BMW 3 SERIES 2001 E46 Drive Away Protection Syst
Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2001, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 2001 E46Pages: 30, PDF Size: 0.7 MB
Page 1 of 30

Initial Print Date: 5/01Revision Date:
Subject Page
Drive Away Protection..................................................................................3
EWS I...........................................................................................................5
EWS II..........................................................................................................8
EWS III (3.2)...............................................................................................16
EWS III (3.3)...............................................................................................20
EWS III D (3-D)...........................................................................................24
Worksheets................................................................................................27
Review Questions.......................................................................................30
Table of Contents
EWS
Page 2 of 30

2
EWS
Drive Away Protection System (EWS)
Model: EWS I/EWS II/EWS III/EWS III D
E31/E34/E36/E38/E39/E46/E52/E53
Production Date: All since 1/94
Objectives
After completion of this module you should be able to:
• Explain the differences in the EWS systems.
• List the components that make up the different EWS systems.
• Describe the operation of each system.
• Understand and relate the data exchange sequence between the EWS and DME.
Page 3 of 30

3
EWS
Drive Away Protection
The first version of Drive Away Protection was installed on production vehicles 9/93
through 12/93.
Purpose of The System
The purpose of the Drive Away Protection system was to reduce vehicle theft as mandat-
ed by the European Insurance Commission to combat the high theft rate in European
Countries.
This first version of the Drive Away Protection System added a circuit from the General
Module to the DME. The added circuit was spliced into the existing code function from the
Board Computer (BC) to the DME.
The components of the Drive Away Protection System are:
• Door Lock Switch
• General Module
• Board Computer
• DME
System Components
Door Lock Switch
The door lock switch provides a 12V (High) signal to the GM when the vehicle is locked from
the outside. The switch also provides a Low signal to the GM when the vehicle is unlocked.
General Module
The GM receives the lock and unlock signals from the door lock switch and signals the
