sensor BMW 525i 2000 E39 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2000, Model line: 525i, Model: BMW 525i 2000 E39Pages: 1002
Page 459 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
--
Fuel Injection I
The PWG potentiometers provide DC voltage signals as in-
put to the ME 7.2 control module for throttle and idle control
functions. Potentiometer signal
1 is the primary signal, poten-
tiometer 2 is used for a plausibility cross-check.
1. Potentiometer 1 ground
2. Potentiometer
1 power
3. Potentiometer 2 ground
4. Potentiometer 2 power
5. Potentiometer 1 signal to ECM
6. Potentiometer 2 signal to ECM
If errors are detected between potentiometer
1 and 2, the
ECM calculates the engine intake air mass (from
MAFsensor
signal) and only utilizes the potentiometer signal that closely
matches the detected
intake air mass. The ECM control mod-
ule uses the air mass signal for a comparative source to pro-
vide fail-safe operation.
If the ECM cannot calculate a
plausible conclusion from the monitored potentiometerthe
EDK motor is switched off and fuel injection cut-out is activat-
ed (no fail-safe operation possible).
EDK is continuously monitored during all phases of engine
operation. If faults are detected, the EDK motor is switched off
and fuel injection cut off is activated. The engine continues to
run extremely roughly at idle speed.
EDK adaptation
When the EDK throttle assembly is replaced, the adaptation
values of the previous EDK must be cleared from the ME 7.2
ECM using the BMW service testeroran equivalentscan tool.
Once the old adaptation values have been cleared, the new
EDK assembly should be installed and adapted as follows:
0 Switch ignition OFF for 10 seconds.
* Switch ignition ON. Afler approximately 30 seconds, the
EDK is briefly activated indicating that the replacement unit
is now adapted to the ME 7.2 system.
NOTE-
This EDK adaptation procedure is also necessary after re-
placing the
ME 7.2 engine control module. However, the ad-
aptation values do not require clearing since they have not
yet been established.
ECM relay, testing
The engine control module (ECM) relay is energized via the
ECM and supplies battery positive
(B+) power to many of the
engine management components and subsystems. If this re-
lay is faulty, the engine will not start.
NOTE-
The ECM relay is also referred to as the DME main relay
Page 461 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection I
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor,
testing
The ECT sensor is located on the front of the engine in the
coolant~thermostat flange. The ECT sensor is a dual temper-
ature sensor. One circuit provides coolant temperature infor-
mation to the ECM while the other circuit provides coolant
temperature information to the instrument cluster.
The ECM determines the correct ignition timing and
airlfuel
mixture required for the engine by monitoring an applied volt-
age
(5 vdc) to the sensor. Thevoltage drop across the sensor
varies as the coolant temperature (sensor resistance) chang-
es.
NOTE-
The ECT sensor is an NTC (negative temperature coeffi-
cient) type sensor. In other words, as the temperature rises,
resistance through the sensor decreases.
If the ETC sensor input is faulty or non-plausible, the MIL is il-
luminated when OBD
II fault criteria are exceeded. The ECM
assumes a substitute value
(80" C/ 176°F) to maintain engine
operation. The ignition timing is set to a
conse~ativelsafe ba-
sic setting.
Disconnect harness from
ECTsensor (A) at coolant flange at
front of engine.
- Check ECT sensor resistance using a multimeter at sensor
terminals
3 and 4. Peel back protective boot (B) to ID termi-
nal numbers on connector housing.
I ECT sensor resistance @ 20" C (68°F) I 2.2 - 2.7 lkCi
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor,
replacing
I WARNING-
/ Due to risk ofpersonal injury, be sure the engine is cold be- I
I fore replacin~~~~sensor. -
-
I
- Disconnect ECT sensor harness.
- Unscrew ECT sensor from cylinder head and install new sen-
sor.
Use new copper sealing washers when installing sensor.
Replace any lost coolant.
