OBD port BMW 530i 2001 E39 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2001, Model line: 530i, Model: BMW 530i 2001 E39Pages: 1002
Page 13 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
General
0 GENERAL, MAINTENANCE covers general vehicle infor-
mation
(010 General) as well as the recommended mainte-
nance schedules and service procedures to perform BMW
scheduled maintenance
work (020 Maintenance).
The next seven sections
(1 through 7) are repair based and
organized by three digit repair groups. Most major sections
begin with a GENERAL repair group,
e.g. 100 Engine-Gen-
eral. These "00 (double zero) groups contain descriptive the-
ory of operation and system troubleshooting information. The
remainder of the repair groups within a section contain the
service and repair information. The last two sections contain
detailed electrical wiring schematics and OBD
II scan tool and
diagnostic information.
Warnings, cautions and notes
Throughout this manual are many passages with the head-
ings WARNING, CAUTION, or NOTE. These very important
headings have different meanings.
WARNING-
The text under this heading warns of unsafe practices that
are very
likely to cause injury, either by direct threat to the per-
son(~) performing the work
orby increasedrisl( of accident or
mechanical failure while
drivinq.
CAUTION-
A CAUTION calls attention to importantprecautions to be ob-
senfed during the repair work that will help prevent acciden-
tally damaging the car or its parts.
NOTE-
A NOTE contains helpful information, tips that will help in do-
ing a betterjob and completing it more easily.
Please read every WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE in
001
General Warnings and Cautions and as they appear in re-
pair procedures. They are very important. Read them before
you begin any maintenance or repair job.
Page 360 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
120-1 2
ignition System
Crankshaftspeedsensor
Crankshaft speed sensor, replacing (M52, M52 TU and
M54 engines)
4 Crankshaft speed sensor for 6-cylinder engine is mounted in
the left rear side of the cylinder block below the starter (ar-
row). The sensor reads a toothed pulse wheel mounted to
the end of the crankshaft.
- if the Engine Control Module (ECM) does not receive a signal
from the crankshaft speed sensor during cranking, the en-
gine will not start.
- If the OBD II svstem misfire detection ~rotocol detects a cat- - - ~~
alysr oarnagin; faLlt oJe to a ma I-nclion in crandshafi speeo
sensor components. Ine Check Engine
lignr (Malfuncrion In-
dicator Light or MIL) will be illuminated.
NOTE-
If the crankshaft speed sensor pulse wheel is damaged, the
engine will have to be disassembled down to the crankshaft
to
reolace the wheel.
- Make certain ignition has been turned off.
- Raise car and support in a safe manner.
WARNING -
Make sure the car is stable and well supported at all times.
Use a professional automotive lift orjacltstands designed for
the ouroose.
A floor iaclc is not adequate support.
- Remove under engine splash guard
4 Working underneath starter:
Cut off wire tie securing crankshaft speed sensor harness
connector (arrow) to sensor.
* Disconnect harness connector.
4 Remove sensor mounting fastener (arrow) and remove sen-
sor from cylinder block.
