller to remove
the race from the stub axle. If you can’t get
the race off with a puller, take the stub axle to
an engineering works and have it pressed off.
13Remove the large circlip that retains the
bearing in the bearing housing (see
illustration), then drive the bearing out of the
bearing housing with a large socket or a
suitable piece of pipe (see illustration).
14Refitting is basically a reversal of removal,
bearing in mind the following points:
a) Fit the new bearing using a large socket
or a suitable piece of pipe, with an
outside diameter the same diameter as
the outer race (see illustration). Don’t
apply force to the inner race. Make sure
the bearing is fully seated against the
back of the bore. Refit the circlip, making
sure it’s fully seated into its groove.
b) BMW dealers use special tools (Part Nos.
23 1 1300, 33 4 080 and 33 4 020) to pull
the stub axle into the bearing, because
the smooth portion between the splined
portion of the stub axle and the flange is a
press-fit, and knocks out the wheel
bearing inner race during refitting of the
stub axle. However, you can refit the stub
axle without these tools, using the old
inner race and a piece of pipe 13 mm
long by 38 mm inside diameter (seeillustration). First, insert the stub axle
through the new bearing until the
threaded portion protrudes from the inner
race. Refit the nut and tighten it until the
splined portion of the stub axle shaft
bottoms against the nut. You’ll need to
hold the stub axle flange with a lever or a
large screwdriver while tightening the nut
(see illustration). Remove the nut, refit
your piece of pipe, centred on the inner
race and refit the nut (see illustration).
Tighten the nut again until it bottoms
against the splines. Remove the nut, refit
the old inner race, refit the nut and tighten
it once more until it bottoms against the
splines. Remove the nut, remove the old
inner race, refit your piece of pipe, refit
the old inner race, refit the nut and tighten
it until it bottoms against the splines.
Remove the nut, the old race and the
pipe. Refit the drive flange, refit the nut
and tighten it securely, but don’t attempt
to tighten it to the final torque until the
vehicle is lowered to the ground.
c) Refit the wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground before tightening the stub axle
nut to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
15The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
16 Steering system-
general information
On 3-Series models, the steering wheel and
steering column are connected to a rack-and-
pinion steering gear (power-assisted where
applicable) via a short universal joint shaft.
When the steering wheel is turned, the
steering column and universal joint turn a
pinion gear shaft on top of the rack. The
pinion gear teeth mesh with the gear teeth of
the rack, so the rack moves right or left in the
housing when the pinion is turned. The
movement of the rack is transmitted through
the track rods and track rod ends to the
steering arms, which are an integral part of
the strut housings.
On 5-Series models, the upper part of the
steering system is identical to a 3-Series.
Instead of a rack-and-pinion set-up, however,
these models use a power-assisted
recirculating ball steering box which steers
the front wheels via a steering linkage
consisting of a Pitman arm, an idler arm, a
centre track rod, a pair of inner track rods,
and two track rod ends.
10•12 Suspension and steering systems
15.14d When you refit the spacer, make
sure it’s centred on the inner race of the
bearing before tightening the nut15.14c Hold the stub axle flange with a
large lever while tightening the nut15.14b You can fabricate your own spacer
tool from a piece of 13 mm long, 38 mm
inside diameter pipe (left); you’ll also need
to use the old inner race (right)
15.14a To refit the new bearing, use a
large socket or a piece of pipe with an
outside diameter the same diameter as the
outer race of the bearing - don’t apply
force to the inner race - and make sure the
bearing is fully seated against the back of
its bore15.13b . . . then drive the bearing out of
the housing with a large socket or a
suitable piece of pipe15.13a Remove the large circlip that
retains the bearing in the housing . . .
