oil BMW 5 SERIES 1991 E34 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 5 SERIES, Model: BMW 5 SERIES 1991 E34Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 21 of 228

Every 6000 miles or 6 months, whichever comes first
1•11
6.17a Unscrew the bolt . . .
1
Every 6000 miles
6 Engine oil and filter change
1
Warning: Prolonged skin contact
with used engine oil is
hazardous. Use a barrier cream
and wear gloves during this procedure.
Change out of oil-soaked clothing
immediately.
1Make sure that you have all the necessary
tools before you begin this procedure (see
illustration). You should also have plenty of rags
or newspapers handy for mopping up oil spills2Start the engine and allow it to reach
normal operating temperature - oil and sludge
will flow more easily when warm. If new oil, a
filter or tools are needed, use the vehicle to go
and get them, thus warming up the engine oil
at the same time.
3Park on a level surface, and switch off the
engine when it’s warmed up. Remove the oil
filler cap from the valve cover.
4Access to the oil drain plug and filter will be
improved if the vehicle can be lifted on a hoist,
driven onto ramps, or supported by axle
stands.
Warning: DO NOT work under a
vehicle supported only by a
hydraulic or scissors-type jack -
always use axle stands!
5If you haven’t changed the oil on this
vehicle before, get under it, and locate the
drain plug and the oil filter. Note that on some
engines, the oil filter is located on the top left-
hand side of the engine. The exhaust
components will be hot as you work, so note
how they are routed to avoid touching them.
6Being careful not to touch the hot exhaust
components, position a drain pan under the
plug in the bottom of the engine.
7Clean the area around the plug, then
remove the plug (see illustration). It’s a good
idea to wear a rubber glove while unscrewing
the plug the final few turns, to avoid being
scalded by hot oil. Hold the drain plug againstthe threads as you unscrew it, then pull it
away from the drain hole suddenly. This will
place your arm out of the way of the hot oil, as
well as reducing the chances of dropping the
drain plug into the drain pan.
8It may be necessary to move the drain pan
slightly as oil flow slows to a trickle. Inspect
the old oil for the presence of metal particles,
which could give early warning of engine
wear.
9After all the oil has drained, wipe off the
drain plug with a clean rag. Any small metal
particles clinging to the plug would
immediately contaminate the new oil.
10Refit the plug and tighten it securely. Use
a new washer if necessary.
11Move the drain pan into position under the
oil filter.
Canister-type oil filter
12Loosen the spin-off type oil filter by
turning it anti-clockwise with a filter spanner.
Any standard filter spanner will work.
13Sometimes the spin-off type oil filter is
screwed on so tightly that it can’t be easily
loosened. If it is, punch a metal bar or long
screwdriver directly through it, and use it as a
T-bar to turn the filter. Be prepared for oil to
spurt out of the canister as it’s punctured.
14Once the filter is loose, use your hands to
unscrew it from the block. Just as the filter is
detached from the block, immediately tilt the
open end up to prevent oil inside the filter
from spilling out.
15Using a clean rag, wipe off the mounting
surface on the block. Also, make sure that
none of the old sealing ring remains stuck to
the mounting surface. It can be removed with
a scraper if necessary.
16Compare the old filter with the new one,
to make sure they are the same type. Smear
some engine oil on the rubber sealing ring of
the new filter, and screw it into place (see
illustration). Overtightening the filter will
damage the sealing ring, so don’t use a filter
spanner. Most filter manufacturers
recommend tightening the filter by hand only.
Normally, they should be tightened three-
quarters of a turn after the sealing ring
contacts the block, but be sure to follow the
directions on the filter or container.
6.1 These tools are required when
changing the engine oil and filter
1 Drain pan- It should be fairly shallow in
depth, but wide enough to prevent spills
2 Rubber gloves- When removing the drain
plug and filter, you will get oil on your
hands (the gloves will prevent burns)
3 Socket bar - Sometimes the oil drain plug
is tight, and a long bar is needed to loosen
it. The correct-size ring spanner may work
just as well
4 Socket- To be used with the bar or a
ratchet (must be the correct size to fit the
drain plug - six-point preferred)
5 Filter spanner - This is a metal band-type
spanner, which requires clearance around
the filter to be effective. This tool is not
required on all engines.
6 Filter spanner- This type fits on the bottom
of the filter and can be turned with a ratchet
or breaker bar (different-size spanners are
available for different types of filters) This
tool is not required on all engines.
6.7 Using a ring spanner to remove the oil
drain plug
6.16 Lubricate the oil filter sealing ring
with clean engine oil before refitting the
filter on the engine
Frequent oil changes are the
most important preventive
maintenance procedures that
can be done by the home
mechanic. As engine oil ages, it
becomes diluted and contaminated,
which leads to premature engine wear.
Page 22 of 228

Cartridge-type oil filter
17Some models are equipped with a
cartridge-type oil filter. Unscrew the bolt,
remove the cover, and lift the filter out (see
illustrations).
18Compare the new cartridge with the old
one, to make sure they are the same type,
then lower it into the housing.
19Using a clean rag, wipe off the mounting
surface of the housing and cover. If necessary,
renew the rubber O-ring (see illustration).
Smear some clean oil on the O-ring and refit
the cover and bolt. Tighten the bolt securely.
All models
20Remove all tools and materials from under
the vehicle, being careful not to spill the oil
from the drain pan, then lower the vehicle.
21Add new oil to the engine through the oil
filler cap in the valve cover. Use a funnel to
prevent oil from spilling onto the top of the
engine. Pour the specified quantity of fresh oil
into the engine. Wait a few minutes to allow the
oil to drain into the sump, then check the level
on the dipstick (see Section 4 if necessary). If
the oil level is correct, refit the filler cap.