DME with a 12V High signal when the vehicle is double locked or with a Low signal when
this vehicle is unlocked.
Board Computer
The Board Computer (BC) through its’ code function provides a High signal to the DME to
disallow vehicle operation or a Low signal to allow vehicle operation.
DME
The DME looks for a High/Low signal from the BC or GM and dependent on the signal, it
will either allow or prevent vehicle operation.
Page 4 of 30
4
EWS
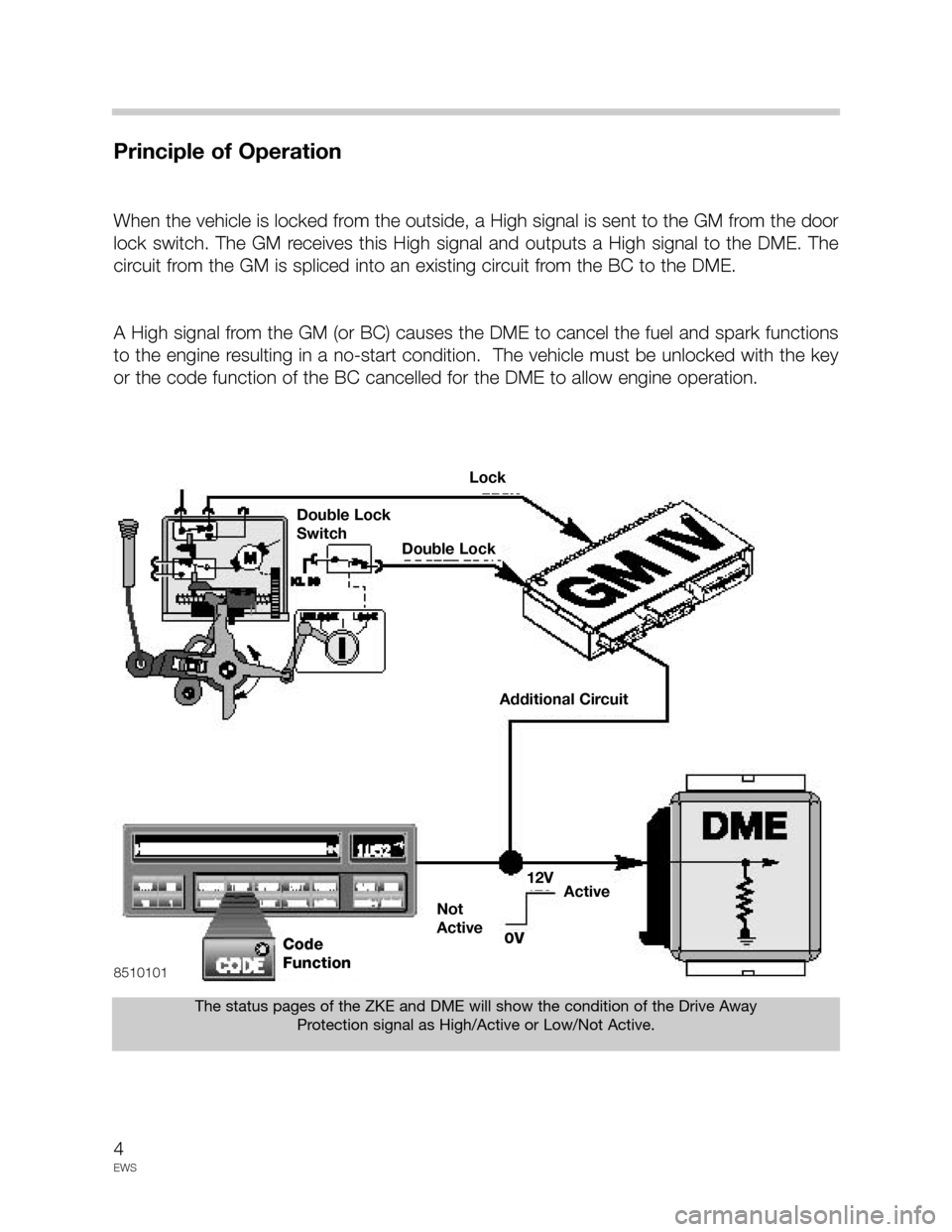
Principle of Operation
When the vehicle is locked from the outside, a High signal is sent to the GM from the door
lock switch. The GM receives this High signal and outputs a High signal to the DME. The
circuit from the GM is spliced into an existing circuit from the BC to the DME.
A High signal from the GM (or BC) causes the DME to cancel the fuel and spark functions
to the engine resulting in a no-start condition. The vehicle must be unlocked with the key
or the code function of the BC cancelled for the DME to allow engine operation.
The status pages of the ZKE and DME will show the condition of the Drive Away
Protection signal as High/Active or Low/Not Active.
8510101
Lock
Double Lock
Double Lock
Switch
Additional Circuit
12VActive
Not
Active
0VCode
Function
Page 5 of 30

5
EWS
EWS I
EWS I was installed on vehicles beginning production 1/94, replacing the original Drive
Away Protection System.
Purpose of the System
The next level of compliancy with the European Insurance Commission required additional
changes from the previous system. An additional component was added called the Starter
Immobilization Relay. This relay module provides added theft prevention and safety fea-
tures.
At the time of introduction the system was referred to as Electronic Drive Away
Protectionwhich in German is E
lectronische Wegfahrsperreor EWS.
The EWS I system consisted of the following components:
• Starter Immobilization Relay
• Door Lock Cylinders and Switch
• General Module
• Board Computer (if equipped)
• Transmission Range Switch
• DME Engine Speed Signal (Beginning 6/94 Production)
• DWA (E31)
System Components
Starter Immobilization Relay
The Starter Immobilization Relay was installed on E31, E34 and E36 vehicles.
It was in the following location:
E36 -In the relay carrier to the left of the steering column.
E31/E34-In the “A” pillar above the footwell kick panel speaker.
The Starter Immobilization Relay functions as a “Smart Relay”, a relay which receives inputs
from various sources looking at the proper combination of input signals before activating a
component, in this case the starter.