Tightening torque
ECT sensor to coolant flange 13 Nm (10 it-lb)
Page 462 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-72
Fuel Injection
I Oxygen sensors, replacing
4 Four Bosch oxygen sensors (2 precatalytic converter sen-
sors and
2 post-catalytic converter sensors) provide a vary-
ing voltage signal
[0.2 vdc (max. lean) to 0.8 vdc (max. rich)]
to the ME
7.2 ECM representing oxygen content in the ex-
haust gas.
WARNING-
Exhaust manifolds and pipes can be hot enough to cause se-
rious burns. Wear suitable heavy gloves and other appropri-
ate protection.
- Using a special oxygen sensor socltet, remove the threaded
sensors from the exhaust system.
- If not already applied, coat the new oxygen sensor threads
with an anti-seize compound before installation. Do not get
compound on the sensor tip.
Tightening torque
Oxygen sensor to exhaust system
50 Nm (37 ft-lb)
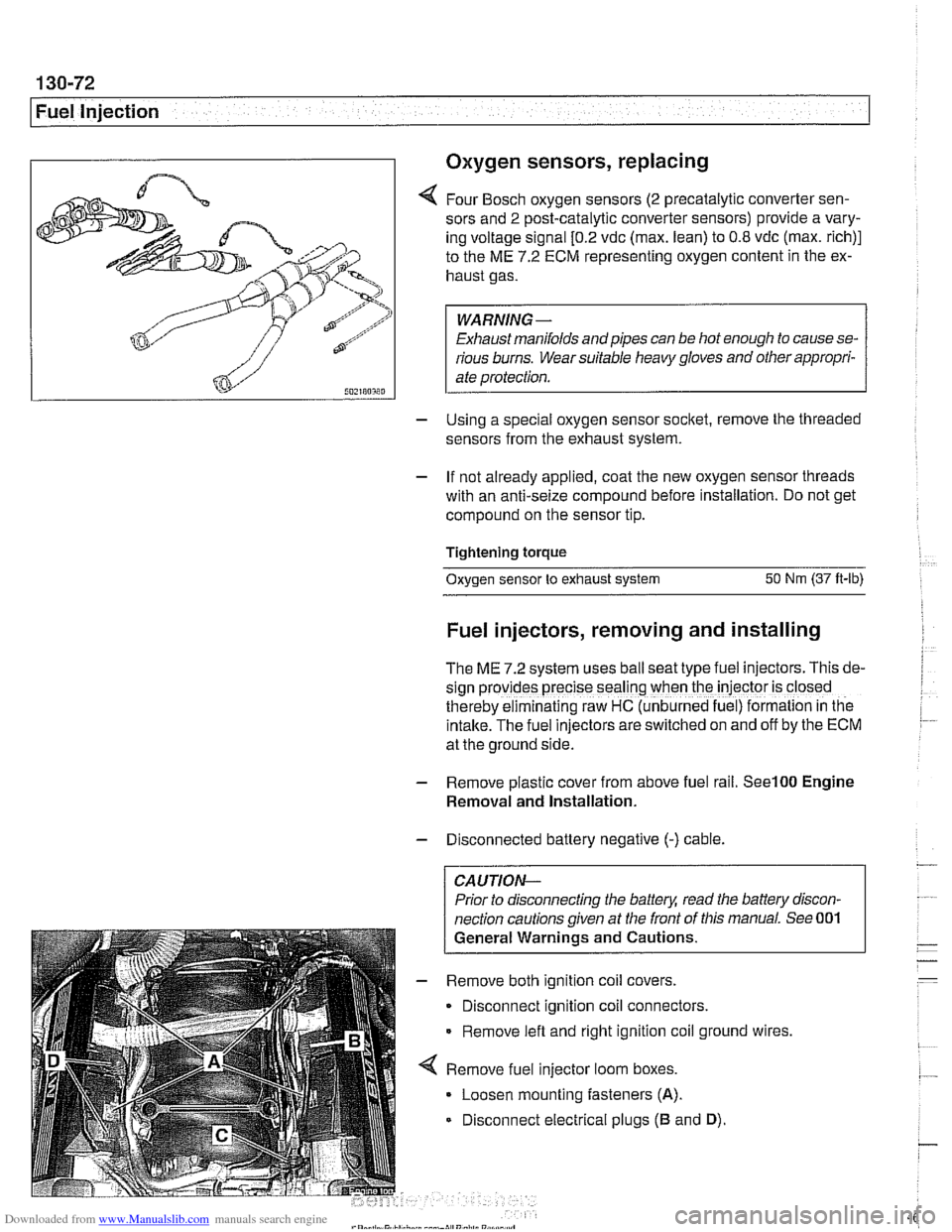
Fuel injectors, removing and installing
The ME 7.2 system uses ball seat type fuel injectors. This de-
sign
prov:des precise seal'ng when the iniector is closed
therebv eiminalinq raw HC (unb~rned fue ) formalion in tne
intake.-~he fuel inkctors areswitched on and off by the ECM
at the ground side.