22Start the engine and run it for about a
minute. The oil pressure warning light may
take a few seconds to go out while the new
filter fills with oil; don’t rev the engine while
the light is on. While the engine is running,
look under the vehicle, and check for leaks at
the sump drain plug and around the oil filter. Ifeither one is leaking, stop the engine and
tighten the plug or filter slightly.
23Wait a few minutes, then recheck the level
on the dipstick. Add oil as necessary.
24During the first few days after an oil
change, make it a point to check frequently
for leaks and proper oil level.
25The old oil drained from the engine cannot
be re-used in its present state, and should be
discarded. Oil reclamation centres and some
service stations will accept the oil, which can
be recycled. After the oil has cooled, it can be
transferred into a container for transport to a
disposal site.
7 Power steering fluid level
check
1
1Check the power steering fluid level
periodically to avoid steering system
problems, such as damage to the pump.
Proceed as follows.Caution: Do not hold the steering
wheel against either stop (full-left
or full-right lock) for more than
five seconds. If you do, the power
steering pump could be damaged.
2On some models, the power steering fluid
reservoir is located on the left side of the
engine compartment, and has a twist-off cap
with an integral fluid level dipstick (see
illustration). Other models use a hydraulic
power steering and brake servo system which
combines the fluid in one reservoir, located at
the right rear corner of the engine
compartment.
3Park the vehicle on level ground, and apply
the handbrake.
4On models with a fluid dipstick, run the
engine until it has reached normal operating
temperature. With the engine at idle, turn the
steering wheel back and forth several times to
get any air out of the steering system. Switch
off the engine, remove the cap by turning it
anti-clockwise, wipe the dipstick clean, and
refit the cap. Remove the cap again, and note
the fluid level. It must be between the two
lines (see illustration).
5On hydraulic servo models, pump the brake
pedal about ten times or until the pedal is firm.
Remove the nut, lift the cap off, and make
sure the fluid is within 6.0 mm of the top of the
reservoir.
6Add small amounts of fluid until the level is
correct (see illustration).
1•12
7.6 Adding fluid to the power steering
reservoir7.4 The power steering fluid level should
be kept between the two arrows near the
upper step on the dipstick7.2 The power steering fluid reservoir
(arrowed) is located on the left side of the
engine compartment
6.19 Renewing the rubber O-ring in the
cover6.17c . . . and lift out the cartridge
Every 6000 miles
6.17b . . . remove the cover . . .
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.
Page 30 of 228

drag when the feeler gauge is moved back
and forth.
6If the gap is too large or too small, loosen
the locknut, insert a hook made from large-
diameter metal wire, and rotate the eccentric
to obtain the correct gap (see illustration).
7Once the gap has been set, hold the
eccentric in position with the hook, and
retighten the locknut securely. Recheck the
clearance - sometimes it’ll change slightly
when the locknut is tightened. If so, re-adjust
until it’s correct.
8On the M10 engine, the valves are adjusted
in the firing order, which is 1-3-4-2. After
adjusting No 1 cylinder valves, rotate the
crankshaft half a turn (180º), then check and
adjust the valves on No 3 cylinder. Repeat the
procedure on the remaining cylinders.
9On M20 and M30 engines, the valves are
adjusted following the firing order, which is
1-5-3-6-2-4. After adjusting No 1 cylinder
valves, rotate the crankshaft a third of a turn
(120º), then check and adjust the valves on No
5 cylinder. Repeat the procedure for the
remaining cylinders.
10Refit the valve cover (use a new gasket)
and tighten the mounting nuts evenly and
securely.
11Start the engine and check for oil leakage
between the valve cover and the cylinder
head.19 Throttle linkage -
check and lubrication
1
1The throttle linkage should be checked and
lubricated periodically to ensure its proper
operation.
2Check the linkage to make sure it isn’t
binding.
3Inspect the linkage joints for looseness, and
the connections for corrosion and damage,
renewing parts as necessary (see
illustration).
4Lubricate the connections with spray
lubricant or lithium-based grease.
20 Air filter renewal
1
Carburettor engines
1Release the spring clips, then unscrew the
centre nut and lift off the cover.
2Remove the air filter element, and wipe
clean the air cleaner body and cover
3Fit the new air filter element, then refit the
cover using a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Fuel injection engines
4Loosen the clamp on the air intake duct,
and detach the duct (see illustration).5Release the air cleaner cover retaining clips
(see illustration).
6Rotate the cover up, lift it off and lift the
element out, noting which way round it is
fitted (see illustrations).
7Wipe the inside of the air cleaner housing
with a clean cloth, then fit the new element. If
the element is marked TOP, be sure the
marked side faces up.
8Refit the cover and secure the clips.
9Connect the air duct and tighten the clamp
screw.
21 Fuel system check
1
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. Work in a well-
ventilated area. If you spill any fuel on your
skin, rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a fire extinguisher on hand. Mop
up spills immediately, but do not store
fuel-soaked rags where they could ignite.
1If you smell fuel while driving or after the
vehicle has been sitting in the sun, inspect the
fuel system immediately.
2Remove the fuel filler cap and inspect it for
damage and corrosion. The gasket should
have an unbroken sealing imprint. If the
gasket is damaged or corroded, fit a new cap.
3Inspect the fuel feed and return lines for
cracks. Make sure that the connections
between the fuel lines and the carburettor or
fuel injection system, and between the fuel
lines and the in-line fuel filter, are tight.