The Starter Immobilization Relay receives input from:
• Ignition Switch • General Module • Board Computer
• Trans Range Switch • DME (>6/94)
And processes output to:
• Starter • DME8510104
Page 6 of 30
6
EWS
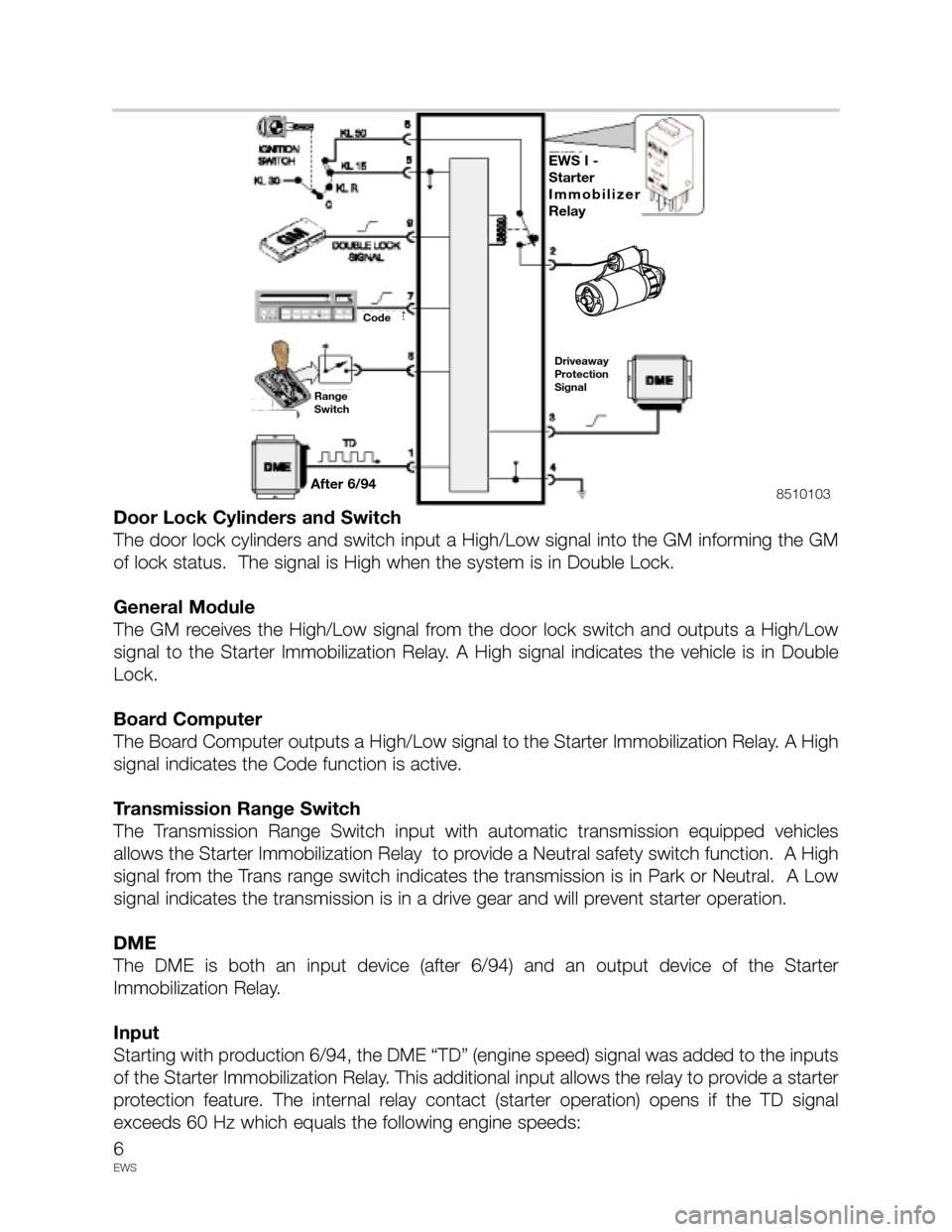
Door Lock Cylinders and Switch
The door lock cylinders and switch input a High/Low signal into the GM informing the GM
of lock status. The signal is High when the system is in Double Lock.
General Module
The GM receives the High/Low signal from the door lock switch and outputs a High/Low
signal to the Starter Immobilization Relay. A High signal indicates the vehicle is in Double
Lock.
Board Computer
The Board Computer outputs a High/Low signal to the Starter Immobilization Relay. A High
signal indicates the Code function is active.
Transmission Range Switch
The Transmission Range Switch input with automatic transmission equipped vehicles
allows the Starter Immobilization Relay to provide a Neutral safety switch function. A High
signal from the Trans range switch indicates the transmission is in Park or Neutral. A Low
signal indicates the transmission is in a drive gear and will prevent starter operation.