- Remove plastic cover from above fuel rail. See100 Engine
Removal and Installation.
- Disconnected battery negative (-) cable.
CAUTION-
Prior to disconnecting the battea read the battery discon-
nection cautions given at the front of this manual. See 001
General Warnings and Cautions.
- Remove both ignition coil covers.
Disconnect ignition coil connectors.
Remove left and right ignition coil ground wires,
4 Remove fuel injector loom boxes.
Loosen mounting fasteners
(A).
Disconnect electrical plugs (B and D).
Page 463 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
( Mass Air Flow Sensor
1" Intake air temp. (NTC)
Sensor qround
Reference voltage . . . -., f fitr mass signal I
Fuel Injection I
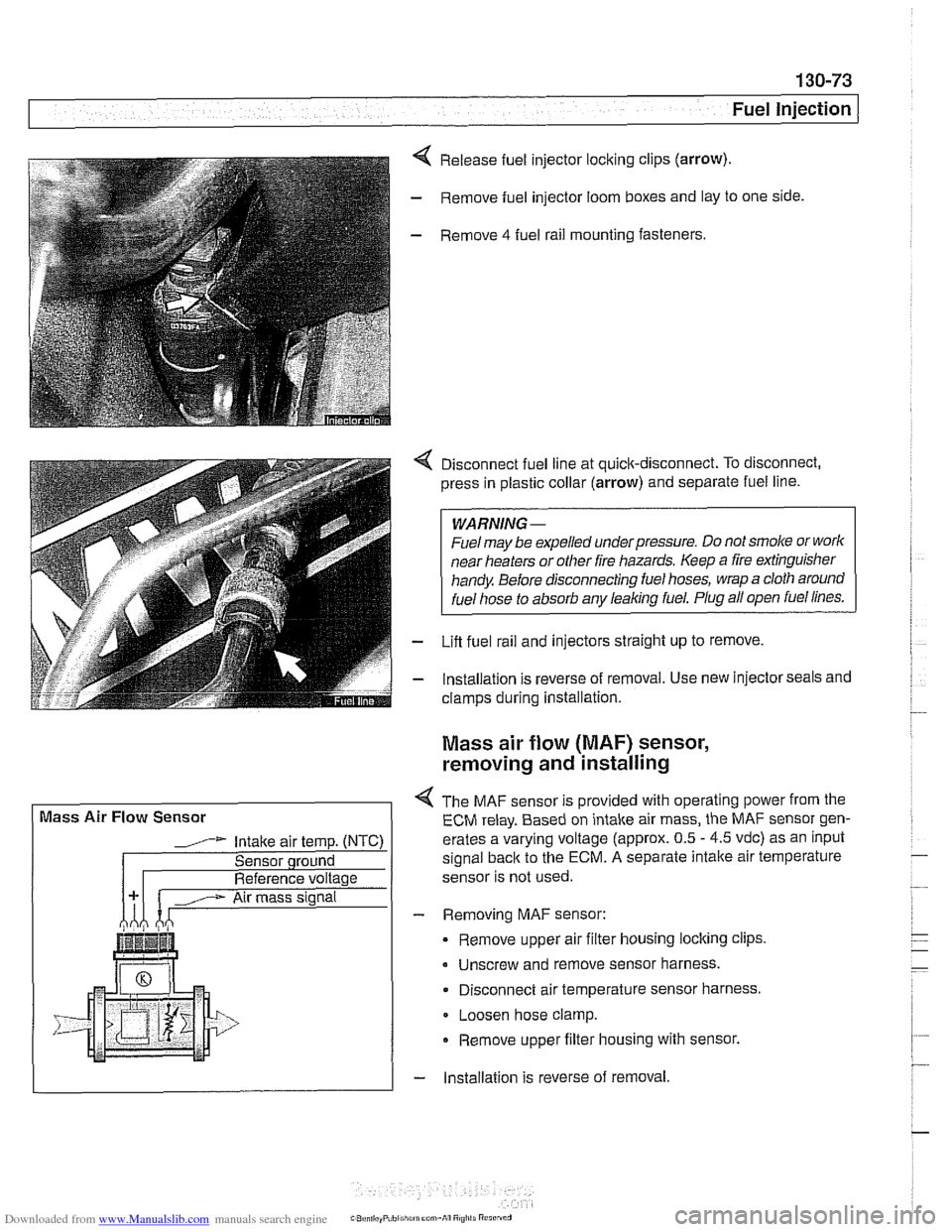
Release fuel injector locking clips (arrow).
- Remove fuel injector loom boxes and lay to one side.
- Remove 4 fuel rail mounting fasteners.
4 Disconnect fuel line at quick-disconnect. To disconnect,
press in plastic collar (arrow) and separate fuel line.
WARNING -
Fuel may be expelled underpressure. Do not srnol(e or work
near heaters or
other fire hazards. Keep a fire extinguisher
handy. Before disconnecting fuel hoses, wrap a cloth around
fuel hose
to absorb anv leakinq fuel. Plug all open fuel lines.
- Lifl fuel rail and injectors straight up to remove.
- lnstallation is reverse of removal. Use new injector seals and
clamps during installation.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor,
removing and installing
4 The MAF sensor is provided with operating power from the
ECM relay. Based on intake air mass, the MAF sensor gen-
erates a varying voltage (approx. 0.5
- 4.5 vdc) as an input
signal
back to the ECM. A separate intalte air temperature
sensor is not used.
- Removing MAF sensor:
Remove upper air filter housing locking clips
Unscrew and remove sensor harness.
Disconnect air temperature sensor harness.
Loosen hose clamp.
Remove upper filter housing with sensor.