Warning: On fuel injection
models, the fuel system must be
depressurised before servicing
fuel system components, as
outlined in Chapter 4.
1•20
20.6b . . . and lift the air filter
element out20.6a Rotate the cover
upwards . . .
20.5 Use a screwdriver to detach the air
cleaner cover clips20.4 Detach the duct from the air cleaner
housing19.3 Check and lubricate the throttle
linkage at the points shown (arrowed) -
fuel injection engine shown
Every 12 000 miles
Page 32 of 228
no cause for concern. Make sure that any fluid
noted is from the struts/shocks, and not from
any other source. If leakage is noted, renew
the struts or shock absorbers in axle pairs (or
as a full set).
7Check the struts/shock absorbers to be
sure that they are securely mounted and
undamaged. Check the upper mountings for
damage and wear. If damage or wear is
noted, renew the struts or shock absorbers.
8If the struts or shock absorbers must be
renewed, refer to Chapter 10 for the
procedure. Always renew both units on the
same axle, or the safety of the vehicle may be
compromised. If possible, renew all four as a
set.
Steering and suspension check
9Inspect the steering system components
for damage and distortion. Look for leaks and
damaged seals, boots and fittings.
10Clean the lower end of the steering
knuckle. Have an assistant grasp the lower
edge of the tyre and move the wheel in and
out, while you look for movement at the
steering knuckle-to-axle arm balljoints.
Inspect the balljoint boots for tears (see
illustration). If there is any movement, or the
boots are torn or leaking, the balljoint(s) must
be renewed.
11Grasp each front tyre at the front and rear
edges, push in at the front, pull out at the rear
and feel for play in the steering linkage. If any
free play is noted, check the steering gear
mountings and the track rod balljoints for
looseness. If the steering gear mountings are
loose, tighten them. If the track rods are
loose, the balljoints may be worn (check to
make sure the nuts are tight). Additional
steering and suspension system information
can be found in Chapter 10.
25 Driveshaft gaiter check
1
1The driveshaft gaiters are very important
because they prevent dirt, water and foreign
material from entering and damaging the
constant velocity (CV) joints. External oil and
grease contamination can cause the gaitermaterial to deteriorate prematurely, so it’s a
good idea to wash the gaiters with soap and
water.
2Inspect the gaiters for tears and cracks, as
well as for loose clamps (see illustration). If
there is any evidence of cracks or leaking
lubricant, the gaiter must be renewed (see
Chapter 8).
26 Brake system check
2
Warning: Dust produced by lining
wear and deposited on brake
components may contain
asbestos, which is hazardous to
your health. Do not blow it out with
compressed air, and don’t inhale it! Do not
use petroleum-based solvents to remove
the dust. Brake system cleaner or
methylated spirit should be used to flush
the dust into a drain pan. After the brake
components are wiped with a damp rag,
dispose of the contaminated rag(s) and the
drain pan contents into a covered and
labelled container. Try to use asbestos-
free new parts whenever possible.
Note:In addition to the specified intervals, the
brake system should be inspected each time
the wheels are removed or a malfunction is
indicated. Because of the obvious safety con-
siderations, the following brake system checks
are some of the most important maintenance
procedures you can perform on your vehicle.
Symptoms of brake system
problems
1The disc brakes have built-in electrical wear
indicators which cause a warning light on the
dash to come on when they’re worn to the
renewal point. When the light comes on,
renew the pads immediately, or expensive
damage to the brake discs could result.
2Any of the following symptoms could
indicate a potential brake system defect:
a) Vehicle pulls to one side when the brake
pedal is depressed
b) Brakes make squealing or dragging noises
when applied
c) Brake pedal travel excessived) Brake pedal pulsates (normal if ABS is
working)
e) Brake fluid leaks (usually on the inner side
of the tyre or wheel)
3If any of these conditions are noted, inspect
the brake system immediately.
Brake lines and hoses
Note: Steel brake pipes are used throughout
the brake system, with the exception of
flexible, reinforced hoses at the front wheels
and as connectors at the rear axle. Periodic
inspection of all these lines is very important.
4Park the vehicle on level ground, and
switch off the engine. Remove the wheel
covers. Loosen, but do not remove, the bolts
on all four wheels.
5Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
6Remove the wheels (see “Jacking and
towing” at the front of this book, or refer to
your owner’s handbook, if necessary).
7Check all brake lines and hoses for cracks,
chafing of the outer cover, leaks, blisters, and
distortion. Check the brake hoses at front and
rear of the vehicle for softening, cracks,
bulging, or wear from rubbing on other
components. Check all threaded fittings for
leaks, and make sure the brake hose
mounting bolts and clips are secure.
8If leaks or damage are discovered, they
must be repaired immediately. Refer to
Chapter 9 for detailed brake system repair
procedures.
Disc brakes
9If it hasn’t already been done, raise the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the front wheels.
10The disc brake calipers, containing the
pads, are now visible. Each caliper has an
outer and an inner pad - all pads should be
checked.
11Note the pad thickness by looking
through the inspection hole in the caliper (see
illustration). If the lining material is 2.0 mm
thick or less, or if it is tapered from end to
end, the pads should be renewed (see
Chapter 9). Keep in mind that the lining
1•22
26.11 Look through the caliper inspection
window to inspect the brake pads - the
pad lining which rubs against the disc can
also be inspected by looking through each
end of the caliper25.2 Gently probe the driveshaft boots to
check for cracks24.10 Inspect the balljoint boots for tears
(arrowed)
Every 12 000 miles
Page 36 of 228
the lubricant will be hot, it would be wise to
wear rubber gloves.