- Installation is reverse of removal, noting the following:
Use a new O-ring when installing sensor.
Be sure wiring is routed in same orientation.
Secure sensor using new wire ties.
Use scan tool to read out and clear ECM fault memory.
Page 495 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
160-25
Fuel Tank and Fuel pump1
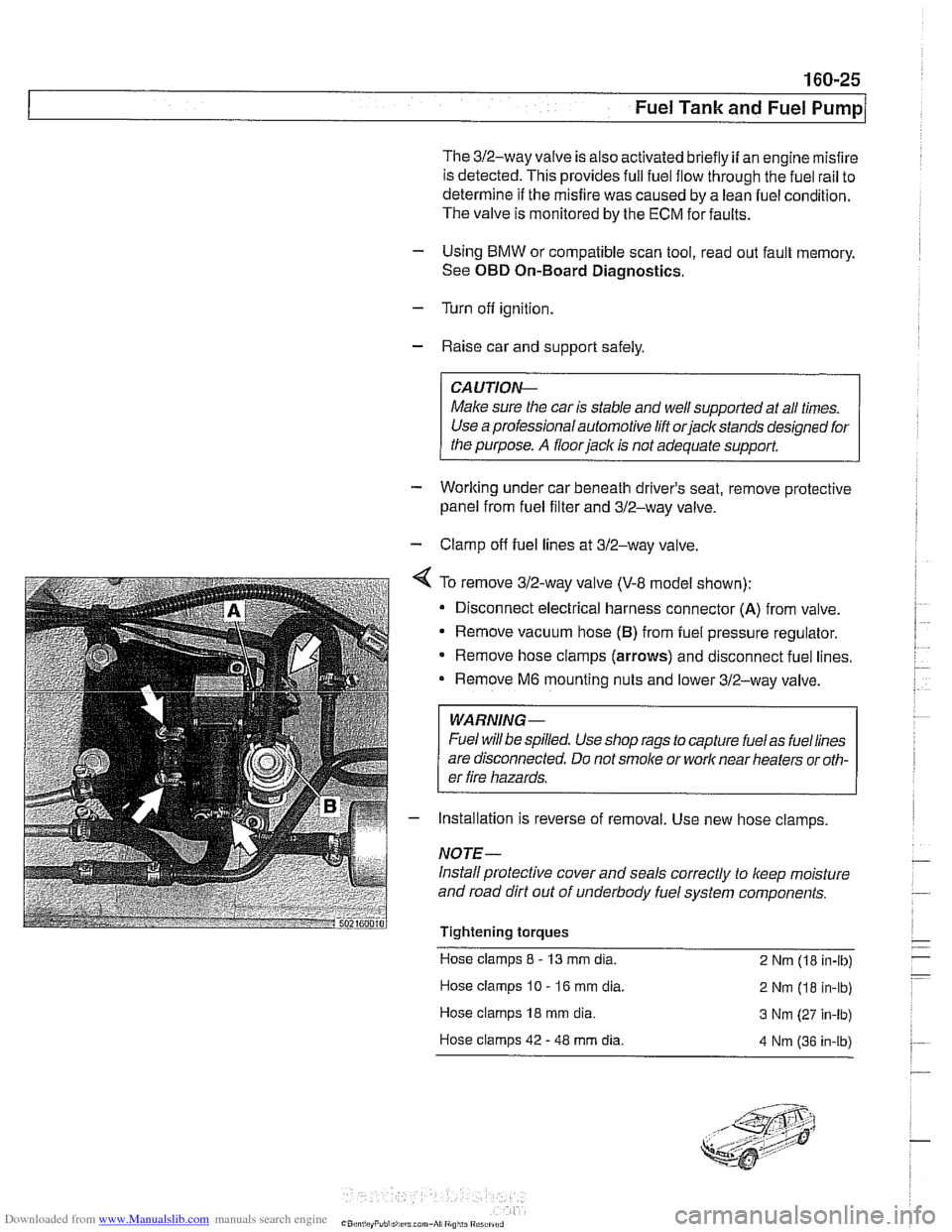
The 312-way valve is also activated briefly if an engine misfire
is detected. This provides full fuel flow through the fuel rail to
determine if the misfire was caused by a lean fuel condition.
The valve is monitored by the ECM forfaults.
- Using BMW or compatible scan tool, read out fault memory.
See
OBD On-Board Diagnostics.
- Turn off ignition.
- Raise car and support safely.
CA UTIOW
Male sure the car is stable and well suppodedat all times.
Use a professional automotive lift
orjack stands designed for
the purpose.
A floor jack is not adequate support.
- Worlting under car beneath driver's seat, remove protective
panel from fuel filter and 312-way valve.
- Clamp off fuel lines at 312-way valve.
4 To remove 312-way valve (V-8 model shown):
Disconnect electrical harness connector
(A) from valve.
Remove vacuum hose
(B) from fuel pressure regulator.
* Remove hose clamps (arrows) and disconnect fuel lines.
Remove
M6 mounting nuts and lower 312-way valve.
WARNING-
Fuel will be spilled. Use shop rags to capture fuelas fuellines
are disconnected. Do not
smoke or work near heaters or oth-
er fire hazards.
- Installation is reverse of removal. Use new hose clamps
NOTE-
Install protective cover and seals correctly to keep moisture
and road dirt out of underbody fuel system components.
Tightening torques Hose clamps
8 - 13 mm dia.
2 Nm (18 in-lb)
Hose clamps
10 - 16 mm dia.
2 Nm (18 in-lb)
Hose clamps
18 mm dia. 3 Nm (27 in-lb)
Hose clamps 42
- 48 mm dia. 4 Nm 136 in-ib)
Page 506 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
170-1 0
I Radiator and Cooling System
Combustion chamber leak test
- If you suspect that combustion chamber pressure is leaking
into the cooling system past the cylinder head gasket, use an
exhaust gas analyzer to test the vapors rising from the cool-
ant at the expansion tank.
CAUTIO&
Use an extension tube above the reservoir neclc to main-
tain distance between the top of the coolant and the gas
analyzer
nozzle. The gas analyzer is easily damaged if it is
allowed to inhale liquid coolant.
* While running engine to checlc for causes of overheat-
ing, observe coolant temperature carefully in order to
avoid engine damage.
Thermostat
If the engine overheats or runs too cool and no other cooling
system tests indicate trouble, the thermostat may be faulty.
In
V-8 models and 6-cvlinder models nroduced afler 911 998
(M52TU or M54 eng'ne), rheelecrricaily heated rhermostal IS
mon tored by [he OBD II diagnostlc software The fault may ic
in the DME software or hardware, or it may lie in the wiring to
the thermostat. See
OED On-Board Diagnostics.
Coolant, draining and filling
(6-cylinder models)
WARNING -
Allow the cooling system to cool before opening or draining
the cooling system.
- Raise front of car and support safely.
WARNING -
Make sure the car is stable and well supported at all times.
Use a professional automotive lift
orjack stands designed for
the purpose. A floor jack is not adequate support.