- lnstallation is reverse of removal
Page 465 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-75
Fuel Injection
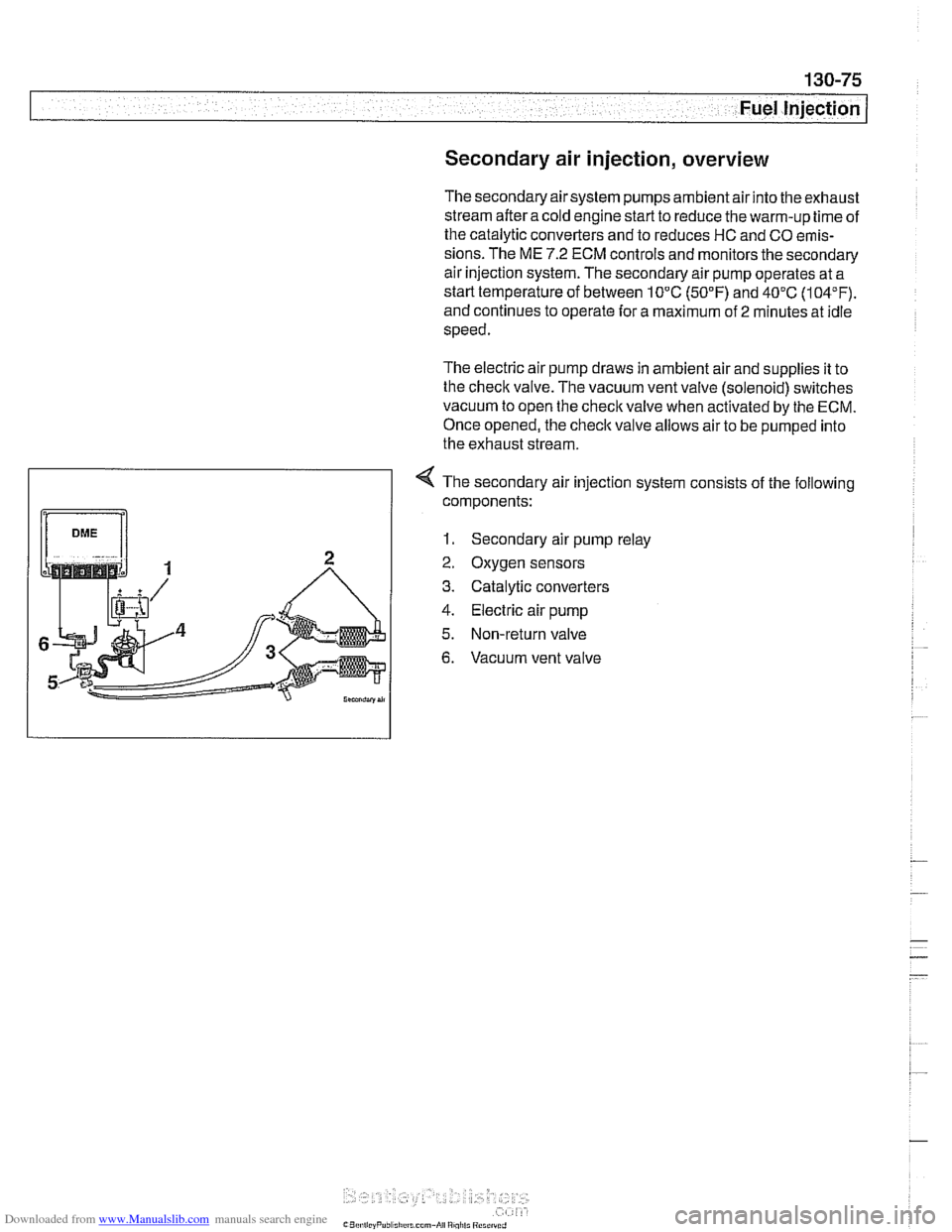
Secondary air injection, overview
The secondary air system pumps ambient air into the exhaust
stream afteracoid engine start to reduce the warm-up time of
the catalytic converters and to reduces HC and CO emis-
sions. The ME
7.2 ECM controls and monitors the secondary
air injection system. The secondary air pump operates at a
starttemperature of between 10°C
(50°F) and 40°C (104°F).
and continues to operate for a maximum of
2 minutes at idle
speed.
The electric air pump draws in ambient air and supplies it to
the
checlc valve. The vacuum vent valve (solenoid) switches
vacuum to open the
checlc valve when activated by the ECM.
Once opened, the checlc
valve allows air to be pumped into
the exhaust stream.