3Raise the vehicle and place it on axle
stands. Make sure it is safely supported, and
as level as possible.
4Move the necessary equipment under the
vehicle, being careful not to touch any of the
hot exhaust components.
5Place the drain pan under the transmission,
and remove the filler/level plug from the side
of the transmission. Loosen the drain plug
(see illustration).
6Carefully remove the drain plug. Be careful
not to burn yourself on the lubricant.
7Allow the lubricant to drain completely.
Clean the drain plug thoroughly, then refit and
tighten it securely.
8Refer to Section 16 and fill the transmission
with new lubricant, then refit the filler/level
plug, tightening it securely.
9Lower the vehicle. Check for leaks at the
drain plug after the first few miles of driving.
32 Differential lubricant change
1
1Drive the vehicle for several miles to warm
up the differential lubricant, then raise the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands.
2Move a drain pan, rags, newspapers and an
Allen key under the vehicle. Since the
lubricant will be hot, wear rubber gloves to
prevent burns.
3Remove the filler/level plug from the
differential; this is the upper of the two plugs.
4With the drain pan under the differential,
loosen the drain plug; this is the lower of the
two plugs (see illustration).
5Carefully unscrew the drain plug until you
can remove it from the case.
6Allow all the oil to drain into the pan, then
refit the drain plug and tighten it securely.
7Refer to Section 17 and fill the differential
with lubricant.
8Refit the filler/level plug and tighten it
securely.
9Lower the vehicle. Check for leaks at the
drain plug after the first few miles of driving.
33 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system check
1
1The function of the evaporative emissions
control system is to draw fuel vapours from
the tank and fuel system, store them in a
charcoal canister, and then burn them during
normal engine operation. This system is
normally only fitted to those vehicles
equipped with a catalytic converter.
2The most common symptom of a fault in
the evaporative emissions system is a strong
fuel odour in the engine compartment. If a fuel
odour is detected, inspect the charcoal
canister and system hoses for cracks. The
canister is located in the front corner of the
engine compartment on most models (see
illustration).
3Refer to Chapter 6 for more information on
the evaporative emissions system.
34 Service indicator light
resetting
4
Service indicator lights
1All models covered in this manual are
equipped with various service indicator lights
on the facia, which automatically go on when
the mileage interval is reached. These lights
can only be turned off by using a special tool
which plugs into the service connector
located in the engine compartment.
2Although the service light resetting tool can
be obtained from a dealer, reasonably-priced
alternatives may also be available from
aftermarket sources. When obtaining a tool, it
is important to know the vehicle year and
model, and whether the service connector has
15 or 20 pins (see illustrations). Once the
proper tool is obtained, it is a simple matter to
plug it into the service connector and,
following the tool manufacturer’s instructions,
reset the service lights. Note: The brake
warning light will not automatically reset if the
sensor on the brake pad (or its wiring) isdamaged because it is worn through: it must
be repaired first.
3The service lights are controlled by the
Service Indicator (SI) board in the instrument
cluster, which is powered by rechargeable
batteries. Should these batteries fail,
problems will develop in the SI board.
Symptoms of failed batteries include the
inability to reset the service lights and
malfunctions affecting the tachometer,
temperature gauge and radio operation. Refer
to Chapter 12 for more information on the SI
board.
Every 60 000 miles
35 Engine timing belt renewal
5
Note:This is not included in the
manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, but is
strongly recommended as a precaution
against the timing belt failing in service. If the
timing belt fails while the engine is running,
extensive engine damage could be caused.
Refer to Chapter 2A, Section 10.
1•26
34.2b An aftermarket service light
resetting tool such as this one can be
plugged into the service connector and
used to reset the service lights
34.2a The earlier 15-pin connector
(arrowed) is mounted near the front of the
engine. The 20-pin connector used on later
models is located in the left rear corner of
the engine compartment33.2 Inspect the hoses (arrowed) at the
top of the evaporative emissions charcoal
canister for damage32.4 Remove the differential drain plug
with an Allen key
Every 24 000 miles
Page 37 of 228

2A
General
Displacement
3-series, E30 body style
316i (1988 to 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1596 cc (M40/4-cylinder engine)
316 (1983 to 1988) and 318i (1983 to 1987) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1766 cc (M10/4-cylinder engine)
318i (1987 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1796 cc (M40/4-cylinder engine)
320i (1987 to 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1990 cc (M20/6-cylinder engine)
325i (1987 to 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2494 cc (M20/6-cylinder engine)
5-series, E28 body style (“old-shape”)
518 (1981 to 1985) and 518i (1985 to 1988) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1766 cc (M10/4-cylinder engine)
525i (1981 to 1988) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2494 cc (M30/6-cylinder engine)
528i (1981 to 1988) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2788 cc (M30/6-cylinder engine)
535i (1985 to 1988) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3430 cc (M30/6-cylinder engine)
M535i (1985 to 1988) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3430 cc (M30/6-cylinder engine)
5-series, E34 body style (“new-shape”)
518i (1990 to 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1796 cc (M40/4-cylinder engine)
520i (1988 to 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1990 cc (M20/6-cylinder engine)
525i (1988 to 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2494 cc (M20/6-cylinder engine)
530i (1988 to 1991) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2986 cc (M30/6-cylinder engine)
535i (1988 to 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3430 cc (M30/6-cylinder engine)
Firing order
Four-cylinder engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2
Six-cylinder engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5-3-6-2-4
Lubrication system
Oil pressure (all engines)
At idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 to 2.0 bars
Running (for example, at 4000 rpm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 bars or above (typically)
Oil pump rotor clearance - M40 engine
(body-to-outer rotor/outer rotor-to-inner rotor) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.12 mm to 0.20 mm
Oil pump pressure relief valve spring length - M40 engine . . . . . . . . . . 84.1 mm
Chapter 2 Part A:
In-car engine repair procedures
Camshaft - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Compression check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Crankshaft rear oil seal - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Cylinder head - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Cylinder head - dismantling and inspection . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Drivebelt check, adjustment and renewal . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Engine mountings - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Engine oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine overhaul - general information . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Exhaust manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Flywheel/driveplate - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Front oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Intake manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5Oil pump - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Repair operations possible with the engine in the vehicle . . . . . . . . 2