Page 158 of 228
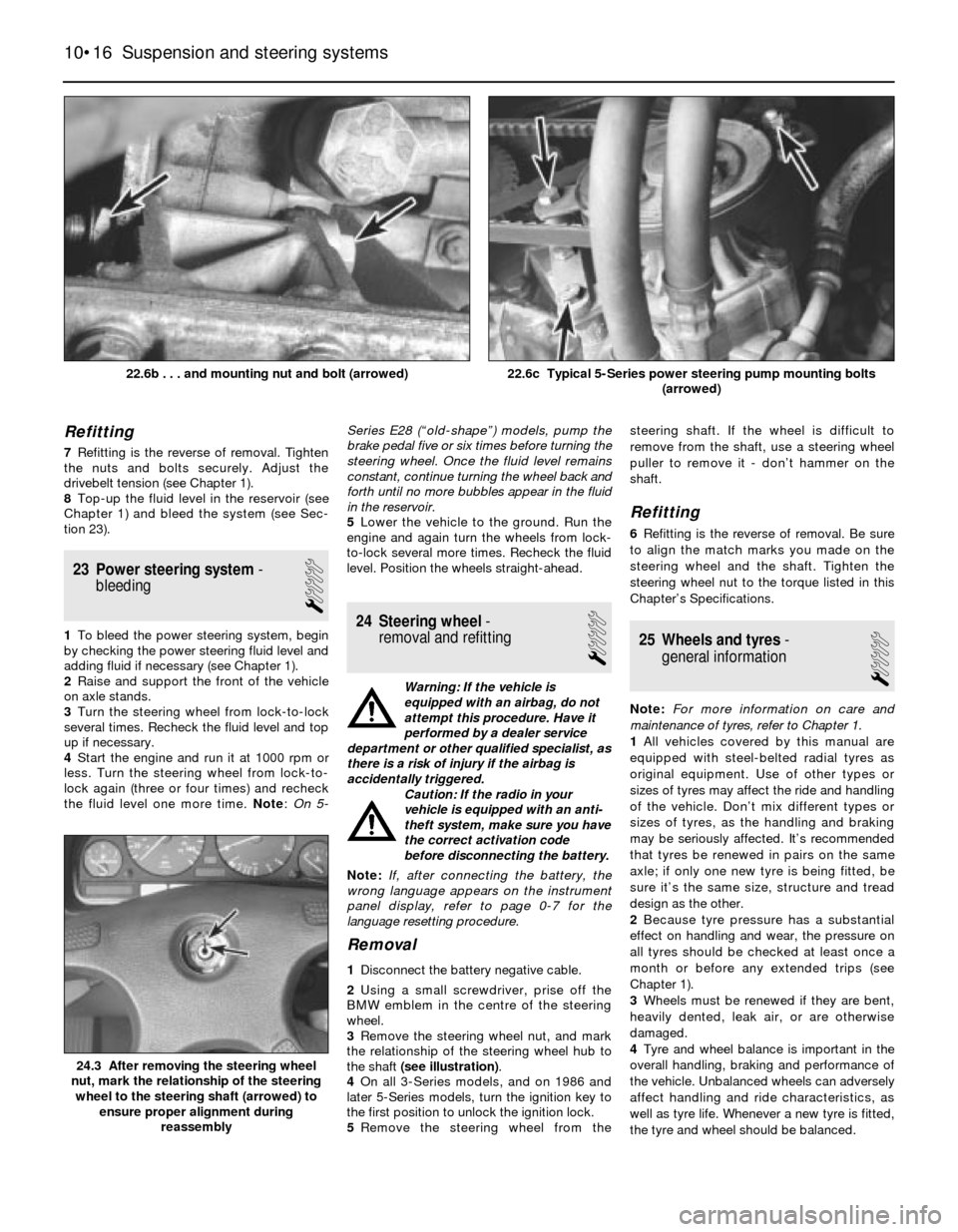
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the nuts and bolts securely. Adjust the
drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1).
8Top-up the fluid level in the reservoir (see
Chapter 1) and bleed the system (see Sec-
tion 23).
23 Power steering system-
bleeding
1
1To bleed the power steering system, begin
by checking the power steering fluid level and
adding fluid if necessary (see Chapter 1).
2Raise and support the front of the vehicle
on axle stands.
3Turn the steering wheel from lock-to-lock
several times. Recheck the fluid level and top
up if necessary.
4Start the engine and run it at 1000 rpm or
less. Turn the steering wheel from lock-to-
lock again (three or four times) and recheck
the fluid level one more time. Note:On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models, pump the
brake pedal five or six times before turning the
steering wheel. Once the fluid level remains
constant, continue turning the wheel back and
forth until no more bubbles appear in the fluid
in the reservoir.