DME
The DME is both an input device (after 6/94) and an output device of the Starter
Immobilization Relay.
Input
Starting with production 6/94, the DME “TD” (engine speed) signal was added to the inputs
of the Starter Immobilization Relay. This additional input allows the relay to provide a starter
protection feature. The internal relay contact (starter operation) opens if the TD signal
exceeds 60 Hz which equals the following engine speeds:
8510103
EWS I -
Starter
Immobilizer
Relay
After 6/94
Driveaway
Protection
Signal
Range
Switch
Code
Page 7 of 30

7
EWS
• 4 cylinder =1800 RPM
• 6 or 12 cylinder =1200 RPM
• 8 cylinder =900 RPM
The relay contacts will close when the exceeded Hz value drops to 5Hz below the maxi-
mum value. This is intended as a safety feature to prevent starter motor activation when the
engine is running above these speeds.
Output
The DME receives a High/Low signal from the Starter Immobilization Relay. When the sig-
nal is High, the DME does not activate injector or ignition operation.
DWA (E31)
The DWA outputs a High/Low signal to the Starter Immobilization Relay indicating the con-
dition of the alarm system. A High signal indicates the alarm is armed, preventing vehicle
starting.
Principle of Operation
The EWS Starter Immobilization Relay receives it’s inputs from the Ignition switch, GM (or
DWA), BC, Trans Range Switch and the DME (after 6/94). The relay will prevent engine
starting if:
• The vehicle is locked from the outside. The GM receives the High signal from the
door lock switch and sends a High signal to the EWS.
• The BC Code function is set.