Rocker arm and shaft assembly - dismantling, inspection
and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Sump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Timing belt and sprockets - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . 10
Timing belt covers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Timing chain and sprockets - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . 8
Timing chain covers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston - locating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Valve clearance check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Valve cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Valves - servicing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
2A•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
Page 38 of 228

Torque wrench settingsNm
Timing chain tensioner plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Timing belt tensioner bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Camshaft sprocket-to-camshaft bolt
M10 and M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
M20 and M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Flange to camshaft (M30 engine) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Timing chain or belt covers-to-engine
M6 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
M10 (bolt size) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Crankshaft pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Crankshaft hub bolt or nut
M10 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
M20 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
M30 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 440
M40 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
Cylinder head bolts*
M10 four-cylinder engine
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Stage 2 (wait 15 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 33°
Stage 3 (engine at normal operating temperature) . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 25°
M20 six-cylinder engine with hex-head bolts
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Stage 2 (wait 15 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Stage 3 (engine at normal operating temperature) . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 25°
M20 six-cylinder engine with Torx-head bolts
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 90°
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 90°
M30 six-cylinder engine (up to and including 1987 model year)
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Stage 2 (wait 15 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 33°
Stage 3 (engine at normal operating temperature) . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 33°
M30 six-cylinder engine (from 1988 model year)
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Stage 2 (wait 20 minutes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Stage 3 (engine at normal operating temperature) . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 35°
M40 four-cylinder engine
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 90°
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten an additional 90°
Intake manifold-to-cylinder head bolts
M8 bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
M7 bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
M6 bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Exhaust manifold-to-cylinder head nuts
M6 nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
M7 nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Flywheel/driveplate bolts
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Intermediate shaft sprocket bolt (M20 engines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Sump-to-block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 to 11
Oil pump bolts (except M40 engines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Oil pump sprocket bolts (M10 and M30 engines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Oil pump cover plate-to-engine front end cover (M40 engines) . . . . . . . 9
Front end cover-to-engine bolts (M20 and M40 engines)
M6 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Crankshaft rear oil seal retainer-to-block bolts
M6 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
* BMW recommend that the cylinder head bolts are renewed as a matter of course.
2A•2 In-car engine repair procedures
Page 39 of 228
1 General information
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to in-
vehicle engine repair procedures. All
information concerning engine removal and
refitting and engine block and cylinder head
overhaul can be found in Chapter 2B.
The following repair procedures are based
on the assumption that the engine is still fitted
in the vehicle. If the engine has been removed
from the vehicle and mounted on a stand,
many of the steps outlined in this Part of
Chapter 2 will not apply.
The Specifications included in this Part of
Chapter 2 apply only to the procedures
contained in this Part. Chapter 2B contains
the Specifications necessary for cylinder head
and engine block rebuilding.
The single overhead camshaft four- and
six-cylinder engines covered in this manual
are very similar in design. Where there are
differences, they will be pointed out.
The means by which the overhead
camshaft is driven varies according to engine
type; M10 and M30 engines use a timing
chain, while M20 and M40 engines have a
timing belt.
2 Repair operations possible
with the engine in the vehicle
Many major repair operations can be
accomplished without removing the engine
from the vehicle.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and help keep dirt out of
the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (see Chapter 11 if necessary).
Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint. Special pads are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for gasket or seal
renewal, the repairs can generally be made
with the engine in the vehicle. The intake and
exhaust manifold gaskets, sump gasket,
crankshaft oil seals and cylinder head gasket
are all accessible with the engine in place.
Exterior components, such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator, the distributor and the fuel system
components, can be removed for repair with
the engine in place.
The cylinder head can be removed without
removing the engine, so this procedure is
covered in this Part of Chapter 2. Camshaft,
rocker arm and valve component servicing ismost easily accomplished with the cylinder
head removed; these procedures are covered
in Part B of this Chapter. Note, however, that
the camshaft on the M40 engine may be
removed with the engine in the vehicle since it
is retained by bearing caps.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine in
the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved.
3 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
No 1 piston- locating
2
Note 1:The following procedure is based on
the assumption that the distributor (if
applicable) is correctly fitted. If you are trying
to locate TDC to refit the distributor correctly,
piston position must be determined by feeling
for compression at the No 1 spark plug hole,
then aligning the ignition timing marks or
inserting the timing tool in the flywheel, as
applicable.
Note 2:The No 1 cylinder is the one closest to
the radiator.
1Top Dead Centre (TDC) is the highest point
in the cylinder that each piston reaches as it
travels up and down when the crankshaft
turns. Each piston reaches TDC on the
compression stroke and again on the exhaust
stroke, but TDC generally refers to piston
position on the compression stroke.
2Positioning the piston at TDC is an essential
part of many procedures, such as timing belt
or chain removal and distributor removal.