4 The secondary air injection system consists of the following
components:
1. Secondary air pump relay
2. Oxygen sensors
3. Catalytic converters
4. Electric air pump
5. Non-return valve
6. Vacuum vent valve
Page 466 of 1002
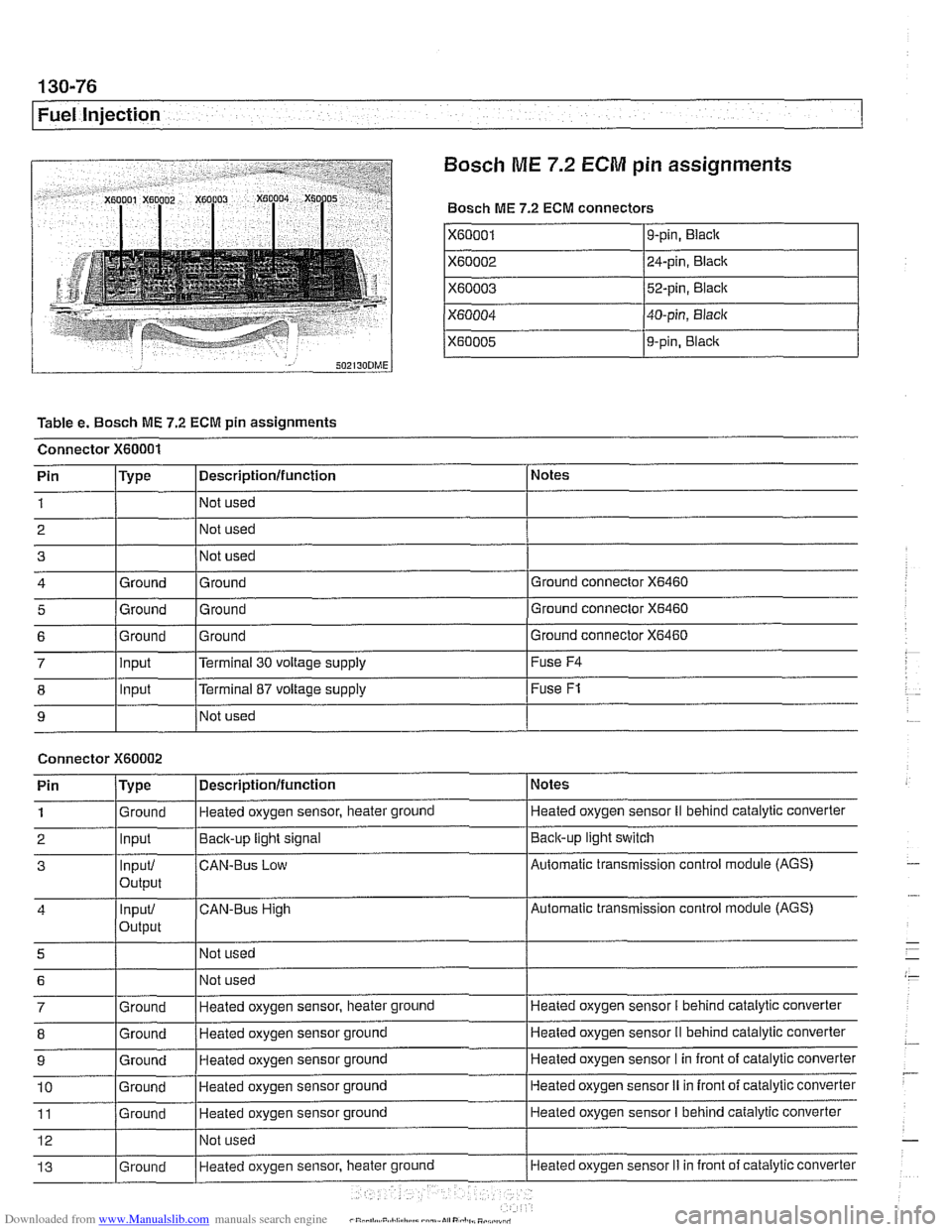
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-76
Fuel Injection
Bosch
ME 7.2 ECM pin assignments
Bosch ME 7.2 ECM connectors
X60001
X60002
X60003
X60004
X60005
Table e. Bosch ME 7.2 ECM pin assignments
Connector
X60001
I I I
8 1 lnput [Terminal 87 voltage supply I Fuse F1
9-pin, Black
24-pin, Black
52-pin, Black
40-pin, Black
9-pin,
Blaclc
I I I
9 I NO^ used I
Notes
Ground connector
X6460
Ground connector X6460
Pin 1
2 3
4
5
Connector X60002
Ground connector X6460 6
Pin
/Type I Descriptionlfunction 1 Notes
Type
Ground
Ground
7 llnput l~errninai 30 voltage supply I Fuse F4
Descriptionlfunction
Not used
Not used
Not used
Ground Ground
Ground Ground
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
. . - Ground Input
Input/
output
input/
Output
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground Heated oxygen sensor, heater ground
Back-up
light signal
CAN-BUS Low
CAN-Bus High
Not used Not used
Heated oxygen sensor, heater ground
Heated oxygen sensor ground
Heated oxygen sensor ground
Heated oxygen sensor ground
Heated oxygen sensor ground
Not used
Heated oxvaen sensor, heater
ground
Heated oxygen sensor II behind catalylic converter
Baclcup light switch
Automatic transmission control module (AGS)
Automatic transmission control module (AGS)
Heated oxygen sensor
I behind catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
II behind catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor I in front of catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
II in front of catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
I behind catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
Ii in front of catalytic converter
Page 467 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel lnjection
I 1- I
4 /output l~em~erature signal. E-box fan I E-box fan
Connector
X60002 (continued)
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Input
Input
Input
Input
Ground
Output Heated
oxygen sensor signal
Heated oxygen sensor signal
Heated oxygen sensor signal
Heated oxygen sensor signal
Not used
Heated oxygen sensor, heater ground
Not used
Not used
Not used
Terminal 85 control
Not used Heated oxygen sensor
II behind catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
I in front of catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
I1 in front of catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor
I behind catalytic converter
Heated oxygen sensor I in front of catalytic converter
Engine control module relay
Connector
X60003
Ground
Output Input
Ground
Output
Input
Input
Output
Output
Input
Pin 1
2
3