• A DWA High signal is received. (E31only)
• A Low signal is received from the Trans Range Switch.
• The engine speed signal from the DME exceeds 60Hz. (after 6/94)
The Ignition and injection functions of the DME are disabled and the KL50 start signal to
the starter is opened to prevent starter operation.
Workshop Hints:
Starter Immobilization Relays are different for manual and automatic vehicles, check to ensure correct
relay is installed.
The Starter Immobilization Relay is not on the Diagnostic Link. Conventional troubleshooting techniques
using the DISplus, a DVOM and the correct ETM are necessary.
Loss of input from the GM or BC will allow the engine to start.
Loss of input from the Trans Range Switch will NOTallow the engine to start.
Page 8 of 30
8
EWS
EWS II
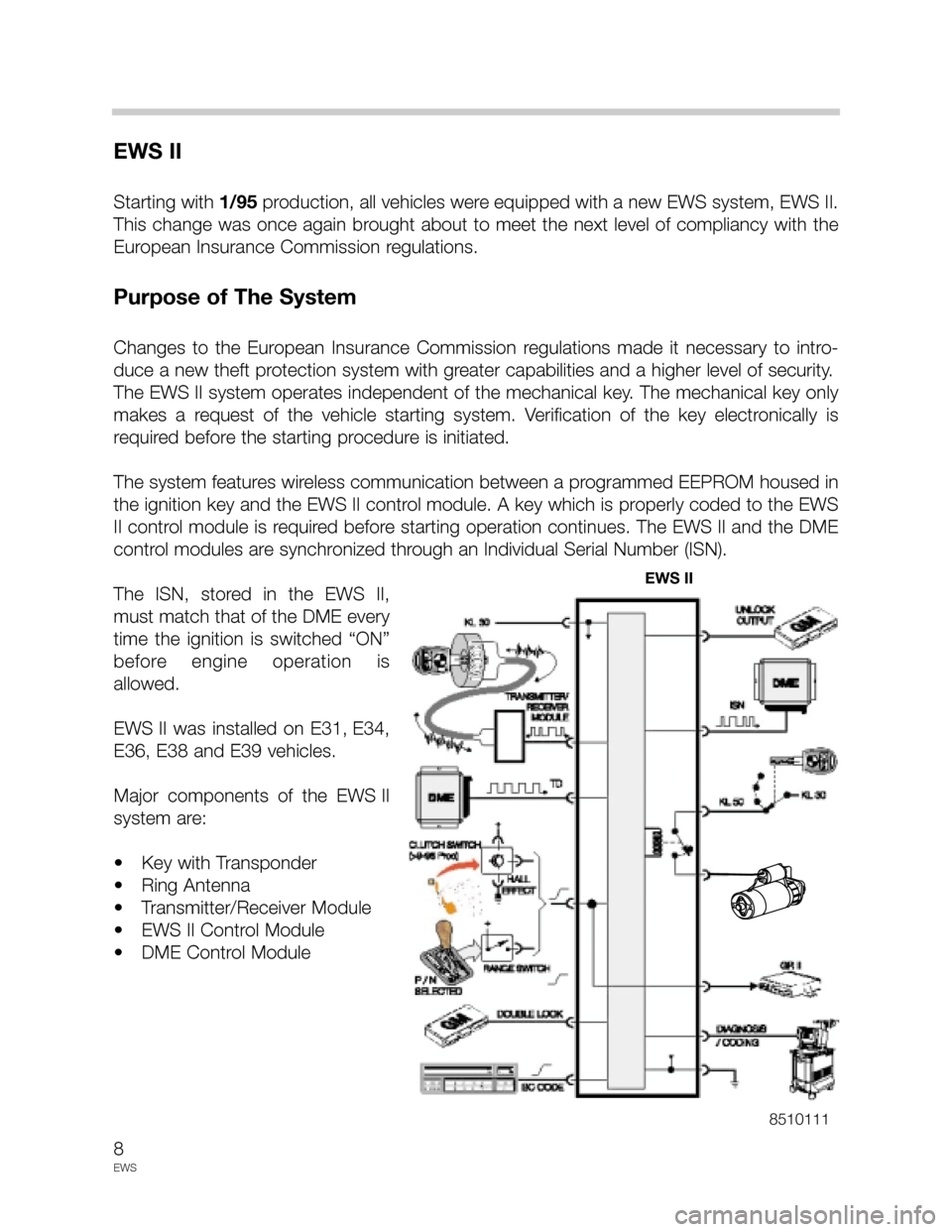
Starting with 1/95production, all vehicles were equipped with a new EWS system, EWS II.
This change was once again brought about to meet the next level of compliancy with the
European Insurance Commission regulations.
Purpose of The System
Changes to the European Insurance Commission regulations made it necessary to intro-
duce a new theft protection system with greater capabilities and a higher level of security.
The EWS II system operates independent of the mechanical key. The mechanical key only
makes a request of the vehicle starting system. Verification of the key electronically is
required before the starting procedure is initiated.
The system features wireless communication between a programmed EEPROM housed in
the ignition key and the EWS II control module. A key which is properly coded to the EWS