3Before beginning this procedure, be sure to
place the transmission in Neutral, and apply
the handbrake or chock the rear wheels. Also,
disable the ignition system by detaching the
coil wire from the centre terminal of the
distributor cap, and earthing it on the engine
block with a jumper wire. Remove the spark
plugs (see Chapter 1).
4In order to bring any piston to TDC, the
crankshaft must be turned using one of the
methods outlined below. When looking at the
front of the engine, normal crankshaft rotation
is clockwise.
(a) The preferred method is to turn the
crankshaft with a socket and ratchet
attached to the bolt threaded into the
front of the crankshaft.
(b) A remote starter switch, which may save
some time, can also be used. Follow the
instructions included with the switch.
Once the piston is close to TDC, use a
socket and ratchet as described in the
previous paragraph.
(c) If an assistant is available to turn the
ignition switch to the Start position in
short bursts, you can get the piston close
to TDC without a remote starter switch.Make sure your assistant is out of the
vehicle, away from the ignition switch,
then use a socket and ratchet as
described in (a) to complete the
procedure.
5Note the position of the terminal for the
No 1 spark plug lead on the distributor cap. If
the terminal isn’t marked, follow the plug lead
from the No 1 cylinder spark plug to the cap
(No 1 cylinder is nearest the radiator).
6Use a felt-tip pen or chalk to make a mark
directly below the No 1 terminal on the
distributor body or timing cover.
7Detach the distributor cap, and set it aside
(see Chapter 1 if necessary).
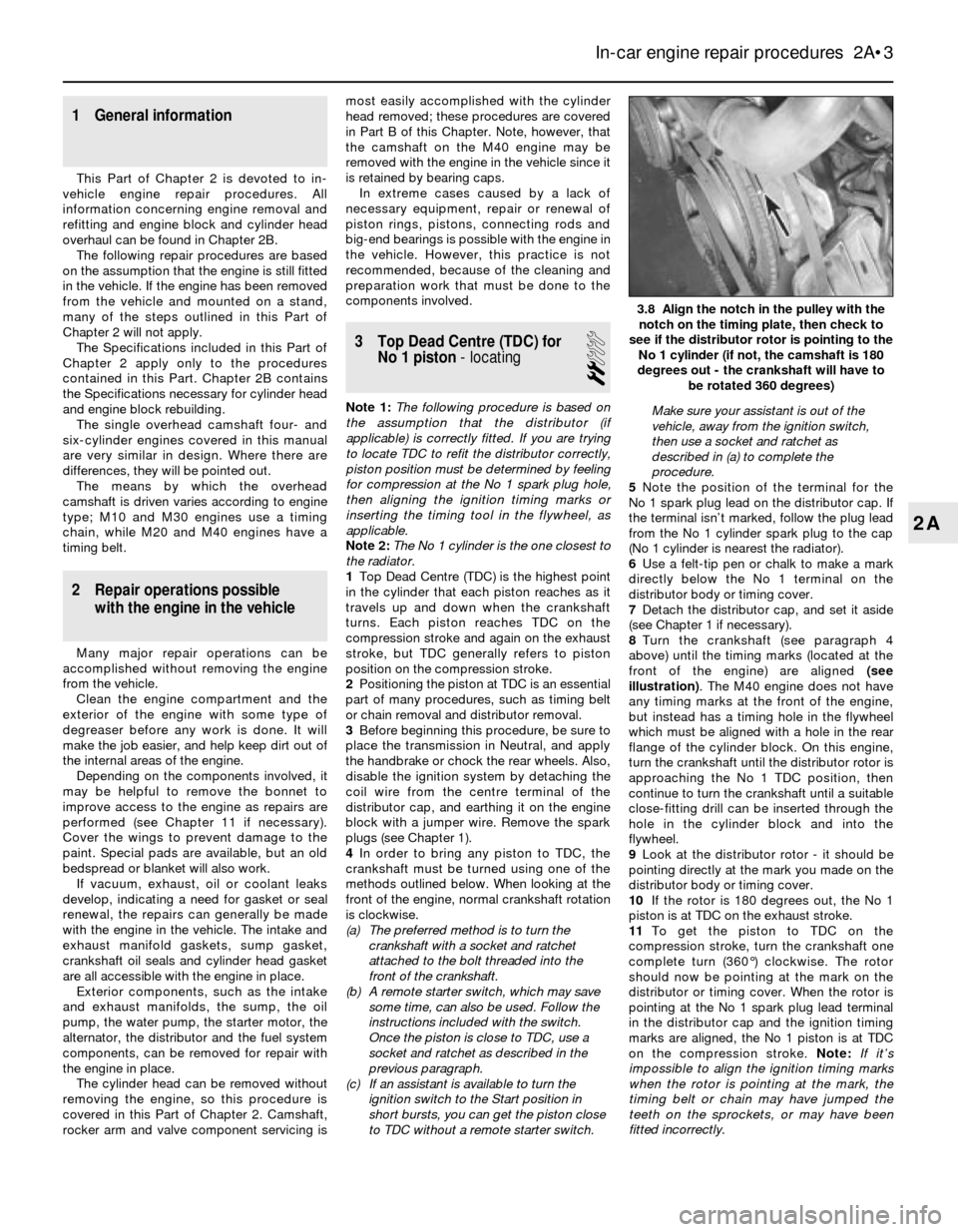
8Turn the crankshaft (see paragraph 4
above) until the timing marks (located at the
front of the engine) are aligned (see
illustration). The M40 engine does not have
any timing marks at the front of the engine,
but instead has a timing hole in the flywheel
which must be aligned with a hole in the rear
flange of the cylinder block. On this engine,
turn the crankshaft until the distributor rotor is
approaching the No 1 TDC position, then
continue to turn the crankshaft until a suitable
close-fitting drill can be inserted through the
hole in the cylinder block and into the
flywheel.