5Lower the vehicle to the ground. Run the
engine and again turn the wheels from lock-
to-lock several more times. Recheck the fluid
level. Position the wheels straight-ahead.24 Steering wheel-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: If the vehicle is
equipped with an airbag, do not
attempt this procedure. Have it
performed by a dealer service
department or other qualified specialist, as
there is a risk of injury if the airbag is
accidentally triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Using a small screwdriver, prise off the
BMW emblem in the centre of the steering
wheel.
3Remove the steering wheel nut, and mark
the relationship of the steering wheel hub to
the shaft (see illustration).
4On all 3-Series models, and on 1986 and
later 5-Series models, turn the ignition key to
the first position to unlock the ignition lock.
5Remove the steering wheel from thesteering shaft. If the wheel is difficult to
remove from the shaft, use a steering wheel
puller to remove it - don’t hammer on the
shaft.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to align the match marks you made on the
steering wheel and the shaft. Tighten the
steering wheel nut to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
25 Wheels and tyres-
general information
1
Note:For more information on care and
maintenance of tyres, refer to Chapter 1.
1All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with steel-belted radial tyres as
original equipment. Use of other types or
sizes of tyres may affect the ride and handling
of the vehicle. Don’t mix different types or
sizes of tyres, as the handling and braking
may be seriously affected. It’s recommended
that tyres be renewed in pairs on the same
axle; if only one new tyre is being fitted, be
sure it’s the same size, structure and tread
design as the other.
2Because tyre pressure has a substantial
effect on handling and wear, the pressure on
all tyres should be checked at least once a
month or before any extended trips (see
Chapter 1).
3Wheels must be renewed if they are bent,
heavily dented, leak air, or are otherwise
damaged.
4Tyre and wheel balance is important in the
overall handling, braking and performance of
the vehicle. Unbalanced wheels can adversely
affect handling and ride characteristics, as
well as tyre life. Whenever a new tyre is fitted,
the tyre and wheel should be balanced.
10•16 Suspension and steering systems
24.3 After removing the steering wheel
nut, mark the relationship of the steering
wheel to the steering shaft (arrowed) to
ensure proper alignment during
reassembly
22.6c Typical 5-Series power steering pump mounting bolts
(arrowed)22.6b . . . and mounting nut and bolt (arrowed)
Page 204 of 228
REF•3
REF
MOT Test Checks
Exhaust system
MStart the engine. With your assistant
holding a rag over the tailpipe, check the
entire system for leaks. Repair or renew
leaking sections.
Jack up the front and rear of the vehicle,
and securely support it on axle stands.
Position the stands clear of the suspension
assemblies. Ensure that the wheels are
clear of the ground and that the steering
can be turned from lock to lock.
Steering mechanism
MHave your assistant turn the steering from
lock to lock. Check that the steering turns
smoothly, and that no part of the steering
mechanism, including a wheel or tyre, fouls
any brake hose or pipe or any part of the body
structure.
MExamine the steering rack rubber gaiters
for damage or insecurity of the retaining clips.
If power steering is fitted, check for signs of
damage or leakage of the fluid hoses, pipes or
connections. Also check for excessive
stiffness or binding of the steering, a missing
split pin or locking device, or severe corrosion
of the body structure within 30 cm of any
steering component attachment point.