II control module is required before starting operation continues. The EWS II and the DME
control modules are synchronized through an Individual Serial Number (ISN).
The ISN, stored in the EWS II,
must match that of the DME every
time the ignition is switched “ON”
before engine operation is
allowed.
EWS II was installed on E31, E34,
E36, E38 and E39 vehicles.
Major components of the EWS II
system are:
• Key with Transponder
• Ring Antenna
• Transmitter/Receiver Module
• EWS II Control Module
• DME Control Module
8510111
EWS II
Page 9 of 30
9
EWS
System Components
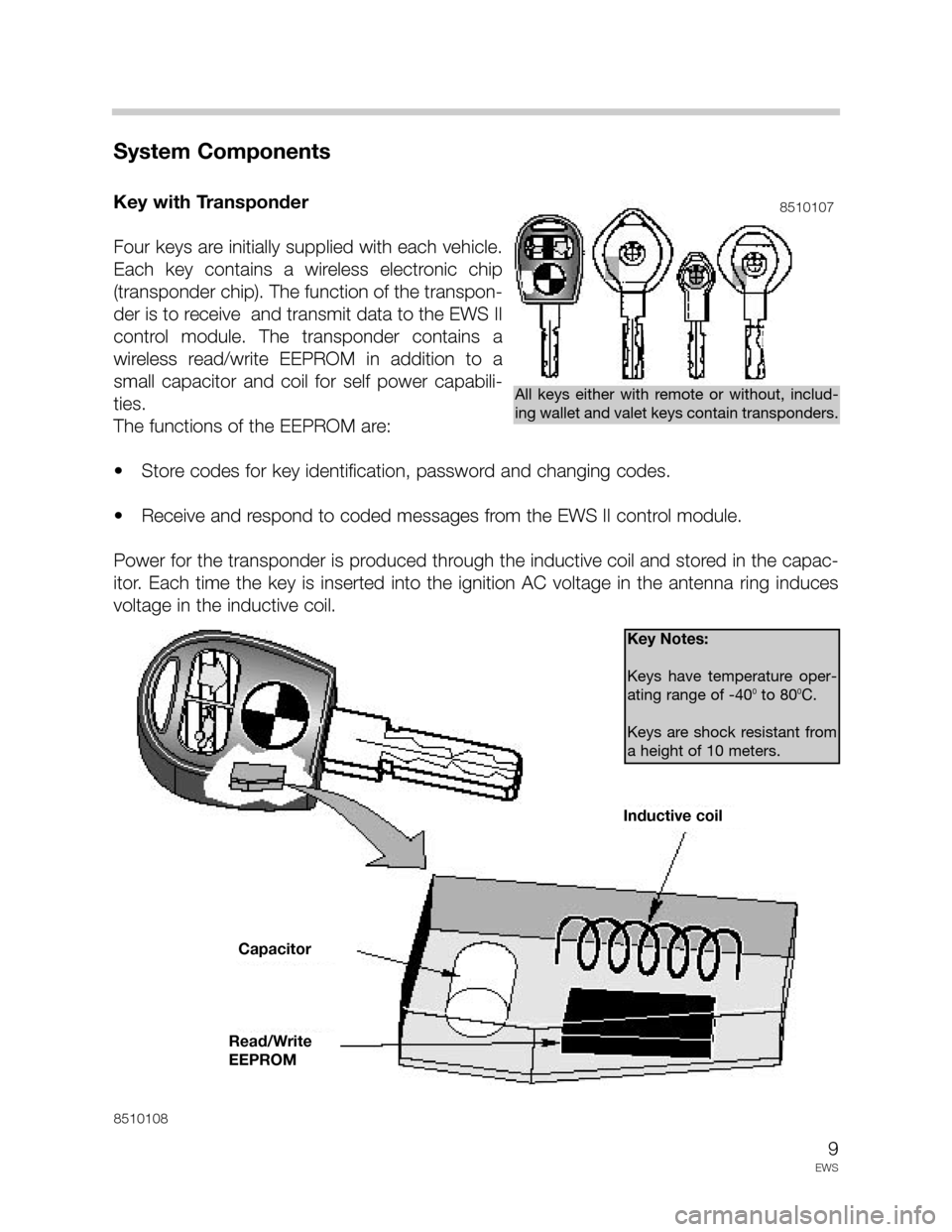
Key with Transponder
Four keys are initially supplied with each vehicle.
Each key contains a wireless electronic chip
(transponder chip). The function of the transpon-
der is to receive and transmit data to the EWS II
control module. The transponder contains a
wireless read/write EEPROM in addition to a
small capacitor and coil for self power capabili-
ties.
The functions of the EEPROM are:
• Store codes for key identification, password and changing codes.
• Receive and respond to coded messages from the EWS II control module.
Power for the transponder is produced through the inductive coil and stored in the capac-
itor. Each time the key is inserted into the ignition AC voltage in the antenna ring induces
voltage in the inductive coil.
All keys either with remote or without, includ-
ing wallet and valet keys contain transponders.
8510108
8510107
Key Notes:
Keys have temperature oper-
ating range of -40
0to 800C.
Keys are shock resistant from
a height of 10 meters.