9Look at the distributor rotor - it should be
pointing directly at the mark you made on the
distributor body or timing cover.
10If the rotor is 180 degrees out, the No 1
piston is at TDC on the exhaust stroke.
11To get the piston to TDC on the
compression stroke, turn the crankshaft one
complete turn (360°) clockwise. The rotor
should now be pointing at the mark on the
distributor or timing cover. When the rotor is
pointing at the No 1 spark plug lead terminal
in the distributor cap and the ignition timing
marks are aligned, the No 1 piston is at TDC
on the compression stroke. Note:If it’s
impossible to align the ignition timing marks
when the rotor is pointing at the mark, the
timing belt or chain may have jumped the
teeth on the sprockets, or may have been
fitted incorrectly.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•3
3.8 Align the notch in the pulley with the
notch on the timing plate, then check to
see if the distributor rotor is pointing to the
No 1 cylinder (if not, the camshaft is 180
degrees out - the crankshaft will have to
be rotated 360 degrees)
2A
Page 40 of 228
12After the No 1 piston has been positioned
at TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for
any of the remaining pistons can be located
by turning the crankshaft and following the
firing order. Mark the remaining spark plug
lead terminal locations just like you did for the
No 1 terminal, then number the marks to
correspond with the cylinder numbers. As you
turn the crankshaft, the rotor will also turn.
When it’s pointing directly at one of the marks
on the distributor, the piston for that particular
cylinder is at TDC on the compression stroke.
4 Valve cover-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Detach the breather hose from the valve
cover.
3On M20 engines, unbolt and remove the
intake manifold support bracket and, if
applicable, the bracket for the engine sensors
or idle air stabiliser (it will probably be
necessary to disconnect the electrical
connectors from the sensors and stabiliser).
4On M30 engines, disconnect the electrical
connector for the airflow sensor. Unclip the
electrical harness, moving it out of the way.
5Where necessary on M30 engines, remove
the hoses and fittings from the intake air hose,
then loosen the clamp and separate the hose
from the throttle body. Unscrew the mounting
nuts for the air cleaner housing, and remove
the housing together with the air hose and
airflow sensor.
6Remove the valve cover retaining nuts and
washers (see illustrations). Where necessary,
disconnect the spark plug lead clip or coverfrom the stud(s), and set it aside. It will usually
not be necessary to disconnect the leads from
the spark plugs.
7Remove the valve cover and gasket.
Discard the old gasket. On the M40 engine,
also remove the camshaft cover (see
illustrations). If applicable, remove the semi-
circular rubber seal from the cut-out at the
front of the cylinder head.
Refitting
8Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the valve cover and cylinder head.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Gasket
removal solvents are available at
motor factors, and may prove helpful.
After all gasket material has been
removed, the gasket surfaces can be
degreased by wiping them with a rag
dampened with a suitable solvent.
9If applicable, place a new semi-circular
rubber seal in the cut-out at the front of the
cylinder head, then apply RTV-type gasket
sealant to the joints between the seal and the
mating surface for the valve cover gasket.
Note:After the sealant is applied, you should
refit the valve cover and tighten the nuts within
ten minutes.
10Refit the camshaft cover (M40 engine), the
valve cover and a new gasket. Refit the
washers and nuts; tighten the nuts evenly and
securely. Don’t overtighten these nuts - theyshould be tight enough to prevent oil from
leaking past the gasket, but not so tight that
they warp the valve cover.
11The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
5 Intake manifold-
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Allow the engine to cool completely, then
relieve the fuel pressure on fuel-injection