Not used
Ground for electronic components
Voltage supply for hot
film mass air flow sensor
Signal EDK (electric throttle actuator) Hot film mass air flow sensor, ground
Electric throttle actuator
Not used
Voltage signal, terminal 30h
Alternator
D+ (terminal 61) signal
Injection signal
Injection signal
VANOS valve, signal
Type
Output
Output
Output
Ground connector
X6460
Hot film mass air flow sensor
Electric throttle actuator
Hot film mass air flow sensor
Electric throttle actuator, voltage supply
Starter
Alternator (generator)
Cylinder
7 fuel injection valve
Cylinder 6 fuel injection valve
VANOS valve, cylinder
5-8
Descriptionlfunction
Injection signal
Injection signal
Signal evaporative emission valve Notes
Cylinder 2 fuel injector valve
Cylinder 3 fuel injector valve
Evaporative emission valve
Page 468 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
I Fuel Injection
Connector X60003 (continued) Electric throttle actuator
25
- 27 28
29
30
31
32
33
I I I
36 jlnput I Knoclc sensor 2, signal 1 Knock sensor
I I I
Input
26
Output
Output
input
Output
Input
I ' I . I
43 1 ln~ut I Electric throttle actuator, signal (Electric throttle actuator
Ground, electric throttle actuator
1 Not
used
Hot film mass air flow sensor
34
- 37
38
39
40
41
42
injection signal
Injection
signal
VANOS valve, signal
Not used
Thermostat characteristic map, signal
Crankshaft position sensor, signal
Not used
35 l~round I~nock sensor, shield 1 ~nock sensor
Cylinder
8 fuel injection valve
Cylinder
5 fuel injection valve
VANOS valve, cylinders
1-4
Characteristic map
Crankshaft positionlrpm sensor
input
input
Ground
Input
Output
Output
Innut
Hot film mass air flow sensor, signal
I
44
45 46
47
48
49
50
51
52
Connector )(GO004
Knock sensor 4, signal
Knock sensor, shield
Oil
level (thermal)
Injection, signal
Injection, signal
Electric throttle actuator, signal
Not used
Ground
Crankshaft position sensor, signal
Not used
Knoclc sensor, shield
Knock sensor
1, signal
Knock sensor
3, signal
Knock sensor, shield
Secondary air injection pump valve, signal
'
Ground
Input
Ground
input Input
Ground
Input
I' I ... I . ~
Knock sensor
Knocic sensor
Oil level sensor
Cylinder
4 fuel injection valve
Cylinder
1 fuel injection valve
Electric throttle actuator
Crankshaft sensor shield
Crankshaft
positionlrprn sensor
Knock sensor
Knock sensor
Knock sensor
Knock sensor
Secondary air injection pump valve
Notes
Instrument cluster
Integrated instrument cluster control
Secondary air injection pump
relay
Pin
1
2
3
Electric (auxiliary) cooling fan 4
Type
Output
Output
Outout
Descriptionlsignal type
Charge indicator signal (terminal
61)
Voltage signal, terminal 30h
Secondam air pump relay, activation
Input
5
Signal, electric (auxiliary) cooling fan, signal
I~ot used
Page 469 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection I
Connector X60004 (continued)