- Remove splash shield from under engine.
4 Loosen radiator bleed screw at top radiator fitting (arrow).
- Remove cap from radiator expansion tank. Set temperature
controls to
full warm.
gallon pail underneath radiator.
Page 966 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-6
On-Board Diagnostics
Fuel system monitoring. This monitor looks at the fuel
delivery needed (long
/short term fuel trim) for proper engine
operation based on programmed data. If too much or not
enough fuel is delivered over a predetermined time, a DTC is
set and the MIL illuminates.
Fuel trim refers to adiustments to base fuel schedule.
Lono- ., term fuel trim refers to gradual adjustments to the fuel
calibration adjustment as compared to short term fuel trim.
Long term fuel trim adjustments compensate for gradual
changes that occur over time.
Fuel system monitoring monitors the calculated injection time
(ti) in relation to enginespeed, load and precatalyticconverter
oxygen
sensor(s) signals.
Using this data, the system optimizes fuel delivery for all
engine operating conditions.
Evaporative system monitoring. This monitor checks the
the fuel storage system and related fuel lines for leaks. It can
detect very small leaks anywhere in the system.
A leak detection unit (LDP or DMTL) is used to pressurize the
evaporative control system on a continuous basis (as the
drive cycle allows) and to
check system integrity.
Drive cycle
The OED II drive cycle is an important concept in
understanding OBD
II requirements. The purpose of the drive
cycle is to run ail of the emission-related on-board diagnostics
over a broad range of driving conditions.
A drive cycle is considered complete when all of the
diagnostic monitors have run their tests without interruption.
~ora drive cycle to be initiated, the vehicle must be started
cold and brought up to
1 60°F and at least 40°F above its
original starting temperature.
Readiness codes
Inspection/maintenance (I/M) readiness codes are mandated
as part of OBD
II. The readiness code is stored aftercomplete
diagnostic monitoring of specified components and systems
is carried out. The readiness code function was designed to
prevent manipulating an
I/M emission test procedure by
clearing faults codes or disconnecting the ECM or battery.
Page 994 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
4 INDEX
Door window anti-trap
512-4 convenience openinglclosing 512.4
regulator and motor 512-1 1
service
512-5 switches 512-3
see also Switches
Double
VANOS see VANOS
Drive
axle
CV joint 331-15 CV joint boot 331-15
rernovinglinstalling 331-14
Drive belt
see Maintenance
Driveabiiity troubleshooting
100-4
Driveaway protection
see EWS (eiectronic immobilization)
Driveshaft aligning
260-7
center bearing, replacing 260-12 CV joint, replacing 260-14
itex-disc, replacing 260-1 1
iront centering guide, replacing 260-13
rernovinglinstailing 260-6
lroubleshooting 260-3
U-joint 260-3
DSC
see Braires
DTC (diagnostic trouble code)
OBD-8
DWA
see Anti-theft alarm
ECM (engine control module)
see 130 under appropriate
iuei
injection system
ECT (engine coolant temperature)
sensor see 130 under appropriate
iuei
injection system
EDK adaptation
130-69
MS 43.0 130-35
EHC see Electronic iieigiit control (EHC)
Electric cooling fan
see Cooling system, cooling
fan
see also Cooiing system, eiectric fan
Electrical switches
see Switches
Electrical system abbreviations
600-14 bus System 600-4
component location table 610-3
components
photos
610-36
Sport Wagon 610-81 engine 121-2
troubleshooting 600-15
voltage and polarily 600-5 wire color codes 600-12
wiring diagrams 600-12
Electrical wiring diagrams
ELE-1
Eiectricaliy heated thermostat
(characteristic map)
170-4
Eiectronic height control (EHC)
300-8, 330-44
Eiectronic immobilization
see EWS (electronic immobilization)
Eiectronics box
(E-box)
610-37
Emergencies
010-18
Emergency brake see
BraBes, parking brake Engine
see also Cylinder head and valvetrain
applications
100-2
compression, testing 113-5
cooling see Cooiing system
crankshaft front oil seai
see Crankshaft oil seals
cyiinder leak-down test 113-8
diagnostic testing 113-1
drive belts
see Maintenance
driveability troubleshooting
100-4
engine management systems 100-2
see also Ignition
see also Fuel injection
fuel supply
130-6
ground connections 100-5
see also 61 0 identilying ieatures 100-3
lubrication svstem
see
~ubricetion system
mount
on-board diagnostics
OBD-I
oxygensensor
see Fuel injection
see also Exhaust system
Dreventive maintenance
see Maintenance
removal/installation
Engine control module (ECM)
see 130 under appropriate iuel
injection system
Engine cooiant temperature (ECT)
sensor see 130 under appropriate iuel
injection
system
Engine cooling fan
see Cooiing system, electric fan
Engine hood
41
0-6 raising to service position 410-6
Engine troubleshooting
see Engine, driveability troubleshooting
EVa~oratiVe control svstem
160-3 see also 130 under aDDroDriate iuel
injection system
Evaporator see
NC
Evaporator temperature sensor see
NC