engines (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Drain the engine coolant (see Chapter 1)
below the level of the intake manifold. If the
coolant is in good condition, it can be saved
and reused.
4On fuel injection engines, loosen the hose
clamp and disconnect the large air inlet hose
from the throttle body. It may also be
necessary to remove the entire air
cleaner/inlet hose assembly to provide
enough working room (see Chapter 4).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
4.7b Removing the camshaft cover on the
M40 engine4.7a Removing the valve cover on the
M40 engine4.7c Removing the valve cover gasket on
the M40 engine
4.6b Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M20 six-cylinder engines4.6a Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M10 four-cylinder engines
Page 41 of 228
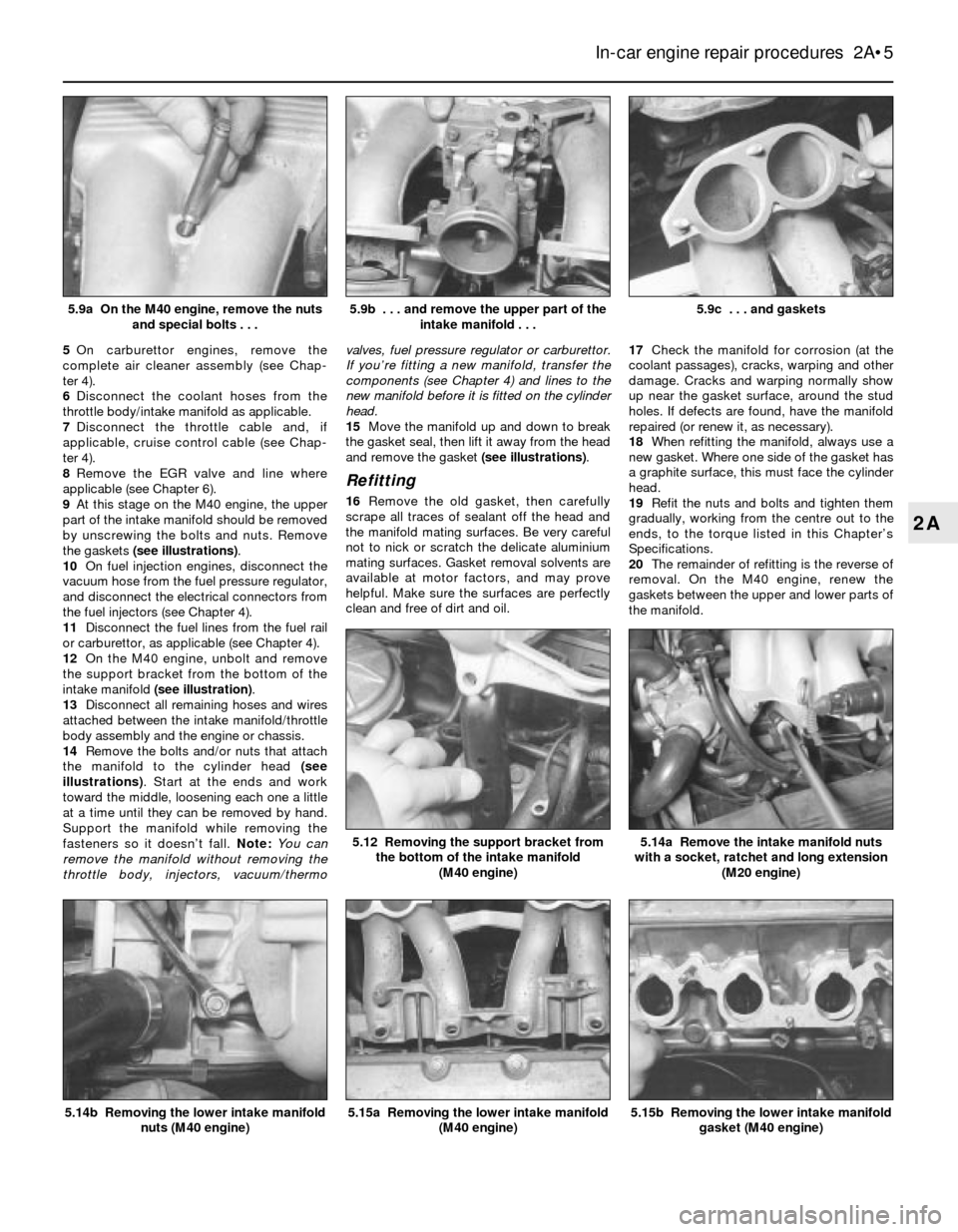
5On carburettor engines, remove the
complete air cleaner assembly (see Chap-
ter 4).
6Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
throttle body/intake manifold as applicable.
7Disconnect the throttle cable and, if
applicable, cruise control cable (see Chap-
ter 4).
8Remove the EGR valve and line where
applicable (see Chapter 6).
9At this stage on the M40 engine, the upper
part of the intake manifold should be removed
by unscrewing the bolts and nuts. Remove
the gaskets (see illustrations).
10On fuel injection engines, disconnect the
vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator,
and disconnect the electrical connectors from
the fuel injectors (see Chapter 4).
11Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel rail
or carburettor, as applicable (see Chapter 4).
12On the M40 engine, unbolt and remove
the support bracket from the bottom of the
intake manifold (see illustration).
13Disconnect all remaining hoses and wires
attached between the intake manifold/throttle
body assembly and the engine or chassis.
14Remove the bolts and/or nuts that attach
the manifold to the cylinder head (see
illustrations). Start at the ends and work
toward the middle, loosening each one a little
at a time until they can be removed by hand.
Support the manifold while removing the
fasteners so it doesn’t fall. Note: You can
remove the manifold without removing the
throttle body, injectors, vacuum/thermovalves, fuel pressure regulator or carburettor.
If you’re fitting a new manifold, transfer the
components (see Chapter 4) and lines to the
new manifold before it is fitted on the cylinder
head.
15Move the manifold up and down to break
the gasket seal, then lift it away from the head
and remove the gasket (see illustrations).
Refitting
16Remove the old gasket, then carefully
scrape all traces of sealant off the head and
the manifold mating surfaces. Be very careful
not to nick or scratch the delicate aluminium
mating surfaces. Gasket removal solvents are
available at motor factors, and may prove
helpful. Make sure the surfaces are perfectly
clean and free of dirt and oil.17Check the manifold for corrosion (at the
coolant passages), cracks, warping and other
damage. Cracks and warping normally show
up near the gasket surface, around the stud
holes. If defects are found, have the manifold
repaired (or renew it, as necessary).
18When refitting the manifold, always use a
new gasket. Where one side of the gasket has
a graphite surface, this must face the cylinder
head.
19Refit the nuts and bolts and tighten them
gradually, working from the centre out to the
ends, to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
20The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal. On the M40 engine, renew the
gaskets between the upper and lower parts of
the manifold.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•5
5.9c . . . and gaskets5.9b . . . and remove the upper part of the
intake manifold . . .5.9a On the M40 engine, remove the nuts
and special bolts . . .
5.15b Removing the lower intake manifold
gasket (M40 engine)5.15a Removing the lower intake manifold
(M40 engine)
5.14a Remove the intake manifold nuts
with a socket, ratchet and long extension
(M20 engine)5.12 Removing the support bracket from
the bottom of the intake manifold
(M40 engine)
5.14b Removing the lower intake manifold
nuts (M40 engine)
2A