Inductive coil
Capacitor
Read/Write
EEPROM
Page 10 of 30
10
EWS
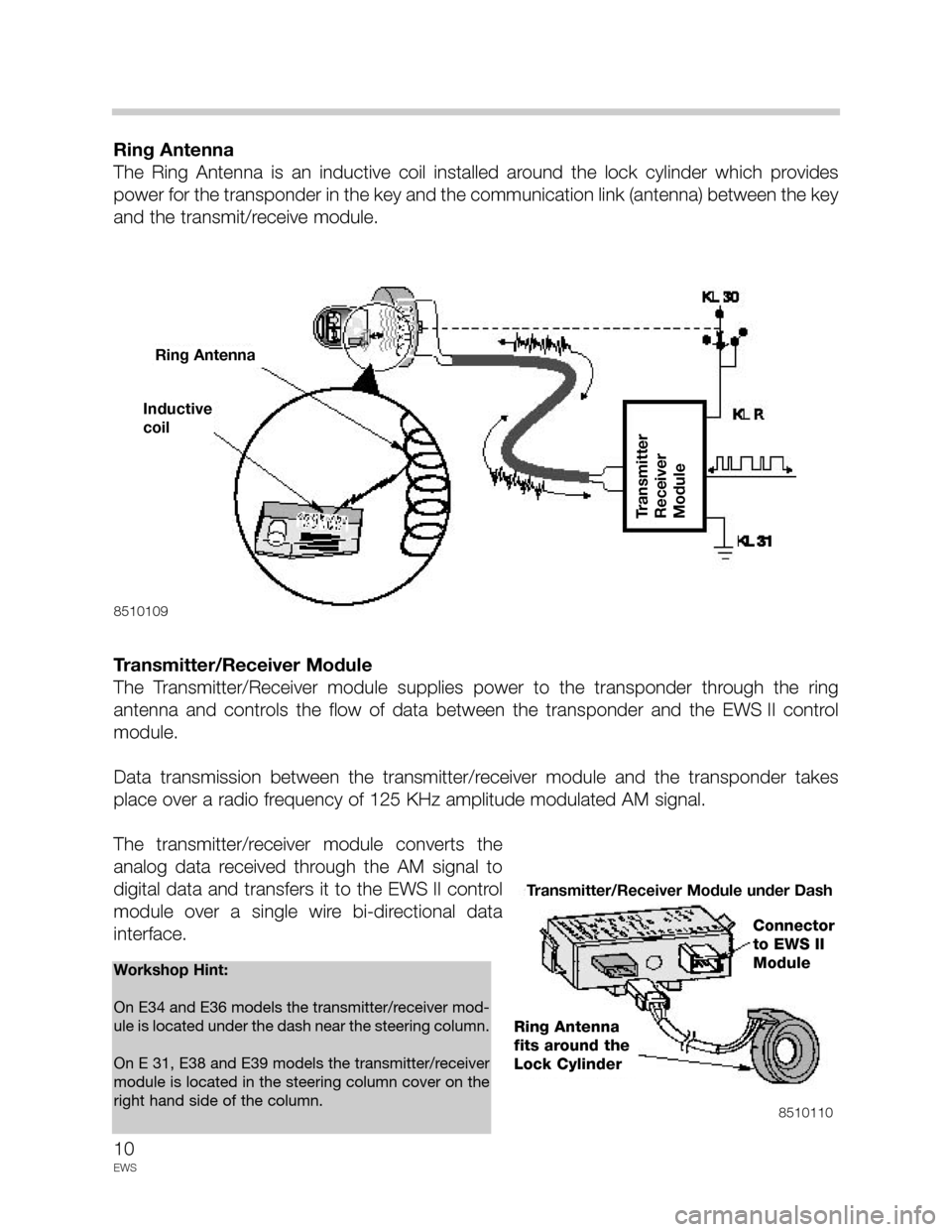
Ring Antenna
The Ring Antenna is an inductive coil installed around the lock cylinder which provides
power for the transponder in the key and the communication link (antenna) between the key
and the transmit/receive module.
Transmitter/Receiver Module
The Transmitter/Receiver module supplies power to the transponder through the ring
antenna and controls the flow of data between the transponder and the EWS II control
module.
Data transmission between the transmitter/receiver module and the transponder takes
place over a radio frequency of 125 KHz amplitude modulated AM signal.
The transmitter/receiver module converts the
analog data received through the AM signal to
digital data and transfers it to the EWS II control
module over a single wire bi-directional data
interface.
8510109
8510110
Workshop Hint:
On E34 and E36 models the transmitter/receiver mod-
ule is located under the dash near the steering column.
On E 31, E38 and E39 models the transmitter/receiver
module is located in the steering column cover on the
right hand side of the column.
Inductive
coil
Ring Antenna
Transmitter
Receiver
Module
Transmitter/Receiver Module under Dash
Connector
to EWS II
Module
Ring Antenna
fits around the
Lock Cylinder