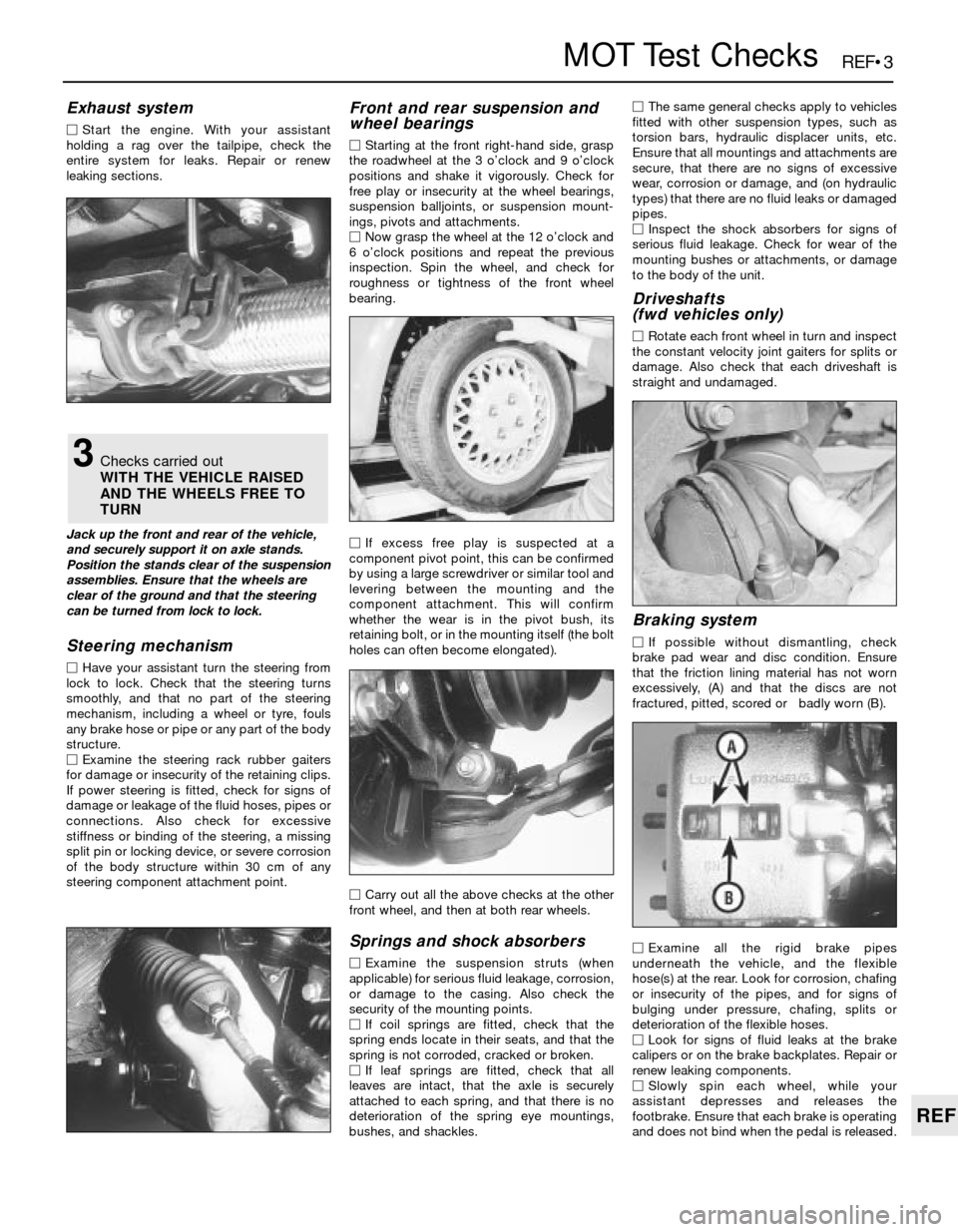
Front and rear suspension and
wheel bearings
MStarting at the front right-hand side, grasp
the roadwheel at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock
positions and shake it vigorously. Check for
free play or insecurity at the wheel bearings,
suspension balljoints, or suspension mount-
ings, pivots and attachments.
MNow grasp the wheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions and repeat the previous
inspection. Spin the wheel, and check for
roughness or tightness of the front wheel
bearing.
MIf excess free play is suspected at a
component pivot point, this can be confirmed
by using a large screwdriver or similar tool and
levering between the mounting and the
component attachment. This will confirm
whether the wear is in the pivot bush, its
retaining bolt, or in the mounting itself (the bolt
holes can often become elongated).
MCarry out all the above checks at the other
front wheel, and then at both rear wheels.
Springs and shock absorbers
MExamine the suspension struts (when
applicable) for serious fluid leakage, corrosion,
or damage to the casing. Also check the
security of the mounting points.
MIf coil springs are fitted, check that the
spring ends locate in their seats, and that the
spring is not corroded, cracked or broken.
MIf leaf springs are fitted, check that all
leaves are intact, that the axle is securely
attached to each spring, and that there is no
deterioration of the spring eye mountings,
bushes, and shackles.MThe same general checks apply to vehicles
fitted with other suspension types, such as
torsion bars, hydraulic displacer units, etc.
Ensure that all mountings and attachments are
secure, that there are no signs of excessive
wear, corrosion or damage, and (on hydraulic
types) that there are no fluid leaks or damaged
pipes.
MInspect the shock absorbers for signs of
serious fluid leakage. Check for wear of the
mounting bushes or attachments, or damage
to the body of the unit.