8 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
9
Output 0
Input
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
39
llnput lsignal l~oolant outlet temperature sensor
Output
Output
Ground
Input
Output
I I - I
40 /output Istart signal Istarter relay
Pedal position sensor (PWG), signal
Output Input
Output
input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
input
Input
Output
Input/-output
Input/-output
37
Connector X60003
Pedal position sensor
Fuel pump relay, activation
Oil pressure indicator Pedal position sensor (PWG), ground
Pedal position sensor (PWG), signal
Pedal position sensor (PWG), power supply
Not used
Not used Fuel
pump relay
Instrument cluster
Pedal position sensor
Pedal position sensor
Pedal position sensor
Engine speed signal output (TD)
Not used
Signal
back-up light
DM-TL (diagnostic module,
tank leakage)
Signal oil level sensor
Right rear wheel speed, signal
Clutch pedal position switch, signal
Brake light switch, signal
Not used
Voltage supply, terminal
15
Data link, MFL (multi-function steering wheel)
Brake light test signal
AJC compressor signal
DM-TL (diagnostic module, tank
leakage)
Not used
Diagnosis signal
TxD
Communication link (EWS)
Not used
Not used
CAN-BUS hiqh
38 1 Ground l~round I Coolant outlet temperature sensor
OED II plug
Integrated instrument cluster control module (IKE)
Light module
ABSIDSC control module
Clutch pedal position switch
Brake light switch
Fuse
F14
Airbag contact coil spring
Brake light switch
Heating and
A/C control module
OBD
II plug
Electronic immobilizer (EWS)
CAN-Bus link
CAN-Bus link
Input/-output CAN-Bus low
Page 474 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Tank and Fuel Pump
Evaporative system troubleshooting
- Start by accessing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using a
BMW or BMW compatible aftermarket scan tool.
For purposes of OBD
II emissions compliance, the DME
system sets a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) when it de-
tects a leak that is equal or larger than minimum
lealc
sensed by system.
Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) is illuminated upon sec-
ond recurrence of fault. See OBD On-Board Diagnostics.
- When leak testing, observe following conditions to obtain
plausible results:
Fuel tank
'1, to 'I., full.
0 Vehicle parked for at least 2 hours to allow fuel to reach
room temperature.
Ideal fuel temperature is 10"- 20°C
(50"
- 68" F).
Do not refuel immediately before
lealc test.
- If a leak is detected, check the following areas:
* Fuel filter cap (leaking or off).
Fuel tank ventilation lines leaking at fuel
tank or activated
carbon canister.
i
Tank ventilation valve leaking (in engine compartment).
Fuel level
sensorlfuel pump cap leaking.
Evaporative system component replacement is covered later
in
th~s group in Fuel Tank and Fuel Lines.