Driveshafts
(fwd vehicles only)
MRotate each front wheel in turn and inspect
the constant velocity joint gaiters for splits or
damage. Also check that each driveshaft is
straight and undamaged.
Braking system
MIf possible without dismantling, check
brake pad wear and disc condition. Ensure
that the friction lining material has not worn
excessively, (A) and that the discs are not
fractured, pitted, scored or badly worn (B).
MExamine all the rigid brake pipes
underneath the vehicle, and the flexible
hose(s) at the rear. Look for corrosion, chafing
or insecurity of the pipes, and for signs of
bulging under pressure, chafing, splits or
deterioration of the flexible hoses.
MLook for signs of fluid leaks at the brake
calipers or on the brake backplates. Repair or
renew leaking components.
MSlowly spin each wheel, while your
assistant depresses and releases the
footbrake. Ensure that each brake is operating
and does not bind when the pedal is released.
3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE RAISED
AND THE WHEELS FREE TO
TURN
Page 205 of 228

REF•4MOT Test Checks
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test can
be carried out later to check that the vehicle
pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-bearing
areas. (These include chassis box sections,
side sills, cross-members, pillars, and all
suspension, steering, braking system and
seat belt mountings and anchorages.) Any
corrosion which has seriously reduced the
thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allowthe engine speed to return to idle, and watch
for smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000 rpm;
if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less, this
counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
Page 215 of 228

REF•14Fault Finding
Brakes
Note:Before assuming that a brake problem exists, make sure that:
a) The tyres are in good condition and properly inflated (Chapter 1).
b) The wheel alignment (tracking) is correct (Chapter 10).
c) The vehicle is not loaded with weight in an unequal manner.
Vehicle pulls to one side during braking
m mIncorrect tyre pressures (Chapter 1).
m mWheel alignment (tracking) incorrect (Chapter 10)
m mUnmatched tyres on same axle.
m mRestricted brake lines or hoses (Chapter 9).
m mMalfunctioning caliper assembly (Chapter 9).
m mLoose suspension parts (Chapter 10).
m mLoose calipers (Chapter 9).
Noise (high-pitched squeal) when the brakes are
applied
m mFront and/or rear disc brake pads worn out. The noise comes from
the wear sensor rubbing against the disc. Renew the pads
immediately (Chapter 9).
Brake vibration (pedal pulsates)
Note:If the vehicle has ABS, it is normal for the brake pedal to pulsate
when the system is working.
m mExcessive lateral disc run-out (Chapter 9).
m mParallelism not within specifications (Chapter 9).
m mUneven pad wear - caused by caliper not sliding, due to improper
clearance or dirt (Chapter 9).
m mDefective disc (Chapter 9).
Excessive brake pedal travel
m
mPartial brake system failure (Chapter 9).
m mInsufficient fluid in master cylinder (Chapters 1 and 9).
m mAir trapped in system (Chapters 1 and 9).
Excessive pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m
mMalfunctioning brake servo unit (Chapter 9).
m mPartial system failure (Chapter 9).
m mExcessively-worn pads or shoes (Chapter 9).
m mCaliper piston stuck or sluggish (Chapter 9).
m mBrake pads contaminated with oil or grease (Chapter 9).
m mNew pads fitted and not yet seated. It will take a while for the new
material to seat against the disc.
Dragging brakes
m mMaster cylinder pistons not returning correctly (Chapter 9).
m mRestricted brakes lines or hoses (Chapters 1 and 9).
m mIncorrect handbrake adjustment (Chapter 9).
m mRear drum brake self-adjuster mechanism faulty (when applicable)
(Chapter 9).
Grabbing or uneven braking action
m mMalfunction of brake servo unit (Chapter 9).
m mBinding brake pedal mechanism (Chapter 9).
Brake pedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m
mAir in hydraulic lines (Chapter 9).
m mMaster cylinder mounting bolts loose (Chapter 9).
m mMaster cylinder defective (Chapter 9).
Brake pedal travels to the floor with little resistance
m
mLittle or no fluid in the master cylinder reservoir, caused by leaking
caliper piston(s), loose, damaged or disconnected brake lines
(Chapter 9).
Handbrake does not hold
m mHandbrake linkage incorrectly adjusted (Chapter 9).
m mHandbrake shoe linings worn out or contaminated (Chapter 9).